Lipreading Method Based on Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Convolution
-
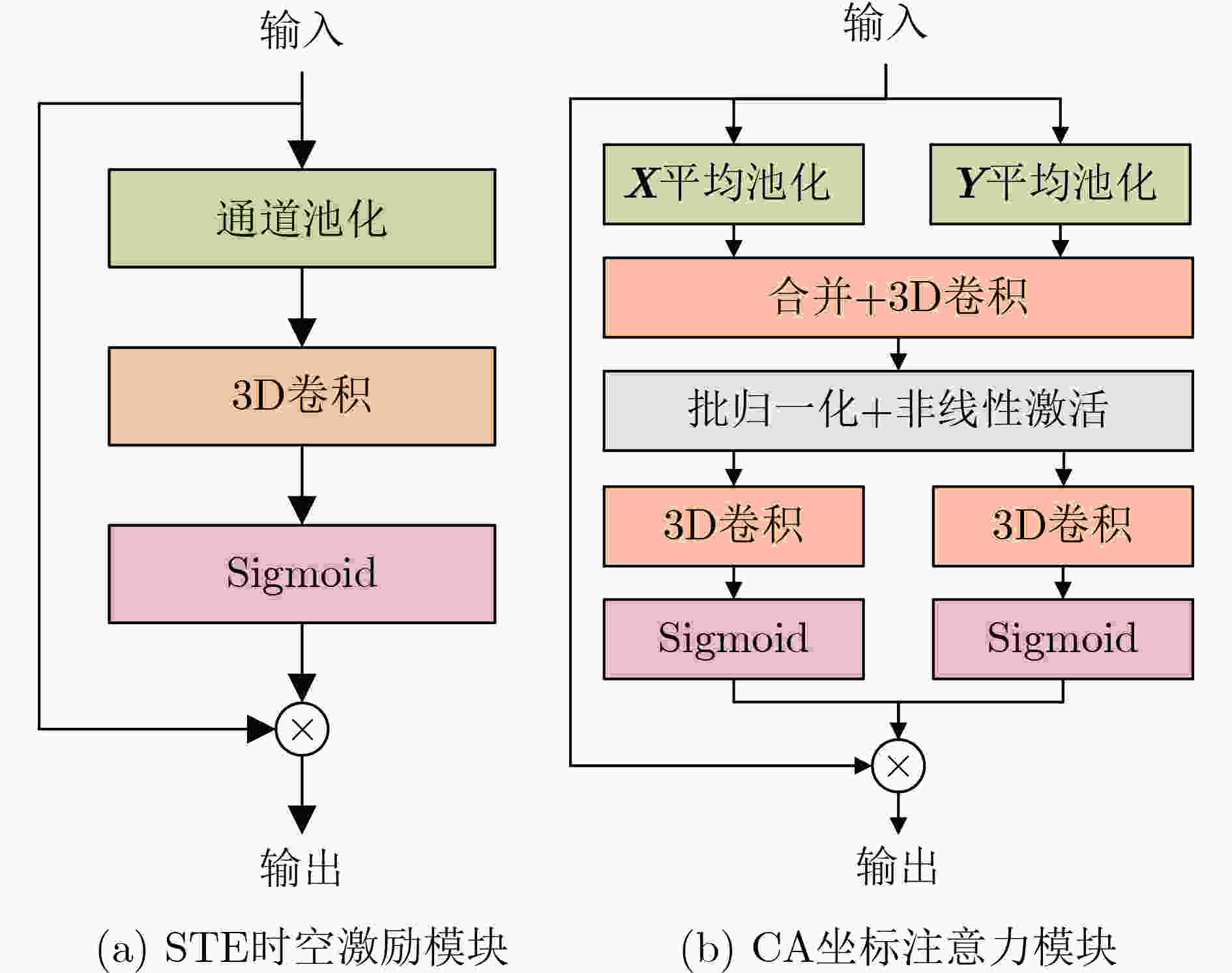
摘要: 现有的唇语识别模型大多采用将单层的3维卷积与2维卷积神经网络结合的方式,从唇语视频序列中挖掘出时空联合特征。然而,由于单层的3维卷积不能很好地提取时间信息,同时2维卷积神经网络对细粒度的唇语特征的挖掘能力有限,该文提出一种多尺度唇语识别网络(MS-LipNet)以改善唇语识别任务。该文在Res2Net网络中,采用3维时空卷积替代传统的2维卷积以更好地提取时空联合特征,同时提出时空坐标注意力模块,使网络关注于任务相关的重要区域特征。在LRW和LRW-1000数据集上进行实验,验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Most of the existing lipreading models use a combination of single-layer 3D convolution and 2D convolutional neural networks to extract spatio-temporal joint features from lip video sequences. However, due to the limitations of single-layer 3D convolutions in capturing temporal information and the restricted capability of 2D convolutional neural networks in exploring fine-grained lipreading features, a Multi-Scale Lipreading Network (MS-LipNet) is proposed to improve lip reading tasks. In this paper, 3D spatio-temporal convolution is used to replace traditional two-dimensional convolution in Res2Net network to better extract spatio-temporal joint features, and a spatio-temporal coordinate attention module is proposed to make the network focus on task-related important regional features. The effectiveness of the proposed method was verified through experiments conducted on the LRW and LRW-1000 datasets.
-
表 1 不同方法在LRW和LRW-
1000 数据集上的识别准确率对比(%)方法 LRW LRW- 1000 Two-Stream ResNet18+BiLSTM[18] 84.07 – 2×ResNet18+BiGRU[19] 84.13 41.93 ResNet18+3×BiGRU+MI[30] 84.41 38.79 ResNet18+MS-TCN[9] 85.30 41.40 SE-ResNet18+BiGRU[13] 85.00 48.00 3D-ResNet18+BiGRU+TSM[20] 86.23 44.60 ResNet18+HPConv+self-attention[19] 86.83 – WPCL+APFF[31] 88.30 49.40 ResNet-18+DC-TCN[10] 88.36 43.65 2DCNN+BiGRU+Lip Segmentation[32] 90.38 – ResNet18+DC-TCN+TimeMask[33] 90.40 – MS-LipNet 91.56 50.68 表 2 MS-LipNet网络不同组件的消融实验结果(%)
数据增强 注意力模块 LRW LRW- 1000 Mixup Cutout STCA × × × 90.95 50.12 √ × × 91.06 50.40 × √ × 91.01 50.42 × × √ 91.21 50.25 √ √ × 91.18 50.06 √ × √ 91.39 50.56 × √ √ 91.48 50.50 √ √ √ 91.56 50.68 表 3 Cutout的不同取值对实验结果的影响(%)
n_holes length LRW LRW- 1000 0 0 91.39 50.50 1 11 91.41 50.51 1 22 91.44 50.53 1 44 91.42 50.55 2 11 91.49 50.54 2 22 91.56 50.68 2 44 91.43 50.58 3 11 91.50 50.65 3 22 91.37 50.59 3 44 90.72 50.51 -
[1] TAYLOR S L, MAHLER M, THEOBALD B J, et al. Dynamic units of visual speech[C]. ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2012: 275–284. [2] LI Dengshi, GAO Yu, ZHU Chenyi, et al. Improving speech recognition performance in noisy environments by enhancing lip reading accuracy[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4): 2053. doi: 10.3390/s23042053. [3] IVANKO D, RYUMIN D, and KARPOV A. Automatic lip-reading of hearing impaired people[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2019, XLII-2/W12: 97–101. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-2-W12-97-2019. [4] GONZALEZ-LOPEZ J A, GOMEZ-ALANIS A, DOÑAS J M M, et al. Silent speech interfaces for speech restoration: A review[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 177995–178021. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3026579. [5] EZZ M, MOSTAFA A M, and NASR A A. A silent password recognition framework based on lip analysis[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 55354–55371. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982359. [6] 王昌海, 许昱玮, 张建忠. 基于层次分类的手机位置无关的动作识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(1): 191–197. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160253.WANG Changhai, XU Yuwei, and ZHANG Jianzhong. Hierarchical classification-based smartphone displacement free activity recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2017, 39(1): 191–197. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160253. [7] STAFYLAKIS T and TZIMIROPOULOS G. Combining residual networks with LSTMs for lipreading[C]. 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. [8] STAFYLAKIS T, KHAN M H, and TZIMIROPOULOS G. Pushing the boundaries of audiovisual word recognition using residual networks and LSTMs[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2018, 176/177: 22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2018.10.003. [9] MARTINEZ B, MA Pingchuan, PETRIDIS S, et al. Lipreading using temporal convolutional networks[C]. ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 6319–6323. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9053841. [10] MA Pingchuan, WANG Yijiang, SHEN Jie, et al. Lip-reading with densely connected temporal convolutional networks[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 2856–2865. doi: 10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00290. [11] TRAN D, WANG Heng, TORRESANI L, et al. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6450–6459. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00675. [12] QIU Zhaofan, YAO Ting, and MEI Tao. Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3D residual networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5534–5542. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.590. [13] CHEN Hang, DU Jun, HU Yu, et al. Automatic lip-reading with hierarchical pyramidal convolution and self-attention for image sequences with no word boundaries[C]. 22nd Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Brno, Czechia, 2021: 3001–3005. [14] GAO Shanghua, CHENG Mingming, ZHAO Kai, et al. Res2Net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(2): 652–662. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2938758. [15] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [16] HOU Qibin, ZHOU Daquan, and FENG Jiashi. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13708–13717. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01350. [17] CHUNG J S and ZISSERMAN A. Lip reading in the wild[C]. 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, China, 2017: 87–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-54184-6_6. [18] WENG Xinshuo and KITANI K. Learning spatio-temporal features with two-stream deep 3D CNNs for lipreading[C]. 30th British Machine Vision Conference 2019, Cardiff, UK, 2019. [19] XIAO Jingyun, YANG Shuang, ZHANG Yuanhang, et al. Deformation flow based two-stream network for lip reading[C]. 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2020), Buenos Aires, Argentina , 2020: 364–370. doi: 10.1109/FG47880.2020.00132. [20] HAO Mingfeng, MAMUT M, YADIKAR N, et al. How to use time information effectively? Combining with time shift module for lipreading[C]. ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, Canada, 2021: 7988–7992. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414659. [21] 任永梅, 杨杰, 郭志强, 等. 基于多尺度卷积神经网络的自适应熵加权决策融合船舶图像分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1424–1431. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200102.REN Yongmei, YANG Jie, GUO Zhiqiang, et al. Self-adaptive entropy weighted decision fusion method for ship image classification based on multi-scale convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1424–1431. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200102. [22] FENG Dalu, YANG Shuang, SHAN Shiguang, et al. Learn an effective lip reading model without pains[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.07557, 2020. [23] XUE Feng, YANG Tian, LIU Kang, et al. LCSNet: End-to-end lipreading with channel-aware feature selection[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications, 2023, 19(1s): 28. doi: 10.1145/3524620. [24] FU Yixian, LU Yuanyao, and NI Ran. Chinese lip-reading research based on ShuffleNet and CBAM[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(2): 1106. doi: 10.3390/app13021106. [25] DEVRIES T and TAYLOR G W. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552, 2017. [26] ZHANG Hongyi, CISSE M, DAUPHIN Y N, et al. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization[C]. 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018. [27] YANG Shuang, ZHANG Yuanhang, FENG Dalu, et al. LRW-1000: A naturally-distributed large-scale benchmark for lip reading in the wild[C]. 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), Lille, France, 2019: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/FG.2019.8756582. [28] KING D E. Dlib-ml: A machine learning toolkit[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2009, 10: 1755–1758. [29] LOSHCHILOV I and HUTTER F. Decoupled weight decay regularization[C]. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2017. [30] ZHAO Xing, YANG Shuang, SHAN Shiguang, et al. Mutual information maximization for effective lip reading[C]. 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2020), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2020: 420–427. doi: 10.1109/FG47880.2020.00133. [31] TIAN Weidong, ZHANG Housen, PENG Chen, et al. Lipreading model based on whole-part collaborative learning[C]. ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 2425–2429. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9747052. [32] MILED M, MESSAOUD M A B, and BOUZID A. Lip reading of words with lip segmentation and deep learning[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(1): 551–571. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13321-0. [33] MA Pingchuan, WANG Yujiang, PETRIDIS S, et al. Training strategies for improved lip-reading[C]. ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 2022: 8472–8476. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746706. -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
