Improved Topology of Modular High-voltage Power Converter with Input Series Output Series Configuration
-
摘要: 模块化高压电源具有高效率、高可靠性、可重构性等特点在大功率高压器件中得到广泛应用。其中基于串并联谐振变换器的输入串联输出串联型功率变换拓扑适用于高频高压工作环境,具有减少功率损耗,绕组介质损耗,利用多级变压器寄生参数等优势,有广泛的应用前景。目前关于该拓扑的研究主要集中于理论分析和效率优化,在实际高压环境应用中多级变压器绕组间存在的高压隔离问题还未得到有效解决,该文提出多级变压器共用原边绕组的设计,简化传统变压器单级绕制方式所存在的高压隔离问题。然而该绕制方案会造成多级变压器不均压和电压发散现象,因此该文同时基于利用变压器和倍压整流电路中二极管的寄生参数,提出改进的拓扑设计,有效解决了分压不均问题,进行了仿真验证与试验验证。仿真结果与实验结果均证明了所提共用原边绕组的高压隔离结构和改进拓扑的有效性。Abstract: The modular high-voltage power supply, characterized by high efficiency, reliability, and reconfigurability, has found widespread application in high-power high-voltage devices. Among them, the input series output series topology based on the series-parallel resonant converter is suitable for high-frequency high-voltage operating environments, offering advantages such as reduced power losses, winding dielectric losses, and utilizing parasitic parameters of multi-stage transformer. It has broad prospects for application. Current research on this topology primarily focuses on theoretical analysis and efficiency optimization. In practical high-voltage environments, the high-voltage isolation issues between windings of multi-stage transformers have not been effectively addressed. In this paper, a design of shared primary windings for multi-stage transformers is proposed to simplify the high-voltage isolation issues inherent in traditional transformer single-stage winding methods. However, this winding scheme can lead to non-uniform voltage distribution and voltage divergence in multi-stage transformers. Therefore, based on utilizing the parasitic parameters of diodes in transformers and voltage doubling rectifier circuits, an improved topology design is proposed to effectively address the uneven voltage distribution issue. Simulation and experimental validations were conducted, and the results from both simulations and experiments confirm the effectiveness of the proposed high-voltage isolation structure with shared primary windings and the improved topology.
-
表 1 不同级联方式应用场景
级联方式 输入串联输出串联 输入串联输出并联 输入并联输出串联 输入并联输出并联 适用场合 高输入、输出电压 高输入电压高输出电流 高输入电流高输出电压 高输入、输出电流 表 2 谐振变换器分类及应用场景
特点 LC串联 LC并联 LCC串并联 LLC串并联 CLL串并联 电压增益 0.5~1.0 1.0~10.0 0.5~3.0 1.0~2.5 1.0~2.5 传输效率(%) 90 90 96 97 96 适用场合 中压大功率 中压大电流 高压大功率 中压高效率 中压高频率 表 3 电气性能参数和谐振元件参数
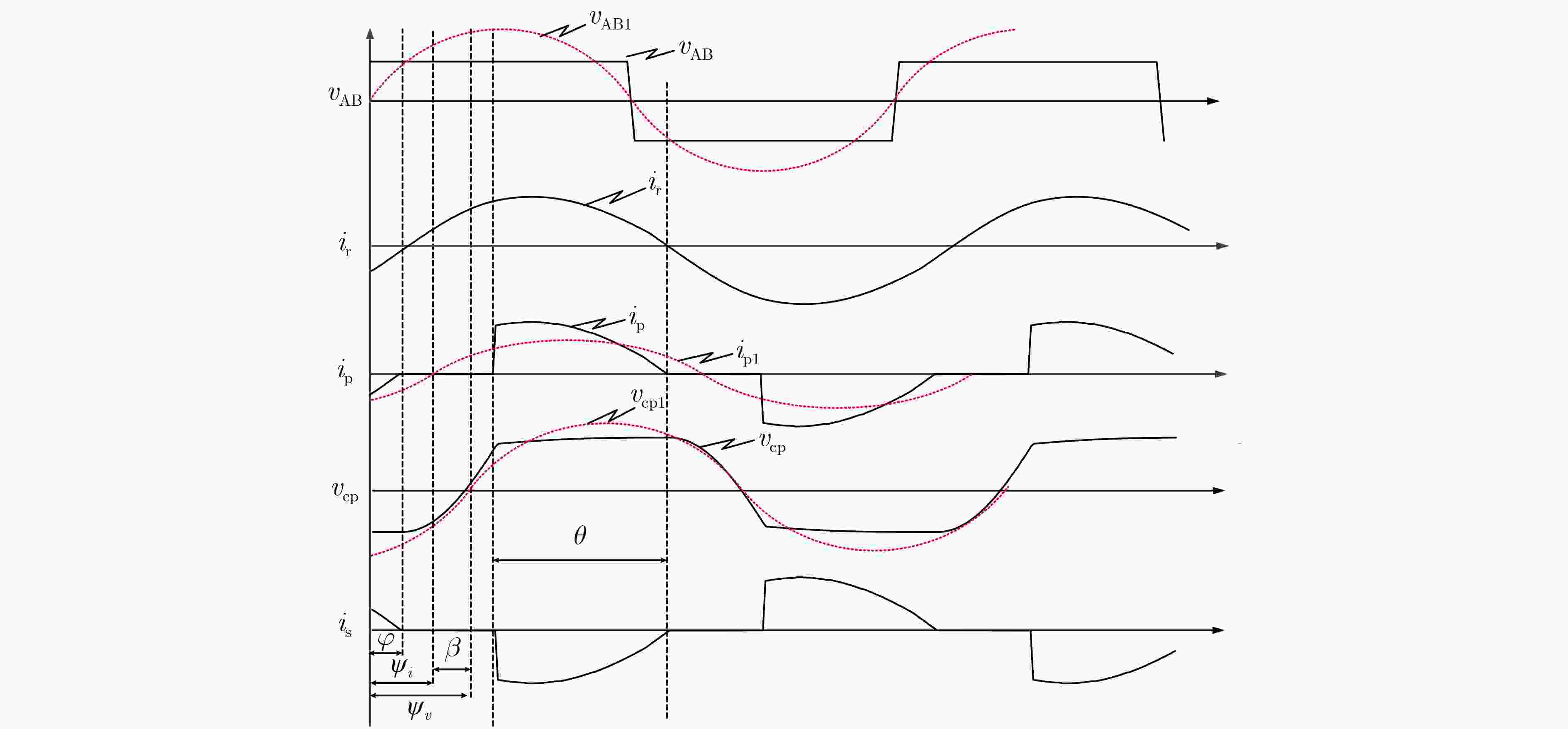
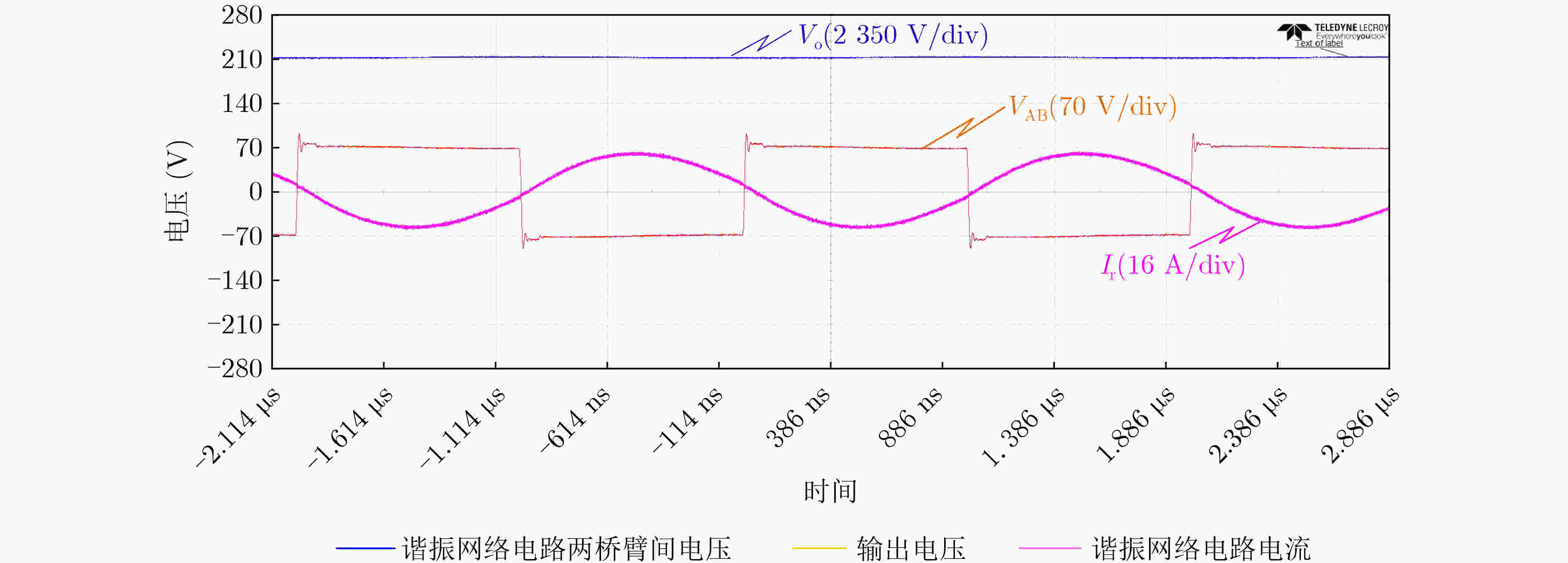
参数名称 描述 参数值 Vin 输入电压 70 V Vo 输出电压 7100 VC1, C2,···, C6n 倍压整流电路电容 47 nF Ro 负载电阻 100 kΩ Lr 串联谐振电感 12.5 μH Cr 串联谐振电容 10 nF fs 开关频率 500 kHz -
[1] ZHUGE Yingjian, LIANG Junrui, FU Minfan, et al. Comprehensive overview of power electronics intensive solutions for high-voltage pulse generators[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Power Electronics, 2024, 5: 1–20. doi: 10.1109/OJPEL.2023.3340220. [2] FENG Hongyu, LIN Hongyi, XU Jiasheng, et al. A phase-shifting control IPOS high-voltage generator with low output voltage ripple for X-ray[C]. The 11th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia, Jeju Island, Korea, Republic of, 2023: 235–240. doi: 10.23919/ICPE2023-ECCEAsia54778.2023.10213709. [3] CHOUDHARY S N and ELANGOVAN D. High gain, naturally clamped Dc to Dc converter for X-ray application[C]. 2016 International Conference on Computation of Power, Energy Information and Commuincation, Melmaruvathur, India, 2016: 587–592. doi: 10.1109/ICCPEIC.2016.7557298. [4] 王泽庭, 杨旭. 大功率高压LCC谐振电源重要参数研究与设计[J]. 电气传动, 2018, 48(2): 53–57. doi: 10.19457/j.1001-2095.20180210.WANG Zeting and YANG Xu. Design and research of important parameters for high power high voltage LCC resonant power supply[J]. Electric Drive, 2018, 48(2): 53–57. doi: 10.19457/j.1001-2095.20180210. [5] MARTIN-RAMOS J A, DIAZ J, PERNIA A M, et al. Dynamic and steady-state models for the PRC-LCC resonant topology with a capacitor as output filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2007, 54(4): 2262–2275. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2007.894763. [6] MAO Saijun, POPOVIC J, FERREIRA J A, et al. Equivalent circuit model for modular high voltage power generation architectures[C]. 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Cincinnati, USA, 2017: 3098–3102. doi: 10.1109/ECCE.2017.8096565. [7] 伍梁. 高压直流LCC谐振变换器状态轨迹控制策略及其模块化级联技术[D]. [博士论文], 浙江大学, 2020. doi: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2020.000695.WU Liang. State trajectory control strategy and modular cascade technology of high voltage LCC resonant converter[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2020. doi: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2020.000695. [8] CHEN Wu and RUAN Xinbo. Modularization structure for series-parallel connected converters[C]. The 2008 Twenty-Third Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Austin, USA, 2008. doi: 10.1109/APEC.2008.4522928. [9] 曲璐. 输入串联型组合变换器控制策略关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.QU Lu. Study on key technologies of input series combination converters control strategy[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. [10] KROICS K, ZAKIS J, SUZDALENKO A, et al. A simplified approach to input voltage balancing for series connected isolated DC-DC converters[C]. The 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Karlsruhe, Germany, 2016. doi: 10.1109/EPE.2016.7695415. [11] YU Mengyuan, SHA Deshang, and LIAO Xiaozhong. Hybrid phase shifted full bridge and LLC half bridge DC–DC converter for low-voltage and high-current output applications[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2014, 7(7): 1832–1840. doi: 10.1049/iet-pel.2013.0778. [12] 张翔, 郑晟, 张军明. 一种高压宽范围输入辅助电源的设计[J]. 电力电子技术, 2011, 45(7): 127–129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-100X.2011.07.046.ZHANG Xiang, ZHENG Sheng, and ZHANG Junming. The design of auxiliary power supply with wide range and high input voltage[J]. Power Electronics, 2011, 45(7): 127–129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-100X.2011.07.046. [13] ZHENG Jiaqiang, LU Shujing, and LI Jiaqi. LLC and LCC analysis and comparison of resonant converters[C]. The 35th Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation, Zhanjiang, China, 2020: 226–231. doi: 10.1109/YAC51587.2020.9337641. [14] 夏冰, 阮新波, 陈武. 高压大功率场合LCC谐振变换器的分析与设计[J]. 电工技术学报, 2009, 24(5): 60–66. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.2009.05.011.XIA Bing, RUAN Xinbo, and CHEN Wu. Analysis and design of LCC resonant converter for high voltage and high power applications[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2009, 24(5): 60–66. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.2009.05.011. [15] 李康康. 模块化高压直流谐振电源的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华中科技大学, 2017.LI Kangkang. The research of modular high voltage DC power supply based on resonant and soft-switching converter[D]. [Master dissertation], Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017. [16] 杨晓光, 高正, 席利根, 等. 输入并联输出串联LCC变换器的设计[J]. 电气传动, 2021, 51(4): 47–51. doi: 10.19457/j.1001-2095.dqcd20574.YANG Xiaoguang, GAO Zheng, XI Ligen, et al. Design of an input-parallel output-series LCC converter[J]. Electric Drive, 2021, 51(4): 47–51. doi: 10.19457/j.1001-2095.dqcd20574. [17] MAO Saijun, POPOVIC J, FERREIRA J A, et al. Comparative analysis and evaluation of high voltage power generation architectures[C]. 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Cincinnati, USA, 2017: 4753–4760. doi: 10.1109/ECCE.2017.8096809. [18] MAO Saijun, LI Chengmin, LI Wuhua, et al. Unified equivalent steady-state circuit model and comprehensive design of the LCC resonant converter for HV generation architectures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33(9): 7531–7544. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2017.2774147. [19] SON S H, KWON C H, KIM T H, et al. Development of 120 kV and 60 kW three phase LCC resonant converter for electron beam welding system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2023, 51(10): 2813–2822. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2023.3288116. [20] LIN Chudi, HE Liqun, LI Xiaohui, et al. Modeling and digital control of 100kV/50kW high voltage power supply based on PPSS-LCC for X-ray generator[C]. The IEEE 4th International Electrical and Energy Conference, Wuhan, China, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/CIEEC50170.2021.9510975. [21] 李自成, 袁保山. 改进型低纹波Cockcroft-Walton倍压电路及其特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(17): 64–67,77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.17.012.LI Zicheng and YUAN Baoshan. Advanced low ripple Cockcroft-Walton voltage multiplier circuit and its characteristics research[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(17): 64–67,77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.17.012. -






 下载:
下载:
















 下载:
下载:
