Design and Optimization of Secure Transmission Scheme for Rate-Splitting Multiple Access System
-
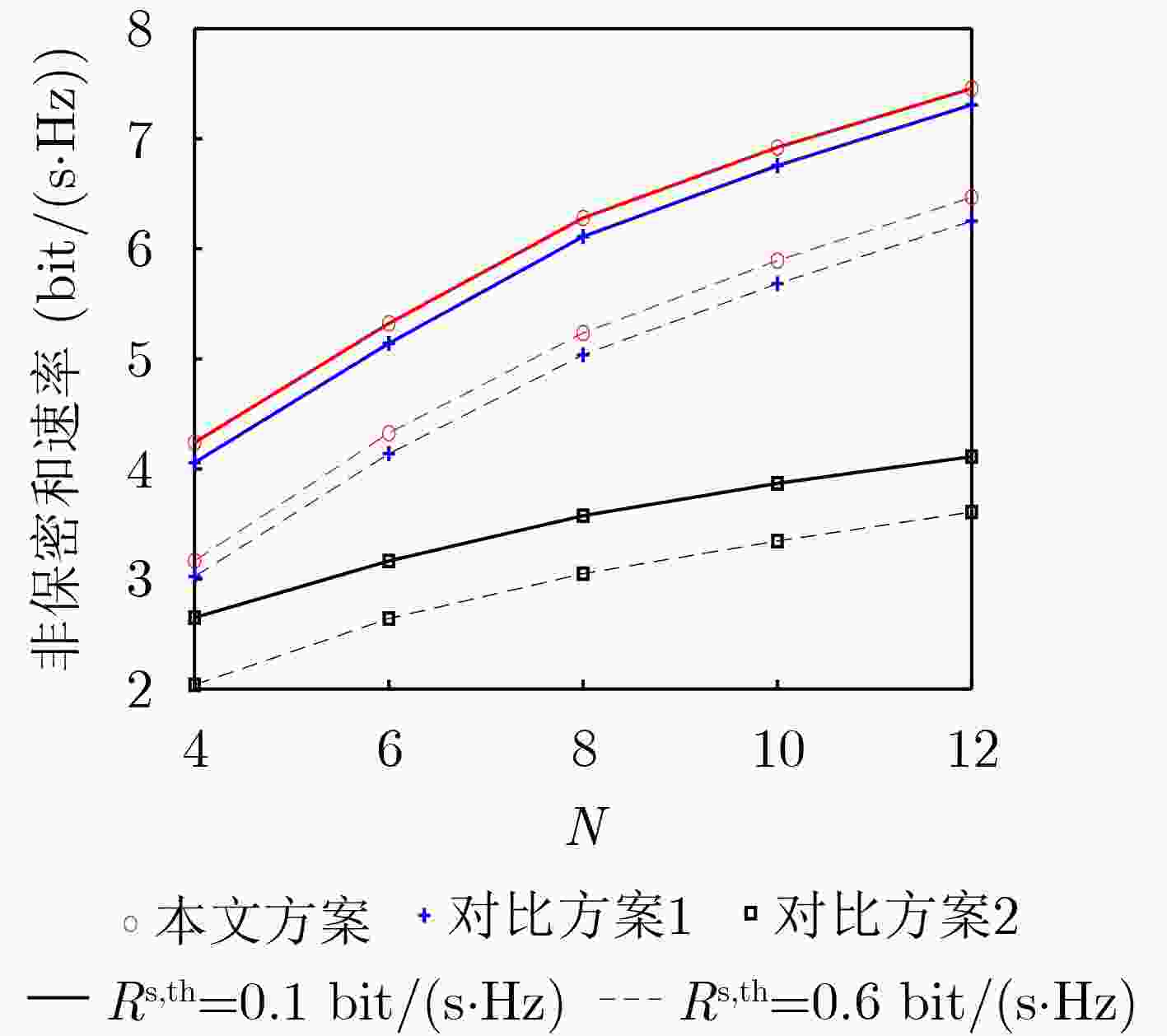
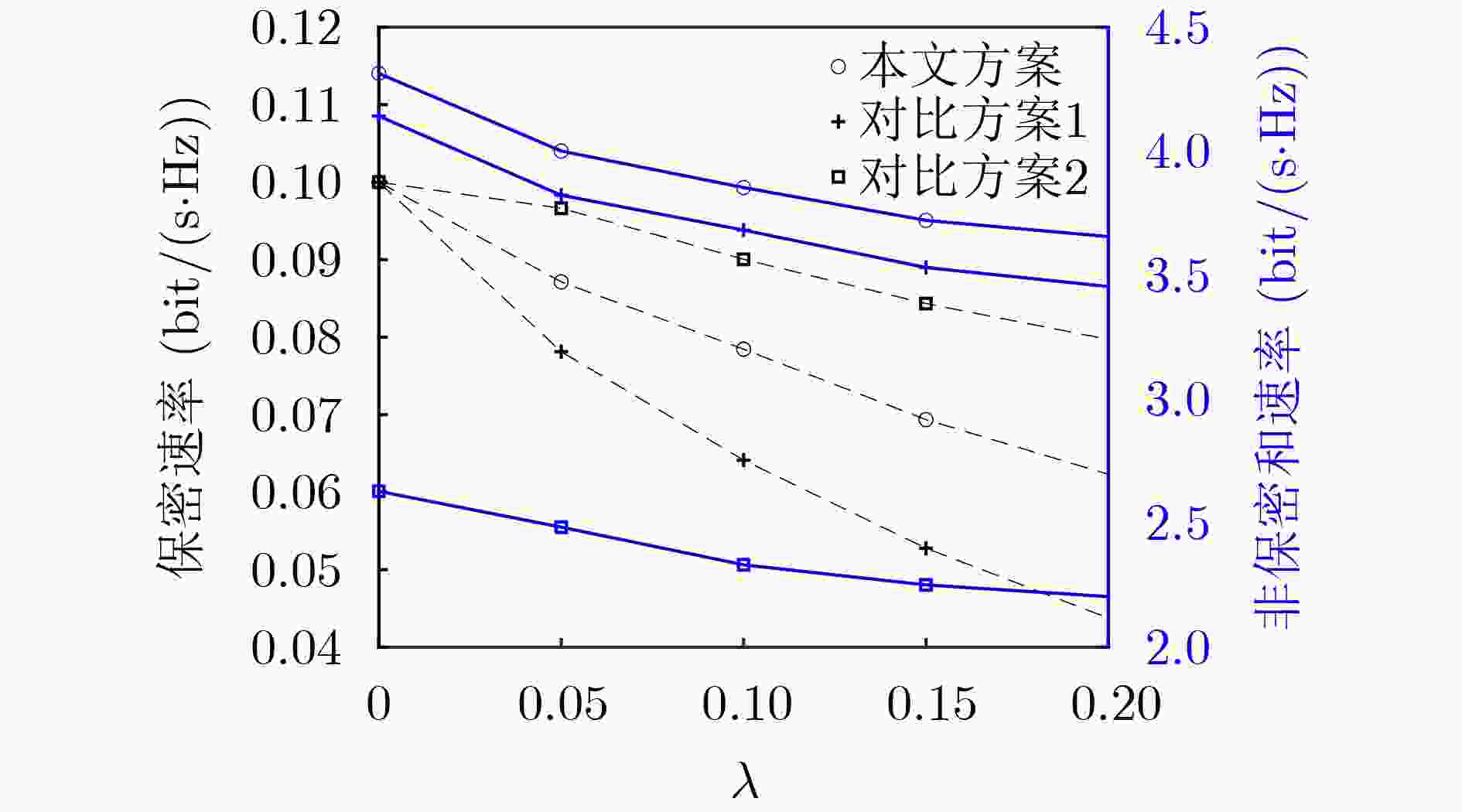
摘要: 该文研究基于速率分割多址接入的两用户下行安全传输的方案设计与优化问题。考虑发给两用户的部分消息需要在用户间保密的场景,在保证保密消息传输速率的条件下最大化非保密消息传输和速率。公共流仅传输非保密消息,而私有流分时传输非保密消息和保密消息,对各消息流发送预编码矢量,速率分割、私有流非保密和保密消息传输时长分配等进行联合优化。通过将原问题分解为两层优化问题,并利用二分搜索、松弛变量、连续凸逼近等方法将原问题进行转化和求解。仿真结果显示,相较于私有流仅传输保密消息的速率分割多址接入和分时的空分多址接入方案,所提出的方案能获得更高非保密传输速率。Abstract: The design and optimization issues of secure downlink transmission scheme for two users based on rate-splitting multiple access are studied. Considering a scenario where partial messages sent to two users need to be kept confidential between users, the sum rate of non-confidential messages is maximized while ensuring the transmission rate of confidential messages. The common stream only carries the non-confidential messages, while the private streams carry both the non-confidential and confidential messages in a time-sharing manner. Transmit precoding vectors for each message flow, rate splitting, transmission time allocation for the private streams of non-confidential and confidential messages are jointly optimized. By decomposing the original problem into a two-level optimization problem and using methods such as binary search, relaxation variables, and successive convex approximation, the original problem is transformed and solved. The simulation results show that the proposed scheme can achieve higher non-confidential sum rate compared to the rate-splitting multiple access, where the private streams carry only the confidential messages, and space division multiple access with time-sharing between non-confidential messages and confidential messages.
-
Key words:
- Rate splitting /
- Multiple access /
- Physical layer security /
- Precoding
-
1 优化问题的求解算法
(1)初始化参数:迭代次数n=0,收敛因子ε, ${t^{\{ 0\} }}$, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{\text{c}}^{\{ 0\} } $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{p,}}k}^{\{ 0\} } $,
$ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{s,}}k}^{\{ 0\} } $, $ \rho _{{\text{p,}}k}^{\{ 0\} } $, $ \rho _{{\text{s,}}k}^{\{ 0\} } $, $ \rho _{{\text{c,}}k,i}^{\{ 0\} } $, $ \nu _{\bar k,k}^{\{ 0\} } $(2) while (3) n=n+1 (4) 将优化问题中的$ {{\mathbf{\tilde f}}_{\text{c}}} $, $ {{\mathbf{\tilde f}}_{{\text{p,}}k}} $, $ {{\mathbf{\tilde f}}_{{\text{s,}}k}} $, $ {\tilde \rho _{{\text{p,}}k}} $, $ {\tilde \rho _{{\text{s,}}k}} $, $ {\tilde \rho _{{\text{c,}}k,i}} $和$ {\tilde \nu _{\bar k,k}} $分别
置为$ {\mathbf{f}}_{\text{c}}^{\{ n - 1\} } $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{p,}}k}^{\{ n - 1\} } $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{s,}}k}^{\{ n - 1\} } $, $ \rho _{{\text{p,}}k}^{\{ n - 1\} } $, $ \rho _{{\text{s,}}k}^{\{ n - 1\} } $, $ \rho _{{\text{c,}}k,i}^{\{ n - 1\} } $
和$ \nu _{\bar k,k}^{\{ n - 1\} } $求解问题(24),得到最优解$ {\mathbf{f}}_{\text{c}}^* $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{p,}}k}^* $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{s,}}k}^* $, $ \rho _{{\text{p,}}k}^* $,
$ \rho _{{\text{s,}}k}^* $, $ \rho _{{\text{c,}}k,i}^* $, $ \nu _{\bar k,k}^* $和${t^*}$(5)更新$ {\mathbf{f}}_{\text{c}}^{\{ n\} } = {\mathbf{f}}_{\text{c}}^* $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{p,}}k}^{\{ n\} } = {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{p,}}k}^* $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{s,}}k}^{\{ n\} } = {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{s,}}k}^* $, $ \rho _{{\text{p,}}k}^{\{ n\} } = \rho _{{\text{p,}}k}^* $,
$ \rho _{{\text{s,}}k}^{\{ n\} } = \rho _{{\text{s,}}k}^* $, $ \rho _{{\text{c,}}k,i}^{\{ n\} } = \rho _{{\text{c,}}k,i}^* $, $ \nu _{\bar k,k}^{\{ n\} } = \nu _{\bar k,k}^* $, ${t^{\{ n\} }} = {t^*}$(6) until $ \left| {\dfrac{{{t^{\{ n\} }} - {t^{\{ n - 1\} }}}}{{{t^{\{ n\} }}}}} \right| \le \varepsilon $ (7)输出:${t^*}$, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{\text{c}}^* $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{p,}}k}^* $, $ {\mathbf{f}}_{{\text{s,}}k}^* $和$c_k^*$ 2 时长分配系数的优化求解
(1) l<θ<u,初始化l=0,u=1,收敛因子$\delta $ (2) while (3) θ = (l+u)/2 (4)调用算法1求解第2层优化问题 (5)若当前θ下问题有可行解,则l=θ;否则u=$\theta $ (6) until u–l≤ $\delta $ (7)输出最优的θ*=$\theta $ -
[1] MAO Yijie, DIZDAR O, CLERCKX B, et al. Rate-splitting multiple access: Fundamentals, survey, and future research trends[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(4): 2073–2126. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3191937. [2] LIU Yuanwei, QIN Zhijin, ELKASHLAN M, et al. Nonorthogonal multiple access for 5G and beyond[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(12): 2347–2381. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2768666. [3] CLERCKX B, MAO Yijie, JORSWIECK E A, et al. A primer on rate-splitting multiple access: Tutorial, myths, and frequently asked questions[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(5): 1265–1308. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3242718. [4] CLERCKX B, MAO Yijie, SCHOBER R, et al. Rate-splitting unifying SDMA, OMA, NOMA, and multicasting in MISO broadcast channel: A simple two-user rate analysis[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(3): 349–353. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2954518. [5] LIU Penglu, LI Yong, CHENG Wei, et al. Active intelligent reflecting surface aided RSMA for millimeter-wave hybrid antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(9): 5287–5302. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3285290. [6] 雷维嘉, 张智, 雷宏江, 等. 速率分割多址接入系统中的协作中继传输策略与优化[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2024, 47(2): 58–65. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2023-096.LEI Weijia, ZHANG Zhi, LEI Hongjiang, et al. Cooperative relay transmission strategy and optimization in rate-splitting multiple access system[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2024, 47(2): 58–65. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2023-096. [7] SI Zhiwen, YIN Longfei, and CLERCKX B. Rate-splitting multiple access for multigateway multibeam satellite systems with feeder link interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(3): 2147–2162. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3144487. [8] PAPAZAFEIROPOULOS A and RATNARAJAH T. Rate-splitting robustness in multi-pair massive MIMO relay systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(8): 5623–5636. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2847668. [9] TONG Yuqiao, LI Dongdong, YANG Zhutian, et al. Cooperative rate splitting secure transmission with an untrusted user relay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 72(2): 2667–2671. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3211763. [10] TONG Yuqiao, LI Dongdong, YANG Zhutian, et al. Outage analysis of rate splitting networks with an untrusted user[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(2): 2626–2631. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3209794. [11] XIA Huiyun, MAO Yijie, CLERCKX B, et al. Weighted sum-rate maximization for rate-splitting multiple access based secure communication[C]. 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Austin, USA, 2022: 19–24. doi: 10.1109/WCNC51071.2022.9771854. [12] FU Hao, FENG Suili, TANG Weijun, et al. Robust secure beamforming design for two-user downlink MISO rate-splitting systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(12): 8351–8365. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3021725. [13] XIA Huiyun, ZHOU Xiaokang, HAN Shuai, et al. Security-reliability tradeoff in RSMA-based communications against eavesdropper collusion[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(9): 1504–1507. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3279860. [14] XIA Huiyun, HAN Shuai, and LI Cheng. Max-min fair optimization in RSMA-assisted secure communications with artificial noise[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(12): 3181–3184. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3328782. [15] JOUDEH H and CLERCKX B. Sum-rate maximization for linearly precoded downlink multiuser MISO systems with partial CSIT: A rate-splitting approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(11): 4847–4861. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2016.2603991. -





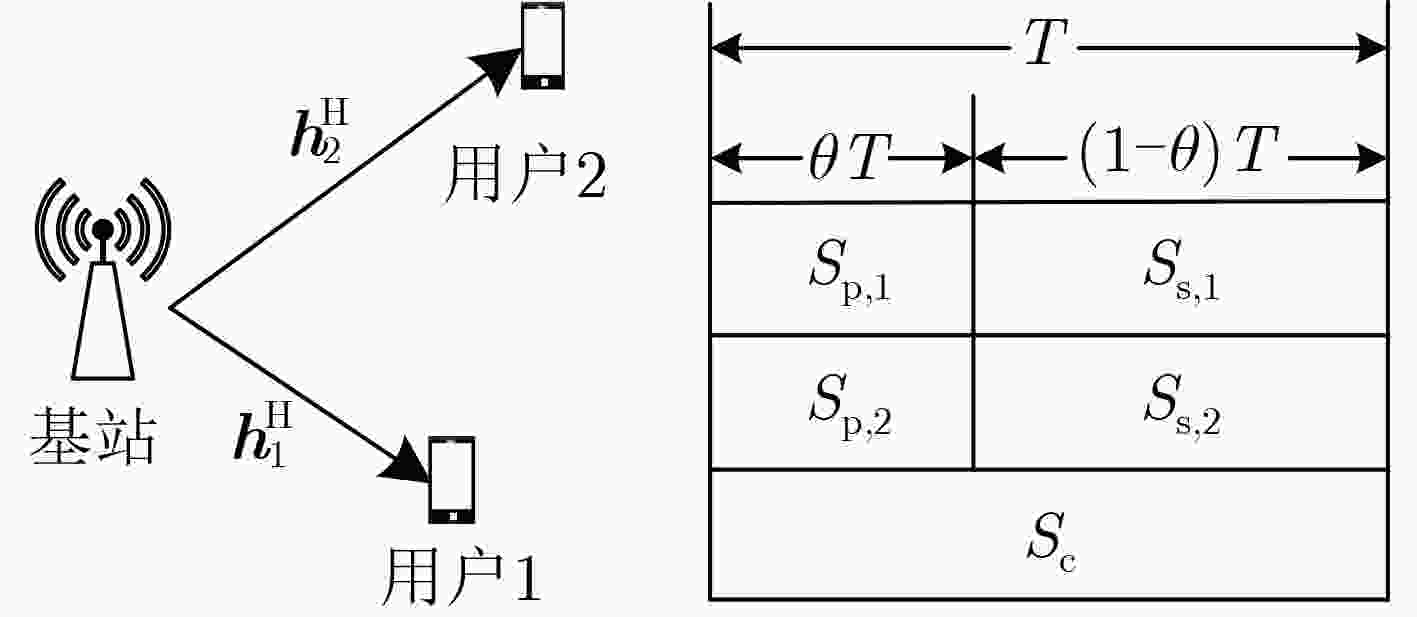
 下载:
下载:
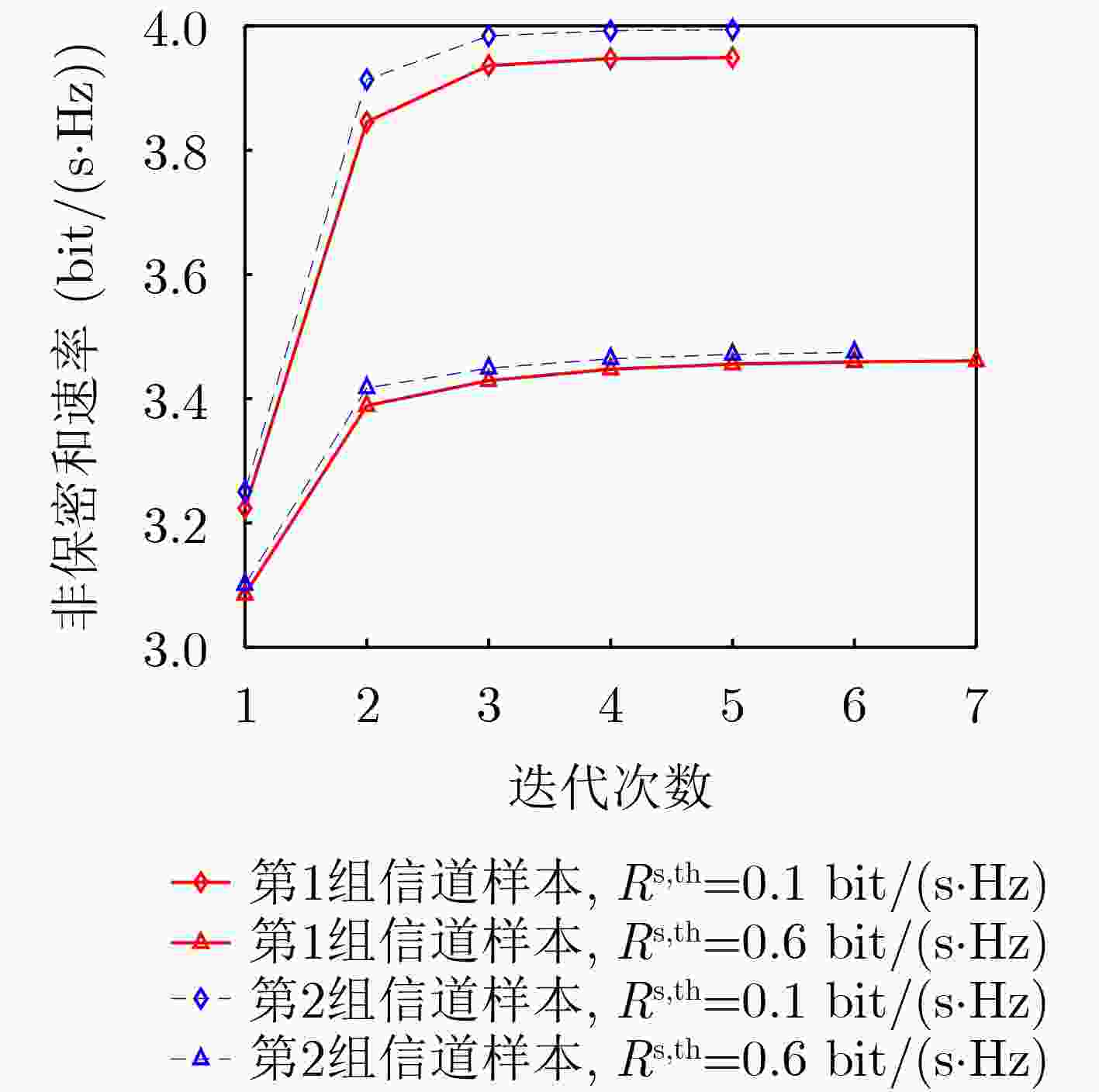
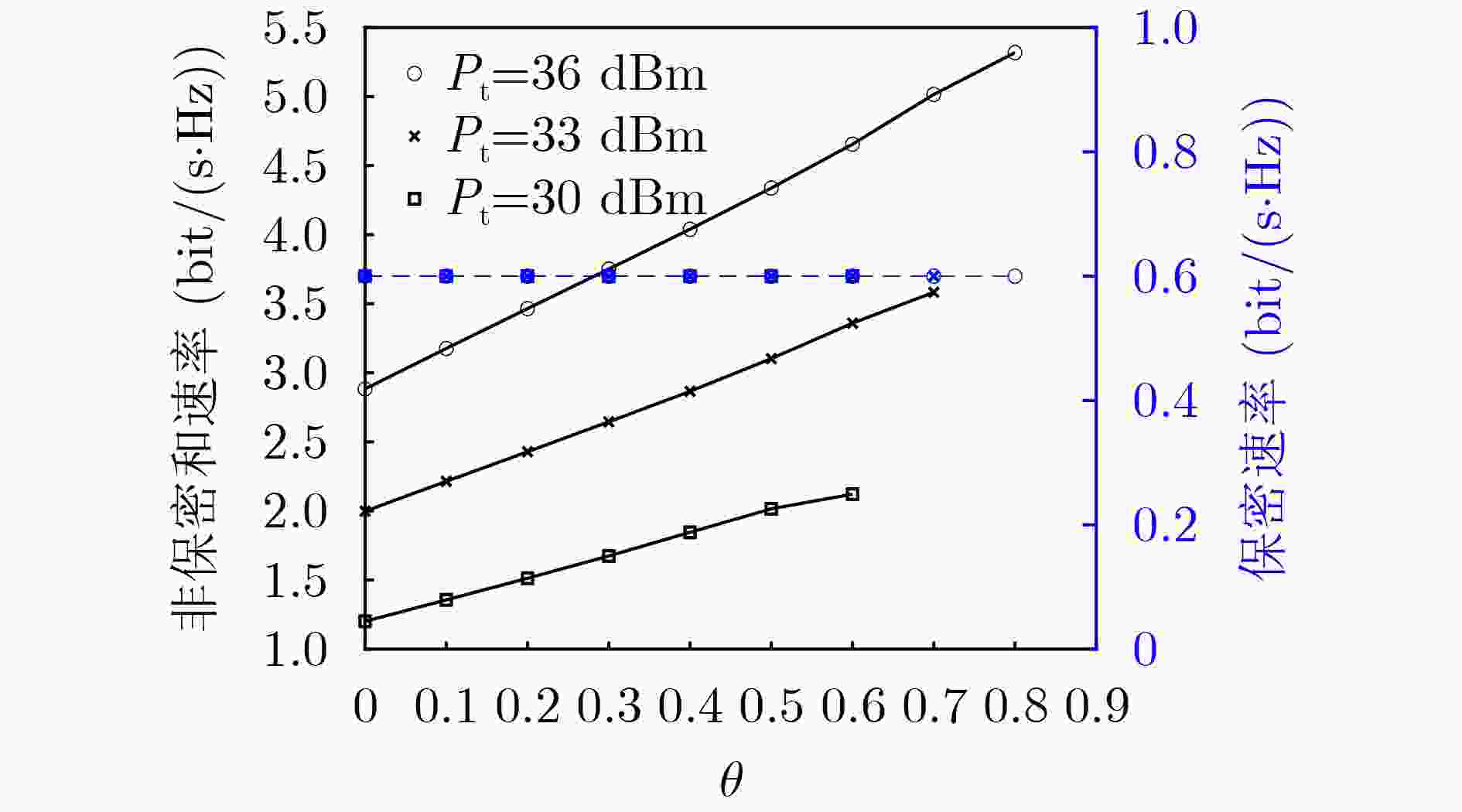
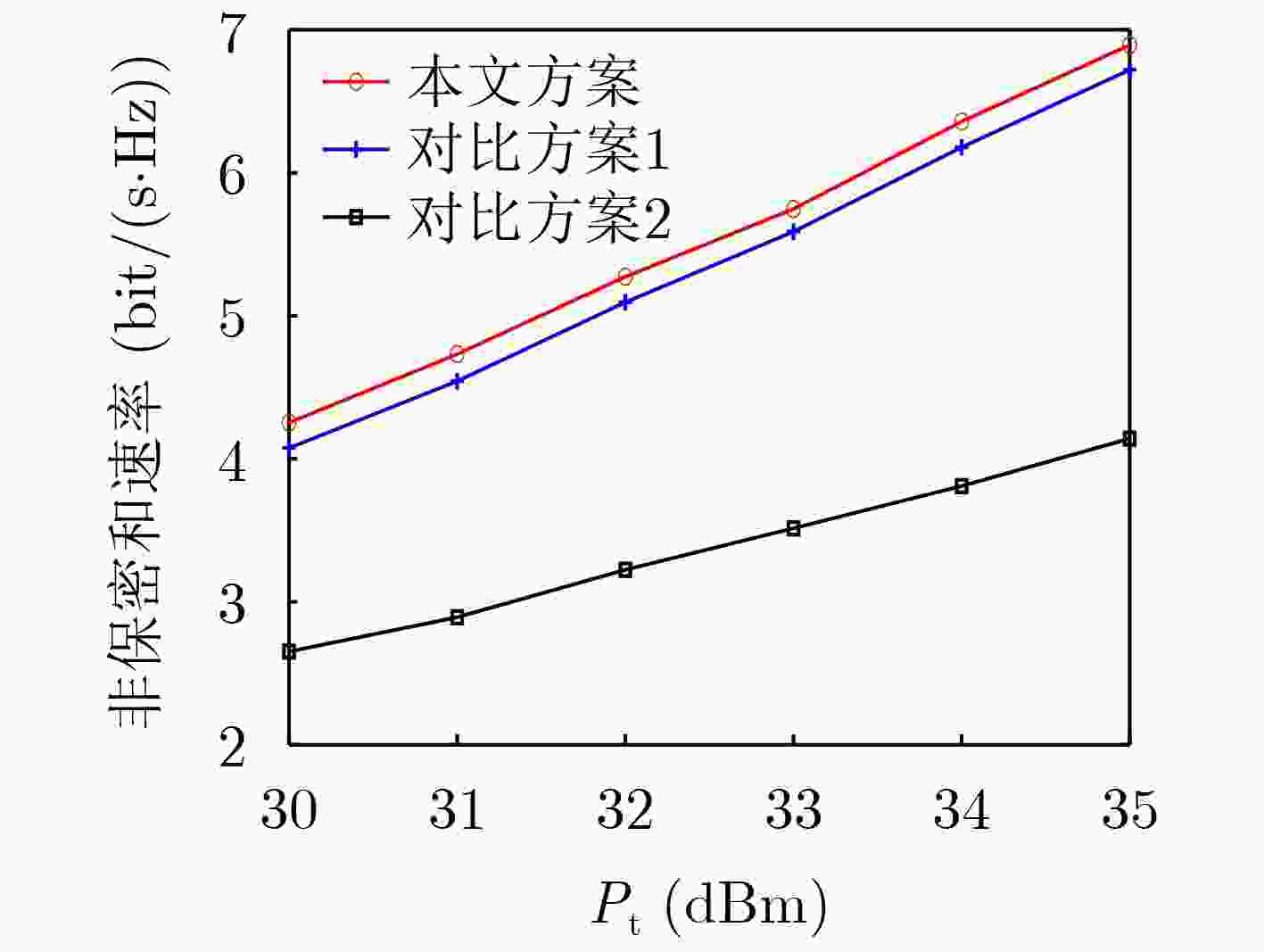



 下载:
下载:
