An Interpretable Vulnerability Detection Method Based on Graph and Code Slicing
-
摘要: 深度学习已被广泛应用于漏洞检测,其主流方法可分为基于代码序列和基于代码图两类:前者易因忽视结构而误报,后者则难以捕获执行顺序。此外,两者普遍缺乏可解释性,难以定位漏洞根源。为此,该文提出一种基于图和代码切片的可解释性漏洞检测方法GSVD。该模型通过门控图卷积网络提取代码多维度图(AST, DDG, CDG)的结构语义,并结合“污点”分析驱动的代码切片与双向长短时记忆网络,精准捕获代码序列特征,实现二者优势互补。同时,引入HITS算法思想,设计VDExplainer解释器,直观揭示了模型的决策过程。实验表明,GSVD在Devign数据集上准确率达64.57%,优于多种基线模型,证明了其在有效检测漏洞的同时,能实现代码行级的可解释定位。Abstract:
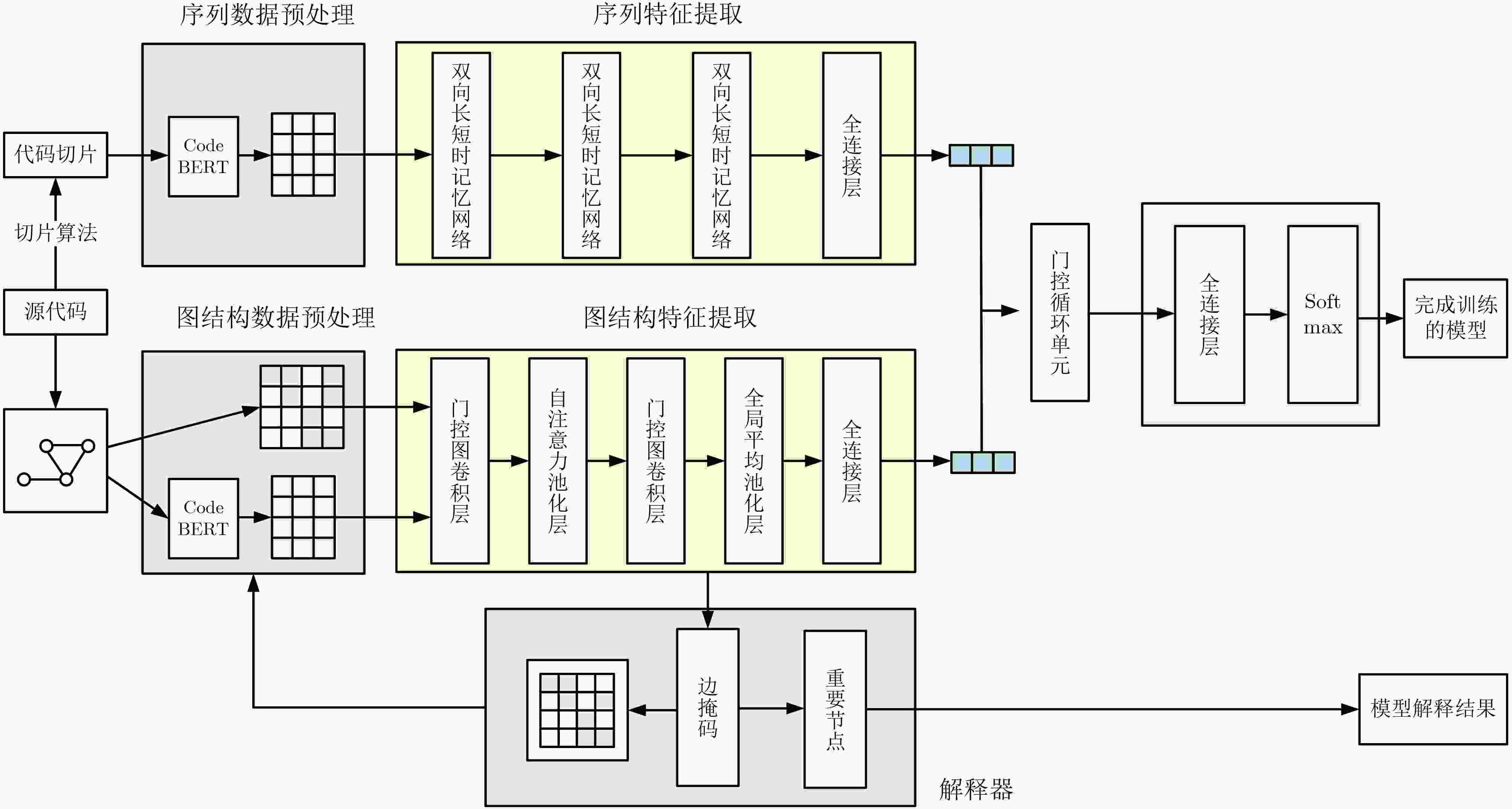
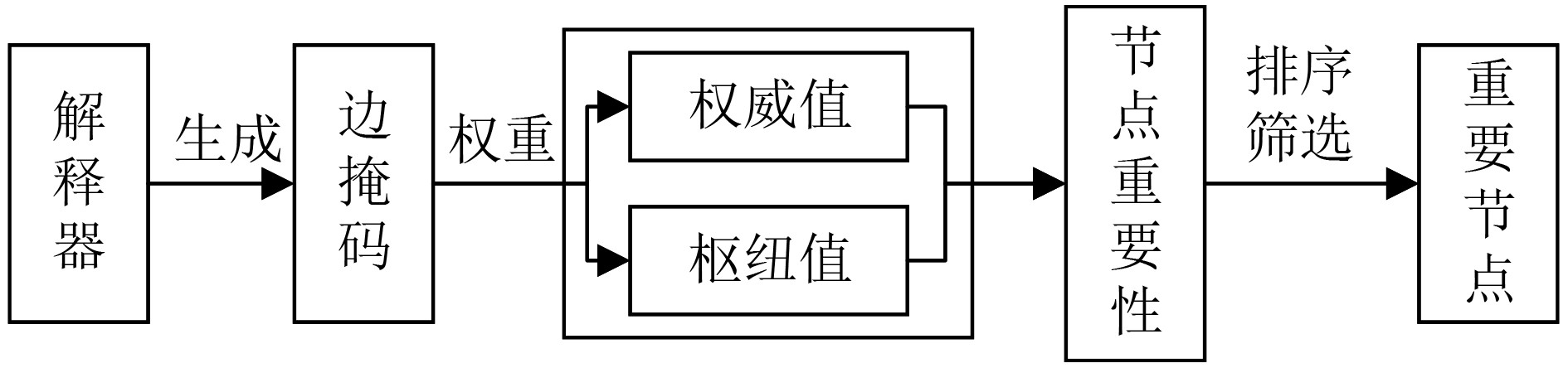
Objective Deep learning technology is widely applied to source code vulnerability detection. Existing approaches are mainly sequence-based or graph-based. Sequence-based models convert structured code into linear sequences, which leads to the loss of syntactic and structural information and often results in a high false positive rate. Graph-based models capture structural features but cannot represent execution order, and their detection granularity is usually limited to the function level. Both types of methods lack interpretability, which restricts the ability of developers to locate vulnerability sources. Large Language Models (LLMs) show progress in code understanding; however, they still exhibit high computational cost, hallucination risk in security analysis, and insufficient modeling of complex program logic. To address these issues, an interpretable vulnerability detection method based on Graph and Slicing Vulnerability Detection (GSVD) is proposed. Structural semantics and sequential information are integrated, and fine-grained, line-level explanations are provided for prediction results. Methods The proposed method consists of four modules: code graph feature extraction, code sequence feature extraction, feature fusion, and an interpreter module (Fig. 1). First, the source code is normalized, and the Joern static analysis tool is applied to generate multiple code graphs, including the Abstract Syntax Tree (AST), Data Dependency Graph (DDG), and Control Dependency Graph (CDG). These graphs represent program structure, data flow, and control flow, respectively. Node features are initialized using CodeBERT embeddings combined with one-hot encodings of node types. Based on the adjacency matrix of each graph, a Gated Graph Convolutional Network (GGCN) with a self-attention pooling layer is employed to extract deep structural semantic features. A code slicing algorithm based on taint analysis (Algorithm 1) is then designed. In this algorithm, taint sources are identified, and taints are propagated according to data and control dependencies to generate concise slices associated with potential vulnerabilities. Unrelated code is removed, and the resulting slices are processed using a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network to capture long-range sequential dependencies. After graph and sequence features are extracted, a gating mechanism is applied for feature fusion. The fused feature vectors are further processed using a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), which learns dependencies between structural and sequential representations through dynamic state updates. To support vulnerability detection and localization, a Vulnerability Detection Explainer (VDExplainer) is designed. Inspired by the Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search (HITS) algorithm, node “authority” and “hub” scores are iteratively computed under an edge-mask constraint to estimate node importance and provide node-level interpretability. Results and Discussions The effectiveness of the GSVD model is evaluated through comparative experiments on the Devign dataset (FFmpeg + Qemu), as shown in ( Table 2 ). GSVD is compared with several baseline models and achieves the highest accuracy and F1-score, reaching 64.57% and 61.89%, respectively. Recall increases to 62.63%, indicating improved vulnerability detection capability and reduced missed reports. To evaluate the GRU-based fusion module, three fusion strategies are compared: feature concatenation, weighted sum, and attention mechanism (Table 3 ). GSVD achieves the best overall performance. Although its precision (61.17%) is slightly lower than that of the weighted sum method (63.33%), accuracy, recall, and F1-score exhibit more balanced performance. Ablation studies (Tables 4 ~5 ) further demonstrate the contribution of the slicing algorithm. The taint propagation-based slicing method reduces the average number of code lines from 51.98 to 17.30, corresponding to a reduction of 66.72%, and lowers the data redundancy rate to 6.42%. In comparison, VulDeePecker and SySeVR report redundancy rates of 19.58% and 22.10%, respectively. This reduction in noise yields a 1.53% improvement in F1-score, confirming that the slicing module enhances focus on critical code segments. The interpretability of GSVD is validated on the Big-Vul dataset using the VDExplainer module (Table 6 ). Compared with the standard Graph Neural Network Explainer (GNNExplainer), higher localization accuracy is achieved at all evaluation thresholds. When 50% of the nodes are selected, localization accuracy increases by 7.65%, demonstrating the advantage of VDExplainer in node-level vulnerability explanation.Conclusions The GSVD model overcomes the limitations of single-modal methods by integrating graph structures with taint-based code slicing. Both detection accuracy and interpretability are improved. The VDExplainer enables node-level and line-level localization, enhancing practical applicability. Experimental results confirm the advantages of the proposed method in vulnerability detection and explanation. -
Key words:
- Vulnerability detection /
- Deep learning /
- Graph neural network /
- Code slicing /
- Interpretability
-
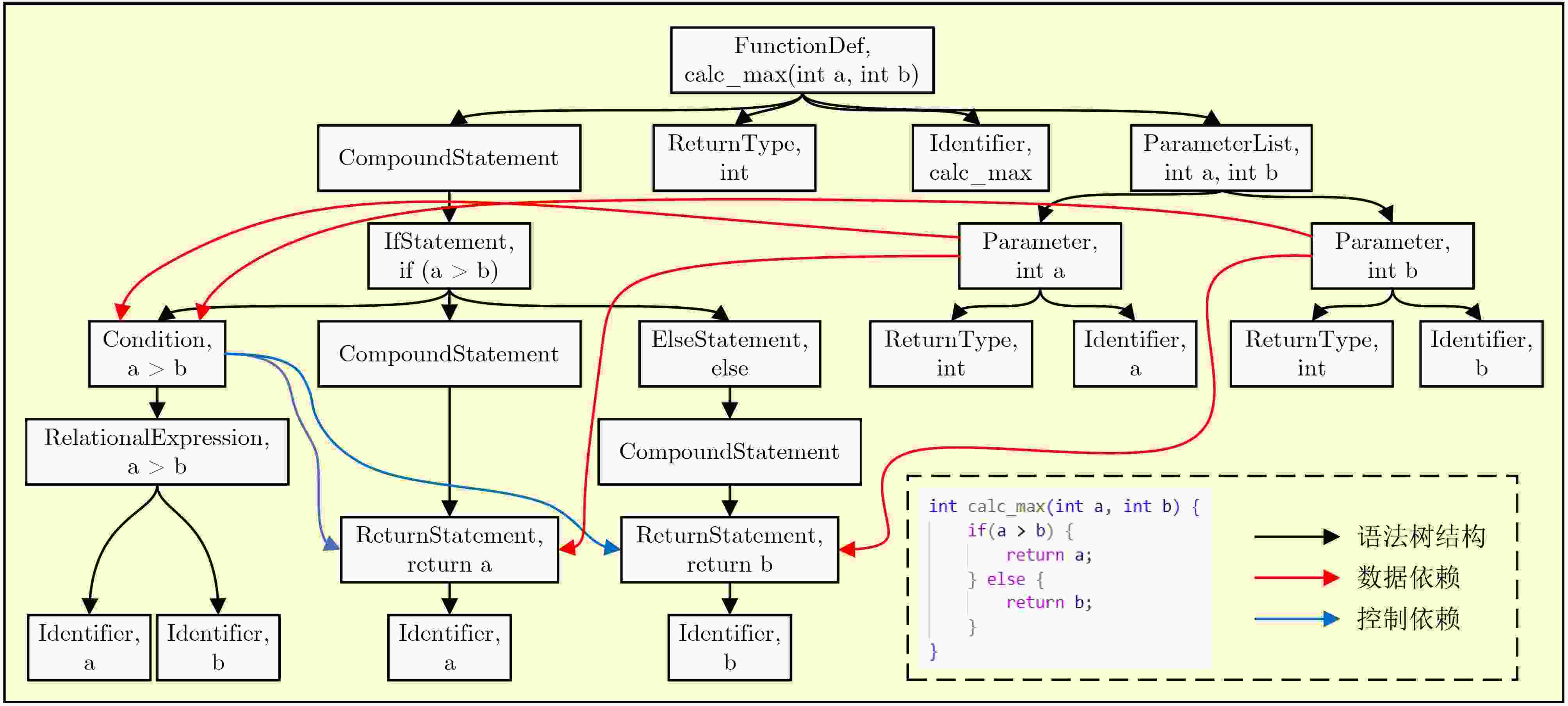
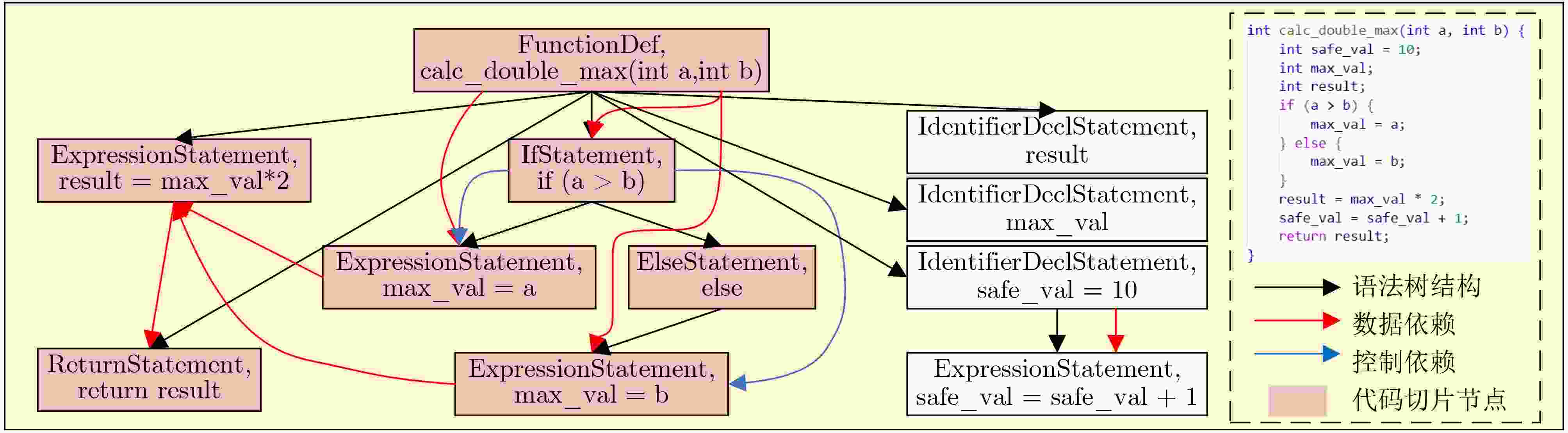
1 代码切片算法
输入:抽象语法树AST,数据依赖图DDG,控制依赖图CDG,
初始污点变量集合${T_0}$输出:污染语句集合S 1:T← ${T_0}$ // 初始化污点序列 2:S← $\varnothing $ // 初始化污染语句集合 3:for each 语句 s ∈ AST (深度优先遍历) do 4: if s含外部输入then 5: 将输入变量加入T,并令S ← S ∪ {s} 6: else if s 依赖于T中变量then //数据依赖传播 7: if s 为赋值语句 x = f(y) then 8: if y ∈ T, x $\notin $ T then T ← T ∪ {x}, S ← S ∪ {s} 9: else if x ∈ T, y ${{\notin}} $T then T ← T − {x} // 消毒 10: else if s 为函数调用 z = f(x1,x2, ···, xn) then 11: if $\exists $xi∈T then T ← T∪{z的输出变量}, S ← S∪{s} 12: else T ← T − {z的输出变量} // 消毒 13: else S ← S ∪ {s} 14: end if 15: if s ∈ S then // 控制依赖传播 16: for each c ∈ CDG.control_dependents(s) do 17: 将c中变量加入 T,并令S ← S ∪ {c} 18: end for 19: end if 20:end for 21:return S ≠ $ \varnothing $? S: AST 表 1 数据集统计特征分布
特征指标 训练集 验证集 测试集 样本总数 21 854 2 732 2 732 平均函数长度 51.71 49.84 51.98 平均语句数 41.84 40.80 41.81 平均AST深度 13.26 13.27 13.23 表 2 GSVD实验结果(%)
Accuracy Precision Recall F1-Score Cppcheck 57.96 79.55 11.34 19.85 FlawFinder 52.04 46.69 34.41 39.62 BiLSTM 59.37 / / / TextCNN 60.69 / / / RoBERTa 61.05 / / / CodeBERT 62.08 / / / Devign 59.22 57.23 44.46 50.04 ReGVD_GCN 61.90 62.62 42.31 50.50 ReGVD_GGCN 62.12 61.58 46.61 53.06 Zeng’s 64.49 64.29 51.08 56.93 GSVD 64.57 61.17 62.63 61.89 1 表 3 特征融合方法对比(%)
Accuracy Precision Recall F1-Score 特征拼接 63.36 59.75 61.99 60.85 加权求和 63.14 63.33 46.93 53.91 注意力机制 62.55 59.54 57.68 58.60 GSVD 64.57 61.17 62.63 61.89 表 4 数据重复度对比(%)
方法 数据重复率 未切片 0.20 Vuldeepecker 19.58 SySeVR 22.10 Ours 6.42 表 5 代码切片影响
准确率(%) 精确率(%) 召回率(%) F1得分(%) 源代码平均行数 未切片 64.13 61.30 59.44 60.36 51.98 切片 64.57 61.17 62.63 61.89 17.30 表 6 解释器解释定位实验(%)
解释器 重要节点筛选比例 漏洞定位准确率
GNNExplainer30 18.37 40 28.94 50 41.12
VDExplainer30 24.30 40 35.68 50 48.77 -
[1] GAO Qing, MA Sen, SHAO Sihao, et al. CoBOT: Static C/C++ bug detection in the presence of incomplete code[C]. The 26th Conference on Program Comprehension, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2018: 385–388. doi: 10.1145/3196321.3196367. [2] ZHANG Yu, HUO Wei, JIAN Kunpeng, et al. SRFuzzer: An automatic fuzzing framework for physical SOHO router devices to discover multi-type vulnerabilities[C]. The 35th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, San Juan, USA, 2019: 544–556. doi: 10.1145/3359789.3359826. [3] LI Zhen, ZOU Deqing, XU Shouhuai, et al. VulDeePecker: A deep learning-based system for vulnerability detection[C]. The 25th Annual Network and Distributed Systems Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2018. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2018.23158. [4] ZOU Deqing, WANG Sujuan, XU Shouhuai, et al. μVulDeePecker: A deep learning-based system for multiclass vulnerability detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2021, 18(5): 2224–2236. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2019.2942930. [5] LI Zhen, ZOU Deqing, XU Shouhuai, et al. SySeVR: A framework for using deep learning to detect software vulnerabilities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(4): 2244–2258. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2021.3051525. [6] ZHOU Yaqin, LIU Shangqing, SIOW J, et al. Devign: Effective vulnerability identification by learning comprehensive program semantics via graph neural networks[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 915. doi: 10.5555/3454287.3455202. [7] FENG Qi, FENG Chendong, and HONG Weijiang. Graph neural network-based vulnerability predication[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME), Adelaide, Australia, 2020: 800–801. doi: 10.1109/ICSME46990.2020.00096. [8] NGUYEN V A, NGUYEN D Q, NGUYEN V, et al. ReGVD: Revisiting graph neural networks for vulnerability detection[C]. The ACM/IEEE 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings, Pittsburgh, USA, 2022: 178–182. doi: 10.1145/3510454.3516865. [9] CHAKRABORTY S, KRISHNA R, DING Yangruibo, et al. Deep learning based vulnerability detection: Are we there yet?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2022, 48(9): 3280–3296. doi: 10.1109/TSE.2021.3087402. [10] ALI G M A and CHEN Hongsong. Contract-guardian: A bagging-based gradient boosting decision tree for detection vulnerability in smart contract[J]. Cluster Computing, 2025, 28(8): 528. doi: 10.1007/s10586-025-05230-2. [11] GUO Daya, ZHU Qihao, YANG Dejian, et al. DeepSeek-Coder: When the Large Language Model Meets Programming -- The Rise of Code Intelligence[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.14196, 2024.GUO Daya, ZHU Qihao, YANG Dejian, et al. DeepSeek-Coder: When the Large Language Model Meets Programming -- The Rise of Code Intelligence[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.14196, 2024. [12] DeepSeek-AI, ZHU Qihao, GUO Daya, et al. DeepSeek-Coder-V2: Breaking the Barrier of Closed-Source Models in Code Intelligence[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.11931, 2024.DeepSeek-AI, ZHU Qihao, GUO Daya, et al. DeepSeek-Coder-V2: Breaking the Barrier of Closed-Source Models in Code Intelligence[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.11931, 2024. [13] AGHAEI E, NIU Xi, SHADID W, et al. SecureBERT: A domain-specific language model for cybersecurity[C]. 18th International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Networks, Kansas, USA, 2022: 39–56. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-25538-0_3. [14] SUN Yuqiang, WU Daoyuan, XUE Yue, et al. LLM4Vuln: A Unified Evaluation Framework for Decoupling and Enhancing LLMs' Vulnerability Reasoning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.16185, 2025.SUN Yuqiang, WU Daoyuan, XUE Yue, et al. LLM4Vuln: A Unified Evaluation Framework for Decoupling and Enhancing LLMs' Vulnerability Reasoning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.16185, 2025. [15] FAR S M T and FEYZI F. Large language models for software vulnerability detection: A guide for researchers on models, methods, techniques, datasets, and metrics[J]. International Journal of Information Security, 2025, 24(2): 78. doi: 10.1007/s10207-025-00992-7. [16] ZHOU Xin, CAO Sicong, SUN Xiaobing, et al. Large language model for vulnerability detection and repair: Literature review and the road ahead[J]. ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, 2025, 34(5): 145. doi: 10.1145/3708522. [17] YING R, BOURGEOIS D, YOU Jiaxuan, et al. GNNExplainer: Generating explanations for graph neural networks[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 829. doi: 10.5555/3454287.3455116. [18] FAN Jiahao, LI Yi, WANG Shaohua, et al. A C/C++ code vulnerability dataset with code changes and CVE summaries[C]. The 17th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories, Seoul, Korea, 2020: 508–512. doi: 10.1145/3379597.3387501. [19] D'ABRUZZO PEREIRA J and VIEIRA M. On the use of open-source C/C++ static analysis tools in large projects[C]. 2020 16th European Dependable Computing Conference (EDCC), Munich, Germany, 2020: 97–102. doi: 10.1109/EDCC51268.2020.00025. [20] FERSCHKE O, GUREVYCH I, and RITTBERGER M. FlawFinder: A modular system for predicting quality flaws in wikipedia[C]. CLEF 2012 Evaluation Labs and Workshop, Online Working Notes, Rome, Italy, 2012: 1178. [21] GRAVES A. Long short-term memory[M]. GRAVES A. Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 37–45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-24797-2_4. [22] CHEN Yahui. Convolutional neural network for sentence classification[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Waterloo, 2015. [23] LIU Yinhan, OTT M, GOYAL N, et al. RoBERTa: A robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020. [24] FENG Zhangyin, GUO Daya, TANG Duyu, et al. CodeBERT: A pre-trained model for programming and natural languages[C]. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, 2020: 1536–1547. doi: 10.18653/v1/2020.findings-emnlp.139. [25] ZENG Ciling, ZHOU Bo, DONG Huoyuan, et al. A general source code vulnerability detection method via ensemble of graph neural networks[C]. The 6th International Conference on Frontiers in Cyber Security, Chengdu, China, 2023: 560–574. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-9331-4_37. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
