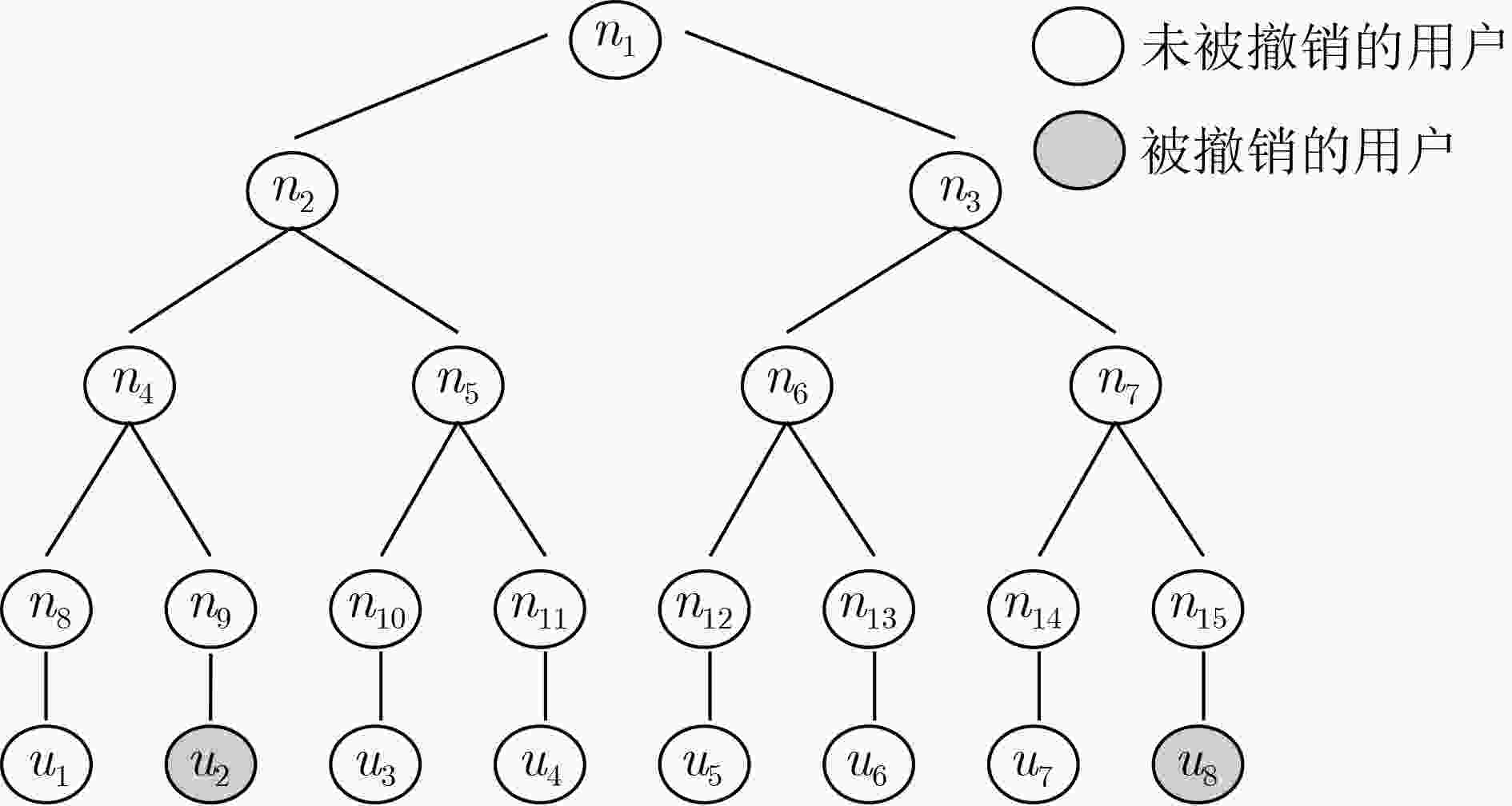
TTRC-ABE: Traitor Traceable and Revocable CLWE-based ABE Scheme from Lattices
-
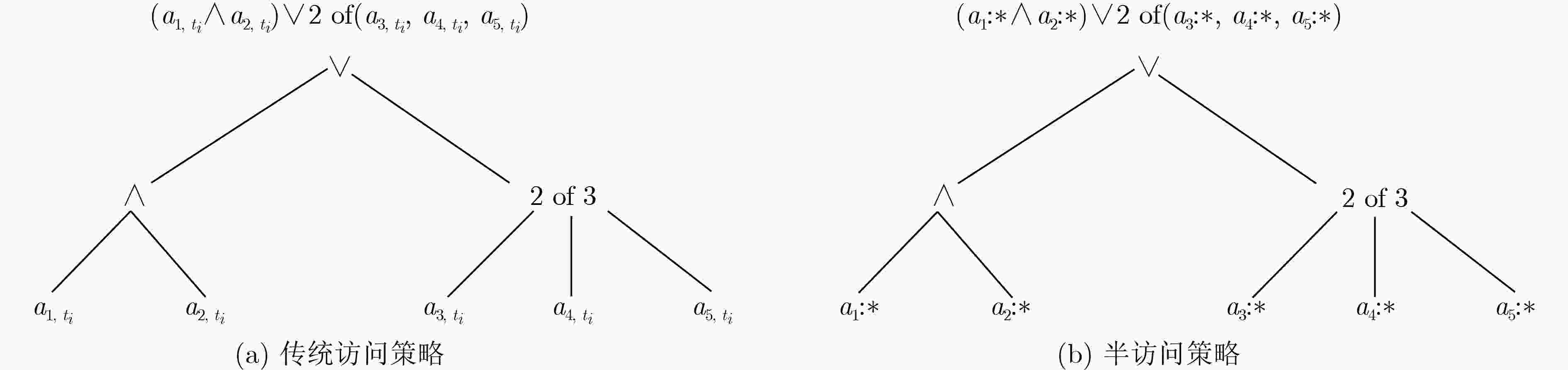
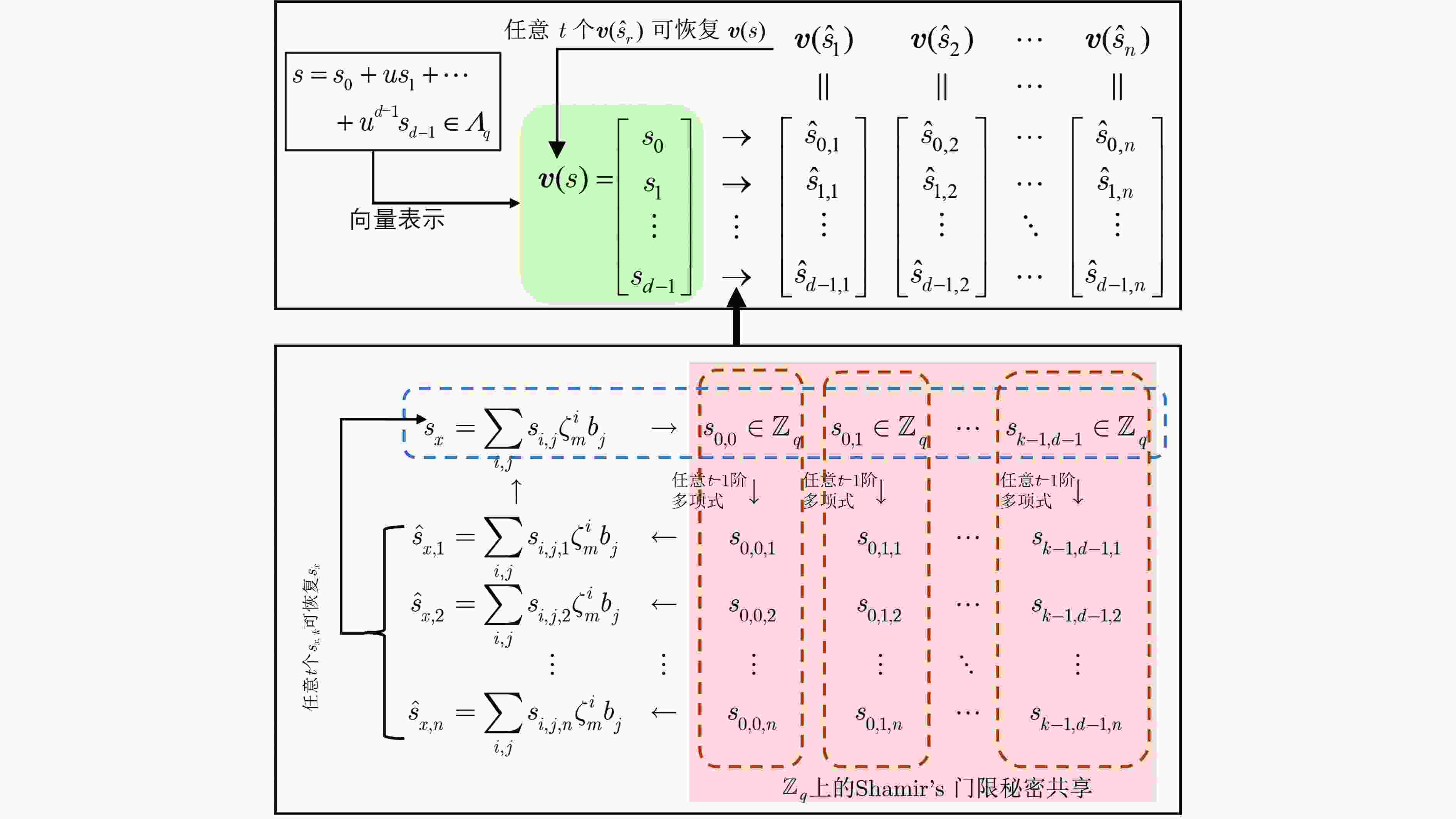
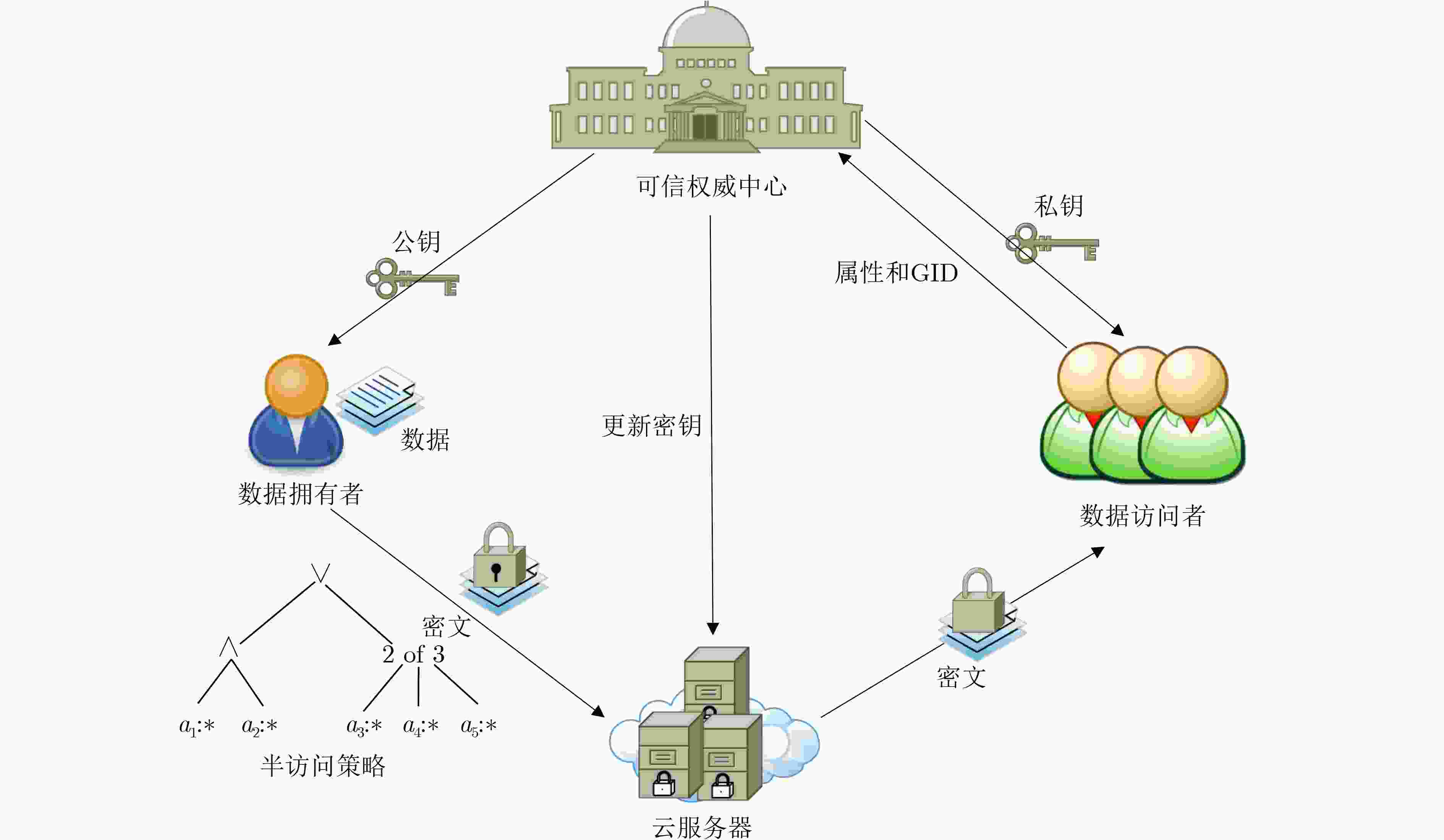
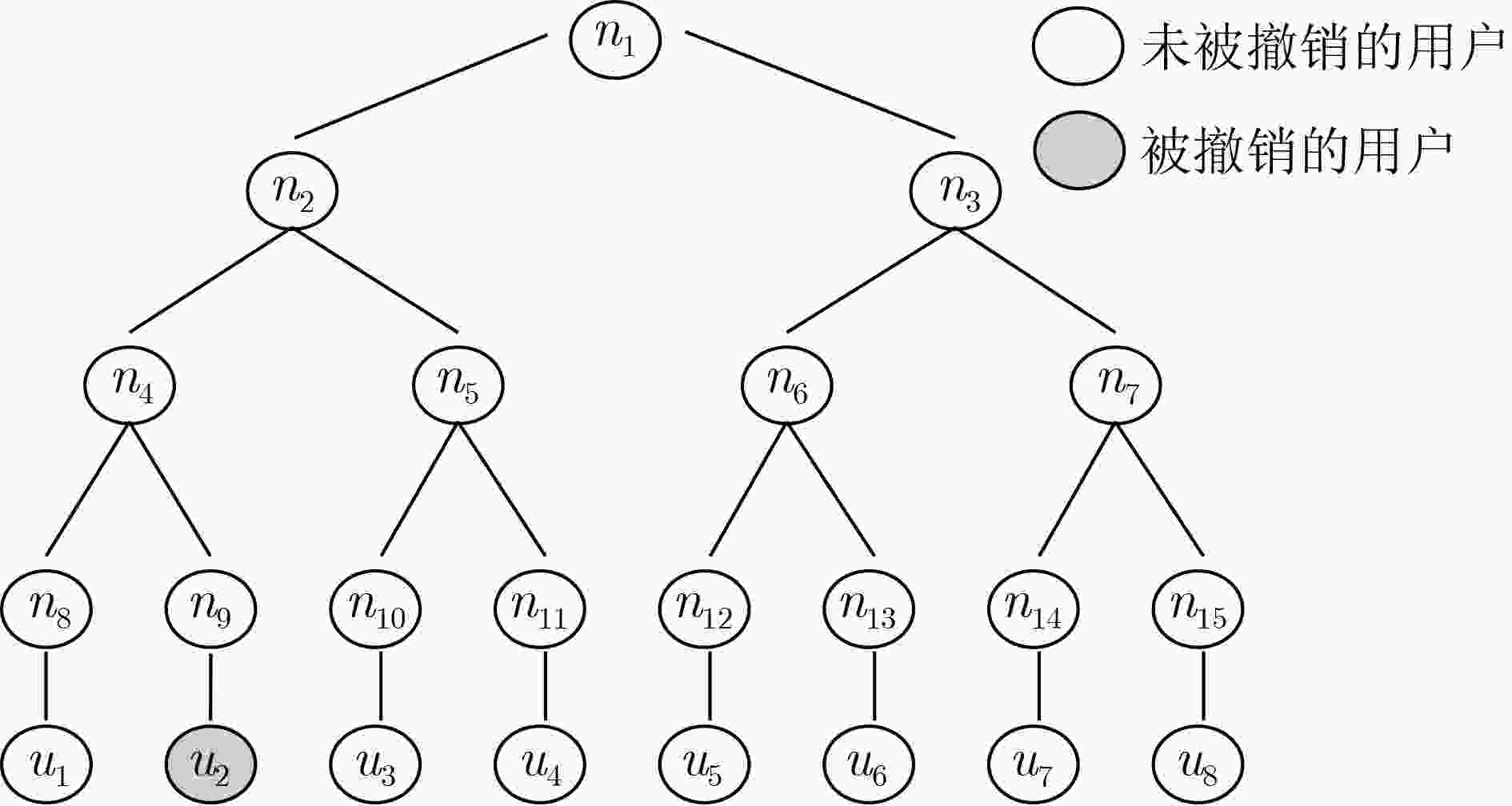
摘要: 格基属性加密方案兼具了格密码抵抗量子计算攻击的优势和属性基加密细粒度访问控制灵活授权的优势,是格密码研究的热点。已有的基于带误差学习问题/环上带误差学习问题(LWE/RLWE)的格基属性加密方案存在不支持叛逆者追踪与撤销的问题,即当解密密钥泄露时,无法准确确认用户的身份并及时撤销该叛逆用户,此外,访问策略中的属性可能会暴露敏感信息,需要对用户属性隐私进行保护。针对上述问题,该文基于2022 年国际密码学顶刊(JoC)上提出的循环代数LWE(CLWE)问题,提出一种支持叛逆用户追踪与撤销,并同时保护属性隐私的格基属性加密方案。该方案通过将用户唯一身份信息全局标识(GID)与完全二叉树的叶子节点值绑定,并根据解密密钥中的GID跟踪恶意用户,进而通过更新撤销列表和密文,实现叛逆者的追踪和撤销;另外,通过利用2维(属性标签,属性值)属性结构代替传统的1维(属性值)属性结构,并结合半访问策略结构和循环代数上的扩展型Shamir门限秘密共享方案,对用户的属性值进行隐藏,进而防止用户属性隐私泄露;最后,该方案在标准模型中被证明是安全的。性能分析表明,与其他相关格基属性加密方案相比,该方案的系统公钥尺寸、密文尺寸、平均意义下的密文膨胀率较小,且支持叛逆者的追踪撤销和属性隐私保护。
-
关键词:
- 循环代数带误差学习问题 /
- 属性基加密 /
- 叛逆者追踪 /
- 叛逆者撤销 /
- 隐私保护
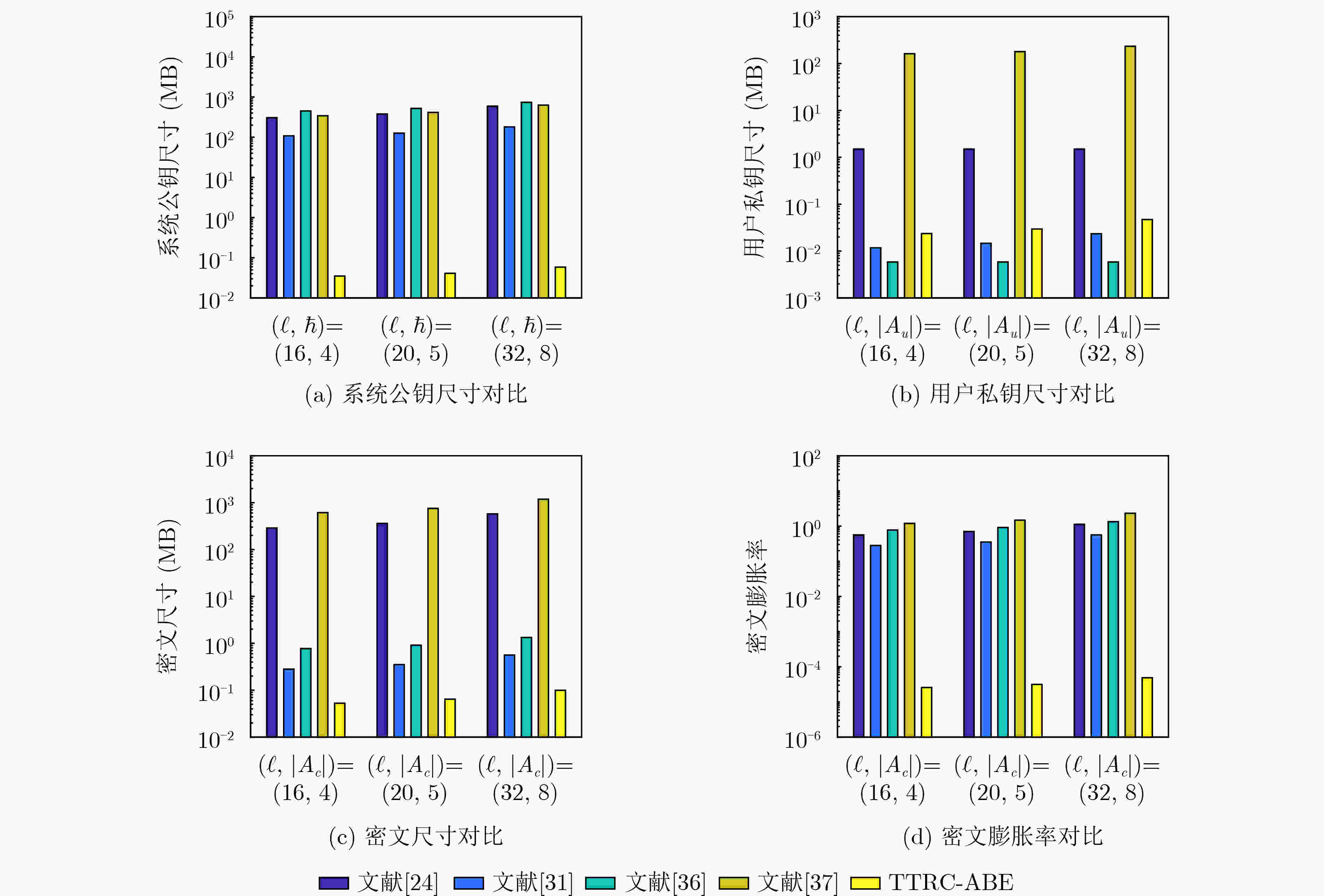
Abstract:Objective With the advancement of quantum computing, lattice-based cryptography has emerged as a key approach for constructing post-quantum secure cryptographic primitives due to its inherent resistance to quantum attacks. Among these primitives, lattice-based Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) is particularly notable for its ability to provide fine-grained access control and flexible authorization, making it suitable for data-sharing applications, such as cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT). However, existing lattice-based ABE schemes, especially those based on Learning With Errors (LWE) or Ring-LWE (RLWE), exhibit limitations that hinder their practical deployment. A significant issue is the absence of traitor tracing and revocation mechanisms, which leaves these schemes vulnerable to key abuse, where malicious users can share decryption keys without detection or prevention. Furthermore, the exposure of attribute values in access policies creates a privacy risk, as sensitive user information may be inferred from these values. These limitations undermine the security and privacy of lattice-based ABE systems, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios where accountability and privacy are critical. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel Traitor Traceable and Revocable CLWE-based ABE (TTRC-ABE) scheme, which employs a new variant of LWE called Cyclic Algebra LWE (CLWE). The proposed scheme aims to achieve three key objectives: (1) to introduce an efficient traitor tracing mechanism to identify malicious users and a revocation mechanism to prevent revoked users from decrypting messages; (2) to enhance attribute privacy by concealing attribute values in access policies; and (3) to improve the efficiency of lattice-based ABE schemes, specifically in terms of public key size, ciphertext size, and ciphertext expansion rate. By addressing these critical issues, TTRC-ABE contributes to the advancement of lattice-based cryptography and provides a viable solution for secure, privacy-preserving data sharing in quantum-vulnerable environments. Methods In the TTRC-ABE scheme, each user’s Global IDentity (GID) is bound to the leaf nodes of a complete binary tree. This binding enables the tracing of malicious users by identifying their GIDs embedded in decryption keys. To revoke compromised users, their GIDs are added to a revocation list, and the ciphertext is updated accordingly, ensuring that any revoked user cannot decrypt the message, even if they possess a valid decryption key. Additionally, the traditional one-dimensional attribute structure (attribute value only) is replaced with a two-dimensional structure (attribute label, attribute value). The attribute labels act as public identifiers, while the attribute values remain confidential. This separation allows for the concealment of sensitive attribute values while still enabling effective access control. A semi-access policy structure is combined with an extended Shamir’s secret sharing scheme over cyclic algebra to conceal attribute values in access policies, preventing adversaries from inferring sensitive user information. Furthermore, the proposed scheme utilizes CLWE, a new variant of LWE that offers improved efficiency and security properties. A formal security proof for TTRC-ABE is provided in the standard model. The security of the scheme relies on the hardness of the CLWE problem, which is believed to be resistant to quantum computing attacks. Results and Discussions The proposed TTRC-ABE scheme demonstrates significant improvements over existing lattice-based ABE schemes in terms of functionality, security, and efficiency. The scheme successfully integrates traitor tracing and revocation features, effectively preventing key abuse by identifying malicious users and revoking their access to encrypted data. By adopting a two-dimensional attribute structure and a semi-access policy, the scheme conceals attribute values in access policies, ensuring that sensitive user information remains confidential, even when the access policy is publicly accessible. Performance analysis shows that TTRC-ABE supports traitor tracing and revocation, protects attribute privacy, and is resistant to quantum computing attacks ( Table 2 ). Compared to related lattice-based ABE schemes, TTRC-ABE significantly reduces the public key size, ciphertext size, and average ciphertext expansion rate (Table 3 ,Figure 7 ). These improvements enhance the practicality of the scheme for real-world applications, especially in resource-constrained environments.Conclusions This paper presents a novel TTRC-ABE scheme that addresses the limitations of existing lattice-based ABE schemes. By integrating traitor tracing and revocation mechanisms, the scheme effectively prevents key abuse and ensures system integrity. The introduction of a two-dimensional attribute structure and a semi-access policy enhances attribute privacy, safeguarding sensitive user information from leakage. Furthermore, the use of CLWE improves the scheme’s efficiency, reducing public key size, ciphertext size, and ciphertext expansion rate. Security analysis confirms that TTRC-ABE is secure in the standard model, making it a robust solution for post-quantum secure ABE. Future work will focus on extending the scheme to support more complex access policies, such as hierarchical and multi-authority structures, and optimizing its performance for large-scale applications. Additionally, the integration of TTRC-ABE with other cryptographic primitives, such as homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation, will be explored to enable more advanced data-sharing scenarios. -
表 1 符号说明
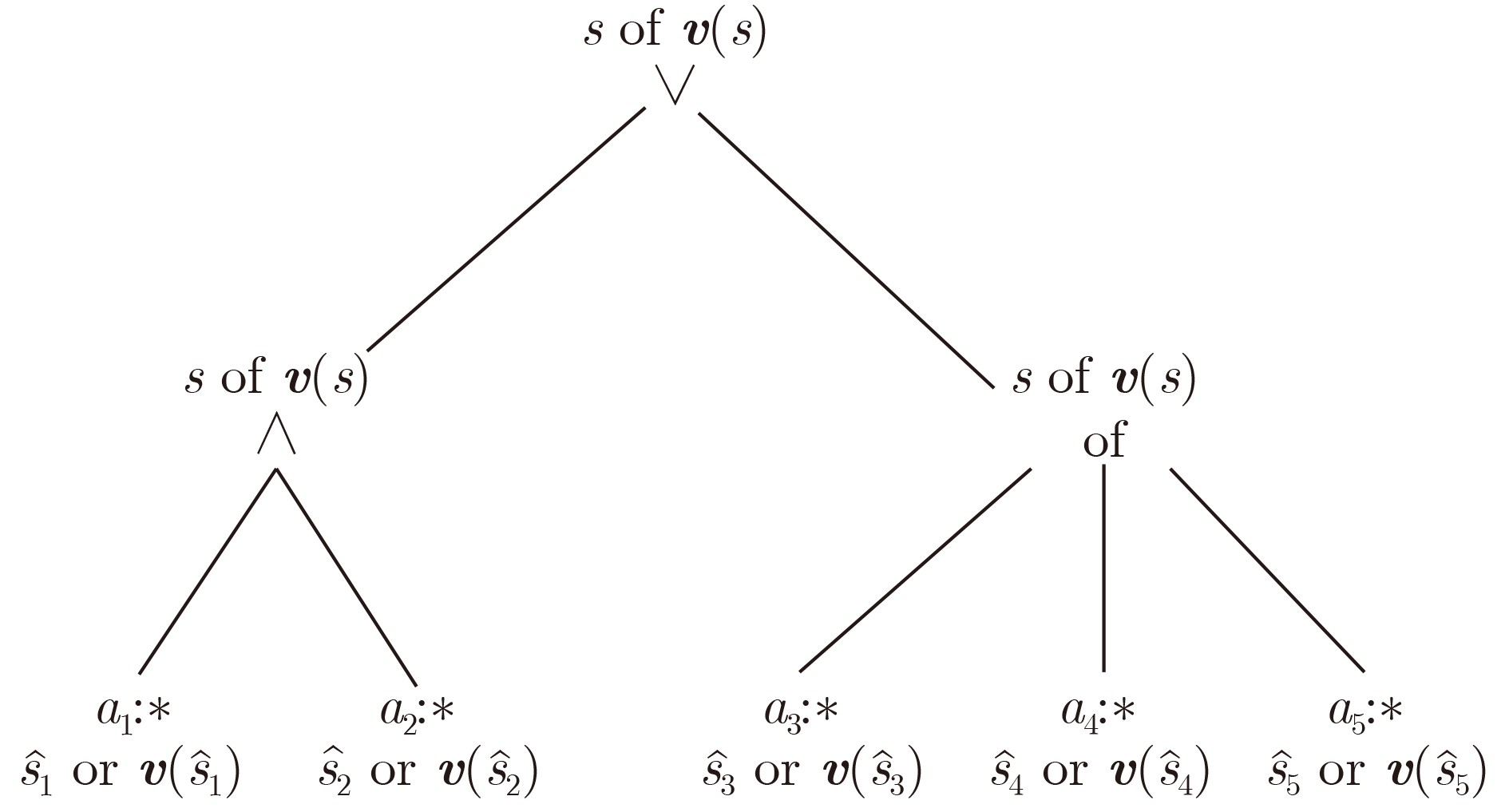
符号 描述 $K = \mathbb{Q}({\zeta _m})$ 分圆域 $L/K$ K的伽罗瓦扩张 $\mathcal{C} = (L/K,\theta ,\gamma ) = \oplus _{i = 0}^{d - 1}{u^i}L$ 循环代数 ${(\zeta _m^i)_{i \in \{ 0,\varphi (m) - 1\} }}$ K的$\mathbb{Q}$基 ${({b_j})_{j \in \{ 0,d - 1\} }}$ L的K基 ${\mathcal{O}_K} = \mathbb{Z}({\zeta _m})$ K的整数环 ${\mathcal{O}_L} = \mathbb{Z}({b_j},{\zeta _m})$ L的整数环 ${\mathcal{O}_{L,q}} = {\mathcal{O}_L}/q{\mathcal{O}_L} = \mathbb{Z}({b_j},{\zeta _m})/q\mathbb{Z}({b_j},{\zeta _m})$ ${\mathcal{O}_L}$的商环 $\varLambda : = \oplus _{i = 0}^{d - 1}{u^i}{\mathcal{O}_L}$ 循环代数的整数阶 ${\varLambda _q}: = \oplus _{i = 0}^{d - 1}{u^i}{\mathcal{O}_{L,q}}$ $\varLambda $的商环 $ a \in \mathcal{C} $, ${\boldsymbol{v}}(a)$ a的向量表示 $ a \in \mathcal{C} $, $ {\boldsymbol{F}}(a) $ a的矩阵表示 表 2 TTRC-ABE方案与相关ABE方案的功能对比
表 3 TTRC-ABE方案与相关格基ABE方案的存储开销对比
方案 系统公钥尺寸 用户私钥尺寸 密文尺寸 明文 密文膨胀率 困难
问题[24] $ \text{(}\ell + 1)nm{\mathrm{log}}_{2}q + n{\mathrm{log}}_{2}q $ $ 2mn $ $ \ell mn{\log _2}q + n{\log _2}q $ n $ \ell m{\log _2}q + {\log _2}q $ RLWE [31] $(\hbar + 2)nm{\log _2}q + n{\log _2}q$ $2m|{A_u}|$ $2|{A_c}|m{\log _2}q + {\log _2}q$ 1 $2|{A_c}|m{\log _2}q + {\log _2}q$ LWE [36] $ (\ell + 2|U| - 1)nm{\log _2}q $ $4mk,(k = \omega (\log \lambda ))$ $(\ell + |U| + 1)m{\log _2}q + k{\log _2}q$ 1 $(\ell + |U| + 1)m{\log _2}q + k{\log _2}q$ LWE [37] $(\ell + 3|{N_{\rm{AA}}}|)nm{\log _2}q$ $ (|{A_u}| + \log |U| + 3|{N_{\rm{AA}}}|)nm{\log _2}q $ $ (2\ell + 2|{N_{\rm{AA}}}|)mn{\log _2}q $ n $ (2\ell + 2|{N_{\rm{AA}}}|)m{\log _2}q $ RLWE TTRC-ABE $(\hbar + 2)nd{\log _2}q$ $|{A_u}|nd{\log _2}q + nd$ $2|{A_c}|nd{\log _2}q + nd{\log _2}q$ nd $2|{A_c}|{\log _2}q + {\log _2}q$ CLWE $\ell $:系统属性总数;$\hbar $:本方案和文献[31]中系统属性标签的最大数目;d:伽罗瓦扩张的次数,根据文献[40],d=2,3,4即可。
$ |{A_u}| $:用户属性个数;$ |{A_c}| $:密文中属性个数;$ |{A_u}| \le \hbar \lt \ell $, $ |{A_c}| \le \hbar \lt \ell $。
密文膨胀率:密文尺寸/明文尺寸。
$|U|$:系统中用户总数,$|{N_{\rm{AA}}}|$:系统属性机构总数,文献[37]是支持多属性机构的,对比时可将机构数设为1。 -
[1] SAHAI A and WATERS B. Fuzzy identity-based encryption[C]. The 24th Annual International Conference on Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Aarhus, Denmark, 2005: 457–473. doi: 10.1007/11426639_27. [2] REGEV O. On lattices, learning with errors, random linear codes, and cryptography[C]. The 37th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Baltimore, USA, 2005: 84–93. doi: 10.1145/1060590.1060603. [3] LYUBASHEVSKY V, PEIKERT C, and REGEV O. On ideal lattices and learning with errors over rings[C]. 29th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, French, Riviera, 2010: 1–23. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-13190-5_1. [4] ZHANG Ruoqing, HUI L, YU S, et al. A traceable outsourcing CP-ABE scheme with attribute revocation[C]. The 2017 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ICESS, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 363–370. doi: 10.1109/Trustcom/BigDataSE/ICESS.2017.259. [5] NING Jianting, CAO Zhenfu, DONG Xiaolei, et al. White-box traceable CP-ABE for cloud storage service: How to catch people leaking their access credentials effectively[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2018, 15(5): 883–897. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2016.2608343. [6] HAN Dezhi, PAN Nannan, and LI K C. A traceable and revocable ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption scheme based on privacy protection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(1): 316–327. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2020.2977646. [7] ZHAO Yang, LIU Zhaozhong, AN Jingmin, et al. A traceable and revocable attribute-based encryption scheme based on policy hiding in smart healthcare scenarios[C]. The 17th International Conference on Information Security Practice and Experience, Taipei, China, 2022: 624–639. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-21280-2_35. [8] HE Xu, LI Lixiang, and PENG Haipeng. An enhanced traceable CP-ABE scheme against various types of privilege leakage in cloud storage[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2023, 136: 102833. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2023.102833. [9] LIU Xiao, WEI Zhenyang, LI Gaoxiang, et al. An enhanced traceable access control scheme based on multi-authority CP-ABE for cloud-assisted e-health system[J]. Computer Networks, 2024, 254: 110766. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2024.110766. [10] ZHANG Jiang and ZHANG Zhenfeng. A ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption scheme without pairings[C]. The 7th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Beijing, China, 2011: 324–340. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-34704-7_23. [11] ZHANG Jiang, ZHANG Zhenfeng, and GE Aijun. Ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption from lattices[C]. The 7th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security, Seoul, Korea, 2012: 16–17. doi: 10.1145/2414456.2414464. [12] AGRAWAL S, BOYEN X, VAIKUNTANATHAN V, et al. Functional encryption for threshold functions (or fuzzy IBE) from lattices[C]. The 15th International Conference on Practice and Theory in Public Key Cryptography, Darmstadt, Germany, 2012: 280–297. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-30057-8_17. [13] BOYEN X. Attribute-based functional encryption on lattices[C]. The 10th Theory of Cryptography Conference on Theory of Cryptography, Tokyo, Japan, 2013: 122–142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-36594-2_8. [14] LIU Ximeng, MA Jiangeng, XIONG Jinbo, et al. Threshold attribute-based encryption with attribute hierarchy for lattices in the standard model[J]. IET Information Security, 2014, 8(4): 217–223. doi: 10.1049/iet-ifs.2013.0111. [15] GORBUNOV S, VAIKUNTANATHAN V, and WEE H. Attribute-based encryption for circuits[C]. The 45th Annual ACM symposium on Theory of Computing, Palo Alto, USA, 2013: 545–554. doi: 10.1145/2488608.2488677. [16] ZHAO Jian, GAO Haiying, and ZHANG Junqi. Attribute-based encryption for circuits on lattices[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2014, 19(5): 463–469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0214.2014.05.005. [17] BONEH D, GENTRY C, GORBUNOV S, et al. Fully key-homomorphic encryption, arithmetic circuit ABE and compact garbled circuit[C]. The 33rd Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014: 533–556. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55220-5_30. [18] ZHU Weiling, YU Jianping, WANG Ting, et al. Efficient attribute-based encryption from R-LWE[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2014, 23(4): 778–782. doi: 10.23919/CJE.2014.10851999. [19] GORBUNOV S and VINAYAGAMURTHY D. Riding on asymmetry: Efficient ABE for branching programs[C]. The 21st International Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Auckland, New Zealand, 2015: 550–574. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-48797-6_23. [20] 吴立强, 杨晓元, 韩益亮. 基于理想格的高效模糊身份加密方案[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(4): 775–782. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.00775.WU Liqiang, YANG Xiaoyuan, and HAN Yiliang. An efficient FIBE scheme based on ideal lattices[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(4): 775–782. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.00775. [21] ZHANG Guoyan, QIN Jing, and QAZI S. Multi-authority attribute-based encryption scheme from lattices[J]. Journal of Universal Computer Science, 2015, 21(3): 483–501. doi: 10.3217/jucs-021-03-0483. [22] BRAKERSKI Z and VAIKUNTANATHAN V. Circuit-ABE from LWE: Unbounded attributes and semi-adaptive security[C]. The 36th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 2016: 363–384. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-53015-3_13. [23] 孙泽栋, 祝跃飞, 顾纯祥, 等. 基于RLWE的密钥策略属性加密体制[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(S1): 125–131. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016258.SUN Zedong, ZHU Yuefei, GU Chunxiang, et al. RLWE-based key-policy ABE scheme[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(S1): 125–131. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016258. [24] DAI Wei, DORÖZ Y, POLYAKOV Y, et al. Implementation and evaluation of a lattice-based key-policy ABE scheme[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(5): 1169–1184. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2779427. [25] 闫玺玺, 刘媛, 李子臣, 等. 新的格上多机构属性基加密方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 811–817. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170628.YAN Xixi, LIU Yuan, LI Zichen, et al. New multi-authority attribute-based encryption scheme on lattices[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 811–817. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170628. [26] GÜR K D, POLYAKOV Y, ROHLOFF K, et al. Practical applications of improved Gaussian sampling for trapdoor lattices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2019, 68(4): 570–584. doi: 10.1109/TC.2018.2874479. [27] TSABARY R. Fully secure attribute-based encryption for t-CNF from LWE[C]. The 39th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 2019: 62–85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-26948-7_3. [28] WANG Geng, LIU Zhen, and GU Dawu. Ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption for circuits from LWE assumption[C]. The 21st International Conference on Information and Communications Security, Beijing, China, 2019: 278–396. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-41579-2_22. [29] LIU Yuan, WANG Licheng, LI Lixiang, et al. Secure and efficient multi-authority attribute-based encryption scheme from lattices[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 3665–3674. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2888850. [30] ARRAWAL S and YAMADA S. Optimal broadcast encryption from pairings and LWE[C]. The 39th Annual International Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Zagreb, Croatia, 2020: 13–43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-45721-1_2. [31] LIU Yuan, WANG Licheng, SHEN Xiaoying, et al. Space-efficient key-policy attribute-based encryption from lattices and two-dimensional attributes[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2020, 2020: 2345369. doi: 10.1155/2020/2345369. [32] ZHAO Siyu, JIANG Rui, and BHARGAVA B. RL-ABE: A revocable lattice attribute based encryption scheme based on R-LWE problem in cloud storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2022, 15(2): 1026–1035. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2020.2973256. [33] DATTA P, KOMARGODSKI I, and WATERS B. Decentralized multi-authority ABE for DNFs from LWE[C]. The 40th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Zagreb, Croatia, 2021: 177–209. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-77870-5_7. [34] WATERS B, WEE H, and WU D J. Multi-authority ABE from lattices without random oracles[C]. The 20th International Conference on Theory of Cryptography, Chicago, USA, 2022: 651–679. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-22318-1_23. [35] WEE H. Optimal broadcast encryption and CP-ABE from evasive lattice assumptions[C]. The 4lst Annual international Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Trondheim, Norway, 2022: 217–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-07085-3_8. [36] LUO Fucai, AL-KUWARI S, WANG Haiyan, et al. Revocable attribute-based encryption from standard lattices[J]. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 2023, 84: 103698. doi: 10.1016/j.csi.2022.103698. [37] HUANG Boxue, GAO Juntao, and LI Xuelian. Efficient lattice-based revocable attribute-based encryption against decryption key exposure for cloud file sharing[J]. Journal of Cloud Computing, 2023, 12(1): 37. doi: 10.1186/s13677-023-00414-w. [38] AGRAWAL S, KUMARI S, and YAMADA S. Attribute based encryption for Turing machines from lattices[C]. The 44th Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2024: 352–386. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-68382-4_11. [39] XIE Shuwei, ZHANG Leyou, WU Qing, et al. Flexibly expressive and revocable multi-authority KP-ABE scheme from RLWE for internet of medical things[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2024, 152: 103179. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2024.103179. [40] GROVER C, MENDELSOHN A, LING C, et al. Non-commutative ring learning with errors from cyclic algebras[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2022, 35(3): 22. doi: 10.1007/s00145-022-09430-6. [41] MENDELSOHN A and LING Cong. Fractional non-norm elements for division algebras, and an application to cyclic learning with errors[J]. Advances in Mathematics of Communications, 2024, 18(2): 410–424. doi: 10.3934/amc.2023043. [42] LANGLOIS A and STEHLÉ D. Worst-case to average-case reductions for module lattices[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2015, 75(3): 565–599. doi: 10.1007/s10623-014-9938-4. [43] ZHAO Puning and LAI Lifeng. Minimax optimal Q learning with nearest neighbors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2025, 71(2): 1300–1322. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2024.3522347. [44] ZHANG Pengfei, CHENG Xiang, SU Sen, et al. Effective truth discovery under local differential privacy by leveraging noise-aware probabilistic estimation and fusion[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 261: 110213. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.110213. [45] FENG Jun, WU Yefan, SUN Hong, et al. Panther: Practical secure two-party neural network inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025, 20: 1149–1162. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2025.3526063. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
