Hybrid Scene Representation Method Integrating Neural Radiation Fields and Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
-
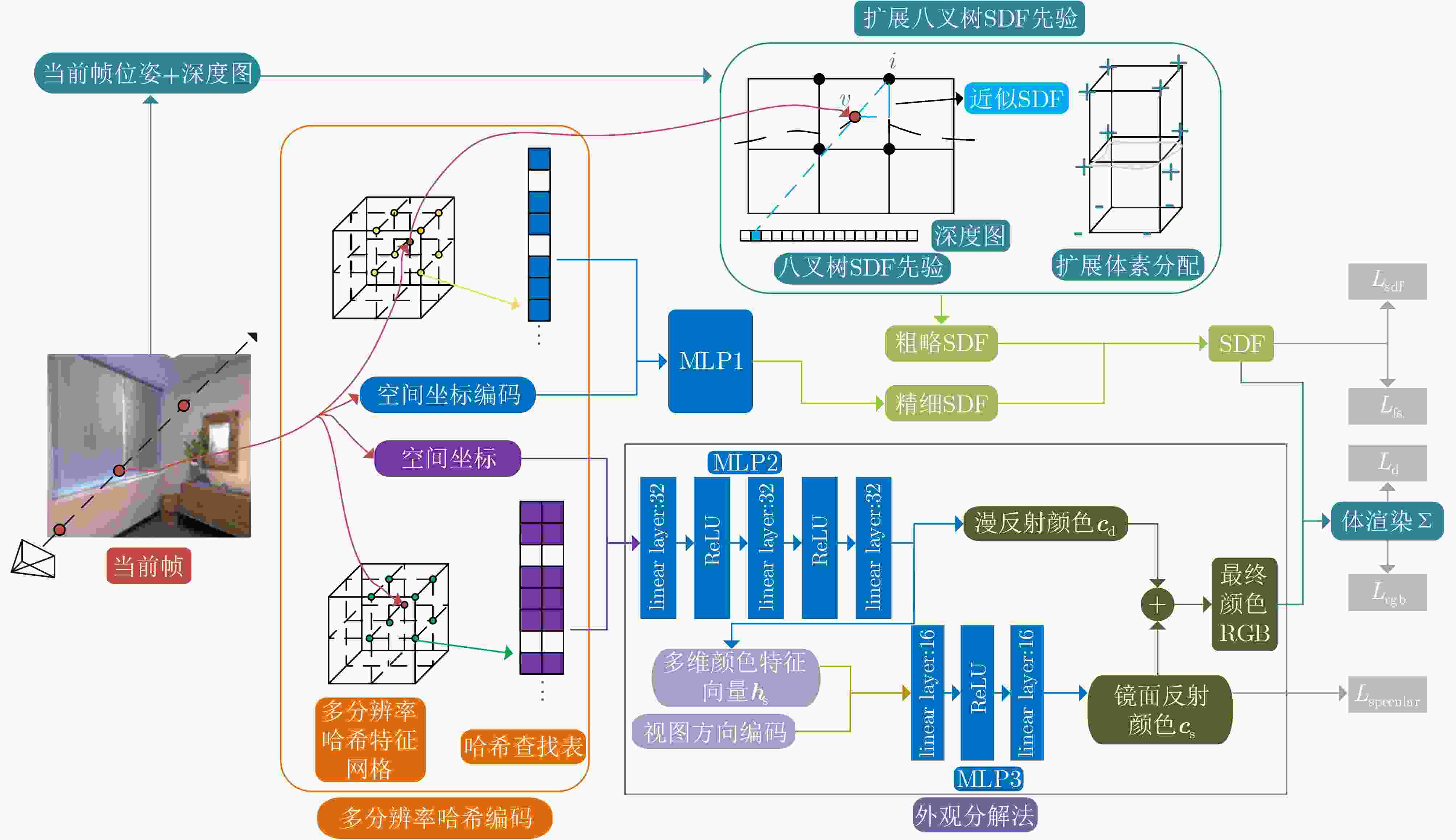
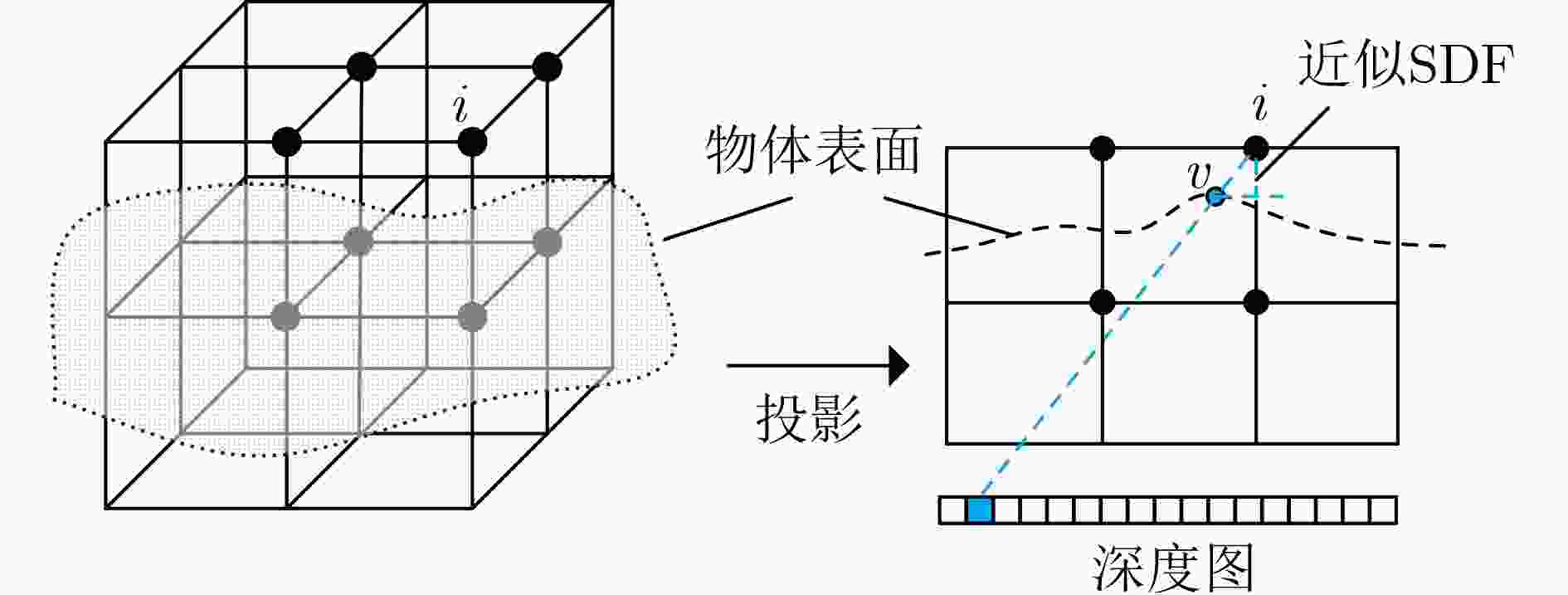
摘要: 目前,传统显式场景表示的同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)系统对场景进行离散化,不适用于连续性场景重建。该文提出一种基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的混合场景表示的深度相机(RGB-D)SLAM系统,利用扩展显式八叉树符号距离函数(SDF)先验粗略表示场景,并通过多分辨率哈希编码以不同细节级别表示场景,实现场景几何的快速初始化,并使场景几何更易于学习。此外,运用外观颜色分解法,结合视图方向将颜色分解为漫反射颜色和镜面反射颜色,实现光照一致性的重建,使得重建结果更加真实。通过在Replica和TUM RGB-D数据集上进行实验,Replica数据集场景重建完成率达到93.65%,相较于Vox-Fusion定位精度,在Replica数据集上平均领先87.50%,在TUM RGB-D数据集上平均领先81.99%。
-
关键词:
- 同时定位与地图构建系统 /
- 神经辐射场 /
- 混合场景表示 /
- 镜面反射
Abstract: Currently, traditional explicit scene representation Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) systems discretize the scene and are not suitable for continuous scene reconstruction. A RGB-D SLAM system based on hybrid scene representation of Neural Radiation Fields (NeRF) is proposed in this paper. The extended explicit octree Signed Distance Functions (SDF) prior is used to roughly represent the scene, and multi-resolution hash coding is used to represent the scene with different details levels, enabling fast initialization of scene geometry and making scene geometry easier to learn. In addition, the appearance color decomposition method is used to decompose the color into diffuse reflection color and specular reflection color based on the view direction to achieve reconstruction of lighting consistency, making the reconstruction result more realistic. Through experiments on the Replica and TUM RGB-D dataset, the scene reconstruction completion rate of the Replica dataset reaches 93.65%. Compared with the Vox-Fusion positioning accuracy, it leads on average by 87.50% on the Replica dataset and by 81.99% on the TUM RGB-D dataset. -
表 1 超参设定值
超参 设定值 超参 设定值 超参 设定值 超参 设定值 L 16 F2 2 Mf 11 ${\alpha _3}$ 0.000 01 T 216 ${N_t}$ 1024 ${\alpha _1}$ 5.0 ${\alpha _4}$ 1000 F1 1 $ M $ 32 ${\alpha _2}$ 0.1 ${\alpha _5}$ 10 表 2 Replica数据集重建质量对比
方法 重建质量指标 Depth
L1(cm)↓Acc.
(cm)↓Comp.
(cm)↓Comp.
Ratio(%)↑iMAP 4.64 3.62 4.93 80.50 NICE-SLAM 3.53 2.85 3.00 89.33 Vox-Fusion 2.91 2.37 2.28 92.86 vMAP 3.33 3.20 2.39 92.99 DNS SLAM 3.16 2.76 2.74 91.73 本文 1.76 2.29 2.11 93.65 表 3 Replica数据集轨迹误差
方法 room0 room1 office0 office1 office3 office4 平均值 iMAP 70.00 4.53 2.32 1.74 58.40 2.62 23.27 NICE-SLAM 1.69 2.04 0.99 0.90 3.97 3.08 2.11 Vox-Fusion 1.37 4.70 8.48 2.04 1.11 2.94 3.44 vMAP / / / / / / / DNS SLAM 0.49 0.46 0.34 0.35 0.62 0.60 0.48 本文 0.41 0.52 0.31 0.37 0.46 0.53 0.43 表 4 TUM-RGBD数据集轨迹误差
方法 fr1/desk fr2/xyz fr3/office 平均值 iMAP 4.9 2.0 5.8 4.23 NICE-SLAM 2.7 1.8 3.0 2.50 Vox-Fusion 3.5 1.5 26.0 10.33 vMAP 2.6 1.6 3.0 2.40 DNS SLAM / / / / 本文 2.0 1.5 2.1 1.86 表 5 Replica数据集消融实验的定量分析
Acc.(cm)↓ Comp.(cm)↓ Comp. Ratio(%)↑ w/o 八叉树SDF先验 2.99 2.20 93.88 w/o 扩展体素分配 2.88 2.10 95.05 w/o 外观颜色分解 2.36 1.95 95.36 本文 2.27 1.92 95.75 表 6 添加体素的点的阈值分析
点数量阈值 Acc.(cm)↓ Comp.(cm)↓ Comp. Ratio(%)↑ 5 5.00 2.08 93.11 10/本文 2.27 1.92 95.75 15 2.37 1.94 95.67 20 2.29 1.93 95.63 表 7 Replica数据集损失函数消融实验
Acc.(cm)↓ Comp.(cm)↓ Comp. Ratio(%)↑ w/o $ {{L}_{{\mathrm{rgb}}}} $ 2.47 1.94 95.68 w/o $ {{L}_{\text{d}}} $ 2.48 1.93 95.54 w/o $ {{L}_{{\text{specular}}}} $ 2.45 1.95 95.64 w/o $ {{L}_{{\text{sdf}}}} $ 2.68 2.04 94.68 w/o $ {{L}_{{f_{\text{s}}}}} $ 2.30 1.95 95.46 本文 2.27 1.92 95.75 表 8 Replica数据集性能对比
方法 Avg. fps↑ GPU Mem. (G)↓ param. (M)↓ iMAP 0.13 6.44 0.32 NICE-SLAM 0.61 4.70 17.4 Vox-Fusion 0.74 21.22 0.87 vMAP 4.03 \ 0.66 DNS SLAM 0.13 \ \ 本文 4.93 2.93 0.34 -
[1] HORNUNG A, WURM K M, BENNEWITZ M, et al. OctoMap: An efficient probabilistic 3D mapping framework based on octrees[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2013, 34(3): 189–206. doi: 10.1007/s10514-012-9321-0. [2] OLEYNIKOVA H, TAYLOR Z, FEHR M, et al. Voxblox: Incremental 3D euclidean signed distance fields for on-board MAV planning[C]. 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 1366–1373. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2017.8202315. [3] NEWCOMBE R A, IZADI S, HILLIGES O, et al. KinectFusion: Real-time dense surface mapping and tracking[C]. 2011 10th IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, Basel, Switzerland, 2011: 127–136. doi: 10.1109/ISMAR.2011.6092378. [4] FEHR M, FURRER F, DRYANOVSKI I, et al. TSDF-based change detection for consistent long-term dense reconstruction and dynamic object discovery[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, Singapore, 2017: 5237–5244. doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2017.7989614. [5] DAI A, NIEßNER M, ZOLLHÖFER M, et al. BundleFusion: Real-time globally consistent 3D reconstruction using on-the-fly surface reintegration[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG), 2017, 36(4): 76a. doi: 10.1145/3072959.3054739. [6] NIEßNER M, ZOLLHÖFER M, IZADI S, et al. Real-time 3D reconstruction at scale using voxel hashing[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG), 2013, 32(6): 169. doi: 10.1145/2508363.2508374. [7] KÄHLER O, PRISACARIU V A, REN C Y, et al. Very high frame rate volumetric integration of depth images on mobile devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2015, 21(11): 1241–1250. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2015.2459891. [8] WANG Kaixuan, GAO Fei, and SHEN Shaojie. Real-time scalable dense surfel mapping[C]. 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 2019: 6919–6925. doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2019.8794101. [9] WHELAN T, SALAS-MORENO R F, GLOCKER B, et al. ElasticFusion: Real-time dense SLAM and light source estimation[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2016, 35(14): 1697–1716. doi: 10.1177/0278364916669237. [10] RUETZ F, HERNÁNDEZ E, PFEIFFER M, et al. OVPC mesh: 3D free-space representation for local ground vehicle navigation[C]. 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 2019: 8648–8654. doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2019.8793503. [11] ZHONG Xingguang, PAN Yue, BEHLEY J, et al. SHINE-mapping: Large-scale 3D mapping using sparse hierarchical implicit neural representations[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 2023: 8371–8377. doi: 10.1109/ICRA48891.2023.10160907. [12] MILDENHALL B, SRINIVASAN P P, TANCIK M, et al. NeRF: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2021, 65(1): 99–106. doi: 10.1145/3503250. [13] SUCAR E, LIU Shikun, ORTIZ J, et al. iMAP: Implicit mapping and positioning in real-time[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 6209–6218. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00617. [14] ZHU Zihan, PENG Songyou, LARSSON V, et al. NICE-SLAM: Neural implicit scalable encoding for slam[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 12776–12786. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01245. [15] YANG Xingrui, LI Hai, ZHAI Hongjia, et al. Vox-Fusion: Dense tracking and mapping with voxel-based neural implicit representation[C]. 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Singapore, 2022: 499–507. doi: 10.1109/ISMAR55827.2022.00066. [16] KONG Xin, LIU Shikun, TAHER M, et al. vMAP: Vectorised object mapping for neural field SLAM[C]. The 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 952–961. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00098. [17] LI Kunyi, NIEMEYER M, NAVAB N, et al. DNS SLAM: Dense neural semantic-informed SLAM[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2312.00204, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2312.00204. [18] WU Xingming, LIU Zimeng, TIAN Yuxin, et al. KN-SLAM: Keypoints and neural implicit encoding SLAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 2512712. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3378264. [19] WANG Haocheng, CAO Yanlong, WEI Xiaoyao, et al. Structerf-SLAM: Neural implicit representation SLAM for structural environments[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2024, 119: 103893. doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2024.103893. [20] MÜLLER T, EVANS A, SCHIED C, et al. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG), 2022, 41(4): 102. doi: 10.1145/3528223.3530127. [21] TANG Jiaxiang, ZHOU Hang, CHEN Xiaokang, et al. Delicate textured mesh recovery from NeRF via adaptive surface refinement[C]. The 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 17693–17703. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01626. [22] ZHANG Xiuming, SRINIVASAN P P, DENG Boyang, et al. NeRFactor: Neural factorization of shape and reflectance under an unknown illumination[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG), 2021, 40(6): 237. doi: 10.1145/3478513.3480496. [23] WANG Peng, LIU Lingjie, LIU Yuan, et al. NeuS: Learning neural implicit surfaces by volume rendering for multi-view reconstruction[C]. The 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 2081. [24] YARIV L, GU Jiatao, KASTEN Y, et al. Volume rendering of neural implicit surfaces[C]. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 367. [25] AZINOVIĆ D, MARTIN-BRUALLA R, GOLDMAN D B, et al. Neural RGB-D surface reconstruction[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 6280–6291. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00619. [26] STRAUB J, WHELAN T, MA Lingni, et al. The replica dataset: A digital replica of indoor spaces[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1906.05797, 2019. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1906.05797. [27] STURM J, ENGELHARD N, ENDRES F, et al. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems[C]. 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 2012: 573–580. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2012.6385773. -





 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:
