Collaborative Optimization Strategies for Matrix Multiplication-Accumulation Operators on Commercial Processing-In-Memory Architectures
-
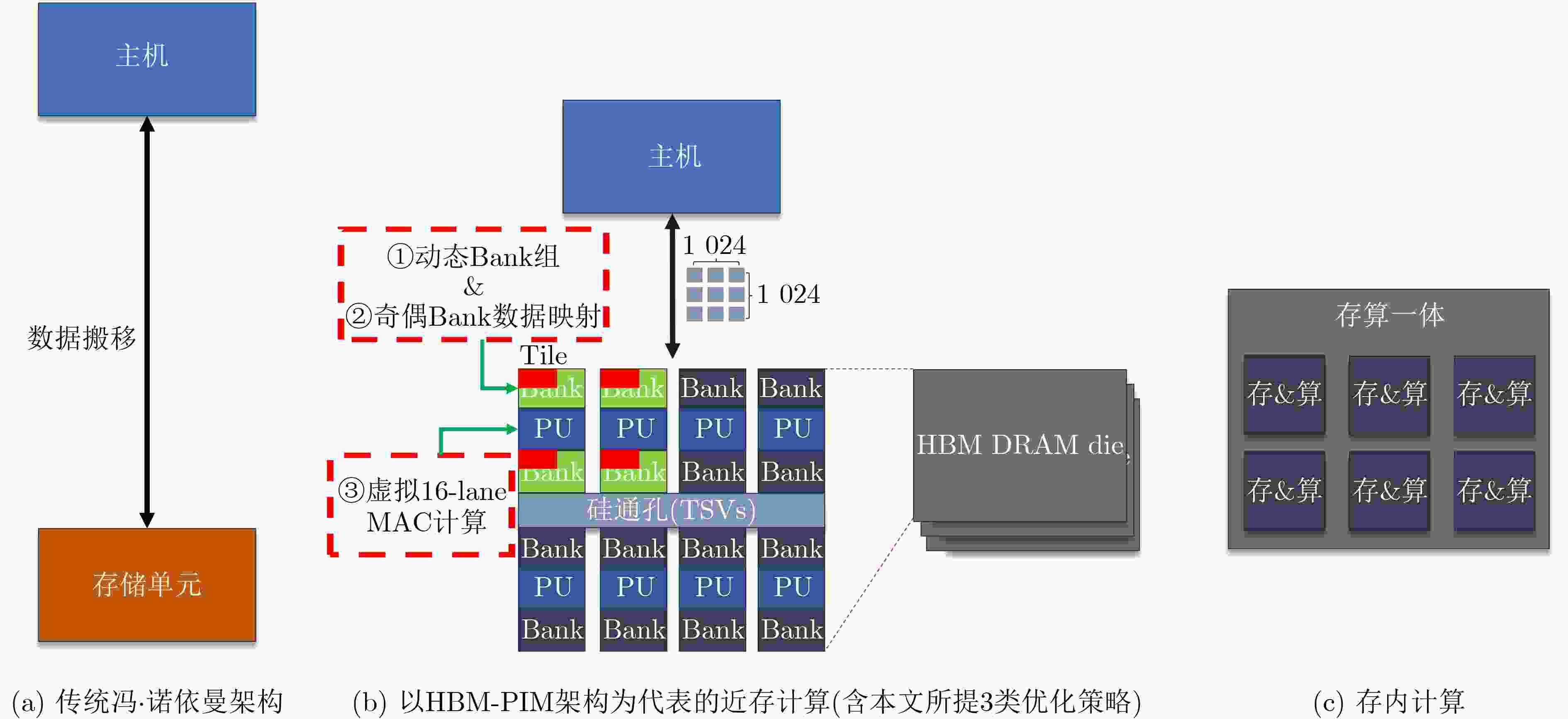
摘要: 由于近存架构对数据密集型程序加速的潜力,Samsung等公司推出基于高带宽存储器与存内计算(HBM-PIM)的近存芯片用于大模型加速,得益于HBM的高带宽和天然并行特性,近存计算表现出对大模型极佳的加速。该文发现,矩阵规模变化时,HBM-PIM架构的加速性能表现出不稳定性,限制了大模型部署的加速提升。为了释放HBM-PIM的加速潜力,该文深度分析了不同规模算子在HBM-PIM上性能差异的根本原因在于当前HBM-PIM对矩阵乘数据划分、映射和执行的支持不足,进而提出融合动态Bank分配、奇偶Bank交错式地址映射与分片虚拟化计算优化方法,有效提高了资源利用率和计算并行性。评估结果表明,所提方法对不同规模的矩阵计算都取得了1.894~8.225的加速比,相比优化前,性能平均提升了2.7倍。该文所提方案有效增强了PIM体系结构在多尺度任务下的可扩展性与适配能力,为AI算子在存内计算平台上的高效映射与调度提供了有益参考。Abstract:
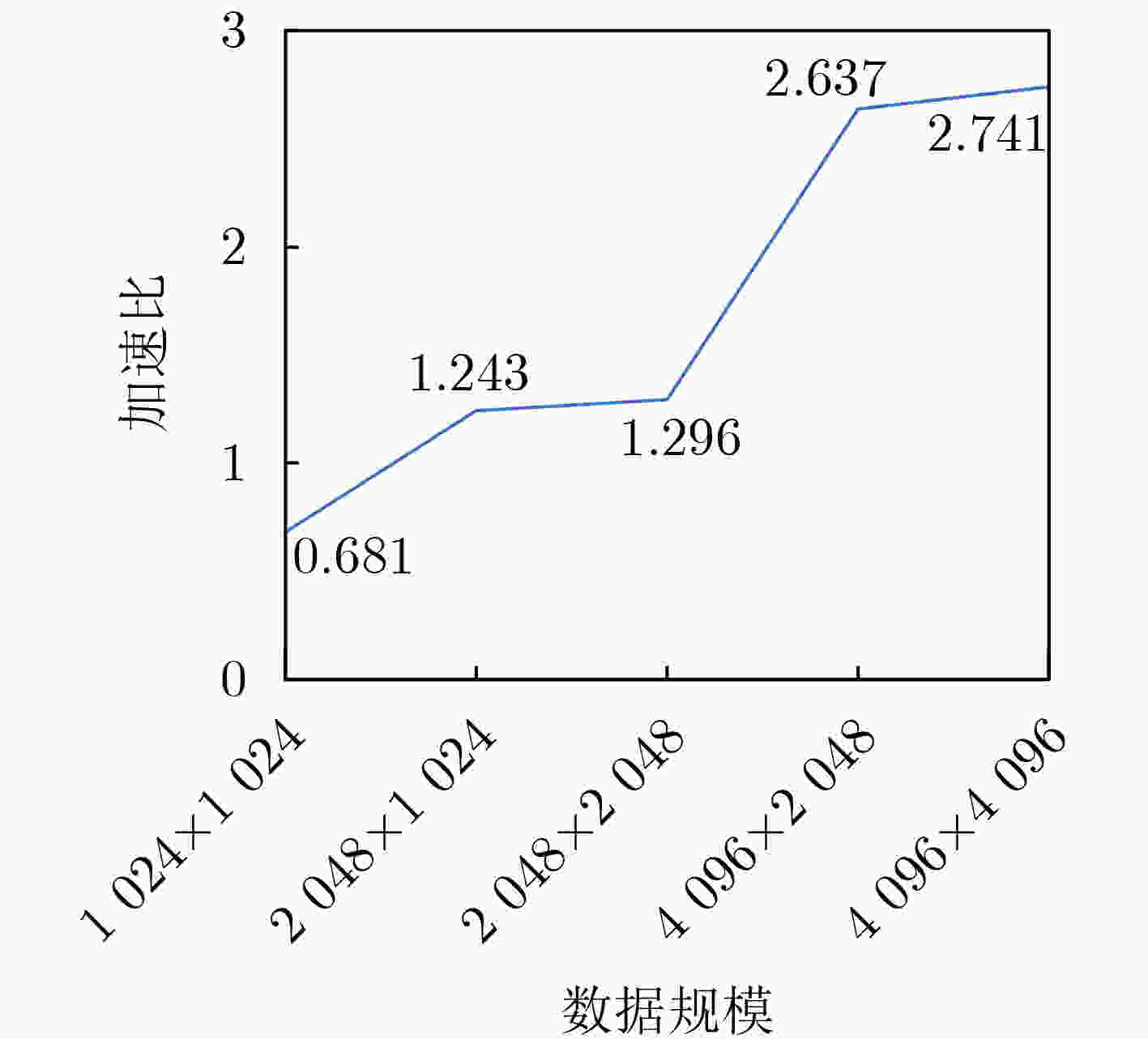
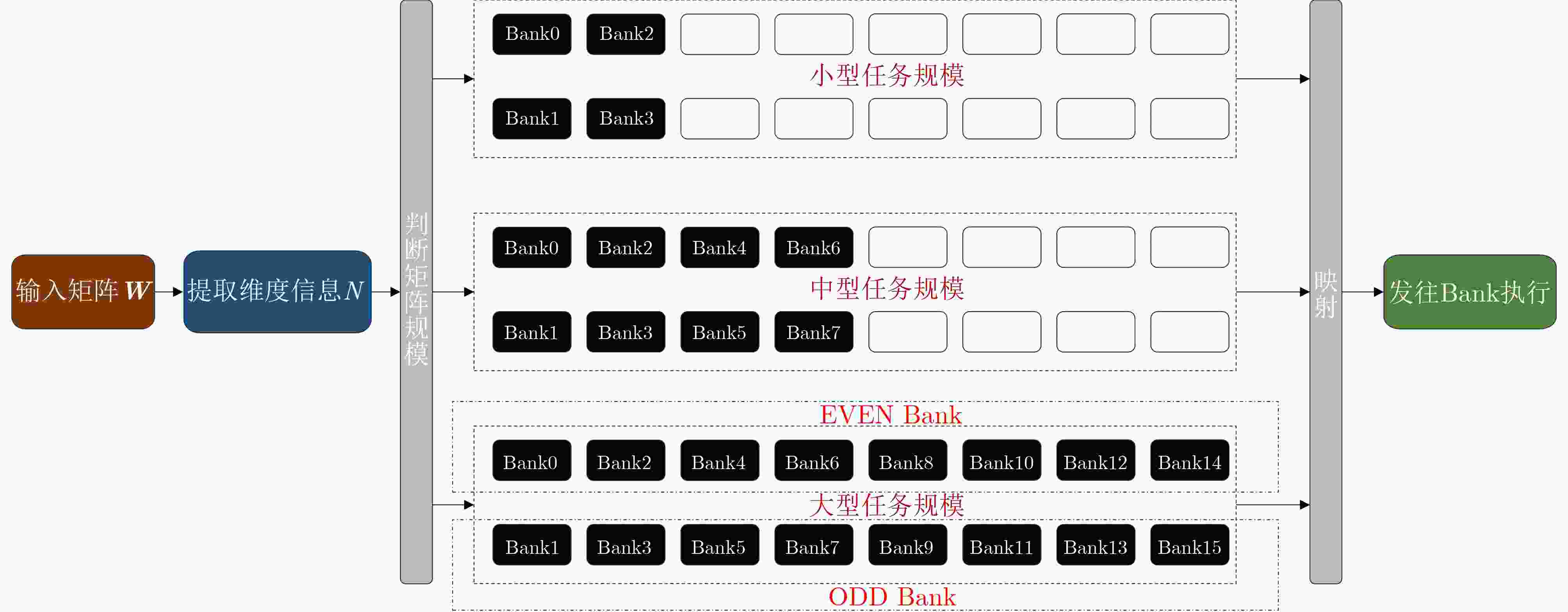
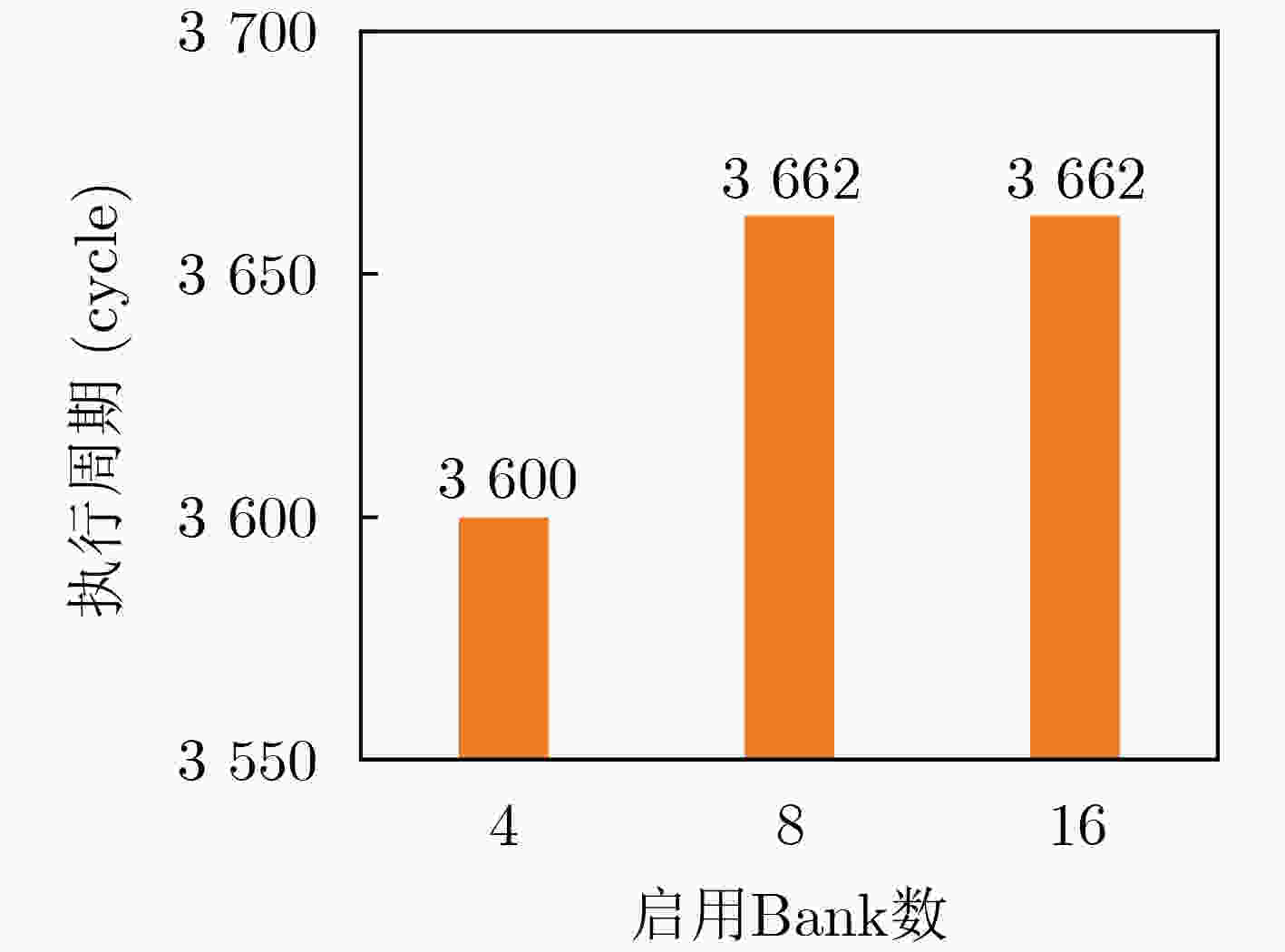
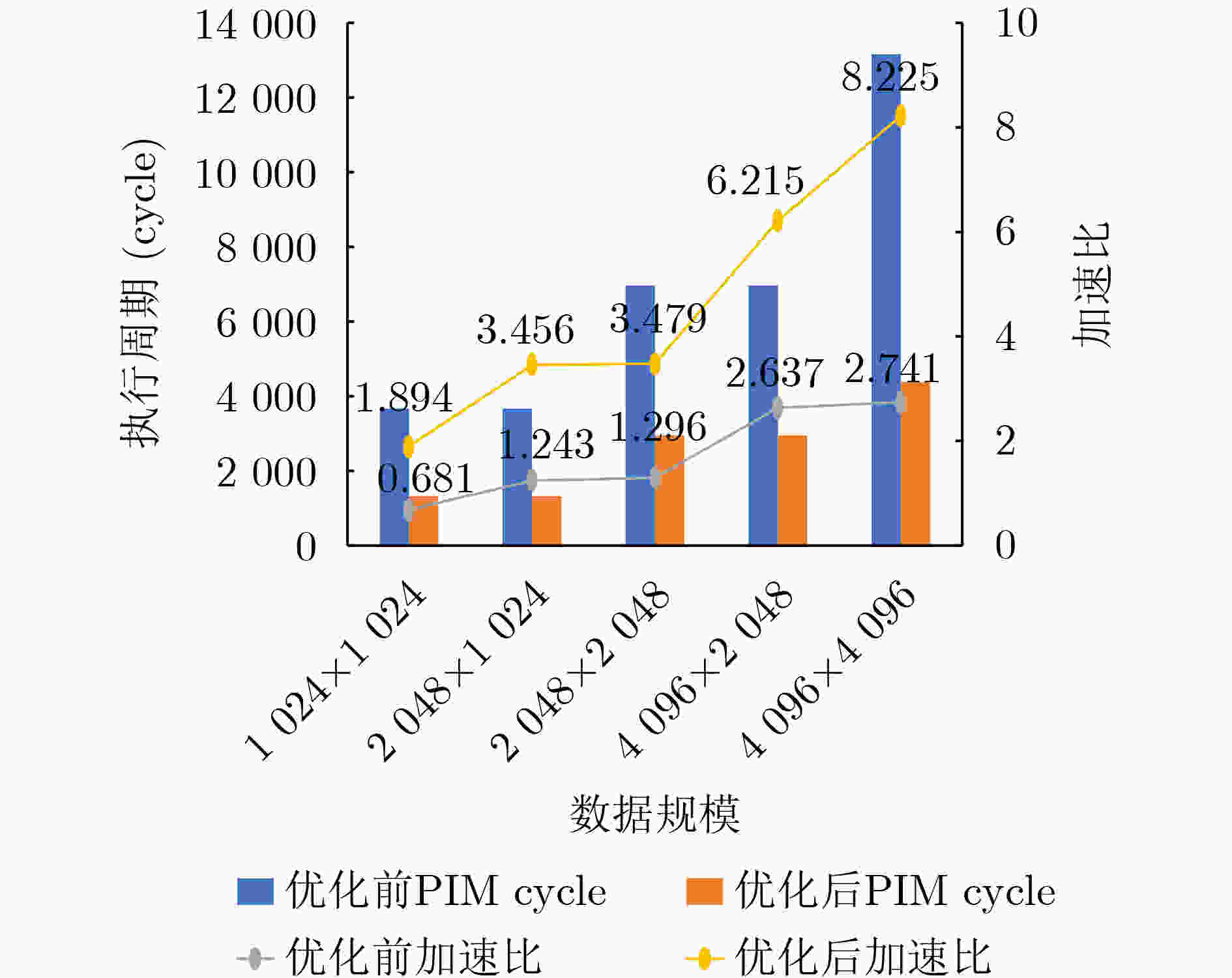
Objective Processing-In-Memory (PIM) architectures have emerged as a promising solution to the memory wall problem in modern computing systems by bringing computation closer to data storage. By minimizing data movement between processor and memory, PIM reduces data transfer latency and energy consumption, making it well suited for data-intensive applications such as deep neural network inference and training. Among various PIM implementations, Samsung’s High Bandwidth Memory Processing-In-Memory (HBM-PIM) platform integrates simple computing units within HBM devices, leveraging high internal bandwidth and massive parallelism. This architecture shows strong potential to accelerate compute- and memory-bound AI operators. However, our observations reveal that the acceleration ratio of HBM-PIM fluctuates considerably with matrix size, resulting in limited scalability for large model deployment and inefficient utilization for small- and medium-scale workloads. Addressing these fluctuations is essential to fully exploit the potential of HBM-PIM for scalable AI operator acceleration. This work systematically investigates the causes of performance divergence across matrix scales and proposes an integrated optimization framework that improves both scalability and adaptability in heterogeneous workload environments. Methods Comprehensive performance profiling is conducted on matrix-vector multiplication GEneral Matrix Vector Multiplication (GEMV) operators executed on an HBM-PIM simulation platform ( Fig. 2 ,Fig. 3 ), covering matrix sizes from 1 024 × 1 024 to 4 096 × 4 096. Profiling results (Table 1 ,Table 2 ) indicate that at smaller matrix scales, hardware resources such as DRAM banks are underutilized, leading to reduced bank-level parallelism and inefficient execution cycles. To address these bottlenecks, a collaborative optimization framework is proposed, consisting of three complementary strategies. First, a Dynamic Bank Allocation Strategy (DBAS) is employed to configure the number of active banks according to input matrix dimensions, ensuring alignment of computational resources with task granularity and preventing unnecessary activation of idle banks. Second, an Odd-Even Bank Interleaved Address Mapping (OEBIM) mechanism is applied to distribute data blocks evenly across active banks, thereby reducing access hotspots and enhancing memory-level parallelism. Third, a Virtual Tile Execution Framework is implemented to logically aggregate multiple fine-grained operations into coarser-grained execution units, effectively reducing the frequency of barrier synchronization and host-side instruction dispatches (Algorithm 1,Fig. 5 ,Fig. 6 ). Each strategy is implemented and evaluated under controlled conditions using a cycle-accurate HBM-PIM simulator (Table 3 ). Integration is performed while maintaining compatibility with existing hardware configuration constraints, including the 8-lane register file limits per DRAM bank.Results and Discussions Experimental results ( Fig. 7 ) show that the optimization framework delivers consistent and substantial performance improvements across different matrix scales. For instance, with a 2 048 × 2 048 matrix input, the acceleration ratio increased from 1.296 (baseline) to 3.479 after optimization. With a 4 096 × 4 096 matrix, it improved from 2.741 (baseline) to 8.225. Across all tested sizes, the optimized implementation achieved an average performance gain of approximately 2.7× relative to the baseline HBM-PIM configuration. Beyond raw acceleration, the framework improved execution stability by preventing the performance degradation observed in baseline implementations under smaller matrices. These results demonstrate that the combination of dynamic resource allocation, balanced address mapping, and logical operation aggregation effectively mitigates resource underutilization and scheduling inefficiencies inherent to HBM-PIM architectures. Further analysis confirms that the framework enhances scalability and adaptability without requiring substantial hardware modifications. By aligning resource activation granularity with workload size and reducing host-device communication overhead, the framework achieves better utilization of available parallelism at both memory and computation levels. This leads to more predictable performance scaling under heterogeneous workloads and strengthens the feasibility of deploying AI operators on commercial PIM systems.Conclusions This study presents a collaborative optimization framework to address performance instability of GEMV operators on commercial HBM-PIM architectures under varying matrix scales. By combining dynamic bank allocation, odd-even interleaved address mapping, and virtual tile execution strategies, the framework achieves consistent and scalable acceleration across small to large matrices while enhancing execution stability and resource utilization. These findings provide practical guidance for software-hardware co-optimization in PIM-based AI acceleration platforms and serve as a reference for the design of future AI accelerators targeting data-intensive tasks. Future work will focus on extending the framework to additional AI operators, validating its effectiveness on real hardware prototypes, and investigating integration with compiler toolchains for automated operator mapping and scheduling. -
表 1 Bank状态行为分布量化
数据规模 Bank
状态总数Idle
状态数量Precharge
状态数量Activate
状态数量2 048×2 048 14 274 560 12 662 464 79 296 457 600 4 096×4 096 26 963 968 23 870 272 122 368 820 928 表 2 Bank0~7 2 048×2 048数据规模激活行数量详细统计
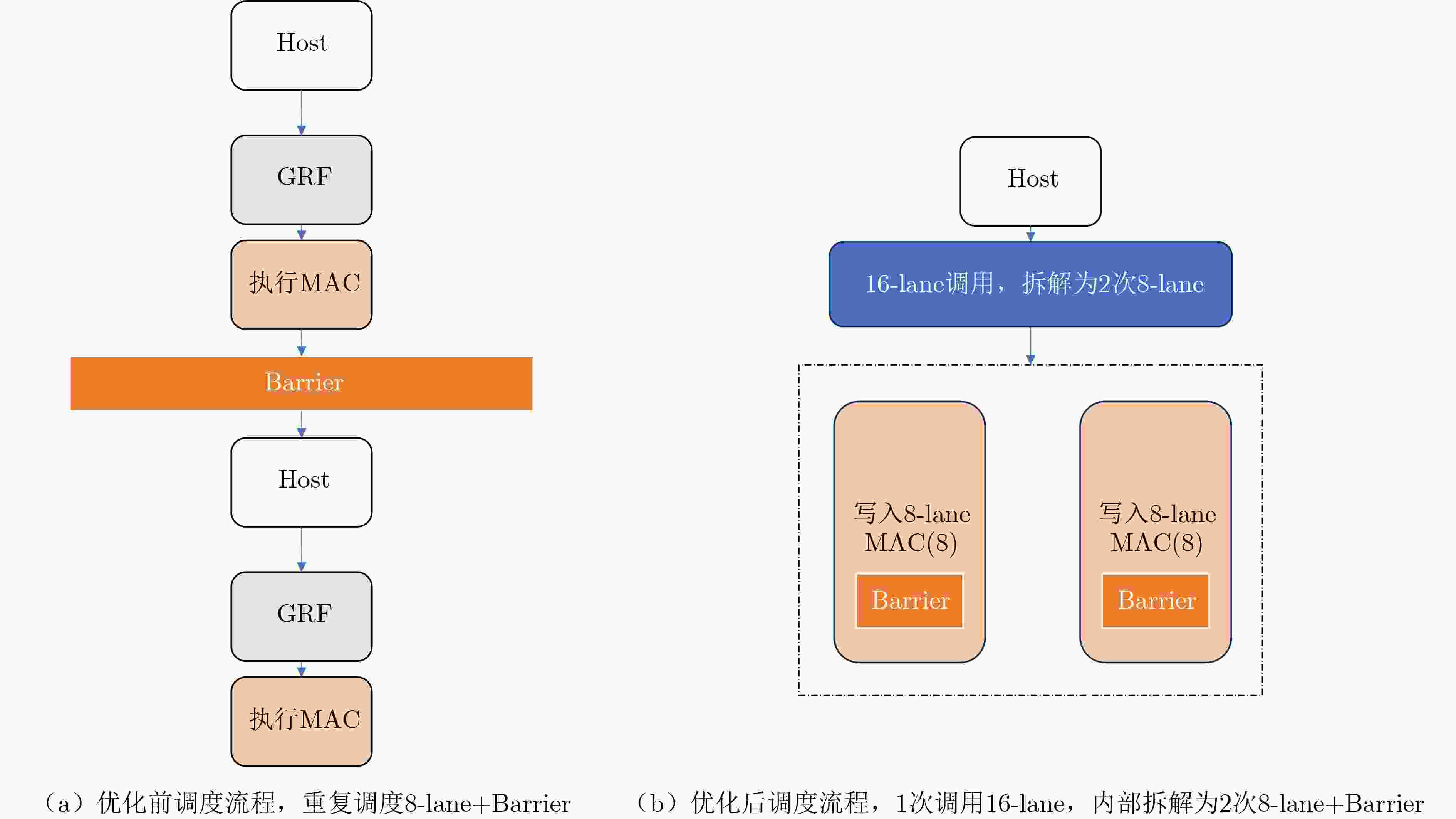
Bank ID 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 激活行数量 163 200 229 568 4 224 4 224 4 224 4 224 4 224 4 352 1 分片虚拟化计算指令封装与执行
输入:数据数组operand,虚拟Tile长度16,硬件lane宽度为8 输出:完成1次Tile运算结果 (1) 初始化:remain $ \leftarrow $ 16,offset $ \leftarrow $ 0 (2) 循环处理每8-lane数据: (3) cur_load $ \leftarrow $ min(remain,8) (4) 写入cur_load条数据至GRF (5) 每通道执行addBarrier()同步 (6) 调用addTransactionAll()触发MAC运算 (7) remain $ \leftarrow $ remain $ - $ cur_load,offset $ \leftarrow $ offset $ + $
cur_load(8) 重复步骤(3)~(7)直至remain = 0 (9) 返回 表 3 实验平台与资源配置参数
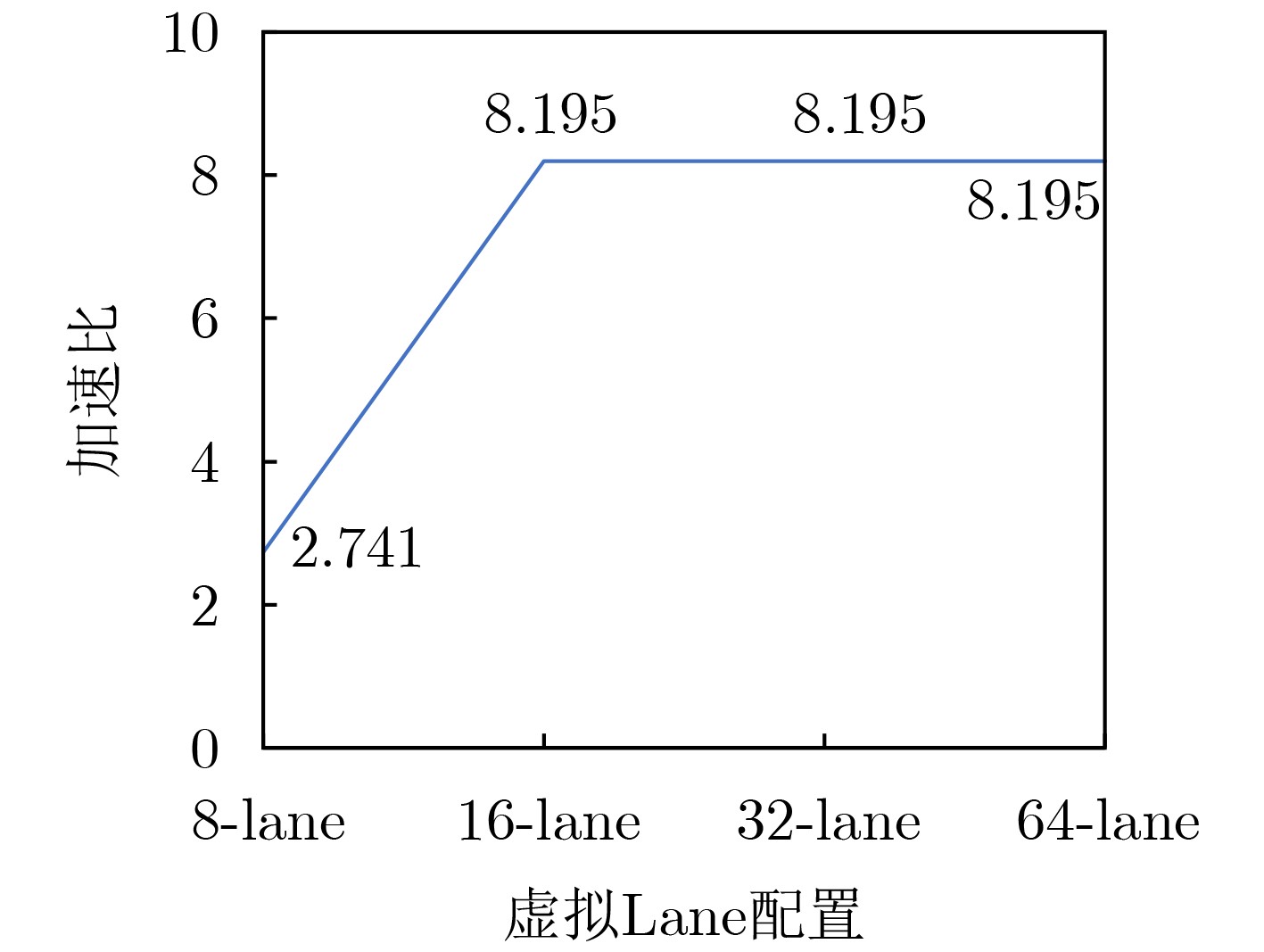
类别 操作系统 模拟器平台 模拟精度 Bank数 GRF 配置参数 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Samsung Pimsimulator Cycle-Level 16 8-lane 表 4 各优化策略下不同矩阵规模的加速比
数据规模 Baseline DBAS 奇偶Bank交错映射 分片虚拟化计算 协同优化 1 024×1 024 0.681 0.693 0.686 1.869 1.894 2 048×1 024 1.243 1.264 1.251 3.427 3.456 2 048×2 048 1.296 1.308 1.305 3.438 3.479 4 096×2 048 2.637 2.661 2.656 6.152 6.215 4 096×4 096 2.741 2.754 2.751 8.195 8.225 表 5 本文协同优化策略与UniNDP方案横向对比
对比维度 UniNDP 本文协同优化策略 算子类型 MVM(GEMV) GEMV 测试数据规模 4 096×4 096 4 096×4 096 对HBM-PIM性能提升 1.02× 3.00× 不同数据规模平均性能提升 1.10×~1.62× 平均提升2.70×,
规模越大越优 -
[1] GHOLAMI A, YAO Zhewei, KIM S, et al. AI and memory wall[J]. IEEE Micro, 2024, 44(3): 33–39. doi: 10.1109/MM.2024.3373763. [2] CHI Ping, LI Shuangchen, XU Cong, et al. PRIME: A novel processing-in-memory architecture for neural network computation in ReRAM-based main memory[J]. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 2016, 44(3): 27–39. doi: 10.1145/3007787.3001140. [3] DAKKAK A, LI Cheng, XIONG Jinjun, et al. Accelerating reduction and scan using tensor core units[C]. The ACM International Conference on Supercomputing, Phoenix, USA, 2019: 46–57. doi: 10.1145/3330345.3331057. [4] ALIAN M, MIN S W, ASGHARIMOGHADDAM H, et al. Application-transparent near-memory processing architecture with memory channel network[C]. The 51st Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Fukuoka, Japan, 2018: 802–814. doi: 10.1109/MICRO.2018.00070. [5] GÓMEZ-LUNA J, EL HAJJ I, FERNANDEZ I, et al. Benchmarking a new paradigm: An experimental analysis of a real processing-in-memory architecture[J]. arXiv: 2105.03814, 2021: 1–25. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2105.03814. [6] KIM J and KIM Y. HBM: Memory solution for bandwidth-hungry processors[C]. 2014 IEEE Hot Chips 26 Symposium, Cupertino, USA, 2014: 1–24. doi: 10.1109/HOTCHIPS.2014.7478812. [7] LEE S, KANG S H, LEE J, et al. Hardware architecture and software stack for PIM based on commercial DRAM technology: Industrial product[C]. 2021 ACM/IEEE 48th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Valencia, Spain, 2021: 43–56. doi: 10.1109/ISCA52012.2021.00013. [8] KIM D, KUNG J, CHAI S, et al. Neurocube: A programmable digital neuromorphic architecture with high-density 3D memory[J]. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 2016, 44(3): 380–392. doi: 10.1145/3007787.3001178. [9] ASGARI B, HADIDI R, CAO Jiashen, et al. FAFNIR: Accelerating sparse gathering by using efficient near-memory intelligent reduction[C]. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture, Seoul, Korea (South), 2021: 908–920. doi: 10.1109/HPCA51647.2021.00080. [10] WANG Haoyang, ZHANG Shengbing, FAN Xiaoya, et al. NDPGNN: A near-data processing architecture for GNN training and inference acceleration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2024, 43(11): 3997–4008. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2024.3446871. [11] LEE S, KIM K, OH S, et al. A 1ynm 1.25V 8Gb, 16Gb/s/pin GDDR6-based accelerator-in-memory supporting 1TFLOPS MAC operation and various activation functions for deep-learning applications[C]. 2022 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ISSCC42614.2022.9731711. [12] DAI Guohao, ZHU Zhenhua, FU Tianyu, et al. DIMMining: Pruning-efficient and parallel graph mining on near-memory-computing[C]. The 49th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, New York, USA, 2022: 130–145. doi: 10.1145/3470496.3527388. [13] KE Liu, GUPTA U, CHO B Y, et al. RecNMP: Accelerating personalized recommendation with near-memory processing[C]. 2020 ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Valencia, Spain, 2020: 790–803. doi: 10.1109/ISCA45697.2020.00070. [14] WILKINSON F, COCKREAN A, LIN Weichen, et al. Assessing the GPU offload threshold of GEMM and GEMV kernels on modern heterogeneous HPC systems[C]. The SC24-W: Workshops of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Atlanta, USA, 2024: 1481–1495. doi: 10.1109/SCW63240.2024.00188. [15] HONG Ke, DAI Guohao, XU Jiaming, et al. FlashDecoding++: Faster large language model inference on GPUs[C]. The 41st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 2024: 1–15. [16] IBRAHIM M A, ISLAM M, and AGA S. PIMnast: Balanced data placement for GEMV acceleration with processing-in-memory[C]. The SC24-W: Workshops of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Atlanta, USA, 2024: 970–981. doi: 10.1109/SCW63240.2024.00137. [17] XIE Tongxin, ZHU Zhenhua, LI Bing, et al. UniNDP: A unified compilation and simulation tool for near DRAM processing architectures[C]. 2025 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture, Las Vegas, USA, 2025: 624–640. doi: 10.1109/HPCA61900.2025.00054. [18] Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology. PIMSimulator[EB/OL]. https://github.com/SAITPublic/PIMSimulator. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
