Research on Task Offloading and Resource Allocation Algorithms in Cloud-edge-end Collaborative Computing for the Internet of Things
-
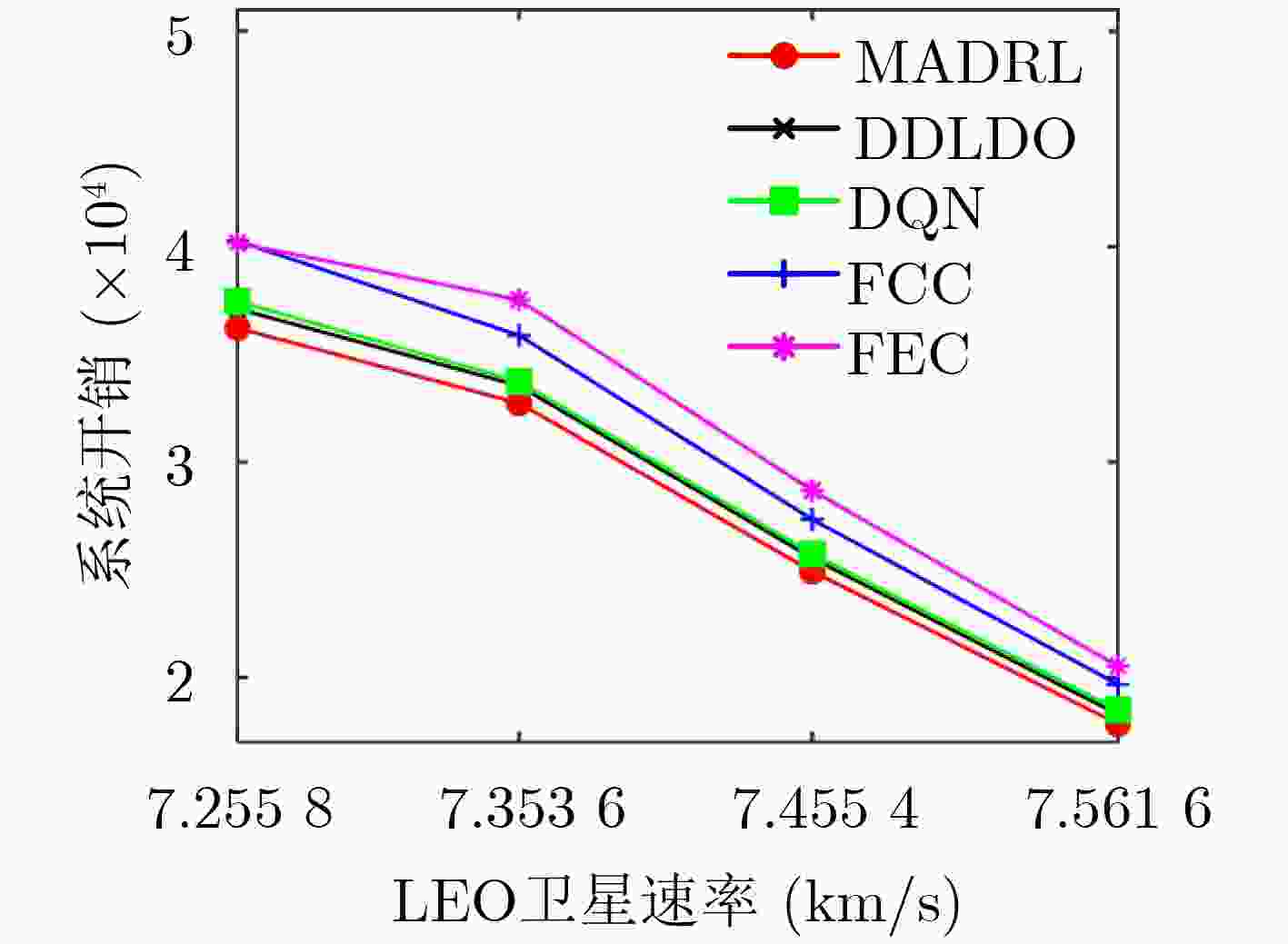
摘要: 为满足远郊和灾区物联网(IoT)设备的时延与能耗需求,该文构建了由IoT终端、低地球轨道(LEO)卫星和云计算中心组成的新型动态卫星物联网模型。在时延、能耗等实际约束条件下,将系统时延与能耗加权和视为系统开销,构造了最小化系统开销的任务卸载、功率和计算资源联合分配问题。针对动态任务到达场景,提出一种模型辅助的自适应深度强化学习(MADRL)算法,实现任务卸载决策、通信资源和计算资源的联合配置。该算法将问题分为两部分解决,第1部分通过模型辅助、二分搜索算法和梯度下降法优化了通信资源与计算资源;第2部分通过自适应深度强化学习算法训练出Q网络以适应随机任务的到达,进行卸载决策优化。该算法实现了有效的资源分配和可靠及时的任务卸载决策,且在降低系统开销方面表现出优异的效果。仿真结果表明,引入卫星的移动性,使得系统开销降低了41%。引入星间协作技术,使系统开销降低了22.1%。此外,该文所提算法收敛性能好。与基准算法相比,该算法的系统开销降低了3%,在不同环境下的性能表现都是最优。Abstract:
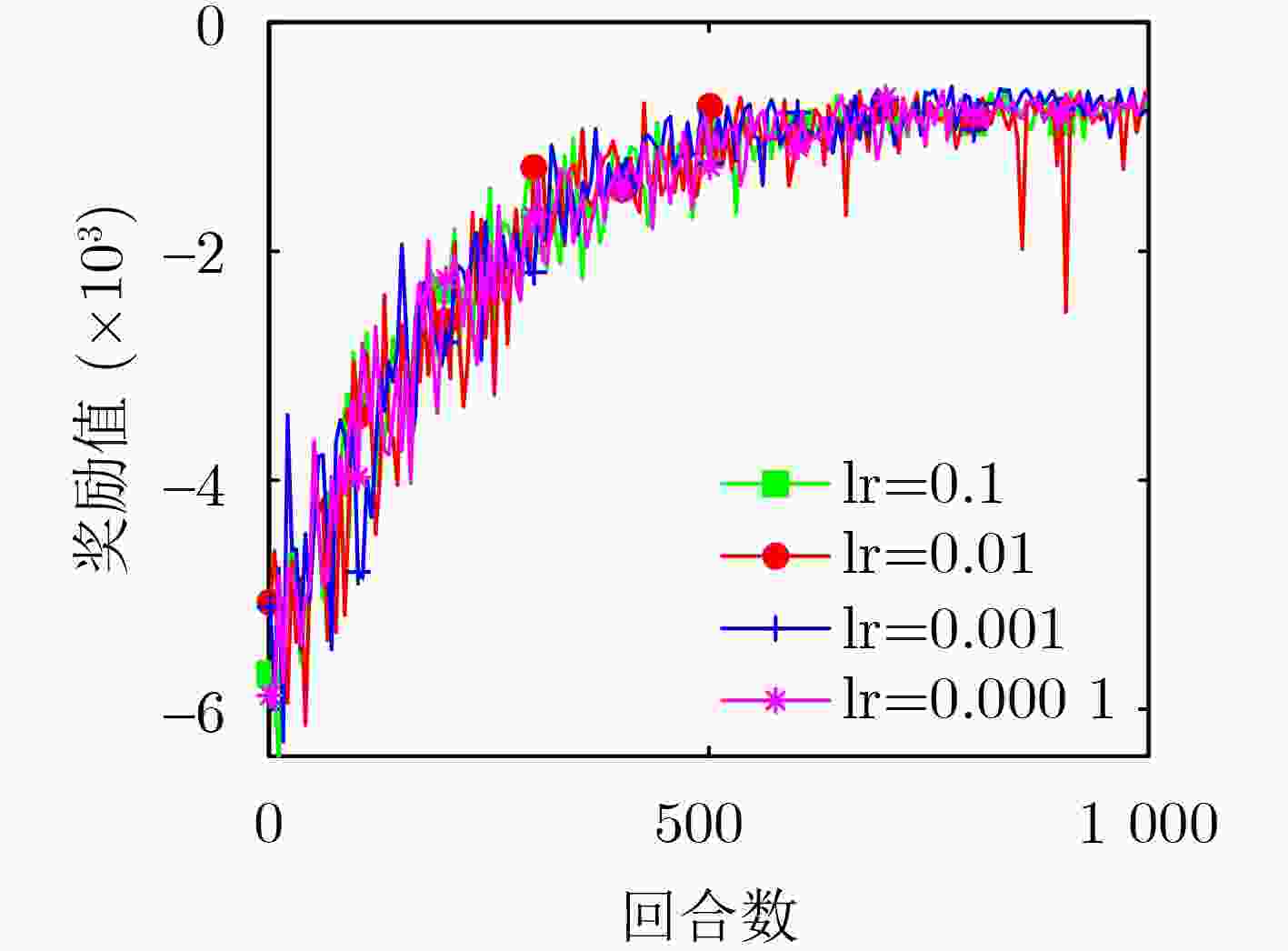
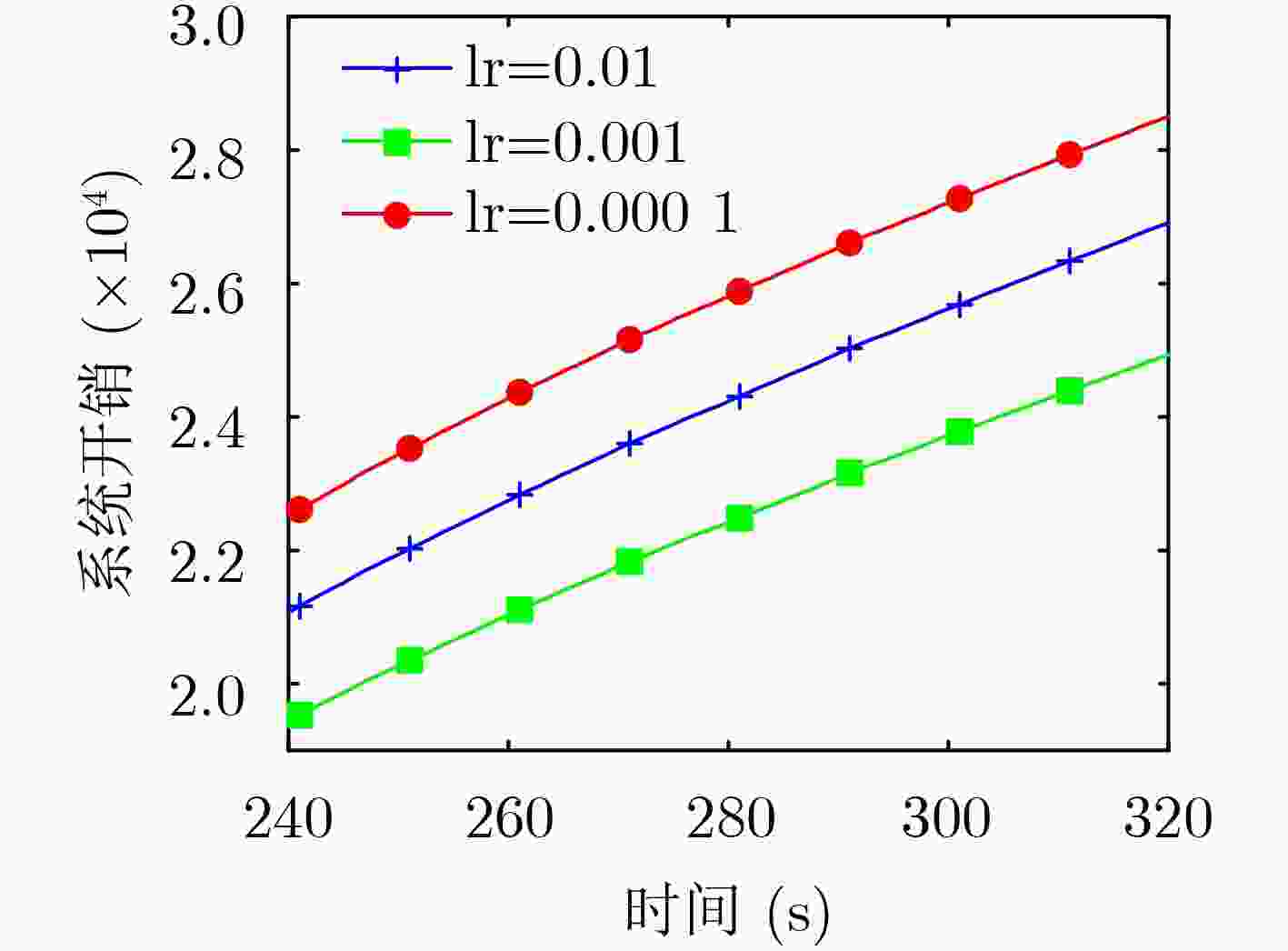
Objective With the rapid pace of digital transformation and the smart upgrading of the economy and society, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become a critical element of new infrastructure. Current wide-area IoT networks primarily rely on 5G terrestrial infrastructure. While these networks continue to evolve, challenges persist, particularly in remote or disaster-affected areas. The high cost and vulnerability of base stations hinder deployment and maintenance in these locations. Satellite networks provide seamless coverage, flexibility, and reliability, making them compelling alternatives to terrestrial networks for achieving global connectivity. Satellite-assisted Internet of Things (SIoT) can deliver ubiquitous and reliable connectivity for IoT devices. Typically, IoT devices offload tasks to edge servers or cloud platforms due to their limited power, computing, and caching resources. Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) helps reduce latency by caching content and placing edge servers closer to IoT devices. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites with integrated processing units can also serve as edge computing nodes. Although cloud platforms offer abundant computing resources and a reliable power supply, the long distance between IoT devices and the cloud results in higher communication latency. With the explosive growth of IoT devices and the diversification of application requirements driven by 5G, it is essential to design a collaborative architecture that integrates cloud, edge, and end devices. Recent research has extensively explored MEC-enhanced SIoT systems. However, many studies focus solely on edge or cloud computing, with little emphasis on their integration, satellite mobility, or resource constraints. Furthermore, LEO satellites providing edge services face challenges due to their limited onboard resources and the high mobility of the satellite constellation, complicating resource allocation and task offloading. Single-satellite solutions may not satisfy performance expectations during peak demand. Inter-Satellite Collaboration (ISC) technology, which utilizes visible light communications, can significantly increase system capacity, extend coverage, reduce individual satellite resource consumption, and prolong network operational life. Although some studies address three-tier architectures involving IoT devices, satellites, and clouds, proposing load balancing mechanisms through ISC for optimizing offloading and resource allocation, many rely on static assumptions about network topologies and user associations. In practice, LEO satellites require frequent switching and dynamic adjustments in offloading strategies to maintain service quality due to their high-speed mobility. Therefore, there is a need for a method of task offloading and resource allocation in a dynamic environment that considers satellite mobility and limited resources. To address these research gaps, this paper proposes a dynamic ISC-enhanced cloud-edge-end SIoT network model. By formulating the joint optimization problem of offloading decisions and resource allocation as a Mixed Integer Non-Linear Programming (MINLP) problem, a Model-assisted Adaptive Deep Reinforcement Learning (MADRL) algorithm is developed to achieve minimum system cost in a changing environment. Methods The LEO satellite mobility model and the SIoT network model with ISC are constructed to analyze end-to-end latency and system energy consumption. This evaluation considers three modes: local computing, edge computing, and cloud computing. A joint optimization MINLP problem is formulated, focusing on task offloading and resource allocation to minimize system costs. A MADRL algorithm is introduced, integrating traditional optimization techniques with deep reinforcement learning. The algorithm operates in two parts. The first part optimizes communication and computational resource allocation using a model-assisted binary search algorithm and gradient descent method. The second part trains a Q-network to adapt offloading decisions based on stochastic task arrivals through an adaptive deep reinforcement learning approach. Results and Discussions Simulation experiments were conducted under various dynamic scenarios. The MADRL algorithm exhibits strong convergence properties, as demonstrated in the analysis. Comparisons of different learning rates and exploration decay factors reveal optimal parameter values. Incorporating satellite mobility reduces system costs by 41% compared to static scenarios, enabling dynamic resource allocation and improved efficiency. Integrating ISC reduces system costs by 22.1%. This demonstrates the effectiveness of inter-satellite load balancing in improving resource utilization. Additionally, the MADRL algorithm achieves a 3% reduction in system costs compared to the Deep Q Learning (DQN) algorithm, highlighting its adaptability and efficiency in dynamic environments. System costs decrease as satellite speed increases, with the MADRL algorithm consistently outperforming other methods. Conclusions This paper presents an innovative dynamic SIoT model that integrates IoT devices, LEO satellites, and a cloud computing center. The model addresses the latency and energy consumption issues faced by IoT devices in remote and disaster-stricken areas. The task offloading and resource allocation problem that minimizes system cost is constructed by incorporating ISC techniques to enhance satellite edge performance and by taking satellite mobility into account. A MADRL algorithm that combines traditional optimization with deep reinforcement learning is proposed. This approach effectively optimizes task offloading decisions and resource allocation. Simulation results demonstrate that our model and algorithm significantly reduce system costs. Specifically, the incorporation of satellite mobility and ISC technology leads to cost reductions of 41% and 22.1%, respectively. Compared to benchmark algorithms, the MADRL shows superior performance across various test environments, highlighting its significant application advantages. -
表 1 基本符号及其含义
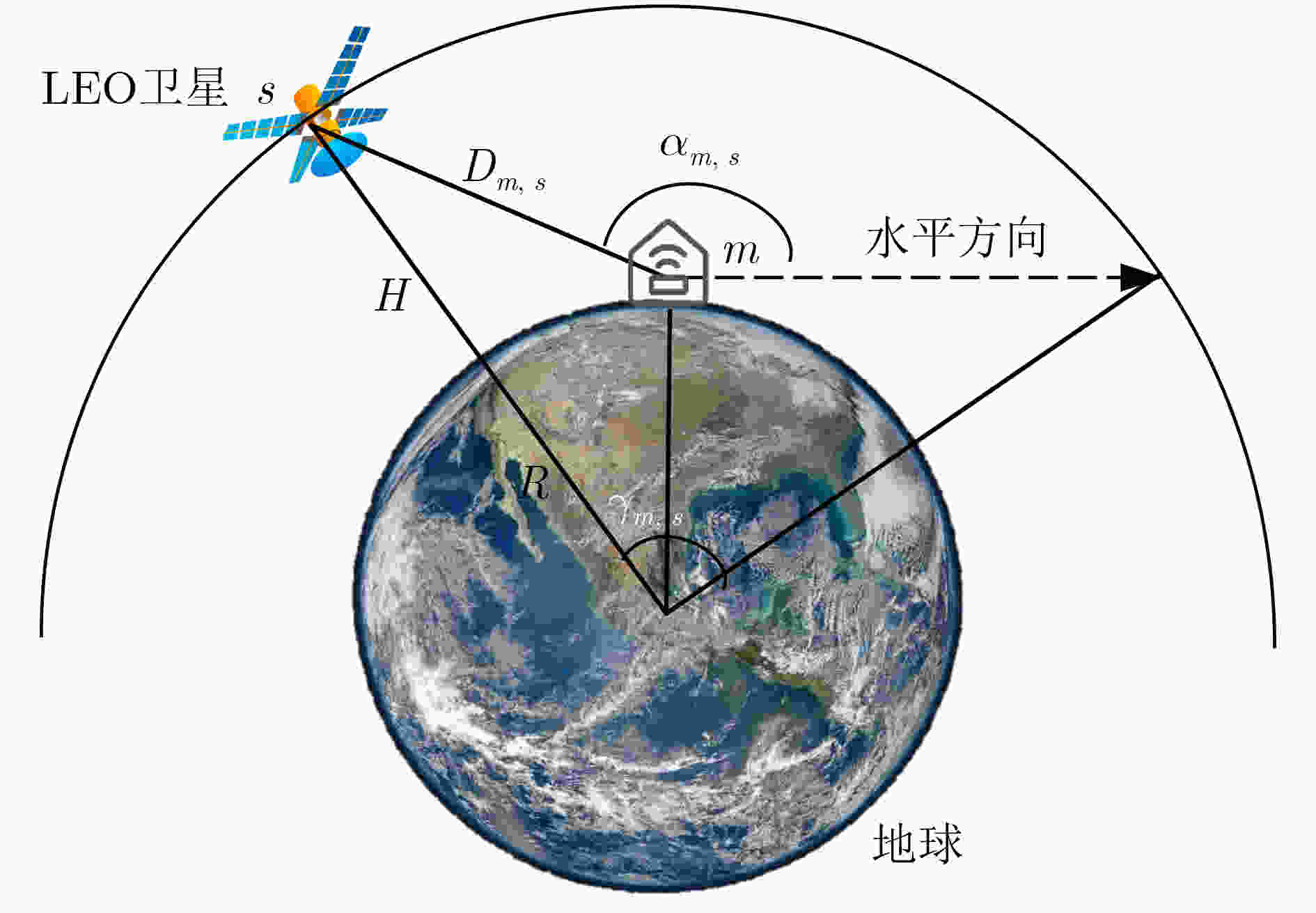
符号 含义 $\mathcal{M}$ 设备集合 $\mathcal{D}$ 灾区设备集合 $\mathcal{R}$ 远郊设备集合 $\mathcal{S}$ LEO卫星集合 $d_m^n$ 时隙n设备m生成任务的大小 $c_m^n$ 时隙n设备m的工作负载 $w_m^n$ 时隙n设备m处理任务所需CPU周期数 $T_m^{n,\max }$ 时隙n设备m处理任务的最大容忍时延 $x_m^n$ 时隙n设备m的任务卸载决策 $f_m^n$ 时隙n设备m的CPU工作频率 $p_m^n$ 时隙n设备m的传输功率 $t_m^n$ 时隙n设备m的系统时延 $e_m^n$ 时隙n设备m的系统能耗 $c_m^n$ 时隙n设备m的系统开销 1 自适应DRL算法
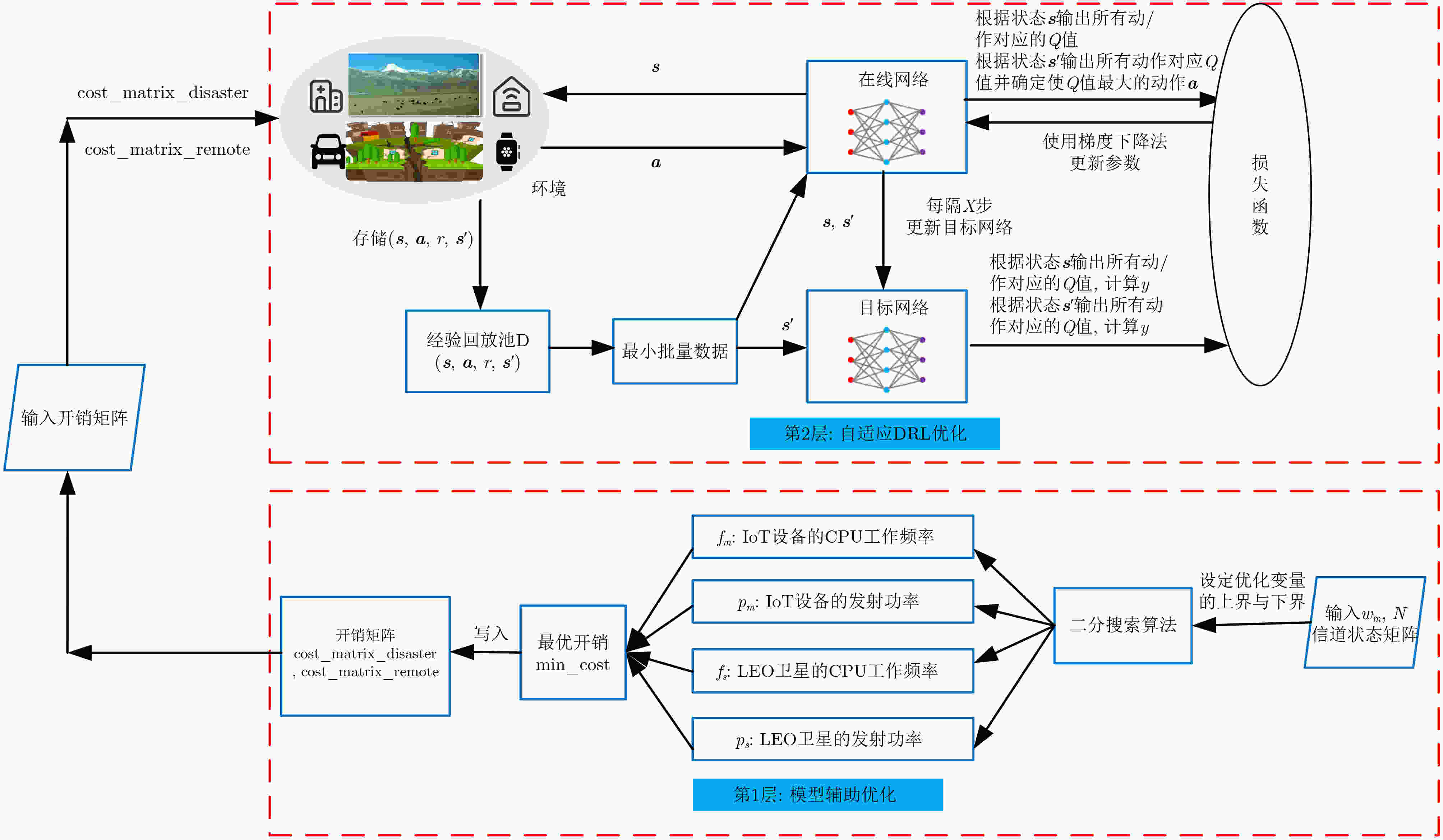
输入:开销矩阵 (1)初始化在线网络Q和目标网络Q_hat (2)初始化训练参数 (3) for episode =1 to n_ep do (4) 初始化状态 s (5) for n=1 to N do (6) 根据$\varepsilon $贪婪策略选择动作a (7) 更新状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}}' $ (8) end for (9) end for (10) if ${\mathcal{D}} $的大小≥ n_b: (11) 从D中随机抽取最小批量转移元组 (12) 根据任务状态选择DQN或DDQN计算y值 (13) end if (14)计算损失函数${\text{Loss}}(\theta )$ (15)更新在线网络Q (16)每隔X步,更新目标网络:Q_hat=Q (17)更新状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}} \leftarrow {\boldsymbol{s}}' $ (18)返回Q网络 表 2 主要参数设置
参数 值 灾区设备数D 300 远郊设备数R 5 卫星服务范围半径r 1 400 km 任务大小$d_m^n$ [1e2,1e3,1e4,1e5,1e6] bit 任务负载$c_m^n$ [1,1.5] kcycle/bit 最大容忍时延$T_m^{n,\max }$ [0.05,0.1] s 电气系数${{\varepsilon }}$ 10–28 信道带宽B 10 MHz 天线增益G 20 dBi 噪声温度T 290 K IoT设备m的最大能耗$E_m^{\max }$ 5 W LEO卫星s的最大能耗$E_s^{\max }$ 2 000 W 云计算中心单核CPU工作频率$f_{\text{c}}$ 1.45 GHz 云计算中心核心数${N_{\text{c}}}$ 256 -
[1] 工业和信息化部. 物联网新型基础设施建设三年行动计划(2021-2023年)[R]. 2021.Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China. A three-year action plan for the construction of new IoT infrastructure[R]. 2021. [2] CUI Gaofeng, DUAN Pengfei, XU Lexi, et al. Latency optimization for hybrid GEO–LEO satellite-assisted IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(7): 6286–6297. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3222831. [3] DE COLA T and BISIO I. QoS optimisation of eMBB services in converged 5G-satellite networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 12098–12110. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3011963. [4] KANEKO K, NISHIYAMA H, KATO N, et al. Construction of a flexibility analysis model for flexible high-throughput satellite communication systems with a digital channelizer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(3): 2097–2107. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2736010. [5] BOERO L, BRUSCHI R, DAVOLI F, et al. Satellite networking integration in the 5G ecosystem: Research trends and open challenges[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(5): 9–15. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1800052. [6] CHIEN W C, LAI C F, HOSSAIN M S, et al. Heterogeneous space and terrestrial integrated networks for IoT: Architecture and challenges[J]. IEEE Network, 2019, 33(1): 15–21. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1800182. [7] RANAWEERA P, JURCUT A D, and LIYANAGE M. Survey on multi-access edge computing security and privacy[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 1078–1124. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3062546. [8] LI Chengcheng, ZHANG Yasheng, XIE Renchao, et al. Integrating edge computing into low earth orbit satellite networks: Architecture and prototype[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 39126–39137. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3064397. [9] WANG Dezhi, WANG Wei, KANG Yuhan, et al. Distributed data offloading in ultra-dense LEO satellite networks: A stackelberg mean-field game approach[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2023, 17(1): 112–127. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3226400. [10] TANG Zhixuan, YU Kai, YANG Guannan, et al. New bridge to cloud: An ultra-dense LEO assisted green computation offloading approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2023, 7(2): 552–564. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2022.3208819. [11] YU Shuai, GONG Xiaowen, SHI Qian, et al. EC-SAGINs: Edge-computing-enhanced space–air–ground-integrated networks for internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(8): 5742–5754. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3052542. [12] LIU Yi, JIANG Li, QI Qi, et al. Energy-efficient space–air–ground integrated edge computing for internet of remote things: A federated DRL approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(6): 4845–4856. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3220677. [13] TANG Qingqing, FEI Zesong, LI Bin, et al. Stochastic computation offloading for LEO satellite edge computing networks: A learning-based approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(4): 5638–5652. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3307707. [14] ZHU Xiangming and JIANG Chunxiao. Delay optimization for cooperative multi-tier computing in integrated satellite-terrestrial networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(2): 366–380. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3227083. [15] ZHANG Shanghong, CUI Gaofeng, LONG Yating, et al. Joint computing and communication resource allocation for satellite communication networks with edge computing[J]. China Communications, 2021, 18(7): 236–252. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2021.07.019. [16] TANG Qingqing, FEI Zesong, LI Bin, et al. Computation offloading in LEO satellite networks with hybrid cloud and edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(11): 9164–9176. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3056569. [17] CAO Bin, ZHANG Jintong, LIU Xin, et al. Edge–cloud resource scheduling in space–air–ground-integrated networks for internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(8): 5765–5772. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3065583. [18] LI Zhipeng, LI Meng, and WANG Qian. Predator–prey model based asymmetry resource allocation in satellite–terrestrial network[J]. Symmetry, 2021, 13(11): 2113. doi: 10.3390/sym13112113. [19] LEE Y and CHOI J P. Connectivity analysis of mega-constellation satellite networks with optical intersatellite links[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 4213–4226. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3090914. [20] ZHANG Hangyu, LIU Rongke, KAUSHIK A, et al. Satellite edge computing with collaborative computation offloading: An intelligent deep deterministic policy gradient approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(10): 9092–9107. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3233383. [21] GAO Xiangqiang, HU Yingmeng, SHAO Yingzhao, et al. Hierarchical dynamic resource allocation for computation offloading in LEO satellite networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(11): 19470–19484. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3367937. [22] 易必杰. 面向空天地一体化网络的计算卸载策略研究[D]. [博士/硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2023. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2023.002544.YI Bijie. Research on computing offloading strategy for space-air-ground integrated network[D]. Xidian University, 2023. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2023.002544. [23] FANG Hai, JIA Yangyang. WANG Yuanle, et al. Matching game based task offloading and resource allocation algorithm for satellite edge computing networks[C]. Proceedings of 2022 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Shenzhen, China, 2022: 1–5, doi: 10.1109/ISNCC55209.2022.9851813. [24] 郭子桢, 梁俊, 肖楠, 等. 软件定义卫星网络多控制器可靠部署算法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2021, 55(2): 158–165. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202102019.GUO Zizhen, LIANG Jun, XIAO Nan, et al. Multi-controller reliable deployment algorithm for software defined satellite network[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(2): 158–165. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202102019. [25] KUROSE J and ROSS K. Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach[M]. 6th ed. Boston: Pearson, 2012. [26] 谢希仁. 计算机网络[M]. 4版. 大连: 大连理工大学出版社, 2003.XIE Xiren. Computer Networking[M]. 4th ed. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 2003. [27] QI Xiaoxin, ZHANG Bing, QIU Zhiliang, et al. Using inter-mesh links to reduce end-to-end delay in walker delta constellations[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(9): 3070–3074. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3095227. [28] YOU Changsheng, HUANG Kaibin, and CHAE H. Energy efficient mobile cloud computing powered by wireless energy transfer[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(5): 1757–1771. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2545382. [29] NOWAK R. Generalized binary search[C]. 2008 46th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, USA, 2008: 568–574. doi: 10.1109/ALLERTON.2008.4797609. [30] AVRIEL M. Nonlinear Programming: Analysis and Methods[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1976. [31] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236. [32] VAN HASSELT H, GUEZ A, and SILVER D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning[C]. The Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, Arizona, 2016: 2094–2100. [33] SHUAI Jiaqi, CUI Haixia, HE Yejun, et al. Dynamic satellite edge computing offloading algorithm based on distributed deep learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(16): 27790–27802. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3404830. -





 下载:
下载:
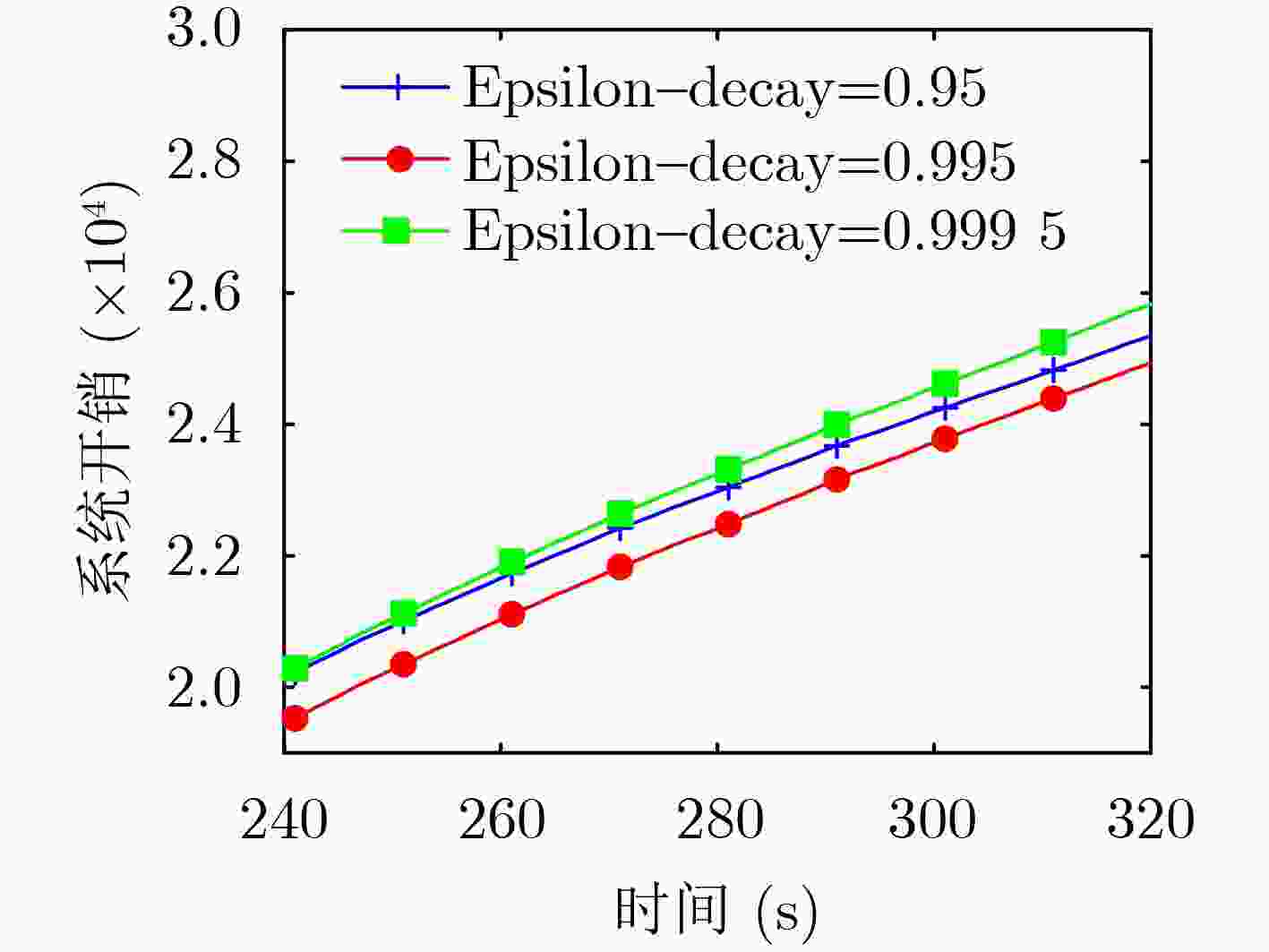
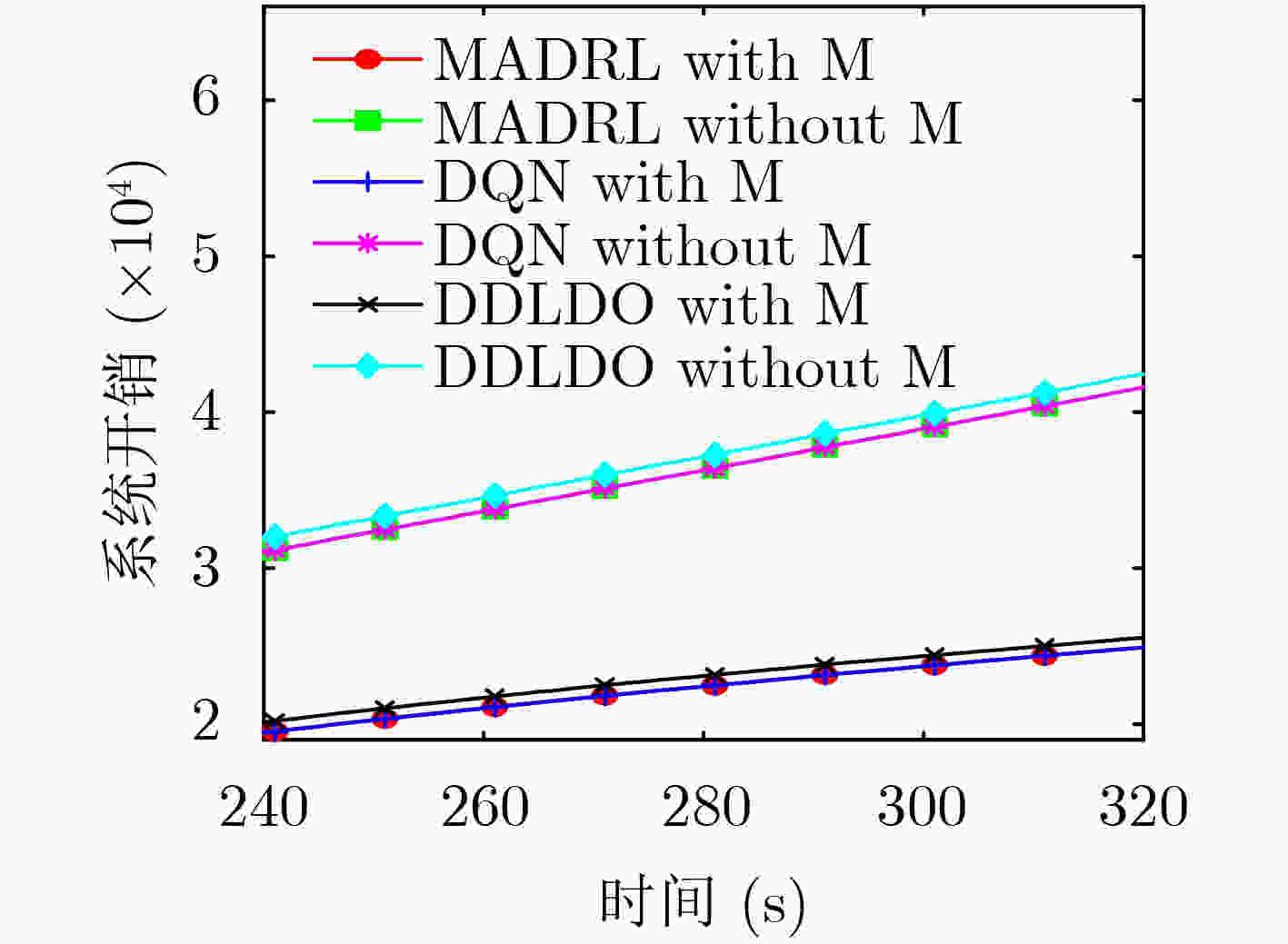
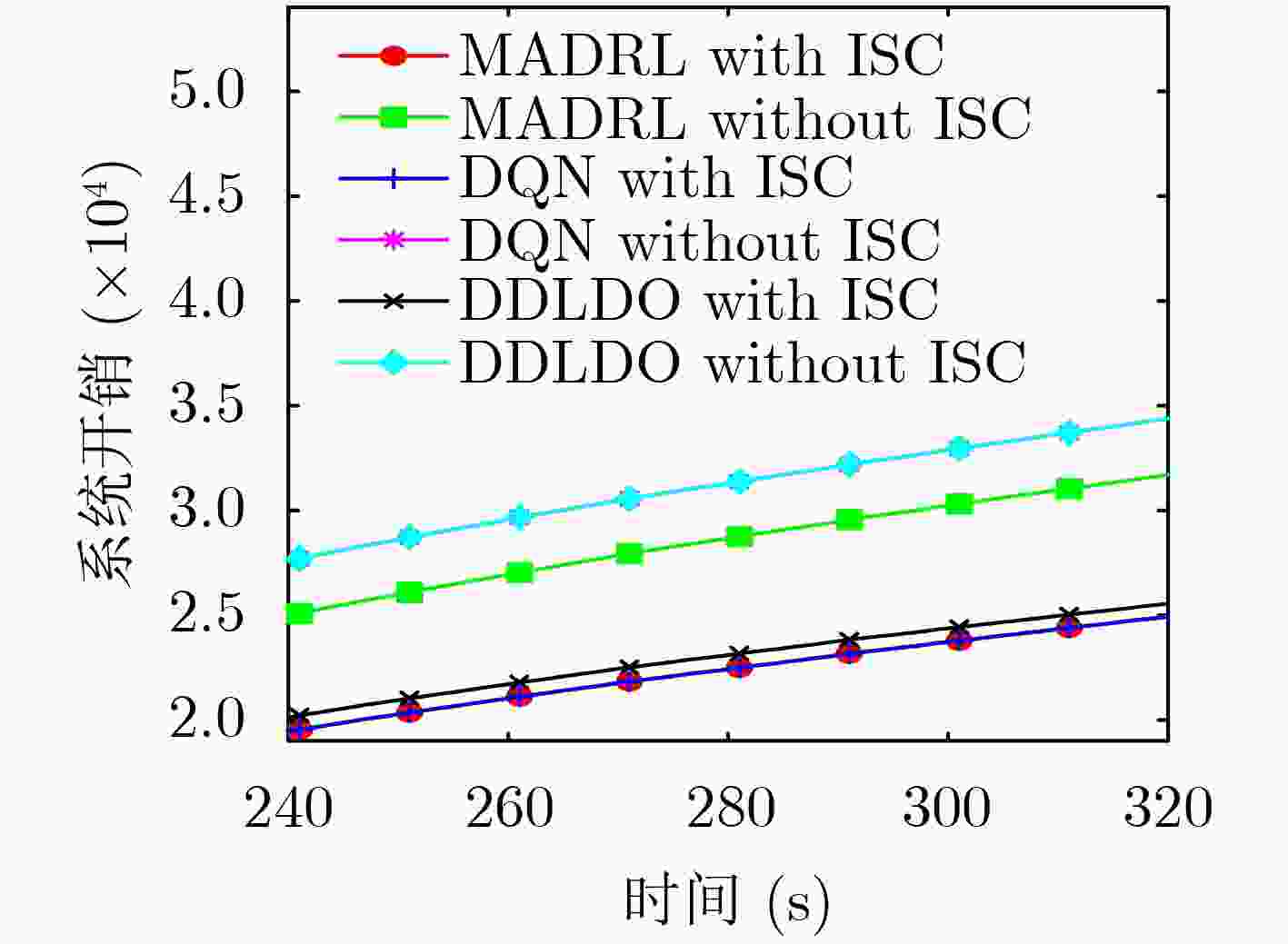
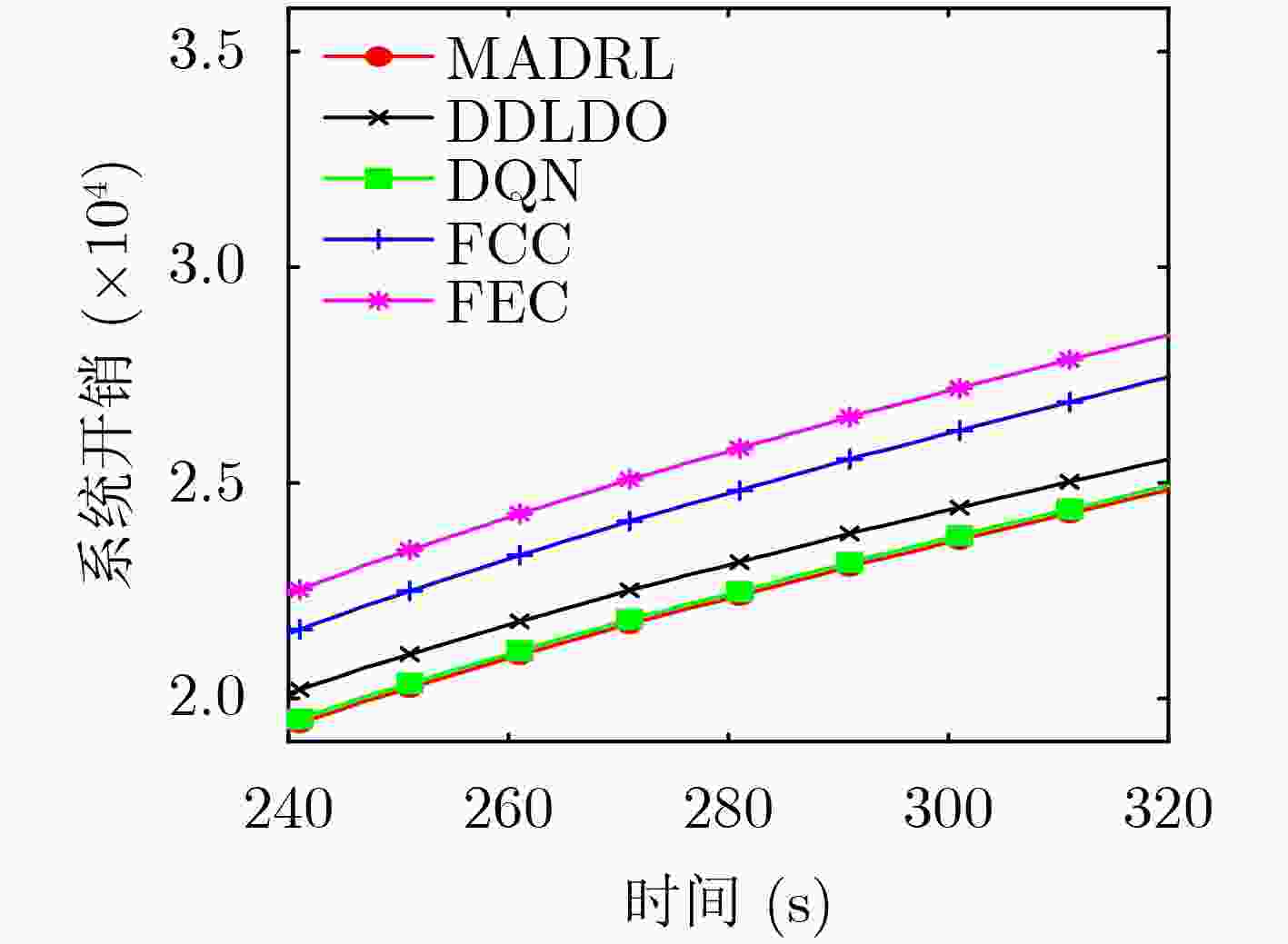


 下载:
下载:
