Time-Series Information-Driven Parallel Interactive Multiple Model Algorithm for Underwater Target Tracking
-
摘要: 随着水下目标运动形式的多样化和复杂化,现有的交互式多模型算法(IMM)在面对目标状态切换时存在模型切换缓慢及跟踪精度不足的问题。为此,该文在经典IMM算法的基础上,提出一种基于时序信息的并行交互式多模型目标跟踪算法(TIP-IMM)。该算法通过比较相邻时刻的模型概率变化趋势,动态修正状态转移矩阵的参数,再经归一化处理实现状态转移矩阵的自适应更新。同时利用并行IMM框架和信息熵来动态更新模型概率,避免因过度修正状态转移矩阵而导致的跟踪精度下降。仿真结果表明,与现有算法相比,所提算法对目标的预测精度提高了3.52%~7.87%。同时模型的切换速度更快,有效地提高了水下目标跟踪精度。Abstract:
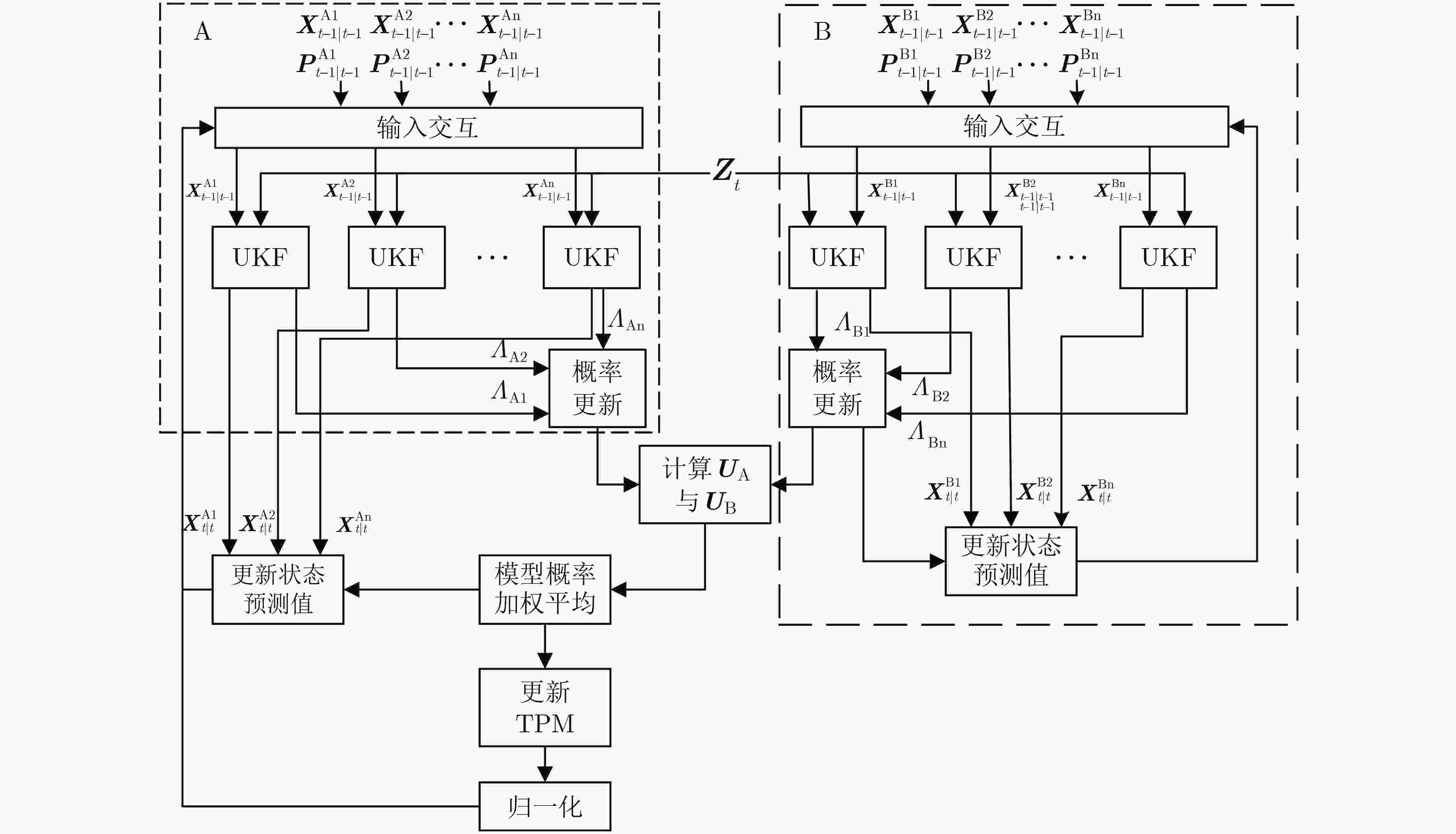
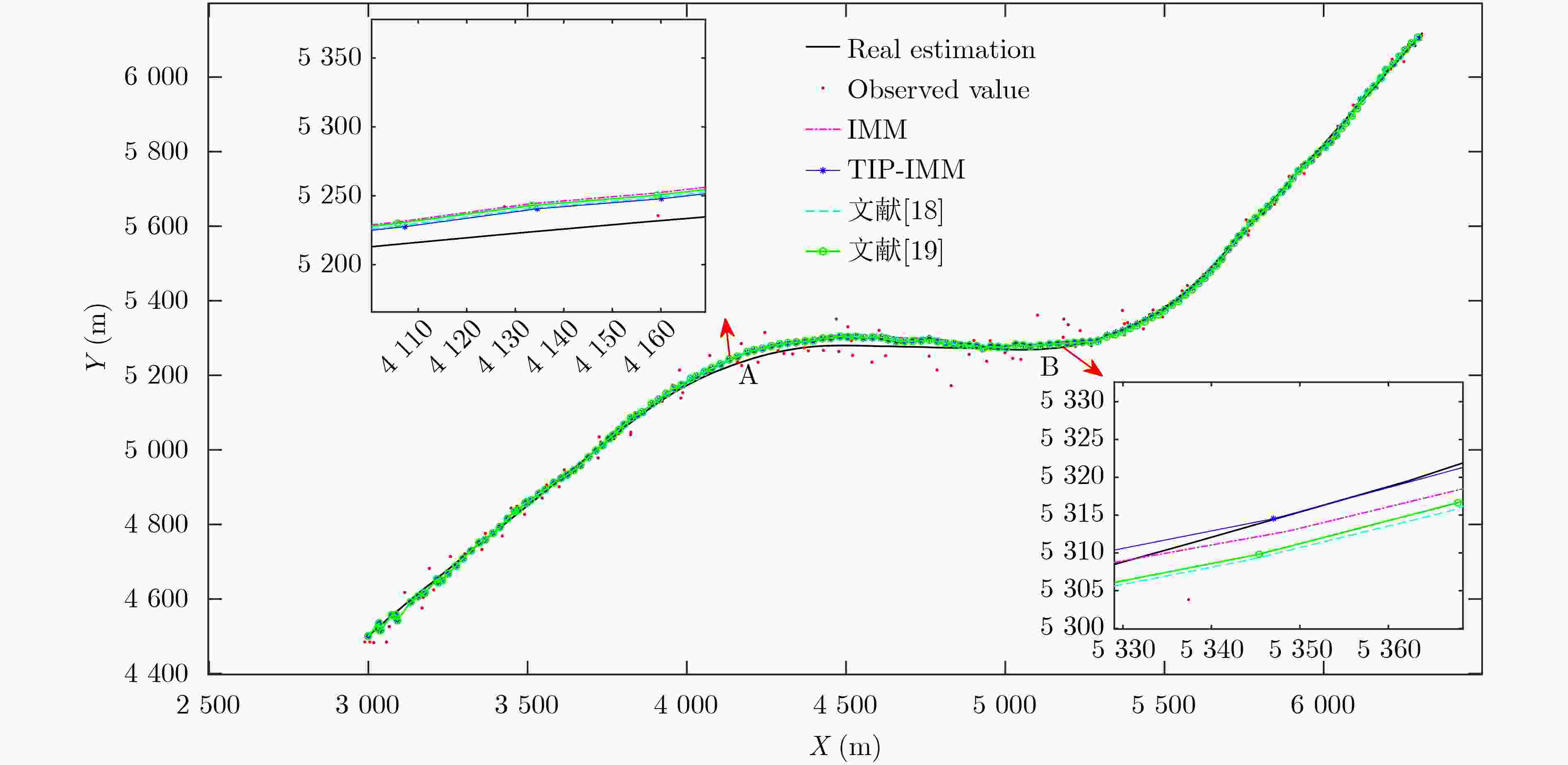
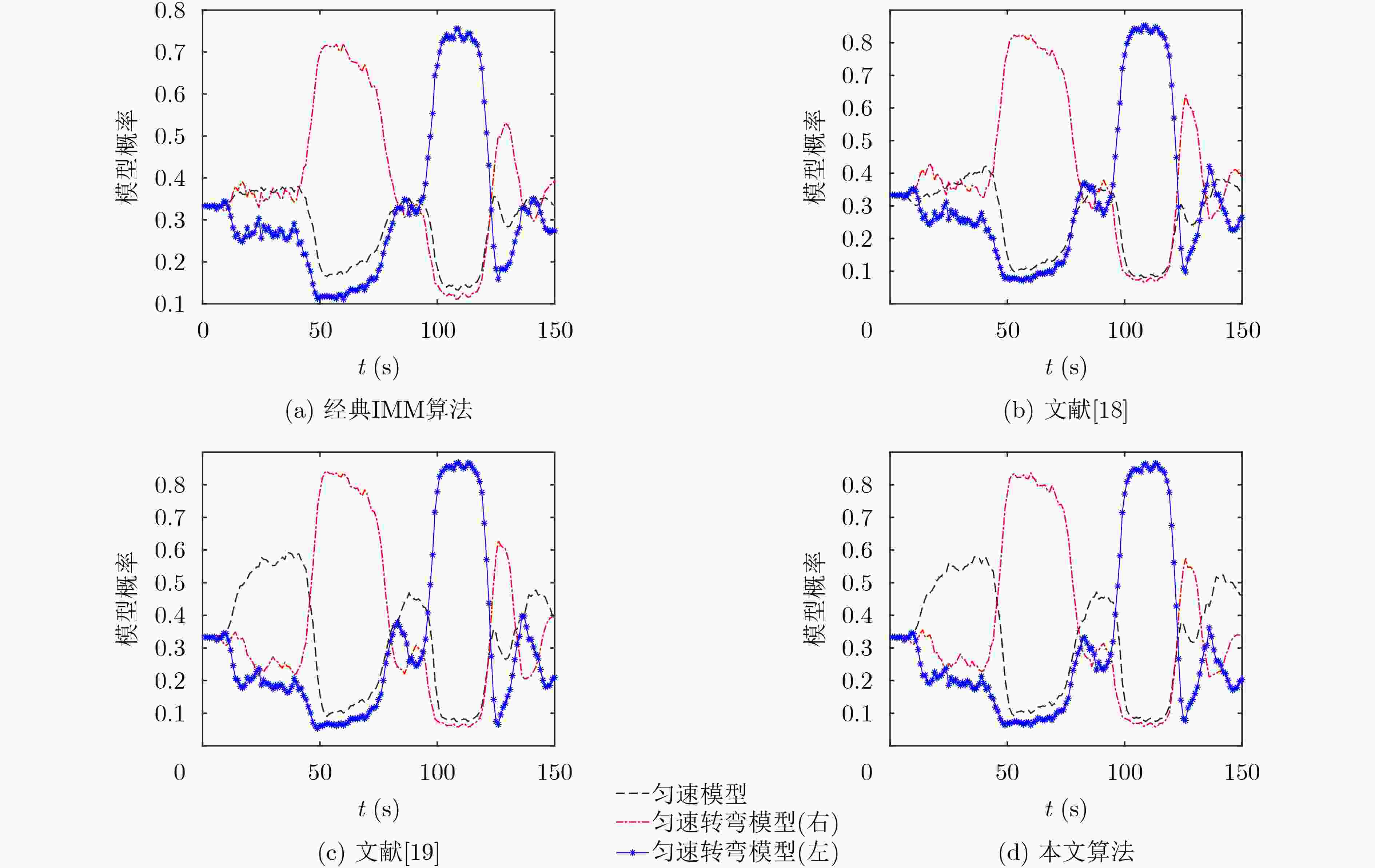
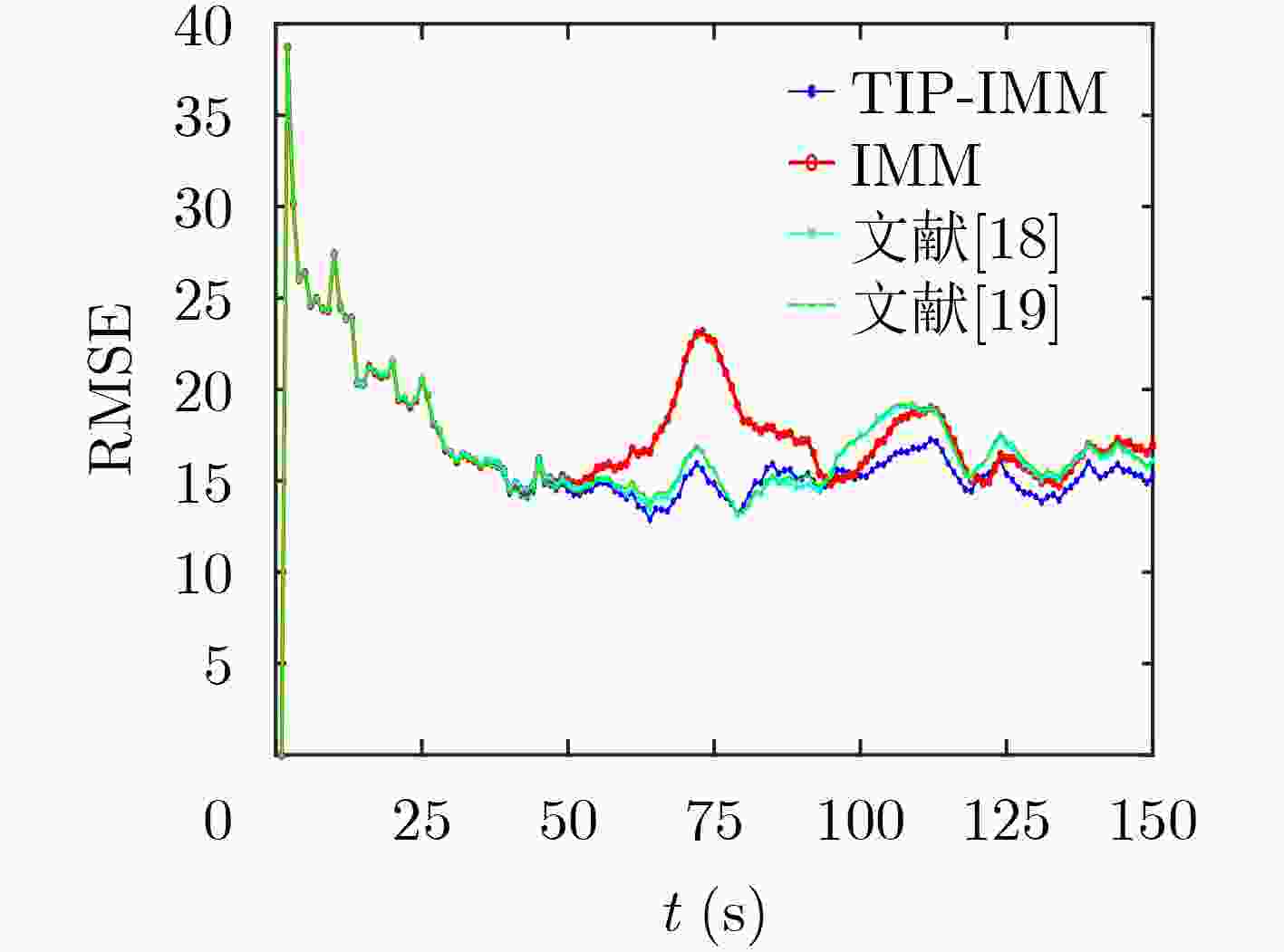
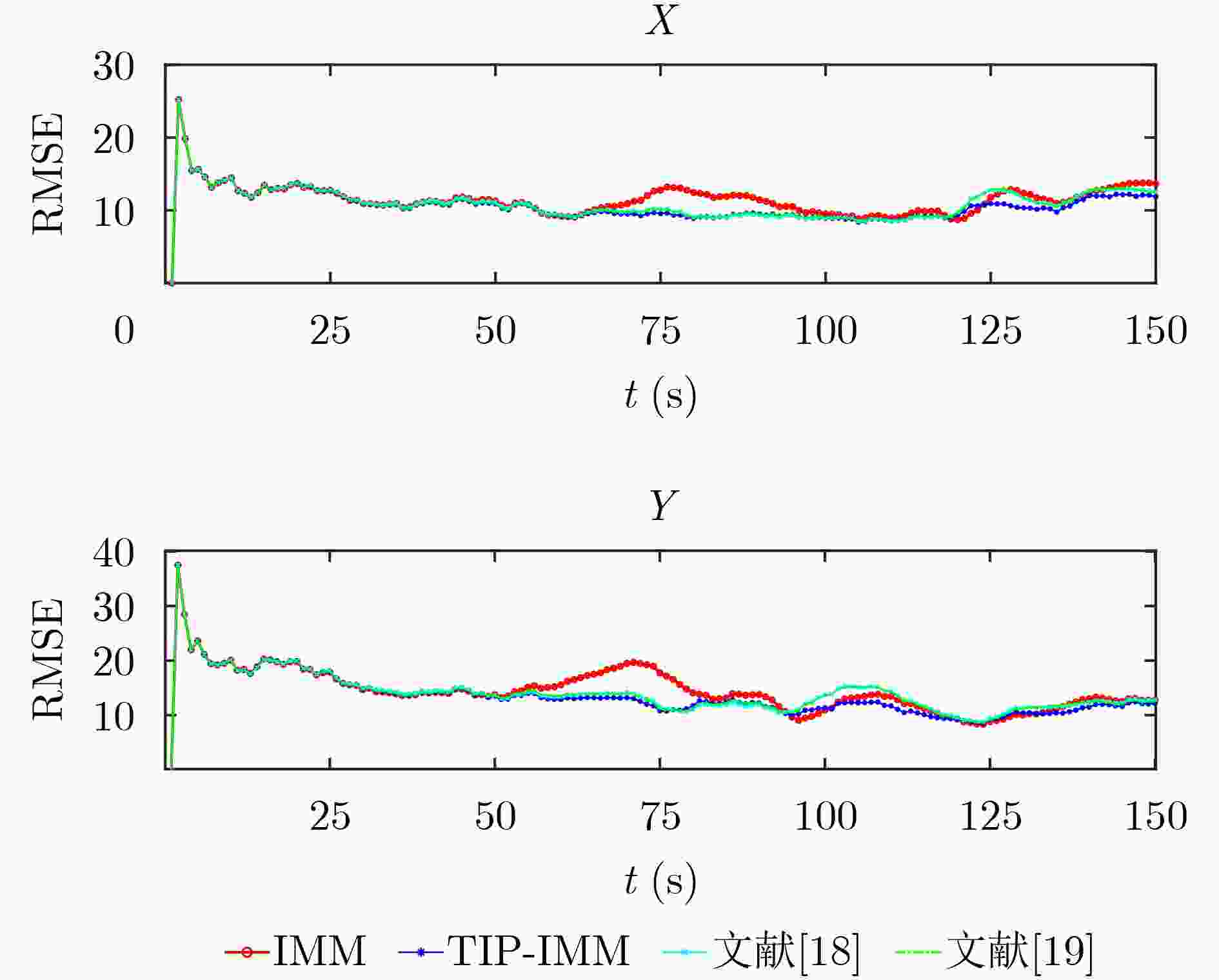
Objective Accurate underwater target tracking is critical in marine surveillance, military reconnaissance, and resource management. The nonlinear, stochastic, and uncertain motion of underwater targets, exacerbated by complex environmental dynamics, limits the effectiveness of traditional tracking methods. The Interacting Multiple Model (IMM) algorithm addresses this challenge by integrating several motion models and adaptively switching between them based on the target’s dynamic state. Such adaptability enables improved tracking under abrupt motion transitions, such as submarine maneuvers or the irregular paths of unmanned underwater vehicles. However, the classical IMM algorithm relies on a fixed Transition Probability Matrix (TPM), which can delay model switching and reduce tracking accuracy in highly dynamic settings. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes an adaptive IMM algorithm that incorporates timing information, parallel processing, and information entropy. These enhancements improve model-switching speed and accuracy, increase adaptability to environmental changes, and boost overall tracking performance and stability. Methods This study proposes a Temporal Information Parallel Interacting Multiple Model (TIP-IMM) target tracking algorithm that integrates temporal information, information entropy evaluation, and parallel processing to adaptively correct the TPM. At each time step, the algorithm identifies the model with the highest probability and assesses whether this model remains dominant across consecutive time steps. If consistent, it is designated the main model. The algorithm then evaluates changes in the main model’s probability relative to other models and updates the TPM based on defined correction rules. A parallel structure is introduced: Module A performs TPM correction, while Module B executes a standard IMM algorithm. Both modules operate concurrently. Information entropy is employed to quantify the uncertainty of the model probability distribution. When entropy is low in Module A, its corrected results are prioritized; when entropy is high, the system places greater reliance on Module B to ensure stable and robust performance under varying conditions. Results and Discussions The proposed TIP-IMM algorithm is evaluated through simulation experiments, demonstrating improved tracking accuracy and stability. True motion and observation trajectories are generated using predefined initial parameters and a motion model. Filtering results from TIP-IMM are compared with those of three benchmark algorithms. The estimated trajectories from TIP-IMM align more closely with the true trajectories, as confirmed by the enlarged views in panels A and B ( Fig. 2 ). Analysis of model probability evolution during filtering indicates that TIP-IMM exhibits smaller fluctuations during model transitions and identifies the dominant model more rapidly than the comparison methods (Fig. 3 ). To quantify tracking performance, Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) serves as the evaluation metric. TIP-IMM consistently yields lower and smoother RMSE curves across the full trajectory and in both X and Y directions (Figs. 4 and5 ). Furthermore, average RMSE (ARMSE) serves as a comprehensive indicator. TIP-IMM achieves lower errors in both position and velocity estimates (Table 2 ), consistent with the trend observed in RMSE analysis. Although the algorithm incurs a slightly higher runtime than the reference methods, its execution time remains within the millisecond range, meeting the real-time requirements of practical applications (Table 3 ).Conclusions This study proposes a TIP-IMM algorithm to address limitations of the classical IMM algorithm, particularly model-switching delays and over-smoothing during abrupt target motion changes. By incorporating temporal correlation of model probabilities, parallel processing, and information entropy, TIP-IMM improves responsiveness and transition smoothness in dynamic environments. Simulation experiments confirm that TIP-IMM achieves faster and more accurate model switching than existing methods. Compared with the traditional IMM and benchmark algorithms, TIP-IMM improves overall tracking accuracy by 3.52% to 7.87% across multiple scenarios. It also reduces estimation error recovery time while maintaining high accuracy during sudden motion transitions. These results demonstrate the algorithm’s enhanced adaptability, robustness, and stability, making it well suited for underwater target tracking applications. -
表 1 目标运动情况
时间(s) 1~40 41~70 71~90 91~115 116~150 运动状态 直线运动 匀速转弯 –1.2 (°)/s 直线运动 匀速转弯 1.8 (°)/s 直线运动 表 2 4种算法的误差对比
-
[1] PERKOVIČ M, GUCMA L, and FEUERSTACK S. Maritime security and risk assessments[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2024, 12(6): 988. doi: 10.3390/jmse12060988. [2] PRASETYO K A, ANSORI A, and SUSETO B. Maritime defense strategy education as an effort of the indonesian government in maintaining maritime security[J]. International Journal of Asian Education, 2023, 4(1): 58–67. doi: 10.46966/ijae.v4i1.325. [3] YUE Wenrong, XU Feng, and YANG Juan. Tracking-by-detection algorithm for underwater target based on improved multi-kernel correlation filter[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(2): 323. doi: 10.3390/rs16020323. [4] JIA Shuyi, ZHANG Yun, and WANG Guohong. Highly maneuvering target tracking using multi-parameter fusion singer model[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28(5): 841–850. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2017.05.03. [5] ZHANG Licheng, PENG Kun, ZHAO Xingmo, et al. New fuel consumption model considering vehicular speed, acceleration, and jerk[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 27(2): 174–186. doi: 10.1080/15472450.2021.2000406. [6] DENG Mingjun, LI Shuhang, JIANG Xueqing, et al. Vehicle trajectory prediction method based on “Current” statistical model and cubature Kalman filter[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(11): 2464. doi: 10.3390/electronics12112464. [7] HAN Guoxing, LIU Fuyun, DENG Jucai, et al. An adaptive vehicle tracking enhancement algorithm based on fuzzy interacting multiple model robust cubature Kalman filtering[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2024, 43(1): 191–223. doi: 10.1007/s00034-023-02497-x. [8] BLOM H A P and BAR-SHALOM Y. The interacting multiple model algorithm for systems with markovian switching coefficients[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1988, 33(8): 780–783. doi: 10.1109/9.1299. [9] SUN Lifan, ZHANG Jinjin, YU Haofang, et al. Tracking of maneuvering extended target using modified variable dtructure multiple-model based on adaptive grid best model augmentation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(7): 1613. doi: 10.3390/rs14071613. [10] XU Hong, PAN Qin, XU Heng, et al. Adaptive IMM smoothing algorithms for jumping markov system with mismatched measurement noise covariance matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 5467–5480. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3392552. [11] TIAN Ye, JIANG Hong, DING Quanxin, et al. Turn rate estimation based adaptive IMM algorithm for maneuvering target tracking[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 383/390: 5609–5614. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.383-390.5609. [12] WANG Gang. ML estimation of transition probabilities in jump Markov systems via convex optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1492–1502. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545204. [13] LUO Yalun, LI Zhaoming, LIAO Yurong, et al. Adaptive Markov IMM based multiple fading factors strong tracking CKF for maneuvering hypersonic-target tracking[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(20): 10395. doi: 10.3390/app122010395. [14] 许登荣, 程水英, 包守亮. 自适应转移概率交互式多模型跟踪算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(9): 2113–2120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.009.XU Dengrong, CHENG Shuiying, and BAO Shouliang. Interacting multiple model algorithm based on adaptive transition probability[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(9): 2113–2120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.009. [15] LEE I H and PARK C G. An improved interacting multiple model algorithm with adaptive transition probability matrix based on the situation[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2023, 21(10): 3299–3312. doi: 10.1007/s12555-022-0989-4. [16] ZHANG Zhao, GUO Hongwu, HE Jiaxing, et al. Adaptive interactive multiple model target tracking algorithm based on markov matrix with acceleration correction factor[C]. Proceedings of 2022 China Automation Congress (CAC), Xiamen, China, 2022: 3227–3232. doi: 10.1109/CAC57257.2022.10055933. [17] XIE Guo, SUN Lanlan, WEN Tao, et al. Adaptive transition probability matrix-based parallel IMM algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(5): 2980–2989. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2922305. [18] 王平波, 刘杨. 基于改进自适应IMM-UKF算法的水下目标跟踪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 1999–2005. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211128.WANG Pingbo and LIU Yang. Underwater target tracking algorithm based on improved adaptive IMM-UKF[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 1999–2005. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211128. [19] 王小敏, 雷筱, 张亚东. 基于改进自适应IMM算法的高速列车组合定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 817–825. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230251.WANG Xiaomin, LEI Xiao, and ZHANG Yadong. Combined positioning of high-speed train based on improved adaptive IMM algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 817–825. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230251. [20] LIBÓRIO M P, KARAGIANNIS R, DINIZ A M A, et al. The use of information entropy and expert opinion in maximizing the discriminating power of composite indicators[J]. Entropy, 2024, 26(2): 143. doi: 10.3390/e26020143. [21] LI Yuankai, LOU Jiaxin, TAN Xiaosu, et al. Adaptive kernel learning Kalman filtering with application to model-free maneuvering target tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 78088–78101. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3193101. [22] 孙大军, 张艺翱, 滕婷婷, 等. 单站水下方位频率机动目标运动分析方法[J]. 声学学报, 2024, 49(4): 683–695. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023077.SUN Dajun, ZHANG Yiao, TENG Tingting, et al. A single-platform underwater maneuvering target motion analysis method based on bearing and frequency measurements[J]. Acta Acustica, 2024, 49(4): 683–695. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023077. [23] TIAN Feng, ZHANG Haoyu, and FU Weibo. Research on extended target-tracking algorithms of sea surface navigation radar[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(3): 616. doi: 10.3390/electronics12030616. [24] GUO Caifa, DAI Zhengxu, YANG Lei, et al. Application of the strong tracking UKF in the maneuvering target tracking[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2016, 679(1): 012048. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/679/1/012048. [25] DAI Hongde, DAI Shaowu, CONG Yuancai, et al. Performance comparison of EKF/UKF/CKF for the tracking of ballistic target[J]. TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2012, 10(7). doi: 10.11591/telkomnika.v10i7.1564. [26] LIU Haoran, JIANG Qiumei, QIN Yuha, et al. Double layer weighted unscented Kalman underwater target tracking algorithm based on sound speed profile[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 112982. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112982. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
