Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification Combining Visual-Textual Matching and Graph Embedding
-
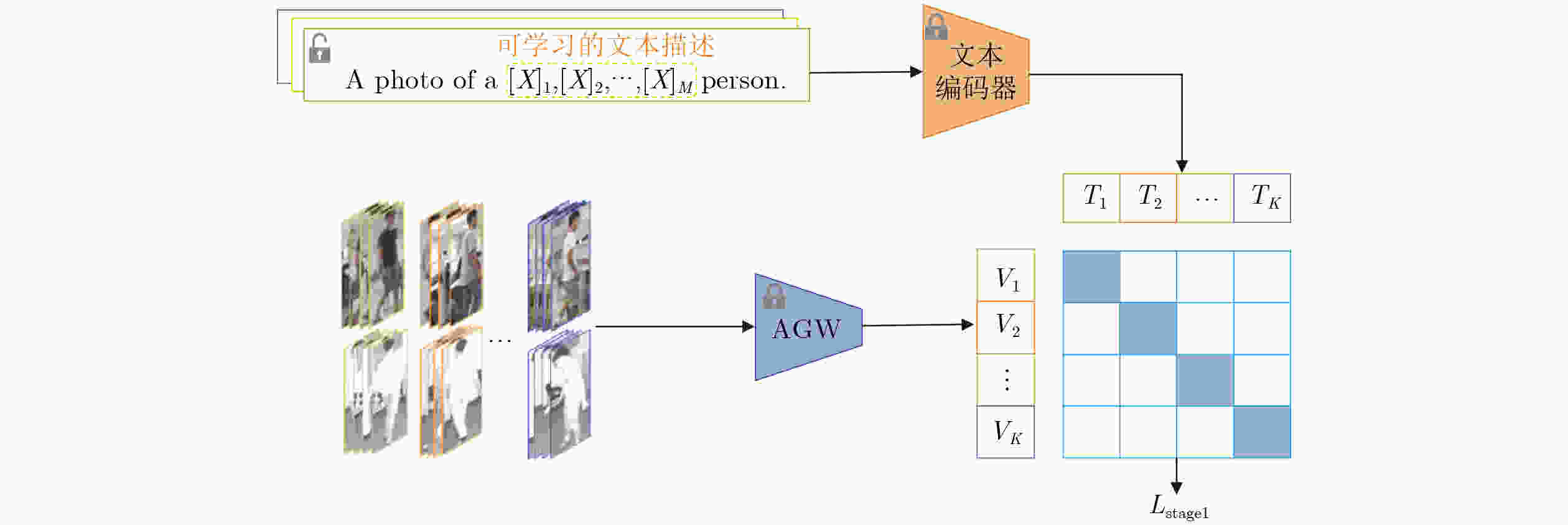
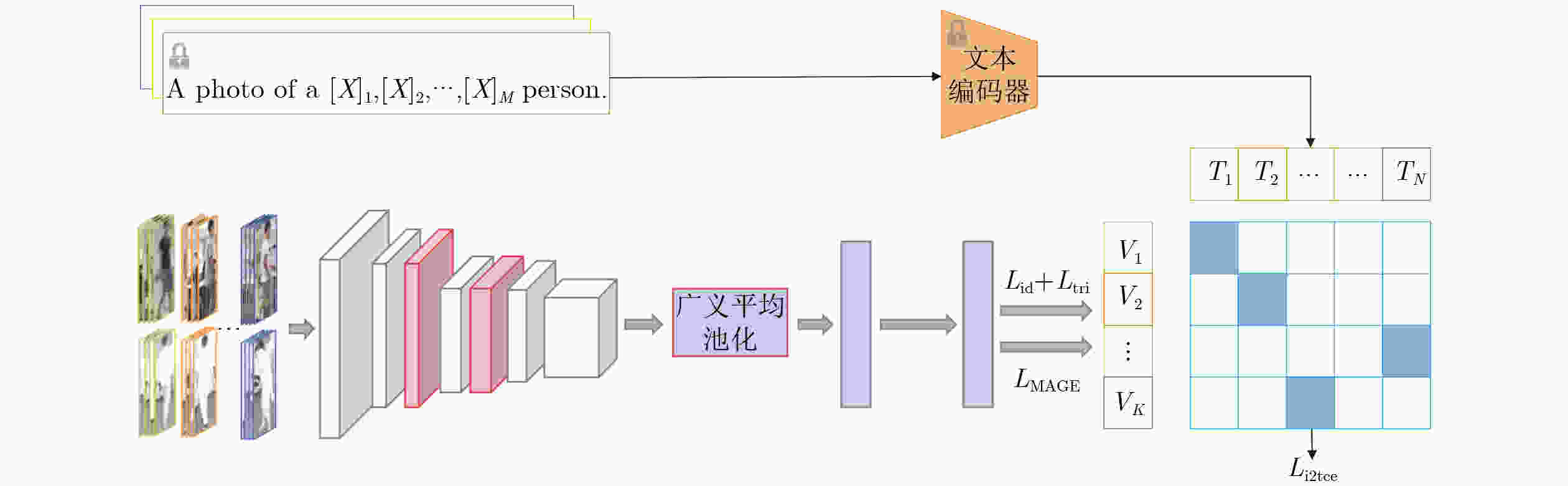
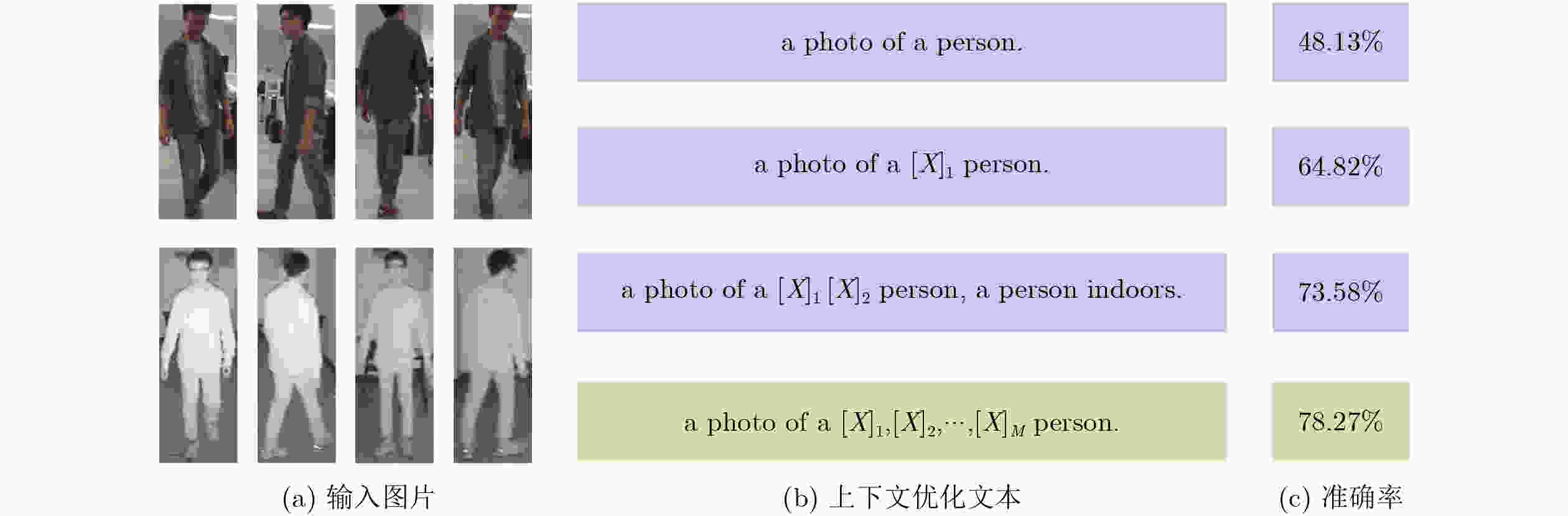
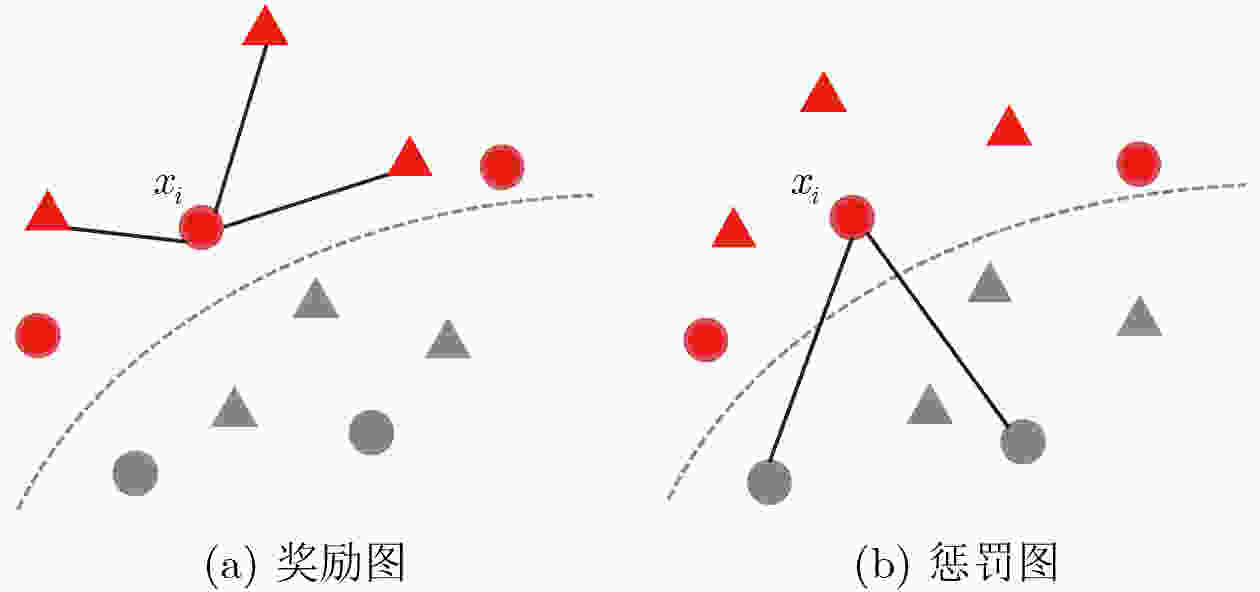
摘要: 对于可见光-红外跨模态行人重识别(Re-ID),大多数方法采用基于模态转换的策略,通过对抗网络生成图像,以此建立不同模态间的相互联系。然而这些方法往往不能有效降低模态间的差距,导致重识别性能不佳。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于视觉文本匹配和图嵌入的双阶段跨模态行人重识别方法。该方法通过上下文优化方案构建可学习文本模板,生成行人描述作为模态间的关联信息。具体而言,在第1阶段基于图片-文本对的预训练(CLIP)模型实现同一行人不同模态间的统一文本描述作为先验信息辅助降低模态差异。同时在第2阶段引入基于图嵌入的跨模态约束框架,设计模态间自适应损失函数,提升行人识别准确率。为了验证所提方法的有效性,在SYSU-MM01和RegDB数据集上进行了大量实验,其中SYSU-MM01数据集上的首次命中(Rank-1)和平均精度均值(mAP)分别达到64.2%, 60.2%。实验结果表明,该文所提方法能够提升可见光-红外跨模态行人重识别的准确率。
-
关键词:
- 行人重识别 /
- 跨模态 /
- 图片-文本对的预训练模型 /
- 上下文优化 /
- 图嵌入
Abstract: For cross-modal person Re-IDentification (Re-ID) in visible-infrared images, methods using modality conversion and adversarial networks yield associative information between modalities. However, these approaches fall short in effective feature recognition. Thus, a two-stage approach using visual-text matching and graph embedding for enhanced re-identification effectiveness is proposed in this paper. A context-optimized scheme is utilized by the method to construct learnable text templates that generate person descriptions as associative information between modalities. Specifically, in the first stage, unified text descriptions of the same person across different modalities are utilized as prior information, assisting in the reduction of modality differences, based on the Contrastive Language–Image Pre-training (CLIP) model. Meanwhile, in the second stage, a cross-modal constraint framework based on graph embedding is applied, and a modality-adaptive loss function is designed, aiming to improve person recognition accuracy. The method’s efficacy has been confirmed through extensive experiments on the SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets, with a Rank-1 accuracy of 64.2% and mean Average Precision (mAP) of 60.2% on SYSU-MM01 being achieved, thereby demonstrating significant improvements in cross-modal person re-identification. -
表 1 在SYSU-MM01的All-search模式下和其他方法对比实验结果(%)
方法 单镜头 多镜头 Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP Zero-padding[13] 14.8 54.1 71.3 16.0 – 61.4 78.4 10.9 HCML[15] 14.3 53.2 69.2 16.2 – – – – BDTR[16] 27.3 67.0 81.7 27.3 – – – – eBDTR[17] 27.8 67.3 81.3 28.4 – – – – Hi-CMD[4] 34.9 77.6 – 35.9 – – – – DPMBN[18] 37.0 79.5 89.9 40.3 – – – – LZM[19] 45.0 89.0 – 45.9 – – – – AlignGAN[8] 42.4 85.0 93.7 40.7 51.5 89.4 95.7 33.9 Xmodal[20] 49.9 89.8 96.0 50.7 47.6 88.1 96.0 36.1 DDAG[21] 54.8 90.4 95.8 53.0 – – – – SFANET[22] 60.5 91.8 95.2 53.9 – – – – MID[23] 60.3 92.9 96.7 59.4 – – – – CM-NAS[24] 60.8 92.1 96.8 58.9 68.0 94.8 97.9 52.4 Baseline(AGW)[12] 47.5 84.4 92.1 47.7 – – – – 本文方法 64.2 92.5 96.1 60.2 71.0 90.0 94.0 52.4 表 2 在RegDB数据集和其他方法对比实验结果(%)
方法 可见光图像查询红外图像 红外图像查询可见光图像 Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP Zero-padding[13] 17.8 34.2 44.4 18.9 16.6 34.7 44.3 17.8 HCML[15] 24.4 47.5 56.8 20.0 21.7 45.0 55.6 22.2 BDTR[16] 33.6 58.6 67.4 32.8 32.9 58.5 68.4 32.0 eBDTR[17] 34.6 59.0 68.7 33.46 34.2 58.7 68.6 32.5 AlignGAN[8] 57.9 – – 53.6 56.3 – – 53.4 Xmodal[20] 62.2 83.1 91.7 60.2 – – – – DDAG[21] 69.3 86.2 91.5 63.5 68.1 85.2 90.3 61.8 SFANET[22] 76.3 91.0 94.3 68.0 70.2 85.2 89.2 63.8 Baseline(AGW)[12] 70.1 86.2 – 66.4 70.5 87.1 – 65.9 本文方法 73.0 88.1 94.4 67.7 72.8 87.1 90.1 66.2 表 3 在SYSU-MM01的All-search模式单镜头设置下实验结果(%)
方法 Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 mAP Baseline 47.5 – 86.2 47.7 Baseline+CLIP 60.2 80.2 87.8 56.1 Baseline+CLIP+MAGE 62.9 82.7 90.1 58.6 表 4 损失函数的选择对实验指标的影响(%)
$ {L_{{\text{i2t}}}} $ $ {L_{{\text{id}}}} $ $ {L_{{\text{tri}}}} $ $ {L_{{\text{MAGE}}}} $ Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 mAP √ √ √ 51.6 75.8 83 42.9 √ √ √ 60.5 83.4 90.6 56.7 √ √ 4.4 12.3 22.2 5.3 √ √ 62.8 85.3 91.7 59.2 √ √ √ √ 64.2 86.5 92.5 60.2 表 5 不同图像编码器下采用单阶段和双阶段对实验指标的影响(%)
表 6 参数$ \alpha $在不同取值下的实验结果(%)
$ \alpha $ SYSU-MM01 Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 mAP 0.5 56.0 80.4 88.6 54.8 0.05 62.3 83.1 89.6 58.5 0.005 62.9 82.7 90.1 58.6 0.0005 59.6 83.1 90.1 56.9 -
[1] 张永飞, 杨航远, 张雨佳, 等. 行人再识别技术研究进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2023, 28(6): 1829–1862. doi: 10.11834/jig.230022.ZHANG Yongfei, YANG Hangyuan, ZHANG Yujia, et al. Recent progress in person re-ID[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2023, 28(6): 1829–1862. doi: 10.11834/jig.230022. [2] 王粉花, 赵波, 黄超, 等. 基于多尺度和注意力融合学习的行人重识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 3045–3052. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190998.WANG Fenhua, ZHAO Bo, HUANG Chao, et al. Person re-identification based on multi-scale network attention fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 3045–3052. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190998. [3] LI Shuang, LI Fan, LI Jinxing, et al. Logical relation inference and multiview information interaction for domain adaptation person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023. doi: 10.1109/tnnls.2023.3281504. [4] CHOI S, LEE S, KIM Y, et al. Hi-CMD: Hierarchical cross-modality disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10254–10263. doi: 10.1109/cvpr42600.2020.01027. [5] HUANG Nianchang, LIU Jianan, LUO Yongjiang, et al. Exploring modality-shared appearance features and modality-invariant relation features for cross-modality person re-identification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 135: 109145. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109145. [6] ZHANG Yukang and WANG Hanzi. Diverse embedding expansion network and low-light cross-modality benchmark for visible-infrared person re-identification[C]. The 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 2153–2162. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00214. [7] DAI Pingyang, JI Rongrong, WANG Haibin, et al. Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training[C]. The Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 677–683. [8] WANG Guan’an, ZHANG Tianzhu, CHENG Jian, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 3622–3631. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00372. [9] 寇旗旗, 黄绩, 程德强, 等. 基于语义融合的域内相似性分组行人重识别[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(7): 153–162. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022136.KOU Qiqi, HUANG Ji, CHENG Deqiang, et al. Person re-identification with intra-domain similarity grouping based on semantic fusion[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(7): 153–162. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022136. [10] LI Siyuan, SUN Li, and LI Qingli. CLIP-ReID: Exploiting vision-language model for image re-identification without concrete text labels[C]. The 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 1405–1413. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i1.25225. [11] MORSING L H, SHEIKH-OMAR O A, and IOSIFIDIS A. Supervised domain adaptation using graph embedding[C]. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 2021: 7841–7847. doi: 10.1109/icpr48806.2021.9412422. [12] YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing, LIN Gaojie, et al. Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(6): 2872–2893. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054775. [13] WU Ancong, ZHENG Weishi, YU Hongxing, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5390–5399. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.575. [14] NGUYEN D T, HONG H G, KIM K W, et al. Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 605. doi: 10.3390/s17030605. [15] YE Mang, LAN Xiangyuan, LI Jiawei, et al. Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification[C]. The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 7501–7508. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.12293. [16] YE Mang, WANG Zheng, LAN Xiangyuan, et al. Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking[C]. The Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1092–1099. [17] YE Mang, LAN Xiangyuan, WANG Zheng, et al. Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 407–419. doi: 10.1109/tifs.2019.2921454. [18] XIANG Xuezhi, LV Ning, YU Zeting, et al. Cross-modality person re-identification based on dual-path multi-branch network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(23): 11706–11713. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2936916. [19] BASARAN E, GÖKMEN M, and KAMASAK M E. An efficient framework for visible–infrared cross modality person re-identification[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2020, 87: 115933. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2020.115933. [20] LI Diangang, WEI Xing, HONG Xiaopeng, et al. Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 4610–4617. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i04.5891. [21] YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing, CRANDALL D J, et al. Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 229–247. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_14. [22] LIU Haojie, MA Shun, XIA Daoxun, et al. SFANet: A spectrum-aware feature augmentation network for visible-infrared person reidentification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(4): 1958–1971. doi: 10.1109/tnnls.2021.3105702. [23] HUANG Zhipeng, LIU Jiawei, LI Liang, et al. Modality-adaptive mixup and invariant decomposition for RGB-infrared person re-identification[C]. The 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022: 1034–1042. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i1.19987. [24] FU Chaoyou, HU Yibo, WU Xiang, et al. CM-NAS: Cross-modality neural architecture search for visible-infrared person re-identification[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 11803–11812. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01161. [25] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. -





 下载:
下载:

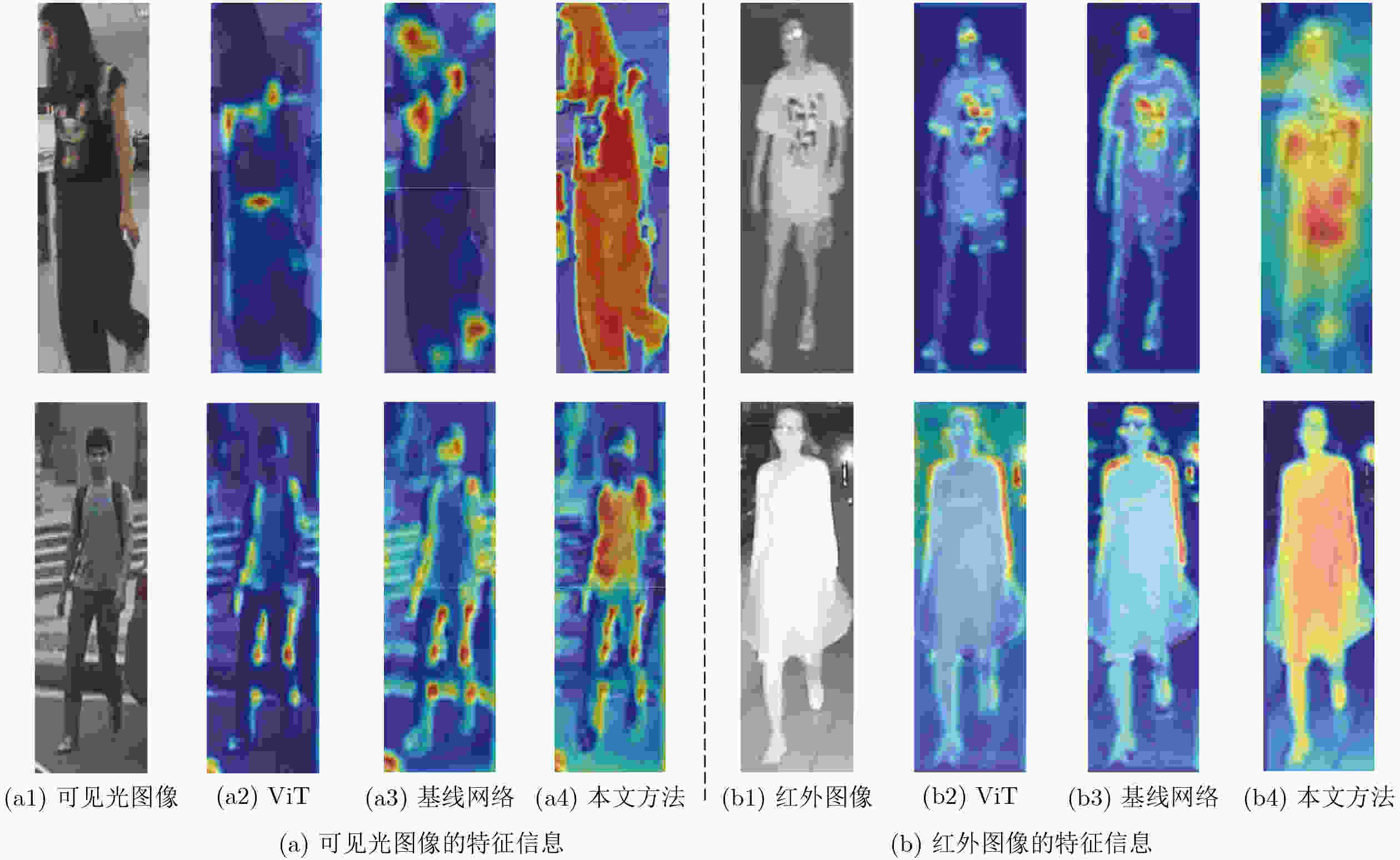


 下载:
下载:
