Joint Multi-Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter for Bearings-only Multi-target Tracking
-
摘要: 现有的多模型-高斯混合-概率假设密度(MM-GM-PHD)滤波器被广泛用于不确定机动目标跟踪,但它不能在不同模型下保持并行的估计,导致各模型的似然值滞后于目标机动。为此,该文提出一种联合多高斯混合概率假设密度(JMGM-PHD)滤波器,并将其用于纯方位多目标跟踪。首先,推导了JMGM模型,其中每个单目标状态估计由一组并行的、带模型概率的高斯函数描述,该状态估计的概率由一个非负的权重来表征。一组权值、模型概率、均值和协方差被统称为JMGM分量。根据贝叶斯规则,推导了JMGM分量的更新方法。然后,利用JMGM模型近似多目标PHD。根据交互式多模型(IMM)规则,推导出JMGM分量的交互、预测和估计方法。将所提JMGM-PHD滤波器应用于纯方位跟踪(BOT)时,针对同时执行平移和旋转的观测站,基于复合函数求导规则推导出一种计算线性化观测矩阵的方法。所提JMGM-PHD滤波器保持了单模型PHD滤波器的形式,但能够自适应地跟踪不确定机动目标。仿真结果表明,JMGM-PHD滤波器克服了似然值滞后于目标机动的问题,在跟踪精度和计算成本方面均优于MM-GM-PHD滤波器。Abstract: The Multi-Model Gaussian Mixture-Probability Hypothesis Density (MM-GM-PHD) filter is widely used in uncertain maneuvering target tracking, but it does not maintain parallel estimates under different models, leading to the model-related likelihood lagging behind unknown target maneuvers. To solve this issue, a Joint Multi-Gaussian Mixture PHD (JMGM-PHD) filter is proposed and applied to bearings-only multi-target tracking in this paper. Firstly, a JMGM model is derived, where each single-target state estimate is described by a set of parallel Gaussian functions with model probabilities, and the probability of this state estimate is characterized by a nonegative weight. The weights, model-related probabilities, means and covariances are collectively called JMGM components. According to the Bayesian rule, the updating method of the JMGM components is derived. Then, the multi-target PHD is approximated using the JMGM model. According to the Interactive Multi-Model (IMM) rule, the interacting, prediction and estimation methods of the JMGM components are derived. When addressing Bearings-Only Tracking (BOT), a method based on the derivative rule for composite functions is derived to compute the linearized observation matrix of observers that simultaneously performs translations and rotations. The proposed JMGM-PHD filter preserves the form of regular single-model PHD filter but can adaptively track uncertain maneuvering targets. Simulations show that our algorithm overcomes the likelihood lag issue and outperforms the MM-GM-PHD filter in terms of tracking accuracy and computation cost.
-
1 所提JMGM-PHD滤波应用于BOT时的算法
输入:上一时刻PHD $ {v_{k - 1}} $、量测$ {{\boldsymbol{Z}}_k} $、观测站姿态$ (x_k^{\text{O}},y_k^{\text{O}}) $, $ \theta _k^{\text{O}} $ (1) 根据式(12)–式(15)预测PHD,得到式(16)所述的$ {v_{k|k - 1}} $ (2) 根据式(17)–式(21)更新$ {v_{k|k - 1}} $,其中似然的计算见式(29)、
式(30)(3) 剔除权重小于$ {\lambda _{\text{d}}} $的JMGM分量,后根据式(31)–式(35)执行合并 (4) 根据式(24)–式(26)估计目标数、目标状态和多目标模型概率 输出:当前时刻PHD$ {v_k} $,多目标的状态估计$ \hat {\boldsymbol{x}}_k^{(i)} $和模型概率$ u_k^{(m)} $ 表 1 各滤波器平均OSPA误差曲线的均值、最大值和标准差
滤波器 均值 最大值 标准差 MM-GM-PHD 50.150 2 97.146 2 10.729 5 MMF-GM-PHD 74.883 5 100.000 0 19.286 3 JMGM-PHD 41.452 3 62.084 0 8.463 9 表 2 各滤波器的平均运行时间(s)
MM-GM-PHD JMGM-PHD 2.6242 2.2254 -
[1] 严灵杰, 顾杰, 姜余, 等. 基于随机有限集的多目标跟踪技术综述[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2024, 39(1): 81–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2024.01.013.YAN Lingjie, GU Jie, JIANG Yu, et al. Overview of multi-target tracking technology based on random finite set[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2024, 39(1): 81–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2024.01.013. [2] MAHLER R P S. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(4): 1152–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261119. [3] MAHLER R. PHD filters of higher order in target number[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(4): 1523–1543. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4441756. [4] VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter and its implementations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 409–423. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007924. [5] 陈一梅, 刘伟峰, 孔明鑫, 等. 基于GLMB滤波和Gibbs采样的多扩展目标有限混合建模与跟踪算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1445–1456. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180077.CHEN Yimei, LIU Weifeng, KONG Mingxin, et al. A modeling and tracking algorithm of finite mixture models for multiple extended target based on the GLMB filter and Gibbs sampler[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1445–1456. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180077. [6] ÜNEY M, CLARK D E, and JULIER S J. Distributed fusion of PHD filters via exponential mixture densities[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 521–531. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2257162. [7] LI Tiancheng and HLAWATSCH F. A distributed particle-PHD filter using arithmetic-average fusion of Gaussian mixture parameters[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 73: 111–124. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.020. [8] 王奎武, 张秦, 虎小龙. 基于多目标不确定性改进的GM-PHD滤波器[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(12): 3113–3121. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0693.WANG Kuiwu, ZHANG Qin, and HU Xiaolong. Improved GM-PHD filter based on multi-target uncertainty[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(12): 3113–3121. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0693. [9] HUANG Qiao, XIE Lei, and SU Hongye. Estimations of time-varying birth cardinality distribution and birth intensity in Gaussian mixture CPHD filter for multi-target tracking[J]. Signal Processing, 2022, 190: 108321. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108321. [10] WANG Linxi, HU Xiaoxi, HAN Xun, et al. Simulation of CBMeMber multi-target tracking algorithm based on Gauss mixture[C]. The IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology, Xi’an, China, 2019: 1524–1528. doi: 10.1109/ICCT46805.2019.8947076. [11] YANG Chaoqun, CAO Xianghui, and SHI Zhiguo. Road-map aided Gaussian mixture labeled multi-Bernoulli filter for ground multi-target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(6): 7137–7147. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3240740. [12] 邵鹏飞, 王蕾, 王方勇. 基于序贯蒙特卡洛与概率假设密度滤波的主动分布式声纳多目标跟踪[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(5): 941–949. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.05.013.SHAO Pengfei, WANG Lei, and WANG Fangyong. Active distributed sonar multi-target tracking based on SMC-PHD filtering[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(5): 941–949. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.05.013. [13] CAO Chenghu, ZHAO Yongbo, PANG Xiaojiao, et al. Sequential Monte Carlo cardinalized probability hypothesized density filter based on Track-Before-Detect for fluctuating targets in heavy-tailed clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 169: 107367. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107367. [14] WANG Haihuan, LYU Xiaoyong, and MA Long. Adaptive cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter based on cubature Kalman[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7667–7671. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0670. [15] HOU Liming, LIAN Feng, DE ABREU G T F, et al. Robust δ-generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli filter for nonlinear systems with heavy-tailed noises[C]. The IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion, Rustenburg, South Africa, 2020: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/FUSION45008.2020.9190250. [16] ZHAO Shunyi, AHN C K, SHI Peng, et al. Bayesian state estimation for Markovian jump systems: Employing recursive steps and pseudocodes[J]. IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Magazine, 2019, 5(2): 27–36. doi: 10.1109/MSMC.2018.2882145. [17] DU Xue, HU Xianbo, HU Junsheng, et al. An adaptive interactive multi-model navigation method based on UUV[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 267: 113217. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113217. [18] ZHOU Gongjian, ZHU Bin, and YE Xiaoping. Switch-constrained multiple-model algorithm for maneuvering target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4414–4433. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3242944. [19] PUNITHAKUMAR K, KIRUBARAJAN T, and SINHA A. Multiple-model probability hypothesis density filter for tracking maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(1): 87–98. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4516991. [20] DA Kai, LI Tiancheng, ZHU Yongfeng, et al. Gaussian mixture particle jump-Markov-CPHD fusion for multitarget tracking using sensors with limited views[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2020, 6: 605–616. doi: 10.1109/TSIPN.2020.3016478. [21] 杨标, 朱圣棋, 余昆, 等. 贪婪的量测划分机制下的多传感器多机动目标跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 1962–1969. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200498.YANG Biao, ZHU Shengqi, YU Kun, et al. Multi-sensor multiple maneuvering targets tracking algorithm under greedy measurement partitioning mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 1962–1969. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200498. [22] CAO Chenghu and ZHAO Yongbo. A multiple-model generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli filter based on blocked Gibbs sampling for tracking maneuvering targets[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 186: 108119. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108119. [23] WU Sunyong, DONG Xudong, ZHAO Jun, et al. A fast implementation of interactive-model generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli filter for interval measurements[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 164: 345–353. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.05.028. [24] TURNER J D, MCMAHON J, and ZAVLANOS M M. Receding horizon tracking of an unknown number of mobile targets using a bearings-only sensor[C]. 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Philadelphia, USA, 2022: 7327–7334. doi: 10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9811882. [25] ZHANG Yuexing, LI Yiping, LI Shuo, et al. A multi-AUV bearings-only multi-target tracking method based on the fast LMB filter[C]. The 4th International Conference on Control and Robotics, Guangzhou, China, 2022: 446–451. doi: 10.1109/ICCR55715.2022.10053872. [26] CHEN Jinfeng, MA Hong, LIANG Chengguo, et al. OTHR multipath tracking using the Bernoulli filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 1974–1990. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.120659. [27] SCHUHMACHER D, VO B T, and VO B N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(8): 3447–3457. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.920469. -






 下载:
下载:

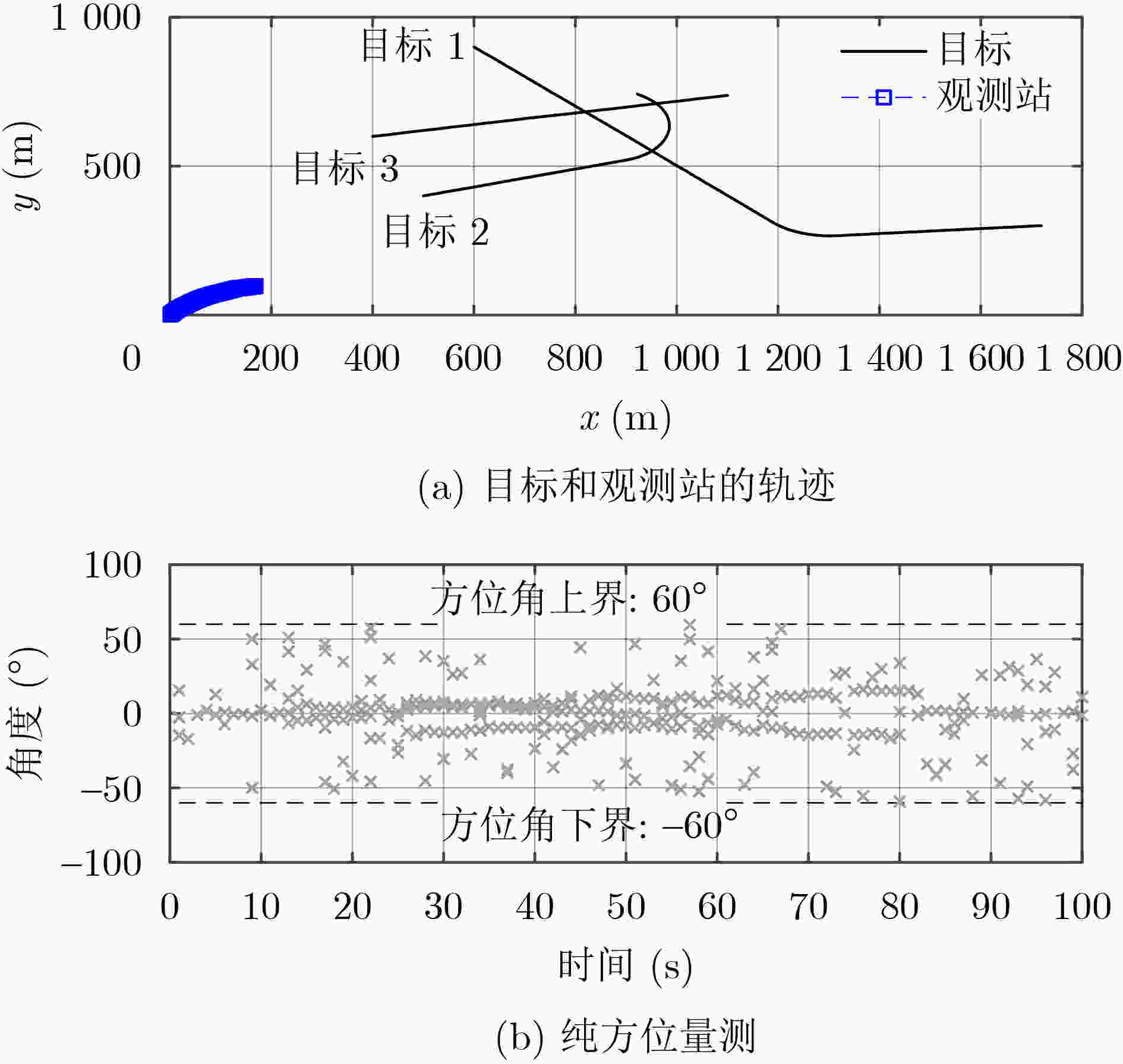

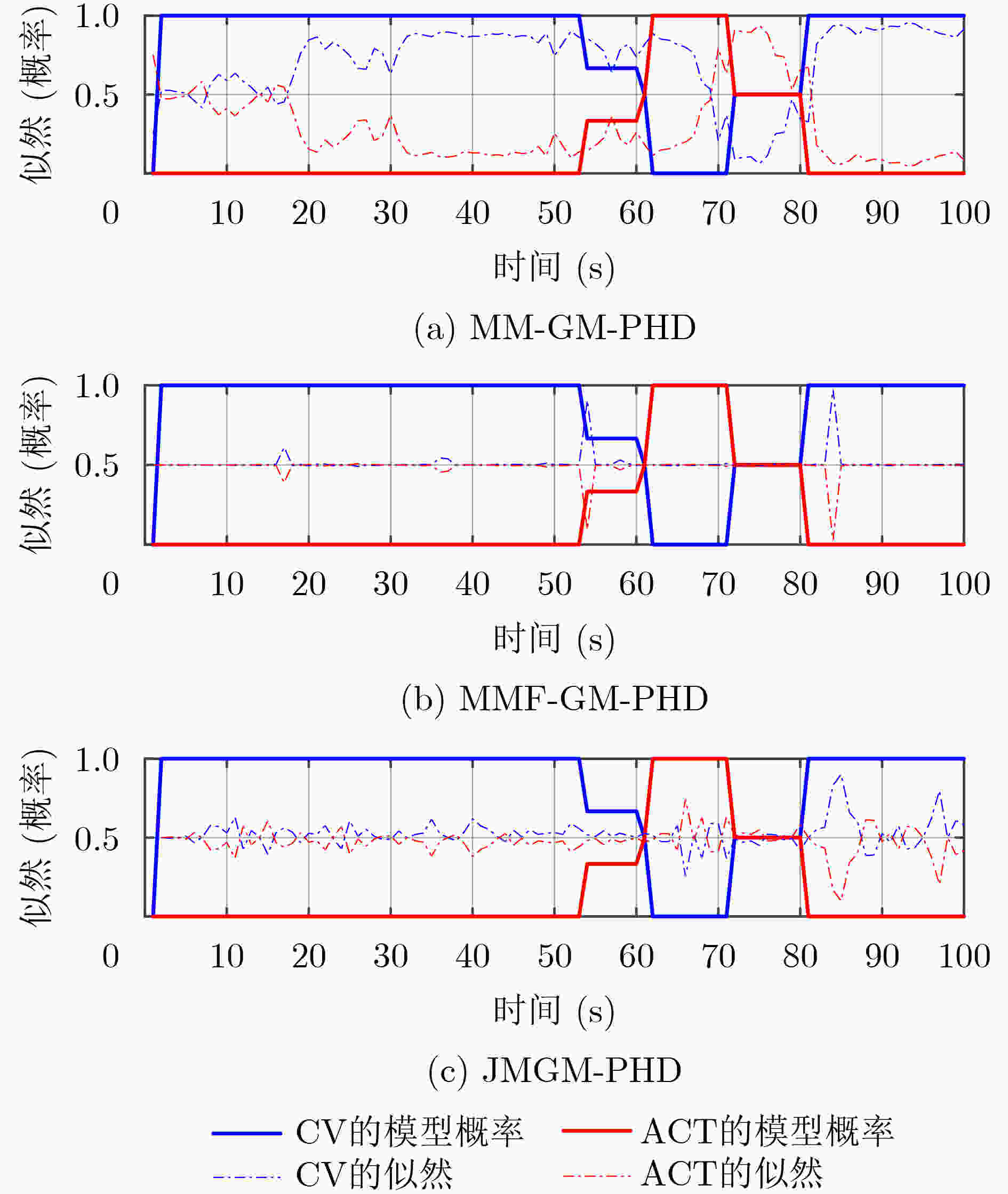
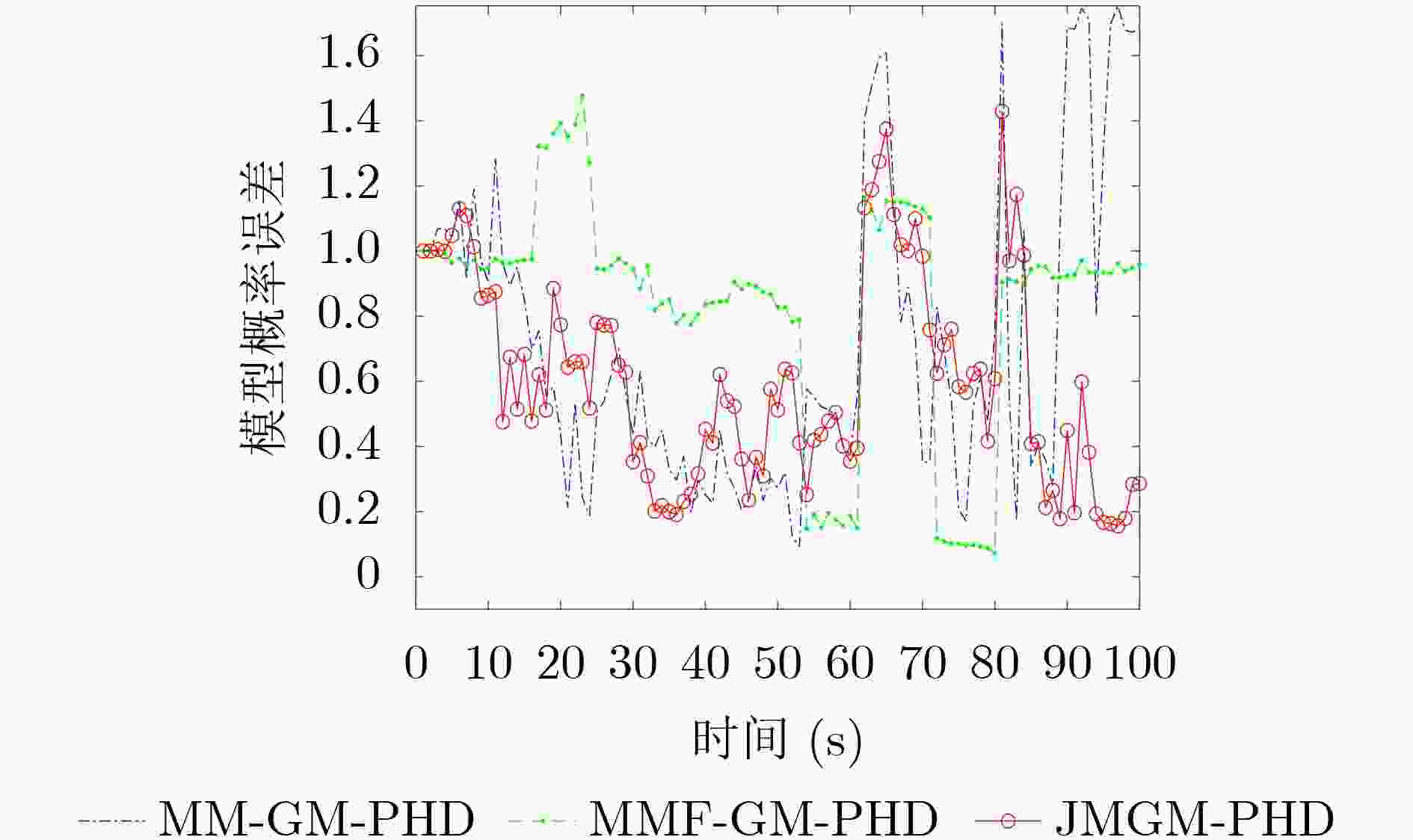
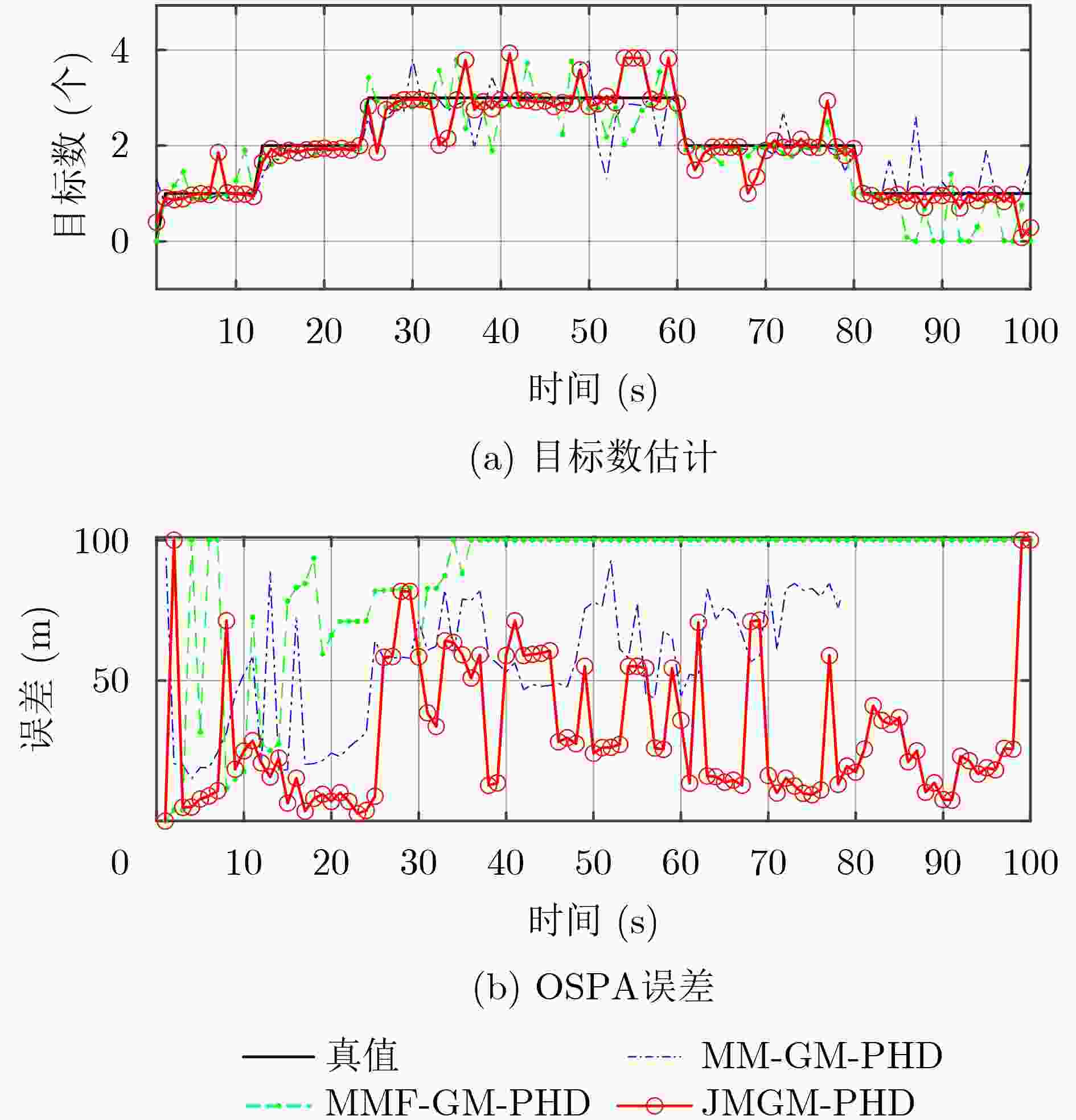




 下载:
下载:
