Research on Signal Detection of Adaptive O-OFDM Symbol Decomposition in Rough Set Information System
-
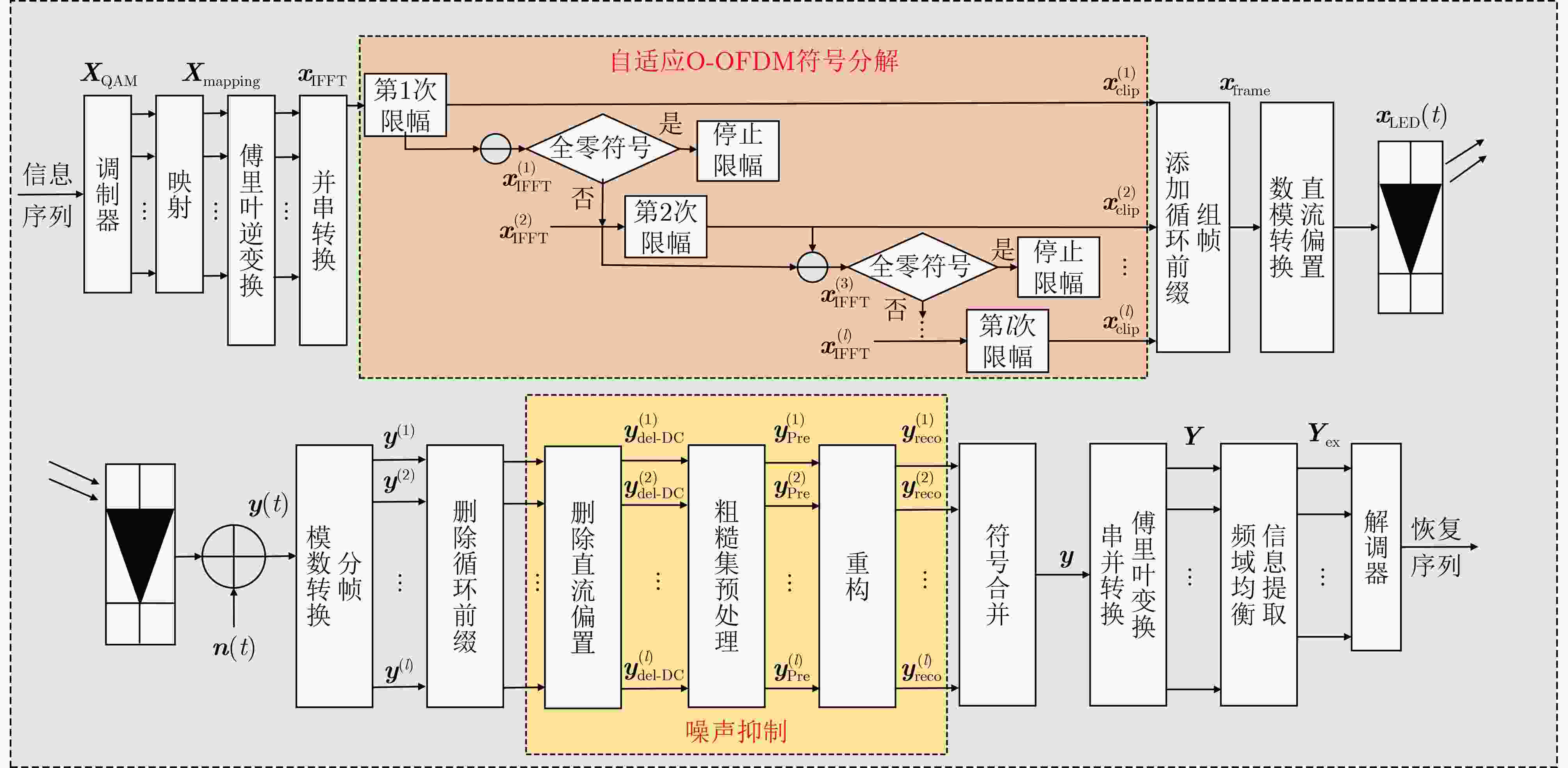
摘要: 自适应光正交频分复用符号分解串行传输(O-OFDM-ASDST)可以有效抑制可见光通信(VLC)中发光二极管(LED)的非线性限幅失真,然而,O-OFDM-ASDST在接收端合并分解符号时会导致加性高斯白噪声(AWGN)叠加,从而引起误码率(BER)恶化。为此,该文基于人工智能粒计算的粗糙集理论(RST)信息系统与不可分辨关系,提出一种O-OFDM-ASDST信号检测算法。首先,将接收端时域抽样值作为论域,并将信号特征作为条件属性构建信息系统。通过决策规则对接收的分解符号进行分类,尽可能分类决策出原本等于门限值和零值的时域抽样值;然后,根据制定的决策规则导出不可分辨关系,并通过属性约简提取处于门限值之间的时域抽样值并进行重构,以达到降低重构算法复杂度的目的;最后,采用蒙特卡罗仿真方法,验证检测算法的性能。结果表明,与对比信号检测算法相比,该文检测算法在房间中心位置的BER性能可获得5.4 dB和1 dB的信噪比(SNR)增益;即使在房间边缘位置,也可以获得5.5 dB和0.8 dB的SNR增益。此外,检测算法的复杂度仅为对比信号检测算法的1/10。综上所述,所提检测算法能够有效抑制AWGN,提高BER性能,并显著降低算法复杂度和处理时延。
-
关键词:
- 可见光通信 /
- O-OFDM符号分解 /
- 信号检测 /
- 粗糙集理论 /
- 属性约简
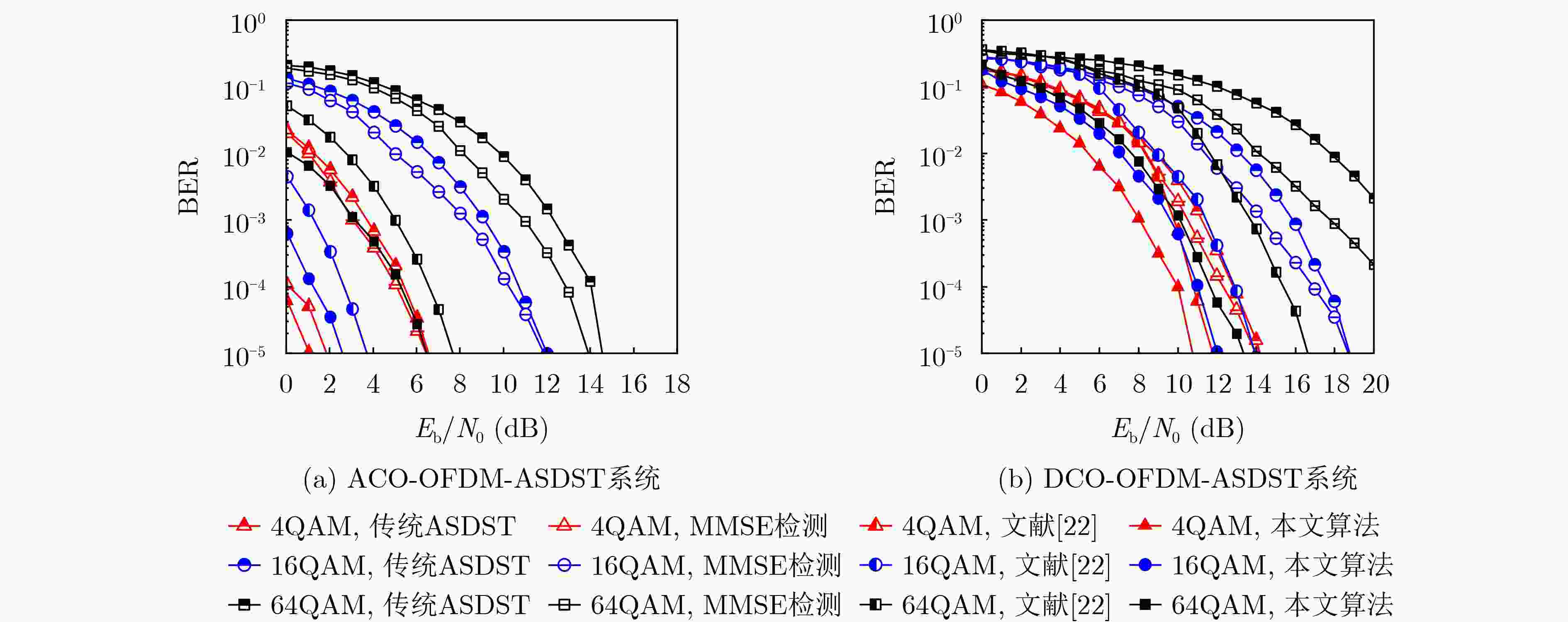
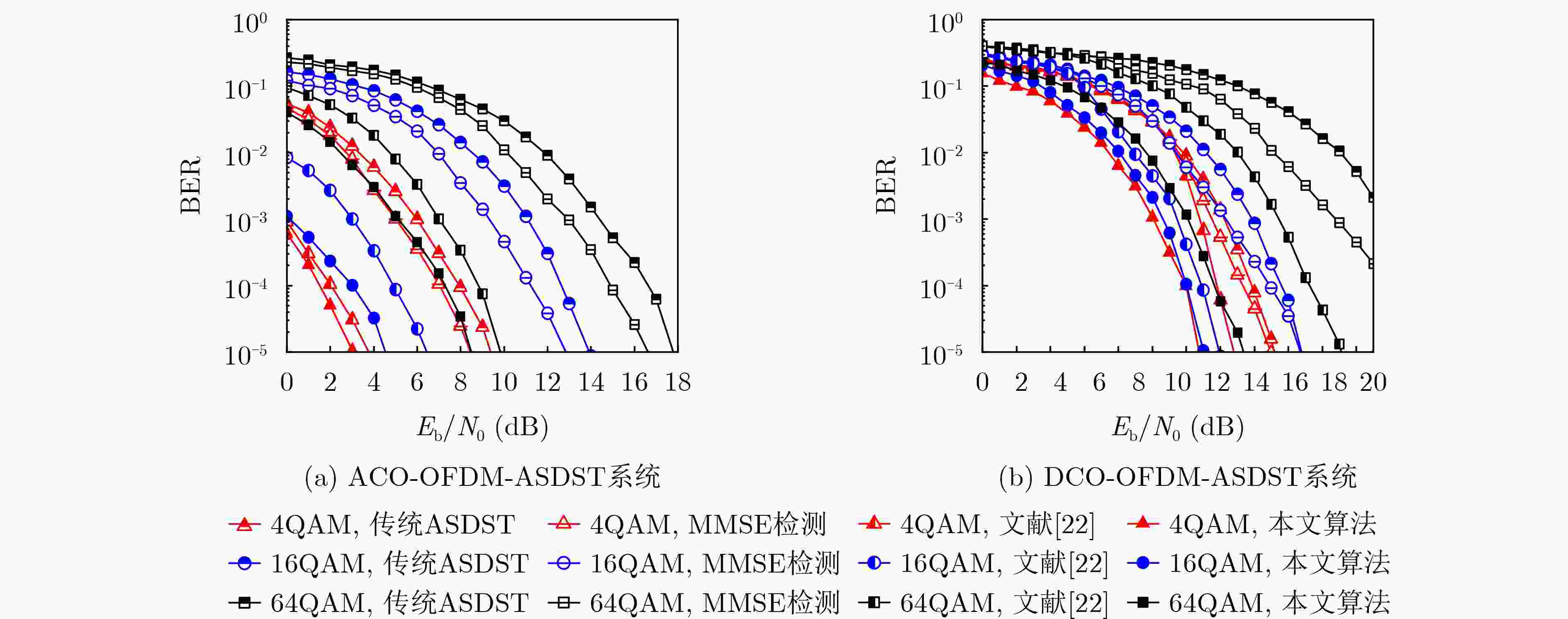
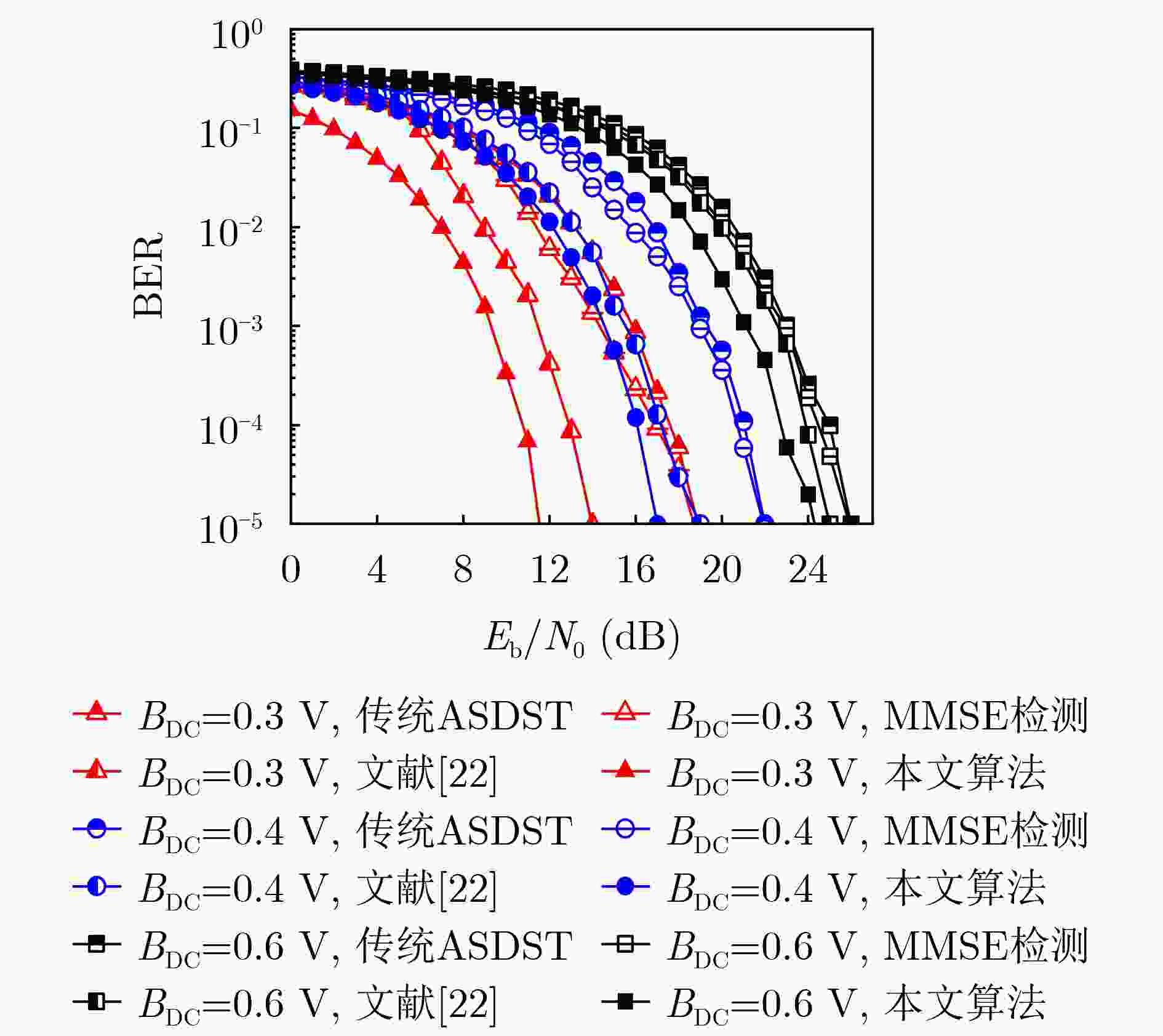
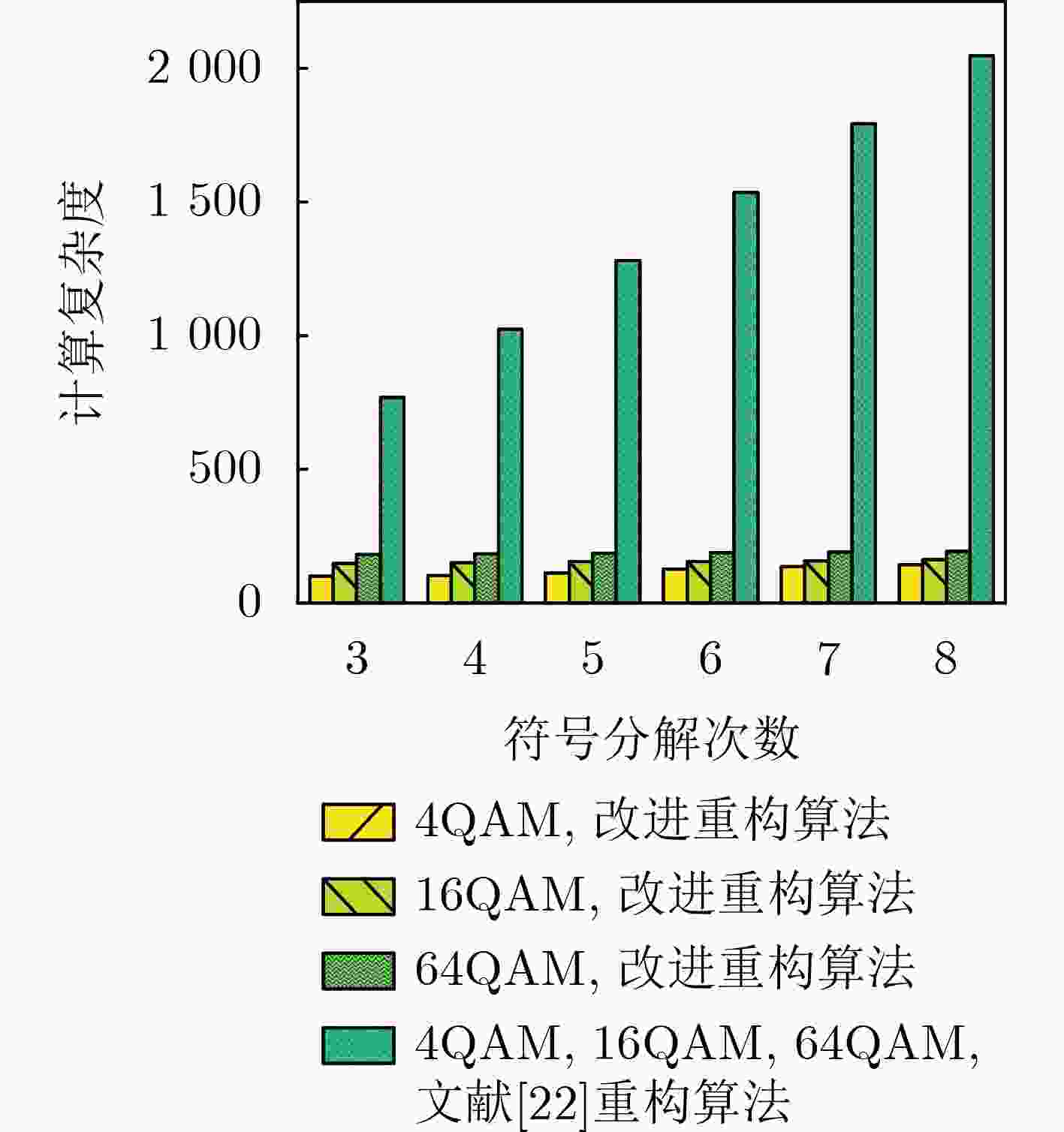
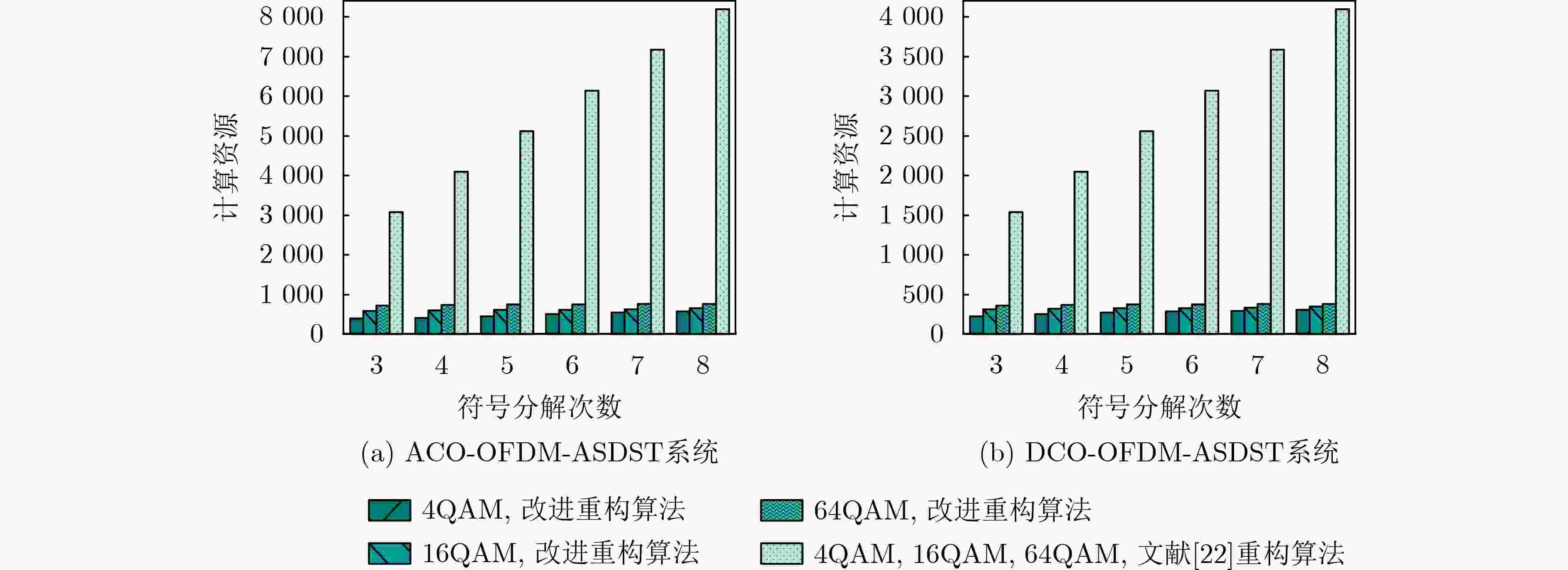
Abstract:Objective Adaptive Optical Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Symbol Decomposition with Serial Transmission (O-OFDM-ASDST) effectively suppresses the nonlinear clipping distortion of Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) in Visible Light Communication (VLC). However, incorporating decomposition symbols in the O-OFDM-ASDST system incorporates Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN), which degrades the Bit Error Rate (BER). To address this issue, this study proposes an O-OFDM-ASDST signal detection algorithm based on the Rough Set Theory (RST) information system and the indiscernibility relation of artificial intelligence particle computing. Methods An O-OFDM-ASDST signal detection algorithm is proposed based on the RST information system and the indiscernibility relation of artificial intelligence particle computing. The algorithm consists of two stages: RST preprocessing and attribute reduction reconstruction. In the first stage, the RST information system is constructed by using preprocessed time-domain sampled values as theoretical domain data. The signal characteristics of these sampled values are converted into symbolic attributes, serving as the conditional attributes of the RST information system, while the upper and lower amplitude thresholds are designated as decision attributes. The RST attribute dependence formula, combined with an attribute importance-based addition and deletion method, is applied to establish decision rules and classify the information system. In the second stage, the indiscernibility relation is derived from the decision rules, and attribute reduction is performed on the constructed information system. This reduction process is applied to the time-domain sampled values within the upper and lower thresholds, followed by reconstruction. Results and Discussions The performance of the proposed detection algorithm is verified using the Monte Carlo simulation method. The results demonstrate that this algorithm effectively suppresses AWGN at the O-OFDM-ASDST receiver, enhances BER performance, and significantly reduces computational complexity and processing delay. For instance, when the PhotoDetector (PD) is positioned at the center of the room [3,3,0.85], the ACO-OFDM-ASDST system achieves Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) gains of approximately 1 dB and 1.2 dB under 4QAM and 16QAM modulation, respectively, at a BER of 10–5. The DCO-OFDM-ASDST system achieves SNR gains of approximately 1 dB and 2 dB under the same conditions ( Fig. 7 ). Similarly, when the PD is located at the edge of the room [0.5,0.5,0.85], the ACO-OFDM-ASDST system achieves SNR gains of approximately 0.8 dB and 1.1 dB for 4QAM and 16QAM, respectively, at a BER of 10–5, while the DCO-OFDM-ASDST system achieves SNR gains of approximately 2.5 dB and 3.2 dB (Fig. 8 ). The proposed detection algorithm also maintains favorable BER performance under different DC bias levels. For example, under 16QAM modulation with DC bias values of 0.3 V, 0.4 V, and 0.6 V, the DCO-OFDM-ASDST system achieves SNR gains of approximately 2.2 dB, 2 dB, and 0.8 dB, respectively, at a BER of 10–5 (Fig. 9 ). Furthermore, the complexity of the proposed detection algorithm in the ACO-OFDM-ASDST system is only one-tenth that of the contrast signal detection algorithm (Fig. 12 ). As the number of symbol decompositions increases, the proposed algorithm requires fewer computing resources compared to the contrast detection algorithm. For instance, in the ACO-OFDM-ASDST system with 4QAM, 16QAM, and 64QAM modulation, when the number of symbol decompositions is 4, the computational resources required by the contrast detection algorithm amount to4096 , whereas those required by the proposed detection algorithm are 408, 600, and 736, respectively. This corresponds to reductions in computational resource consumption by factors of 1/10, 1/7, and 1/6, respectively (Fig. 13 ). Additionally, the proposed detection algorithm exhibits lower processing latency.Conclusions The O-OFDM-ASDST signal detection algorithm is implemented using the RST information system and the indiscernibility relation, effectively suppressing AWGN in decomposed symbols. The simulation results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, demonstrating superior BER performance compared to other signal detection methods. Notably, high BER performance is maintained even at the room’s edge, highlighting the algorithm’s reliability, coverage, and robustness. Additionally, the proposed algorithm exhibits low complexity and reduced processing delay. It not only mitigates LED nonlinear distortion but also effectively suppresses AWGN in decomposition symbols, thereby enhancing BER transmission performance and improving the overall O-OFDM system performance. -
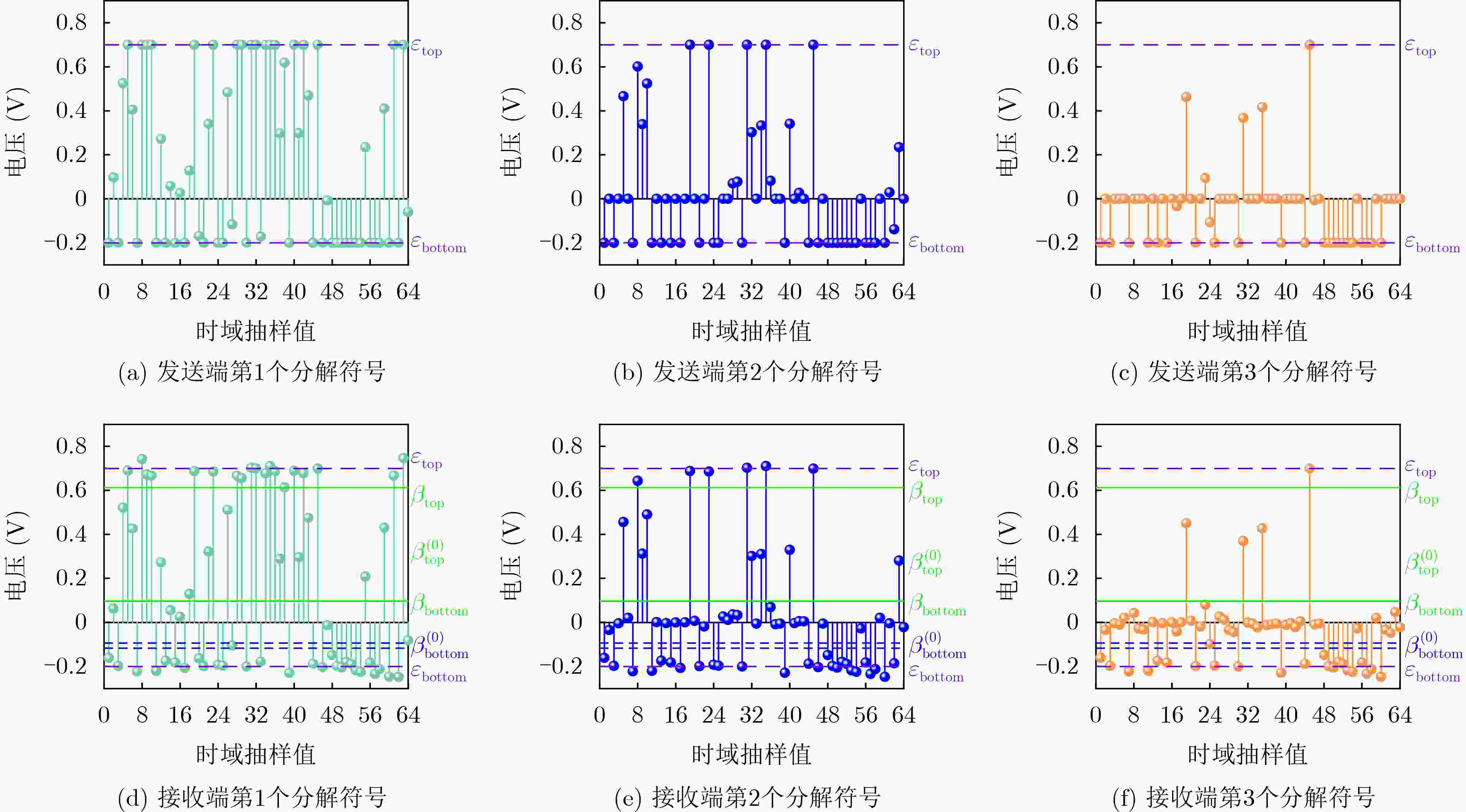
表 1 ACO-OFDM-ASDST信息系统
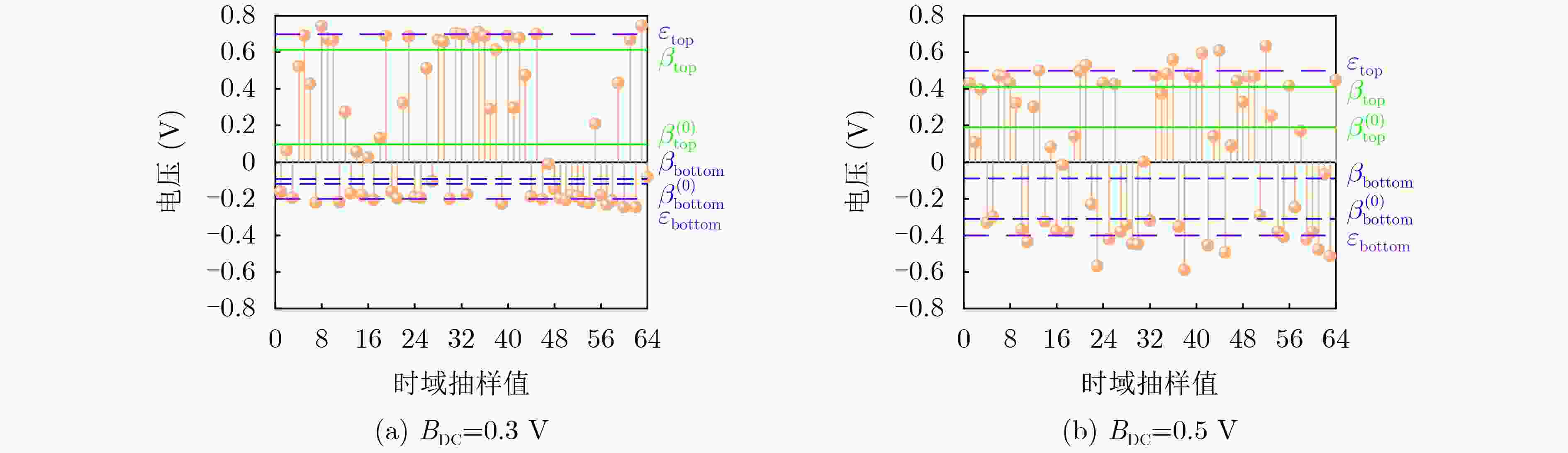
符号时域抽样值 条件属性C 决策属性D U 1 2 3 ${\varepsilon _{{\text{top}}}}$ ${\varepsilon _{{\text{bottom}}}}$ $ {\varepsilon _{{\text{bottom}}}} < {\boldsymbol y}_{{\text{del-DC}}}^{\left( i \right)}\left( k \right) < {\varepsilon _{{\text{top}}}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol y}_{{\text{del-DC}}}^{\left( 1\right)}\left( k \right)} $ Y N N T F F ${{\boldsymbol y}_{{\text{del-DC}}}^{\left( 2\right)}\left( k \right)} $ N Y N F T F ${{\boldsymbol y}_{{\text{del-DC}}}^{\left( 3\right)}\left( k \right)} $ N
NY
NN
YF
FT
FF
T${{\boldsymbol y}_{{\text{del-DC}}}^{\left( 3\right)}\left( k \right)} $ … …
Y…
N…
N…
T…
F…
F${{\boldsymbol y}_{{\text{del-DC}}}^{\left( l\right)}\left( k \right)} $ 表 2 ACO-OFDM-ASDST与DCO-OFDM-ASDST决策规则
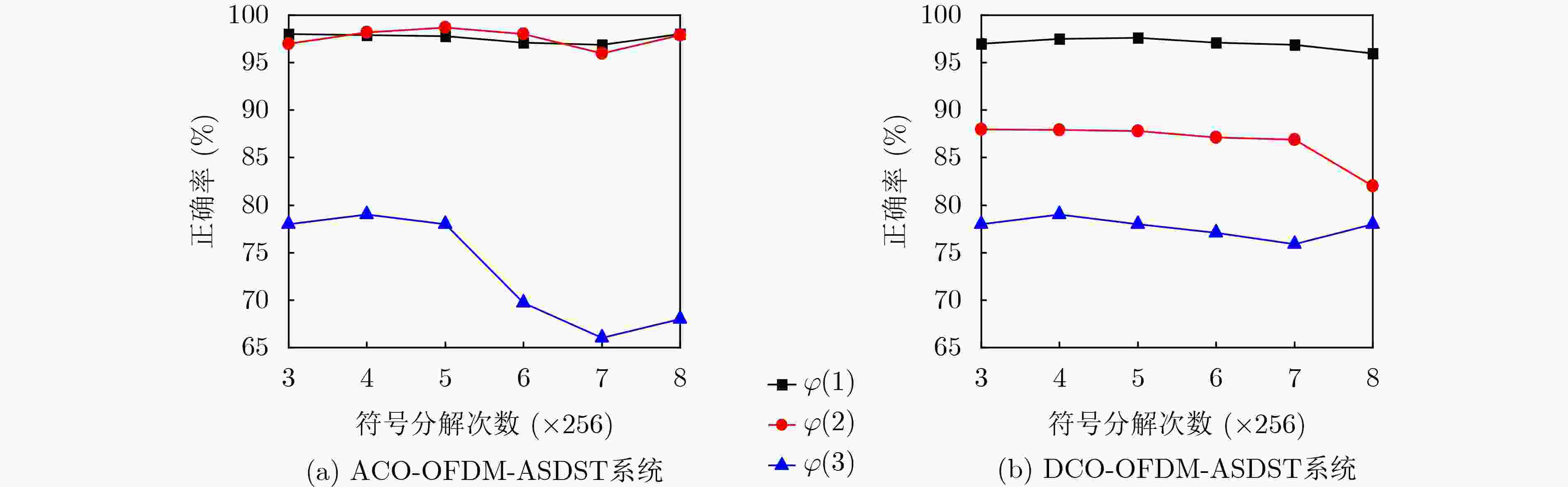
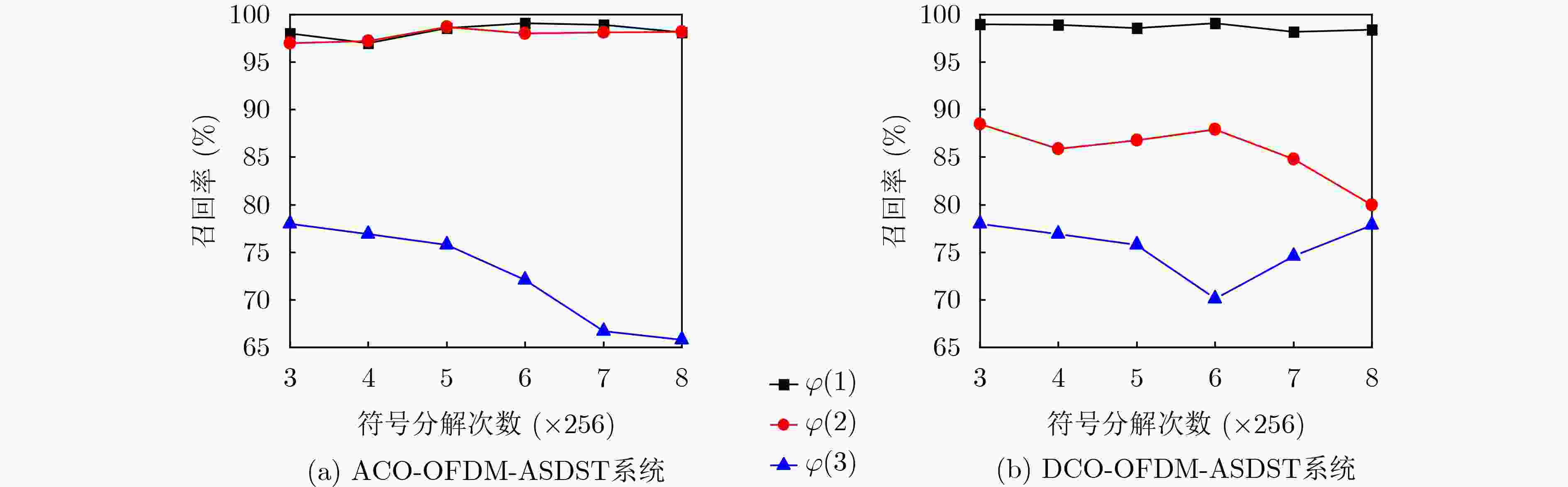
$\varphi \left( n \right)$ 决策规则 O-OFDM-ASDST ACO-OFDM-ASDST DCO-OFDM-ASDST $\varphi \left( 1 \right)$ ${\phi _1}:\left( {1 = Y} \right) \wedge \left( {2 = N} \right),{\phi _2}:\left( {2 = Y} \right) \wedge \left( {1 = N} \right)$ ${\phi _1}:\left( {1 = Y} \right) \wedge \left( {2 = N} \right)$,${\phi _2}:\left( {2 = Y} \right) \wedge \left( {1 = N} \right)$,${\phi _3}:\left( {3 = Y} \right) \wedge \left( {2 = N} \right)$ $\varphi \left( 2 \right)$ ${\phi _1}:\left( {1 = Y} \right) \vee \left( {2 = Y} \right),{\phi _2}:\left( {2 = Y} \right) \vee \left( {1 = Y} \right)$ ${\phi _1}:\left( {1 = Y} \right) \vee \left( {2 = Y} \right)$,${\phi _2}:\left( {2 = Y} \right) \vee \left( {1 = Y} \right)$,
${\phi _3}:\left( {3 = Y} \right) \vee \left( {2 = Y} \right)$$\varphi \left( 3 \right)$ ${\phi _1}:\left( {1 = N} \right) \wedge \left( {2 = N} \right),{\phi _2}:\left( {2 = N} \right) \wedge \left( {1 = N} \right)$ ${\phi _1}:\left( {1 = N} \right) \wedge \left( {2 = N} \right)$,${\phi _2}:\left( {2 = N} \right) \wedge \left( {1 = N} \right)$,
${\phi _3}:\left( {3 = N} \right) \wedge \left( {2 = N} \right)$表 3 仿真参数
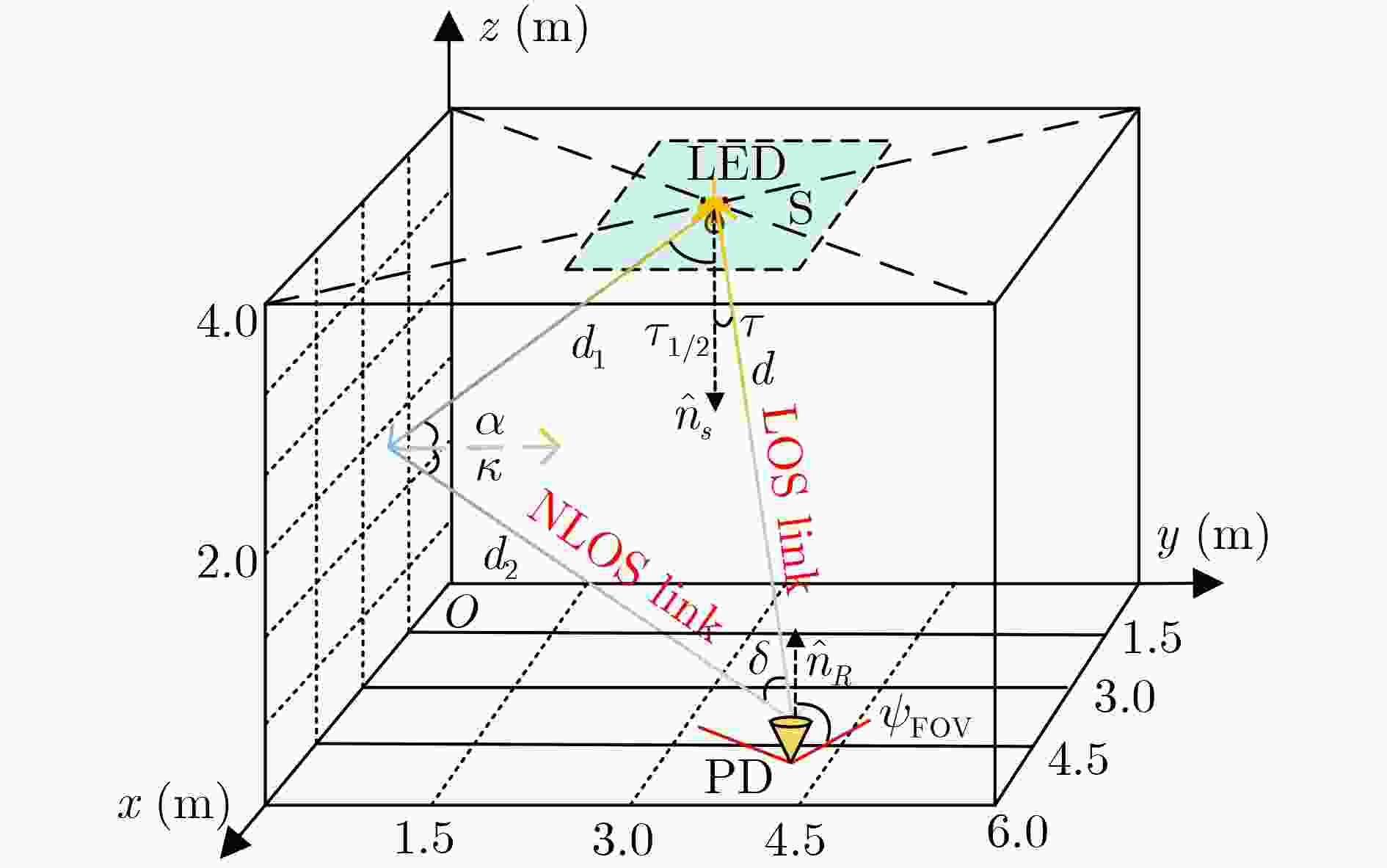
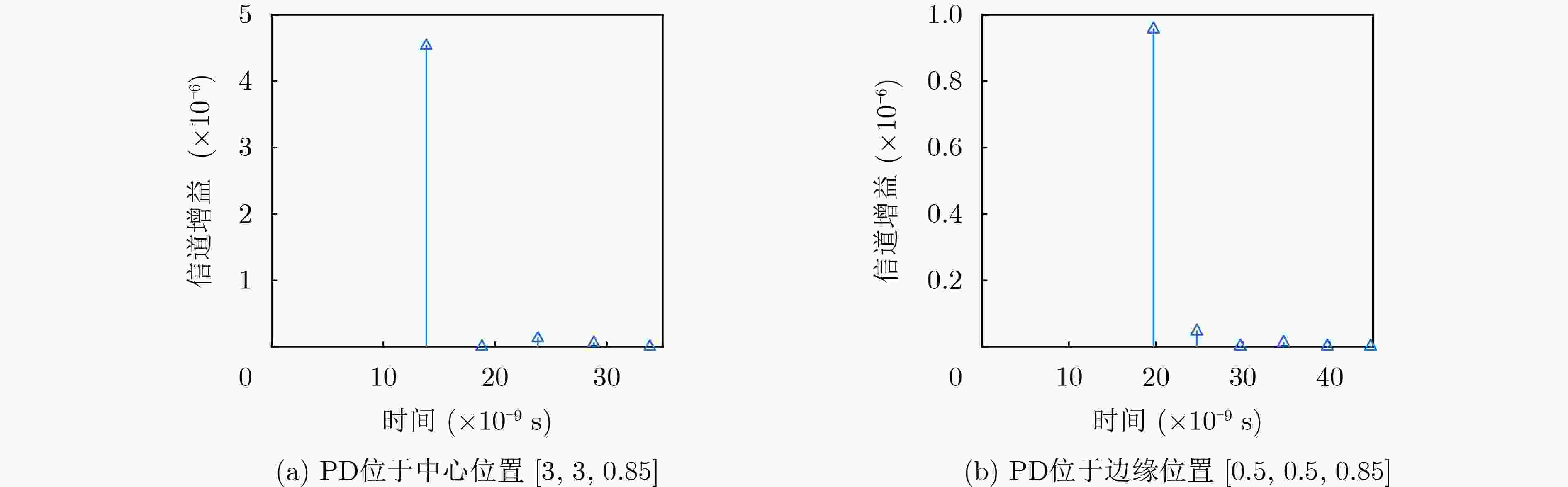
参数 值 LED位置坐标[x, y, z] (m) [3,3,3.5] PD位置坐标[x, y, z] (m) [3,3,0.85] / [0.5,0.5,0.85] PD视场角${\psi _{{\text{FOV}}}}$ (°) 70 LED半功率角${\tau _{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. } 2}}}$ (°) 60 PD的面积AR (cm2) 1 墙面反射率${\rho _i}$ 0.8 反射单元面积$ \Delta A $ (m2) 0.01 表 4 不同重构算法复杂度
算法 复杂度 文献[22]重构算法 $ O\left( {l \times {N_{\text{S}}}} \right) $ 改进重构算法 $ O\left( {N_{\text{S}}^{\left( 1 \right)} + N_{\text{S}}^{\left( 2 \right)} + \cdots + N_S^{\left( l \right)}} \right) $ 表 5 ACO-OFDM-ASDST与DCO-OFDM-ASDST系统实值计算资源
O-OFDM-ASDST系统 文献[22]重构算法 改进重构算法 ACO-OFDM-ASDST系统 $O\left( {4\left( {l \times {N_{\text{S}}}} \right)} \right)$ $O\left( {4N_{\text{S}}^{\left( l \right)}} \right)$ DCO-OFDM-ASDST系统 $O\left( {2\left( {l \times {N_{\text{S}}}} \right)} \right)$ $O\left( {2N_{\text{S}}^{\left( l \right)}} \right)$ -
[1] YANG Ping, XIAO Yue, XIAO Ming, et al. 6G wireless communications: Vision and potential techniques[J]. IEEE Network, 2019, 33(4): 70–75. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2019.1800418. [2] 王铠尧, 洪智勇, 曾志强. 可见光通信系统的符号定时偏移估计方法[J]. 光学学报, 2022, 42(7): 0706007. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0706007.WANG Kaiyao, HONG Zhiyong, and ZENG Zhiqiang. Symbol timing offset estimation method for visible light communication systems[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(7): 0706007. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0706007. [3] SEJAN M A S, RAHMAN M H, AZIZ M A, et al. A comprehensive survey on MIMO visible light communication: Current research, machine learning and future trends[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(2): 739. doi: 10.3390/s23020739. [4] PRASHANT D, VIPUL D, and ATUI K. A survey on visible light communication for 6G: Architecture, application and challenges[C]. 2023 International Conference on Computer, Electronics & Electrical Engineering & Their Applications (IC2E3), Srinagar Garhwal, India, 2023: 1–6. DOI: 10.1109/IC2E357697.2023.10262462. [5] 杨彦兵, 胡超, 鲁邦彦, 等. 基于可见光和射频融合的通信定位一体化系统[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(12): 146–157. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023230.YANG Yanbing, HU Chao, LU Bangyan, et al. Integrated communication and positioning system enabled by fusing visible light and RF[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(12): 146–157. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023230. [6] DIMITROV S and HAAS H. Information rate of OFDM-based optical wireless communication systems with nonlinear distortion[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2013, 31(6): 918–929. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2012.2236642. [7] ELGALA H, MESLEH R, and HAAS H. Non-linearity effects and predistortion in optical OFDM wireless transmission using LEDs[J]. International Journal of Ultra Wideband Communications and Systems, 2009, 1(2): 143–150. doi: 10.1504/IJUWBCS.2009.029003. [8] GREEN R J, JOSHI H, HIGGINS M D, et al. Recent developments in indoor optical wireless systems[J]. IET Communications, 2008, 2(1): 3–10. doi: 10.1049/iet-com:20060475. [9] 方智敬, 陈媛, 王俊杰. 改进的可见光通信系统PTS峰均比抑制方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(7): 2509–2514. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.07.33.FANG Zhijing, CHEN Yuan, and WANG Junjie. Improved PTS peak-to-average ratio suppression method in visible light communication system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(7): 2509–2514. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.07.33. [10] 吴让仲, 刘珂, 周峰, 等. 结合PWC技术的LED室内定位算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(5): 7–12. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.210502.WU Rangzhong, LIU Ke, ZHOU Feng, et al. LED based indoor positioning algorithm combined with PWC[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(5): 7–12. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.210502. [11] YING Kai, YU Zhenhua, BAXLEY R J, et al. Nonlinear distortion mitigation in visible light communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(2): 36–45. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2015.7096283. [12] 张雨桐, 赵黎, 张峰. 基于小波变换的可见光OFDM通信系统性能优化[J]. 激光技术, 2020, 44(2): 261–265. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2020.02.022.ZHANG Yutong, ZHAO Li, and ZHANG Feng. Performance optimization of visible light OFDM communication system based on wavelet transform[J]. Laser Technology, 2020, 44(2): 261–265. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2020.02.022. [13] LI Jianfeng, LIU Xiaoshuang, REN Yahao, et al. Single-FFT receiver with pairwise maximum likelihood for layered ACO-OFDM[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2021, 13(4): 7300906. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2021.3105812. [14] NIWAREEBA R, COX M A, and CHENG Ling. PAPR reduction in optical OFDM using lexicographical permutations with low complexity[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 1706–1713. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3138193. [15] ZENHOM Y A, HAMAD E K I, and ELNABAWY M M. Throughput improvement in ACO-OFDM-based VLC systems using noise cancellation and precoding techniques[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2024, 56(11): 1798. doi: 10.1007/s11082-024-07592-0. [16] XU Xianying, ZHANG Qi, and YUE Dianwu. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing with index modulation based on discrete hartley transform in visible light communications[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2022, 14(3): 7330310. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2022.3174283. [17] DEEPA T, SUSEELA V, and MANI V V. Performance analysis of novel precoding matrix techniques for optical OFDM-based visible light communication systems[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2022, 154: 108293. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108293. [18] CINEMRE I, AYDIN V, and HACIOGLU G. Papr reduction through Gaussian pre-coding in DCO-OFDM systems[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2024, 56(6): 958. doi: 10.1007/s11082-024-06911-9. [19] MESLEH R. LED clipping distortion compensation in optical wireless communication via multiple transmit LEDs[J]. Photonic Network Communications, 2013, 26(1): 25–31. doi: 10.1007/s11107-013-0406-2. [20] 贾科军, 杨博然, 陆皓, 等. 可见光通信光正交频分复用系统符号分解技术抑制LED非线性失真研究[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(4): 0406002. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0406002.JIA Kejun, YANG Boran, LU Hao, et al. LED nonlinearity mitigation for visible light communication optical-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system with symbol decomposing techniques[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(4): 0406002. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0406002. [21] 贾科军, 杨博然, 曹明华, 等. 可见光通信自适应O-OFDM符号分解串行传输系统设计与研究[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(9): 179–189. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020179.JIA Kejun, YANG Boran, CAO Minghua, et al. Design and research of adaptive O-OFDM symbol decomposing with serial transmission system in visible light communication[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(9): 179–189. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020179. [22] 贾科军, 秦翠翠, 蔺莹, 等. 一种自适应O-OFDM符号分解串行传输系统接收机设计[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(7): 1741–1749. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220248.JIA Kejun, QIN Cuicui, LIN Ying, et al. A receiver design for adaptive O-OFDM symbol decomposition serial transmission system[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(7): 1741–1749. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220248. [23] 王国胤, 姚一豫, 于洪. 粗糙集理论与应用研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2009, 32(7): 1229–1246. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2009.01229.WANG Guoyin, YAO Yiyu, and YU Hong. A survey on rough set theory and applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2009, 32(7): 1229–1246. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2009.01229. [24] DIMITROV S, SINANOVIC S, and HAAS H. Double-sided signal clipping in ACO-OFDM wireless communication systems[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kyoto, Japan, 2011: 1–5. DOI: 10.1109/icc.2011.5962752. [25] 董威. 粗糙集理论及其数据挖掘应用[M]. 沈阳: 东北大学出版社, 2014.DONG Wei. Rough Set Theory and Data Mining Applications[M]. Shenyang: Northeastern University Press, 2014. [26] 官礼和. 基于粗糙集理论的不完备信息处理方法研究[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 21(4): 461–466. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2009.04.003.GUAN Lihe. Processing incomplete information methods based on rough set[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications(Natural Science Edition), 2009, 21(4): 461–466. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2009.04.003. [27] 王晓艳, 张楠. 改进粗糙集理论的无线传感器网络静态节点分类算法[J]. 传感技术学报, 2023, 36(8): 1310–1315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2023.08.019.WANG Xiaoyan and ZHANG Nan. Static node classification algorithm based on improved rough set theory in wireless sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2023, 36(8): 1310–1315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2023.08.019. [28] 贾科军, 郝莉, 余彩虹. 室内可见光通信多径信道建模及MIMO-ACO-OFDM系统性能分析[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(7): 0706005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0706005.JIA Kejun, HAO Li, and YU Caihong. Modeling of multipath channel and performance analysis of MIMO-ACO-OFDM system for indoor visible light communications[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(7): 0706005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0706005. [29] 陈泉润, 张涛. 室内可见光通信系统的光源布局优化及性能分析[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(4): 0406003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0406003.CHEN Quanrun and ZHANG Tao. Light source layout optimization and performance analysis of indoor visible light communication system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(4): 0406003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0406003. [30] 李宝龙, 施建锋, 吴勤勤, 等. 可见光通信中融合VOOK和分层OFDM的高效频谱混合调制方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2639–2648. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220368.LI Baolong, SHI Jianfeng, WU Qinqin, et al. Spectrum-efficient hybrid modulation based on VOOK and layered OFDM for visible light communications[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2639–2648. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220368. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
