The Design and Implementation of a Secure and Efficient Firmware Trusted Platform Module for RISC-V Platforms
-
摘要: 可信平台模块(TPM)作为提升系统安全性的核心技术,能够提供基于硬件的密钥管理、可信启动和远程认证等安全功能。然而,当前 RISC-V平台普遍缺乏TPM支持,限制了其在嵌入式和云计算场景中的安全能力。为解决这一问题,该文设计并实现了RfTPM—一种面向RISC-V平台的固件可信平台模块(fTPM)架构,无需额外硬件单元或安全扩展即可提供等效的安全功能。针对执行隔离、可信启动、高效通信和安全时钟等关键挑战,在RfTPM中,该文提出了创新解决方案,包括:基于RISC-V物理内存保护(PMP)机制的内存隔离以及结合DRAM物理不可克隆函数(PUF)与Flash锁定的静态数据保护、基于延迟度量扩展的可信启动机制、基于动态权限交换页的高效通信机制以及基于RISC-V硬件计时器的细粒度安全时钟。该文构建了RfTPM的原型系统,对其进行了安全性分析并在Genesys2 FPGA平台模拟的Rocket Core上进行了性能测试。实验结果表明,RfTPM在保证安全性的同时在大多数TPM命令处理中有比较显著的性能优势。Abstract:
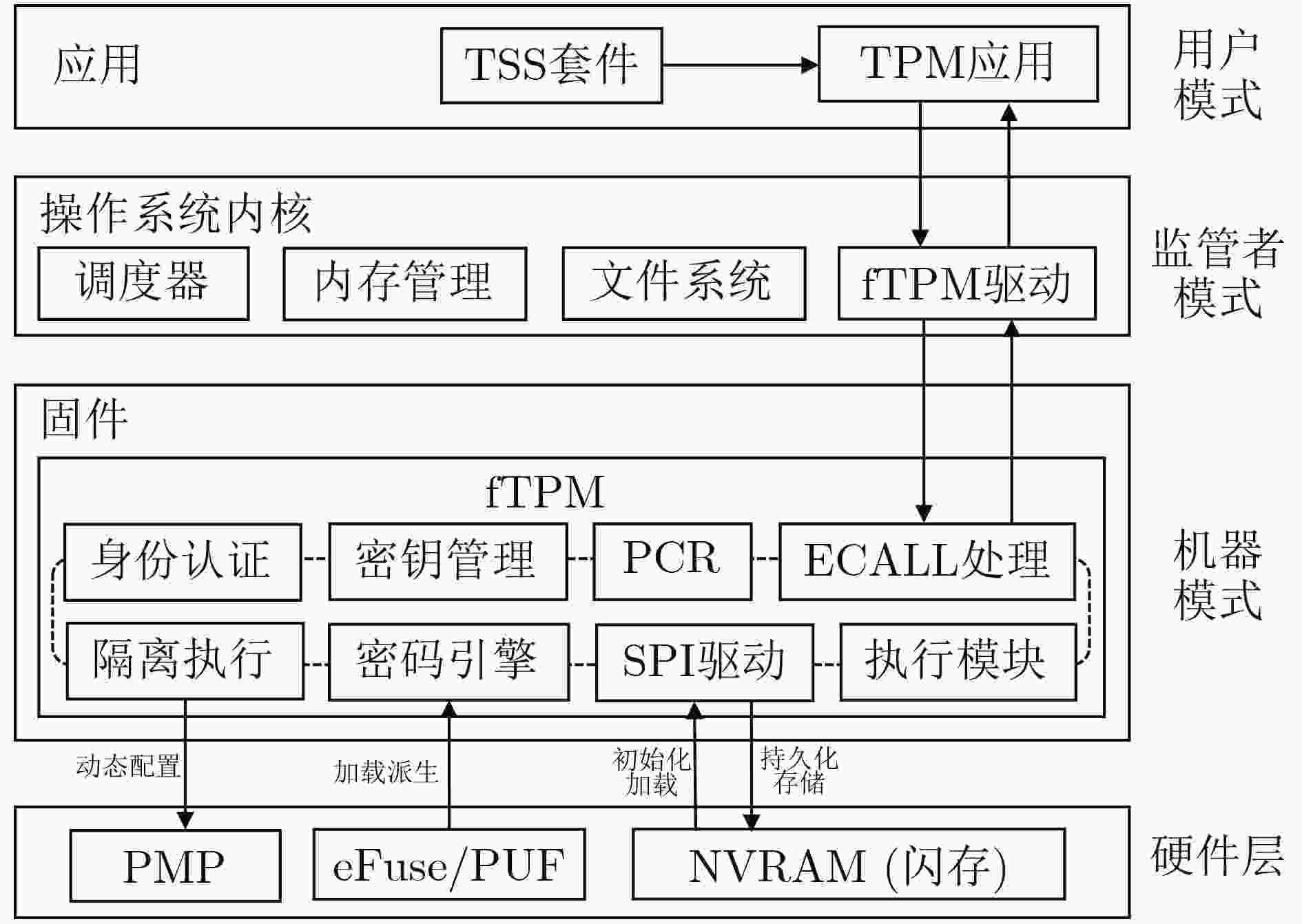
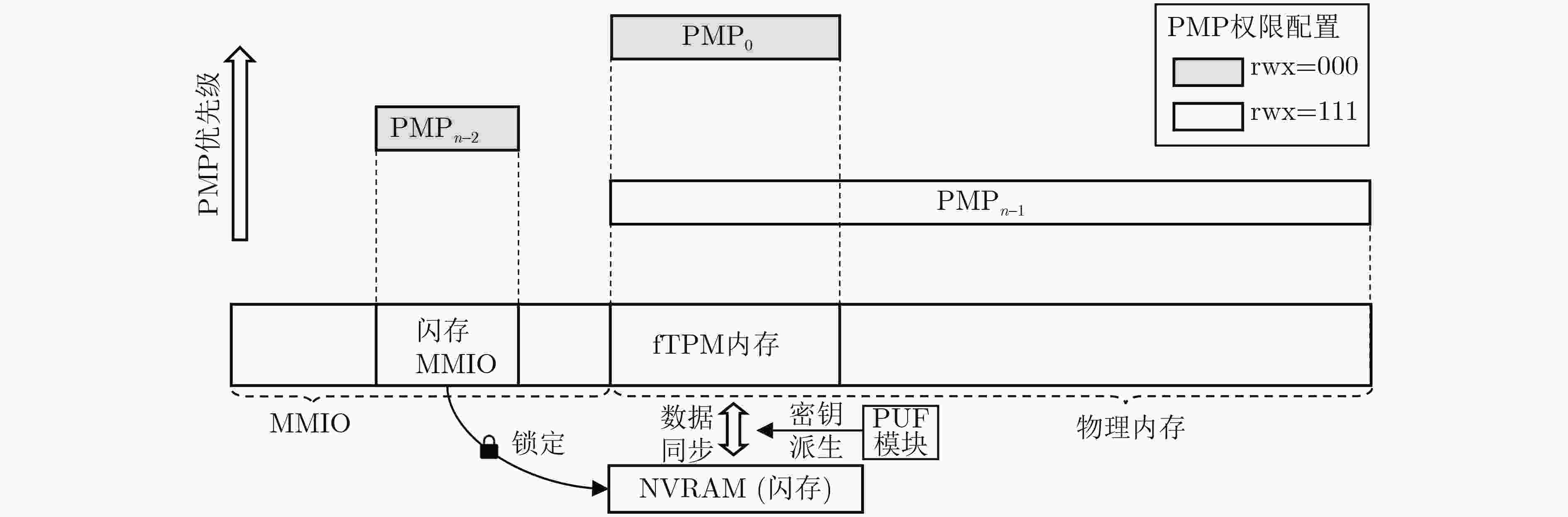
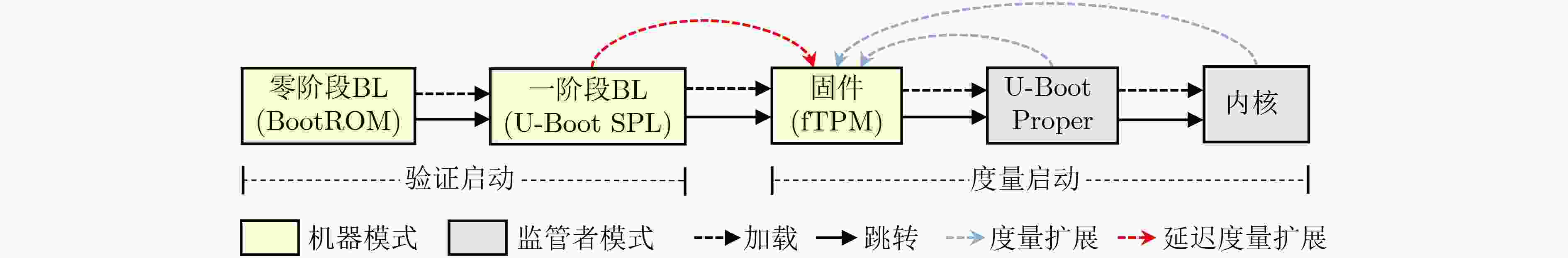
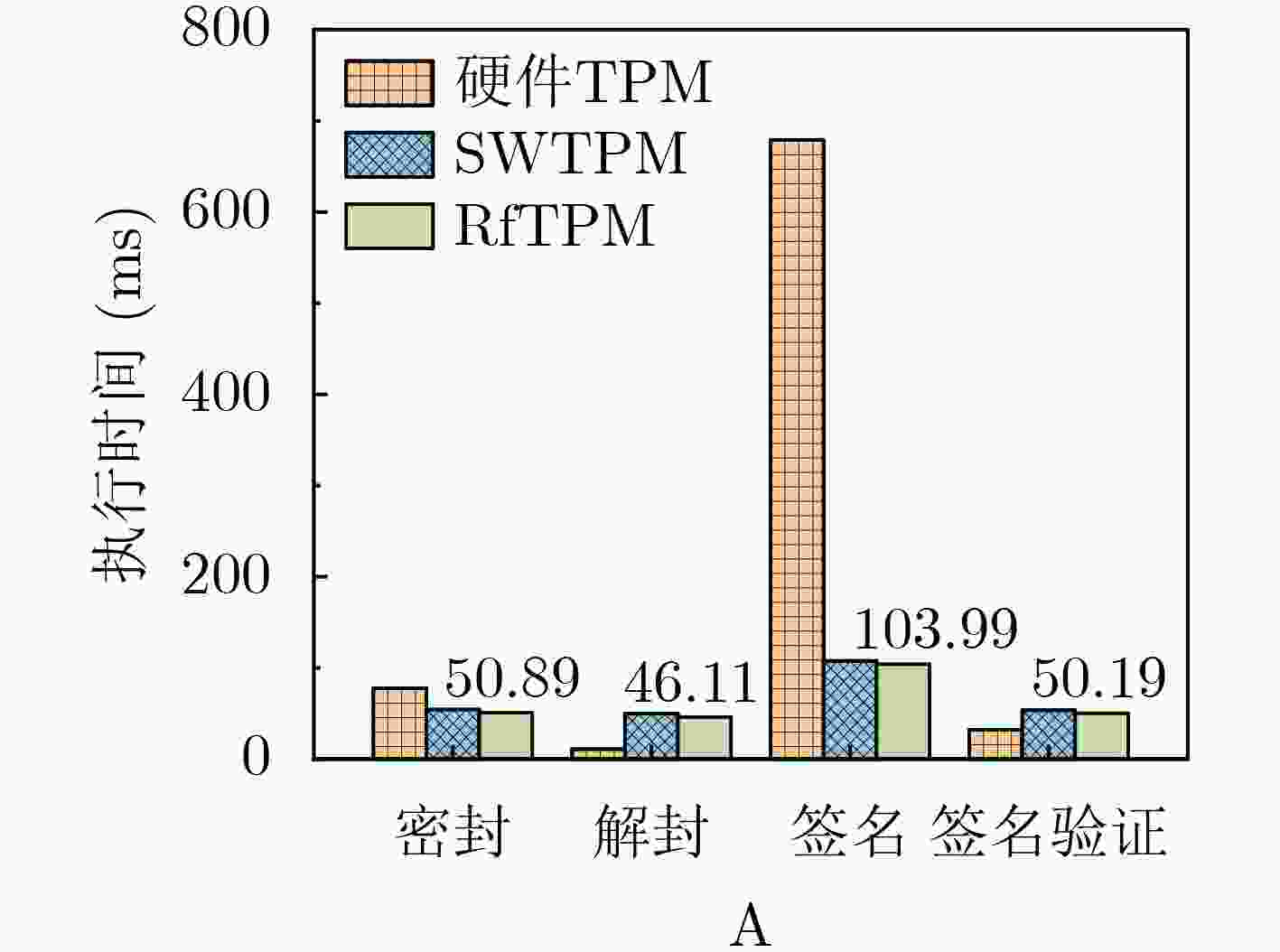
Objective The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a critical technology in modern secure computing systems, providing hardware-based key management, trusted boot, and remote attestation to safeguard sensitive operations in embedded and cloud environments. However, current RISC-V platforms lack native TPM support, presenting a security challenge as these systems are increasingly deployed in diverse application scenarios. To address this limitation, RfTPM—a firmware-based TPM (fTPM) architecture—has been developed to deliver the same security functionality as conventional hardware TPMs without requiring additional hardware components or specialized security extensions. This solution provides an immediate, cost-effective means to secure RISC-V systems while contributing to the advancement of trusted computing on emerging processor architectures. Methods The development of RfTPM incorporates several innovative techniques to overcome the challenges of implementing TPM functionalities in firmware. The design utilizes the RISC-V Physical Memory Protection (PMP) mechanism to enforce strict memory isolation, ensuring that fTPM code and data are inaccessible to unauthorized processes. A novel static data protection strategy is introduced, combining a DRAM-based Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) with Flash locking to secure the generation and storage of cryptographic root keys, preventing rollback attacks on persistent fTPM data. To secure the boot process, RfTPM employs a delay measurement extension mechanism, which divides the boot sequence into two phases: a verification phase where each boot stage is measured and authenticated before control is transferred, and a subsequent measurement phase that continuously validates system integrity according to TPM standards. The architecture also features a dynamic permission exchange page, enabling zero-copy communication across different privilege levels by dynamically configuring PMP permissions, reducing data transfer overhead. Additionally, a fine-grained secure clock is established using the native RISC-V hardware timer to counter timing-based attacks. The solution is prototyped as a secure extension module within OpenSBI, integrated with a dedicated kernel driver and an adapted TPM Software Stack (TSS), and evaluated on a Genesys2 FPGA board simulating a Rocket Core running Linux. Results and Discussions Comprehensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that RfTPM meets stringent security requirements while offering significant performance benefits over both traditional hardware TPMs and conventional software TPM implementations. In a benchmark involving 2048-bit RSA key generation ( Fig. 4 ), the hardware TPM required approximately 17.28 seconds to complete the operation, whereas the RfTPM implementation achieved the same task in just 2.18 seconds, representing a 7 times improvement. Further tests evaluating sealing, unsealing, signing, and verification commands (Fig. 5 ) reveal performance enhancements ranging from 3.7% to 8.2%, primarily due to the efficiency of the zero-copy communication mechanism. Additional evaluations of cryptographic operations show that RfTPM improved RSA encryption and decryption by 8.2% and 8.0%, respectively, and AES encryption and decryption by 9.1% and 9.2% (Fig. 6 ). Although the NVRAM startup process in RfTPM incurs minor overhead—measured at 5.28 milliseconds compared to 0.9 milliseconds for conventional software TPMs—this delay is negligible, as NVRAM initialization occurs only once during system boot and does not impact overall runtime performance. Memory footprint analysis further reveals that while conventional software TPMs may consume approximately 1 536 kB of physical memory, the combined footprint of the fTPM and OpenSBI firmware in RfTPM is only 956 kB, which can be reduced to 808 kB through compiler optimizations. These results collectively confirm that RfTPM not only provides robust defense against various security threats, including TOCTOU and rollback attacks, but also enhances operational efficiency, making it an optimal solution for secure computing on RISC-V platforms.Conclusions In summary, RfTPM represents the first comprehensive firmware-based TPM architecture specifically tailored for RISC-V platforms, effectively addressing critical challenges such as secure execution, trusted boot integrity, efficient inter-layer communication, and precise timekeeping without incurring additional hardware costs. By integrating advanced techniques—including PMP-based memory isolation, DRAM PUF-enhanced static data protection, a dual-phase boot process with delay measurement extension, dynamic permission exchange for zero-copy communication, and a hardware-based secure clock—RfTPM delivers robust security functionality that matches or exceeds that of traditional hardware TPMs. Experimental results confirm that RfTPM upholds rigorous security standards while offering substantial performance and resource utilization advantages over both hardware TPMs and existing software TPMs. The open-sourcing of core components further fosters community collaboration and provides a platform for future research focused on refining trusted computing solutions for emerging architectures like RISC-V. Future work may explore additional hardware optimizations, such as native AES instruction support, and further enhancements to file system performance to increase the efficiency and robustness of fTPM implementations. -
1 基于受保护 DRAM PUF 的密钥生成算法
输入:受保护的 DRAM 区域;重读次数repeat_count;位稳定
性的阈值threshold输出:生成的稳定密钥Key 1 Key ← $\varnothing $ 2 response_set ← $\varnothing $ 3 for i in range(0, repeat_count): 4 response ← $\varnothing $ 5 初始化受保护 DRAM 为全“0”或全“1” 6 读取受保护 DRAM 状态并记录为 response 7 response_set.add(response) 8 end for 9 bit_statistics ← 统计每个位在 response_set 中为“1”的频率 10 for idx in bit_statistics: 11 if bit_statistics[idx] ≥ threshold: 12 Key.add(1) 13 else: 14 Key.add(0) 15 end if 16 end for 17 return Key -
[1] CHALLENER D, YODER K, CATHERMAN R, et al. A Practical Guide to Trusted Computing[M]. Upper Saddle River: IBM Press, 2007. [2] 张焕国, 罗捷, 金刚, 等. 可信计算研究进展[J]. 武汉大学学报: 理学版, 2006, 52(5): 513–518. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8836.2006.05.001.ZHANG Huanguo, LUO Jie, JIN Gang, et al. Development of trusted computing research[J]. Journal of Wuhan University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 52(5): 513–518. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8836.2006.05.001. [3] 沈昌祥, 张焕国, 王怀民, 等. 可信计算的研究与发展[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2010, 40(2): 139–166. doi: 10.1360/zf2010-40-2-139.SHEN Changxiang, ZHANG Huanguo, WANG Huaimin, et al. Research on trusted computing and its development[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2010, 53(3): 405–433. doi: 10.1007/s11432-010-0069-x. [4] 张焕国, 李晶, 潘丹铃, 等. 嵌入式系统可信平台模块研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2011, 48(7): 1269–1278.ZHANG Huanguo, LI Jing, PAN Danling, et al. Trusted platform module in embedded system[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2011, 48(7): 1269–1278. [5] ARTHUR W, CHALLENER D, and GOLDMAN K. A Practical Guide to TPM 2.0: Using the Trusted Platform Module in the New Age of Security[M]. Berkeley: Springer, 2015. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4302-6584-9. [6] SVENDA P, DUFKA A, BROZ M, et al. TPMScan: A wide-scale study of security-relevant properties of TPM 2.0 chips[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2024, 2024(2): 714–734. doi: 10.46586/tches.v2024.i2.714-734. [7] RAJ H, SAROIU S, WOLMAN A, et al. fTPM: A software-only implementation of a TPM chip[C]. 25th USENIX Security Symposium, Washington, USA, 2016: 841–856. [8] Intel Corporation. Intel® coreTM processors[EB/OL]. https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000094205/processors/intel-core-processors.html, 2024. [9] JACOB H N, WERLING C, BUHREN R, et al. faulTPM: Exposing AMD fTPMs’ Deepest Secrets[C]. 2023 IEEE 8th European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Delft, Netherlands, 2023: 1128–1142. doi: 10.1109/EuroSP57164.2023.00069. [10] COSTAN V and DEVADAS S. Intel SGX explained[EB/OL]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/086, 2016. [11] AMD. AMD SEV-SNP: Strengthening VM isolation with integrity protection and more[R]. 2020: 1450–1465. [12] CUI Enfang, LI Tianzheng, and WEI Qian. RISC-V instruction set architecture extensions: A survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 24696–24711. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3246491. [13] LI Tianzheng, CUI Enfang, WU Yuting, et al. TeleVM: A lightweight virtual machine for RISC-V architecture[J]. IEEE Computer Architecture Letters, 2024, 23(1): 121–124. doi: 10.1109/LCA.2024.3394835. [14] KIM J S, PATEL M, HASSAN H, et al. The DRAM latency PUF: Quickly evaluating physical unclonable functions by exploiting the latency-reliability tradeoff in modern commodity DRAM devices[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Vienna, Austria, 2018: 194–207. doi: 10.1109/HPCA.2018.00026. [15] TEHRANIPOOR F, KARIMIAN N, XIAO Kan, et al. DRAM based intrinsic physical unclonable functions for system level security[C]. Proceedings of the 25th edition on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, Pittsburgh, USA, 2015: 15–20. doi: 10.1145/2742060.2742069. [16] RISC-V Software Source. OpenSBI: RISC-V open source supervisor binary interface[EB/OL]. https://github.com/riscv-software-src/opensbi, 2024. [17] Chipsalliance. Rocket chip generator[EB/OL]. https://github.com/chipsalliance/rocket-chip, 2024. [18] Kgoldman. IBM software TPM 2.0[EB/OL]. https://github.com/kgoldman/ibmswtpm2, 2024. [19] WANG Juan, WANG Jie, FAN Chengyang, et al. SvTPM: SGX-based virtual trusted platform modules for cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2023, 11(3): 2936–2953. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2023.3243891. [20] NARAYANAN V, CARVALHO C, RUOCCO A, et al. Remote attestation of confidential VMs using ephemeral vTPMs[C]. The 39th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Austin, USA, 2023: 732–743. doi: 10.1145/3627106.3627112. [21] WU Jiangxing. Cyberspace endogenous security and safety problems[M]. WU Jiangxing. Cyber Resilience System Engineering Empowered by Endogenous Security and Safety. Singapore: Springer, 2024: 1–73. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-0116-2_1. [22] CHEN Hongsong, HAN Xintong, and ZHANG Yiying. Endogenous security formal definition, innovation mechanisms, and experiment research in industrial Internet[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2024, 29(2): 492–505. doi: 10.26599/TST.2023.9010034. [23] GUO Jinnan, PIETZUCH P, PAVERD A, et al. Trustworthy AI using confidential federated learning[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2024, 67(9): 48–53. doi: 10.1145/3677390. [24] CHEN Hongsong, TAO Zimei, WANG Zhiheng, et al. Merkle multi-branch hash tree-based dynamic data integrity auditing for B5G network cloud storage[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2025, 89: 103981. doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2025.103981. [25] FRITZMANN T, SIGL G, and SEPÚLVEDA J. RISQ-V: Tightly coupled RISC-V accelerators for post-quantum cryptography[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2020, 2020(4): 239–280. doi: 10.13154/tches.v2020.i4.239-280. [26] DE CASTELNAU J. Software optimization for a RISC-V accelerator: A case study[EB/OL]. https://infoscience.epfl.ch/server/api/core/bitstreams/472275ca-4a0a-4f5b-831d-1082a77f98f2/content, 2024. [27] SCHIAVONE P D, CONTI F, ROSSI D, et al. Slow and steady wins the race? A comparison of ultra-low-power RISC-V cores for internet-of-things applications[C]. 2017 27th International Symposium on Power and Timing Modeling, Optimization and Simulation (PATMOS), Thessaloniki, Greece, 2017: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/PATMOS.2017.8106976. [28] LEE D, KOHLBRENNER D, SHINDE S, et al. Keystone: An open framework for architecting trusted execution environments[C]. The Fifteenth European Conference on Computer Systems, Heraklion, Greece, 2020: 38. doi: 10.1145/3342195.3387532. [29] LIU Chang, WU Yanjun, WU Jingzheng, et al. A buffer overflow detection and defense method based on RISC-V instruction set extension[J]. Cybersecurity, 2023, 6(1): 45. doi: 10.1186/s42400-023-00164-x. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
