Design of Private Set Intersection Protocol Based on National Cryptographic Algorithms
-
摘要: 现有的隐私集合求交协议存在安全漏洞不可控的风险,此外计算效率不能满足实际应用需求。该文提出一种基于国密算法SM2和SM3的隐私集合求交协议SM-PSI,采用国产安全芯片对协议中的关键算法如含数据加密、非交互零知识证明等进行了硬件加速设计,通过理论分析证明了协议在半诚实敌手模型下的安全性。使用模拟数据集进行实验,结果表明,在相同的安全等级下,所提协议通过软硬件协同优化,其计算效率显著优于现有方法,计算速度比CPU运行最优方案SpOT-Light的PSI协议平均提升4.2倍,比DH-IPP方案平均提升6.3倍。该研究为实现我国网络空间安全自主可控提供了重要支撑。Abstract:
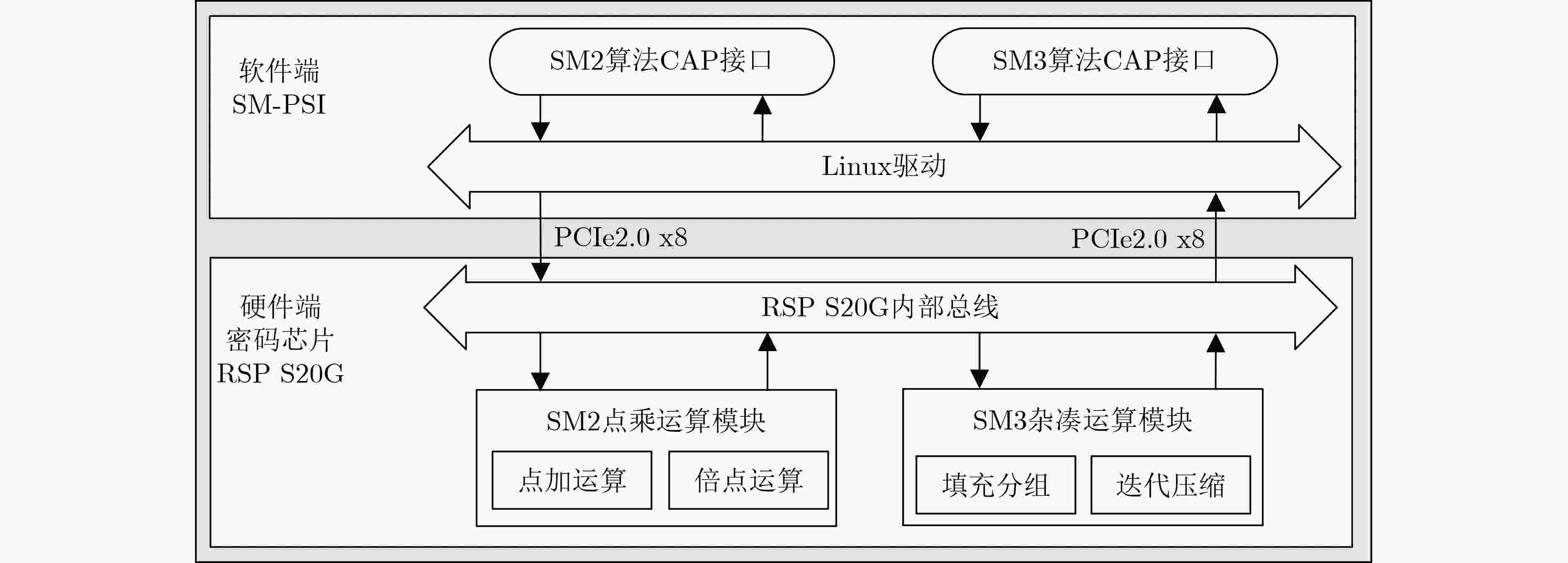
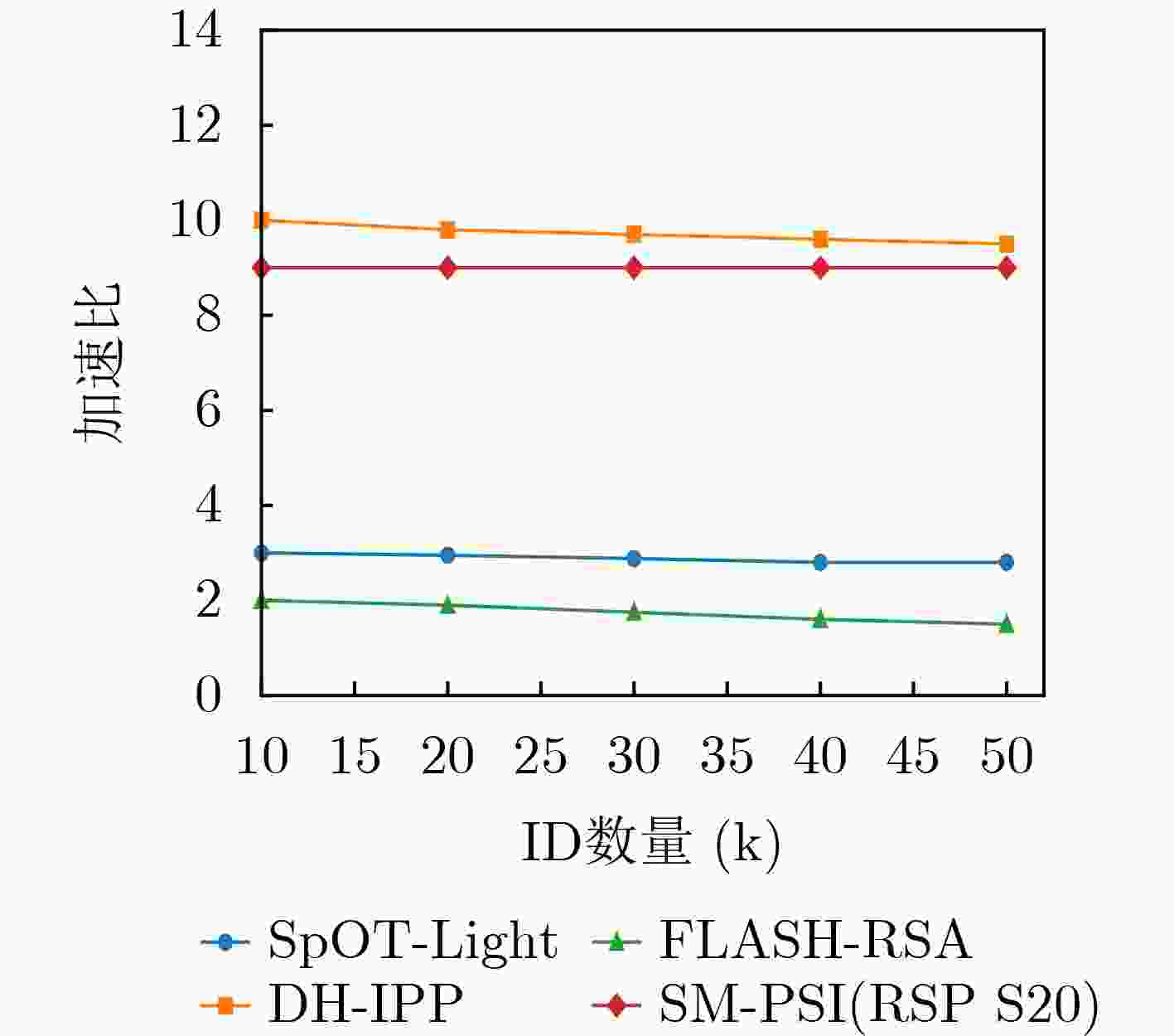
Objective The rapid development of global digital transformation has exposed Private Set Intersection (PSI) as a key bottleneck constraining the digital economy. Although technical innovations and architectural advances in PSI protocols continue to emerge, current protocols face persistent challenges, including algorithmic vulnerabilities in international cryptographic primitives and limited computational efficiency when applied to large-scale datasets. To address these limitations, this study integrates domestic SM2 elliptic curve cryptography and the SM3 cryptographic hash function to enhance PSI protocol performance and protect sensitive data, providing technical support for China’s cyberspace security. A PSI protocol based on national cryptographic standards (SM-PSI) is proposed, with hardware acceleration of core cryptographic operations implemented using domestic security chips. This approach achieves simultaneous improvements in both security and computational efficiency. Methods SM-PSI integrates the domestic SM2 and SM3 cryptographic algorithms to reveal only the intersection results without disclosing additional information, while preserving the privacy of each participant’s input set. By combining SM2 elliptic curve public-key encryption with the SM3 hash algorithm, the protocol reconstructs encryption parameter negotiation, data obfuscation, and ciphertext mapping processes, thereby eliminating dependence on international algorithms such as RSA and SHA-256. An SM2-based non-interactive zero-knowledge proof mechanism is designed to verify the validity of public–private key pairs using a single communication round. This reduces communication overhead, mitigates man-in-the-middle attack risks, and prevents private key exposure. The domestic reconfigurable cryptographic chip RSP S20G is integrated to offload core computations, including SM2 modular exponentiation and SM3 hash iteration, to dedicated hardware. This software-hardware co-acceleration approach significantly improves protocol performance. Results and Discussions Experimental results on simulated datasets demonstrate that SM-PSI, through hardware-software co-optimization, significantly outperforms existing protocols at comparable security levels. The protocol achieves an average speedup of 4.2 times over the CPU-based SpOT-Light PSI scheme and 6.3 times over DH-IPP ( Table 3 ), primarily due to offloading computationally intensive operations, including SM2 modular exponentiation and SM3 hash iteration, to dedicated hardware. Under the semi-honest model, SM-PSI reduces both the number of dataset encryption operations and communication rounds, thereby lowering data transmission volume and computational overhead. Its computational and communication complexities are substantially lower than those of SpOT-Light, DH-IPP, and FLASH-RSA, making it suitable for large-scale data processing and low-bandwidth environments (Table 1 ). Simulation experiments further show that the hardware-accelerated framework consistently outperforms CPU-only implementations, achieving a peak speedup of 9.0 times. The speedup ratio exhibits a near-linear relationship with dataset size, indicating stable performance as the ID data volume increases with minimal efficiency loss (Fig. 3 ). These results demonstrate SM-PSI’s ability to balance security, efficiency, and scalability for practical privacy-preserving data intersection applications.Conclusions This study proposes SM-PSI, a PSI protocol that integrates national cryptographic algorithms SM2 and SM3 with hardware-software co-optimization. By leveraging domestic security chip acceleration for core operations, including non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs and cryptographic computations, the protocol addresses security vulnerabilities presented in international algorithms and overcomes computational inefficiencies in large-scale applications. Theoretical analysis confirms its security under the semi-honest adversary model, and experimental results demonstrate substantial performance improvements, with an average speedup of 4.2 times over CPU-based SpOT-Light and 6.3 times over DH-IPP. These results establish SM-PSI as an efficient and autonomous solution for privacy-preserving set intersection, supporting China’s strategic objective of achieving technical independence and high-performance computation in privacy-sensitive environments. Prospects Future work will extend this research by exploring more efficient PSI protocols based on national cryptographic standards, aiming to improve chip-algorithm compatibility, reduce power consumption, and enhance large-scale data processing efficiency. Further efforts will target optimizing protocol scalability in multi-party scenarios and developing privacy-preserving set intersection mechanisms suitable for multiple participants to meet complex practical application demands. In addition, this research will promote integration with other privacy-enhancing technologies, such as federated learning and differential privacy, to support the development of a more comprehensive privacy protection framework. -
Key words:
- Private Set Intersection (PSI) /
- SM2 /
- SM3 /
- Hardware-software collaboration /
- Semi-honest adversary
-
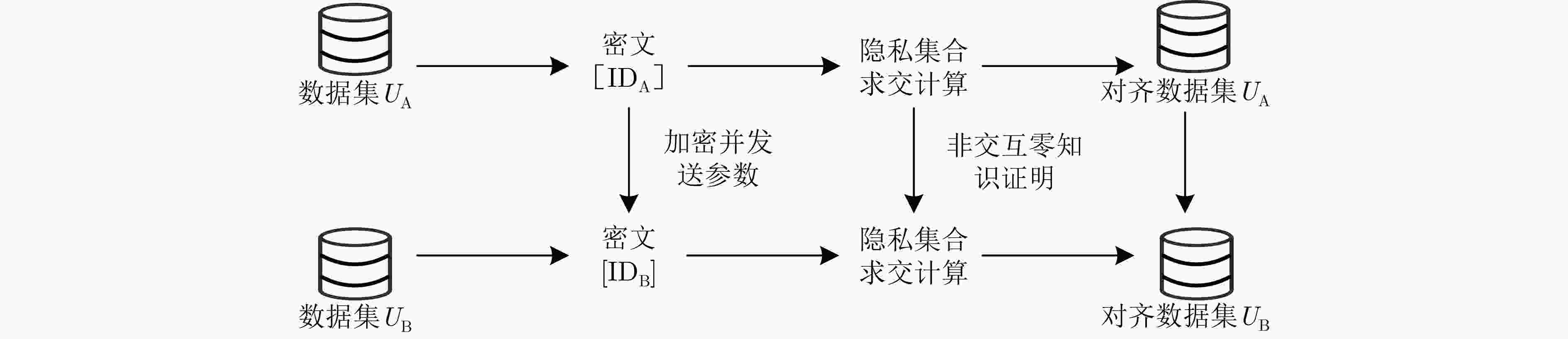
1 基于国密算法的隐私集合求交集协议流程
输入:Alice和Bob分别输入数据集合$ {U_{\text{A}}}{\text{ = \{ }}{U_{{\text{A1}}}}{\text{,}} U_{{\text{A2}}}{\text{,}} \cdots {\text{,}}{U_{{\text{A}}i}}{\text{\} }} $和$ {U_{\text{B}}}{\text{ = \{ }}{U_{{\text{B1}}}}{\text{,}}{U_{{\text{B2}}}}{\text{,}} \cdots {\text{,}}{U_{{\text{B}}j}}{\text{\} }} $ 输出:交集$ {U_{\text{A}}} \cap {U_{\text{B}}} $ 准备:本文假设Alice和Bob视作安全多方计算协议中的两个参与者,Alice和Bob选择同一套SM2椭圆曲线参数,包括:选择大素数P构建
有限域${F_P}$,有限域${F_P}$含P个元素;在有限域$ {F}_{P} $上定义椭圆曲线$E({F_P})$,选择生成元G为椭圆曲线$E({F_P})$的q阶基点$({X_G},{Y_G})$,生成元
G的阶为n;其中,当$k \in Z_q^*$,$[k]G$表示使用椭圆曲线标量乘法计算基点G的k倍点,密码杂凑算法选用SM3,$x\parallel y$代表字节串拼接。
Alice和Bob方按照以下方案步骤进行协同计算出两方加密值而不会泄露其他信息:(1) Bob方进行如下操作: (a) Bob方生成随机数作为该方案私钥$ {d_{\text{B}}} \in Z_{q-1}^* $,私钥$ {d}_{{\mathrm{B}}} $仅由Bob方持有; (b) 计算公钥${P_{\text{B}}} = [{d_{\text{B}}}]G$,Bob方公开公钥信息。 (2) Alice方进行如下操作: (a) 接收Bob方发送的公钥${P_{\text{B}}}$计算椭圆曲线点$S = [h]{P_{\text{B}}}$,其中$h = 1$,若$S$为无穷远点,则报错并退出; (b) 在本次隐私集合求交过程中,生成一个随机数$ k \in Z_{q-1}^* $,计算${c_1} = [k]G = ({x_1},{y_1})$; (c) 计算混淆点$[k]{P_{\text{B}}} = ({x_2},{y_2})$; (d) 计算${c_2}_{{\text{A}}i} = {\text{Hash(}}{x_2}\parallel {U_{{\text{A}}i}}\parallel {y_2}{\text{)}}$,获得密文集合${c_2}_{\text{A}} = \left\{ {{c_{21}},{c_{22}}, \cdots ,{c_{2{\text{A}}i}}} \right\}$; (e) Alice方向$ {{F}}_{{\text{com-ZK}}}^{{R}} $发送指令$({\text{prove,sid||}}1,{c_1},k)$。 (3) Bob方进行如下操作: (a) Bob方接收$ {{F}}_{{\text{com-ZK}}}^{{R}} $返回的消息$({\text{proof-receipt,sid||}}1)$。 (4) Alice方进行如下操作 (a) Alice方选择随机数r,计算$R = [r]G$; (b) Alice方向$ {{F}}_{{\text{com-ZK}}}^{{R}} $发送指令$({\text{response-proof,sid||}}1)$ (c) 生成挑战$c' = {\mathrm{Hash}}(R,{c_1},G)$,计算$s = r + {{k}}c'$,生成${c_3} = (R,s)$,Alice方将$c = ({c_1},{c_3},{c_2}_{\text{A}})$发送Bob方; (d) 零知识证明:Alice方通过零知识证明$(G,R,{c_1}) \in {{{R}}_{{\text{DL}}}}$。 (5) Bob方进行如下操作: (a) 接受Alice方密文集合$c = ({c_1},{c_3},{c_2}_{\text{A}})$; (b) Bob方利用${c_3}$证明${c_1} = [k]G = ({x_1},{y_1})$,生成验证$c' = {\text{Hash}}(R,{c_1},G)$; (c) Bob方接收$ {{F}}_{{\text{com-ZK}}}^{{R}} $返回的消息$({\text{response-proof,sid||}}1,{c_1})$,若没有接收到则中止协议; (d) Bob方接受零知识证明$(G,R,{c_1}) \in {{{R}}_{{\text{DL}}}}$,否则中止协议; (e) 计算并检查$[s]G = R + [c']{c_1}$是否成立; (f) 若成立,则${c_1} = [k]G = ({x_1},{y_1})$,利用私钥$ {d_{\text{B}}} \in Z_{q-1}^* $,计算$[{d_{\text{B}}}]{c_1} = [{d_{\text{B}}}][k]G = ({x_2},{y_2})$; (g) 计算$c_{{2\text{B}}_j} = {\text{Hash(}}{x_2}\parallel {U_{{\text{B}}j}}\parallel {y_2}{\text{)}}$,获得密文集合${c_2}_{\text{B}} = \left\{ {{c_{21}},{c_{22}}, \cdots ,{c_{2{\text{B}}j}}} \right\}$; (h) 得到交集计算结果$ I = {c_{2{\text{A}}}} \cap {c_{2{\text{B}}}} $,双方获得交集结果。 表 1 PSI协议架构对比
表 2 PSI协议复杂度比较
PSI协议 计算复杂度 通信复杂度 类型 SpOT-Light[13] $ t{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{2}}}^2t $ $ 2(\lambda + {\log _2}({N_X}{N_Y})){N_X} + \ell (1 + 1/\lambda ){N_Y} $ 半诚实 DH-IPP[9] $2t{\text{pk}}$ $ \left( {\rho + {{\log }_2}({N_X}{N_Y})} \right){N_X} + \phi {N_Y} + \phi $ 半诚实 FLASH-RSA[11] $2t{\text{pk}}$ $t\rho + {N_X}\nu $ 半诚实 本文 $t + 9{\text{pk}}$ $3\phi + {N_X}\nu $ 半诚实 -
[1] ZHAO Chuan, ZHAO Shengnan, ZHAO Minghao, et al. Secure multi-party computation: Theory, practice and applications[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 476: 357–372. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.10.024. [2] HE Yuanyuan, TAN Xiaoyu, NI Jianbing, et al. Differentially private set intersection for asymmetrical ID alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 3479–3494. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3207911. [3] 高莹, 谢雨欣, 邓煌昊, 等. 面向纵向联邦学习的隐私保护数据对齐框架[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(8): 3419–3427. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231234.GAO Ying, XIE Yuxin, DENG Huanghao, et al. Privacy-preserving data alignment framework for vertical federated learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(8): 3419–3427. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231234. [4] ZHANG Liping, GAO Weihao, CHEN Shukai, et al. A privacy-preserving proximity testing using private set intersection for vehicular ad-hoc networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(10): 7373–7383. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3133566. [5] LAI Chengzhe, ZHANG Hanyue, LU Rongxing, et al. Privacy-preserving medical data sharing scheme based on two-party cloud-assisted PSI[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(9): 15855–15868. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3350029. [6] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 32918.4-2016 信息安全技术 SM2椭圆曲线公钥密码算法 第4部分: 公钥加密算法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China and Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 32918.4-2016 Information security technology-public key cryptographic algorithm SM2 based on elliptic curves-Part4: Public key encryption algorithm[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. [7] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 32905-2016 信息安全技术 SM3密码杂凑算法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China and Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 32905-2016 Information security techniques-SM3 cryptographic hash algorithm[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. [8] MEADOWS C. A more efficient cryptographic matchmaking protocol for use in the absence of a continuously available third party[C]. 1986 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, Oakland, USA, 1986: 134–137. doi: 10.1109/SP.1986.10022. [9] WU Guiming, HE Qianwen, JIANG Jiali, et al. Topgun: An ECC accelerator for private set intersection[J]. ACM Transactions on Reconfigurable Technology and Systems, 2023, 16(4): 52. doi: 10.1145/3603114. [10] DACHMAN-SOLED D, MALKIN T, RAYKOVA M, et al. Efficient robust private set intersection[J]. International Journal of Applied Cryptography, 2012, 2(4): 289–303. doi: 10.1504/IJACT.2012.048080. [11] ZHANG Junxue, CHENG Xiaodian, WANG Wei, et al. FLASH: Towards a high-performance hardware acceleration architecture for cross-silo federated learning[C]. The 20th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Boston, USA, 2023: 1057–1079. [12] PINKAS B, SCHNEIDER T, and ZOHNER M. Faster private set intersection based on OT extension[C]. The 23rd USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2014: 797–812. [13] PINKAS B, ROSULEK M, TRIEU N, et al. SpOT-light: Lightweight private set intersection from sparse OT extension[C]. The 39th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Cham, Germany, 2019: 401–431. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-26954-8_13. [14] BAY A, ERKIN Z, HOEPMAN J H, et al. Practical multi-party private set intersection protocols[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 1–15. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3118879. [15] 于斌, 黄海, 刘志伟, 等. 高性能Ed25519算法硬件架构设计与实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 1821–1827. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200876.YU Bin, HUANG Hai, LIU Zhiwei, et al. High-performance hardware architecture design and implementation of Ed25519 algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 1821–1827. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200876. [16] 刘志伟, 张琦, 黄海, 等. 基于比特重组快速模约简的高面积效率椭圆曲线标量乘法器设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 344–352. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221446.LIU Zhiwei, ZHANG Qi, HUANG Hai, et al. Design of high area efficiency elliptic curve scalar multiplier based on fast modulo reduction of bit reorganization[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(1): 344–352. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221446. [17] HAZAY C and NISSIM K. Efficient set operations in the presence of malicious adversaries[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2012, 25(3): 383–433. doi: 10.1007/s00145-011-9098-x. [18] DE CRISTOFARO E and TSUDIK G. Practical private set intersection protocols with linear complexity[C]. The 14th International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2010: 143–159. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14577-3_13. [19] RABIN M O. Transaction protection by beacons[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 1983, 27(2): 256–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-0000(83)90042-9. [20] PINKAS B, SCHNEIDER T, SEGEV G, et al. Phasing: Private set intersection using permutation-based hashing[C]. The 24th USENIX Security Symposium, Washington, USA, 2015: 515–530. [21] 唐飞, 凌国玮, 单进勇. 基于国密SM2和SM9的加法同态加密方案[J]. 密码学报, 2022, 9(3): 535–549. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000532.TANG Fei, LING Guowei, and SHAN Jinyong. Additive homomorphic encryption schemes based on SM2 and SM9[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2022, 9(3): 535–549. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000532. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
