Dual-Memristor Brain-Like Chaotic Neural Network and Its Application in IoMT Data Privacy Protection
-
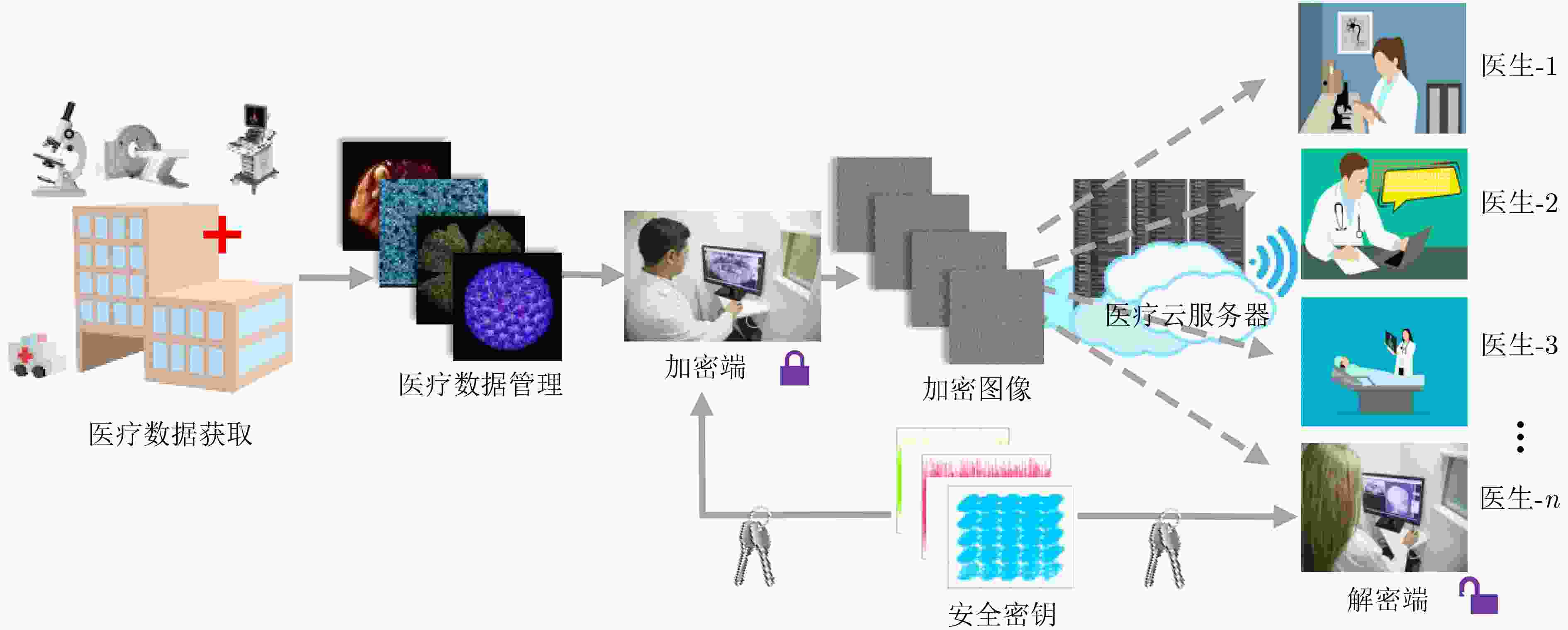
摘要: 近年来,医疗数据泄露频发,严重威胁患者隐私与健康安全,亟需有效的解决方案以保护医疗数据在传输过程中的隐私与安全性。该文提出了一种基于双忆阻类脑混沌神经网络的医疗物联网(Internet of Medical Things, IoMT)数据隐私保护方法,以应对这一挑战。首先,利用忆阻器的突触仿生特性,构建了一种基于Hopfield神经网络的双忆阻类脑混沌神经网络模型,并通过分岔图、Lyapunov指数谱、相图、时域图及吸引盆等非线性动力学工具,深入揭示了模型的复杂混沌动力学特性。研究结果表明,该网络不仅展现出复杂的网格多结构混沌吸引子特性,还具有平面初值位移调控能力,从而显著增强了其密码学应用潜力。为了验证其实用性与可靠性,基于微控制器单元(MCU)搭建了硬件平台,并通过硬件实验进一步确认了模型的复杂动力学行为。基于此模型,该文设计了一种结合双忆阻类脑混沌神经网络复杂混沌特性的高效IoMT数据隐私保护方法。在此基础上,对彩色医疗图像数据的加密效果进行了全面的安全性分析。实验结果表明,该方法在关键性能指标上表现优异,包括大密钥空间、低像素相关性、高密钥敏感性,以及对噪声与数据丢失攻击的强鲁棒性。该研究为IoMT环境下的医疗数据隐私保护提供了一种创新且有效的解决方案,为未来的智能医疗安全技术发展奠定了坚实基础。
-
关键词:
- 忆阻器 /
- 混沌系统 /
- Hopfield神经网络 /
- 多吸引子 /
- 混沌加密
Abstract:Objective In recent years, frequent breaches of medical data have posed significant threats to patient privacy and health security, highlighting the urgent need for effective solutions to protect medical data privacy and security during transmission. This paper proposes a novel data privacy protection method for the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) based on a dual-memristor-inspired brain-like chaotic neural network to address this challenge. Methods Leveraging the synaptic bionic characteristics of memristors, a dual-memristor brain-like chaotic neural network model based on the Hopfield neural network is developed. The complex chaotic dynamics of this model are thoroughly analyzed using nonlinear dynamics tools, including bifurcation diagrams, Lyapunov exponent spectra, phase portraits, time-domain waveforms, and basins of attraction. To validate its practicality and reliability, a hardware platform is created using a Microcontroller Unit (MCU), and hardware experiments confirm the model’s complex dynamic behaviors. Based on this model, an efficient IoMT data privacy protection method is designed by utilizing the complex chaotic properties of the dual-memristor brain-like chaotic neural network. A comprehensive security analysis of the encryption of colored medical image data is also performed. Results and Discussions The results demonstrate that the proposed network not only exhibits complex grid-like multi-structure chaotic attractors but also possesses the capability to regulate planar initial condition displacements, significantly enhancing its potential for cryptographic applications. Experimental findings indicate that this method performs exceptionally well across key metrics, including a large key space, low pixel correlation, high key sensitivity, and strong robustness against noise and data loss attacks. Conclusions This study presents an innovative and effective solution for protecting medical data privacy in IoMT environments, providing a solid foundation for the development of secure technologies in intelligent healthcare systems. -
Key words:
- Memristor /
- Chaotic system /
- Hopfield neural network /
- Multi-attractors /
- Chaotic encryption
-
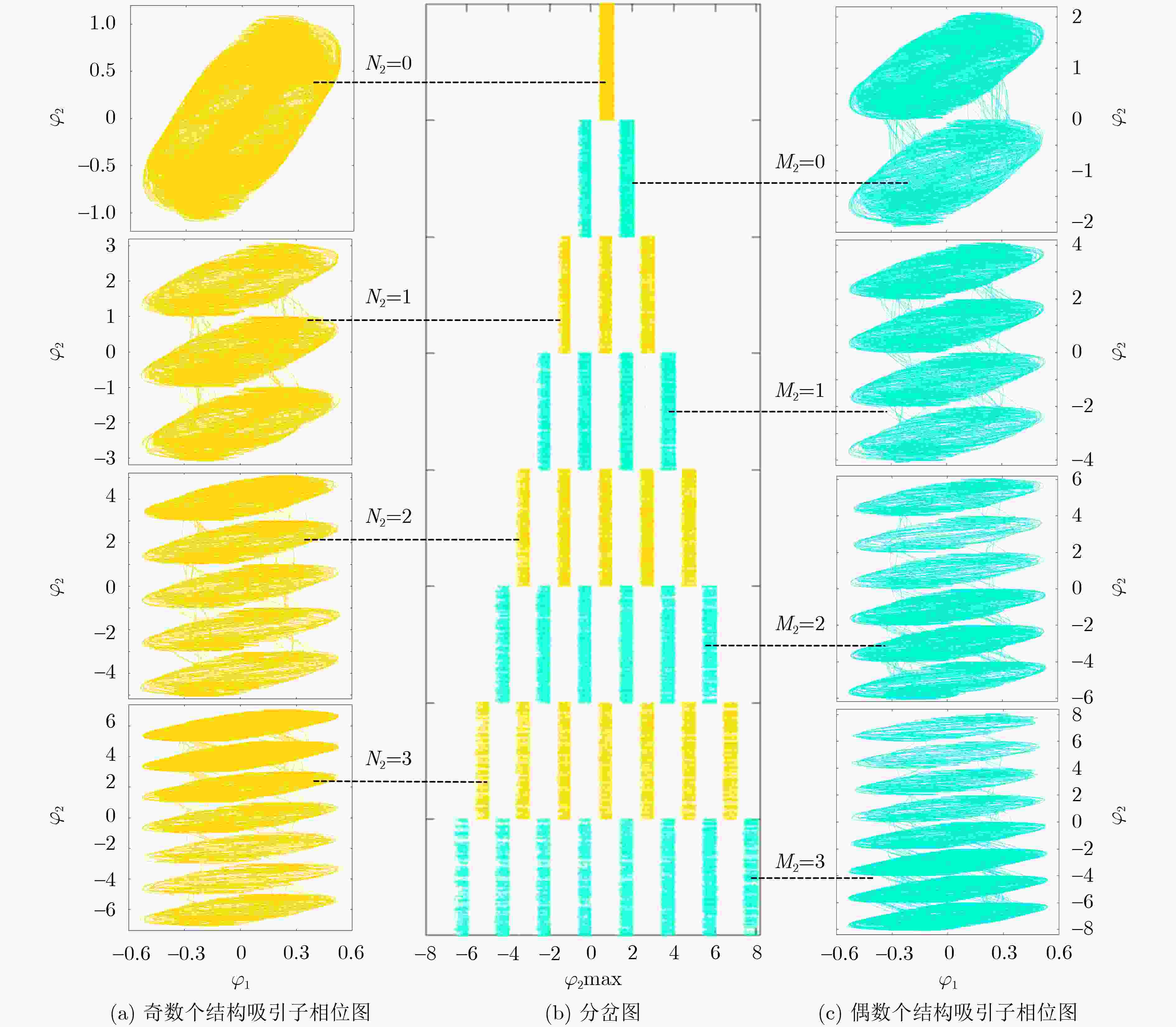
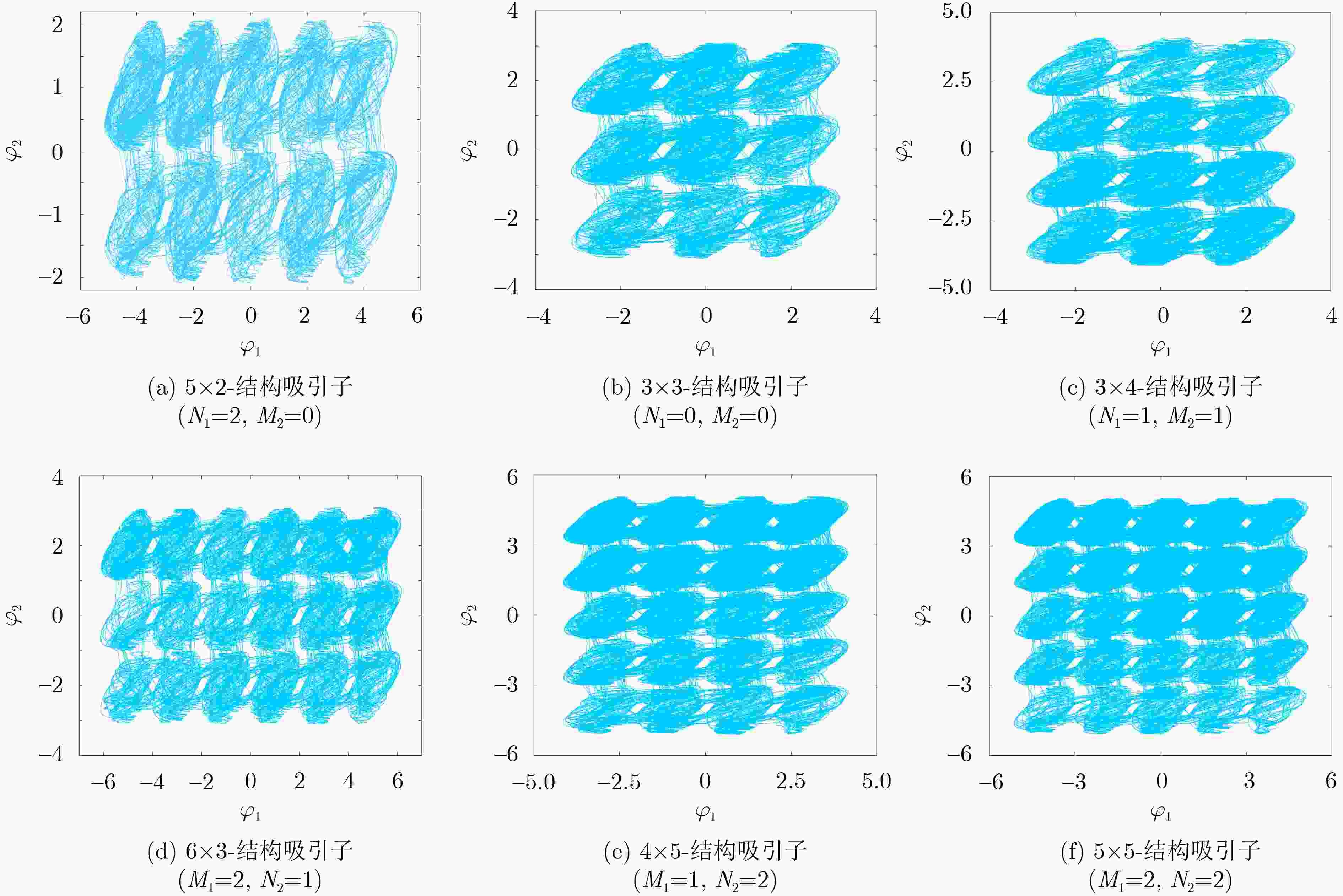
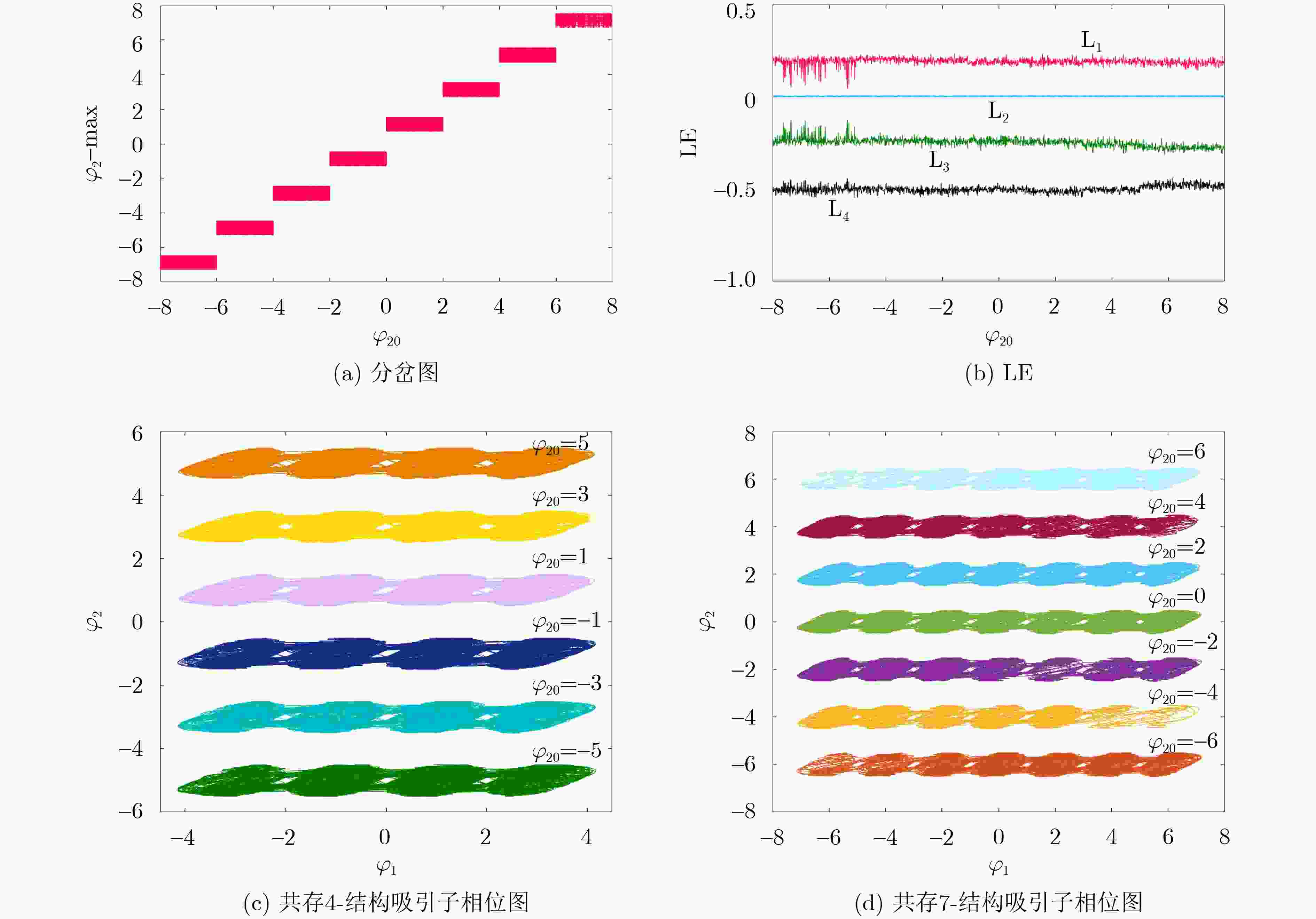
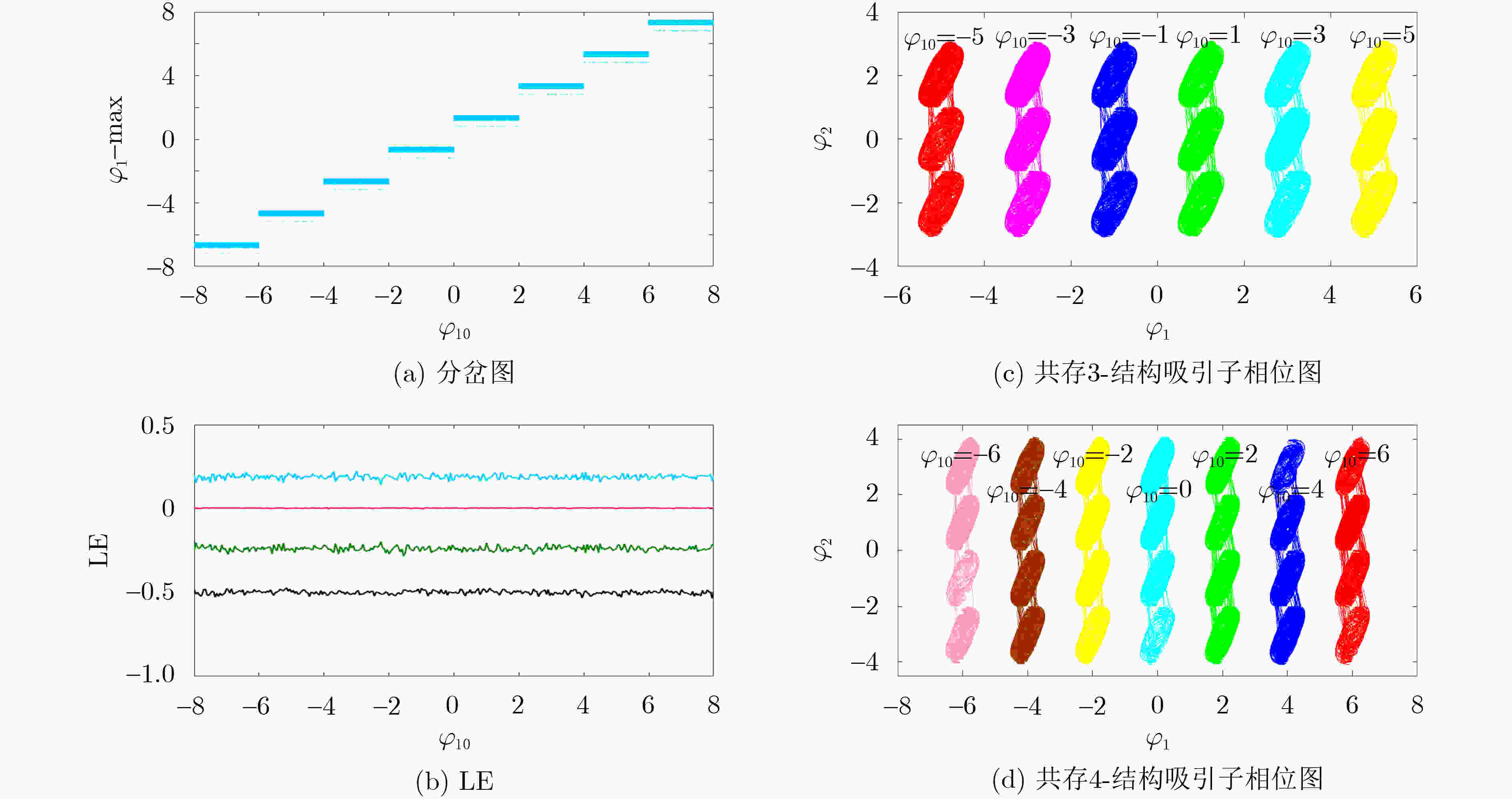
表 1 忆阻突触控制参数与网格吸引子关系
N1/M1 $\varphi_1 $方向(n) N2/M2 $\varphi_2 $方向(m) 0 1/2 0 1/2 1 3/4 1 3/4 2 5/6 2 5/6 … … … … N1/M1 (2N1+1)/(2M1+2) N2/M2 (2N2+1)/(2M2+2) 表 3 原图像与加密图像的相关系数和信息熵
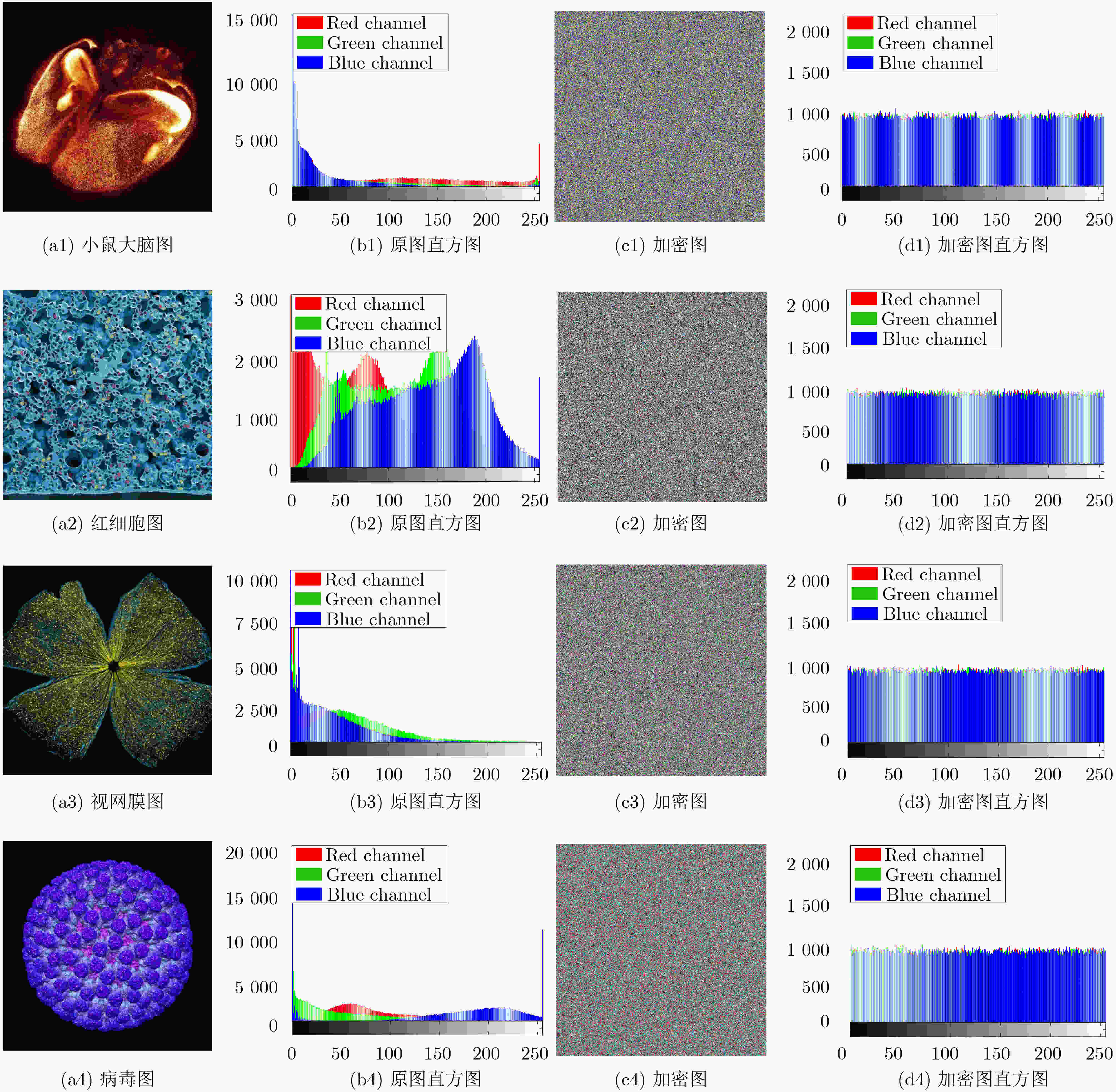
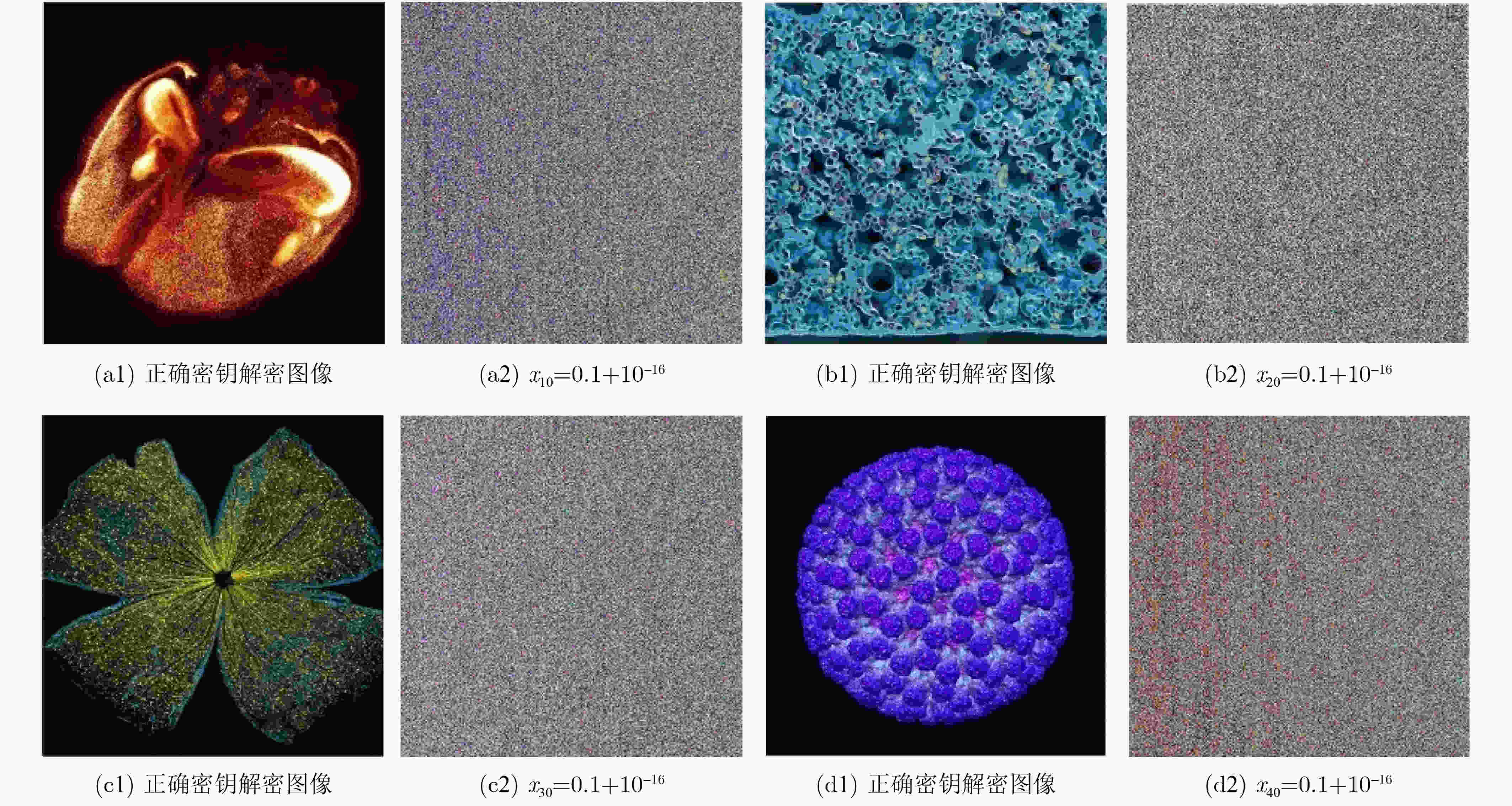
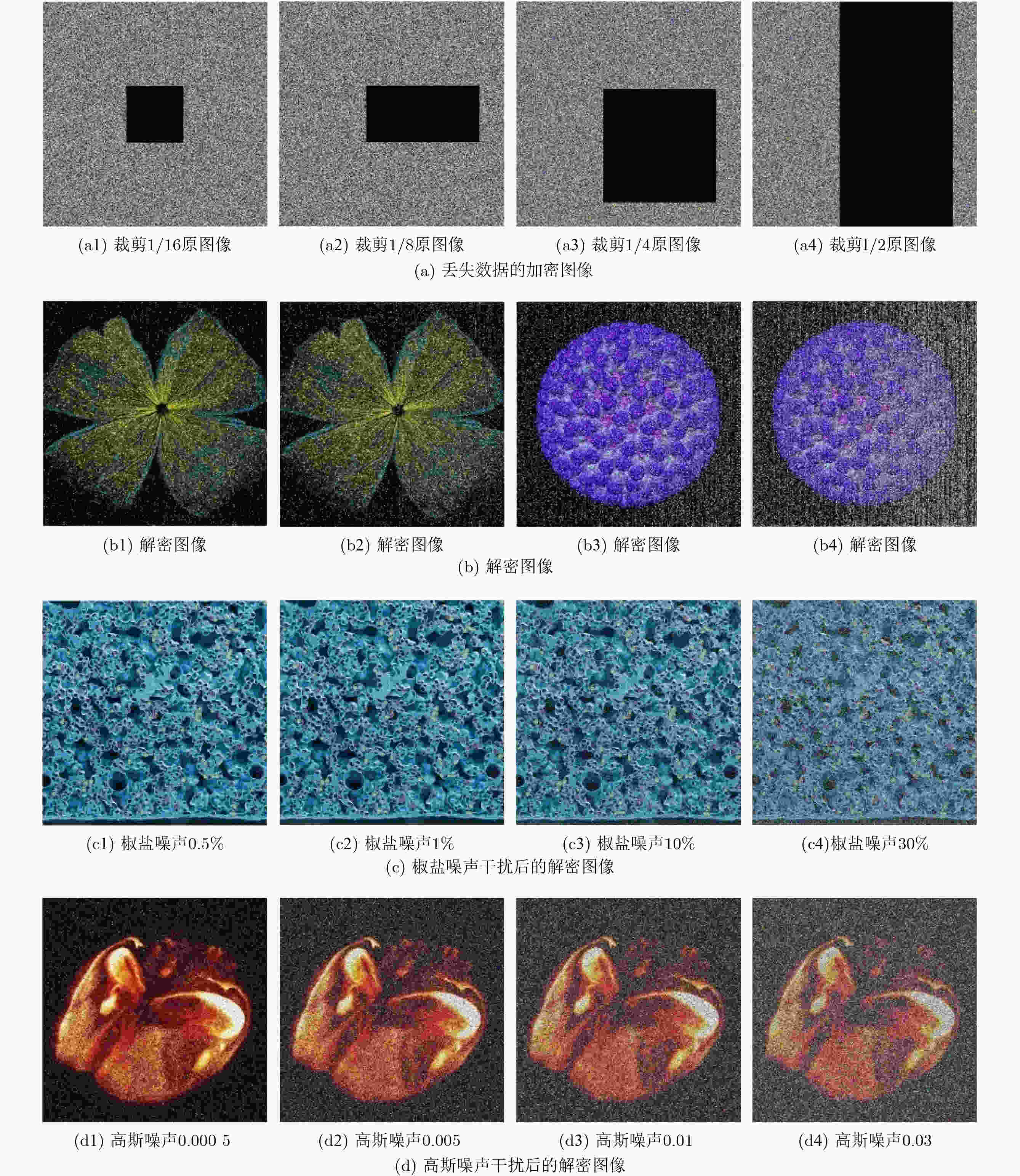
相关系数 信息熵 差分攻击 图像 垂直/水平/对角线 RGB 红R/绿G/蓝B NPCR/UACI 大脑 原图 0.946871 /0.944926 /0.934295 5.5487 6.4159 /4.9046 /4.9319 99.6907 /32.8161 加密图 – 0.0113173 /0.006627 /–0.017526 7.9996 7.9993 /7.9992 /7.9993 红细胞 原图 0.905427 /0.919528 /0.869007 7.7647 6.9389 /76146 /7.6832 99.5060 /34.6095 加密图 0.016132 /0.006560 /0.007012 7.9998 7.9993 /7.9993 /7.9994 视网膜 原图 0.691344 /0.714074 /0.640713 6.1917 6.0691 /6.4005 /5.8215 99.5505 /34.7912 加密图 – 0.006482 /0.005781 /0.011470 7.9997 7.9993 /7.9993 /7.9994 病毒 原图 0.961282 /0.962064 /0.945707 5.2211 5.0190 /4.5569 /5.0514 99.7292 /37.3502 加密图 – 0.015224 /–0.001286 /–0.010731 7.9996 7.9994 /7.9994 /7.9993 表 7 NIST测试
统计测试 通过率 P值 结果 频率测试 0.99 0.474 通过 块内频数测试 0.98 0.596 通过 动向测试 1.00 0.419 通过 最大游程测试 1.00 0.718 通过 二进制矩阵秩测试 0.98 0.384 通过 频谱测试 1.00 0.868 通过 非重叠字匹配测试 0.99 0.637 通过 重叠字匹配测试 0.97 0.249 通过 毛勒通用统计测试 0.99 0.141 通过 线性复杂度测试 0.99 0.485 通过 系列测试 0.98 0.356 通过 近似熵测试 1.00 0.299 通过 累积测试 0.97 0.323 通过 随机游程测试 0.99 0.759 通过 随机游程变量测试 0.97 0.367 通过 -
[1] GHUBAISH A, SALMAN T, ZOLANVARI M, et al. Recent advances in the internet-of-medical-things (IoMT) systems security[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(11): 8707–8718. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3045653. [2] AHMED S F, ALAM M S B, AFRIN S, et al. Insights into internet of medical things (IoMT): Data fusion, security issues and potential solutions[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 102: 102060. doi: 10.1016/J.INFFUS.2023.102060. [3] 陈友荣, 陈浩, 韩蒙, 等. 基于信用等级划分的医疗数据安全共识算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 279–287. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200893.CHEN Yourong, CHEN Hao, HAN Meng, et al. Security consensus algorithm of medical data based on credit rating[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 279–287. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200893. [4] JAVAID M, HALEEM A, SINGH R P, et al. Towards insighting cybersecurity for healthcare domains: A comprehensive review of recent practices and trends[J]. Cyber Security and Applications, 2023, 1: 100016. doi: 10.1016/J.CSA.2023.100016. [5] ZHANG Bowen and LIU Lingfeng. Chaos-based image encryption: Review, application, and challenges[J]. Mathematics, 2023, 11(11): 2585. doi: 10.3390/math11112585. [6] LIU Huipeng, TENG Lin, ZHANG Yijia, et al. Mutil-medical image encryption by a new spatiotemporal chaos model and DNA new computing for information security[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 235: 121090. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121090. [7] MAN Zhenlong, GAO Chang, DAI Yu, et al. Dynamic rotation medical image encryption scheme based on improved Lorenz chaos[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2024, 112(15): 13571–13597. doi: 10.1007/s11071-024-09732-3. [8] 周双, 尹彦力, 王诗雨, 等. n维离散超混沌系统及其在音频加密中的应用[J]. 物理学报, 2024, 73(21): 210501. doi: 10.7498/aps.73.20241028.ZHOU Shuang, YIN Yanli, WANG Shiyu, et al. An n-dimensional discrete hyperchaotic system and its application in audio encryption[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2024, 73(21): 210501. doi: 10.7498/aps.73.20241028. [9] HUA Zhongyun, ZHU Zhihua, YI Shuang, et al. Cross-plane colour image encryption using a two-dimensional logistic tent modular map[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 546: 1063–1083. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.09.032. [10] BAO Han, HUA Zhongyun, WANG Ning, et al. Initials-boosted coexisting chaos in a 2-D sine map and its hardware implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(2): 1132–1140. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2992438. [11] LI Chengqing, TAN Kai, FENG Bingbing, et al. The graph structure of the generalized discrete Arnold's cat map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2022, 71(2): 364–377. doi: 10.1109/TC.2021.3051387. [12] FENG W, WANG Q, LIU H, et al. Exploiting newly designed fractional-order 3D Lorenz chaotic system and 2D discrete polynomial hyper-chaotic map for high-performance multi-image encryption[J]. Fractal and Fractional, 2023, 7(12): 887. doi: 10.3390/fractalfract7120887. [13] STANKEVICH N and VOLKOV E. Chaos–hyperchaos transition in three identical quorum-sensing mean-field coupled ring oscillators[J]. Chaos, 2021, 31(10): 103112. doi: 10.1063/5.0056907. [14] 李春彪, 李泳新, 仲庆, 等. 忆阻超混沌映射的可调控性设计及光纤保密通信系统构建[J]. 通信学报, 2024, 45(4): 171–184. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024086.LI Chunbiao, LI Yongxin, ZHONG Qing, et al. Controllability design of a memristive hyperchaotic map and the construction of optical fiber secure communication system[J]. Journal on Communications, 2024, 45(4): 171–184. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024086. [15] LAI Qiang and CHEN Zhijie. Grid-scroll memristive chaotic system with application to image encryption[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2023, 170: 113341. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113341. [16] HOPFIELD J J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1984, 81(10): 3088–3092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3088. [17] STRUKOV D B, SNIDER G S, STEWART D R, et al. The missing memristor found[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 80–83. doi: 10.1038/nature06932. [18] 董哲康, 杜晨杰, 林辉品, 等. 基于多通道忆阻脉冲耦合神经网络的多帧图像超分辨率重建算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 835–843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190868.DONG Zhekang, DU Chenjie, LIN Huipin, et al. Multi-channel memristive pulse coupled neural network based multi-frame images super-resolution reconstruction algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 835–843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190868. [19] SCHRANGHAMER T F, OBEROI A, and DAS S. Graphene memristive synapses for high precision neuromorphic computing[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5474. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19203-z. [20] YAO Wei, WANG Chunhua, SUN Yichuang, et al. Event-triggered control for robust exponential synchronization of inertial memristive neural networks under parameter disturbance[J]. Neural Networks, 2023, 164: 67–80. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2023.04.024. [21] HE Shaobo, LIU Jun, WANG Huihai, et al. A discrete memristive neural network and its application for character recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 523: 1–8. doi: 10.1016/J.NEUCOM.2022.12.014. [22] CHEN Chengjie, MIN Fuhong, CAI Jianming, et al. Memristor synapse-driven simplified Hopfield neural network: Hidden dynamics, attractor control, and circuit implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2024, 71(5): 2308–2319. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2024.3349451. [23] LAI Qiang, WAN Zhiqiang, and KUATE P D K. Generating grid multi-scroll attractors in memristive neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2023, 70(3): 1324–1336. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3228566. [24] HUANG Lilian, ZHANG Yue, XIANG Jianhong, et al. Extreme multistability in a Hopfield neural network based on two biological neuronal systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(11): 4568–4572. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2022.3183340. [25] 王梦蛟, 杨琛, 贺少波, 等. 一种新型复合指数型局部有源忆阻器耦合的Hopfield神经网络[J]. 物理学报, 2024, 73(13): 130501. doi: 10.7498/aps.73.20231888.WANG Mengjiao, YANG Chen, HE Shaobo, et al. A novel compound exponential locally active memristor coupled Hopfield neural network[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2024, 73(13): 130501. doi: 10.7498/aps.73.20231888. [26] YU Fei, SHEN Hui, YU Qiulin, et al. Privacy protection of medical data based on multi-scroll memristive Hopfield neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2023, 10(2): 845–858. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3223930. [27] LIN Hairong, WANG Chunhua, XU Cong, et al. A memristive synapse control method to generate diversified multistructure chaotic attractors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2023, 42(3): 942–955. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2022.3186516. [28] LAI Qiang, YANG Liang, HU Genwen, et al. Constructing multiscroll memristive neural network with local activity memristor and application in image encryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(7): 4039–4048. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2024.3377011. [29] RANI N, SHARMA S R, and MISHRA V. Grayscale and colored image encryption model using a novel fused magic cube[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, 108(2): 1773–1796. doi: 10.1007/s11071-022-07276-y. [30] LI Xiaoxiao, GUO Xiaopeng, HAN Pengfei, et al. Laplacian redecomposition for multimodal medical image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(9): 6880–6890. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.2975405. [31] ANAND A. A dimensionality reduction-based approach for secured color image watermarking[J]. Soft Computing, 2024, 28(6): 5137–5154. doi: 10.1007/s00500-023-09233-2. [32] MA Jun, HE Yuting, LI Feifei, et al. Segment anything in medical images[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 654. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44824-z. [33] GUAN Hao and LIU Mingxia. Domain adaptation for medical image analysis: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 69(3): 1173–1185. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3117407. [34] ZHOU Nanrun, HU Longlong, HUANG Zhiwen, et al. Novel multiple color images encryption and decryption scheme based on a bit-level extension algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 238: 122052. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122052. [35] 宋昭阳, 王一诺, 王浩文, 等. 基于Hopfield网络“伪吸引子”与交替量子随机行走的抗攻击彩色图像加密方案[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(8): 2030–2042. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211391.SONG Zhaoyang, WANG Yinuo, WANG Haowen, et al. Anti-attack color image encryption scheme based on hopfield network “Pseudo Attractor” and alternating quantum random walk[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(8): 2030–2042. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211391. [36] TENG Lin, WANG Xingyuan, YANG Feifei, et al. Color image encryption based on cross 2D hyperchaotic map using combined cycle shift scrambling and selecting diffusion[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2021, 105(2): 1859–1876. doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-06663-1. [37] 董哲康, 钱智凯, 周广东, 等. 基于忆阻的全功能巴甫洛夫联想记忆电路的设计、实现与分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 2080–2092. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210376.DONG Zhekang, QIAN Zhikai, ZHOU Guangdong, et al. Memory circuit design, implementation and analysis based on memristor full-function Pavlov associative[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 2080–2092. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210376. -





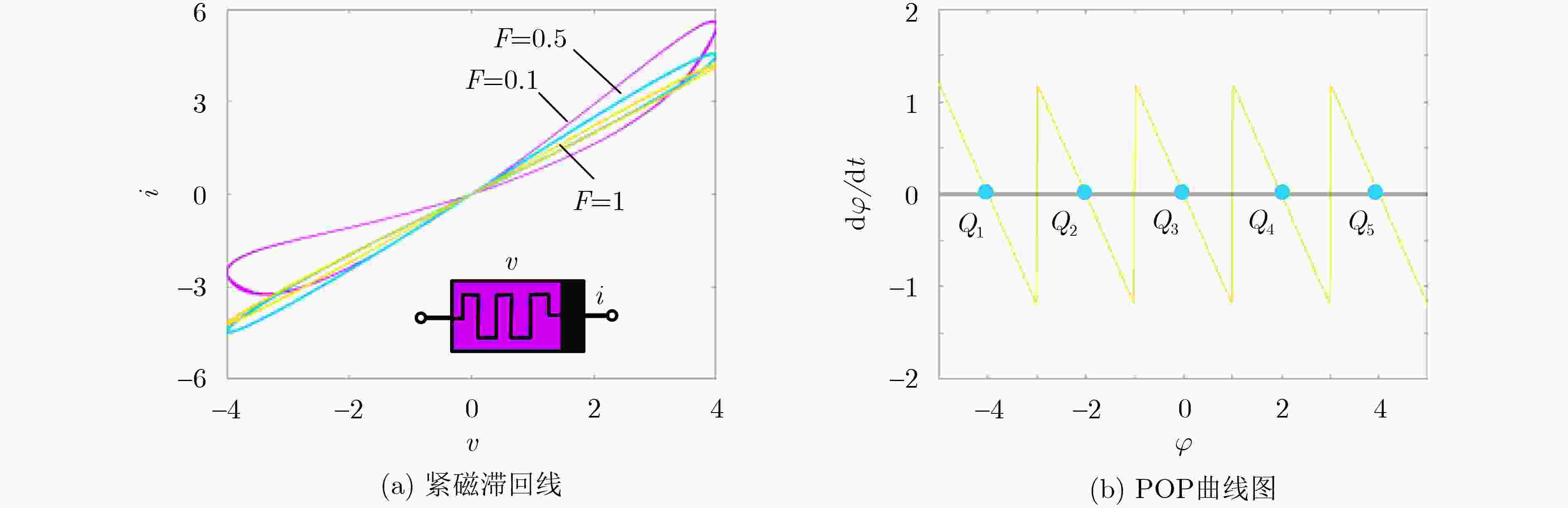
 下载:
下载:
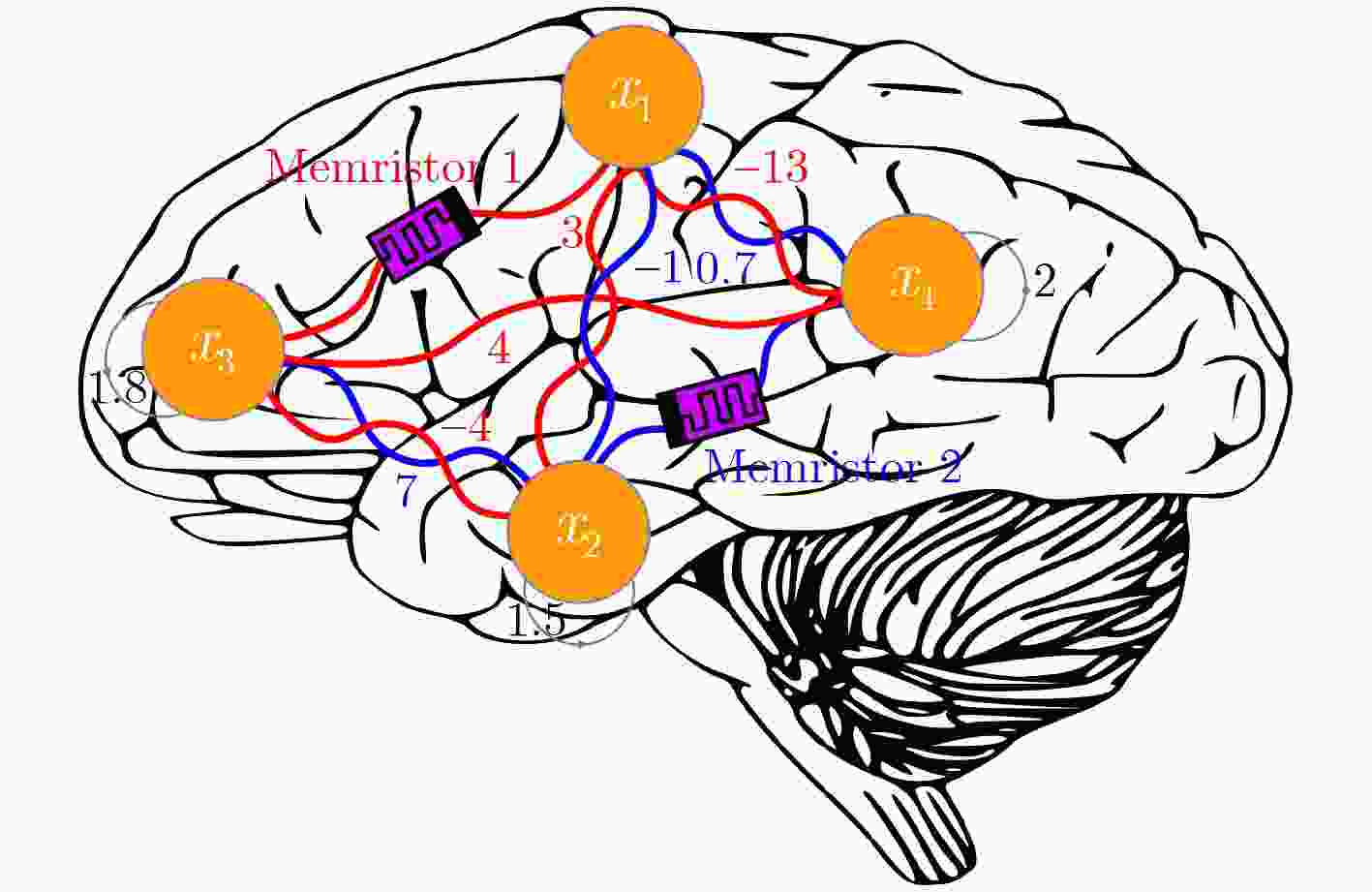
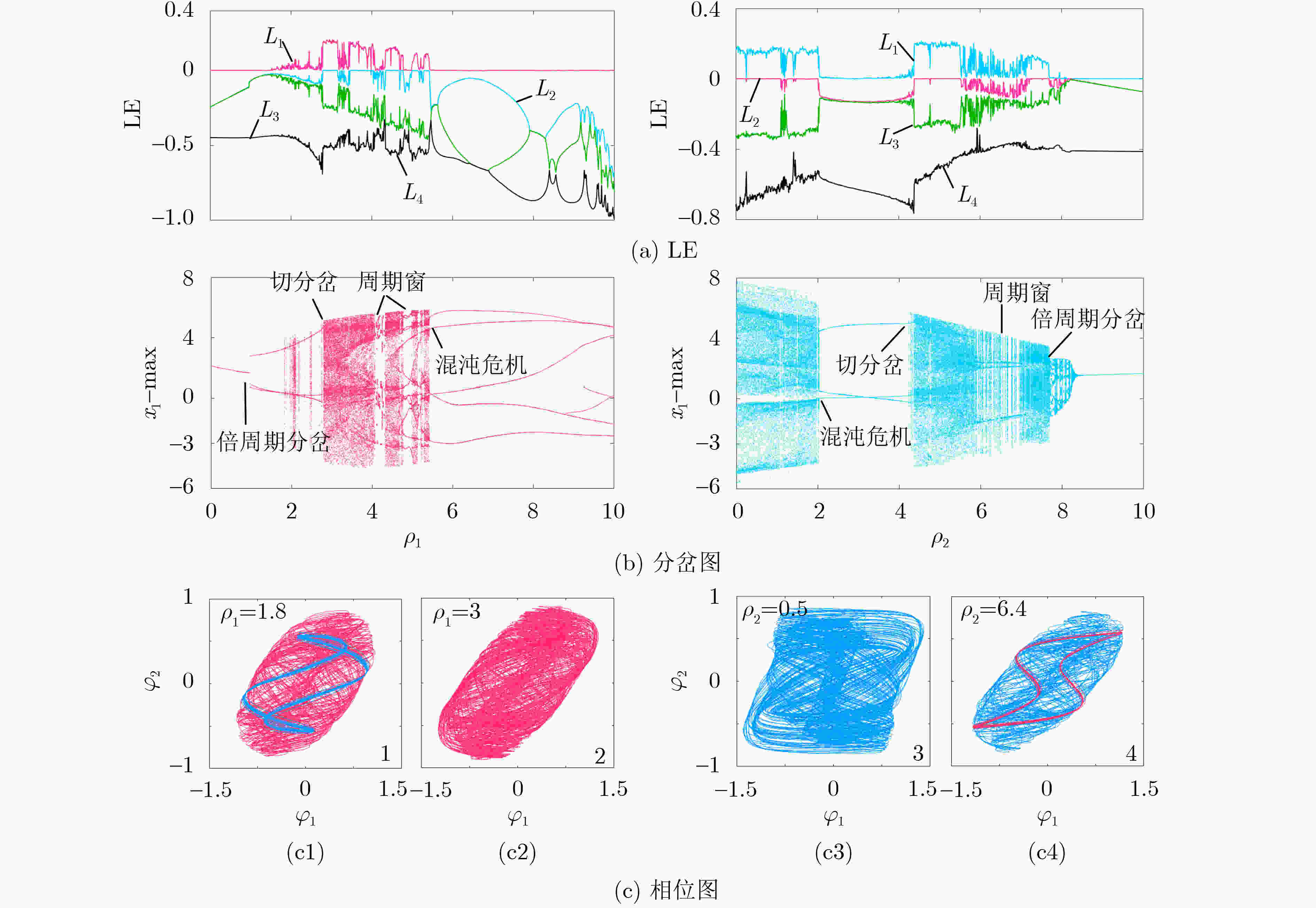
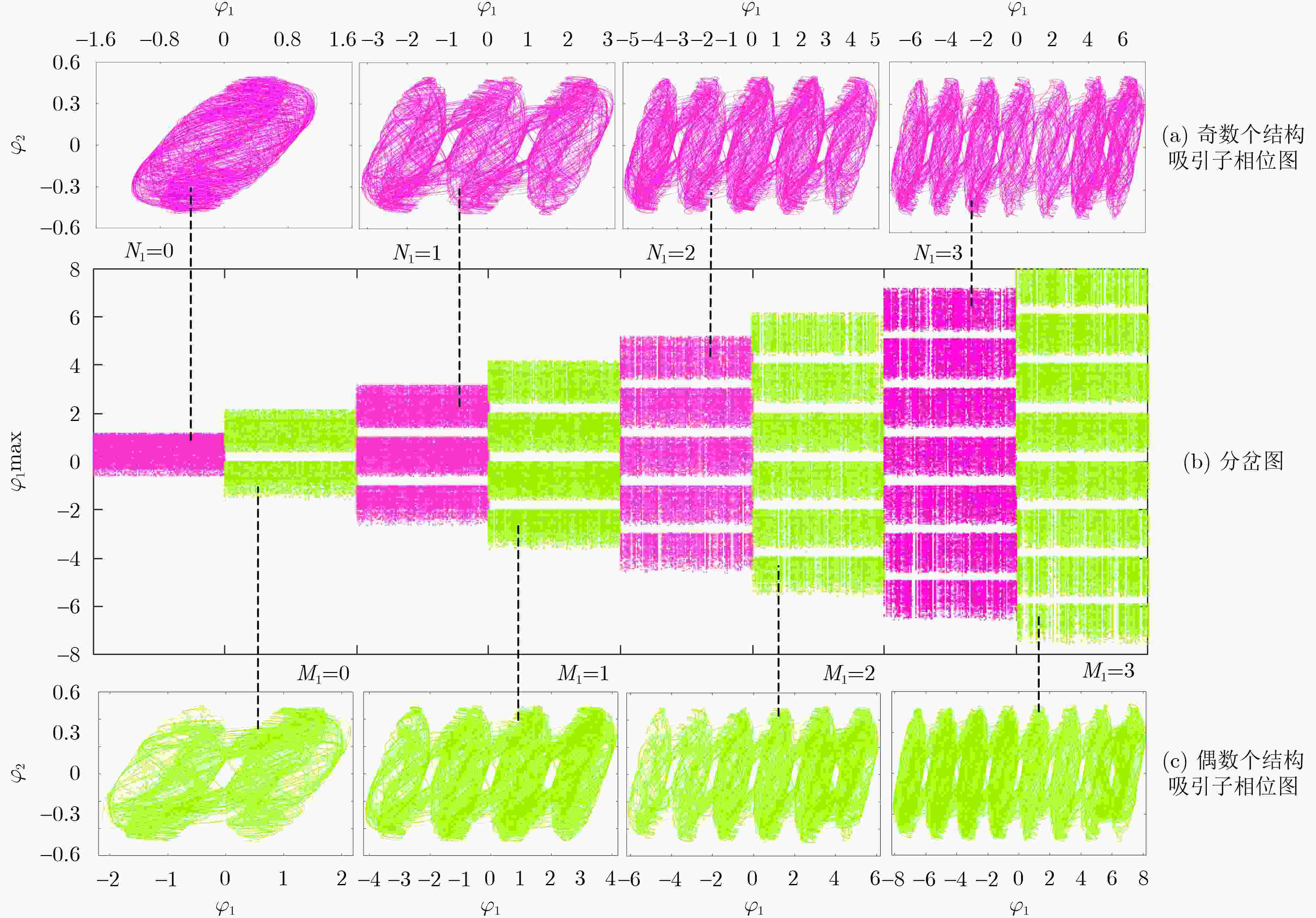
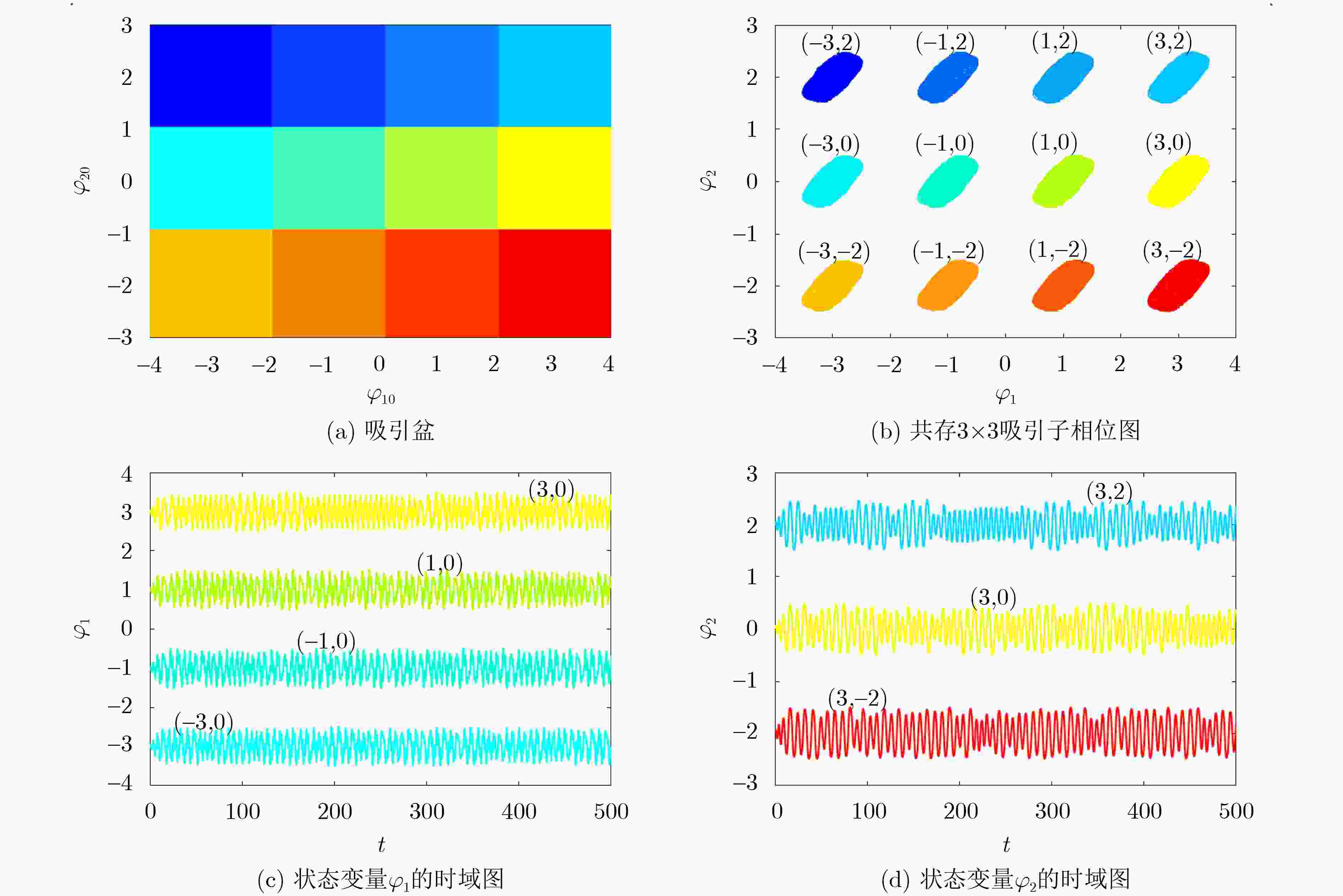
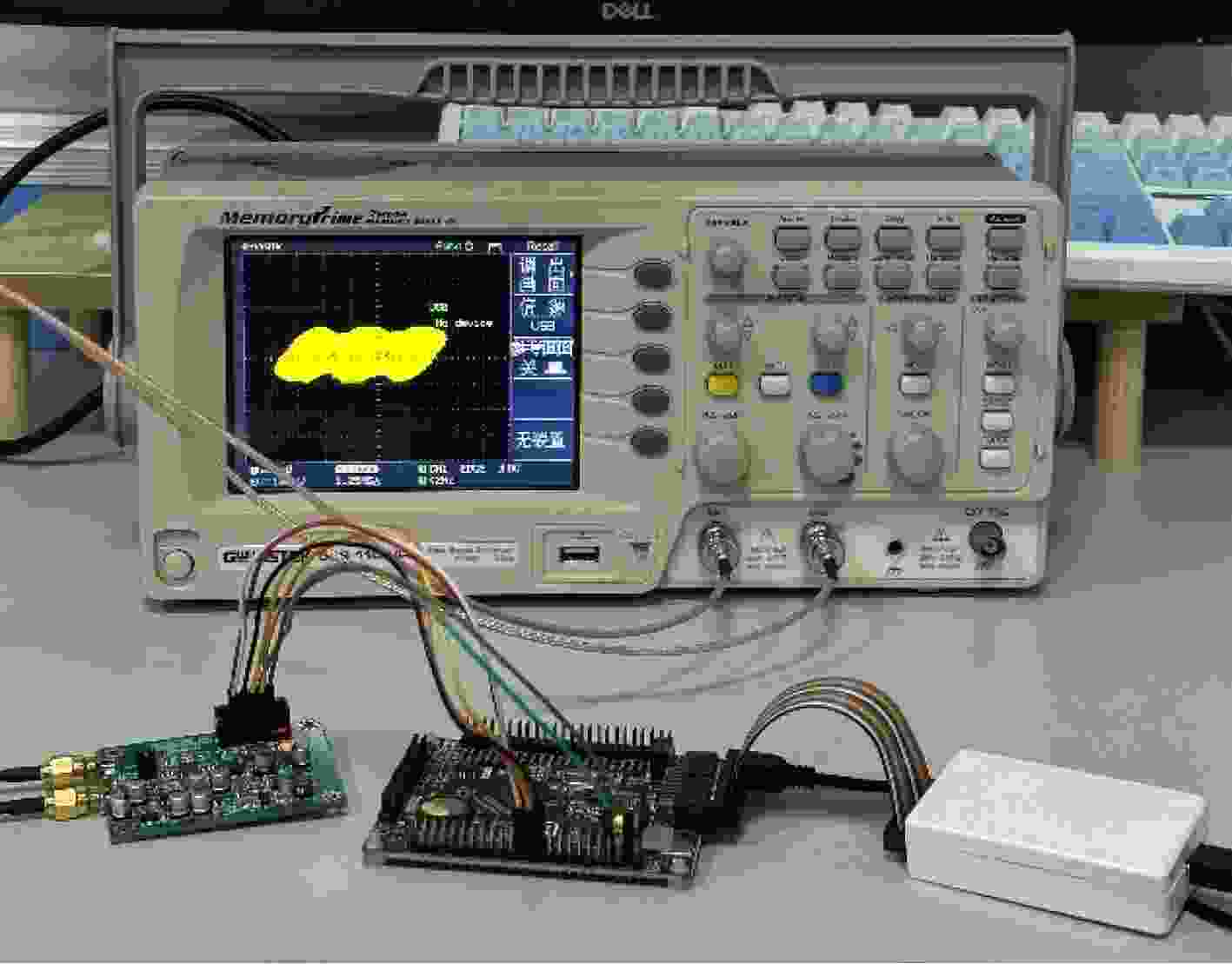
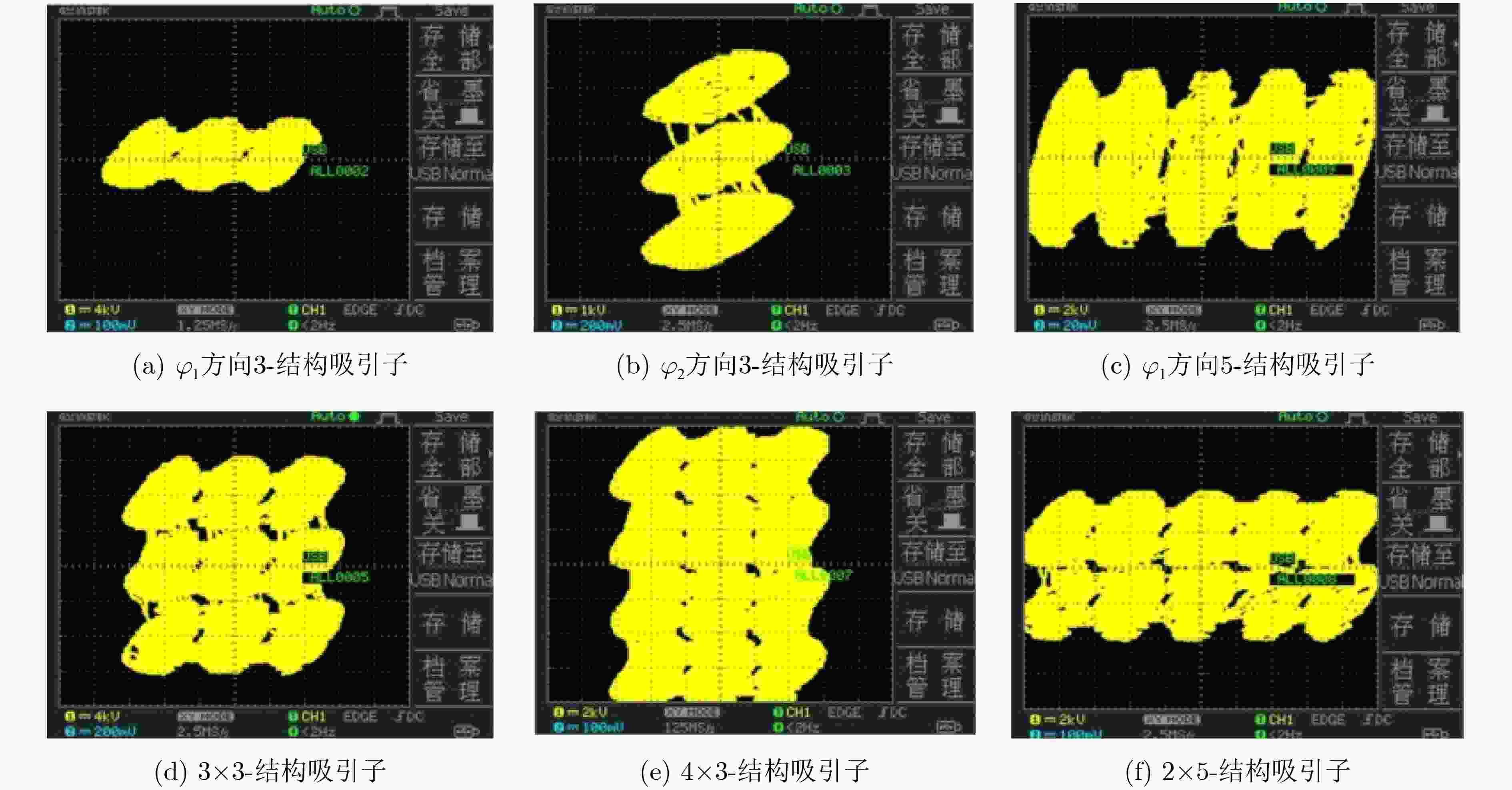


 下载:
下载:
