Texture-Enhanced Infrared-Visible Image Fusion Approach Driven by Denoising Diffusion Model
-
摘要: 针对现有融合算法在处理多源数据时未能充分结合纹理细节和色彩强度信息的问题,该文提出一种去噪扩散模型驱动的红外-可见光图像融合方法。所提方法通过去噪扩散网络提取多尺度空时特征,并结合高频特征增强红外图像边缘信息,利用双向多尺度卷积模块和双向注意力融合模块确保全局信息的充分利用和局部细节的精确捕捉。同时,模型采用自适应结构相似性损失、多通道强度损失和多通道纹理损失对网络进行优化,增强结构一致性,平衡图像色彩和纹理信息的分布。实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,所提方法可有效地保留源图像的纹理、色彩和特征信息,融合效果更符合人类视觉感知。Abstract:
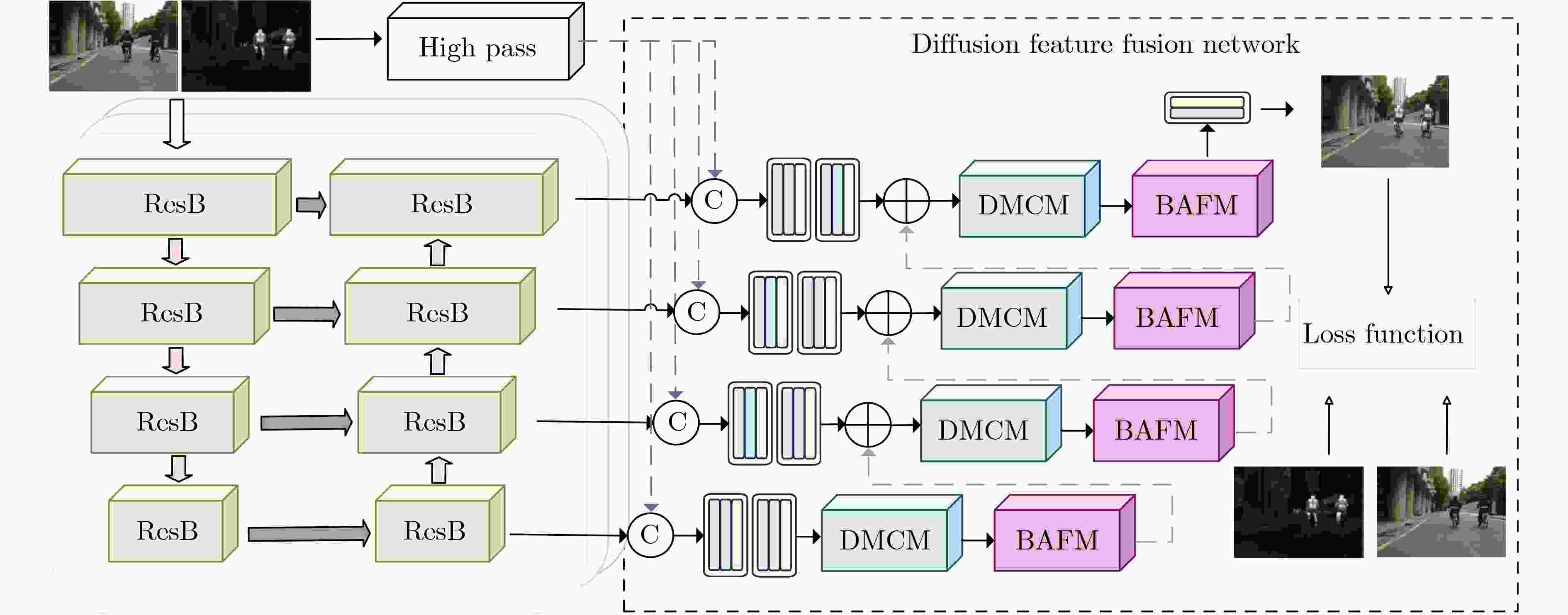
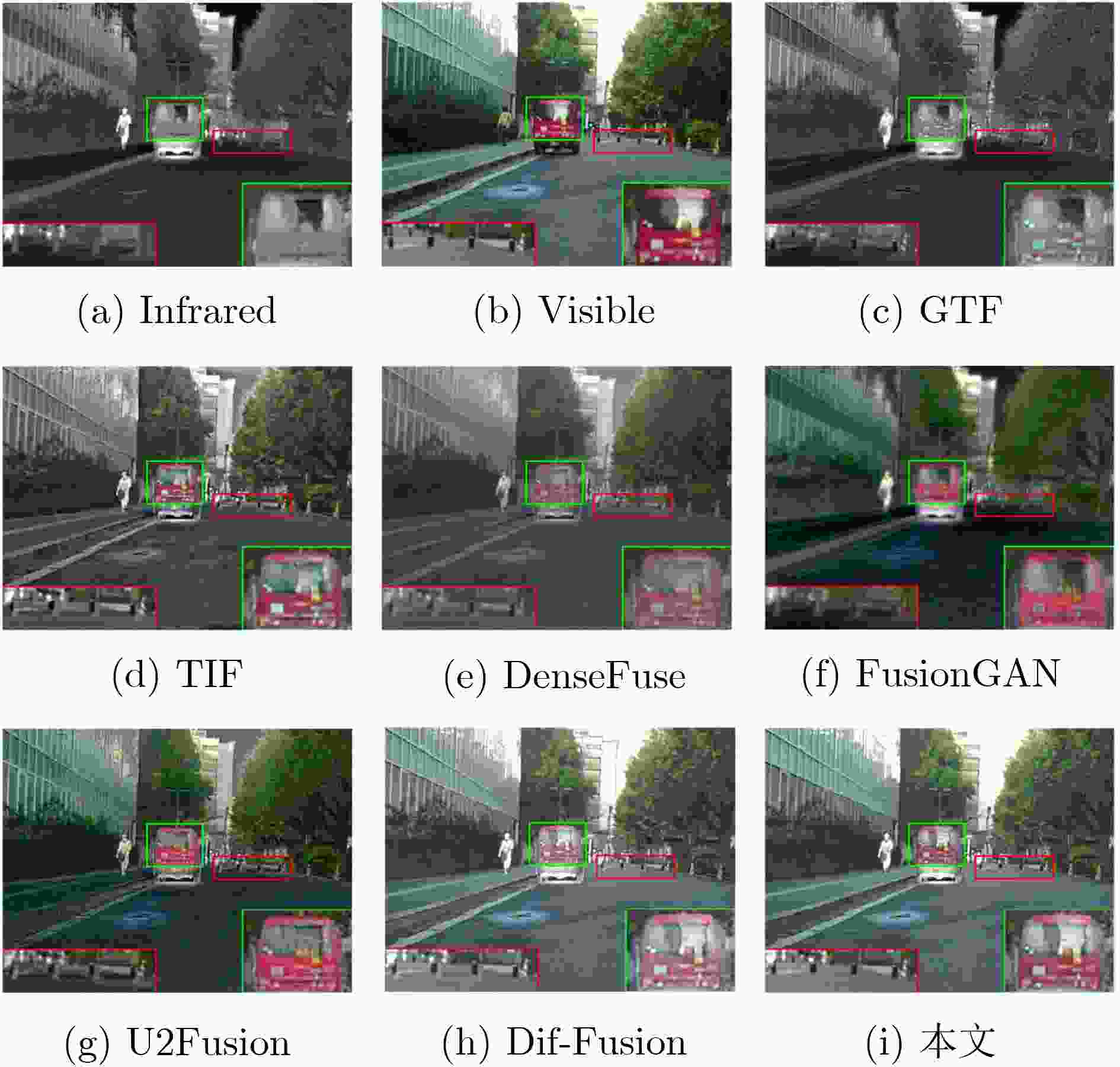
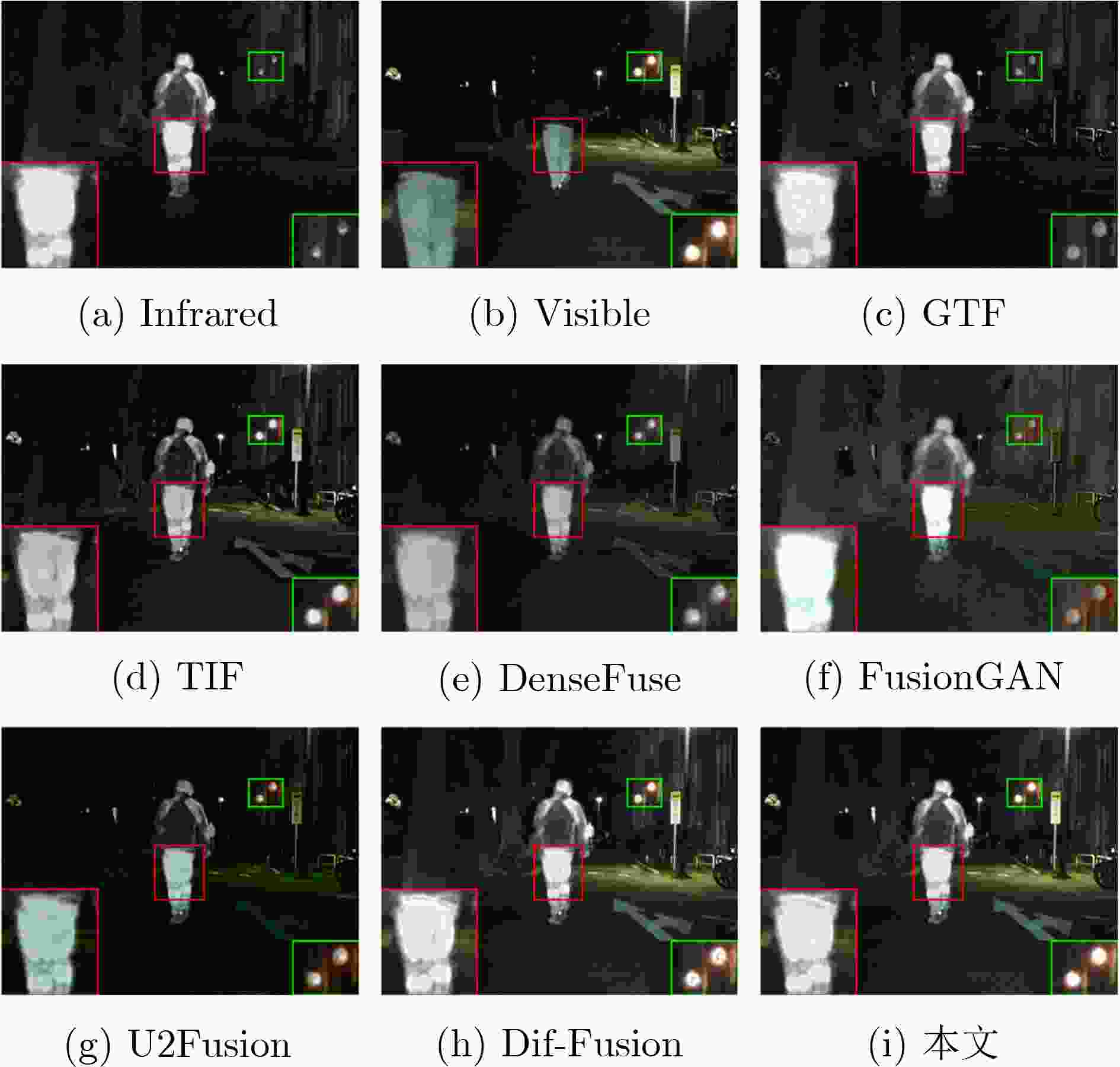
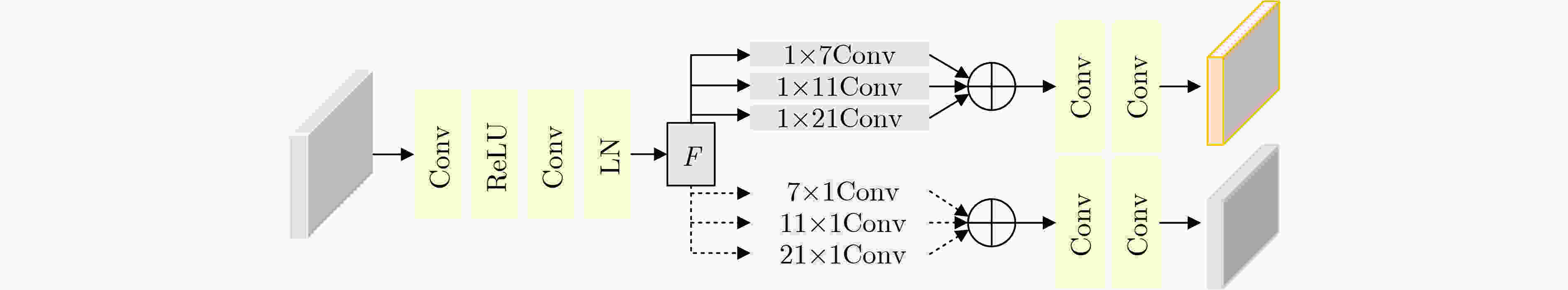
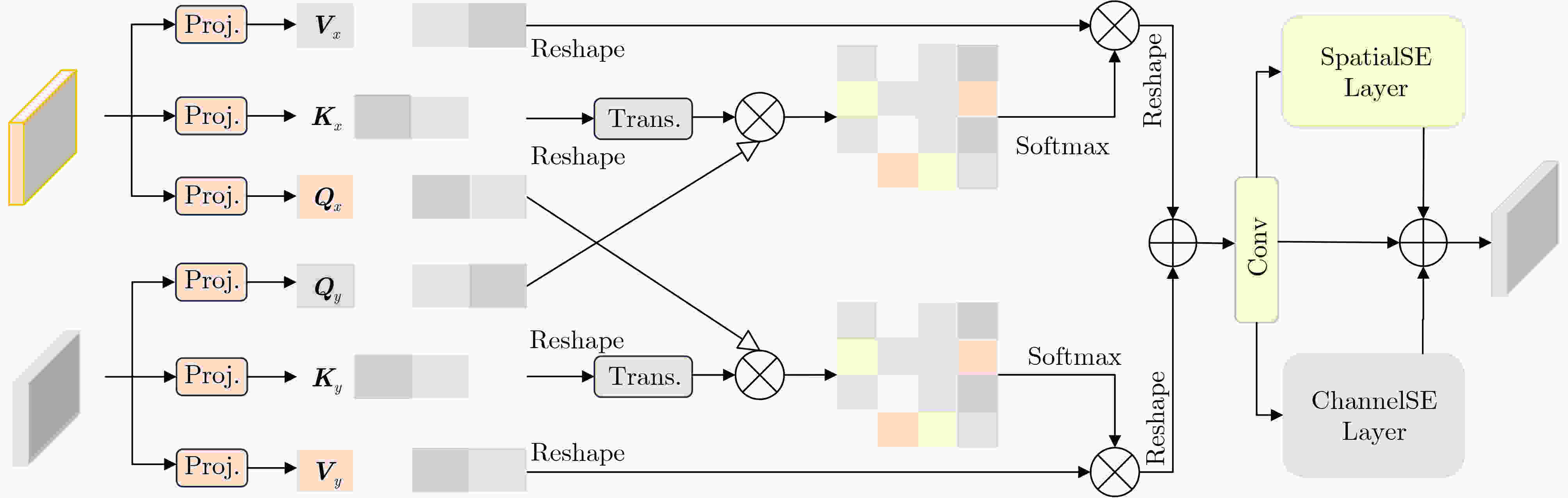
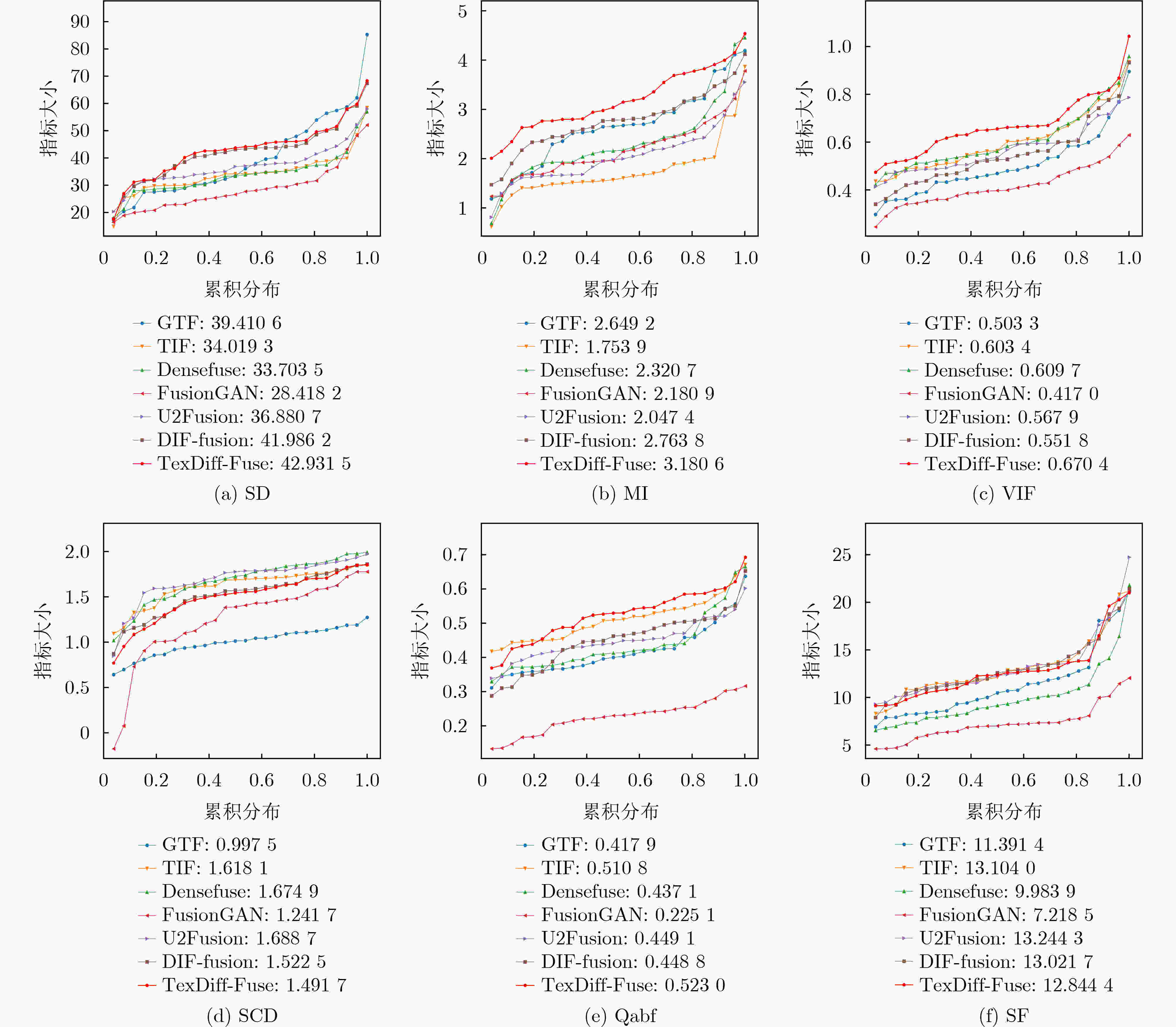
Objective The growing demand for high-quality fusion of infrared and visible images in various applications has highlighted the limitations of existing methods, which often fail to preserve texture details or introduce artifacts that degrade structural integrity and color fidelity. To address these challenges, this study proposes a fusion method based on a denoising diffusion model. The approach employs a multi-scale spatiotemporal feature extraction and fusion strategy to improve structural consistency, texture sharpness, and color balance in the fused image. The resulting fusion images better align with human visual perception and demonstrate enhanced reliability in practical applications. Methods The proposed method integrates a denoising diffusion model to extract multi-scale spatiotemporal features from infrared and visible images, enabling the capture of fine-grained structural and textural information. To improve edge preservation and reduce blurring, a high-frequency texture enhancement module based on convolution operations is employed to strengthen edge representation. A Dual-directional Multi-scale Convolution Module (DMCM) extracts hierarchical features across multiple scales, while a Bidirectional Attention Fusion Module dynamically emphasizes key global information to improve the completeness of feature representation. The fusion process is optimized using a hybrid loss function that combines adaptive structural similarity loss, multi-channel intensity loss, and multi-channel texture loss. This combination improves color consistency, structural fidelity, and the retention of high-frequency details. Results and Discussions Experiments conducted on the Multi-Spectral Road Scenarios (MSRS) and TNO datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization capacity of the proposed method. In daytime scenes ( Fig. 4 ,Fig. 5 ), the method reduces edge distortion and corrects color saturation imbalance, producing sharper edges and more balanced brightness in high-contrast regions such as vehicles and road obstacles. In nighttime scenes (Fig. 6 ), it maintains the saliency of thermal targets and smooth color transitions, avoiding spectral artifacts typically introduced by simple feature fusion. Generalization tests on the TNO dataset (Fig. 7 ) confirm the robustness of the approach. In contrast to the overlapping light source artifacts observed in Dif-Fusion, the proposed method enhances thermal targets while preserving background details. Quantitative evaluation (Table 1 ,Fig. 8 ) shows improved contrast, structural fidelity, and edge preservation.Conclusions This study presents a texture-enhanced infrared–visible image fusion method driven by a denoising diffusion model. By integrating multi-scale spatiotemporal feature extraction, feature fusion, and hybrid loss optimization, the method demonstrates clear advantages in texture preservation, color consistency, and edge sharpness. Experimental results across multiple datasets confirm the fusion quality and generalization capability of the proposed approach. -
表 1 基于MSRS数据集300对图像的融合质量评价
方法 SD MI VIF SCD Qabf SF GTF 18.4947 2.1282 0.5191 0.6865 0.3383 7.2040 TIF 30.1340 1.9763 0.8091 1.3975 0.5869 10.3184 Densefuse 23.1090 2.5867 0.6943 0.2424 0.3638 5.7283 FusionGAN 19.8945 1.9037 0.4705 1.0486 0.1638 4.7341 U2Fusion 21.4602 1.9208 0.5300 1.1730 0.3566 7.3220 Dif-Fusion 40.1729 3.2441 0.8375 1.6182 0.5733 10.9935 本文 40.4309 3.5742 0.9324 1.6497 0.6217 10.8189 表 2 MSRS数据集上不同方法的平均推断时间比较
方法 时间(s) GTF 7.7835 TIF 0.1899 Densefuse 0.0039 FusionGAN 0.0874 U2Fusion 0.9154 Dif-Fusion 1.0682 本文 1.1154 表 3 基于MSRS数据集所得消融实验结果
SD MI VIF SCD Qabf SF w/o att 40.4236 3.1590 0.9099 1.6311 0.6122 10.6749 w/o ir 40.4754 3.4941 0.9007 1.6241 0.6076 10.6420 w/o ssim 40.2905 3.4944 0.9143 1.6228 0.6147 10.6273 本文 40.4309 3.5742 0.9324 1.6497 0.6217 10.8189 -
[1] YE Yuanxin, ZHANG Jiacheng, ZHOU Liang, et al. Optical and SAR image fusion based on complementary feature decomposition and visual saliency features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5205315. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2024.3366519. [2] ZHANG Xingchen and DEMIRIS Y. Visible and infrared image fusion using deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(8): 10535–10554. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3261282. [3] JAIN D K, ZHAO Xudong, GONZÁLEZ-ALMAGRO G, et al. Multimodal pedestrian detection using metaheuristics with deep convolutional neural network in crowded scenes[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 95: 401–414. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.02.014. [4] ZHANG Haiping, YUAN Di, SHU Xiu, et al. A comprehensive review of RGBT tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 5027223. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3436098. [5] HUANG Nianchang, LIU Jianan, LUO Yongjiang, et al. Exploring modality-shared appearance features and modality-invariant relation features for cross-modality person re-identification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 135: 109145. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109145. [6] SHAO Hao, ZENG Quansheng, HOU Qibin, et al. MCANet: Medical image segmentation with multi-scale cross-axis attention[J]. Machine Intelligence Research, 2025, 22(3): 437–451. doi: 10.1007/s11633-025-1552-6. [7] CHEN Jun, LI Xuejiao, LUO Linbo, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 508: 64–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.08.066. [8] KONG Weiwei, LEI Yang, and ZHAO Huaixun. Adaptive fusion method of visible light and infrared images based on non-subsampled shearlet transform and fast non-negative matrix factorization[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2014, 67: 161–172. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2014.07.019. [9] LIU Yu, LIU Shuping, and WANG Zengfu. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation[J]. Information Fusion, 2015, 24: 147–164. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2014.09.004. [10] MA Jiayi, CHEN Chen, LI Chang, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 31: 100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.02.001. [11] MA Jinlei, ZHOU Zhiqiang, WANG Bo, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 82: 8–17. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2017.02.005. [12] LIU Yu, CHEN Xun, CHENG Juan, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks[J]. International Journal of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information Processing, 2018, 16(3): 1850018. doi: 10.1142/s0219691318500182. [13] ZHANG Hao, XU Han, XIAO Yang, et al. Rethinking the image fusion: A fast unified image fusion network based on proportional maintenance of gradient and intensity[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12797–12804. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6975. [14] XU Han, MA Jiayi, JIANG Junjun, et al. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 502–518. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2020.3012548. [15] TANG Linfeng, YUAN Jiteng, ZHANG Hao, et al. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 83/84: 79–92. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.03.007. [16] YANG Chenxuan, HE Yunan, SUN Ce, et al. Multi-scale convolutional neural networks and saliency weight maps for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2024, 98: 104015. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2023.104015. [17] PRABHAKAR K R, SRIKAR V S, and BABU R V. DeepFuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4724–4732. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.505. [18] LI Hui and WU Xiaojun. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2614–2623. doi: 10.1109/tip.2018.2887342. [19] JIAN Lihua, YANG Xiaomin, LIU Zheng, et al. SEDRFuse: A symmetric encoder-decoder with residual block network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5002215. doi: 10.1109/tim.2020.3022438. [20] ZHENG Yulong, ZHAO Yan, CHEN Jian, et al. HFHFusion: A heterogeneous feature highlighted method for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Optics Communications, 2024, 571: 130941. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2024.130941. [21] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [22] MA Jiayi, YU Wei, LIANG Pengwei, et al. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48: 11–26. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.004. [23] MA Jiayi, XU Han, JIANG Junjun, et al. DDcGAN: A Dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4980–4995. doi: 10.1109/tip.2020.2977573. [24] YIN Haitao, XIAO Jinghu, and CHEN Hao. CSPA-GAN: A cross-scale pyramid attention GAN for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 5027011. doi: 10.1109/tim.2023.3317932. [25] CHANG Le, HUANG Yongdong, LI Qiufu, et al. DUGAN: Infrared and visible image fusion based on dual fusion paths and a U-type discriminator[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 578: 127391. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127391. [26] YUE Jun, FANG Leyuan, XIA Shaobo, et al. Dif-Fusion: Toward high color fidelity in infrared and visible image fusion with diffusion models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 5705–5720. doi: 10.1109/tip.2023.3322046. [27] ZHAO Zixiang, BAI Haowen, ZHU Yuanzhi, et al. DDFM: Denoising diffusion model for multi-modality image fusion[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023: 8048–8059. doi: 10.1109/iccv51070.2023.00742. [28] HO J, JAIN A, and ABBEEL P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 574. [29] TOET A. The TNO multiband image data collection[J]. Data in Brief, 2017, 15: 249–251. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.09.038. [30] BANDARA W G C, NAIR N G, and PATEL V M. DDPM-CD: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models as feature extractors for remote sensing change detection[C]. 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Tucson, USA, 2025: 5250–5262. doi: 10.1109/WACV61041.2025.00513. [31] BAVIRISETTI D P and DHULI R. Two-scale image fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency detection[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 76: 52–64. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2016.01.009. [32] RAO Yunjiang. In-fibre Bragg grating sensors[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 1997, 8(4): 355–375. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/8/4/002. [33] QU Guihong, ZHANG Dali, and YAN Pingfan. Information measure for performance of image fusion[J]. Electronics Letters, 2002, 38(7): 313–315. doi: 10.1049/el:20020212. [34] HAN Yu, CAI Yunze, CAO Yin, et al. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity[J]. Information Fusion, 2013, 14(2): 127–135. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2011.08.002. [35] ASLANTAS V and BENDES E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2015, 69(12): 1890–1896. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2015.09.004. [36] XYDEAS C S and PETROVIĆ V. Objective image fusion performance measure[J]. Electronics Letters, 2000, 36(4): 308–309. doi: 10.1049/el:20000267. [37] ESKICIOGLU A M and FISHER P S. Image quality measures and their performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1995, 43(12): 2959–2965. doi: 10.1109/26.477498. -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
