Ground Penetrating Radar Hyperbolic Keypoint Detection and Object Localization Based on Dual YOLOv8-pose Model
-
摘要: 探地雷达(GPR)是一种可用于地下目标识别的无损检测方法。针对现有方法存在不同尺度目标兼容性差、复杂图像识别难度大、无法精确定位等问题,该文提出一种基于双重YOLO姿态模型(YOLOv8-pose)的GPR双曲线关键点检测与目标定位,命名为双重YOLO关键点定位方法(DYKL),用于地下目标的检测与精确定位。所提模型架构包含两个阶段:首先,第1阶段是基于YOLOv8-pose模型的GPR目标检测,以确定候选目标的位置;接着,第1阶段的部分训练权重被共享并传递到第2阶段,后者以此为基础继续训练YOLOv8-pose网络,用于候选目标特征的关键点检测及获取,从而实现地下目标的自动化定位。通过与级联区域卷积网络(Cascade R-CNN)、 更快的区域卷积网络(Faster R-CNN)、 实时对象检测模型(RTMDet)以及“你只看一次”人脸模型(YOLOv7-face)4种先进的深度模型进行比较,所提模型平均识别准确率达到98.8%,性能优于其他模型。结果表明所提DYKL模型具有较高的识别准确性与较强的鲁棒性,可以为地下目标的精确定位提供参考。Abstract: Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is identified as a non-destructive method usable for the identification of underground targets. Existing methods often struggle with variable target sizes, complex image recognition, and precise target localization. To address these challenges, an innovative method is introduced that leverages a dual YOLOv8-pose model for the detection and precise localization of hyperbolic keypoint. This method, termed Dual YOLOv8-pose Keypoint Localization (DYKL), offers a sophisticated solution to the challenges inherent in GPR-based target identification and positioning. The proposed model architecture includes two stages: firstly, the YOLOv8-pose model is employed for the preliminary detection of GPR targets, adeptly identifying regions that are likely to contain these targets. Secondly, building upon the training weights established in the first phase, the model further hones the YOLOv8-pose network. This refinement is geared towards the precise detection of keypoints within the candidate target features, thereby facilitating the automated identification and exact localization of underground targets with enhanced accuracy. Through comparison with four advanced deep-learning models— Cascade Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (Cascade R-CNN), Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (Faster R-CNN), Real-Time Models for object Detection (RTMDet), and You Only Look Once v7(YOLOv7-face), the proposed DYKL model exhibits an average recognition accuracy of 98.8%, surpassing these models. The results demonstrate the DYKL model’s high recognition accuracy and robustness, serving as a benchmark for the precise localization of subterranean targets.
-
Key words:
- Ground penetrating radar /
- Target detection /
- Keypoint detection /
- YOLOv8
-
表 1 GPR目标自动识别算法
文献 模型类别 算法 检测目标 数据集 性能指标(%) 兰天等人[34] 图像学目标检测 基于拟合误差消除双曲线识别模型 / 实测图像和仿真图像 / Pham等人[16] 两阶段目标检测 Faster R-CNN / 50张仿真图像和100张实测图像 / Cui等人[18] 两阶段目标检测 Faster R-CNN 地层界面 / 检测框Pre= 98.3 Zhao等人[20] 两阶段实例分割 Mask R-CNN 隧道衬砌上缺陷位置 / 检测框Pre=96.1
掩模预测Pre=95.6Hou等人[21] 两阶段实例分割 基于MS—RCNN定制锚定方案 树根 95张实测图像 掩膜预测AP50=38.6 Wang等人[26] 单阶段目标检测 SSD引入FPN特征融合层网络和广义交并集损失 / 1 170张仿真图像 检测框Pre=92.0
检测框Rec=90.3Qiu等人[28] 单阶段目标检测 YOLOv5 铁实验材料 412张实测图像 检测框Pre=82.6
检测框Rec=68.0Hu等人[29] 单阶段目标检测 YOLOv5引入注意力机制 地下缺陷 3 256张图像包含实测图像和仿真图像 检测框mAP=85.4 胡荣明等人[30] 单阶段目标检测 YOLOv7 隧道衬砌病害 506张仿真图像和84张实测图像 检测框Pre=97.9
检测框Rec=90.6Wang等人[31] 单阶段目标检测 YOLOv8引入CBAM注意力机制 地下缺陷 837张实测图像 检测框mAP50=90.8
检测框F1=88.3Li等人[32] 单阶段关键点检测 YOLOv4引入关键点回归并增加Wing损失函数 植物根 1 000张仿真图像和2 320张实测图像 检测框Pre=94.0
检测框Rec=96.7方涛涛等人[33] 单阶段关键点检测 YOLOv8引入 CBAM 注意力机制和关键点回归 地下管线 545张实测图像和795张仿真图像 定位水平误差8.6
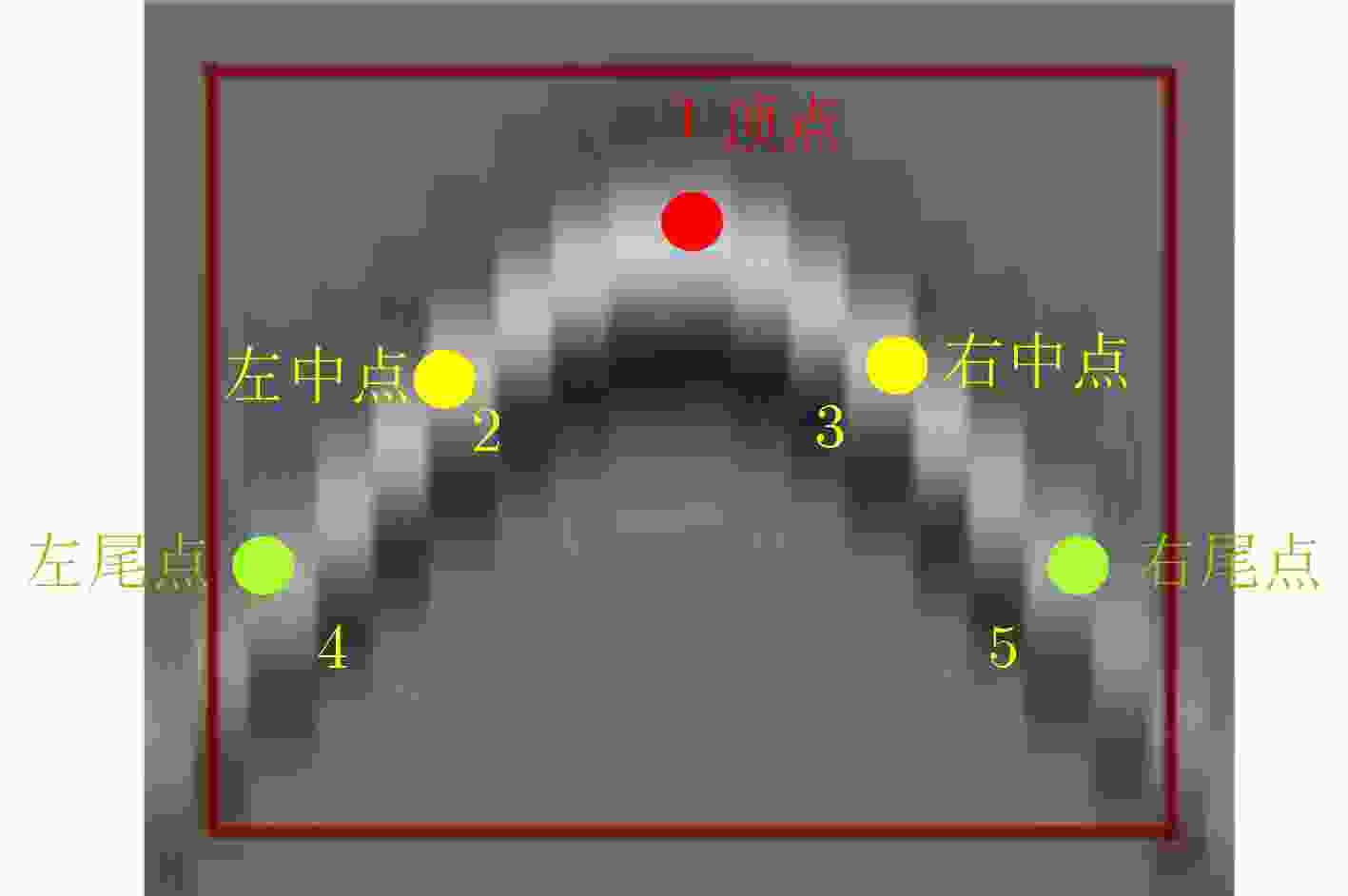
定位深度误差1.8表 2 模型输入图像的数量与尺寸
参数 目标检测阶段 关键点检测阶段 批量大小 32 64 图像尺寸 640×640 128×128 -
[1] LI Jing, LIU Cai, ZENG Zhaofa, et al. Gpr signal denoising and target extraction with the ceemd method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(8): 1615–1619. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2015.2415736. [2] 李洪丽, 鹿琪. 探地雷达在LNAPL污染土壤探测中的应用进展研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(3): 1141–1148. doi: 10.6038/pg2020DD0414.LI Hongli and LU Qi. Progress in application of ground penetrating radar in LNAPL contaminated soil detection of LNAPL[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(3): 1141–1148. doi: 10.6038/pg2020DD0414. [3] 尹德, 叶盛波, 张经纬, 等. 公路结构和介电特性对探地雷达反射回波的影响研究[J]. 电子测量技术, 2018, 41(5): 51–56. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.1700792.YIN De, YE Shengbo, ZHANG Jingwei, et al. Study on the effect of highway structure and dielectric properties on GPR echo[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2018, 41(5): 51–56. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.1700792. [4] 王韵, 王红雨, 常留成, 等. 基于探地雷达的水库坝前淤积土沉积规律研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(4): 152–158. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2021.04.021.WANG Yun, WANG Hongyu, CHANG Liucheng, et al. Study on sedimentation regulation of silted soil in the front of reservoir dam based on GPR[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 35(4): 152–158. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2021.04.021. [5] 覃谭, 赵永辉, 林国聪, 等. 探地雷达在上林湖越窑遗址水下考古中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(3): 624–630. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2018.1290.QIN Tan, ZHAO Yonghui, LIN Guocong, et al. The application of GPR to underwater archaeological investigation of Shanglinhu Yue kiln relics[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(3): 624–630. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2018.1290. [6] 胡进峰, 周正欧. 浅地层探地雷达目标探测和定位新方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2006, 27(4): 371–375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2006.04.010.HU Jinfeng and ZHOU Zhengou. Target detection and orientation in sub-surface penetrating radar data[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2006, 27(4): 371–375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2006.04.010. [7] LIU Yayu, WANG Meiqing, and CAI Qiurong. The target detection for GPR images based on curve fitting[C]. The 2010 3rd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Yantai, China, 2010: 2876–2879. doi: 10.1109/CISP.2010.5646818. [8] LI Wentao, CUI Xihong, GUO Li, et al. Tree root automatic recognition in ground penetrating radar profiles based on randomized hough transform[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(5): 430. doi: 10.3390/rs8050430. [9] MAAS C and SCHMALZL J. Using pattern recognition to automatically localize reflection hyperbolas in data from ground penetrating radar[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2013, 58: 116–125. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2013.04.012. [10] DOU Qingxu, WEI Lijun, MAGEE D R, et al. Real-time hyperbola recognition and fitting in GPR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 51–62. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2016.2592679. [11] PATSIA O, GIANNOPOULOS A, and GIANNAKIS I. Background removal, velocity estimation, and reverse-time migration: A complete GPR processing pipeline based on machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 2003311. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2023.3300276. [12] ZHANG Xiaowei, XUE Fangxiu, WANG Zepeng, et al. A novel method of hyperbola recognition in ground penetrating radar (GPR) B-scan image for tree roots detection[J]. Forests, 2021, 12(8): 1019. doi: 10.3390/f12081019. [13] LIU Bin, ZHANG Jiaqi, LEI Ming, et al. Simultaneous tunnel defects and lining thickness identification based on multi-tasks deep neural network from ground penetrating radar images[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 145: 104633. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104633. [14] XIANG Deliang, PAN Xiaoyu, DING Huaiyue, et al. Two-stage registration of SAR images with large distortion based on superpixel segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5211115. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2024.3392971. [15] 倪志康, 叶盛波, 史城, 等. 一种深度学习辅助的探地雷达定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1265–1273. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211072.NI Zhikang, YE Shengbo, SHI Cheng, et al. A deep learning assisted ground penetrating radar localization method[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1265–1273. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211072. [16] PHAM M T and LEFÈVRE S. Buried object detection from B-scan ground penetrating radar data using faster-RCNN[C]. IGARSS 2018 - 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 6804–6807. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8517683. [17] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2016.2577031. [18] CUI Fan, NING Muwei, SHEN Jiawei, et al. Automatic recognition and tracking of highway layer-interface using faster R-CNN[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2022, 196: 104477. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2021.104477. [19] 来鹏飞, 李伟, 高尧, 等. 基于改进Cascade R-CNN的探地雷达管线目标检测[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2023, 32(2): 102–110. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.008945.LAI Pengfei, LI Wei, GAO Yao, et al. GPR pipeline target detection based on improved Cascade R-CNN[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2023, 32(2): 102–110. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.008945. [20] ZHAO Shuai, SHADABFAR M, ZHANG Dongming, et al. Deep learning-based classification and instance segmentation of leakage-area and scaling images of shield tunnel linings[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2021, 28(6): e2732. doi: 10.1002/stc.2732. [21] HOU Feifei, LEI Wentai, LI Shuai, et al. Deep learning-based subsurface target detection from GPR scans[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(6): 8161–8171. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2021.3050262. [22] HUANG Jian, YANG Xi, ZHOU Feng, et al. A deep learning framework based on improved self-supervised learning for ground-penetrating radar tunnel lining inspection[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2024, 39(6): 814–833. doi: 10.1111/mice.13042. [23] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [24] LIU Hai, LIN Chunxu, CUI Jie, et al. Detection and localization of rebar in concrete by deep learning using ground penetrating radar[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 118: 103279. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103279. [25] 孙学超, 张其道, 尹达, 等. 基于YOLOv5s的探地雷达图像目标检测研究[J]. 交通世界, 2023(7): 3–6. doi: 10.16248/j.cnki.11-3723/u.2023.07.036.SUN Xuechao, ZHANG Qidao, YIN Da, et al. Research on ground penetrating radar image target detection based on YOLOv5s[J]. World of Transportation, 2023(7): 3–6. doi: 10.16248/j.cnki.11-3723/u.2023.07.036. [26] WANG Zhen, LAN Tian, QU Xiaodong, et al. Improved SSD framework for automatic subsurface object indentification for gpr data processing[C]. The 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 2078–2081. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028347. [27] 覃紫馨, 姜彦南, 徐立, 等. 基于YOLO算法的探地雷达道路图像异常自动检测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(27): 11505–11512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.27.004.QIN Zixin, JIANG Yannan, XU Li, et al. Automatic detection of anomalies in GPR images based on YOLO algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(27): 11505–11512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.27.004. [28] QIU Zhi, ZHAO Zuoxi, CHEN Shaoji, et al. Application of an improved YOLOv5 algorithm in real-time detection of foreign objects by ground penetrating radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(8): 1895. doi: 10.3390/rs14081895. [29] HU Haobang, FANG Hongyuan, WANG Niannian, et al. Defects identification and location of underground space for ground penetrating radar based on deep learning[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2023, 140: 105278. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2023.105278. [30] 胡荣明, 李鑫, 竞霞, 等. YOLOv7在探地雷达B-Scan图像解译中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(8): 29–33. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2023.0227.HU Rongming, LI Xin, JING Xia, et al. Application of YOLOv7 in GPR B-Scan image interpretation[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(8): 29–33. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2023.0227. [31] WANG Niannian, ZHANG Zexi, HU Haobang, et al. Underground defects detection based on GPR by fusing simple linear iterative clustering phash (SLIC-Phash) and convolutional block attention module (CBAM)-YOLOv8[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 25888–25905. doi: 10.1109/access.2024.3365959. [32] LI Shupeng, CUI Xihong, GUO Li, et al. Enhanced automatic root recognition and localization in GPR images through a YOLOv4-based deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5114314. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2022.3181202. [33] 方涛涛, 王池社, 王洁, 等. 基于YOLO v8n的探地雷达图像管线定位方法[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2023, 42(11): 170–177. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2305179.FANG Taotao, WANG Chishe, WANG Jie, et al. Ground penetrating radar image pipeline location based on YOLO v8n[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2023, 42(11): 170–177. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2305179. [34] 兰天, 赵毅, 陈宏畅, 等. 基于拟合误差消除的探地雷达图像鲁棒双曲线识别模型[J]. 信号处理, 2023, 39(9): 1699–1710. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.09.014.LAN Tian, ZHAO Yi, CHEN Hongchang, et al. A robust hyperbola recognition model with fitting-errors-based eliminating in GPR B-scan image[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2023, 39(9): 1699–1710. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.09.014. [35] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 7464–7475. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00721. [36] ZHOU Chuande, LU Zhenyu, LV Zhongliang, et al. Metal surface defect detection based on improved YOLOv5[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 20803. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47716-2. [37] 窦智, 高浩然, 刘国奇, 等. 轻量化YOLOv8的小样本钢板缺陷检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(9): 90–100. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2311-0070.DOU Zhi, GAO Haoran, LIU Guoqi, et al. Small sample steel plate defect detection algorithm of lightweight YOLOv8[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(9): 90–100. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2311-0070. [38] XIONG Hongqiang, LI Jing, LI Zhilian, et al. GPR-GAN: A ground-penetrating radar data generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5200114. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3337172. [39] RUSSELL B C, TORRALBA A, MURPHY K P, et al. LabelMe: A database and web-based tool for image annotation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 77(1-3): 157–173. doi: 10.1007/s11263-007-0090-8. [40] CAI Zhaowei and VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: High quality object detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(5): 1483–1498. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2019.2956516. [41] LYU Chengqi, ZHANG Wenwei, HUANG Haian, et al. RTMDet: An empirical study of designing real-time object detectors[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2212.07784, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2212.07784. [42] BOUSMAHA R, LAOUEDJ S, AGGOUNE L, et al. YOLOv7-face: A real-time face detector[C]. The 2023 International Conference on Networking and Advanced Systems (ICNAS), Algiers, Algeria, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICNAS59892.2023.10330470. -






 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载:
