Task Offloading Algorithm for Large-scale Multi-access Edge Computing Scenarios
-
摘要: 基于单智能体强化学习的任务卸载算法在解决大规模多接入边缘计算(MEC)系统任务卸载时,存在智能体之间相互影响,策略退化的问题。而以多智能体深度确定性策略梯度(MADDPG)为代表的传统多智能体算法的联合动作空间维度随着系统内智能体的数量增加而成比例增加,导致系统扩展性变差。为解决以上问题,该文将大规模多接入边缘计算任务卸载问题,描述为部分可观测马尔可夫决策过程(POMDP),提出基于平均场多智能体的任务卸载算法。通过引入长短期记忆网络(LSTM)解决局部观测问题,引入平均场近似理论降低联合动作空间维度。仿真结果表明,所提算法在任务时延与任务掉线率上的性能优于单智能体任务卸载算法,并且在降低联合动作空间的维度情况下,任务时延与任务掉线率上的性能与MADDPG一致。Abstract:
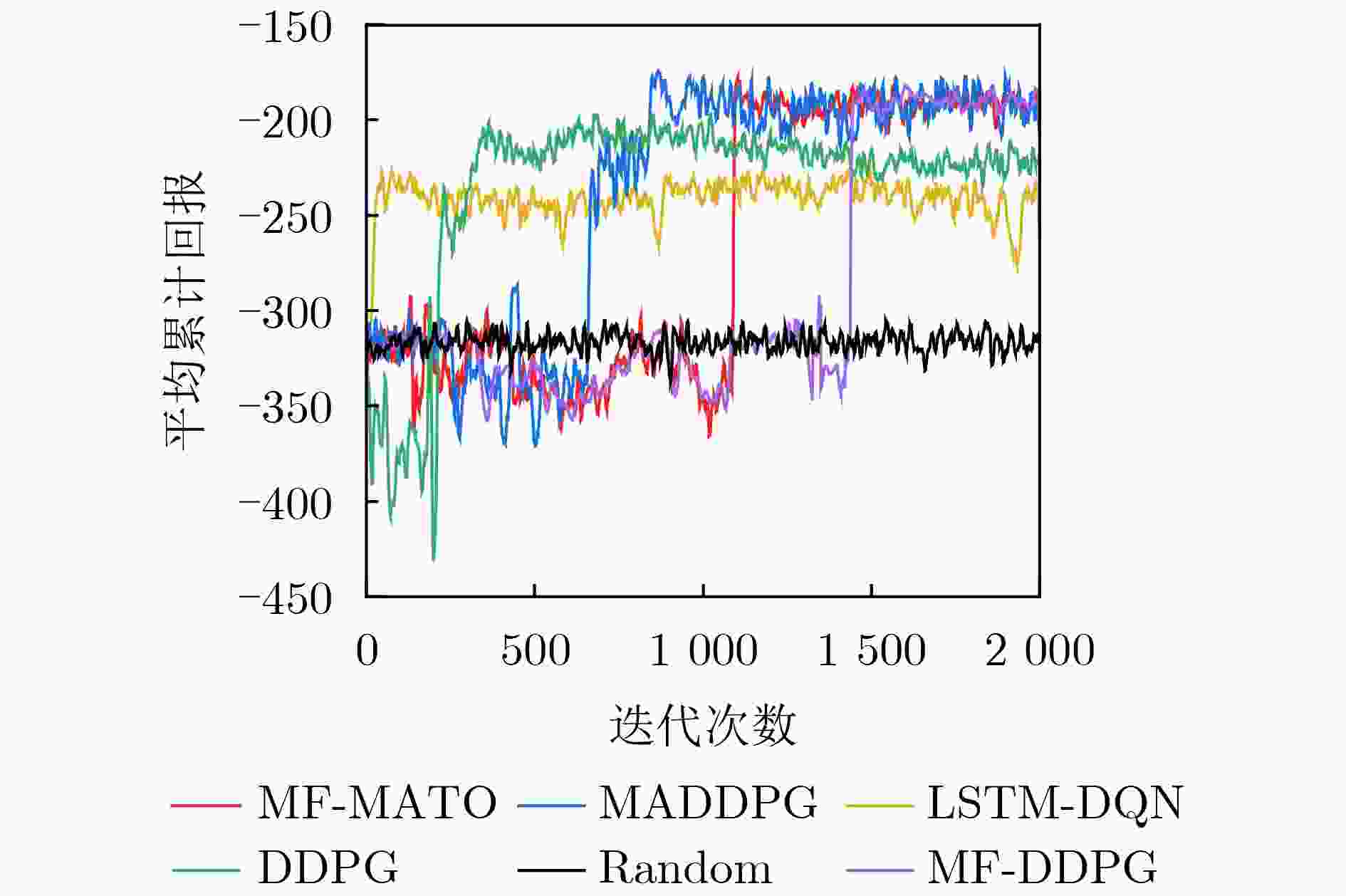
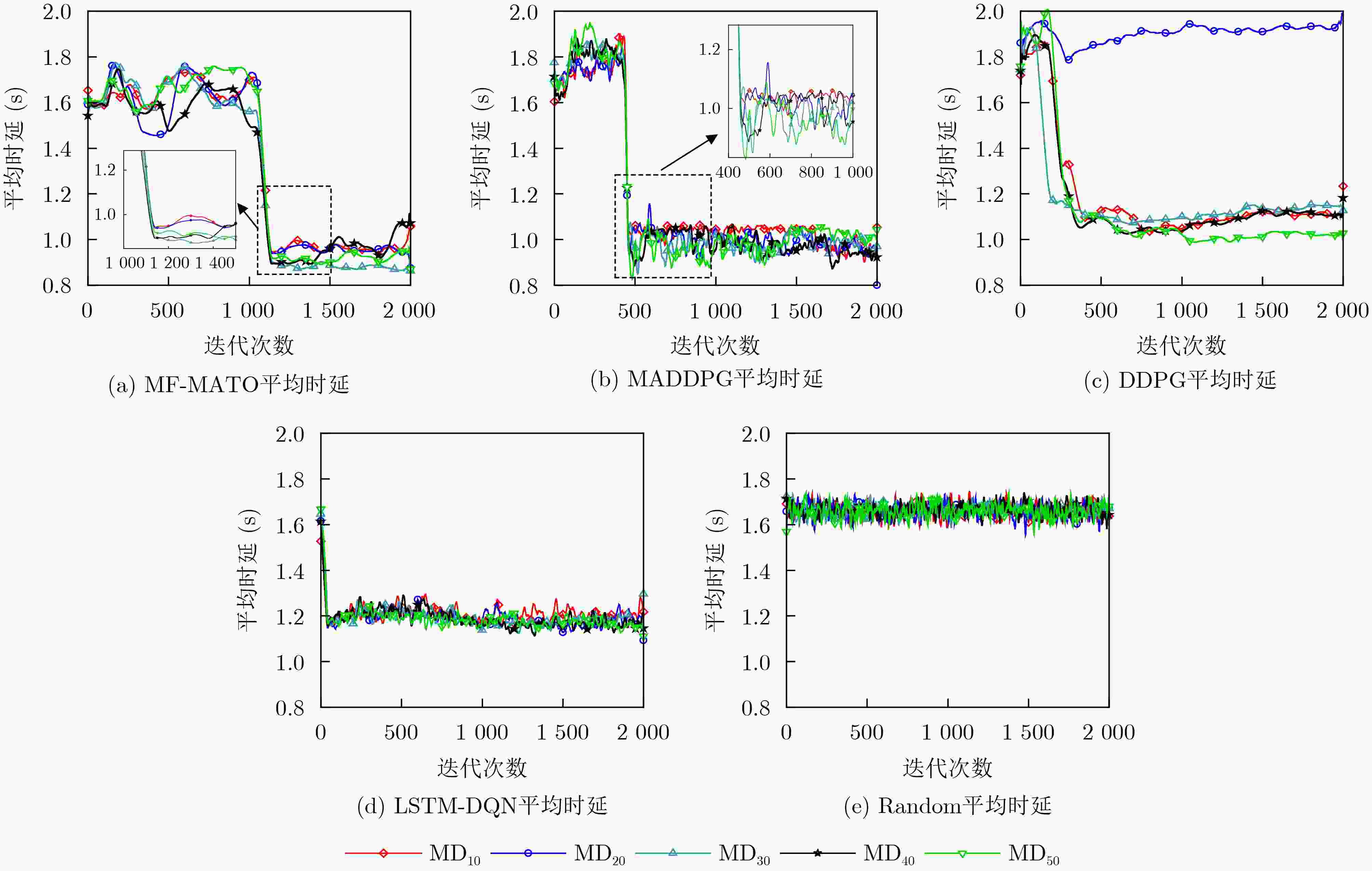
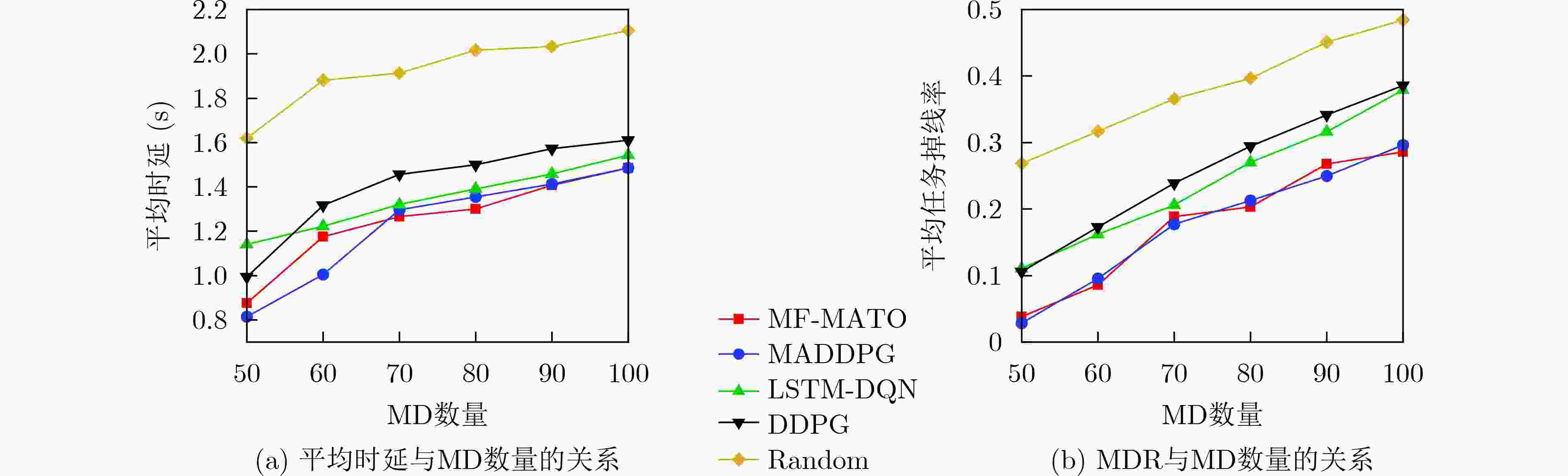
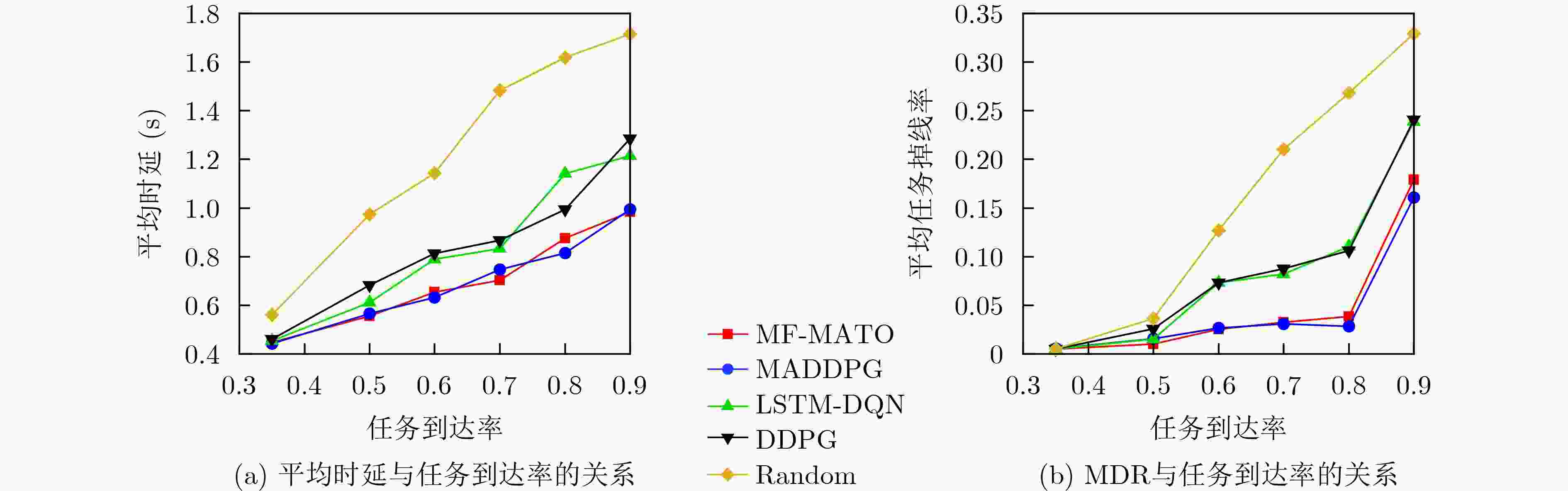
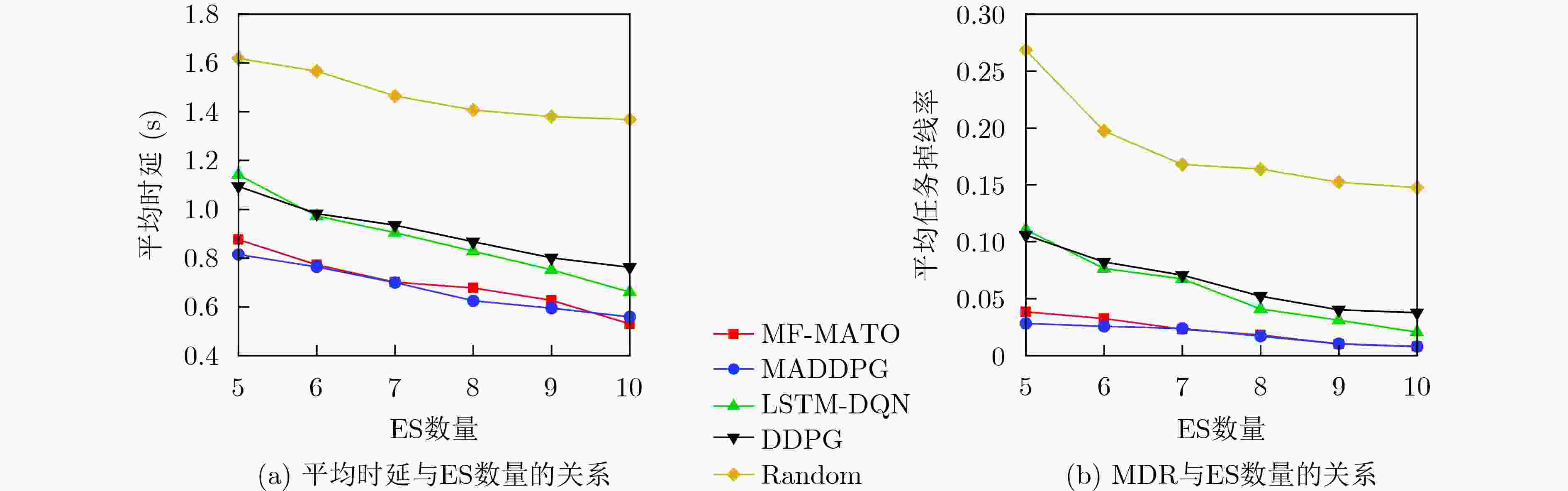
Objective Recently, task offloading techniques based on reinforcement learning in Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) have attracted considerable attention and are increasingly being utilized in industrial applications. Algorithms for task offloading that rely on single-agent reinforcement learning are typically developed within a decentralized framework, which is preferred due to its relatively low computational complexity. However, in large-scale MEC environments, such task offloading policies are formed solely based on local observations, often resulting in partial observability challenges. Consequently, this can lead to interference among agents and a degradation of the offloading policies. In contrast, traditional multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms, such as the Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MADDPG), consolidate the observation and action vectors of all agents, thereby effectively addressing the partial observability issue. Optimal joint offloading policies are subsequently derived through online training. Nonetheless, the centralized training and decentralized execution model inherent in MADDPG causes computational complexity to increase linearly with the number of mobile devices (MDs). This scalability issue restricts the ability of MEC systems to accommodate additional devices, ultimately undermining the system’s overall scalability. Methods First, a task offloading queue model for large-scale MEC systems is developed to handle delay-sensitive tasks with deadlines. This model incorporates both the transmission process, where tasks are offloaded via wireless channels to the edge server, and the computation process, where tasks are processed on the edge server. Second, the offloading process is defined as a Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) with specified observation space, action space, and reward function for the agents. The Mean-Field Multi-Agent Task Offloading (MF-MATO) algorithm is subsequently proposed. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are utilized to predict the current state vector of the MEC system by analyzing historical observation vectors. The predicted state vector is then input into fully connected networks to determine the task offloading policy. The incorporation of LSTM networks addresses the partial observability issue faced by agents during offloading decisions. Moreover, mean field theory is employed to approximate the Q-value function of MADDPG through linear decomposition, resulting in an approximate Q-value function and a mean-field-based action approximation for the MF-MATO algorithm. This mean-field approximation replaces the joint action of agents. Consequently, the MF-MATO algorithm interacts with the MEC environment to gather experience over one episode, which is stored in an experience replay buffer. After each episode, experiences are sampled from the buffer to train both the policy network and the Q-value network. Results and Discussions The simulation results indicate that the average cumulative rewards of the MF-MATO algorithm are comparable to those of the MADDPG algorithm, outperforming the other comparison algorithms during the training phase. (1) The task offloading delay curves for MD using the MF-MATO and MADDPG algorithms show a synchronous decline throughout the training process. Upon reaching training convergence, the delays consistently remain lower than those of the single-agent task offloading algorithm. In contrast, the average delay curve for the single-agent algorithm exhibits significant variation across different MD scenarios. This inconsistency is attributed to the single-agent algorithm’s inability to address mutual interference among agents, resulting in policy degradation for certain agents due to the influence of others. (2) As the number of MD increases, the MF-MATO algorithm’s performance regarding delay and task drop rate increasingly aligns with that of MADDPG, while exceeding all other comparison algorithms. This enhancement is attributed to the improved accuracy of the mean-field approximation as the number of MD rises. (3) A rise in task arrival probability leads to a gradual increase in the average delay and task drop rate curves for both the MF-MATO and MADDPG algorithms. When the task arrival probability reaches its maximum value, a significant rise in both the average delay and task drop rate is observed across all algorithms, due to the high volume of tasks fully utilizing the available computational resources. (4) As the number of edge servers increases, the average delay and task drop rate curves for the MF-MATO and MADDPG algorithms show a gradual decline, whereas the performance of the other comparison algorithms experiences a marked improvement with only a slight increase in computational resources. This suggests that the MF-MATO and MADDPG algorithms effectively optimize computational resource utilization through cooperative decision-making among agents. The simulation results substantiate that, by reducing computational complexity, the MF-MATO algorithm achieves performance in terms of delay and task drop rate that is consistent with that of the MADDPG algorithm. Conclusions The task offloading algorithm proposed in this paper, which is based on LSTM networks and mean field approximation theory, effectively addresses the challenges associated with task offloading in large-scale MEC scenarios. By utilizing LSTM networks, the algorithm alleviates the partially observable issues encountered by single-agent approaches, while also enhancing the efficiency of experience utilization in multi-agent systems and accelerating algorithm convergence. Additionally, mean field approximation theory reduces the dimensionality of the action space for multiple agents, thereby mitigating the computational complexity that traditional MADDPG algorithms face, which increases linearly with the number of mobile devices. As a result, the computational complexity of the MF-MATO algorithm remains independent of the number of mobile devices, significantly improving the scalability of large-scale MEC systems. -
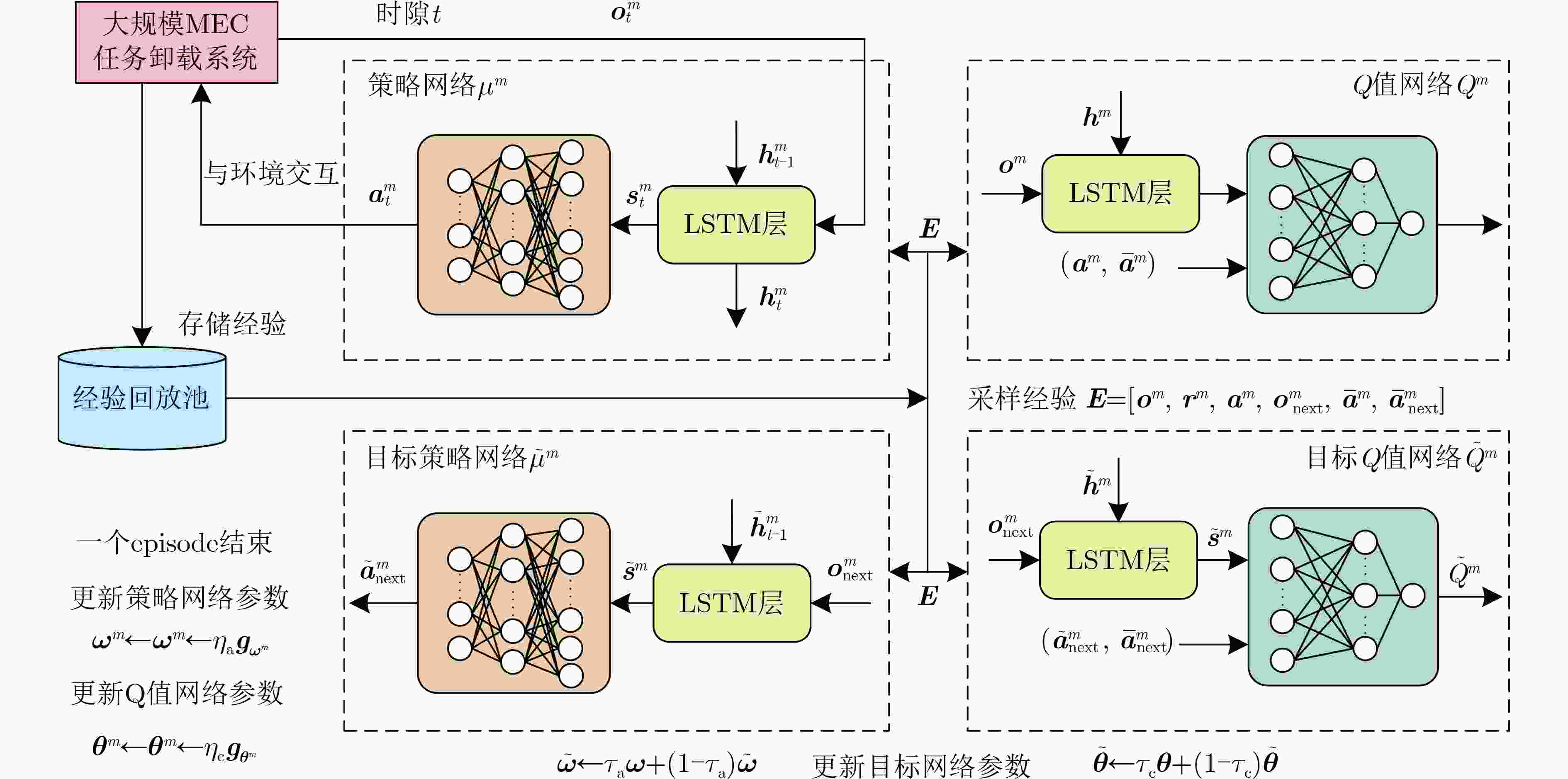
1 MF-MATO算法流程
输入:MEC系统内所有MD在时隙t内的观测向量 输出:MEC系统内所有MD的任务卸载策略 (1) 初始化所有Agent策略网络参数$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^m} $与${H_{\rm a}}$,Q值网络参数$ {{\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^m} $
与${H_{\rm c}}$。选择Adam优化器,并设置学习率$ {\eta _{\rm c}} $, $ {\eta _{\rm a}} $,设置目标网络
软更新系数$ {\tau _{\rm c}} $, $ {\tau _{\rm a}} $;(2) for episode = 1,2,···,I do (3) for m = 1,2,···,M do (4) for t = 1,2,···,T do (5) 每个Agent得到观测${\boldsymbol{o}}_t^m$向量,输入决策网络得到动作
$ {\boldsymbol{a}}_t^m = {\mu ^m}({\boldsymbol{o}}_t^m) $;(6) 由$ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_t} $生成卸载决策并与环境交互,并得到回报$r_t^m$; (7) end for (8) 将一个episode结束后得到的经验E存储至经验池; (9) 从经验池中随机均匀采样经验E; (10) 由式(27)计算策略网络损失函数,并更新网络参数$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^m} $; (11) 由式(28)计算Q值网络损失函数,并更新网络参数$ {{\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^m} $; (12) 软更新目标网络参数 $ {\tilde {\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^m} \leftarrow {\tau _{\rm c}}{{\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^m} + (1 - {\tau _{\rm c}}){\tilde {\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^m} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{\tilde w}}^m} \leftarrow {\tau _{\rm a}}{{\boldsymbol{w}}^m} + (1 - {\tau _{\rm a}}){{\boldsymbol{\tilde w}}^m} $; (13) end for (14) end for 表 1 仿真参数
参数 值 参数 值 $ \varDelta $(s) 0.1 $ f_m^{{\text{device}}} $(GHz) 2.5 $ \lambda $ [0.35,0.90] $ f_n^{{\text{edge}}} $(GHz) 41.8 T 200 $ r_{n,m}^{{\text{tran}}} $(Mbps) 24 $ {\rho _m} $(cycle·Mbit–1) 0.297 $ {\tau ^{{\text{local}}}} $(时隙) 10 $ {\eta _{\mathrm{c}}} $ 0.000 1 $ {\tau ^{{\text{tran}}}} $(时隙) 10 $ {\eta _{\mathrm{a}}} $ 0.000 1 $ {\tau ^{{\text{edge}}}} $(时隙) 10 $ {\tau _{\mathrm{c}}} $ 0.001 M 50~100 $ {\tau _{\mathrm{a}}} $ 0.001 N 5~10 任务数据量(Mbit) 2~5 $\gamma $ 0.9 -
[1] KHAN W Z, AHMED E, HAKAK S, et al. Edge computing: A survey[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 97: 219–235. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.02.050. [2] HUA Haochen, LI Yutong, WANG Tonghe, et al. Edge computing with artificial intelligence: A machine learning perspective[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(9): 184. doi: 10.1145/3555802. [3] LI Tianxu, ZHU Kun, LUONG N C, et al. Applications of multi-agent reinforcement learning in future internet: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(2): 1240–1279. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3160697. [4] FENG Chuan, HAN Pengchao, ZHANG Xu, et al. Computation offloading in mobile edge computing networks: A survey[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2022, 202: 103366. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2022.103366. [5] LUO Quyuan, HU Shihong, LI Changle, et al. Resource scheduling in edge computing: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(4): 2131–2165. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3106401. [6] CHEN Weiwei, WANG Dong, and LI Keqin. Multi-user multi-task computation offloading in green mobile edge cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2019, 12(5): 726–738. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2018.2826544. [7] PORAMBAGE P, OKWUIBE J, LIYANAGE M, et al. Survey on multi-access edge computing for internet of things realization[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(4): 2961–2991. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2849509. [8] SAEIK F, AVGERIS M, SPATHARAKIS D, et al. Task offloading in edge and cloud computing: A survey on mathematical, artificial intelligence and control theory solutions[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 195: 108177. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108177. [9] LI Shancang, XU Lida, and ZHAO Shanshan. 5G internet of things: A survey[J]. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2018, 10: 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2018.01.005. [10] 夏士超, 姚枝秀, 鲜永菊, 等. 移动边缘计算中分布式异构任务卸载算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 2891–2898. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190728.XIA Shichao, YAO Zhixiu, XIAN Yongju, et al. A distributed heterogeneous task offloading methodology for mobile edge computing[J] Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 2891–2898. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190728. [11] RANAWEERA P, JURCUT A D, and LIYANAGE M. Survey on multi-access edge computing security and privacy[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 1078–1124. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3062546. [12] TRAN T X and POMPILI D. Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 856–868. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2881191. [13] BI Suzhi, HUANG Liang, WANG Hui, et al. Lyapunov-guided deep reinforcement learning for stable online computation offloading in mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(11): 7519–7537. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3085319. [14] CHEN Xianfu, ZHANG Honggang, WU Celimuge, et al. Optimized computation offloading performance in virtual edge computing systems via deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 4005–4018. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2876279. [15] HUANG Liang, BI Suzhi, and ZHANG Y J A. Deep reinforcement learning for online computation offloading in wireless powered mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2020, 19(11): 2581–2593. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2928811. [16] CAO Zilong, ZHOU Pan, LI Ruixuan, et al. Multiagent deep reinforcement learning for joint multichannel access and task offloading of mobile-edge computing in industry 4.0[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(7): 6201–6213. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2968951. [17] ZHU Xiaoyu, LUO Yueyi, LIU Anfeng, et al. Multiagent deep reinforcement learning for vehicular computation offloading in IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(12): 9763–9773. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3040768. [18] HEYDARI J, GANAPATHY V, and SHAH M. Dynamic task offloading in multi-agent mobile edge computing networks[C]. 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM38437.2019.9013115. [19] GAO Zhen, YANG Lei, and DAI Yu. Large-scale computation offloading using a multi-agent reinforcement learning in heterogeneous multi-access edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(6): 3425–3443. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3141080. [20] YANG Yaodong, LUO Rui, LI Minne, et al. Mean field multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]. The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 5571–5580. [21] TANG Ming and WONG V W S. Deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in mobile edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(6): 1985–1997. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.3036871. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
