Evolutionary Optimization for Satellite Constellation Task Scheduling Based on Intelligent Optimization Engine
-
摘要: 自21世纪以来,我国航天事业快速发展,遥感卫星已成为国土资源普查以及防灾减灾的关键资源。然而,点群、多频和大区域等复杂目标需求的涌现、卫星资源的差异化以及多类复杂目标一体化调度,对现有卫星任务规划技术提出了挑战。针对该问题,该文设计了一种可演进星群智能任务规划引擎架构,以解决异构星群多元目标的一体化调度问题。通过深入研究模型与算法,实现了“约束-决策-收益”模型的解耦,开发了“全局演化+局部搜索+数据驱动”的优化算法模块。在模型层面,通过目标分解来生成标准任务,并构建了多元复杂目标调度模型。在算法层面,提出了一种基于双模型演化的学习型模因算法(LMA),包括初始解生成策略、全局优化策略及通用化邻域搜索算子模板,增强了解的多样性和全局探索能力。此外,通过数据驱动优化策略和动态多阶段快速插入策略满足了动态调度需求。实验结果表明,该算法在求解质量和速度上均优于经典算法和先进算法,并具有良好的鲁棒性。消融实验验证了初始解生成策略、双模型演进及数据驱动策略的有效性。在不同难度的场景中,该算法能够快速提供高质量的调度方案,展示了其在航天任务调度中的应用潜力。Abstract:
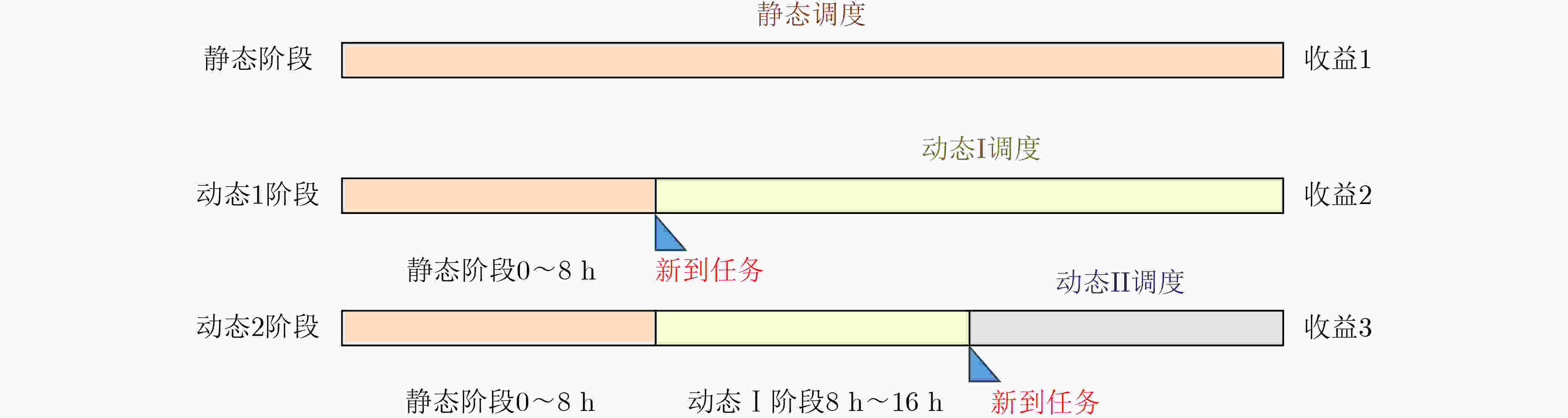
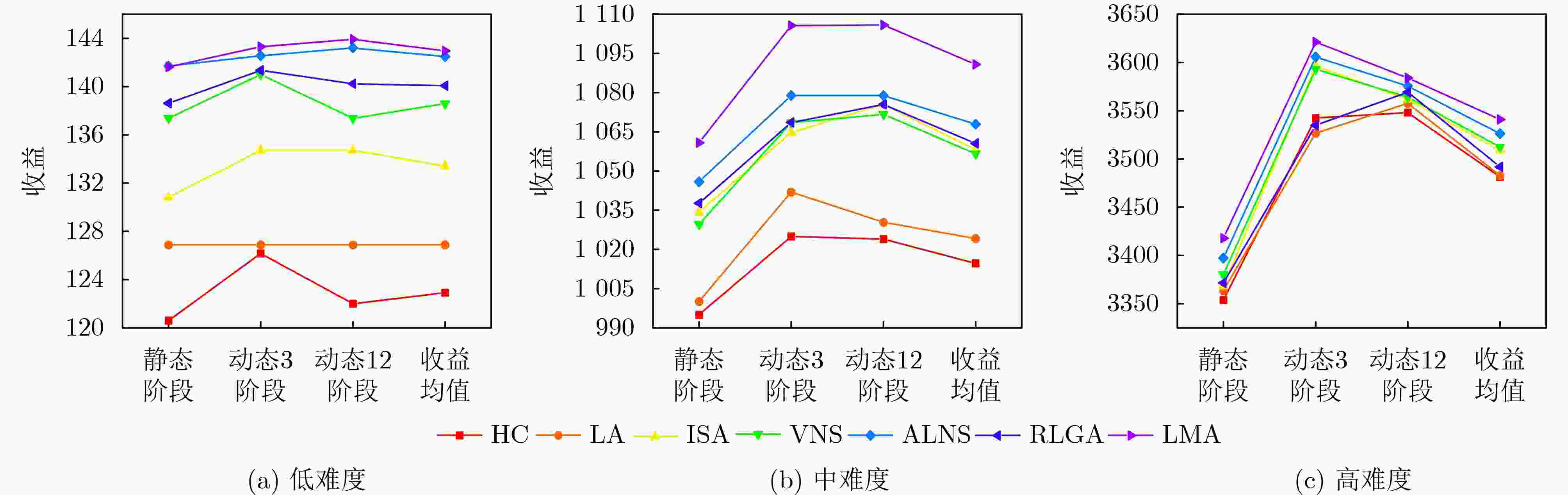
Objective The expansion of China’s aerospace capabilities has led to the widespread deployment of remote sensing satellites for applications such as land resource surveys and disaster monitoring. However, current methods face substantial challenges in the integrated scheduling of complex targets, including multi-frequency observations, dense point clusters, and wide-area imaging. This study develops an intelligent task planning engine architecture tailored for heterogeneous satellite constellations. By applying advanced modeling and evolutionary optimization techniques, the proposed framework addresses the collaborative scheduling of multi-dimensional targets, aiming to overcome key limitations in traditional satellite mission planning. Methods Through systematic analysis of models and algorithms, this study decouples the “Constraint-Decision-Reward” framework and develops an optimization algorithm module featuring “global evolution + local search + data-driven” strategies. At the modeling level, standard tasks are derived via target decomposition, and a multi-dimensional scheduling model for complex targets is established. At the algorithmic level, a Learning Memetic Algorithm (LMA) based on dual-model evolution is proposed. This approach incorporates strategies for initial solution generation, global optimization, and a generalized neighborhood search operator template to improve solution diversity and enhance global exploration capabilities. Additionally, data-driven optimization and dynamic multi-stage rapid insertion strategies are introduced to address real-time scheduling requirements. Results and Discussions Comprehensive experimental comparisons are conducted across three scenario scales—low, medium, and high difficulty—and three task planning scenarios (static scheduling, dynamic three-stage scheduling, and dynamic twelve-stage scheduling). Both classical and advanced algorithms are evaluated. Ablation experiments ( Tables 4 and5 ) assess the contribution of each component within the LMA. In all task scenarios, the proposed method consistently outperforms advanced algorithms, including adaptive large neighborhood search and the reinforcement learning genetic algorithm, as shown inFigure 11 andTable 3 . The algorithm reliably completes iterations within 20 seconds, demonstrating high computational efficiency.Conclusions By standardizing complex targets and generating tasks, this research effectively addresses the integrated scheduling challenge of multi-dimensional objectives across heterogeneous resources. Experimental results show that the LMA outperforms traditional algorithms in terms of both solution quality and computational efficiency. The dual-model evolution mechanism enhances the algorithm’s global search capabilities, while the dynamic insertion strategy effectively handles scenarios with dynamically arriving tasks. These innovations highlight the algorithm’s significant advantages in aerospace mission scheduling. -
表 1 符号说明
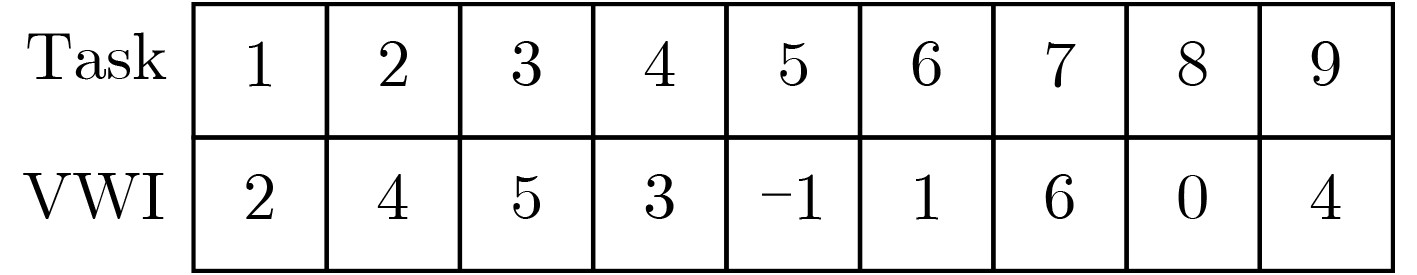
符号 释义 xij 0~1决策变量,任务与窗口之间的关系 zi 任务ti的延长率 ymni 0~1变量,如果ti能被wmn覆盖则为1,否则为0 cmni 0~1变量,如果ti能被wmn地理覆盖则为1,否则为0 wij 任务ti的第j个时间窗口 tis/e/r 任务ti的开始时间/结束时间/分辨率 rij 时间窗口wij的分辨率 Ikoij 0~1变量,若wij在sk的轨道o则为1,否则为0 skot 卫星的单轨最大开机时间 Δt 卫星1次成像的时间 Wi 任务ti的时间窗口集合 wijs/e/m/sat 时间窗口wij的开始时间/结束时间/最大时间/所属卫星 Δaijmn 时间窗口wij和wmn之间姿态角转换大小 gma 区域目标a的第m个网格 ΔK(Δaijmn) 计算时间窗口wij和wmn之间转换时间的函数 1 置换算子模板
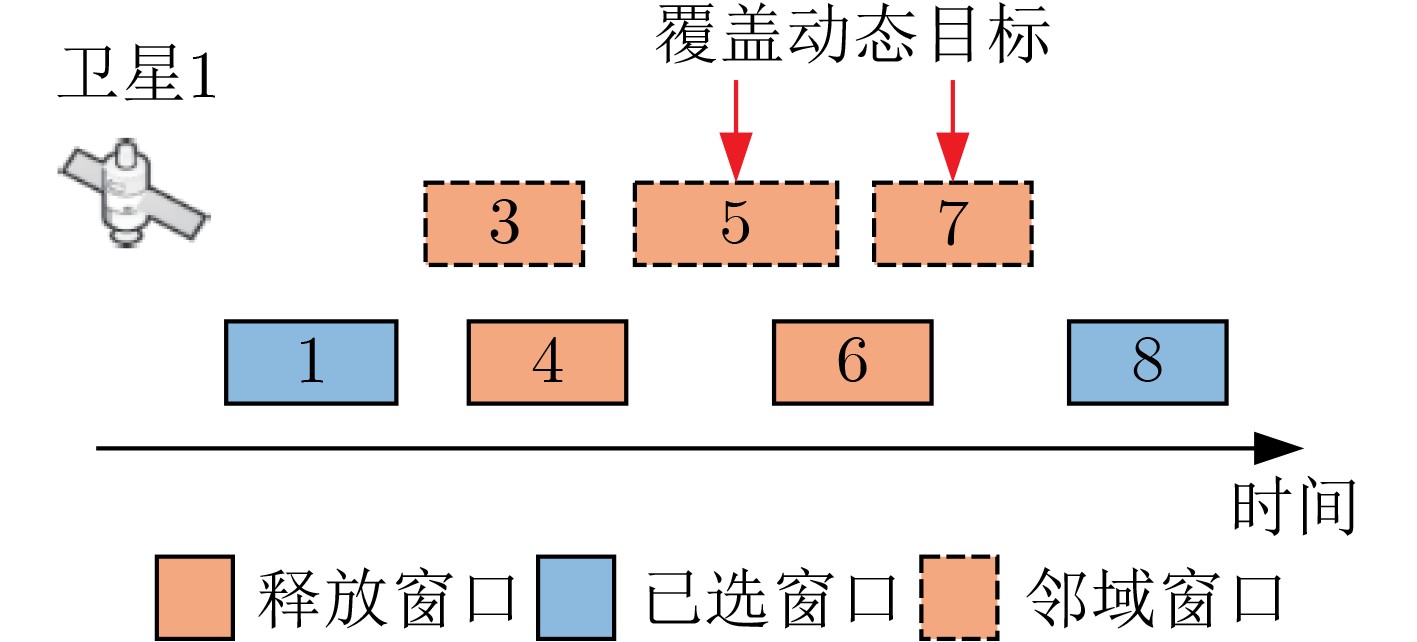
输入:解solution,任务集合taskList,置换任务数量n,置换规则 输出:新的扰动解solution (1) 从taskList随机选择n个任务,记为tasks,记当前解的得分为$f' $ (2) For task in tasks // 循环当前任务列表 (3) 记task的现在的成像窗口为$w' $,并放入preW (4) 按照选择的规则打乱task的成像窗口集合的排列 (5) For w in Wtask // 循环当前任务的成像窗口集合 (6) If w 可行 and w != $w' $ then (7) 将task的成像窗口替换为w (8) Break (9) End If (10) End For (11) End For (12) 计算新方案的得分,记为 f (13) If f < $f' $ then // 当前解相较上一解无变化 (14) 将选择的任务的机会按照preW还原 (15) End If (16) Return solution 2 删除插入算子模板
输入:解solution,任务集合taskList,删除任务数量n,删除规
则,插入规则,内循环次数m输出:新的扰动解solution (1) 将taskList中已完成任务按照指定的删除规则排序 (2) 记taskList中前n个任务为tasks,当前得分为$f' $,tasks中任务
的成像方案为wList(3) 释放wList,根据冲突关系记邻域内可选成像窗口集合为
owList(4) If size(wList) == size(owList) then // 解不会发生变化 (5) continue; (6) Else (7) For i in range(m) // 内循环尝试插入 (8) 按照插入规则对owList排序(首次按照选定规则后随机) (9) 计算新的调度方案收益,记为f (10) If f > $f' $ then // 接受改进解 (11) Break (12) End If (13) End For (14) End If (15) If f <= $f' $ then // 无改进 (16) 将选择的任务的机会按照wList还原 (17) End If (18) Return solution 表 2 场景参数设置(个)
难度 静态阶段 动态阶段追加目标 卫星数量 点目标 区域目标 点目标 区域目标 OPT SAR 低难度 45 5 5 1 20 10 中难度 180 20 20 5 52 28 高难度 450 50 50 10 132 68 表 3 对比实验结果
算法 静态
阶段动态
3阶段动态12阶段 均值 时间(s) 静态
阶段动态
3阶段动态12阶段 均值 时间(s) 静态
阶段动态
3阶段动态12阶段 均值 时间(s) 低难度S1: 45-5-5-1-20-10 低难度S2: 45-5-5-1-20-10 低难度S3: 45-5-5-1-20-10 HC 103.26 116.6 103.26 107.70 4.32 120.61 126.16 122 122.92 5.31 103.19 104.85 105.06 104.36 4.56 LA 110.06 112.62 111.73 111.47 5.26 126.89 126.89 126.89 126.89 4.56 109.81 111.48 111.48 110.92 5.45 ISA 126 132.67 127.95 128.87 5.49 130.82 134.71 134.71 133.41 4.65 122.14 125.47 124.01 123.87 4.65 VNS 121.2 121.2 121.2 121.2 3.44 137.38 140.99 137.38 138.58 3.25 119.69 125.8 126.08 123.85 4.23 ALNS 128.6 127.7 128.5 128.26 2.59 141.71 142.56 143.2 142.49 3.04 122.54 125.8 127.24 125.19 2.83 RLGA 126.67 127.1 129.4 127.72 6.58 138.62 141.35 140.23 140.07 7.26 118.71 124.7 125.35 122.92 7.65 LMA 129.55 129.55 129.55 129.55 2.17 141.63 143.3 143.92 142.95 2.86 122.64 127.64 130.97 127.08 2.85 中难度S4: 180-20-20-5-52-28 中难度S5: 180-20-20-5-52-28 中难度S6: 180-20-20-5-52-28 HC 931.09 964.18 967.29 954.18 11.25 995.03 1024.95 1023.94 1014.64 13.85 945.45 959.61 963.75 956.27 12.58 LA 959.43 978.41 995.22 977.69 12.65 1000.15 1041.92 1030.41 1024.16 14.98 938.59 969.47 978.17 962.08 11.64 ISA 941.37 989.35 984.4 971.71 11.52 1034.31 1064.7 1075.53 1058.18 12.56 963.91 997.22 1004.18 988.44 13.78 VNS 961.77 1001.66 996.49 986.64 10.23 1029.63 1068.52 1071.67 1056.61 11.74 963.63 988.66 990.42 980.90 12.66 ALNS 967.45 995.23 1001.21 987.96 6.54 1045.86 1078.9 1078.9 1067.89 7.43 973.32 1008.43 1015.42 999.06 6.83 RLGA 957.43 987.62 994.23 975.83 15.32 1037.65 1068.54 1075.4 1060.53 17.82 970.65 1001.31 1010.58 994.18 19.52 LMA 972.13 1006.86 1013.14 997.38 4.57 1060.85 1105.65 1105.87 1090.79 4.85 989.52 1017.9 1027.57 1011.66 5.01 高难度S7: 450-50-50-10-132-68 高难度S8: 450-50-50-10-132-68 高难度S9: 450-50-50-10-132-68 HC 3303.16 3507.09 3499.39 3436.55 42.31 3353.85 3542.44 3548.13 3481.4 50.22 3311.29 3507.39 3514.8 3444.49 45.32 LA 3322.6 3497.29 3492.31 3437.4 52.31 3363.81 3526.68 3557.75 3482.75 58.96 3359.47 3535.68 3561.15 3485.43 54.39 ISA 3346.55 3521.12 3518.15 3461.94 58.65 3368.36 3596.54 3561.73 3508.88 54.41 3421.56 3621.59 3562.44 3535.20 55.45 VNS 3353.36 3542.38 3511.74 3469.16 35.21 3380.28 3593.06 3564.04 3512.46 35.32 3423.42 3572.84 3597.37 3531.21 37.32 ALNS 3365.41 3579.27 3531.76 3492.15 19.51 3397.32 3605.7 3575.56 3526.19 18.23 3437.93 3654.72 3631.67 3574.77 17.38 RLGA 3353.76 3517.76 3509.75 3460.42 75.94 3371.52 3534.87 3569.23 3491.87 70.43 3324.41 3552.23 3573.6 3483.41 67.87 LMA 3382.38 3597.94 3558.95 3513.09 17.86 3417.8 3621.05 3583.97 3540.94 18.36 3458.24 3662.31 3655.23 3591.93 16.52 表 4 初始解生成策略
场景 随机 单一策略 混合规则 收益 标准差 收益 标准差 收益 标准差 S1 101.20 5.71 110.37 4.29 109.65 6.5 S2 105.36 5.42 112.45 3.54 112.69 5.85 S3 99.85 3.25 107.51 5.61 108.19 5.32 S4 832.29 21.38 867.45 14.85 879.67 17.12 S5 867.48 21.45 907.34 13.74 921.41 20.35 S6 824.67 19.84 871.99 12.36 881.32 18.74 S7 3252.35 24.53 2991.85 18.32 3301.08 22.32 S8 3255.81 23.67 3307.59 17.65 3320.32 24.32 S9 3305.24 24.32 3319.53 19.65 3340.74 26.32 表 5 双模型演化消融实验
模型 面向卫星 面向任务 双模型演化 收益 时间(s) 收益 时间(s) 收益 时间(s) S1 128.34 1.85 123.85 1.68 129.55 2.17 S2 140.77 2.04 134.21 2.31 142.95 2.86 S3 126.54 1.98 121.53 2.13 127.08 2.85 S4 975.35 3.27 963.84 3.34 997.38 4.57 S5 1062.71 3.52 1065.69 3.48 1090.79 4.85 S6 994.68 3.37 988.18 3.41 1011.66 5.01 S7 3498.36 7.65 3481.32 10.32 3513.09 17.86 S8 3514.81 7.42 3509.58 11.21 3540.94 18.36 S9 3543.34 7.56 3579.53 11.38 3591.93 16.52 -
[1] KUENZER C, OTTINGER M, WEGMANN M, et al. Earth observation satellite sensors for biodiversity monitoring: Potentials and bottlenecks[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2014, 35(18): 6599–6647. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2014.964349. [2] GUO Huadong. Understanding global natural disasters and the role of earth observation[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2010, 3(3): 221–230. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2010.499662. [3] 阮启明, 谭跃进, 李菊芳, 等. 对地观测卫星的区域目标分割与优选问题研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2006, 31(1): 98–100. doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2006.01.034.RUAN Qiming, TAN Yuejin, LI Jufang, et al. Research on segmenting and selecting of area targets[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2006, 31(1): 98–100. doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2006.01.034. [4] 耿远卓, 郭延宁, 李传江, 等. 敏捷凝视卫星密集点目标聚类与最优观测规划[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(3): 613–621. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0800.GENG Yuanzhuo, GUO Yanning, LI Chuanjiang, et al. Optimal mission planning with task clustering for intensive point targets observation of staring mode agile satellite[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(3): 613–621. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0800. [5] WANG Xinwei, WU Guohua, XING Lining, et al. Agile earth observation satellite scheduling over 20 years: Formulations, methods, and future directions[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(3): 3881–3892. doi: 10.1109/jsyst.2020.2997050. [6] SONG Yanjie, OU Junwei, PEDRYCZ W, et al. Generalized model and deep reinforcement learning-based evolutionary method for multitype satellite observation scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(4): 2576–2589. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3345928. [7] YAO Feng, DU Yonghao, LI Lei, et al. General modeling and optimization technique for real-world earth observation satellite scheduling[J]. Frontiers of Engineering Management, 2023, 10(4): 695–709. doi: 10.1007/s42524-023-0263-3. [8] SONG Yanjie, WEI Luona, YANG Qing, et al. RL-GA: A reinforcement learning-based genetic algorithm for electromagnetic detection satellite scheduling problem[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2023, 77: 101236. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2023.101236. [9] LI Lei, DU Yonghao, YAO Feng, et al. Learning memetic algorithm based on variable population and neighborhood for multi-complex target scheduling of large-scale imaging satellites[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2025, 92: 101789. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101789. [10] WU Jian, SONG Bingyu, ZHANG Guoting, et al. A data-driven improved genetic algorithm for agile earth observation satellite scheduling with time-dependent transition time[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 174: 108823. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2022.108823. [11] DU Bin and LI Shuang. A new multi-satellite autonomous mission allocation and planning method[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 163: 287–298. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.11.001. [12] ZHAO Yanbin, DU Bin, and LI Shuang. Agile satellite mission planning via task clustering and double-layer tabu algorithm[J]. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 2020, 122(1): 235–257. doi: 10.32604/cmes.2020.08070. [13] 潘耀, 饶启龙, 池忠明, 等. 改进的遥感卫星成像任务单轨最优团划分聚类方法[J]. 上海航天, 2018, 35(3): 34–40. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2018.03.006.PAN Yao, RAO Qilong, CHI Zhongming, et al. Improved clustering method of spot target based on best clique partition in single orbit for remote sensing satellite imaging[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2018, 35(3): 34–40. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2018.03.006. [14] 张聪, 袁利, 王云鹏, 等. 基于智能聚类的遥感卫星成像任务自主聚合方法[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2022, 48(5): 47–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2022.05.006.ZHANG Cong, YUAN Li, WANG Yunpeng, et al. Autonomous aggregation method for imaging tasks of observation satellite based on intelligent clustering[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2022, 48(5): 47–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2022.05.006. [15] LEMAÎTRE M, VERFAILLIE G, JOUHAUD F, et al. Selecting and scheduling observations of agile satellites[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2002, 6(5): 367–381. doi: 10.1016/S1270-9638(02)01173-2. [16] 章登义, 郭雷, 王骞, 等. 一种面向区域目标的敏捷成像卫星单轨调度方法[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2014, 39(8): 901–905. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20130233.ZHANG Dengyi, GUO Lei, WANG Qian, et al. An improved single-orbit scheduling method for agile imaging satellite towards area target[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(8): 901–905. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20130233. [17] 余婧, 喜进军, 于龙江, 等. 敏捷卫星同轨多条带拼幅成像模式研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2015, 24(2): 27–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2015.02.005.YU Jing, XI Jinjun, YU Longjiang, et al. Study of one-orbit multi-stripes splicing imaging for agile satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2015, 24(2): 27–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2015.02.005. [18] 杨文沅, 贺仁杰, 耿西英智, 等. 面向区域目标的敏捷卫星非沿迹条带划分方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(22): 82–87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.22.014.YANG Wenyuan, HE Renjie, GENG Xiyingzhi, et al. Area target oriented non-along-with-track strip partitioning method for agile satellite[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(22): 82–87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.22.014. [19] LU Zezhong, SHEN Xin, LI Deren, et al. Multiple super-agile satellite collaborative mission planning for area target imaging[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2023, 117: 103211. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2023.103211. [20] GU Yi, HAN Chao, CHEN Yuhan, et al. Large region targets observation scheduling by multiple satellites using resampling particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 1800–1815. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3205565. [21] WU Jian, CHEN Yuning, HE Yongming, et al. Survey on autonomous task scheduling technology for Earth observation satellites[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 33(6): 1176–1189. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2022.000141. [22] 王钧. 成像卫星综合任务调度模型与优化方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2007.WANG Jun. Research on modeling and optimization techniques in united mission scheduling of imaging satellites[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2007. [23] EIBEN A E and SMITH J E. What is an evolutionary algorithm?[M]. EIBEN A E and SMITH J E. Introduction to Evolutionary Computing. 2nd ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 25–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-44874-8_3. [24] MLADENOVIĆ N and HANSEN P. Variable neighborhood search[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 1997, 24(11): 1097–1100. doi: 10.1016/S0305-0548(97)00031-2. [25] SONG Yanjie, OU Junwei, SUGANTHAN P N, et al. Learning adaptive genetic algorithm for earth electromagnetic satellite scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 9010–9025. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3312626. [26] PISINGER D and ROPKE S. Large neighborhood search[M]. GENDREAU M and POTVIN J Y. Handbook of Metaheuristics. 3rd ed. Cham: Springer, 2019: 99–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91086-4_4. [27] WU Jian, YAO Feng, SONG Yanjie, et al. Frequent pattern-based parallel search approach for time-dependent agile earth observation satellite scheduling[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 636: 118924. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.04.003. [28] LIU Zhehan, LIU Jinming, LIU Xiaolu, et al. Knowledge-assisted adaptive large neighbourhood search algorithm for the satellite–ground link scheduling problem[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2024, 192: 110219. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2024.110219. [29] BORGELT C. An implementation of the FP-growth algorithm[C]. The 1st International Workshop on Open Source Data Mining: Frequent Pattern Mining Implementations, Chicago, USA, 2005: 1–5. doi: 10.1145/1133905.1133907. [30] CHEN Cheng, LI Lei, DU Yonghao, et al. A hybrid learning-assisted multi-parallel algorithm for a large-scale satellite-ground networking optimization problem[J/OL]. Frontiers of Engineering Management. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42524-025-4098-y, 2025. [31] CLIFTON J and LABER E. Q-learning: Theory and applications[J]. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application, 2020, 7: 279–301. doi: 10.1146/annurev-statistics-031219-041220. [32] FAN Jianqing, WANG Zhaoran, XIE Yuchen, et al. A theoretical analysis of deep Q-learning[C]. The 2nd Annual Conference on Learning for Dynamics and Control, Berkeley, USA, 2020: 486–489. -





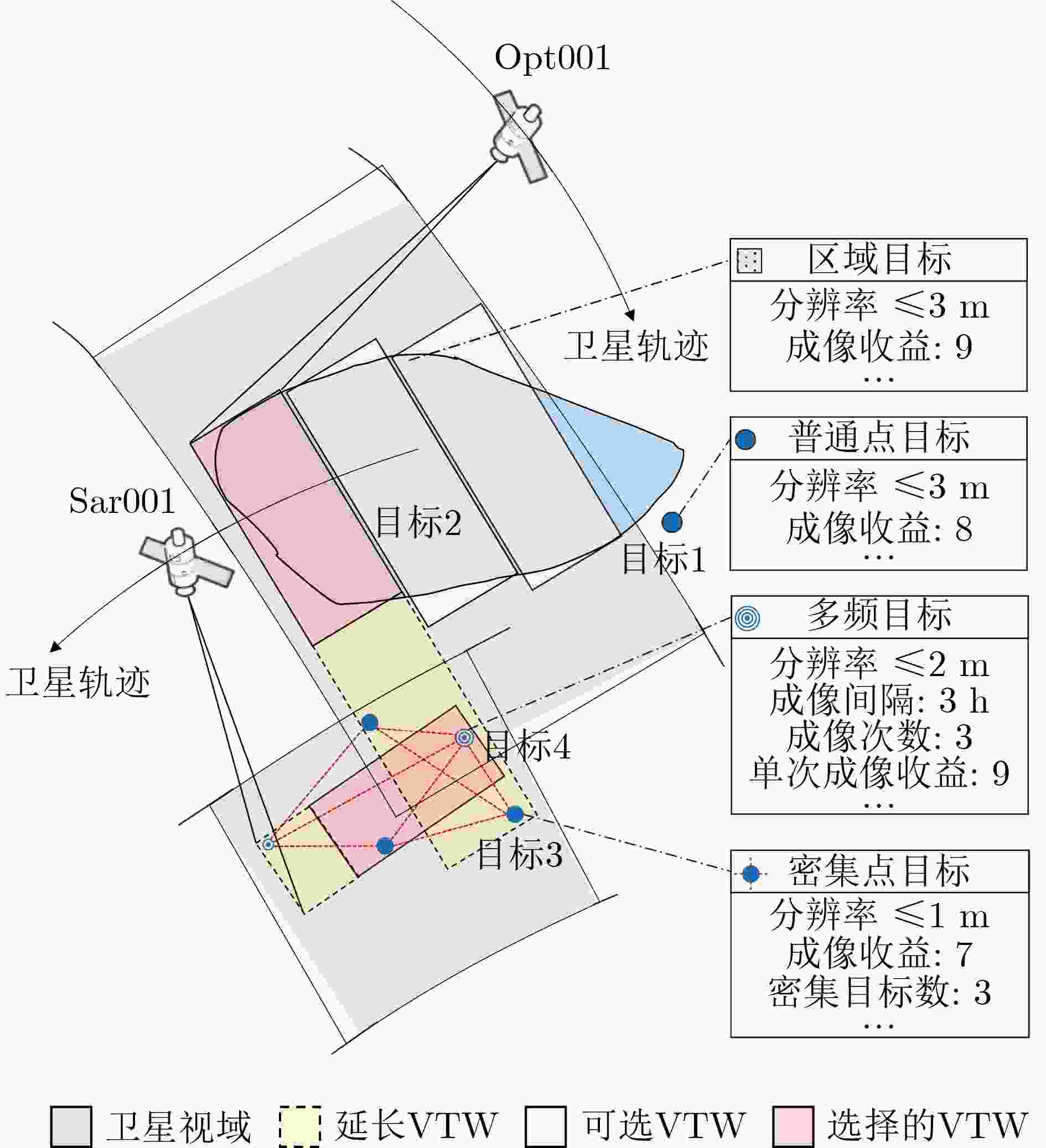
 下载:
下载:

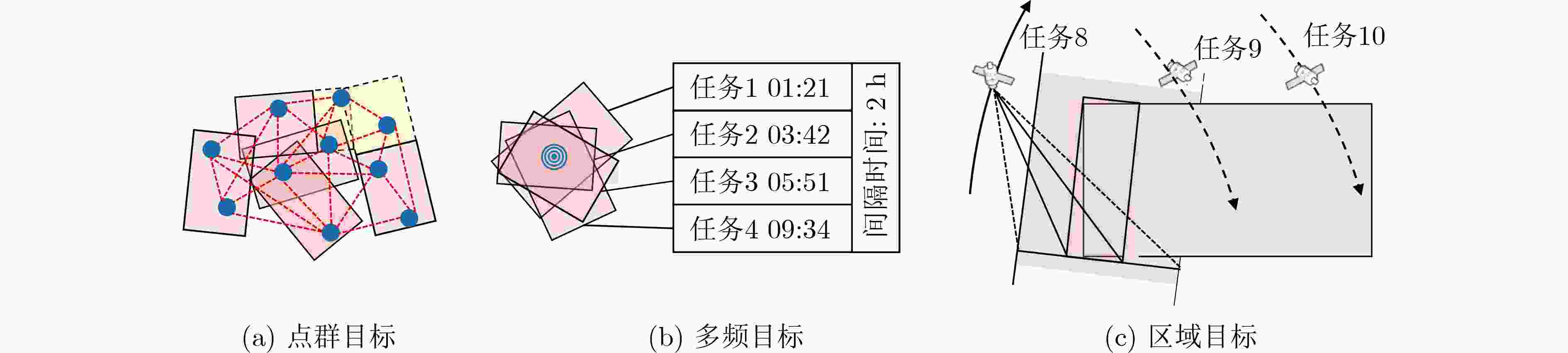

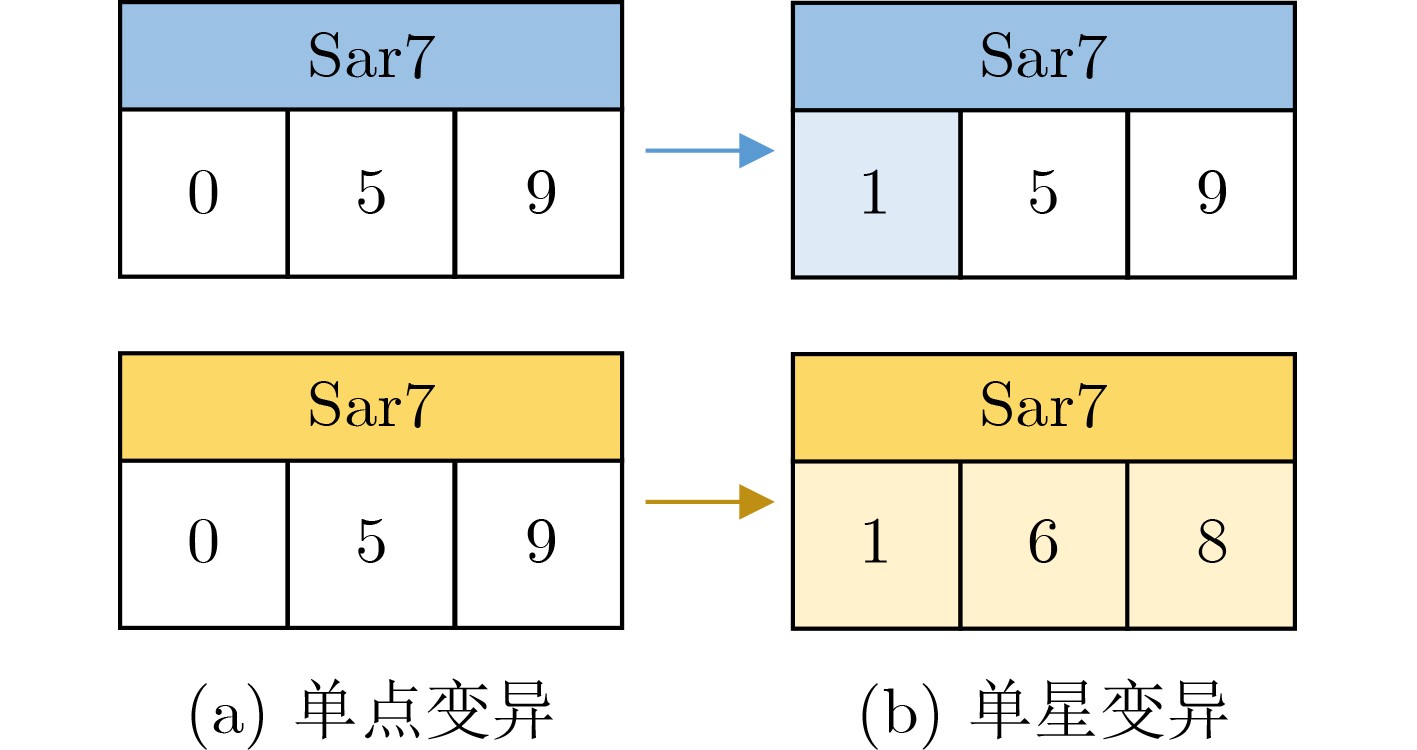
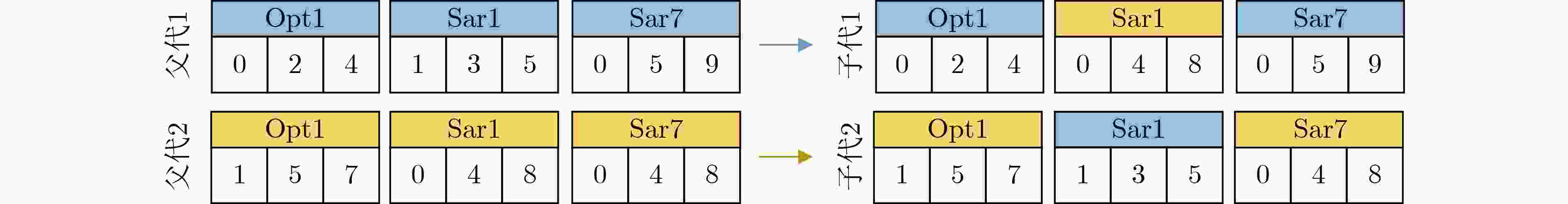



 下载:
下载:
