YOMANet-Accel: A Lightweight Algorithm Accelerator for Pedestrians and Vehicles Detection at the Edge
-
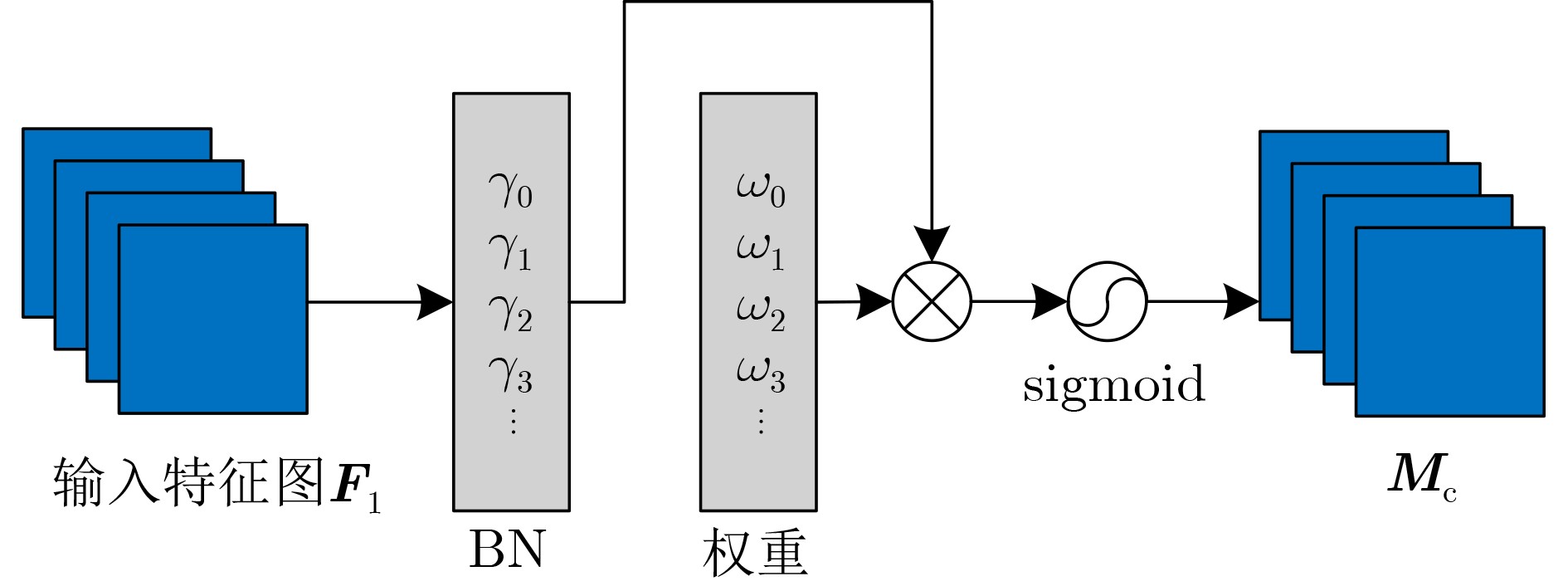
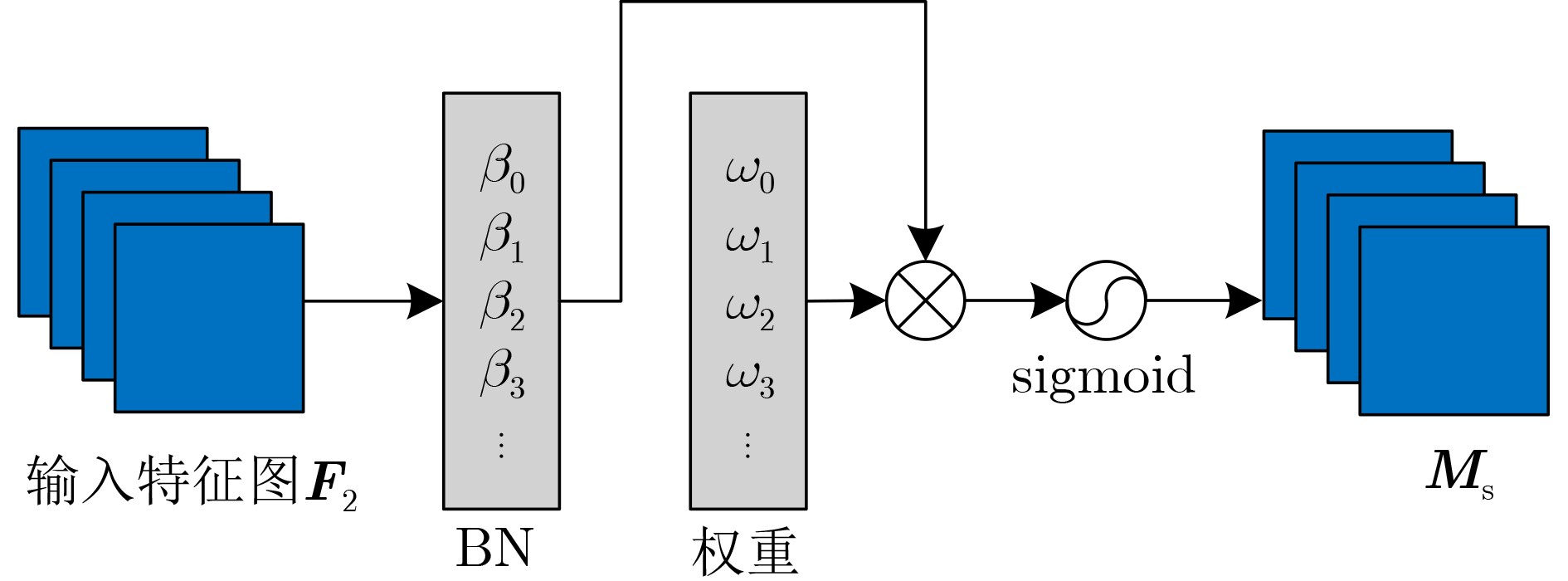
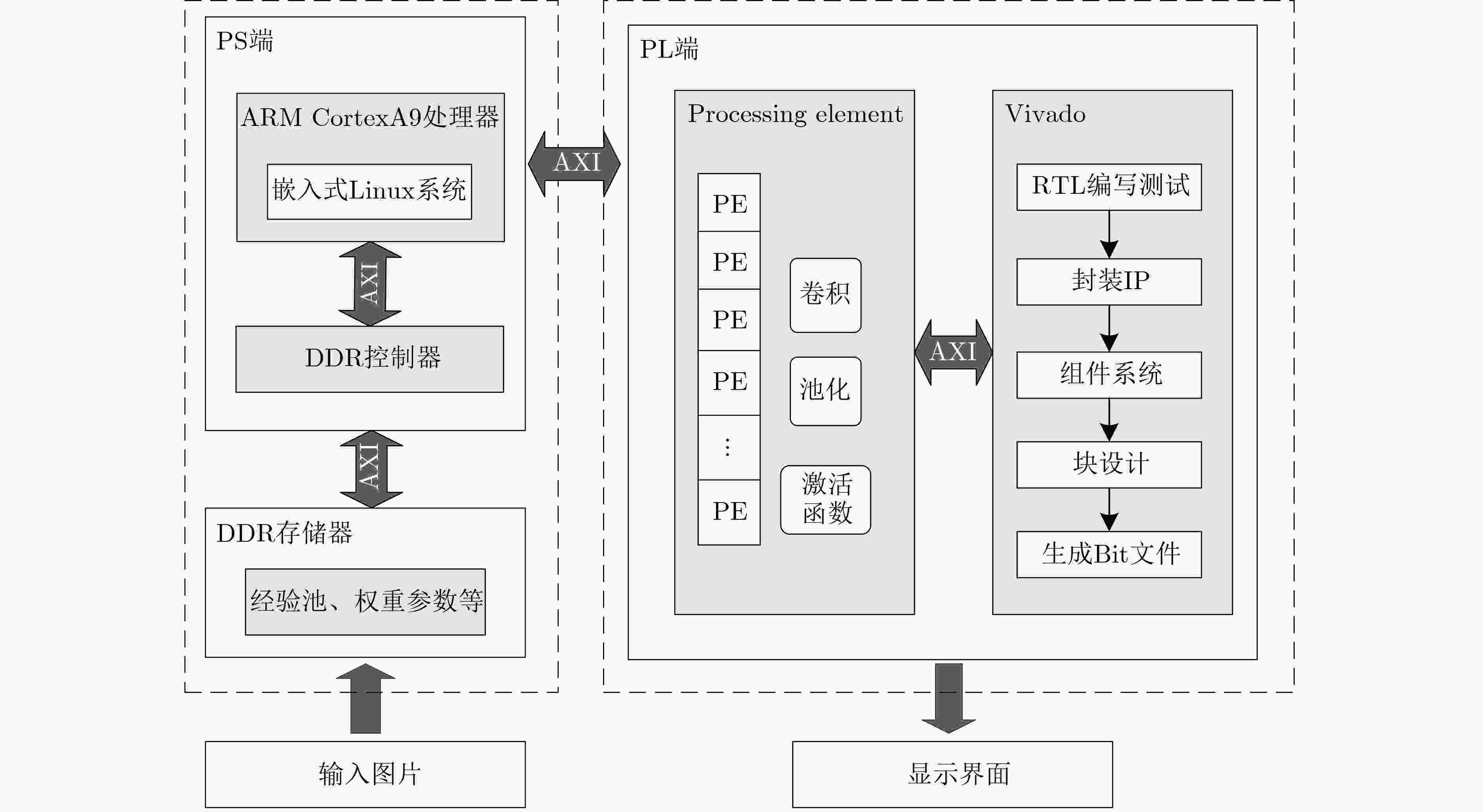
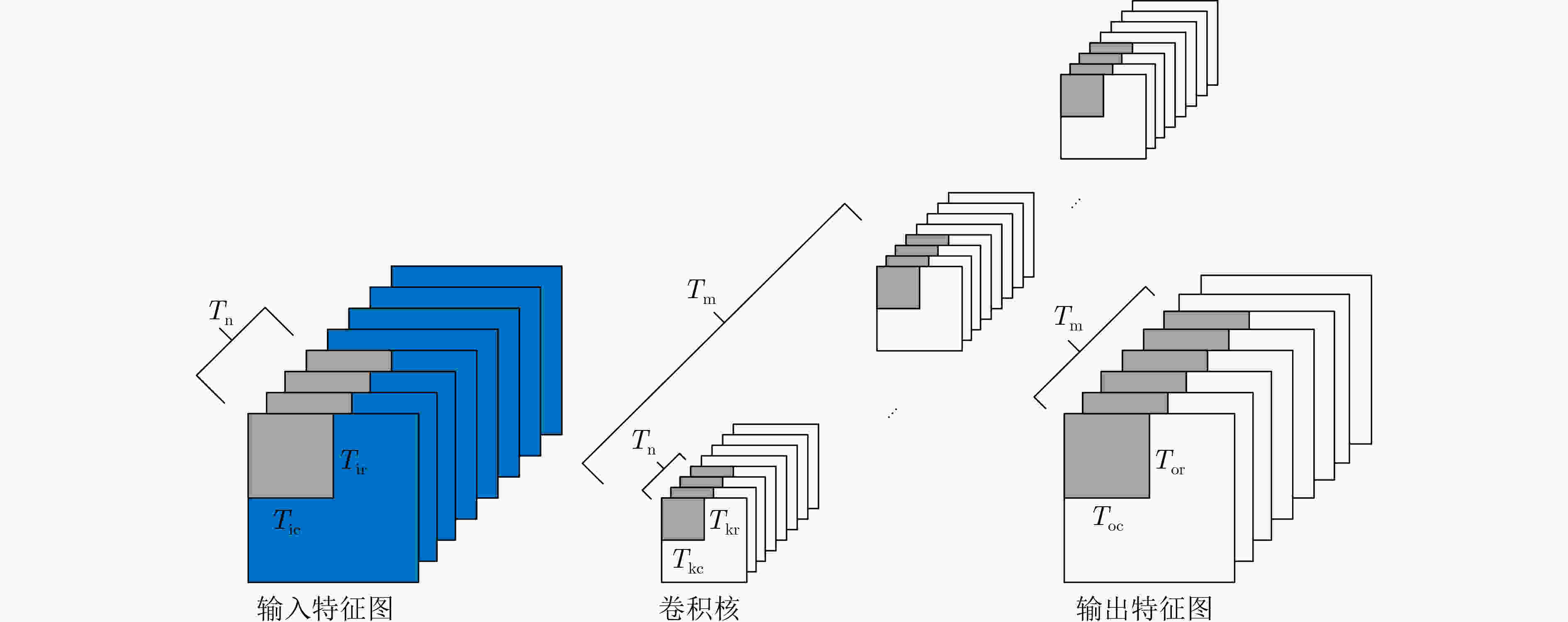
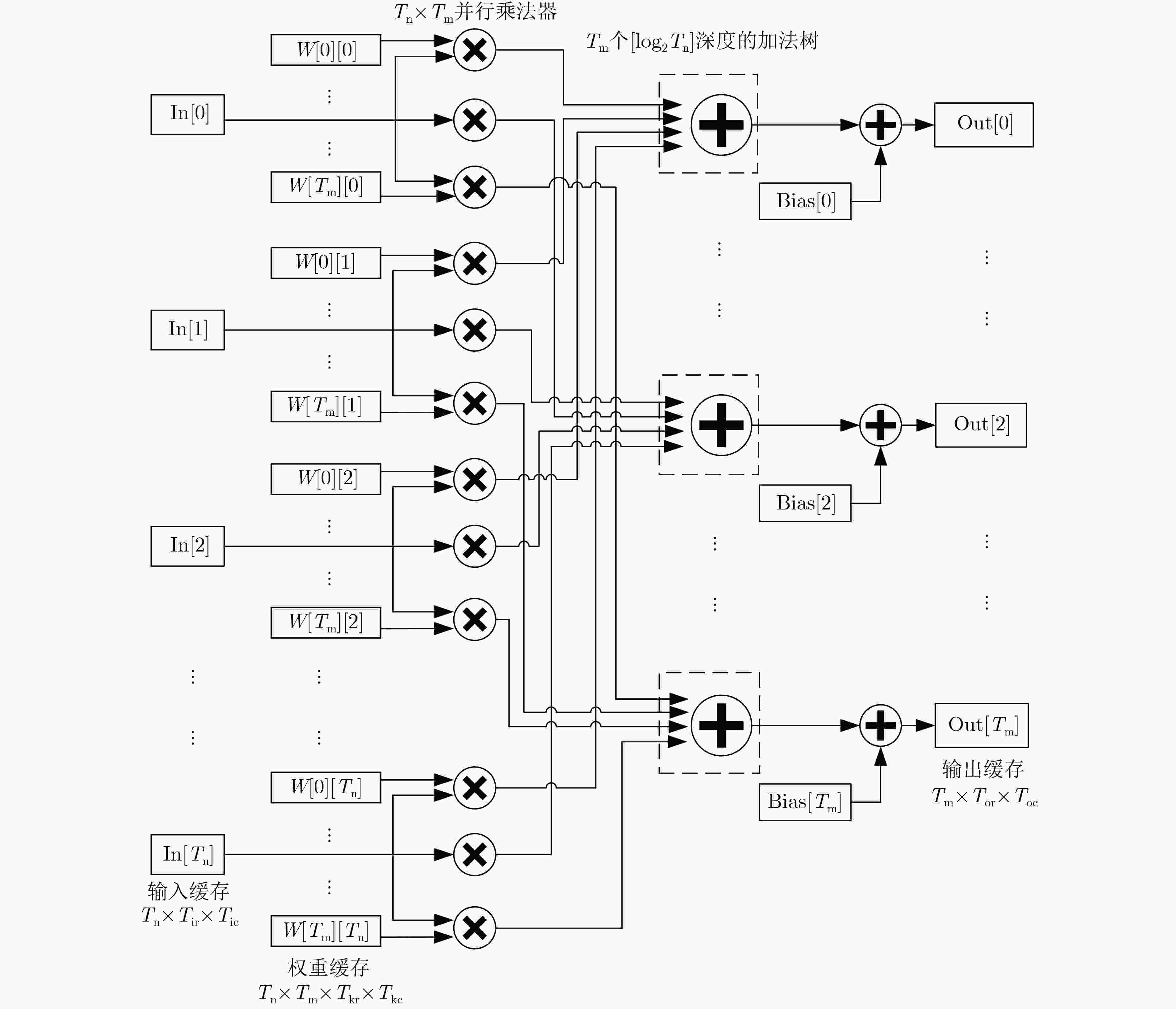
摘要: 针对自动驾驶边缘计算场景中行人车辆检测任务面临的模型计算复杂度高、参数量大导致的部署难题,该文提出一种轻量化神经网络模型YOMANet (Yolo Model Adaptation Network),基于异构FPGA平台设计YOMANet加速器(YOMANet-Accel),实现边缘端人车检测的算法加速。YOMANet算法的主干网络采用轻量型网络MobileNetv2以大幅压缩模型参数量,颈部网络使用深度可分离卷积来代替常规卷积以提升训练速度,并在头部网络嵌入基于归一化的注意力模块(NAM)以增强网络对细节信息的捕获能力。为将YOMANet算法部署到现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)平台,该文针对卷积运算在任务层设计循环分块以调整内循环和外循环的顺序,在运算层对处理引擎单元(PE)设计乘加树,使得多个乘加运算可以同时执行,提高数据的并行计算效率。同时,针对数据存储过程采用双缓存机制来减少数据传输时延,对权重参数和激活函数进行int8数据量化以降低资源消耗。实验结果表明,YOMANet算法在训练平台上的检测精度和检测速度表现优异,对小目标和遮挡目标具备较好的检测能力,有效减少了误检和漏检情况的发生。算法部署到硬件平台后,YOMANet-Accel的目标检测效果保持在较高水平,硬件资源的能效比表现良好,有效发挥了FPGA的并行优势。Abstract:
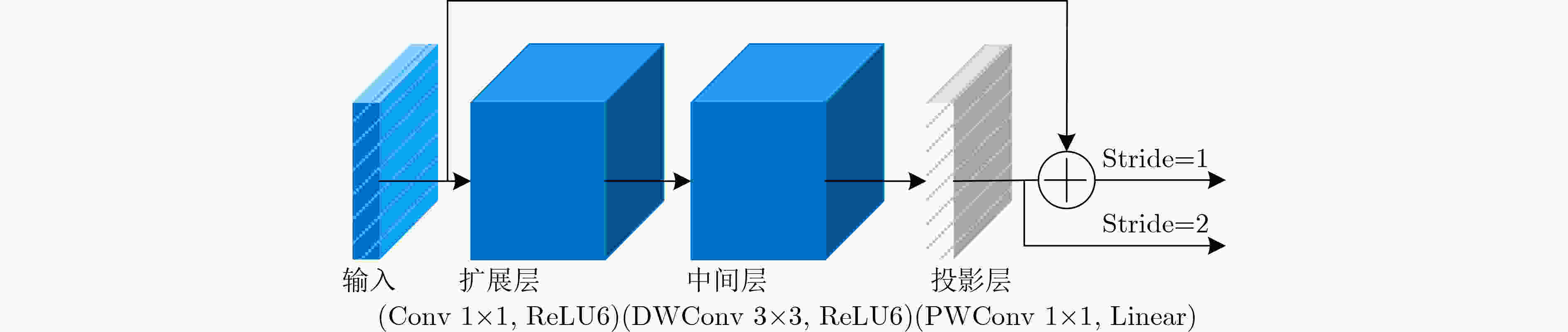
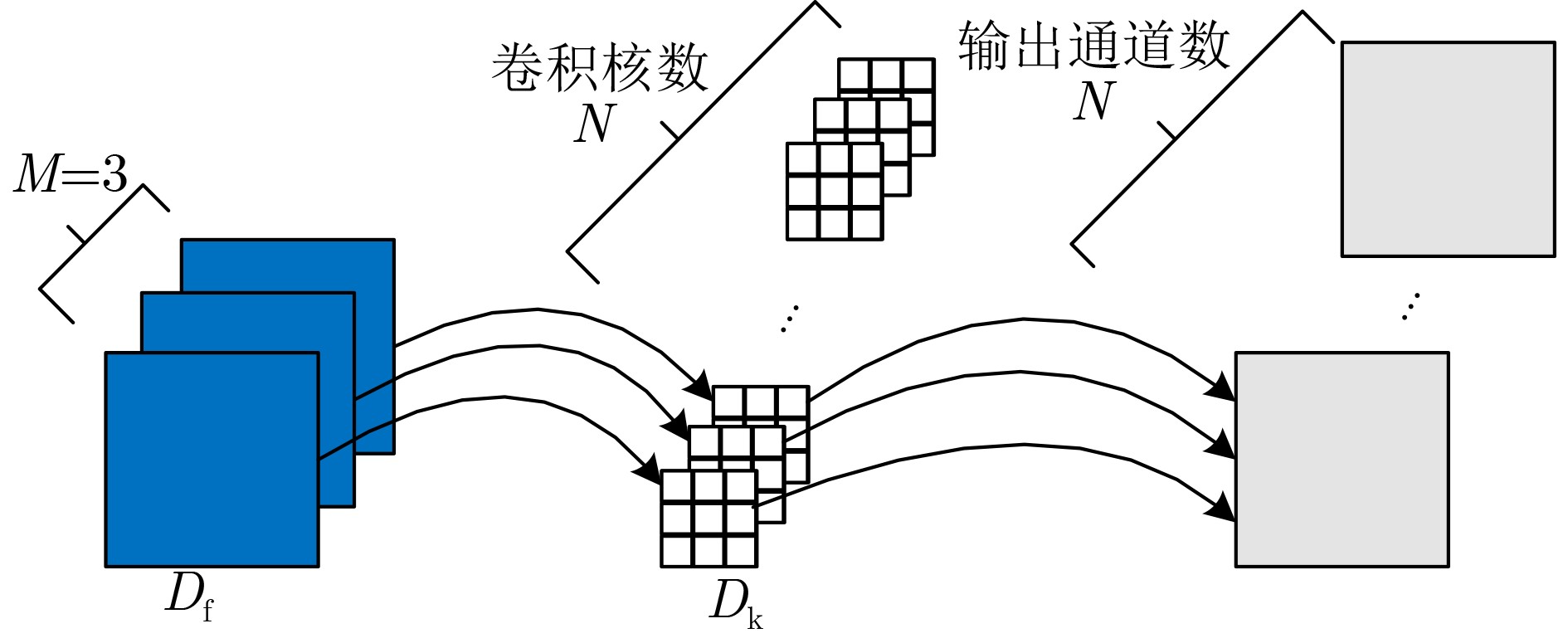
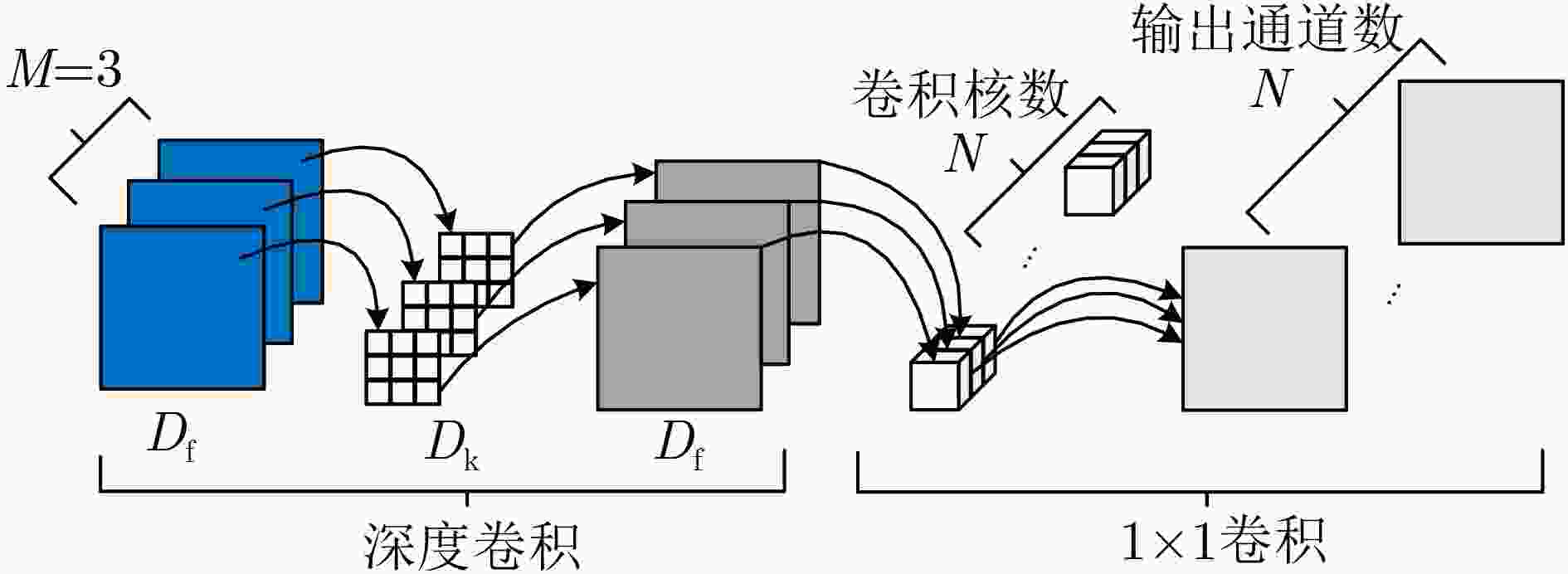
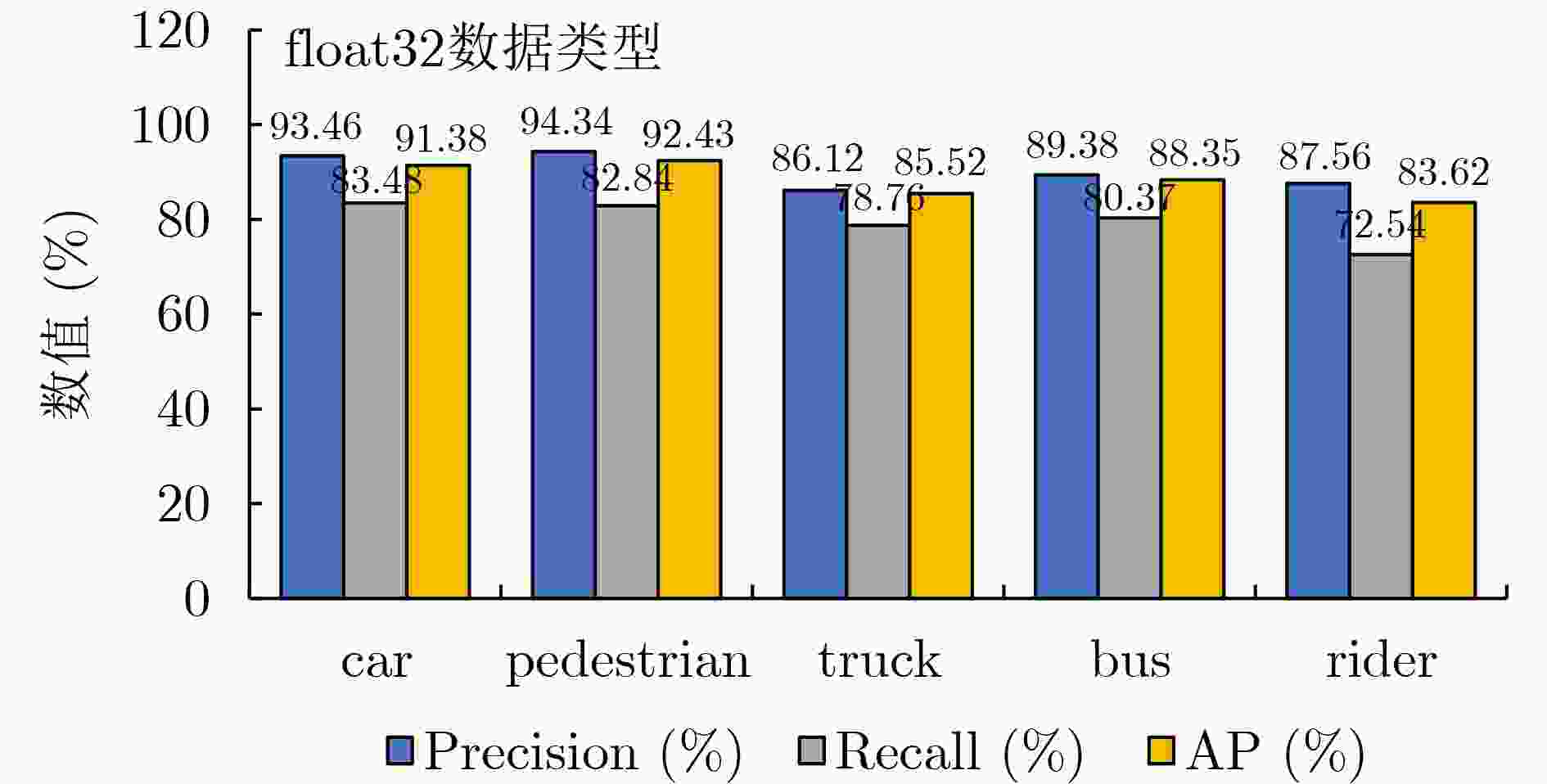
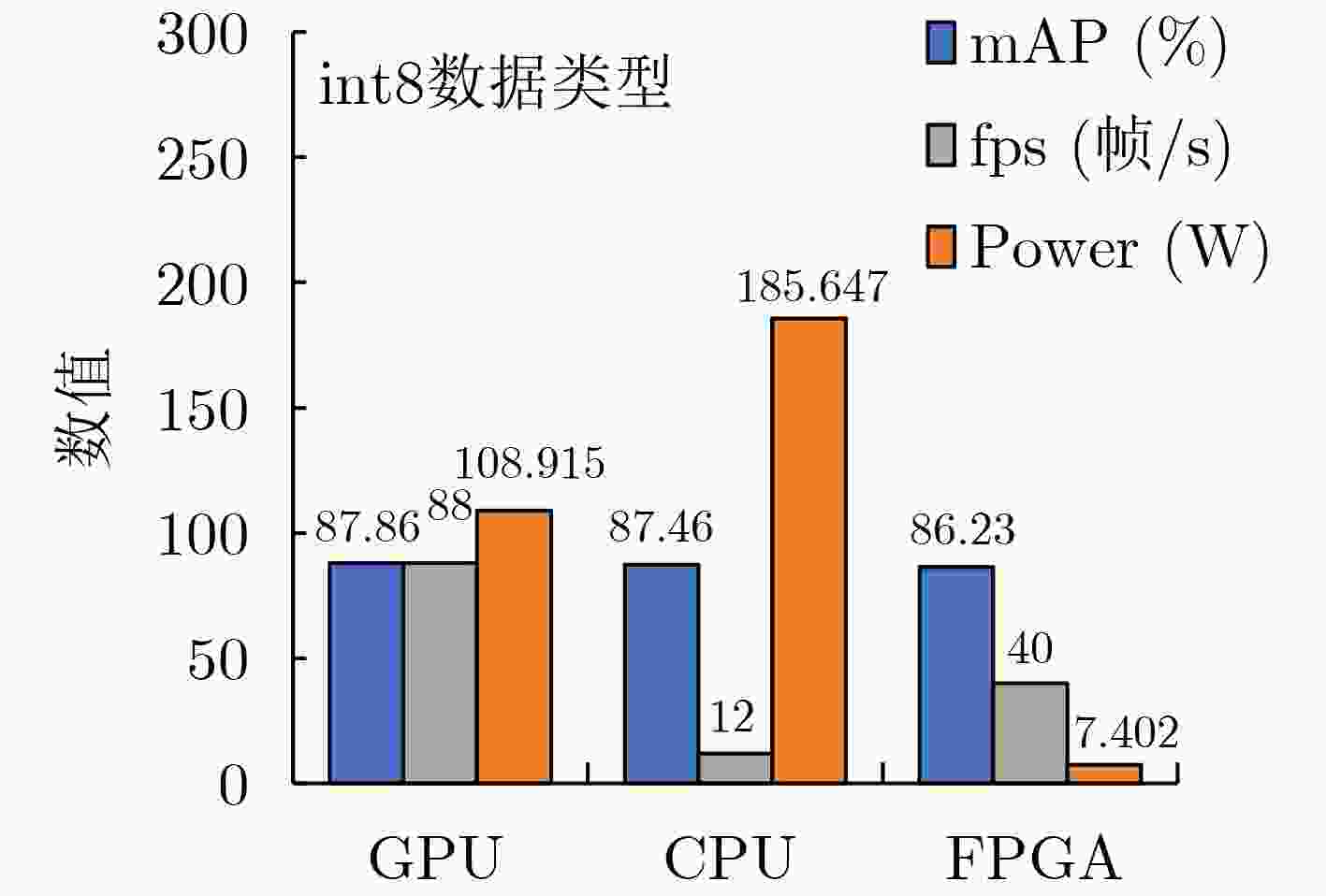
Objective Accurate and real-time detection of pedestrians and vehicles is essential for autonomous driving at the edge. However, deep learning-based object detection algorithms are often challenging to deploy in edge environments due to their high computational demands and complex parameter structures. To address these limitations, this study proposes a soft-hard coordination strategy. A lightweight neural network model, Yolo Model Adaptation Network (YOMANet), is designed, and a corresponding neural network accelerator, YOMANet Accelerator (YOMANet-Accel), is implemented on a heterogeneous Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) platform. This system enables efficient algorithm acceleration for pedestrian and vehicle detection in edge-based autonomous driving scenarios. Methods The lightweight backbone of YOMANet adopts MobileNetv2 to reduce the number of network parameters. The neck network incorporates the Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) and Path Aggregation Network (PANet) structures from YOLOv4 to expand the receptive field and accommodate targets of varying sizes. Depthwise separable convolution replaces standard convolution, thereby reducing training complexity and improving convergence speed. To enhance detail extraction, the Normalization-based Attention Module (NAM) is integrated into the head network, allowing suppression of irrelevant feature weights. For deployment on a FPGA platform, parallel computing and data storage schemes are designed. The parallel computing strategy adopts a loop blocking method to reorder inner and outer loops, enabling access to different output array elements through adjacent loop layers and facilitating parallel processing of output feature map pixels. Multiply-add trees are implemented in the Processing Engine (PE) to support efficient task allocation and operation scheduling. A double-buffer mechanism is introduced in the data storage scheme to increase data reuse, minimize transmission latency, and enhance system throughput. In addition, int8 quantization is applied to both weight parameters and activation functions, reducing the overall parameter size and accelerating parallel computation. Results and Discussions Experimental results on the training platform indicate that YOMANet achieves the inference speed characteristic of lightweight models while maintaining the detection accuracy of large-scale models, thereby improving overall detection performance ( Fig. 12 ,Table 2 ). The ablation study demonstrates that the integration of MobileNetv2 and depthwise separable convolution significantly reduces the number of model parameters. Embedding the NAM attention mechanism does not noticeably increase model size but enhances detail extraction and improves detection of small targets (Table 3 ). Compared with other lightweight algorithms, the enhanced YOMANet shows improved detail extraction and superior detection of small and occluded targets, with substantially lower false and missed detection rates (Fig. 13 ). Results on the accelerator platform reveal that quantization has minimal effect on accuracy while substantially reducing model size, supporting deployment on resource-constrained edge devices (Table 4 ). When deployed on the FPGA platform, YOMANet retains detection accuracy comparable to GPU/CPU platforms, while power consumption is reduced by an order of magnitude, meeting the efficiency requirements for edge deployment (Fig. 14 ). Compared with related accelerator designs, YOMANet-Accel achieves competitive throughput and the highest Digital Signal Processing (DSP) efficiency, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed parallel computing and storage schemes in utilizing FPGA resources (Table 5 ).Conclusions Experimental results demonstrate that YOMANet achieves high detection accuracy and fast inference speed on the training platform, with enhanced performance for small and occluded targets, leading to a reduced missed detection rate. When deployed on the FPGA platform, YOMANet-Accel achieves an effective balance between detection performance and resource efficiency, supporting real-time pedestrian and vehicle detection in edge computing scenarios. -
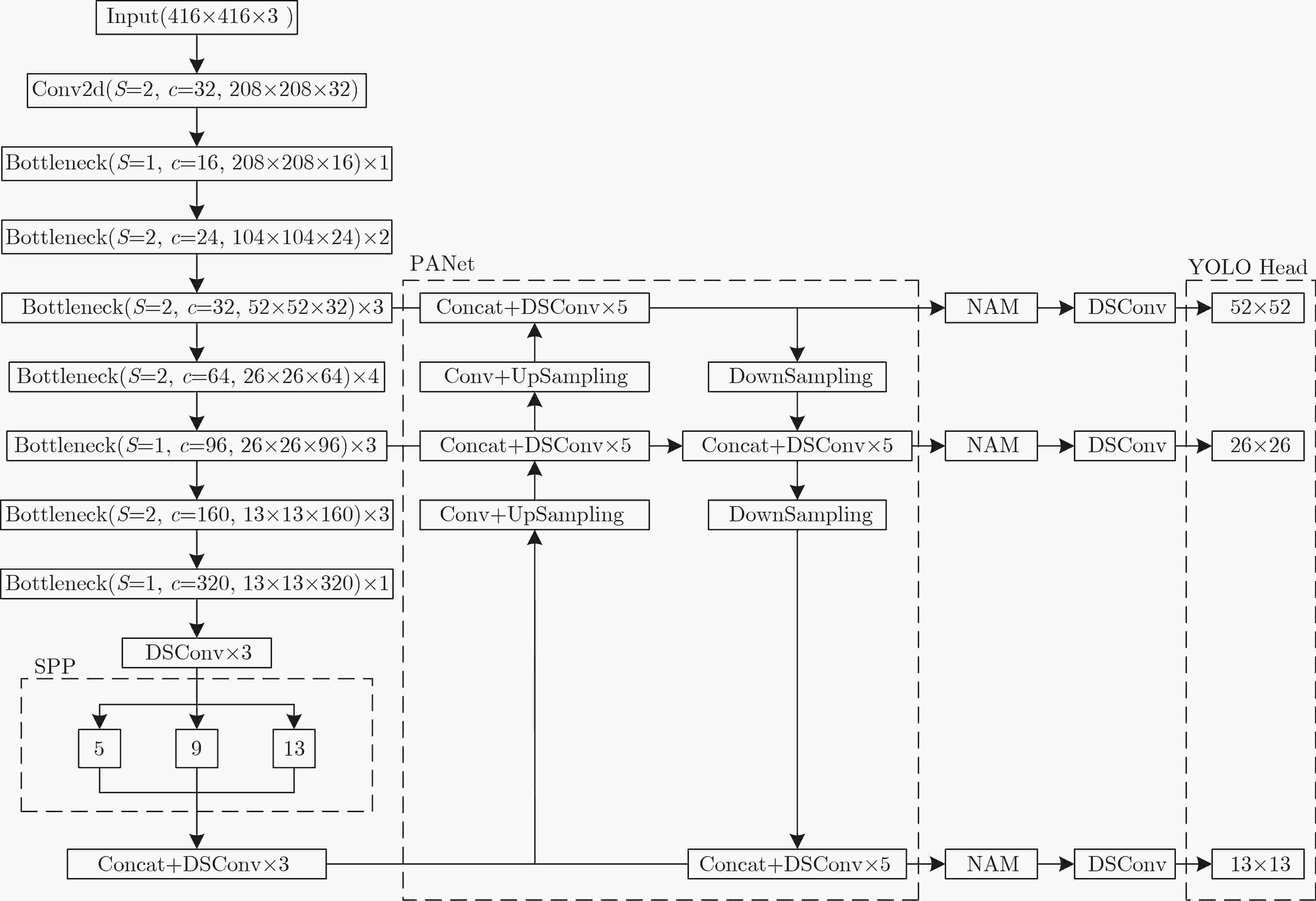
表 1 YOMANet主干网络模型结构
Input Operate t c S Input Operate t c S 416×416×3 Conv2d - 32 2 26×26×32 Bottleneck5-4 6 64 1 208×208×32 Bottleneck2-1 1 16 1 26×26×64 Bottleneck6-1 6 64 1 208×208×16 Bottleneck3-1 6 16 2 26×26×64 Bottleneck6-2 6 64 1 104×104×16 Bottleneck3-2 6 24 1 26×26×64 Bottleneck6-3 6 96 1 104×104×24 Bottleneck4-1 6 24 2 26×26×96 Bottleneck7-1 6 96 2 52×52×24 Bottleneck4-2 6 24 1 13×13×96 Bottleneck7-2 6 96 1 52×52×24 Bottleneck4-3 6 32 1 13×13×96 Bottleneck7-3 6 160 1 52×52×32 Bottleneck5-1 6 32 2 13×13×160 Bottleneck8-1 6 320 1 26×26×32 Bottleneck5-2 6 32 1 13×13×320 DSConv×3 - - - 26×26×32 Bottleneck5-3 6 32 1 表 2 不同算法在GPU平台上的性能比较
Model Backbone Input size Data type mAP@0.5(%) Size(MB) fps Faster RCNN VGG16 600× 1000 float32 90.13 500.67 18 SSD VGG16 512×512 float32 88.13 287.64 28 YOLOv4 CSP-DarkNet53 416×416 float32 88.29 249.48 39 YOLOv5 CSP-DarkNet53 640×640 float32 88.72 223.62 51 CCBA-NMS-YD[7] VGG16 512×512 float32 87.06 - - YOLOv3-Improved[8] Darknet53 416×416 float32 86.24 - - YOLOv5s-RFB-s-ASFF[9] CSP-RFB-s-ASFF 640×640 float32 84.01 - 61 YOLOP-E[28] EfficientNetv2 - float32 79.20 27.6 41.6 YOLOv4-tiny CSP-Darknet53-tiny 416×416 float32 80.69 37.94 74 YOLOv5s CSP-DarkNet53 640×640 float32 83.51 34.46 78 YOLOv7-tiny CSP-PANet 416×416 float32 86.68 32.75 84 YOMANet MobileNetv2 416×416 float32 88.26 30.95 80 表 3 消融实验性能比较
MobileNetv2 DSConv NAM Data type mAP(%) Size(MB) fps Power(W) × × × float32 88.29 249.48 39 167.436 √ × × float32 86.76 80.24 63 123.481 √ √ × float32 86.37 28.89 84 106.274 √ √ √ float32 88.26 30.95 80 108.915 表 4 数据量化前后效果对比
Model Data type mAP@0.5(%) Size(MB) YOMANet float32 88.26 30.95 int8 86.23 7.76 表 5 与相关文献的加速器性能对比
文献[11] 文献[12] 文献[13] 文献[14] 文献[29] 本文 Model YOLOv4-tiny YOLOv3-tiny YOLOv5s Ultranet YOLOv3-tiny YOMANet Backbone CSP-Darknet53 DarkNet53 CSP-DarkNet53 VGG16 DarkNet53 MobileNetv2 FPGA ZYNQ 7020 Nexys A7-100T ZYNQ 7020 ZYNQ ZU3EG ZYNQ XCZU9EG ZYNQ 7020 DSP 220 240 220 360 298 220 Data type 16 bit int8 16 bit 4 bit 16 bit int8 Power (W) 2.750 2.203 3.039 6.650 4.120 7.402 GOPS - 95.08 30.10 126.72 96.60 100.23 GOPS/DSP - 0.396 0.137 0.352 0.324 0.456 GOPS/W - 43.16 9.90 19.06 23.45 13.54 Size (MB) 23.70 - - 15.18 - 7.76 fps (帧/s) - 76.75 - 220.76 17.30 40.15 mAP@0.5(%) 77.80 81.19 40.30 - 31.50 86.23 -
[1] ZHAN Jiao, LIU Jingnan, WU Yejun, et al. Multi-task visual perception for object detection and semantic segmentation in intelligent driving[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(10): 1774. doi: 10.3390/rs16101774. [2] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [3] 谭郁松, 李恬, 张钰森. 面向边缘智能的神经网络模型生成与部署研究[J]. 计算机工程, 2024, 50(8): 1–12. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0068554.TAN Yusong, LI Tian, and ZHANG Yusen. Research on neural network model generation and deployment for edge intelligence[J]. Computer Engineering, 2024, 50(8): 1–12. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0068554. [4] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. [5] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [6] WEI Hongyang, ZHANG Qianqian, HAN Jingjing, et al. SARNet: Spatial Attention Residual Network for pedestrian and vehicle detection in large scenes[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(15): 17718–17733. doi: 10.1007/s10489-022-03217-9. [7] YUAN Zhenhao, WANG Zhiwen, and ZHANG Ruonan. CCBA-NMS-YD: A Vehicle pedestrian detection and tracking method based on improved YOLOv7 and DeepSort[J]. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 2024, 15(7): 309. doi: 10.3390/wevj15070309. [8] 王启明, 何梓林, 张栋林, 等. 基于YOLOv3的雾天场景行人车辆检测方法研究[J]. 控制工程, 2024, 31(3): 510–517. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.20211118.WANG Qiming, HE Zilin, ZHANG Donglin, et al. Research on pedestrian and vehicle detection method based on YOLOv3 in foggy scene[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2024, 31(3): 510–517. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.20211118. [9] 胡丹丹, 张忠婷. 基于改进YOLOv5s的面向自动驾驶场景的道路目标检测算法[J]. 智能系统学报, 2024, 19(3): 653–660. doi: 10.11992/tis.202206034.HU Dandan and ZHANG Zhongting. Road target detection algorithm for autonomous driving scenarios based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2024, 19(3): 653–660. doi: 10.11992/tis.202206034. [10] WANG Haotian, ZHAO Yinghai, and GAO Fan. A convolutional neural network accelerator based on FPGA for buffer optimization[C]. 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 2021: 2362–2367. doi: 10.1109/IAEAC50856.2021.9390606. [11] ZHAO Sijie, GAO Shangshang, WANG Rugang, et al. Acceleration and implementation of convolutional neural networks based on FPGA[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 141: 104188. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2023.104188. [12] KIM M, OH K, CHO Y, et al. A low-latency FPGA accelerator for YOLOv3-tiny with flexible layerwise mapping and dataflow[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2024, 71(3): 1158–1171. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2023.3335949. [13] 刘谦, 王林林, 周文勃. 基于FPGA的YOLOv5s网络高效卷积加速器设计[J]. 电讯技术, 2024, 64(3): 366–375. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.230216003.LIU Qian, WANG Linlin, and ZHOU Wenbo. Design of a YOLOv5s network efficient convolution accelerator powered by FPGA[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2024, 64(3): 366–375. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.230216003. [14] 包振山, 郭俊南, 张文博, 等. UltraAcc: 基于FPGA流水架构的低功耗高性能CNN加速器定制设计[J]. 计算机学报, 2023, 46(6): 1139–1155. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.01139.BAO Zhenshan, GUO Junnan, ZHANG Wenbo, et al. UltraAcc: A customized low power and high performance CNN accelerator with dataflow on FPGAs[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2023, 46(6): 1139–1155. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.01139. [15] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, and LIAO H Y M. Scaled-YOLOv4: Scaling cross stage partial network[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 13024–13033. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01283. [16] JOCHER G, STOKEN A, BOROVEC J, et al. ultralytics/YOLOv5: V4.0 - nn. SiLU() activations, Weights & Biases logging, PyTorch Hub integration[Z]. 2021. doi: 10.5281/ZENODO.4418161. [17] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, Canada, 2022: 7464–7475. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00721. [18] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU Menglong, et al. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510–4520. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474. [19] LIU Yichao, SHAO Zongru, TENG Yueyang, et al. NAM: Normalization-based attention module[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.12419, 2021. [20] ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHOU Xinyu, LIN Mengxiao, et al. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6848–6856. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00716. [21] TAN Mingxing and LE Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6105–6114. [22] HAN Kai, WANG Yunhe, TIAN Qi, et al. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 1577–1586. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00165. [23] HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, 2017. [24] HU Jie, SHEN Li, SUN Gang, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372. [25] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11531–11539. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155. [26] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [27] CORDTS M, OMRAN M, RAMOS S, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3213–3223. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.350. [28] LIU Yulin, LI Gang, HAO Liguo, et al. Research on a lightweight panoramic perception algorithm for electric autonomous mini-buses[J]. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 2023, 14(7): 179. doi: 10.3390/wevj14070179. [29] 任仕伟, 刘朝钾, 李剑铮, 等. 面向端到端目标检测神经网络的高效硬件加速系统设计[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1312–1320. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.004.REN Shiwei, LIU Chaojia, LI Jianzheng, et al. Efficient hardware acceleration system design for end-to-end object detection neural network[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2022, 42(12): 1312–1320. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.004. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
