Precise Hand Joint Motion Analysis Driven by Complex Physiological Information
-
摘要: 手是人体至关重要的组成部分,其高度的灵巧性使我们能够执行各种复杂任务,然而,手部功能障碍会严重影响患者的日常生活,使其难以完成基本的日常活动。该文提出一种基于8通道表面肌电信号(sEMG)的新颖手部运动估计方法,用于解析15个手部关节的运动,旨在提高手部功能障碍患者的生活质量。该方法采用连续去噪网络,结合稀疏注意力机制和多通道注意力机制,有效提取sEMG信号中蕴含的时空特征。网络采用双译码器结构,分别解析含噪姿态和姿态修正范围,并利用双向长短期记忆网络对含噪姿态进行修正,最终实现精准的手部姿态估计。实验结果表明,相比现有方法,该方法在多通道sEMG信号拟合连续手部姿态估计方面表现出更优越的性能,能够解析更多关节,且估计误差更小。Abstract:
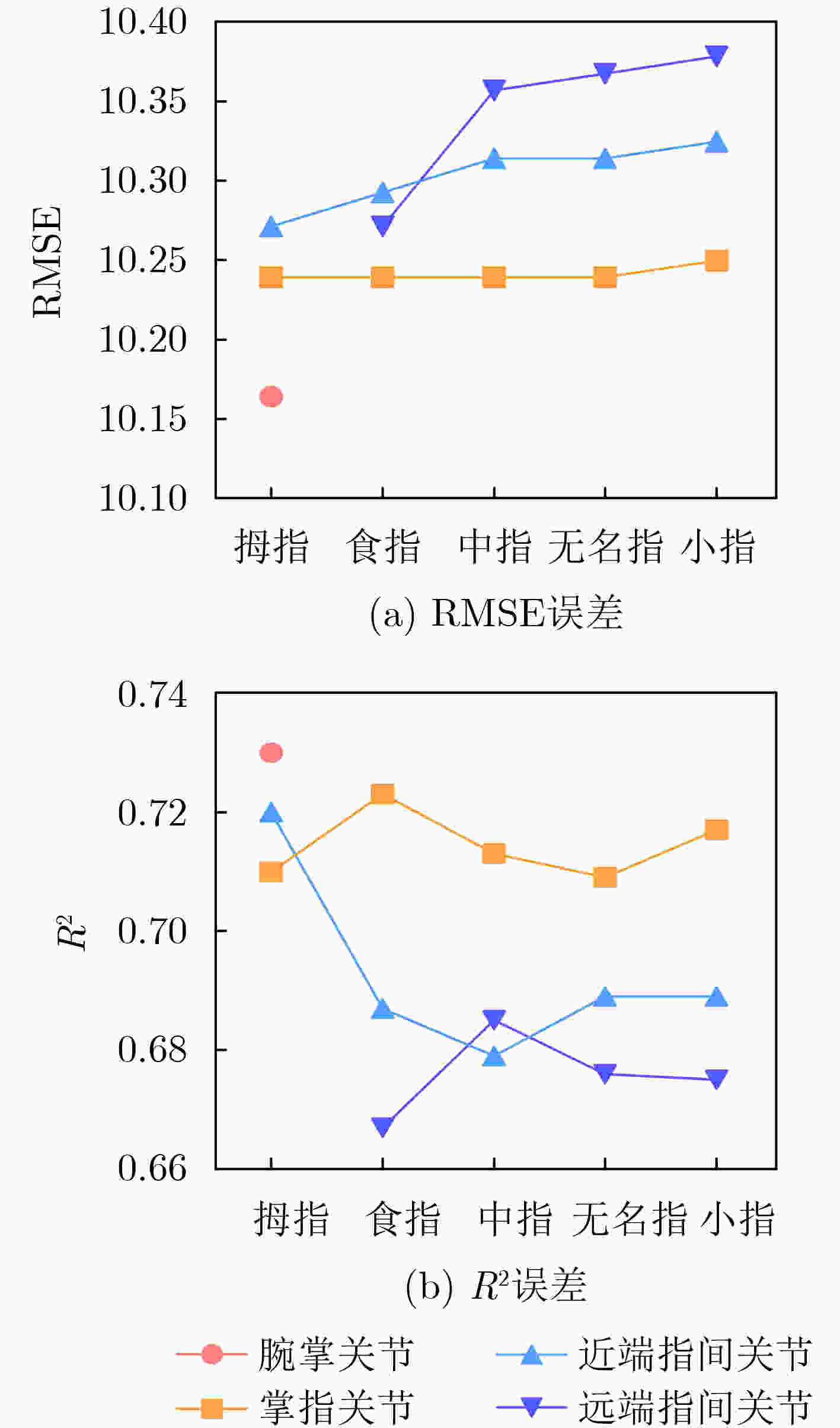
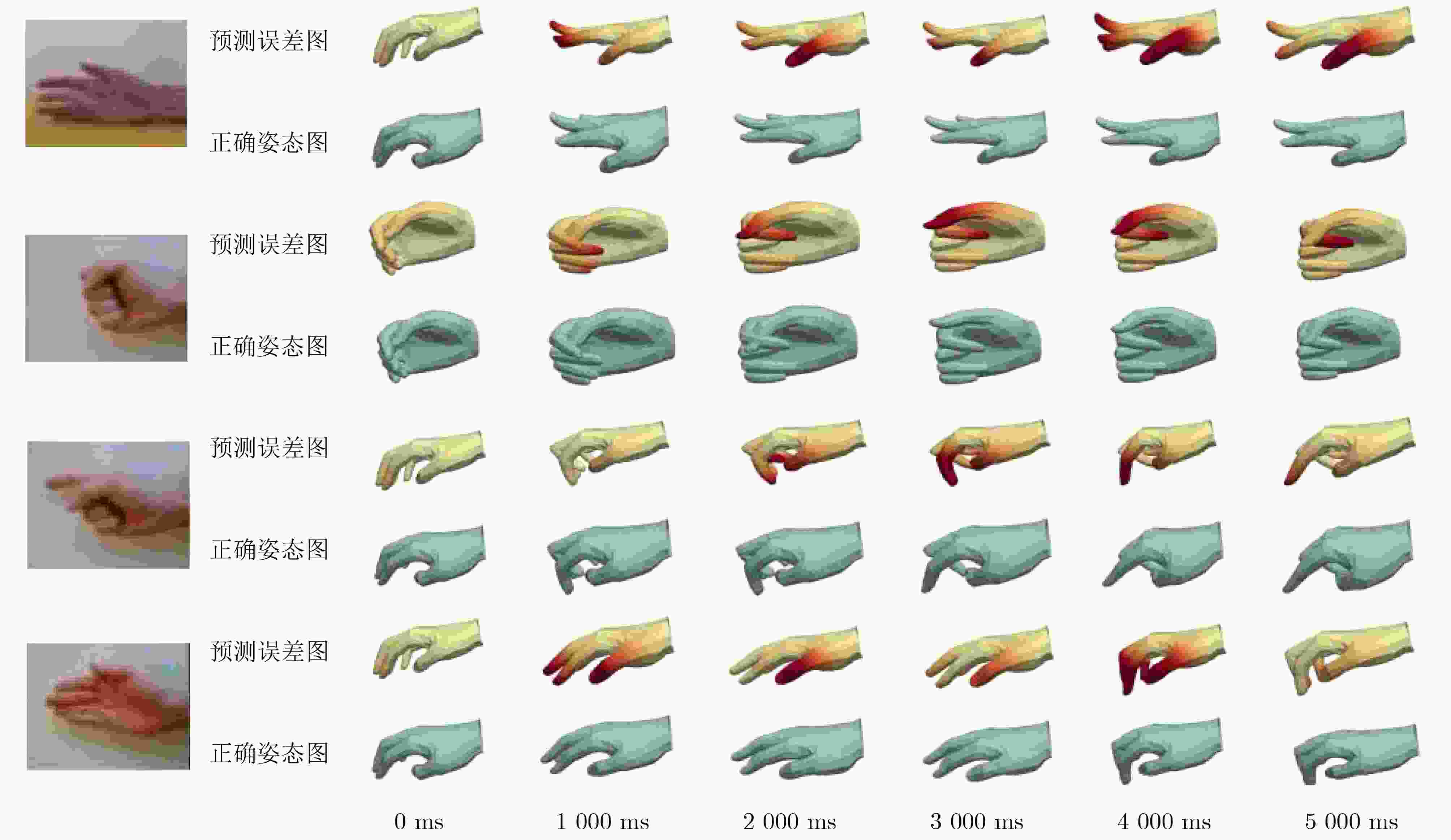
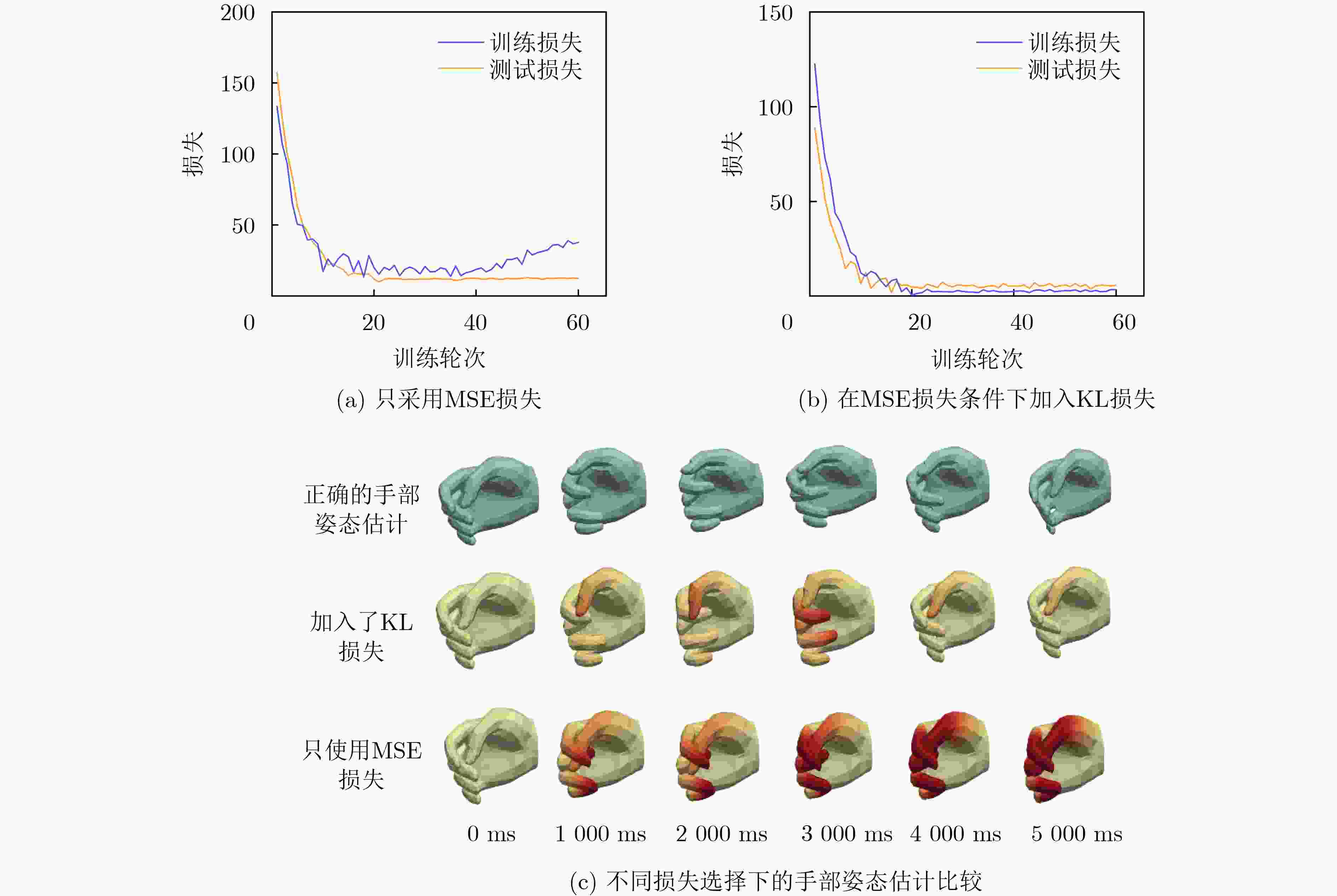
Objective The human hand is a highly dexterous organ essential for performing complex tasks. However, dysfunction due to trauma, congenital anomalies, or disease substantially impairs daily activities. Restoring hand function remains a major challenge in rehabilitation medicine. Virtual Reality (VR) technology presents a promising approach for functional recovery by enabling hand pose reconstruction from surface ElectroMyoGraphy (sEMG) signals, thereby facilitating neural plasticity and motor relearning. Current sEMG-based hand pose estimation methods are limited by low accuracy and coarse joint resolution. This study proposes a new method to estimate the motion of 15 hand joints using eight-channel sEMG signals, offering a potential improvement in rehabilitation outcomes and quality of life for individuals with hand impairment. Methods The proposed method, termed All Hand joints Posture Estimation (AHPE), incorporates a continuous denoising network that combines sparse attention and multi-channel attention mechanisms to extract spatiotemporal features from sEMG signals. A dual-decoder architecture estimates both noisy hand poses and the corresponding correction ranges. These outputs are subsequently refined using a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network to improve pose accuracy. Model training employs a composite loss function that integrates Mean Squared Error (MSE) and Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence to enhance joint angle estimation and capture inter-joint dependencies. Performance is evaluated using the NinaproDB8 and NinaproDB5 datasets, which provide sEMG and hand pose data for single-finger and multi-finger movements, respectively. Results and Discussions The AHPE model outperforms existing methods—including CNN-Transformer, DKFN, CNN-LSTM, TEMPOnet, and RPC-Net—in estimating hand poses from multi-channel sEMG signals. In within-subject validation ( Table 1 ), AHPE achieves a Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) of 2.86, a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.92, and a Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) of 1.79° for MetaCarPophalangeal (MCP) joint rotation angle estimation. In between-subject validation (Table 2 ), the model maintains high accuracy with an RMSE of 3.72, an R2 of 0.88, and an MAD of 2.36°, demonstrating strong generalization. The model’s capacity to estimate complex hand gestures is further confirmed using the NinaproDB5 dataset. Estimated hand poses are visualized with the Mano Torch hand model (Fig. 4 ,Fig. 5 ). The average R2 values for finger joint extension estimation are 0.72 (thumb), 0.692 (index), 0.696 (middle), 0.689 (ring), and 0.696 (little finger). Corresponding RMSE values are 10.217°, 10.257°, 10.290°, 10.293°, and 10.303°, respectively. A grid error map (Fig. 6 ) highlights prediction accuracy, with red regions indicating higher errors.Conclusions The AHPE model offers an effective approach for estimating hand poses from sEMG signals, addressing key challenges such as signal noise, high dimensionality, and inter-individual variability. By integrating mixed attention mechanisms with a dual-decoder architecture, the model enhances both accuracy and robustness in multi-joint hand pose estimation. Results confirm the model’s capacity to reconstruct detailed hand kinematics, supporting its potential for applications in hand function rehabilitation and human-machine interaction. Future work will aim to improve robustness under real-world conditions, including sensor noise and environmental variation. -
表 1 对话内场景下不同模型的RMSE, R2和MAD的参数评估
方法 CNN-Transformer DKFN CNN-LSTM TEMPOnet RPC-Net AHPE RMSE 12.75 4.32 11.97 4.76 3.88 2.86 R2 0.76 0.91 0.73 0.88 0.90 0.92 MAD (°) 3.09 2.12 3.76 2.32 1.92 1.79 表 2 对话间场景下不同模型的RMSE, R2和MAD的参数评估
方法 CNN-Transformer DKFN CNN-LSTM TEMPOnet RPC-Net AHPE RMSE 48.25 8.69 12.50 7.96 4.36 3.72 R2 0.36 0.75 0.66 0.84 0.86 0.88 MAD 21.36 8.32 11.24 6.89 3.07 2.36 表 3 注意力机制有效性评估(RMSE/R2)
数据集 多头注意力机制 多头稀疏注意力机制 AHPE NinaproDB8 30.46/0.356 8 16.32/0.68 3.72/0.88 NinaproDB5 62.21/–1.32 21.32/0.55 10.30/0.72 表 4 双解码器有效性的评估(RMSE/R2)
数据集 单解码器输出 单解码器和单输入 单解码器和双输入 双解码器和双输入 NinaproDB8 18.17/0.52 10.32/0.58 7.32/0.68 3.72/0.88 NinaproDB5 48.72/0.32 20.51/0.54 16.31/0.66 10.30/0.72 表 5 不同长度的时间窗口的效果
窗口长度 100 ms 500 ms 1 000 ms 2 000 ms 时间 45~48 7~9 4 2 RMSE 18.32 10.30 11.8 14.11 R2 0.56 0.72 0.75 0.64 -
[1] SITOLE S P and SUP F C. Continuous prediction of human joint mechanics using EMG signals: A review of model-based and model-free approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Robotics and Bionics, 2023, 5(3): 528–546. doi: 10.1109/TMRB.2023.3292451. [2] ZENG Chao, YANG Chenguang, CHENG Hong, et al. Simultaneously encoding movement and sEMG-based stiffness for robotic skill learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(2): 1244–1252. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2984482. [3] CHEN Qingzheng and TAO Qing. Estimating finger joint angles from surface electromyography using convolutional neural networks[C]. 2024 China Automation Congress, Qingdao, China, 2024. doi: 10.1109/CAC63892.2024.10865263. [4] ZHANG Haoshi, PENG Boxing, TIAN Lan, et al. Continuous Kalman estimation method for finger kinematics tracking from surface electromyography[J]. Cyborg and Bionic Systems, 2024, 5: 0094. doi: 10.34133/cbsystems.0094. [5] ROLANDINO G, GAGLIARDI M, MARTINS T, et al. Developing RPC-Net: Leveraging high-density electromyography and machine learning for improved hand position estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2024, 71(5): 1617–1627. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2023.3346192. [6] PIZZOLATO S, TAGLIAPIETRA L, COGNOLATO M, et al. Comparison of six electromyography acquisition setups on hand movement classification tasks[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(10): e0186132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186132. [7] KRASOULIS A, KYRANOU I, ERDEN M S, et al. Improved prosthetic hand control with concurrent use of myoelectric and inertial measurements[J]. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 2017, 14(1): 71. doi: 10.1186/s12984-017-0284-4. [8] ATZORI M, GIJSBERTS A, CASTELLINI C, et al. Electromyography data for non-invasive naturally-controlled robotic hand prostheses[J]. Scientific Data, 2014, 1(1): 140053. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2014.53. [9] QUIVIRA F, KOIKE-AKINO T, WANG Ye, et al. Translating sEMG signals to continuous hand poses using recurrent neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical & Health Informatics, Las Vegas, USA, 2018. doi: 10.1109/BHI.2018.8333395. [10] WANG Zijian, XIONG Caihua, and ZHANG Qin. Enhancing the online estimation of finger kinematics from sEMG using LSTM with attention mechanisms[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2024, 92: 105971. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2024.105971. [11] BAO Tianzhe, ZHAO Yihui, ZAIDI S A R, et al. A deep Kalman filter network for hand kinematics estimation using sEMG[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2021, 143: 88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2021.01.001. [12] SÎMPETRU R C, CNEJEVICI V, FARINA D, et al. Influence of spatio-temporal filtering on hand kinematics estimation from high-density EMG signals[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2024, 21(2): 026014. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad3498. [13] WENG Zihan, ZHANG Xiabing, MOU Yufeng, et al. A hybrid CNN-transformer approach for continuous fine finger motion decoding from sEMG signals[C]. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications, Xi’an, China, 2024. doi: 10.1109/CIVEMSA58715.2024.10586636. [14] KRASOULIS A, VIJAYAKUMAR S, and NAZARPOUR K. Effect of user practice on prosthetic finger control with an intuitive myoelectric decoder[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 891. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00891. [15] GRACIA-IBÁÑEZ V, VERGARA M, BUFFI J H, et al. Across-subject calibration of an instrumented glove to measure hand movement for clinical purposes[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 20(6): 587–597. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2016.1265950. [16] KUZBORSKIJ I, GIJSBERTS A, and CAPUTO B. On the challenge of classifying 52 hand movements from surface electromyography[C]. 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, USA, 2012. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6347099. [17] JIANG Shuo, GAO Qinghua, LIU Huaiyang, et al. A novel, co-located EMG-FMG-sensing wearable armband for hand gesture recognition[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2020, 301: 111738. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2019.111738. [18] ROLANDINO G, ZANGRANDI C, VIEIRA T, et al. HDE-Array: Development and validation of a new dry electrode array design to acquire HD-sEMG for hand position estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2024, 32: 4004–4013. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2024.3490796. [19] ROMERO J, TZIONAS D, and BLACK M J. Embodied hands: Modeling and capturing hands and bodies together[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2017, 36(6): 245. doi: 10.1145/3130800.3130883. [20] YANG Lixin, ZHAN Xinyu, LI Kailin, et al. CPF: Learning a contact potential field to model the hand-object interaction[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01091. [21] 陈从平, 郁春明, 闫焕章, 等. 基于改进Transformer的三维人体姿态估计[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2024, 43(6): 117–121. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2024)06-0117-05.CHEN Congping, YU Chunming, YAN Huanzhang, et al. 3D human body pose estimation based on improved Transformer[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2024, 43(6): 117–121. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2024)06-0117-05. [22] ZHOU Haoyi, ZHANG Shanghang, PENG Jieqi, et al. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting[C]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 11106–11115. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i12.17325. [23] HU Jie, SHEN Li, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372. [24] TANZARELLA S, DI DOMENICO D, FORSIUK I, et al. Arm muscle synergies enhance hand posture prediction in combination with forearm muscle synergies[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2024, 21(2): 026043. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad38dd. [25] ZANGHIERI M, BENATTI S, BURRELLO A, et al. sEMG-based regression of hand kinematics with temporal convolutional networks on a low-power edge microcontroller[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Omni-Layer Intelligent Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. doi: 10.1109/COINS51742.2021.9524188. -





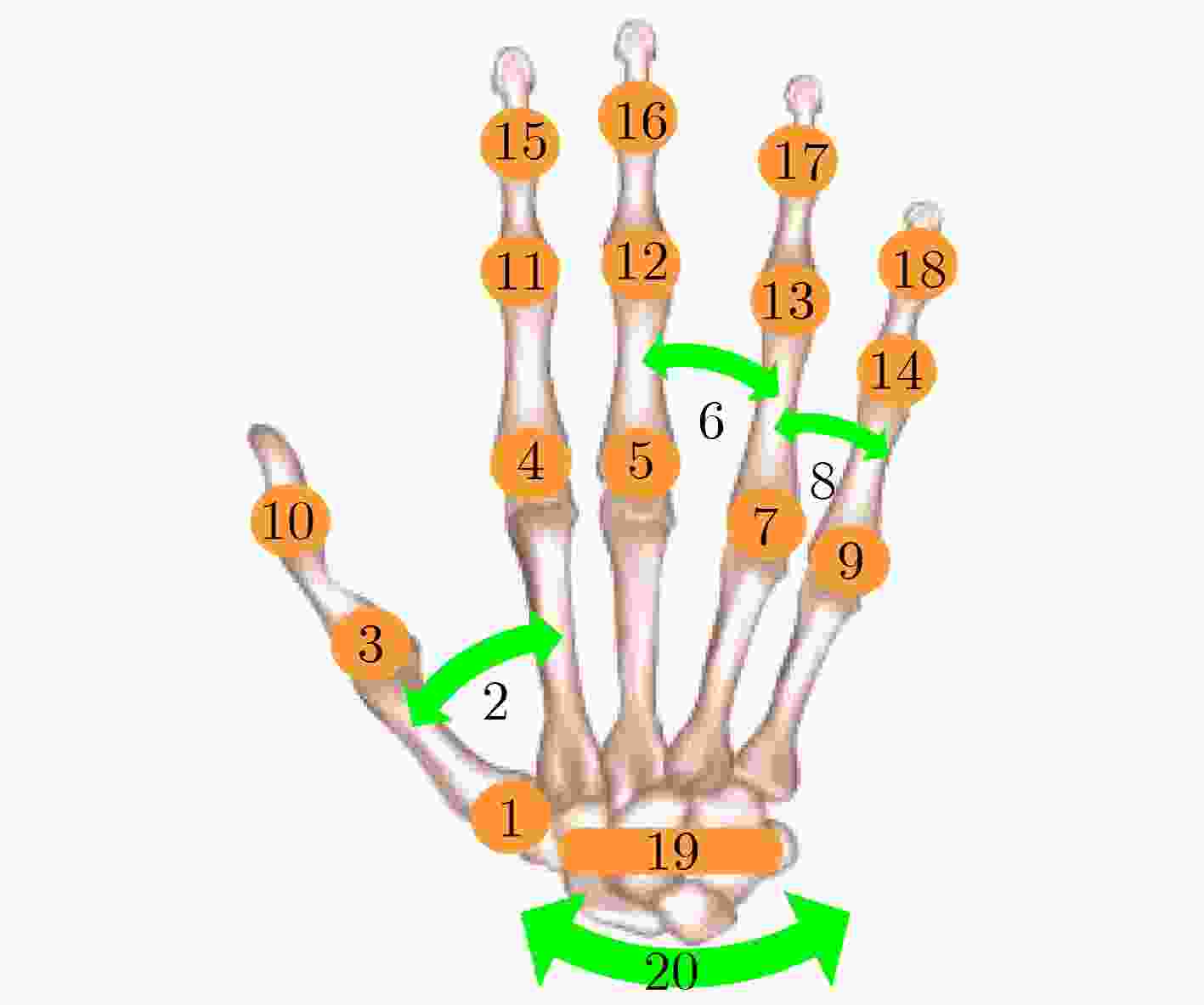
 下载:
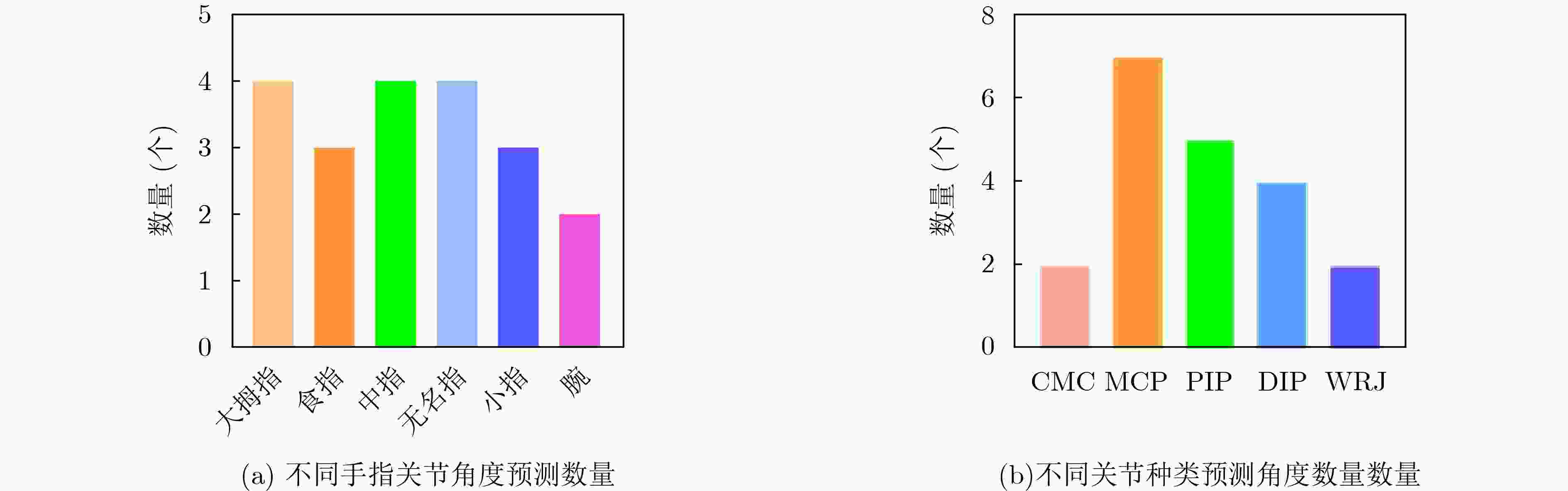
下载:
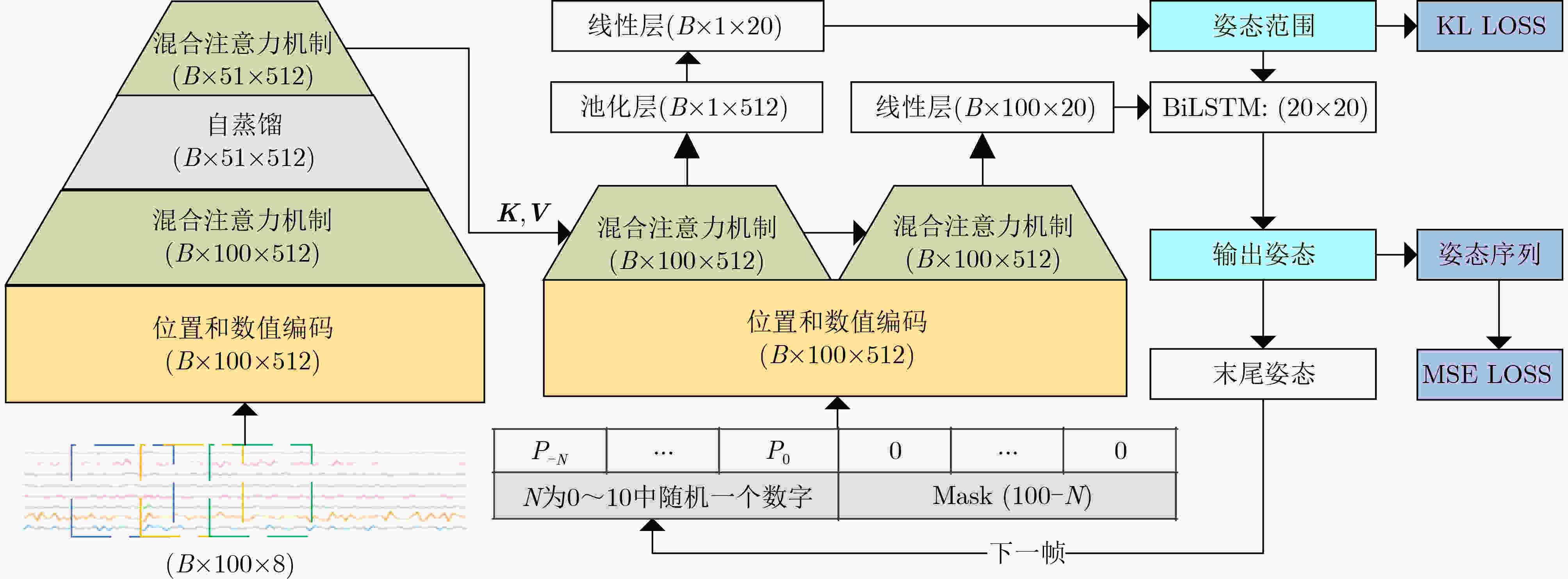


 下载:
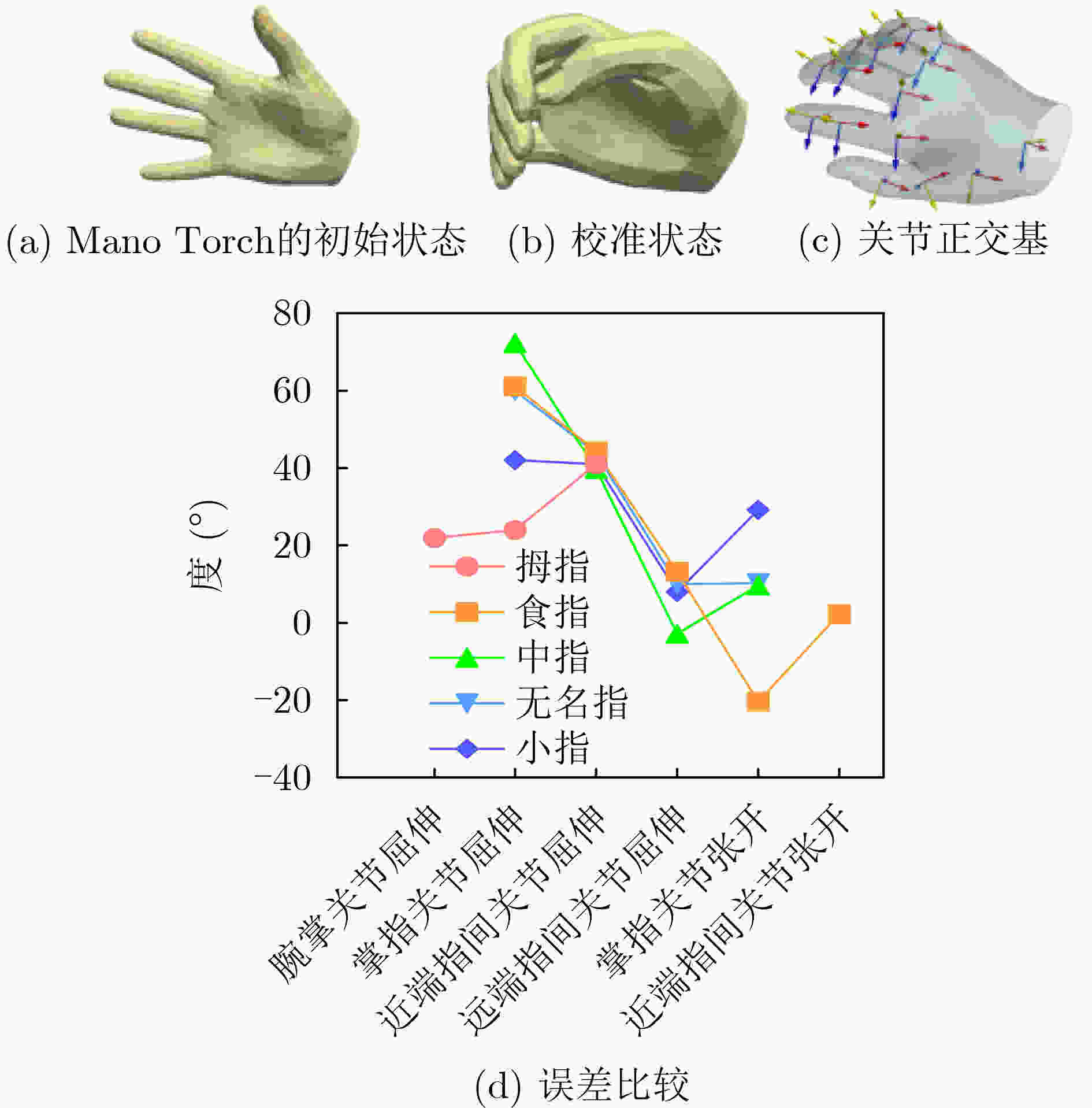
下载:
