A Convert Communication Scheme of Blockchain Based on Image Multilevel Steganography Embedding
-
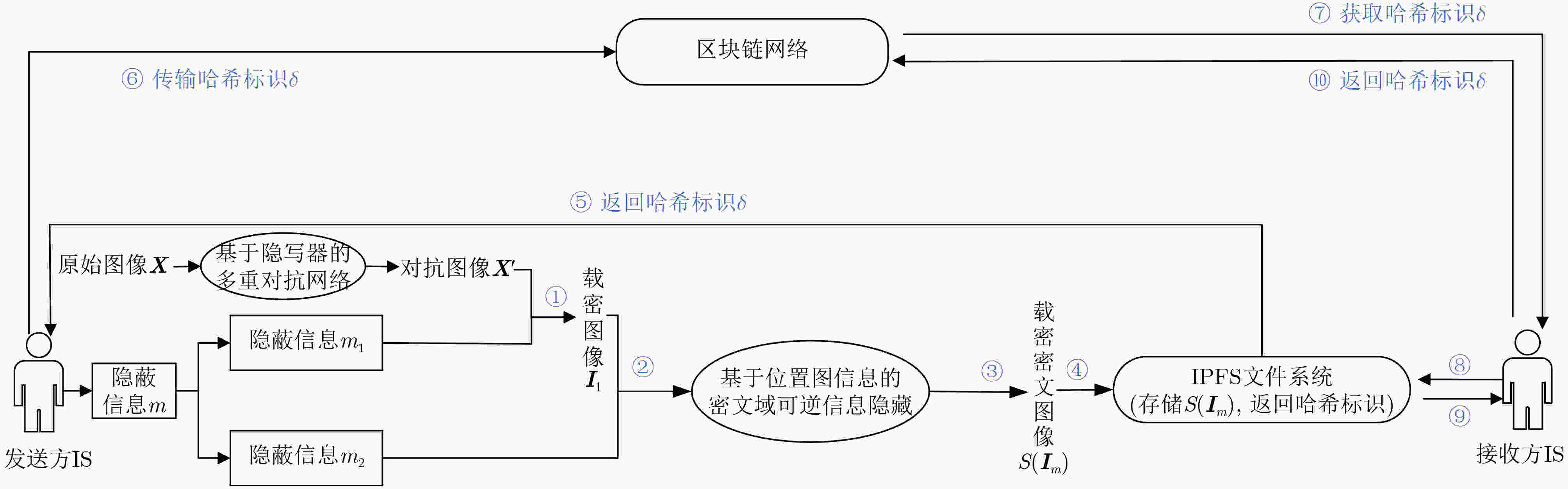
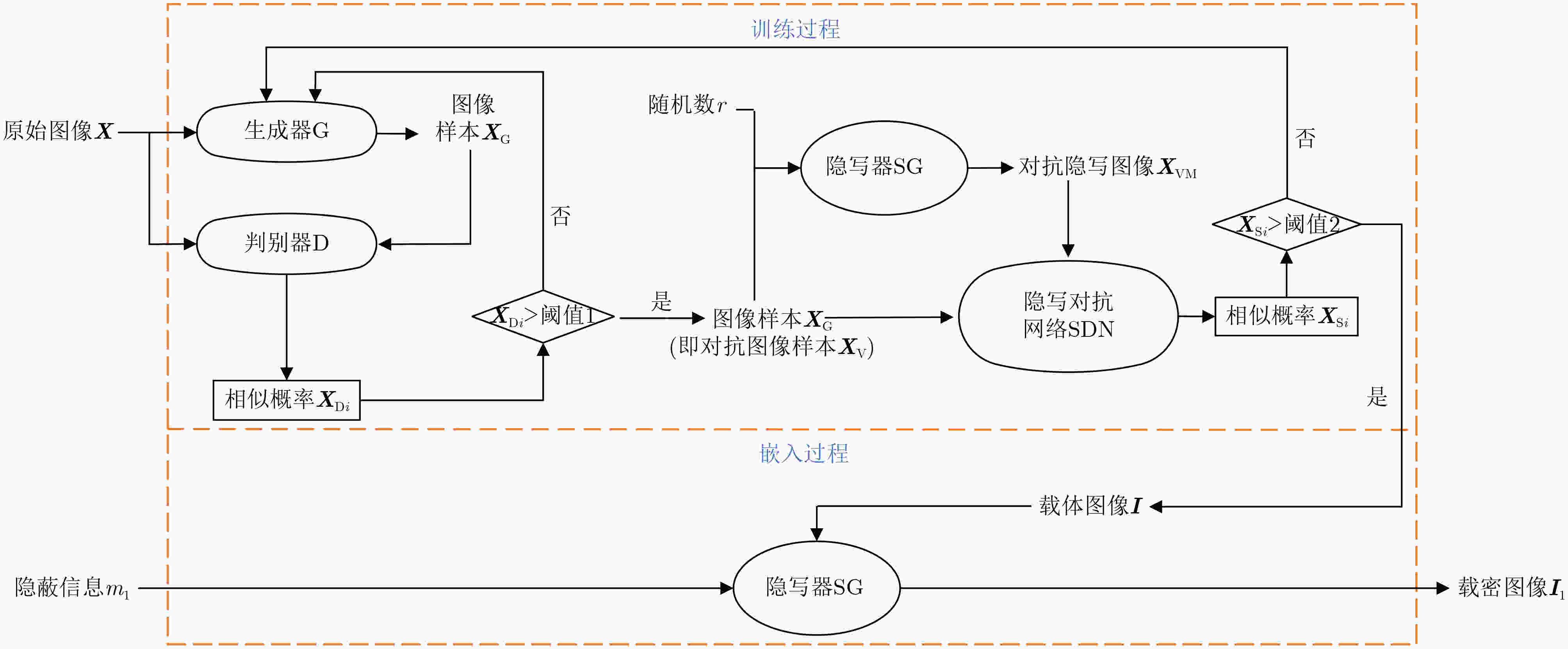
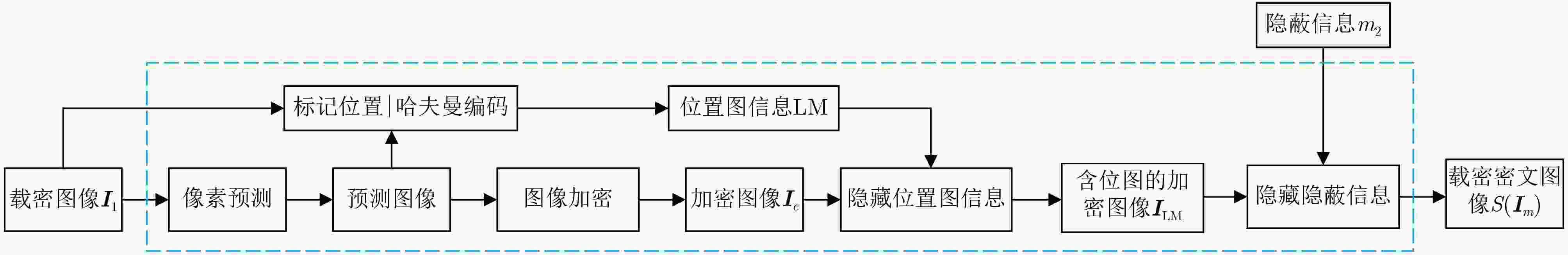
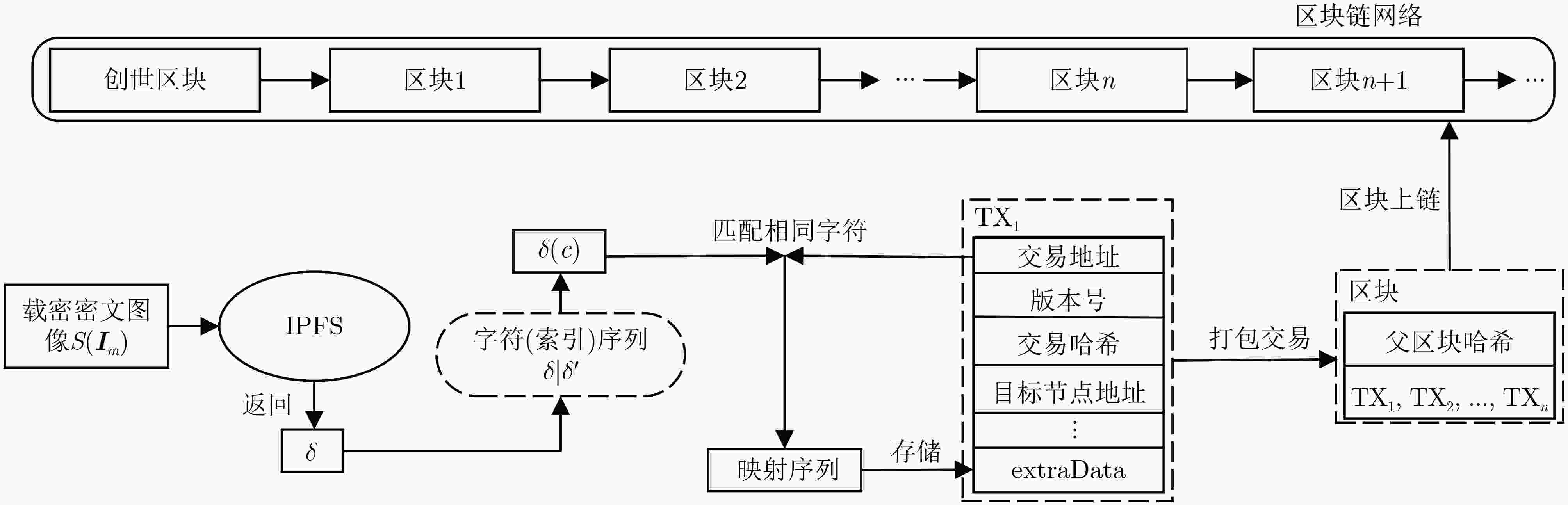
摘要: 针对现有基于图像隐写的区块链隐蔽通信方案利用传统深度学习方法面临的抗隐写分析能力低、信息嵌入率低及信息泄露等问题,该文提出一种基于图像多重隐写嵌入的隐蔽通信方案。首先,构造基于隐写器的多重对抗网络,通过生成对抗网络和隐写分析对抗网络的对抗迭代训练,生成更适合信息隐写的载密图像;其次,利用基于位置图信息的密文域可逆信息隐藏方法,将隐蔽信息嵌入至载密图像,生成含完整隐蔽信息的载密密文图像;最后,将载密密文图像存储至IPFS文件返回唯一标识,利用地址映射的方法将该标识存储至区块链网络中实现隐蔽传输。理论及实验结果表明,相较于传统基于深度学习的区块链隐蔽通信方案,该方案具备更强的抗隐写检测攻击能力和更高的信息嵌入容量,同时减少了通信时延。Abstract:
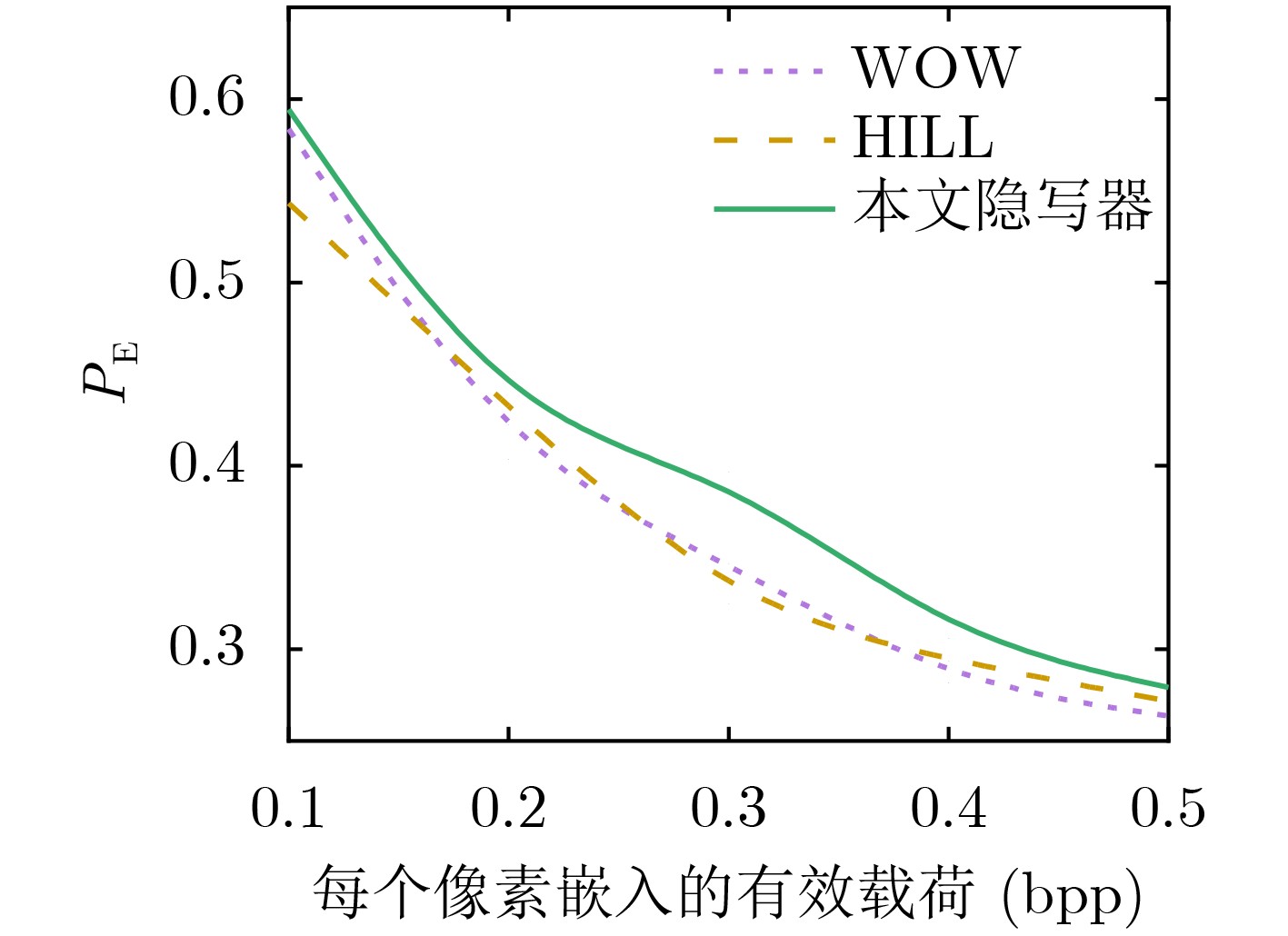
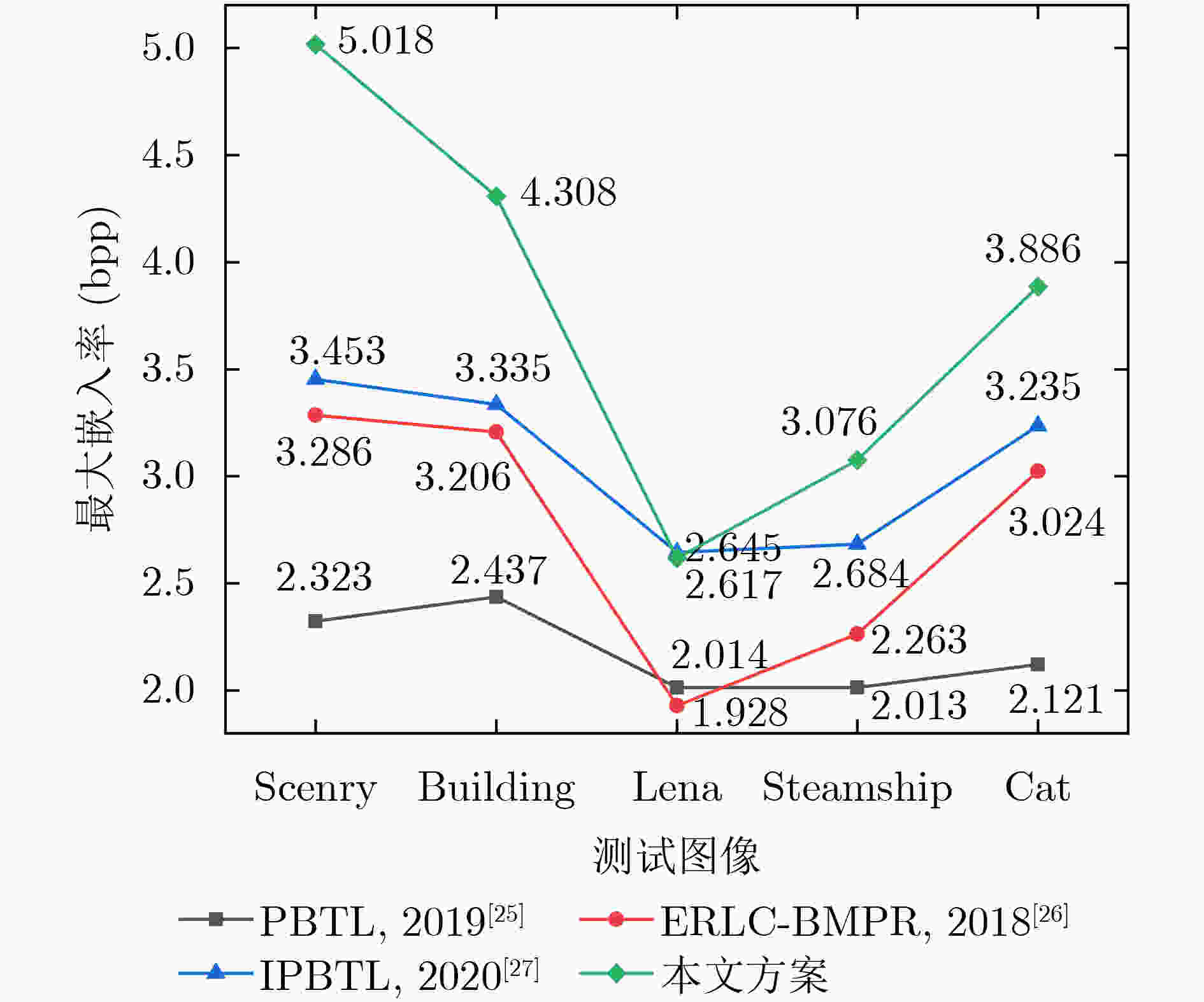
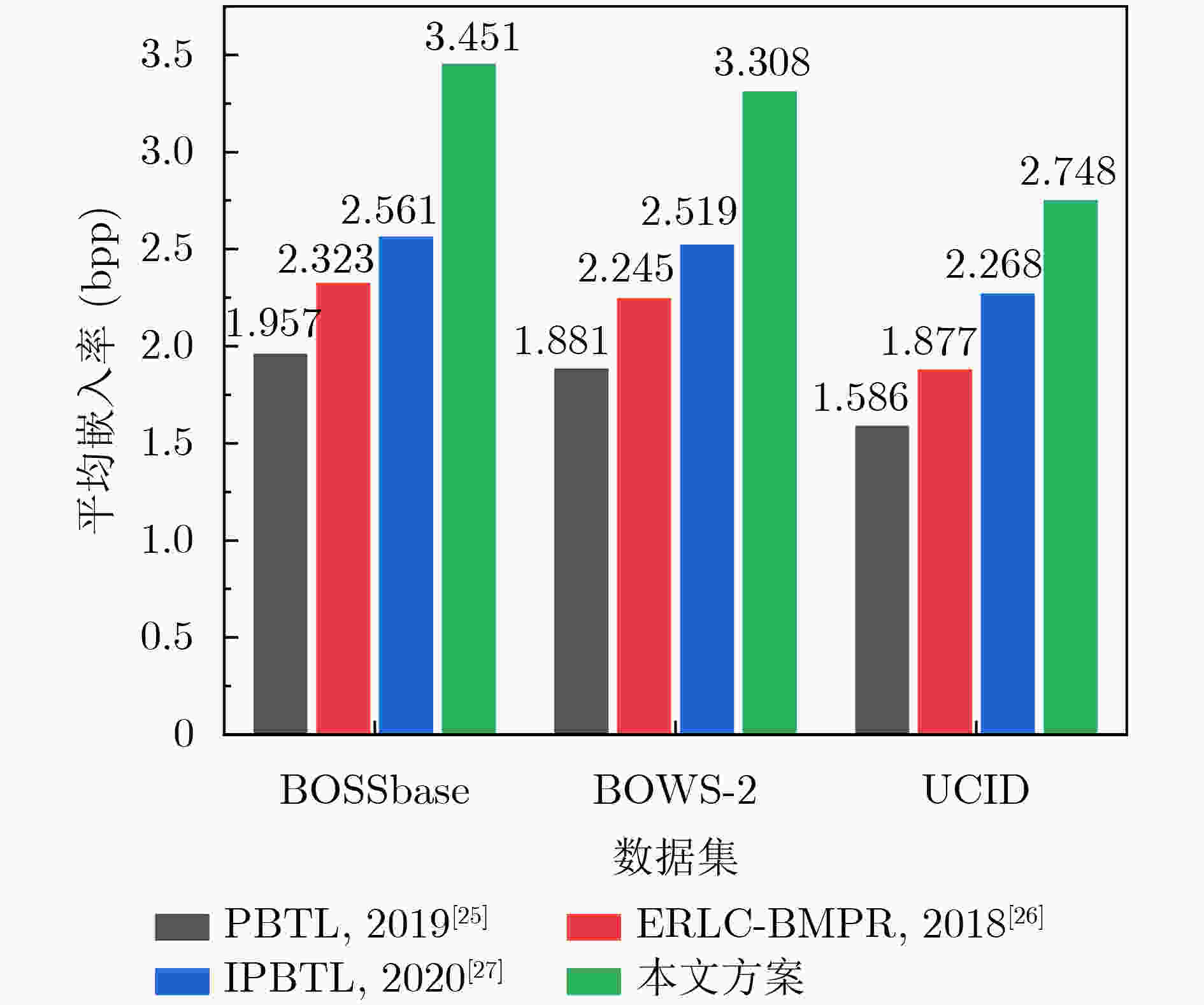
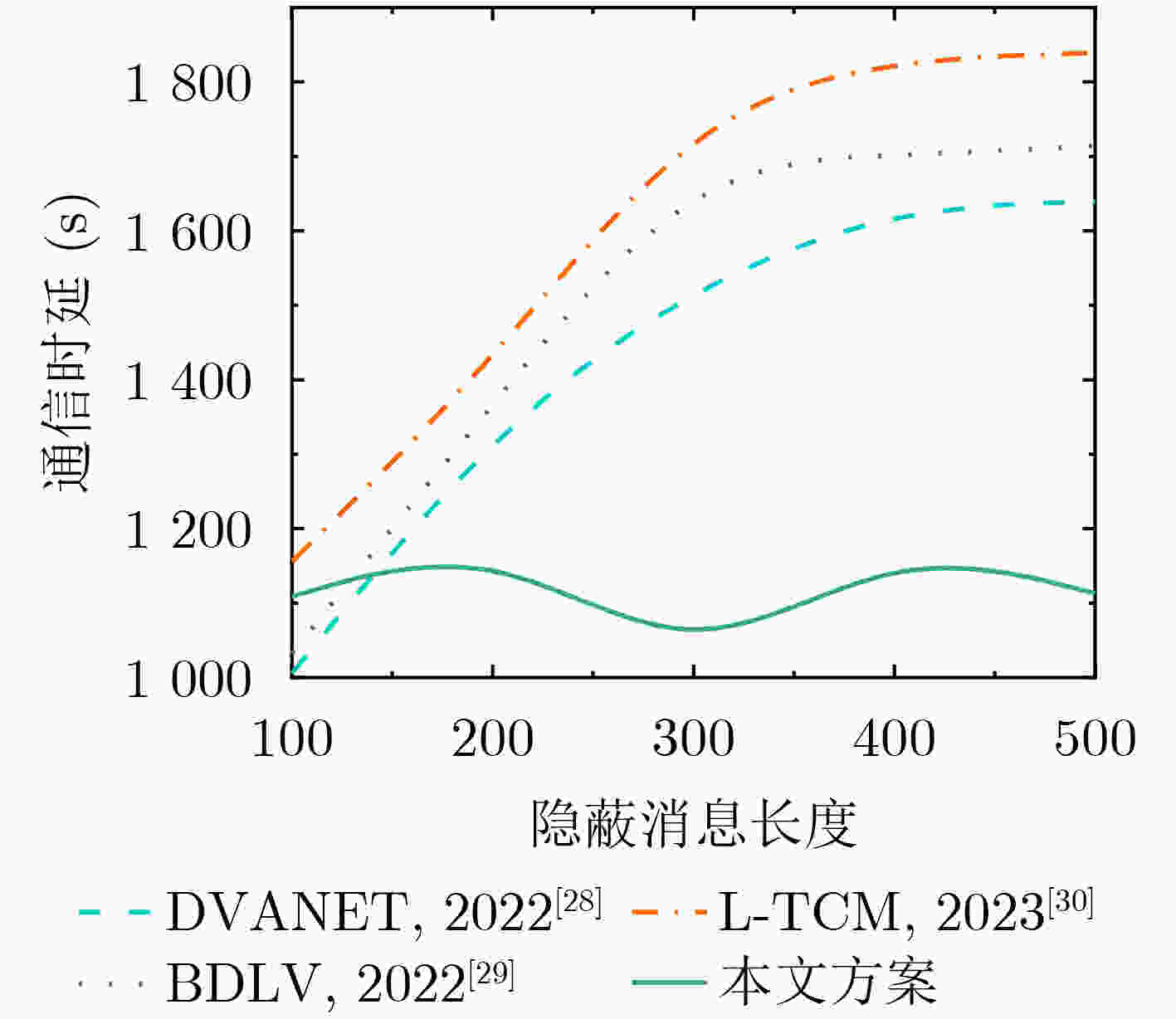
Objective With the advancement of information technology, information security concerns have become increasingly significant, making covert communication technology a critical area of focus. Existing schemes face limitations regarding embedding rate, anti-detection, and communication efficiency. To address these issues, steganographic embedding methods based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have gained considerable attention. This study utilizes the iterative training of GAN and steganalysis adversarial networks to generate stego-images with enhanced anti-detection capabilities. This approach aims to meet the concealment requirements for secure information transmission, while also improving the communication efficiency and security of the information exchange. Methods This study proposes a blockchain-based covert communication scheme utilizing image multilevel steganography. First, a multiple adversarial network for steganography is constructed, generating stego-images with enhanced anti-detection capabilities through the adversarial iterative training of GAN and steganalysis adversarial networks. Next, a reversible data hiding method in the ciphertext domain, based on location map information, is employed to embed the hidden data into the stego-images, resulting in a stego-images that contains the complete hidden information. Finally, the ciphertext image is stored in the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) to assign it a unique identity, and then mapped to an address in the blockchain to enable covert transmission. Results and Discussions To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme in terms of anti-steganography capability, invisibility, embedding capacity, and communication delay, simulation experiments are conducted. Regarding anti-steganography capability, the stego-images generated by the proposed scheme demonstrate strong anti-detection performance, outperforming the WOW and HILL algorithms ( Fig. 7 ). In terms of concealment, the reversible data hiding method in the ciphertext domain, based on location map and spatial domain information, offers high concealment, effectively protecting the image content while enabling lossless restoration (Table 5 ,Table 6 ,Table 7 ). Concerning embedding capacity, the steganography algorithm in this scheme exhibits a high embedding capacity, with an average embedding rate exceeding that of the PBTL, IPBTL, and ERLC-BMPR algorithms (Fig. 9 ). Finally, in terms of communication delay, the proposed scheme results in low covert communication delay, outperforming the DVANET, BDLV, and L-TCM algorithms (Fig. 10 ).Conclusions This paper proposes a blockchain-based covert communication scheme utilizing image multilevel steganography. Simulation experiments validate its advantages in information embedding rate, anti-steganography detection capability, concealment, and communication delay. The results demonstrate the following: 1. In terms of anti-steganography ability, the anti-detection performance of stego-images generated by SRNet+Zhu-Net significantly exceeds that of the WOW and HILL methods; 2. Regarding invisibility and embedding capacity, the proposed reversible data hiding method in the encrypted domain, based on location map and spatial domain information, achieves a high embedding rate and lossless recovery, outperforming the PBTL, IPBTL, and ERLC-BMPR methods; 3. In terms of communication efficiency, this scheme significantly reduces communication delay by combining blockchain and IPFS. Future research will focus on homomorphic encryption and identity authentication mechanisms to further enhance the security of on-chain data. -
Key words:
- Covert communication /
- Blockchain /
- Adversarial network /
- Information hiding
-
表 1 符号变量表
符号 描述 IS 信息发送方 IR 信息接收方 m1 部分隐蔽信息 m2 剩余隐蔽信息 m 隐蔽信息(m = m1 + m2) X 原始图像 XV 对抗图像样本 XVM 对抗隐写图像 I 载体图像 I1 载密图像 Ie 加密图像 ILM 含位置图信息的加密图像 IRpub 接收方公钥 IRpri 接收方私钥 e 图像加密密钥(对称密钥) S(Im) 载密密文图像 $ \delta $ IPFS返回的唯一哈希标识 表 2 像素标记值对应的编码序列
像素标记值 个数统计 概率分布 编码长度 编码序列 2 2 0.040 8 4 0010 3 11 0.224 5 2 01 5 3 0.061 2 3 000 6 31 0.632 7 1 1 8 2 0.040 8 4 0011 表 3 隐写分析对抗网络消融实验结果
隐写分析对抗网络 平均PSNR (dB) 平均SSIM 对抗样本隐写检测(%) 隐写图像检测(%) 训练时间(min) SRNet 45.325 0.979 2 52.3 88.9 962 Xu-Net 46.296 0.982 3 48.6 89.6 1 038 Zhu-Net+Xu-Net 42.539 0.956 3 51.2 87.8 1 369 SRNet+Zhu-Net+Xu-Net 39.689 0.862 4 49.6 86.4 1 738 Zhu-Net 44.569 0.991 4 51.4 89.2 965 SRNet+Zhu-Net 43.647 0.963 2 50.3 86.3 1 345 表 4 判别器和隐写对抗网络损失权重对比
隐写对抗损失权重组合 平均PSNR (dB) 平均SSIM SRNet (%) Xu-Net (%) Zhu-Net (%) Ye-Net (%) $ \alpha = 0.6, \beta = 0.4 $ 38.637 9 0.954 8 50.6 50.1 50.1 49.7 $ \alpha = 0.3, \beta = 0.7 $ 39.107 5 0.961 9 50.2 49.6 49.3 50.2 $ \alpha = 0.1, \beta = 0.9 $ 39.123 6 0.963 0 49.3 50.3 50.2 49.6 $ \alpha = 0.2, \beta = 0.8 $ 39.123 6 0.961 3 50.3 49.7 50.4 50.3 $ \alpha = 0.5, \beta = 0.5 $ 38.864 7 0.954 7 49.3 50.6 50.1 50.8 表 5 载密图像与加密图像的PSNR和SSIM值
载密图像/加密图像 PSNR (dB) SSIM Scenry 7.782 2 0.055 4 Building 8.670 3 0.060 0 Lena 10.072 9 0.021 9 Steamship 7.321 3 0.052 0 Cat 8.375 7 0.056 7 表 6 载密图像与载密密文图像的PSNR和SSIM值
载密图像/载密密文图像 PSNR (dB) SSIM Scenry 7.813 3 0.059 2 Building 8.117 3 0.056 6 Lena 10.078 8 0.021 2 Steamship 7.256 4 0.053 1 Cat 8.330 4 0.058 3 表 7 载密图像与还原后载密图像的PSNR和SSIM值
载密图像/还原后的载密图像 PSNR (dB) SSIM Scenry $ + \infty $ 1 Building $ + \infty $ 1 Lena $ + \infty $ 1 Steamship $ + \infty $ 1 Cat $ + \infty $ 1 表 8 针对Scenry图像文献[24]的编码过程
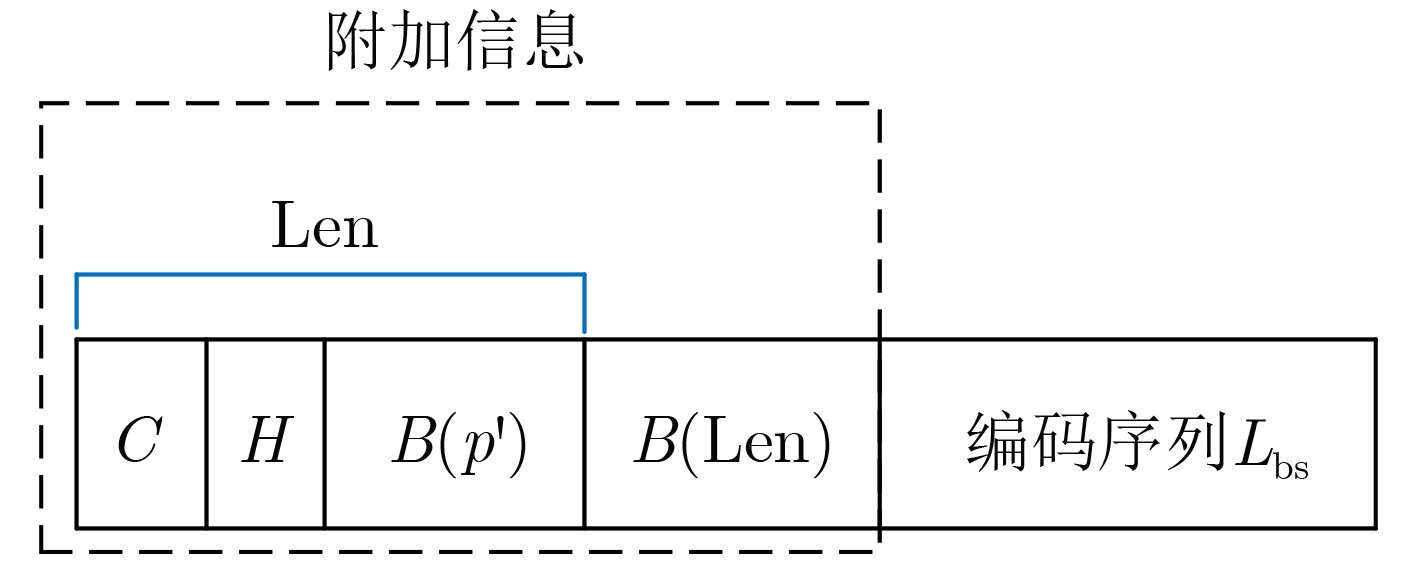
标记值 标记值个数 概率分布 编码序列 嵌入容量 编码序列长度 净嵌入容量 –1 985 – – – – – 0 9 736 0.043 11010 1 5 –4 1 13 082 0.058 1100 2 4 –2 2 10 093 0.045 11011 3 5 –2 3 27 952 0.125 100 4 3 1 4 26 893 0.121 011 5 3 2 5 44 509 0.198 00 6 2 4 6 30 836 0.137 101 7 3 4 7 36 437 0.162 111 8 3 5 8 24 963 0.111 010 8 3 4 合计 224 501 1.000 – 1 286 558 706 697 579 861 表 9 针对Scenry图像本文隐藏方法的编码过程
标记值 标记值个数 概率分布 编码序列 嵌入容量 编码序列长度 净嵌入容量 –1 985 – – – – – 0 9736 0.043 0100 1 4 –3 1 14 823 0.066 1110 2 4 –2 2 13 693 0.062 0101 3 4 –1 3 25 961 0.116 011 4 3 1 4 28 469 0.126 100 5 3 2 5 43 259 0.192 00 6 2 4 6 30 836 0.138 101 7 3 4 7 35 123 0.156 110 8 3 5 8 22 601 0.101 1111 8 4 4 合计 224 501 1 – 1 263 848 691 097 572 751(+131 072) -
[1] ZHENG Tongxing, WANG Huiming, NG D W K, et al. Multi-antenna covert communications in random wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(3): 1974–1987. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2900915. [2] HU Jinsong, LI Hongwei, CHEN Youjia, et al. Covert communication in cognitive radio networks with poisson distributed jammers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(10): 13095–13109. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3398651. [3] HU Jinsong, YE Longjie, CHEN Youjia, et al. Covert communications for text semantic with finite blocklength[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024, 13(10): 2842–2846. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2024.3448614. [4] RATHORE M S, POONGODI M, SAURABH P, et al. A novel trust-based security and privacy model for internet of vehicles using encryption and steganography[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2022, 102: 108–205. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108205. [5] YANG Qinglin, ZHAO Yetong, HUANG Huawei, et al. Fusing blockchain and AI with metaverse: A survey[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society, 2022, 3: 122–136. doi: 10.1109/OJCS.2022.3188249. [6] LIU Yuanni, PAN Ling, and CHEN Shanzhi. A hierarchical blockchain-enabled security-threat assessment architecture for IoV[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2024, 10(4): 1035–1047. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2022.12.019. [7] WANG Lei, FAN Rongfei, HU Han, et al. Age of information minimization for opportunistic channel access[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2024, 72(12): 7449–7465. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2024.3415608. [8] MA Yue, MA Ruiqian, LIN Zhi, et al. Improving age of information for covert communication with time-modulated arrays[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(2): 1718–1731. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3466855. [9] KUMAR R, TRIPATHI R, MARCHANG N, et al. A secured distributed detection system based on IPFS and blockchain for industrial image and video data security[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2021, 152: 128–143. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2021.02.022. [10] ZHANG Ru, ZHU Feng, LIU Jianyi, et al. Depth-wise separable convolutions and multi-level pooling for an efficient spatial CNN-based steganalysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 1138–1150. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2936913. [11] 李敬轩, 胡润文, 阮观奇, 等. 基于手工特征提取与结果融合的CNN音频隐写分析算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(10): 2061–2075. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.02061.LI Jingxuan, HU Runwen, RUAN Guanqi, et al. A CNN based audio steganalysis algorithm by manual feature extraction and result merging[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(10): 2061–2075. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.02061. [12] REINEL T S, RAUL R P, and GUSTAVO I. Deep learning applied to steganalysis of digital images: A systematic review[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 68970–68990. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918086. [13] REINEL T S, BRAYAN A A H, ALEJANDRO B O M, et al. GBRAS-Net: A convolutional neural network architecture for spatial image steganalysis[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 14340–14350. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3052494. [14] 李梦涵, 陈可江, 张卫明, 等. 基于合成语音的计算安全隐写方法[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2022, 8(3): 134–141. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-109x.2022025.LI Menghan, CHEN Kejiang, ZHANG Weiming, et al. Computationally secure steganography based on speech synthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2022, 8(3): 134–141. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-109x.2022025. [15] 李彦峰, 丁丽萍, 吴敬征, 等. 区块链环境下的新型网络隐蔽信道模型研究[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(5): 67–78. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019111.LI Yanfeng, DING Liping, WU Jingzheng, et al. Research on a new network covert channel model in blockchain environment[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(5): 67–78. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019111. [16] ZHANG Lejun, ZHANG Zhijie, WANG Weizheng, et al. Research on a covert communication model realized by using smart contracts in blockchain environment[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(2): 2822–2833. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3057333. [17] 黄冬艳, 李琨. 多地址的时间型区块链隐蔽通信方法研究[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(2): 148–159. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023026.HUANG Dongyan and LI Kun. Research on multi-address time-based blockchain covert communication method[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(2): 148–159. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023026. [18] SHE W, HUO L J, TIAN Z, et al. A double steganography model combining blockchain and interplanetary file system[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2021, 14(5): 3029–3042. doi: 10.1007/s12083-021-01143-0. [19] 张祯, 倪嘉铭, 姚晔, 等. 基于同义词扩展和标签传递机制的文本无载体信息隐藏方法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(9): 173–183. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021139.ZHANG Zhen, NI Jiaming, YAO Ye, et al. Text coverless information hiding method based on synonyms expansion and label delivery mechanism[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(9): 173–183. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021139. [20] DUAN Xintao, JIA Kai, LI Baoxia, et al. Reversible image steganography scheme based on a U-Net structure[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 9314–9323. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2891247. [21] LU Shaoping, WANG Rong, ZHONG Tao, et al. Large-capacity image steganography based on invertible neural networks[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10811–10820. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01067. [22] GUO Mengxi, ZHAO Shijie, LI Yue, et al. Invertible single image rescaling via steganography[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Taipei, China, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICME52920.2022.9859915. [23] SONG Yalin, ZHONG Yuhao, GAN Zhihua, et al. Generative adversarial networks-based image steganography with multiscale features integration[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2022, 31(5): 053028. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.31.5.053028. [24] 吴友情, 郭玉堂, 汤进, 等. 基于自适应哈夫曼编码的密文可逆信息隐藏算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(4): 846–858. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00846.WU Youqing, GUO Yutang, TANG Jin, et al. Reversible data hiding in encrypted images using adaptive huffman encoding strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(4): 846–858. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00846. [25] YI Shuang and ZHOU Yicong. Separable and reversible data hiding in encrypted images using parametric binary tree labeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(1): 51–64. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2844679. [26] CHEN Kaimeng and CHANG C C. High-capacity reversible data hiding in encrypted images based on extended run-length coding and block-based MSB plane rearrangement[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2019, 58: 334–344. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.12.023. [27] WU Youqing, XIANG Youzhi, GUO Yutang, et al. An improved reversible data hiding in encrypted images using parametric binary tree labeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 22(8): 1929–1938. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2952979. [28] CHEN Jianguo, LI Kenli, and YU P S. Privacy-preserving deep learning model for decentralized VANETs using fully homomorphic encryption and blockchain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 11633–11642. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3105682. [29] WANG Shujuan, HU Yingnan, and QI Guanqiu. Blockchain and deep learning based trust management for Internet of Vehicles[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2022, 120: 102627. doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2022.102627. [30] XU Yan, LIU Xinyan, CUI Jie, et al. L-TCM: A lightweight privacy-preserving traffic condition monitoring scheme with source authentication in cloud-assisted VANETs[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17(4): 6138–6147. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2023.3279620. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
