An Intelligent Driving Strategy Optimization Algorithm Assisted by Direct Acyclic Graph Blockchain and Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
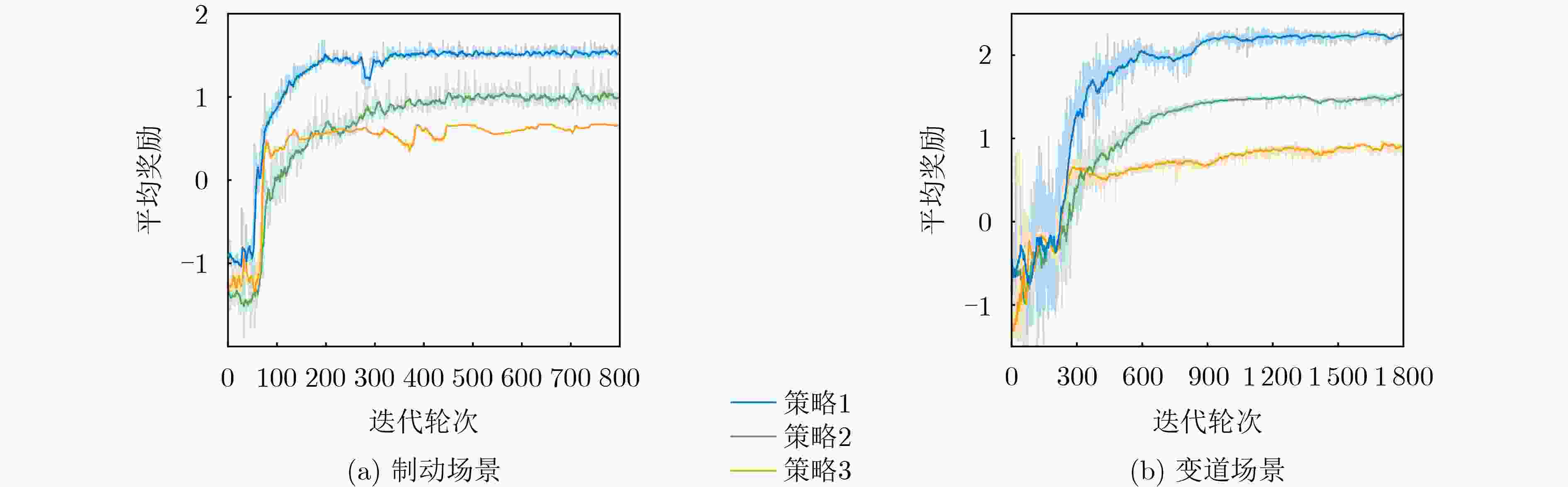
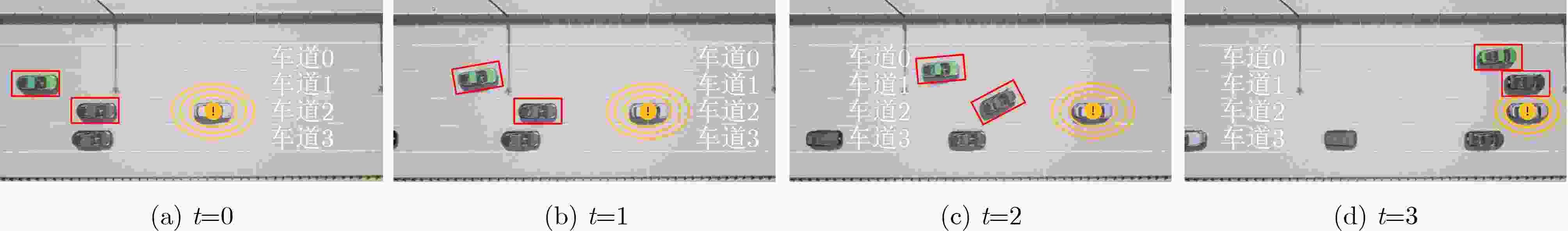
摘要: 深度强化学习(DRL)在智能驾驶决策中的应用日益广泛,通过与环境的持续交互,能够有效提高智能驾驶系统的决策能力。然而,DRL在实际应用中面临学习效率低和数据共享安全性差的问题。为了解决这些问题,该文提出一种基于有向无环图(DAG)区块链辅助深度强化学习的智能驾驶策略优化(D-IDSO)算法。首先,构建了基于DAG区块链的双层安全数据共享架构,以确保模型数据共享的效率和安全性。其次,设计了一个基于DRL的智能驾驶决策模型,综合考虑安全性、舒适性和高效性设定多目标奖励函数,优化智能驾驶决策。此外,提出了一种改进型优先经验回放的双延时确定策略梯度(IPER-TD3)方法,以提升训练效率。最后,在CARLA仿真平台中选取制动和变道场景对智能网联汽车(CAV)进行训练。实验结果表明,所提算法显著提高了智能驾驶场景中模型训练效率,在确保模型数据安全共享的基础上,有效提升了智能驾驶的安全性、舒适性和高效性。Abstract: The application of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) in intelligent driving decision-making is increasingly widespread, as it effectively enhances decision-making capabilities through continuous interaction with the environment. However, DRL faces challenges in practical applications due to low learning efficiency and poor data-sharing security. To address these issues, a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)blockchain-assisted deep reinforcement learning Intelligent Driving Strategy Optimization (D-IDSO) algorithm is proposed. First, a dual-layer secure data-sharing architecture based on DAG blockchain is constructed to ensure the efficiency and security of model data sharing. Next, a DRL-based intelligent driving decision model is designed, incorporating a multi-objective reward function that optimizes decision-making by jointly considering safety, comfort, and efficiency. Additionally, an Improved Prioritized Experience Replay with Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic policy gradient (IPER-TD3) method is proposed to enhance training efficiency. Finally, braking and lane-changing scenarios are selected in the CARLA simulation platform to train Connected and Automated Vehicles (CAVs). Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly improves model training efficiency in intelligent driving scenarios, while ensuring data security and enhancing the safety, comfort, and efficiency of intelligent driving.
-
1 基于DAG区块链辅助DRL的智能驾驶策略优化算法
输入:Critic网络初始参数,Actor网络初始参数,本地迭代轮次
E,学习率η,折现因子γ和更新率τ;输出:最优CAV智能驾驶决策; (1) 车辆服务提供商发布任务 (2) RSU $m$初始化网络参数,并上传至DAG区块链 (3) for CAV $ v $=1 to V do (4) CAV $ v $发送请求向量$ {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} _{v,m}^{{\text{dw}}} $ (5) RSU $m$发送响应向量$ {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} _{m,v}^{{\text{dw}}} $和初始模型 (6) //本地DRL训练 (7) for episode e= 1 to E do (8) for step j = 1 to J do (9) CAV $ v $与环境不断交互 (10) 存储4元组训练样本$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{s}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_t},{{{r}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t{\text{ + 1}}}}} \right\} $到${B_{\text{1}}}$ (11) if step done then (12) 根据式(20)计算$\bar r$ (13) 存储5元组训练样本$ \{ {{\boldsymbol{s}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_t},{{{r}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t{\text{ + 1}}}},\bar r\} $到${B_{\text{2}}}$ (14) end if (15) 根据式(21)更新经验回放池${B_{\text{1}}}$中样本优先级 (16) 根据式(22)更新经验回放池${B_{\text{2}}}$中样本优先级 (17) 从${B_{\text{1}}}$,${B_{\text{2}}}$中抽样N1,N2数量的训练样本 (18) 采用梯度下降方法更新Critic网络 (19) if Critic网络更新2次 then (20) 采用梯度下降方法更新Actor网络 (21) 采用软更新方法更新目标网络 (22) end if (23) end for (24) //上传模型 (25) if 模型质量$ {U_t} \ge {U_{{\text{threshold}}}} $ then (26) CAV $ v $发送新site, $ {\bf{TX}}_{v,m}^{{\text{dw}}} $和请求向量$ {\boldsymbol{\sigma}} _{v,m'}^{{\text{up}}} $ (27) RSU $m'$打包交易向量,将新site添加至DAG (28) end if (29) end for (30) end for -
[1] XU Wenchao, ZHOU Haibo, CHENG Nan, et al. Internet of vehicles in big data era[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(1): 19–35. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510736. [2] TENG Siyu, HU Xuemin, DENG Peng, et al. Motion planning for autonomous driving: The state of the art and future perspectives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(6): 3692–3711. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3274536. [3] LI Guofa, QIU Yifan, YANG Yifan, et al. Lane change strategies for autonomous vehicles: A deep reinforcement learning approach based on transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(3): 2197–2211. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3227921. [4] ZHU Zhuangdi, LIN Kaixiang, JAIN A K, et al. Transfer learning in deep reinforcement learning: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(11): 13344–13362. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3292075. [5] WU Jingda, HUANG Zhiyu, HUANG Wenhui, et al. Prioritized experience-based reinforcement learning with human guidance for autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(1): 855–869. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3177685. [6] CHEN Junlong, KANG Jiawen, XU Minrui, et al. Multiagent deep reinforcement learning for dynamic avatar migration in AIoT-Enabled vehicular metaverses with trajectory prediction[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(1): 70–83. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3296075. [7] ZOU Guangyuan, HE Ying, YU F R, et al. Multi-constraint deep reinforcement learning for smooth action control[C]. The 31st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vienna, Austria, 2022: 3802–3808. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2022/528. [8] HUANG Xiaoge, WU Yuhang, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Distance-aware hierarchical federated learning in blockchain-enabled edge computing network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(21): 19163–19176. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3279983. [9] CAO Bin, WANG Zixin, ZHANG Long, et al. Blockchain systems, technologies, and applications: A methodology perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2023, 25(1): 353–385. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3204702. [10] HUANG Xiaoge, YIN Hongbo, CHEN Qianbin, et al. DAG-based swarm learning: A secure asynchronous learning framework for internet of vehicles[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2023.10.004. [11] XIA Le, SUN Yao, SWASH R, et al. Smart and secure CAV networks empowered by AI-enabled blockchain: The next frontier for intelligent safe driving assessment[J]. IEEE Network, 2022, 36(1): 197–204. doi: 10.1109/MNET.101.2100387. [12] FU Yuchuan, LI Changle, YU F R, et al. An autonomous lane-changing system with knowledge accumulation and transfer assisted by vehicular blockchain[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(11): 11123–11136. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2994975. [13] FAN Bo, DONG Yiwei, LI Tongfei, et al. Blockchain-FRL for vehicular lane changing: Toward traffic, data, and training safety[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(24): 22153–22164. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3303918. [14] YIN Hongbo, HUANG Xiaoge, WU Yuhang, et al. Multi-region asynchronous swarm learning for data sharing in large-scale internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(11): 2978–2982. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3314662. [15] CAO Mingrui, ZHANG Long, and CAO Bin. Toward on-device federated learning: A direct acyclic graph-based blockchain approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(4): 2028–2042. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3105810. -






 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
