Remote Sensing Image Text Retrieval Method Based on Object Semantic Prompt and Dual-Attention Perception
-
摘要: 高分辨率遥感图像场景复杂、语义信息丰富多样且目标尺度多变,容易引起特征空间中不同类别目标的图像特征分布混淆,导致模型难以高效捕获遥感目标文本语义与图像特征的潜在关联,进而影响遥感图像文本检索的精度。针对这一问题,该文提出基于目标语义提示与双注意力感知的遥感图像文本检索方法。该方法首先引入空间-通道协同注意力,利用空间-通道维度注意权重交互捕捉图像全局上下文特征。同时,为了实现遥感图像显著目标信息的多粒度精准表征,模型通过所构建的基于自适应显著性区域目标感知注意力机制,通过动态多尺度目标特征加权聚合,提升对目标局部区域显著性特征聚焦响应。此外,该文设计了目标类别概率先验引导策略,对文本描述进行目标类别语义词频统计,以获取高概率先验目标语义信息,进而指导在跨模态共性嵌入空间中的图像特征聚类,最终实现高效准确的图像-文本特征对齐。该方法在RSICD与RSITMD两组遥感图像文本检索基准数据集上开展实验评估。结果表明,所设计的方法在检索精度指标上展现出了卓越的性能优势。Abstract:
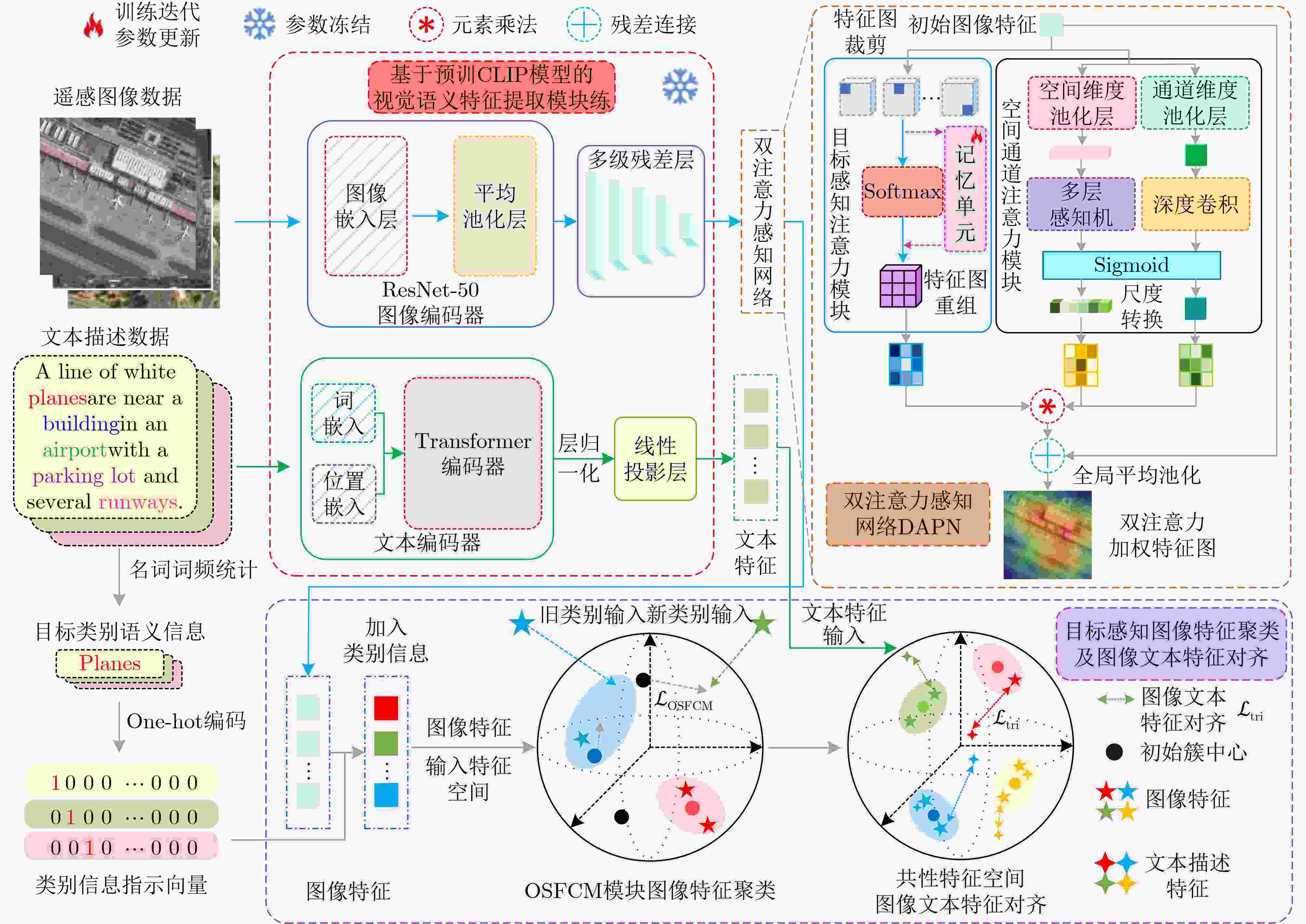
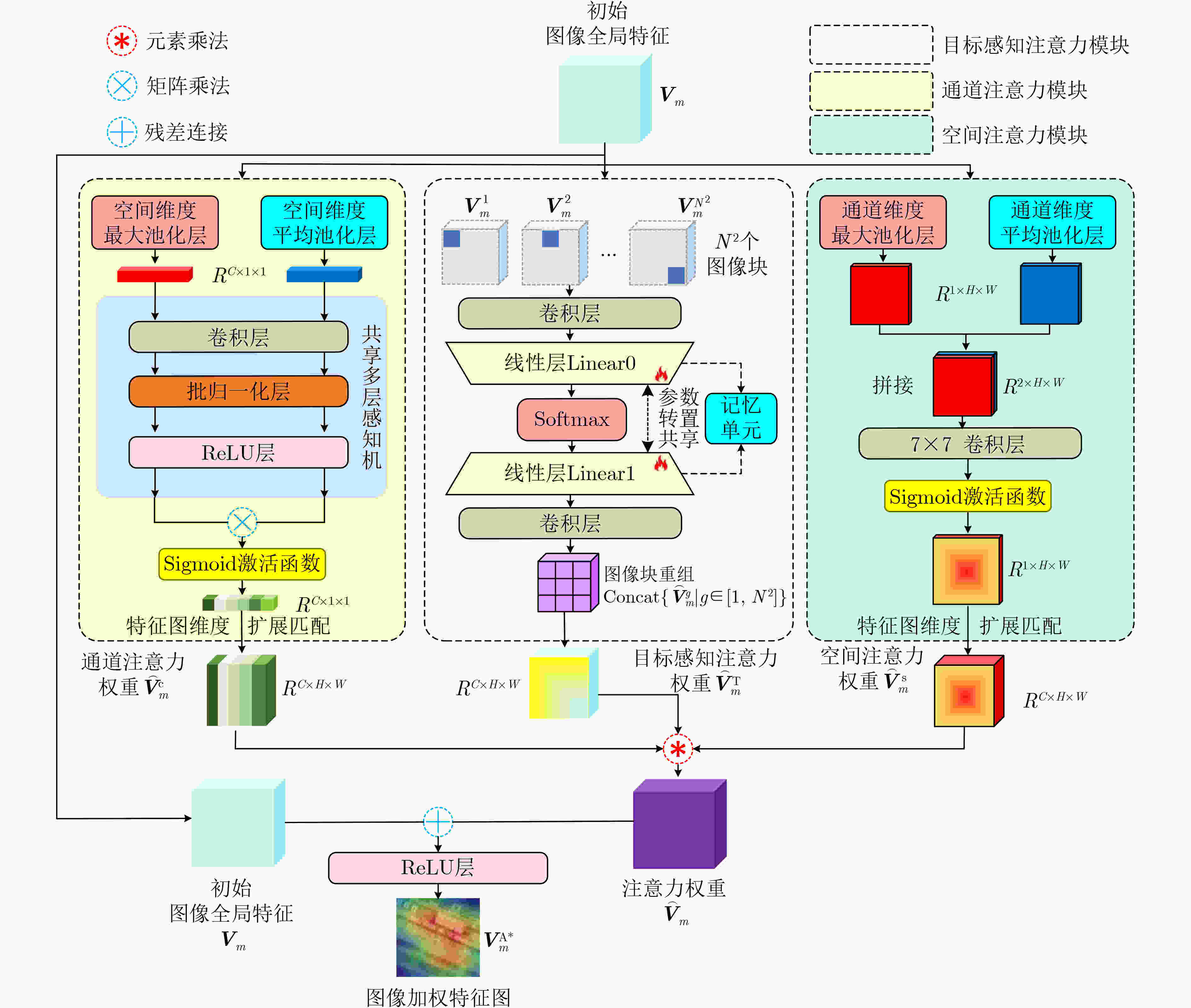
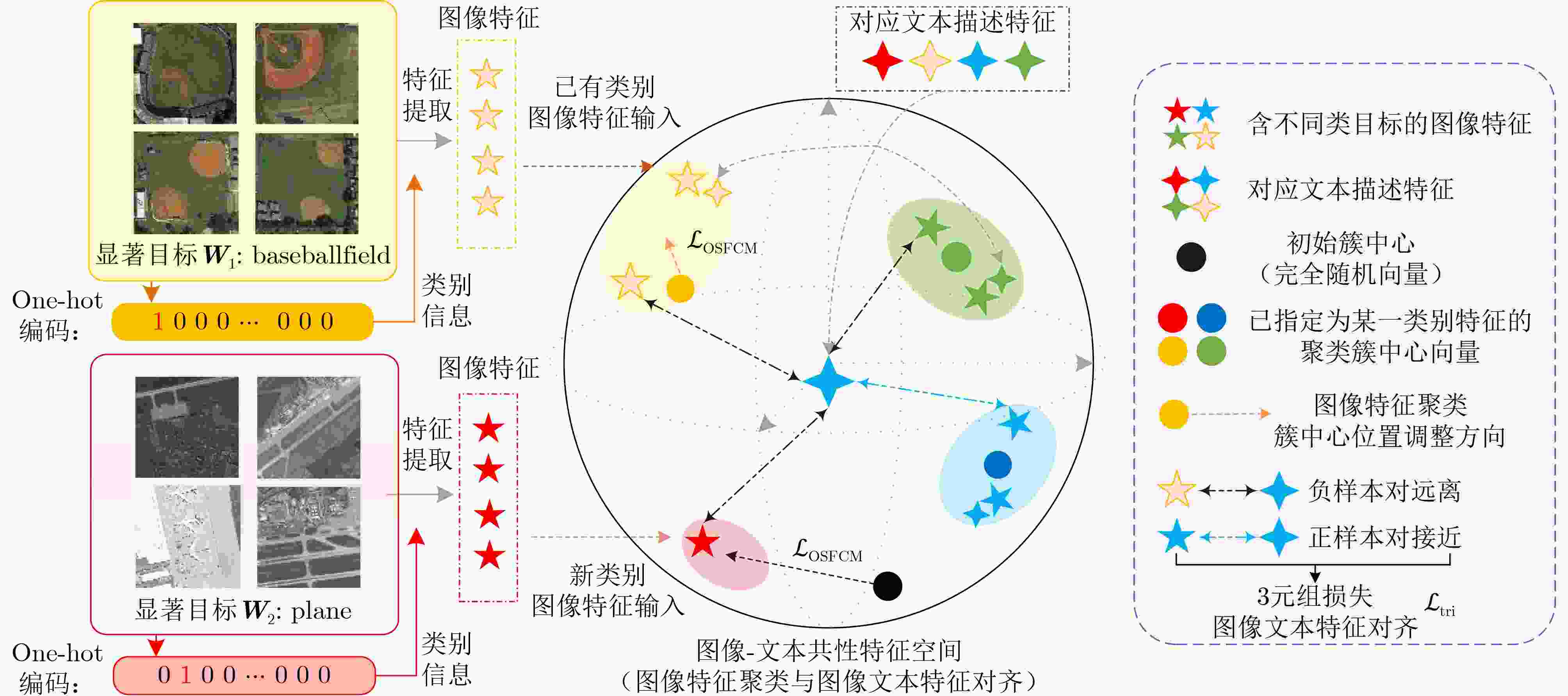
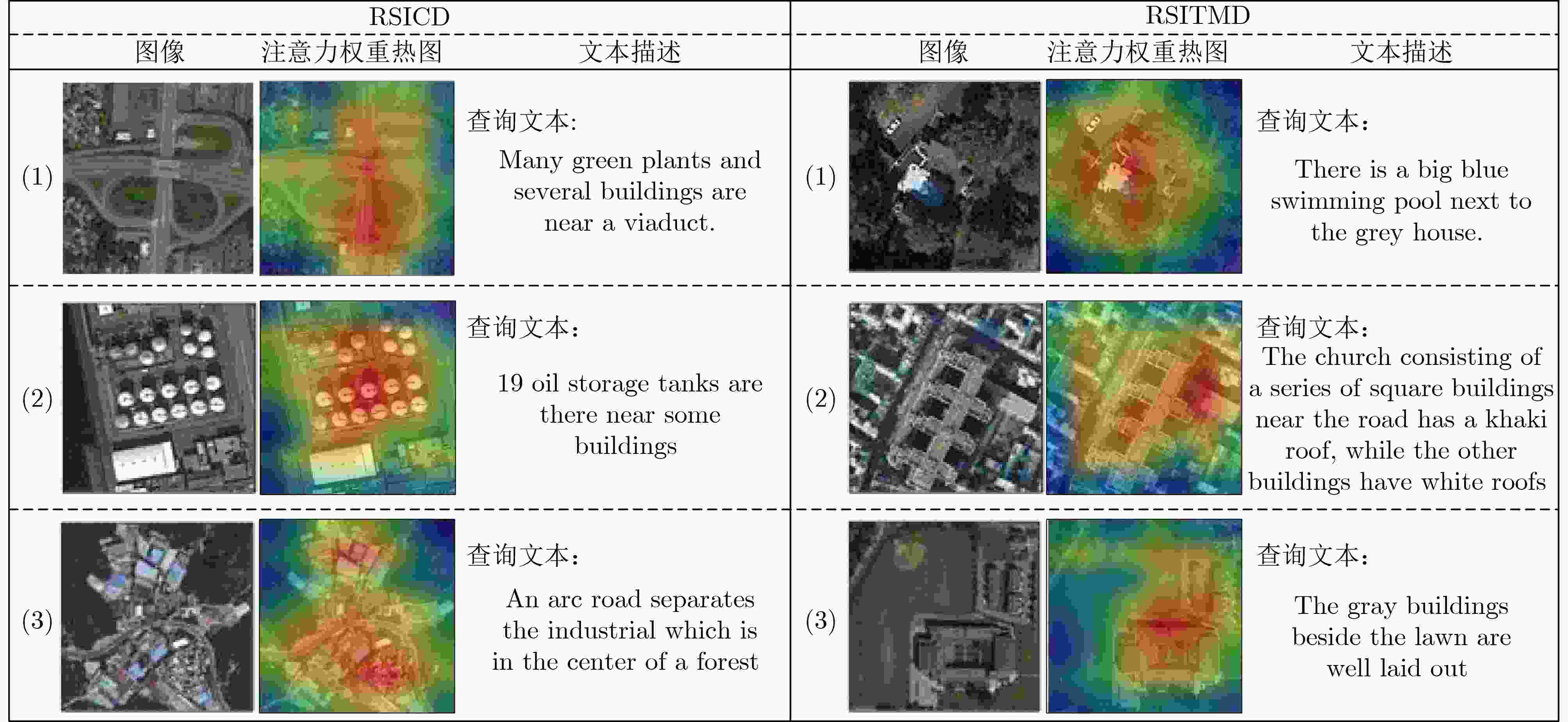
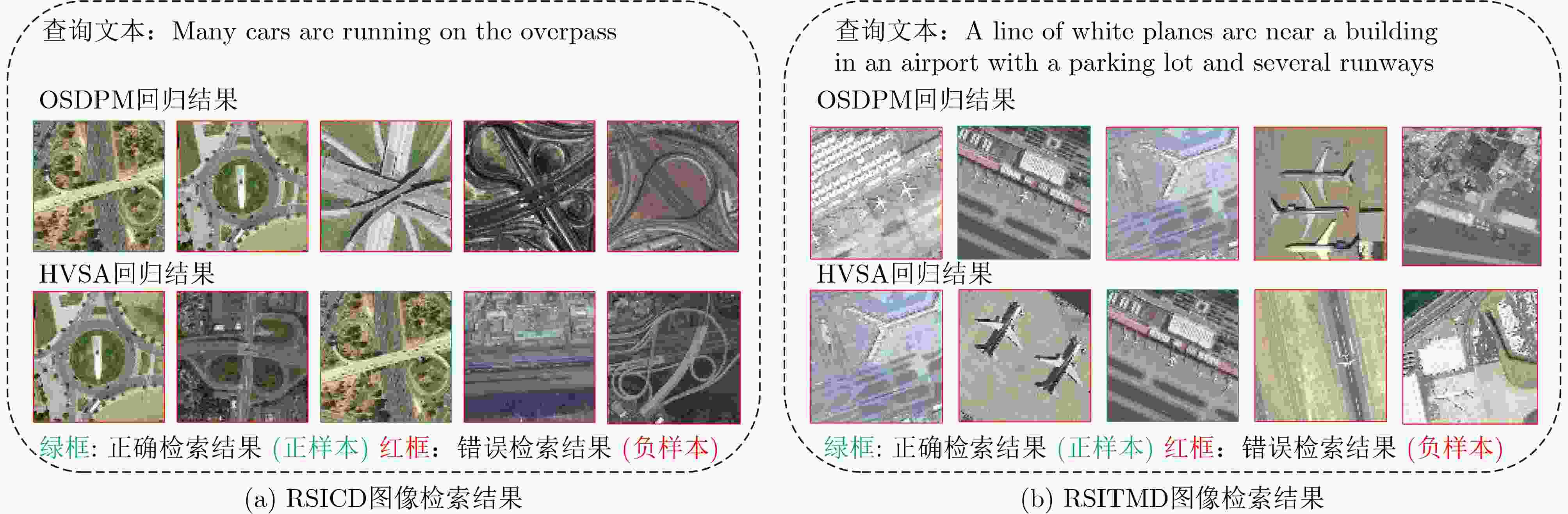
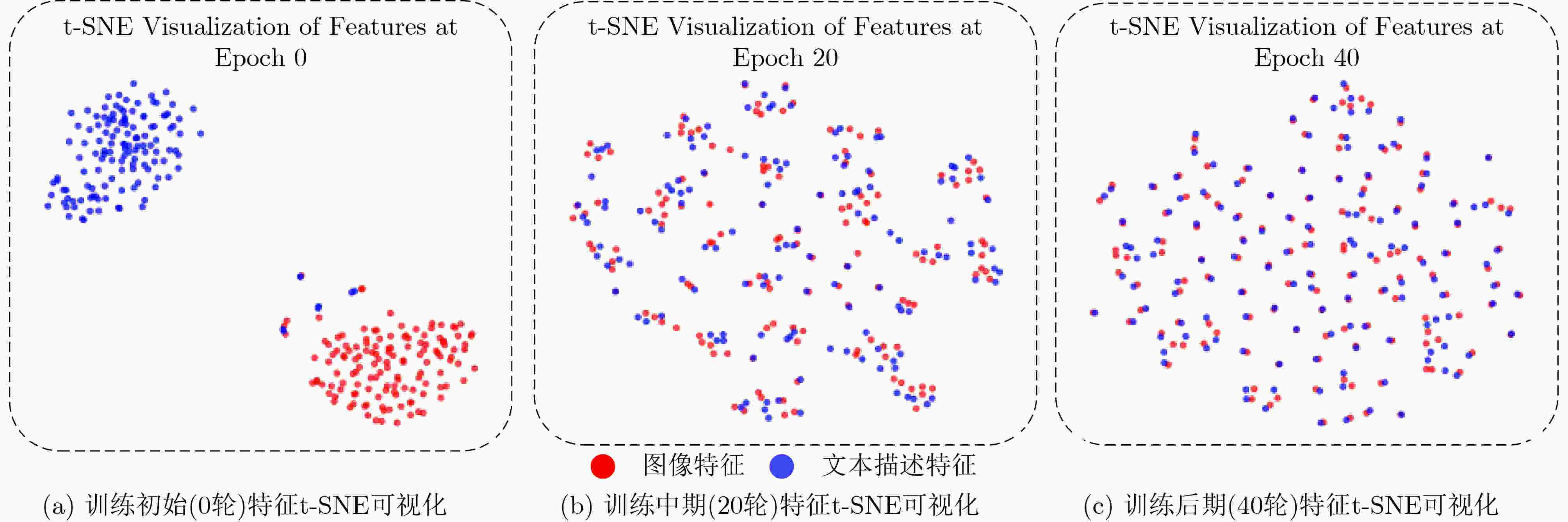
Objective High-resolution remote sensing imagery presents complex scene configurations, diverse semantic associations, and significant object scale variations, often resulting in overlapping feature distributions across categories in the latent space. These ambiguities hinder the model’s ability to capture intrinsic associations between textual semantics and visual representations, reducing retrieval accuracy in image-text retrieval tasks. This study aims to address these challenges by investigating object-level attention mechanisms and cross-modal feature alignment strategies. By dynamically allocating attention weights to salient object features and optimizing image-text feature alignment, the proposed approach enables more precise extraction of semantic information and achieves high-quality cross-modal alignment, thereby improving retrieval accuracy in remote sensing image-text retrieval. Methods Building on the theoretical foundations above, this study proposes an Object Semantic and Dual-attention Perception Model (OSDPM) for remote sensing image-text retrieval. OSDPM first utilizes a pretrained CLIP model to extract features from remote sensing images and their associated textual descriptions. A Dual-Attention Perception Network (DAPN) is then developed to characterize both global contextual information and salient object regions in the imagery. DAPN adaptively enhances the representation of salient objects with large scale variations by dynamically attending to significant local regions and integrating attention across spatial and channel dimensions. To address cross-modal heterogeneity between image and text features, an Object Semantic-aware Feature Clustering Module (OSFCM) is introduced. OSFCM conducts statistical analysis of the frequency of semantic nouns associated with object categories in image-text pairs, extracting high-probability semantic priors for the corresponding images. These semantic cues are used to guide the clustering of image features that exhibit ambiguity in the cross-modal feature space, thereby reducing distribution overlap across object categories. This targeted clustering enables precise alignment between image and text features and improves retrieval performance in remote sensing image-text tasks. Results and Discussions The proposed OSDPM integrates spatial-channel attention and adaptive saliency mechanisms to capture multiscale object information within image features. It then leverages semantic priors from textual descriptions to guide cross-modal feature alignment, improving retrieval performance in remote sensing image-text tasks. Experiments on the RSICD and RSITMD benchmark datasets show that OSDPM outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 9.01% and 8.83%, respectively ( Table 1 ,Table 2 ). Comparative results for image-to-text and text-to-image retrieval (Fig. 6 ,Fig. 7 ) further confirm the superior retrieval accuracy achieved by the proposed approach. Feature heatmap visualizations (Fig. 5 ) indicate that the DAPN effectively captures both global contextual features and local salient object regions, maintaining spatial semantic consistency between visual and textual representations. In addition, t-SNE visualizations across training stages demonstrate that OSFCM mitigates feature distribution overlap among object categories, thereby improving feature alignment accuracy. Ablation studies (Table 3 ) confirm that each module in the proposed network contributes to retrieval performance gains.Conclusions This study proposes a remote sensing image-text retrieval method, OSDPM, to address challenges in object representation and cross-modal semantic alignment caused by complex scenes, diverse semantics, and scale variation in high-resolution remote sensing images. OSDPM first employs a pretrained CLIP model to extract global contextual features from both images and corresponding text descriptions. It then introduces the DAPN to capture salient object features by dynamically attending to significant local regions and adjusting attention across spatial and channel dimensions. Furthermore, the model incorporates an OSFCM, which extracts prior semantic information through frequency analysis of object category terms and uses these priors to guide the clustering of ambiguous image features in the embedding space. This strategy reduces semantic misalignment and facilitates accurate cross-modal mapping between image and text features. Experiments on the RSICD and RSITMD benchmark datasets confirm that OSDPM outperforms existing methods, demonstrating improved accuracy and robustness in remote sensing image-text retrieval. -
Key words:
- Remote sensing images /
- Cross-modal /
- Image-text retrieval /
- CLIP /
- Spatial-channel attention
-
表 1 与其他方法在RSICD测试集上的检索性能比较(%)
图像→文本 文本→图像 Rsum 方法名称 R@1 R@5 R@10 R@1 R@5 R@10 VSE++ 3.38 9.51 17.46 2.82 11.32 18.10 62.59 SCAN t2i 4.39 10.90 17.64 3.91 16.20 26.49 79.53 SCAN i2t 5.85 12.89 19.84 3.71 16.40 26.73 85.42 CAMP-triplet 5.12 12.89 21.12 4.15 15.23 27.81 86.32 CAMP-bee 4.20 10.24 15.45 2.72 12.76 22.89 68.26 MTFN 5.02 12.52 19.74 4.90 17.17 29.49 88.84 LW-MCR(b) 4.57 13.71 20.11 4.02 16.47 28.23 87.11 LW-MCR(d) 3.29 12.52 19.93 4.66 17.51 30.02 87.93 AMFMN-soft 5.05 14.53 21.57 5.05 19.74 31.04 96.98 AMFMN-fusion 5.39 15.08 23.40 4.90 18.28 31.44 98.49 AMFMN-sim 5.21 14.72 21.57 4.08 17.00 30.60 93.18 GaLR 6.50 18.91 29.70 5.11 19.57 31.92 111.71 HVSA 7.47 20.62 32.11 5.51 21.13 34.13 120.97 OSDPM 8.39 22.20 33.21 6.59 22.92 36.67 129.98 表 2 与其他方法在RSITMD测试集上的检索性能比较(%)
图像→文本 文本→图像 Rsum 方法名称 R@1 R@5 R@10 R@1 R@5 R@10 VSE++ 10.38 27.65 39.60 7.79 24.87 38.67 148.96 SCAN t2i 10.18 28.53 38.49 10.10 28.98 43.53 159.81 SCAN i2t 11.06 25.88 39.38 9.82 29.38 42.12 157.64 CAMP-triplet 11.73 26.99 38.05 8.27 27.79 44.34 157.17 CAMP-bee 9.07 23.01 33.19 5.22 23.32 38.36 132.17 MTFN 10.40 27.65 36.28 9.96 31.37 45.84 161.50 LW-MCR(b) 9.07 22.79 38.05 6.11 27.74 49.56 153.32 LW-MCR(d) 10.18 28.98 39.82 7.79 30.18 49.78 166.73 AMFMN-soft 11.06 25.88 39.82 9.82 33.94 51.90 172.42 AMFMN-fusion 11.06 29.20 38.72 9.96 34.03 52.96 175.93 AMFMN-sim 10.63 24.78 41.81 11.51 34.69 54.87 178.29 GaLR 13.05 30.09 42.70 10.47 36.34 53.35 186.00 HVSA 13.20 32.08 45.58 11.43 39.20 57.45 198.94 OSDPM 14.68 35.10 49.48 11.68 39.38 57.45 207.77 表 3 所提出的OSDPM遥感图像文本检索模型在RSICD与RSITMD两组测试集上的消融实验(%)
数据集 CLIP DAPN OSFCM 图像→文本 文本→图像 Rsum R@1 R@5 R@10 R@1 R@5 R@10 RSICD √ 7.47 21.23 32.63 6.23 22.01 35.74 125.31 √ √ 8.23 21.32 32.72 6.29 22.18 36.26 127.01 √ √ √ 8.39 22.20 33.21 6.60 22.92 36.67 129.98 RSITMD √ 13.94 33.41 46.76 12.33 38.86 57.36 202.65 √ √ 15.49 34.14 47.05 12.53 38.68 56.40 204.28 √ √ √ 14.68 35.10 49.48 11.68 39.38 57.45 207.77 -
[1] SUDMANNS M, TIEDE D, LANG S, et al. Big earth data: Disruptive changes in Earth observation data management and analysis?[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2020, 13(7): 832–850. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2019.1585976. [2] ZHOU Weixun, NEWSAM S, LI Congmin, et al. PatternNet: A benchmark dataset for performance evaluation of remote sensing image retrieval[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2018, 145: 197–209. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.01.004. [3] 翁星星, 庞超, 许博文, 等. 面向遥感图像解译的增量深度学习[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(10): 3979–4001. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240172.WENG Xingxing, PANG Chao, XU Bowen, et al. Incremental deep learning for remote sensing image interpretation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(10): 3979–4001. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240172. [4] HUANG Jiaxiang, FENG Yong, ZHOU Mingliang, et al. Deep multiscale fine-grained hashing for remote sensing cross-modal retrieval[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 6002205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3351368. [5] 金澄, 弋步荣, 曾志昊, 等. 一种顾及空间语义的跨模态遥感影像检索技术[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2023, 18(4): 328–335,385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2023.04.005.JIN Cheng, YI Burong, ZENG Zhihao, et al. A cross-modal remote sensing image retrieval technique considering spatial semantics[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2023, 18(4): 328–335,385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2023.04.005. [6] 冯孝鑫, 王子健, 吴奇. 基于三元采样图卷积网络的半监督遥感图像检索[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 644–653. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211478.FENG Xiaoxin, WANG Zijian, and WU Qi. Semi-supervised learning remote sensing image retrieval method based on triplet sampling graph convolutional network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 644–653. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211478. [7] ZHAO Zuopeng, MIAO Xiaoran, HE Chen, et al. Masking-based cross-modal remote sensing image–text retrieval via dynamic contrastive learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5626215. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3406897. [8] WANG Fei, ZHU Xianzhang, LIU Xiaojian, et al. Scene graph-aware hierarchical fusion network for remote sensing image retrieval with text feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4705116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3404605. [9] 张若愚, 聂婕, 宋宁, 等. 基于布局化-语义联合表征遥感图文检索方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(2): 671–683. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0527.ZHANG Ruoyu, NIE Jie, SONG Ning, et al. Remote sensing image-text retrieval based on layout semantic joint representation[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(2): 671–683. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0527. [10] CHEN Yaxiong, HUANG Jinghao, LI Xiaoyu, et al. Multiscale salient alignment learning for remote-sensing image-text retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4700413. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3340870. [11] YANG Rui, WANG Shuang, HAN Yingping, et al. Transcending fusion: A multiscale alignment method for remote sensing image-text retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4709217 . doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3496898. [12] XU Yahui, BIN Yi, WEI Jiwei, et al. Align and retrieve: Composition and decomposition learning in image retrieval with text feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 9936–9948. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2024.3417694. [13] MA Qing, PAN Jiancheng, and BAI Cong. Direction-oriented visual-semantic embedding model for remote sensing image-text retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4704014. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3392779. [14] 钟金彦, 陈俊, 李宇, 等. 基于MFF-SFE的遥感图文跨模态检索方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报(中英文), 2025, 42(2): 236–247. doi: 10.7523/j.ucas.2024.025.ZHONG Jinyan, CHEN Jun, LI Yu, et al. Cross-modal retrieval method based on MFF-SFE for remote sensing image-text[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2025, 42(2): 236–247. doi: 10.7523/j.ucas.2024.025. [15] SUN Yuli, LEI Lin, LI Xiao, et al. Nonlocal patch similarity based heterogeneous remote sensing change detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 109: 107598. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107598. [16] ZHANG Shun, LI Yupeng, and MEI Shaohui. Exploring uni-modal feature learning on entities and relations for remote sensing cross-modal text-image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5626317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3333375. [17] ZHU Jingru, GUO Ya, SUN Geng, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing imagery with invariant domain-level prototype memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5603518. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3243042. [18] LIU Zejun, CHEN Fanglin, XU Jun, et al. Image-text retrieval with cross-modal semantic importance consistency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(5): 2465–2476. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3220297. [19] ZHUANG Jiamin, YU Jing, DING Yang, et al. Towards fast and accurate image-text retrieval with self-supervised fine-grained alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 1361–1372. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3280734. [20] YU Hongfeng, YAO Fanglong, LU Wanxuan, et al. Text-image matching for cross-modal remote sensing image retrieval via graph neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 812–824. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3231851. [21] ABDULLAH T, BAZI Y, AL RAHHAL M M, et al. TextRS: Deep bidirectional triplet network for matching text to remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(3): 405. doi: 10.3390/rs12030405. [22] TANG Xu, HUANG Dabiao, MA Jingjing, et al. Prior-experience-based vision-language model for remote sensing image-text retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5641913. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3464468. [23] YUAN Zhiqiang, ZHANG Wenkai, TIAN Changyuan, et al. Remote sensing cross-modal text-image retrieval based on global and local information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5620616. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3163706. [24] YUAN Zhiqiang, ZHANG Wenkai, FU Kun, et al. Exploring a fine-grained multiscale method for cross-modal remote sensing image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4404119. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3078451. [25] MI Li, DAI Xianjie, CASTILLO-NAVARRO J, et al. Knowledge-aware text-image retrieval for remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5646813. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3486977. [26] LU Xiaoqiang, WANG Binqiang, ZHENG Xiangtao, et al. Exploring models and data for remote sensing image caption generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 2183–2195. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2776321. [27] ZHANG Weihang, LI Jihao, LI Shuoke, et al. Hypersphere-based remote sensing cross-modal text–image retrieval via curriculum learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5621815. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3318227. [28] XU Xing, WANG Tan, YANG Yang, et al. Cross-modal attention with semantic consistence for image–text matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(12): 5412–5425. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2967597. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
