A Modulation Recognition Method Combining Wavelet Denoising Convolution and Sparse Transformer
-
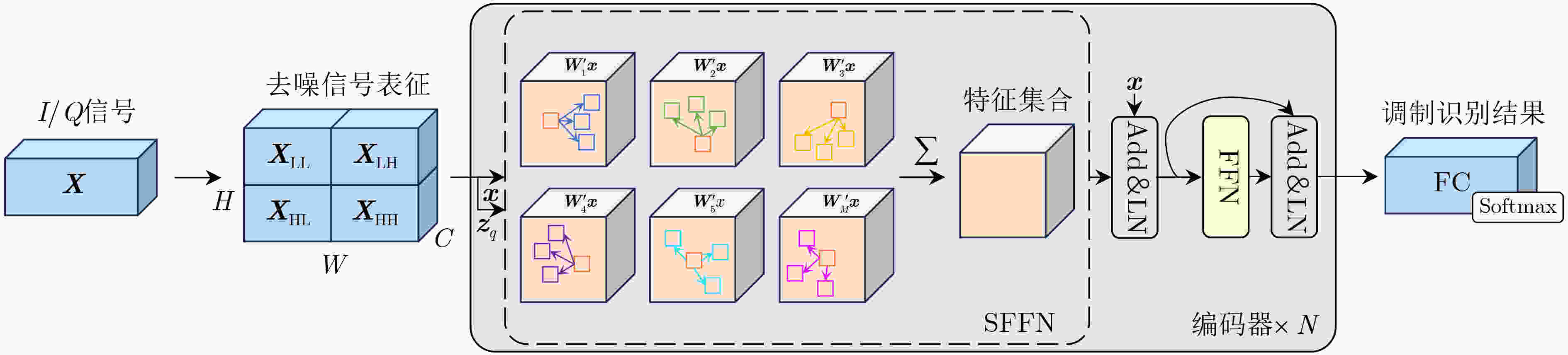
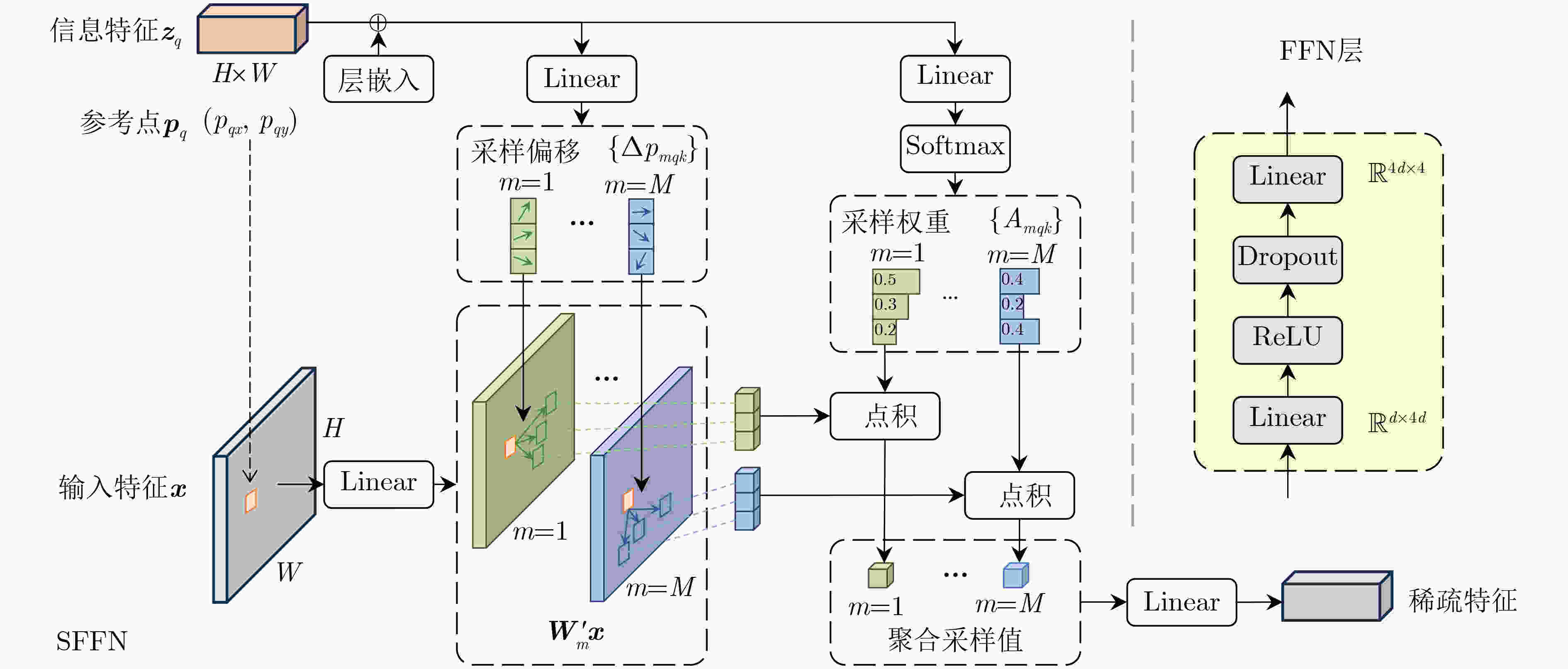
摘要: 针对Transformer模型处理时域信号长度受限以及忽略有序特征元素相关性的问题,该文提出一种结合小波去噪卷积与稀疏Transformer的方法用于调制识别。首先,提出可学习的小波去噪卷积帮助深度学习模型提取合适的去噪信号表征,并将自适应的时频特征纳入目标函数的泛函策略中。然后,设计稀疏前馈神经网络替换传统Transformer中的注意力机制,用于对元素关系进行建模,并根据信号域中的少量关键元素对训练过程的梯度进行有效优化。在公开数据集RadioML 2016.10a和RML22的实验结果表明,稀疏Transformer模型能够分别取得63.84%和71.13%的平均分类准确率。与一系列深度学习模型对比,整体分类准确率提升了4%~10%,进一步证明了方法的有效性。此外,超参数消融实验验证了模型组件在复杂移动通信环境中的鲁棒性和实用性。
-
关键词:
- 调制分类 /
- 深度学习 /
- 稀疏Transformer /
- 小波去噪卷积
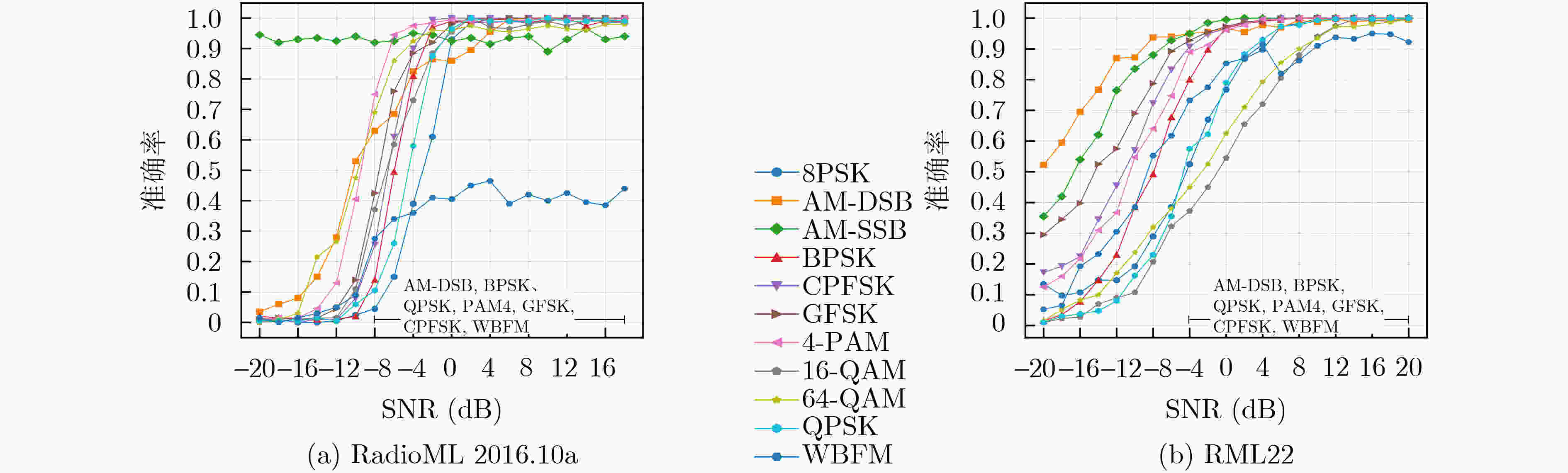
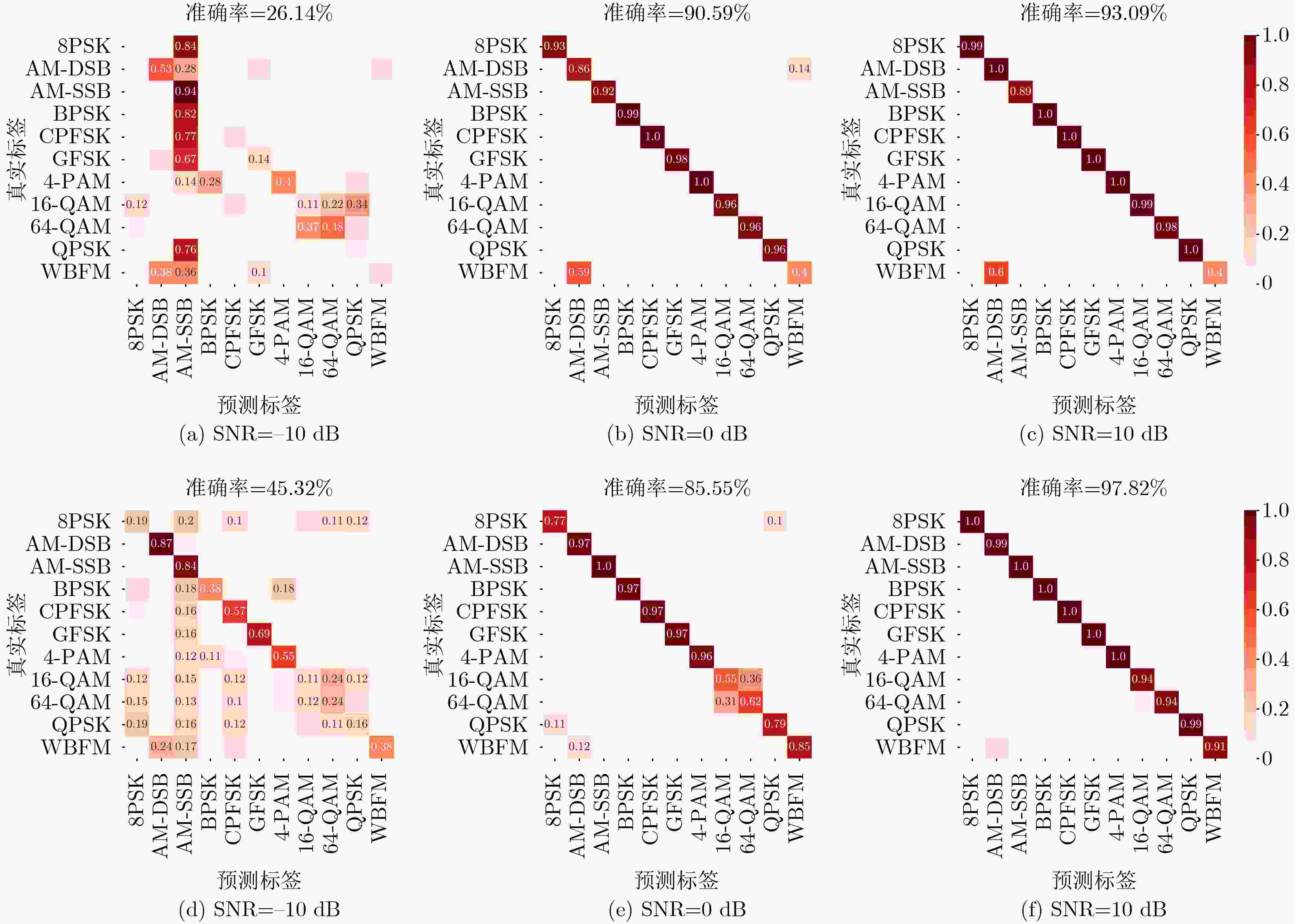
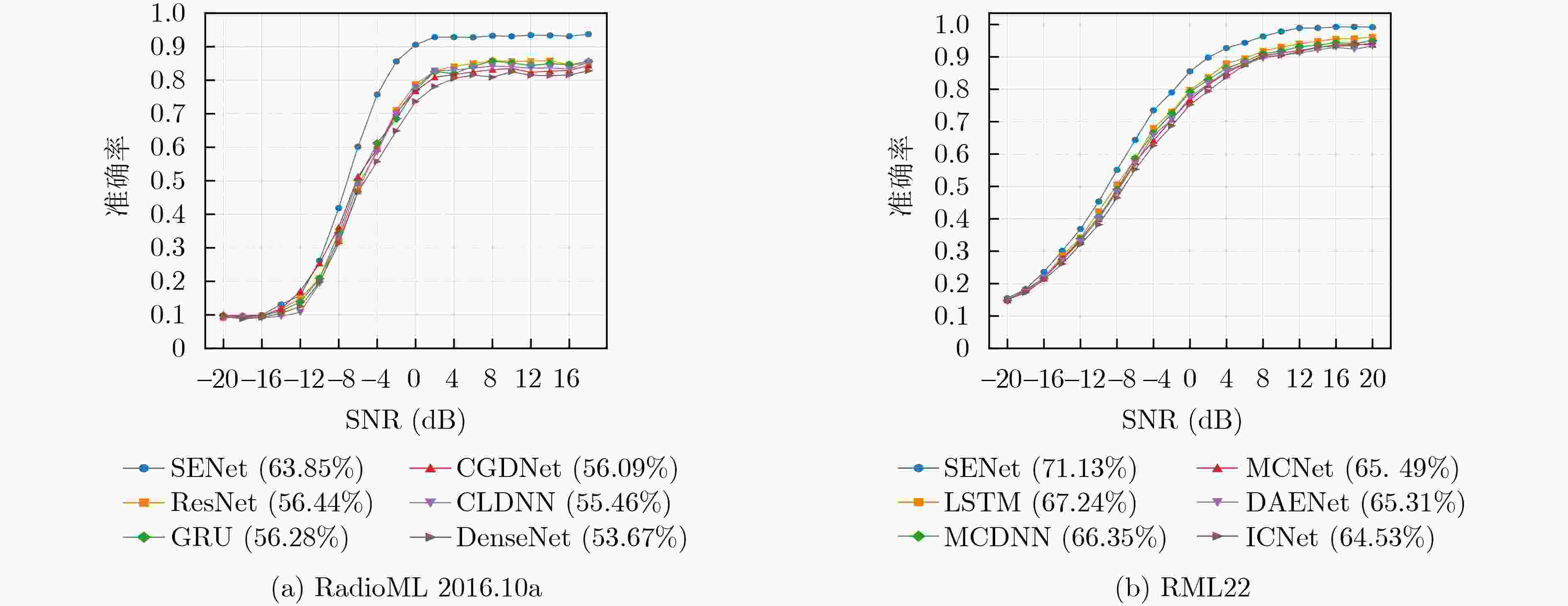
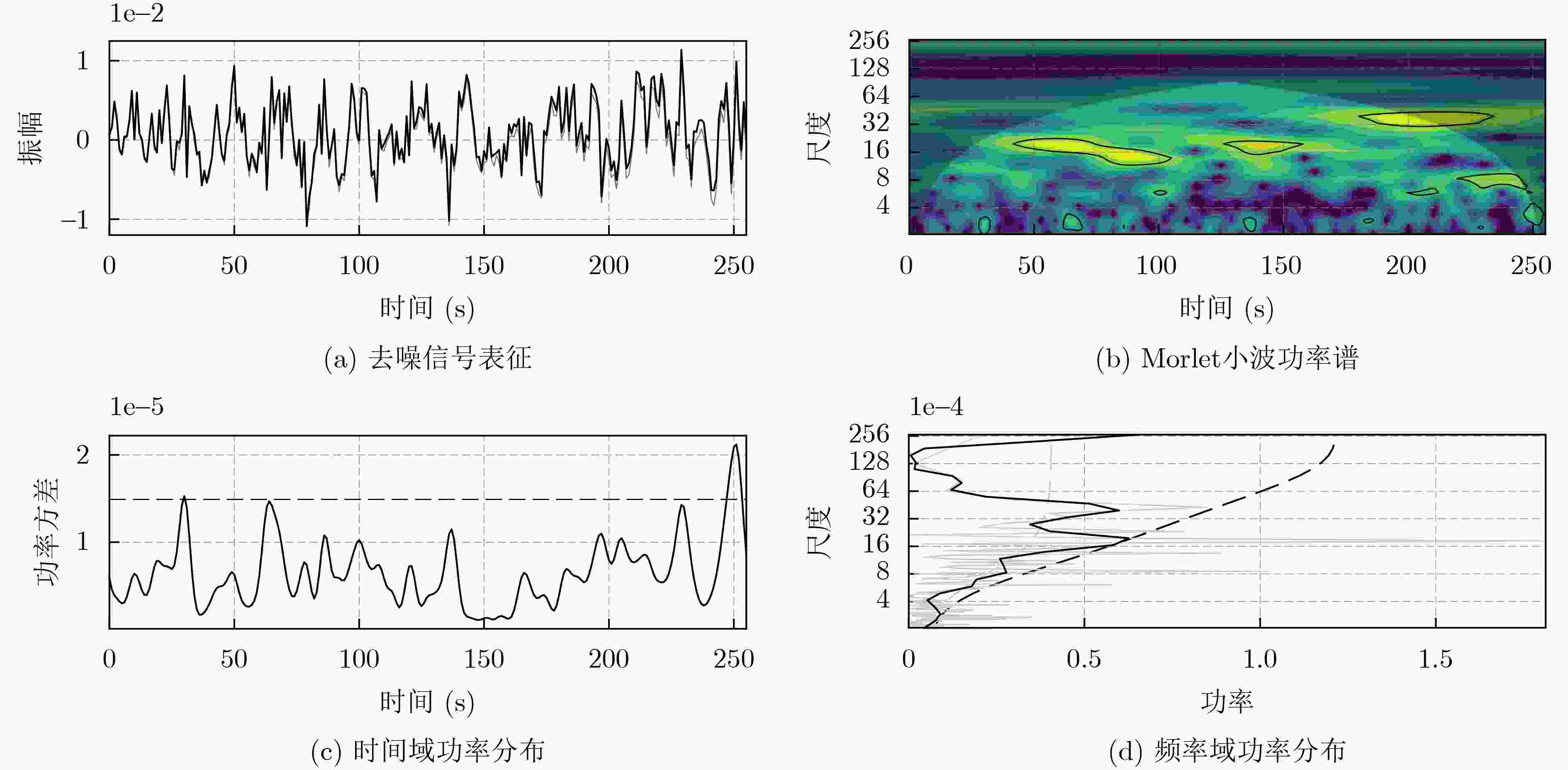
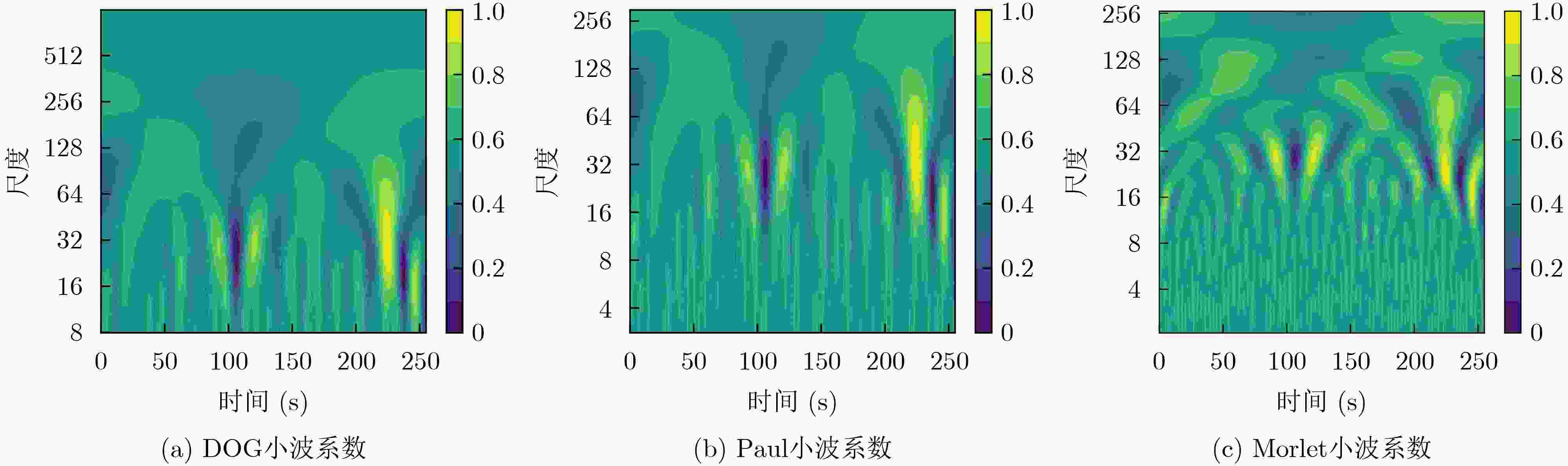
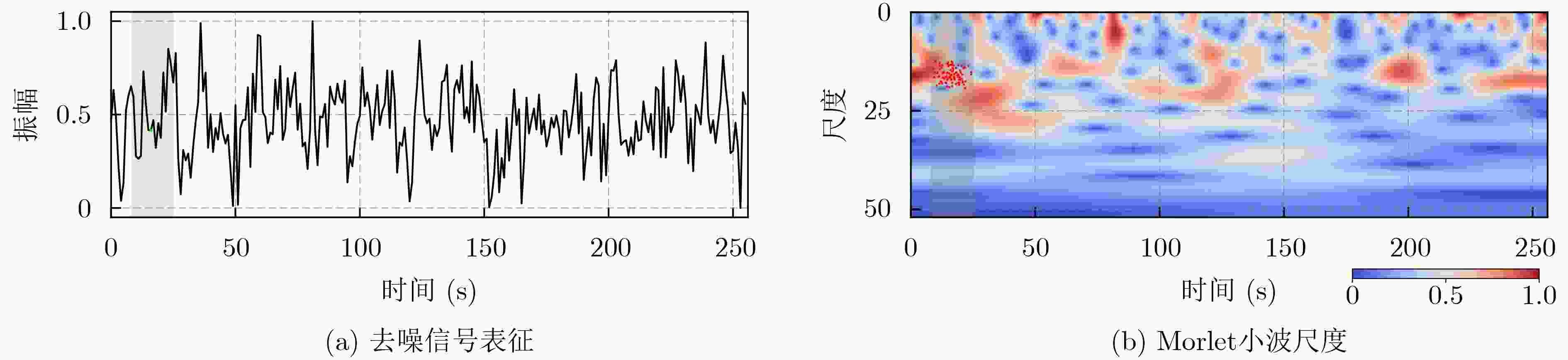
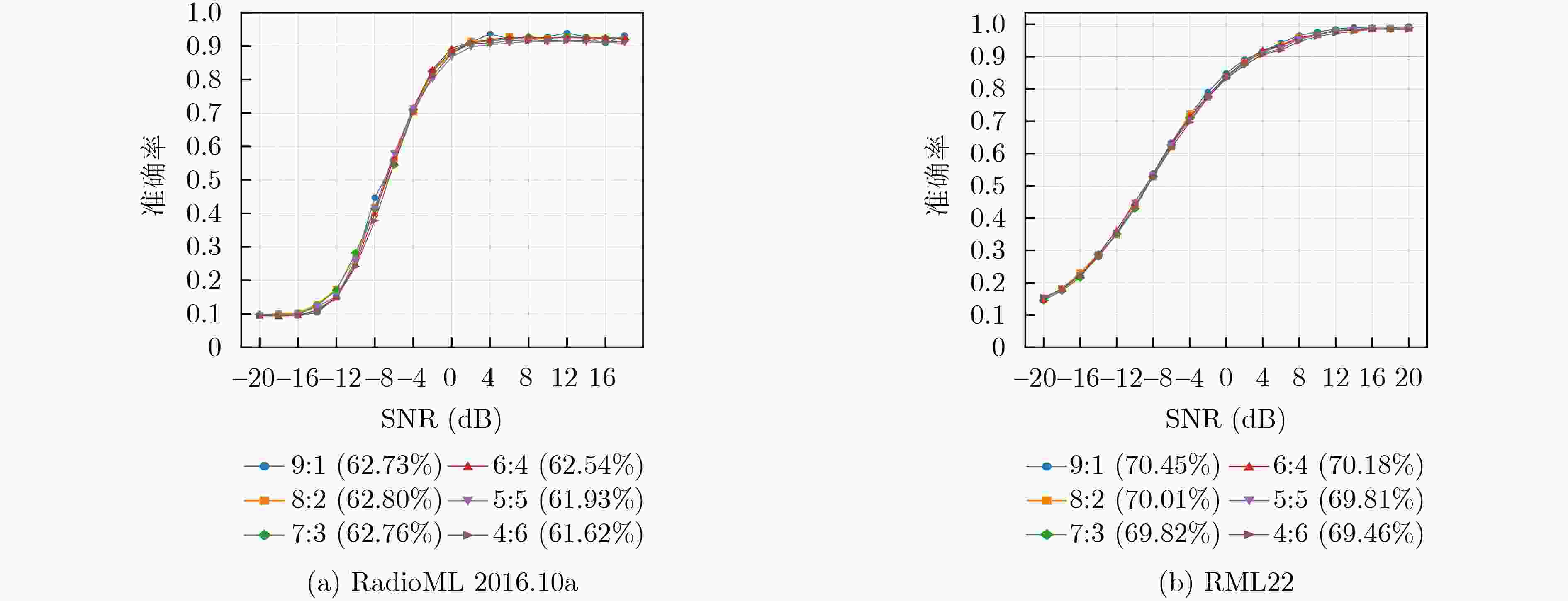
Abstract:Objective Automatic Modulation Classification (AMC) is a key process in signal detection and demodulation, enabling the automatic identification of various modulation schemes in non-cooperative communication scenarios. The high transmission rate and low latency requirements of 6G wireless communications necessitate AMC to accurately and promptly identify different modulation schemes to adapt to complex communication scenes. As integrated 6G communication, sensing, and computing technologies evolve, an increasing number of modulation schemes are being designed and adopted. In the face of a more complex electromagnetic environment, AMC encounters challenges such as low recognition accuracy, susceptibility to environmental interference, and poor robustness. Existing feature selection methods struggle to generalize well in practical applications. By contrast, integrating adaptive feature selection methods with deep learning can generate more reliable and precise classification constraints, even for complex signal features that generalize across time. This study proposes an AMC method that combines learnable wavelet denoising convolution with a sparse Transformer, providing technical support for the advancement of integrated communication, sensing, and computing. Methods In the proposed AMC method combining wavelet denoising convolution and sparse Transformer, the learnable wavelet denoising convolution is proposed to assist deep learning in extracting appropriate denoised signal representations. It incorporates adaptive time-frequency features into the functional strategy of the objective function, delivering accurate spatiotemporal information to the Transformer and mitigating the effects of signal parameter offsets. A Sparse Feedforward Neural Network (SFFN) is then designed to replace the attention mechanism in the Transformer, modeling element relationships based on a limited set of key elements in the signal domain. This approach effectively optimizes gradients during training to address the challenges posed by limited signal length and the disregard of ordered feature element correlations in traditional Transformers. SFFN enhances spatial sampling positions within sparse cells by introducing additional offsets, focusing on a small group of key sampling points around the reference point. Moreover, it learns these offsets from the target task without requiring additional supervision. Given that most AMC frameworks benefit from multi-scale or multidimensional features, the proposed SFFN can be extended to multi-scale features without the need for feature pyramid networks. Results and Discussions During the experimental phase, modulation recognition performance testing, ablation studies, and comparative analyses are conducted on two publicly available datasets (RadioML 2016.10a and RML22) to demonstrate the excellent performance of the proposed method. Experimental results show that the sparse Transformer achieves classification accuracies of 63.84% and 71.13% on RadioML 2016.10a and RML22, respectively ( Fig. 4 ). The primary limitation in modulation recognition performance occurs in the classification between the following modulation schemes: {WBFM, AM-DSB, QPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM, 64QAM} (Fig. 5 ). By comparing the sparse Transformer to a range of deep learning models (including CGDNet, CLDNN, DenseNet, GRU, and ResNet on RadioML 2016.10a, and DAENet, ICNet, LSTM, MCDNN, and MCNet on RML22), experimental results confirm the superior performance of the proposed method (Table 1 ). The classification accuracy of all models at various Signal-to-Noise Ratios (SNRs) is shown to highlight the performance advantage of the proposed method (Fig. 6 ). To qualitatively explore the effect of wavelet denoising convolution on improving classification accuracy, the power spectrum in the wavelet domain, represented by the selected denoised signals in RadioML 2016.10a, is presented (Fig. 7 ). The different wavelet coefficients selected for denoising signal representation reveal the component specificity of different wavelet basis functions in feature extraction, which helps determine the applicable signal types or model architectures (Figure 8 ). The sampling points of interest in the power concentration area are visualized on the wavelet scale map to observe the corresponding relationships between the elements learned by SFFN (Fig. 9 ). Furthermore, the denoised signal representation constructed by wavelet denoising convolution under different hyperparameter settings undergoes an ablation study to evaluate its impact on model performance (Table 2 ). The model structure is ablated and tested to observe the roles played by different modules (Table 3 ). Finally, different numbers of training samples are set to demonstrate the robustness of the model, with less than a 1.5% decrease in classification accuracy when the training set ratio is adjusted from 90% to 40% (Figure 10 ).Conclusions This study addresses the challenges of limited time-domain length and the neglect of ordered feature element correlations in Transformer models for signal processing by proposing an effective AMC method that combines wavelet denoising convolution and sparse Transformer. The proposed method significantly enhances AMC accuracy in complex communication scenarios and demonstrates robustness to model structure and hyperparameter selection. First, the learnable wavelet denoising convolution is proposed to assist deep learning models in adaptively extracting appropriate denoised signal representations. Subsequently, the SFFN module is designed to replace the attention mechanism in the Transformer, effectively modeling spatiotemporal element relationships. Experimental results on two public datasets (RadioML 2016.10a and RML22) show that the proposed method significantly improves AMC accuracy. By comparing a range of deep learning models, the proposed method demonstrates state-of-the-art AMC accuracy and robustness across different communication scenarios. Additionally, visualization experiments and ablation studies further confirm the robustness of the proposed method. -
表 1 调制识别性能对比
数据集 模型 平均分类准确率 (%) 参数量 (M) 计算量 (GFLOPs) 推理时间 (ms) RadioML
2016.10aCGDNet[15] 56.09 0.32 0.37 0.65 CLDNN[16] 55.46 0.51 6.14 2.58 DenseNet[17] 53.67 8.45 1.57 0.54 GRU[18] 56.28 0.65 10.58 4.51 ResNet[19] 56.44 2.56 4.43 0.57 本文SENet 63.84 0.36 10.59 8.16 RML22 DAENet[20] 65.31 8.68 0.91 0.64 ICNet[21] 64.53 0.57 0.91 0.55 LSTM[22] 67.24 0.86 14.10 4.65 MCDNN[23] 66.35 4.56 1.83 1.03 MCNet[24] 65.49 4.55 2.34 1.19 本文SENet 71.13 0.36 10.59 7.54 表 2 在测试集上对小波去噪卷积构建的去噪信号表征进行消融
数据集 S J $\psi $ 平均分类准确率(%) 参数量 计算量(MFLOPs) 推理时间(μs) RadioML
2016.10a3 1 Haar 60.51±0.20 47 0.23 0.87±0.07 5 1 Haar 60.88±0.12 55 0.39 0.94±0.11 7 2 Haar 60.69±0.44 79 0.61 1.16±0.11 3 2 db1 60.36±0.60 55 0.25 1.08±0.05 5 4 db2 60.21±0.73 187 0.45 1.47±0.01 7 4 db4 60.23±0.65 591 0.65 1.87±0.17 RML22 3 1 Haar 67.46±0.33 47 0.23 0.86±0.03 5 1 Haar 67.28±0.65 55 0.39 0.72±0.01 7 2 Haar 67.33±1.14 79 0.61 1.16±0.14 3 2 db1 66.51±0.43 55 0.25 1.05±0.14 5 4 db2 68.78±0.09 187 0.45 1.55±0.43 7 4 db4 67.78±0.92 591 0.65 1.85±0.03 表 3 对测试集上的稀疏前馈神经网络进行消融
数据集 D M K FPNs 平均分类准确率(%) 参数量(M) 计算量(GFLOPs) 推理时间(ms) RadioML
2016.10a– 1 1 – 59.42±0.14 0.29 8.21 5.04±0.06 √ 1 4 – 59.56±0.16 0.29 8.32 5.82±0.04 √ 4 1 – 59.77±0.25 0.29 8.32 4.89±0.17 √ 8 4 – 60.74±0.09 0.32 9.38 6.19±0.01 √ 4 4 FPN 61.04±0.15 0.41 12.16 5.82±0.00 √ 8 8 BiFPN 61.48±0.04 0.47 14.37 7.76±0.00 RML22 – 1 1 – 62.71±0.88 0.29 8.21 4.69±0.02 √ 1 4 – 65.22±0.29 0.29 8.32 5.60±0.04 √ 4 1 – 67.73±0.33 0.29 8.32 5.09±0.07 √ 8 4 – 66.39±0.30 0.32 9.38 6.07±0.10 √ 4 4 FPN 67.84±1.04 0.41 12.16 6.31±0.07 √ 8 8 BiFPN 69.04±0.02 0.47 14.37 8.11±0.05 -
[1] 郭业才, 姚文强. 基于信噪比分类网络的调制信号分类识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825.GUO Yecai and YAO Wenqiang. Modulation signal classification and recognition algorithm based on signal to noise ratio classification network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825. [2] 张正宇, 何睿斯, 杨汨, 等. 面向6G的无线信道语义特征及建模[J]. 电子学报, 2025, 53(1): 14–23. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240595.ZHANG Zhengyu, HE Ruisi, YANG Mi, et al. Semantic characteristics and modeling of wireless channels for 6G[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2025, 53(1): 14–23. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240595. [3] 张思成, 林云, 涂涯, 等. 基于轻量级深度神经网络的电磁信号调制识别技术[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(11): 12–21. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020237.ZHANG Sicheng, LIN Yun, TU Ya, et al. Electromagnetic signal modulation recognition technology based on lightweight deep neural network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(11): 12–21. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020237. [4] 孟磊, 曲卫, 马爽, 等. 基于LSTM的雷达脉冲重复间隔调制模式识别[J]. 现代雷达, 2021, 43(1): 50–57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2021.01.008.MENG Lei, QU Wei, MA Shuang, et al. Radar PRI Modulation pattern recognition method based on LSTM[J]. Modern Radar, 2021, 43(1): 50–57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2021.01.008. [5] KONG Weisi, JIAO Xun, XU Yuhua, et al. A transformer-based contrastive semi-supervised learning framework for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2023, 9(4): 950–962. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2023.3264908. [6] HU Mutian, MA Jitong, YANG Zhengyan, et al. Feature fusion convolution-aided transformer for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(10): 2643–2647. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3298941. [7] KONG Weisi, YANG Qinghai, JIAO Xun, et al. A transformer-based CTDNN structure for automatic modulation recognition[C]. The 7th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2021: 159–163. doi: 10.1109/ICCC54389.2021.9674558. [8] ZHU Xizhou, SU Weijie, LU Lewei, et al. Deformable DETR: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. [9] ZHANG Qi and DENG Linfeng. An intelligent fault diagnosis method of rolling bearings based on short-time Fourier transform and convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2023, 23(2): 795–811. doi: 10.1007/s11668-023-01616-9. [10] ZHOU Jie, MENG Ming, GAO Yunyuan, et al. Classification of motor imagery EEG using wavelet envelope analysis and LSTM networks[C]. Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Shenyang, China, 2018: 5600–5605. doi: 10.1109/CCDC.2018.8408108. [11] O'SHEA T J, ROY T, and CLANCY T C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 168–179. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2797022. [12] SATHYANARAYANAN V, GERSTOFT P, and EL GAMAL A. RML22: Realistic dataset generation for wireless modulation classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(11): 7663–7675. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3254490. [13] 崔凯, 崔天舒, 朱岩, 等. 基于多尺度时序特征的信号调制样式识别算法[J]. 信号处理, 2021, 37(8): 1507–1517. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.08.018.CUI Kai, CUI Tianshu, ZHU Yan, et al. Signal modulation pattern recognition algorithm based on multiscale temporal features[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2021, 37(8): 1507–1517. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.08.018. [14] DAI Jifeng, QI Haozhi, XIONG Yuwen, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 764–773. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.89. [15] NJOKU J N, MOROCHO-CAYAMCELA M E, and LIM W. CGDNet: Efficient hybrid deep learning model for robust automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Networking Letters, 2021, 3(2): 47–51. doi: 10.1109/LNET.2021.3057637. [16] WEST N E and O’SHEA T. Deep architectures for modulation recognition[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks, Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/DySPAN.2017.7920754. [17] LIU Xiaoyu, YANG Diyu, and EL GAMAL A. Deep neural network architectures for modulation classification[C]. The 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2017: 915–919. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2017.8335483. [18] HONG Dehua, ZHANG Zilong, and XU Xiaodong. Automatic modulation classification using recurrent neural networks[C]. The 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2017: 695–700. doi: 10.1109/CompComm.2017.8322633. [19] LU Xiao, TAO Mengyuan, FU Xue, et al. Lightweight network design based on ResNet structure for modulation recognition[C]. IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference, Norman, USA, 2021: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTC2021-Fall52928.2021.9625558. [20] KE Ziqi and VIKALO H. Real-time radio technology and modulation classification via an LSTM auto-encoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(1): 370–382. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3095855. [21] HERMAWAN A P, GINANJAR R R, KIM D S, et al. CNN-based automatic modulation classification for beyond 5G communications[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(5): 1038–1041. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2970922. [22] RAJENDRAN S, MEERT W, GIUSTINIANO D, et al. Deep learning models for wireless signal classification with distributed low-cost spectrum sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(3): 433–445. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2835460. [23] XU Jialang, LUO Chunbo, PARR G, et al. A spatiotemporal multi-channel learning framework for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1629–1632. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2999453. [24] HUYNH-THE T, HUA C H, PHAM Q V, et al. MCNet: An efficient CNN architecture for robust automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(4): 811–815. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2968030. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
