A Secure Multi-Party Strings Sorting Protocol Based on National Cryptographic Algorithm
-
摘要: 保密排序问题由百万富翁问题衍生而来,是安全多方计算研究的基本问题,多参与方字符串排序对于数据库保密查询及电子投票求和问题的研究具有重要意义。现有保密排序问题的研究多集中在私密数据排序或者两方字符串排序,高效的多参与方字符串排序方案尚处于探索中,该文基于改进的SM2同态加密算法与门限密码算法,提出半诚实模型下的保密多方单字符排序协议,进一步构造基于权重的保密单字符排序协议以及保密多方字符串排序协议。使用模拟范例对3种协议进行安全性证明,并对协议进行性能分析与仿真实验,结果表明该文提出的保密多方单字符排序协议与保密多方字符串排序协议性能相较现有同类方案均有明显提升。Abstract: The secure sorting problem is derived from the millionaire problem and is a fundamental problem in secure multi-party computation research. Multi-party string sorting is of great significance for the research of database confidential queries and electronic voting sum problems. The existing research on secure sorting problems mostly focuses on private data sorting or two-party string sorting. Efficient multi-party string sorting schemes are still being explored. Based on the improved SM2 homomorphic encryption algorithm and threshold cryptography algorithm, this paper first proposes a confidentiality multi-party single character sorting protocol in a semi honest model, and then designs a weight-based confidentiality single character sorting protocol and a confidentiality multi-party string sorting protocol. Simulation paradigm is used to demonstrate the security of three protocols. The paper conducts performance analysis and simulation experiments on the three protocols. The results show that the performance of the proposed secure multi-party single character sorting protocol and secure multi-party string sorting protocol is significantly improved compared to existing similar schemes.
-
1 保密多方单字符排序协议
输入:$ {P_1},{P_2}, \cdots ,{P_n} $各自的字符$ {s_1},{s_2}, \cdots ,{s_n} $。 输出:Pi($ i \in [1,n] $)获得字符si根据字典序的排序结果Ri。 准备阶段:n个参与者Pi($ i \in [1,n] $),它们商定椭圆曲线$ {E_p} $以及椭圆曲线的一个基点G,Pi任意选择私钥$ {\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_i} \in {{Z}}_{q - 1}^* $,计算公钥
$ {\text{p}}{{\text{k}}_i} = [{\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_i}]G $,n个参与者共同生成公钥$ {\text{pk}} $。$ {P_1},{P_2}, \cdots ,{P_n} $随机生成m个仅自己知道的随机数$ {k_{ih}} \in {{Z}}_{q - 1}^* $,其中$ h \in [1,m] $。1: Pi$ (i \in [1,n]) $将自己所拥有的字符si按照式(1)构造对应的m维向量$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_i}{\text{ = (}}{v_{i1}},{v_{i2}}, \cdots ,{v_{im}}{\text{)}} $。 2: P1应用公钥pk对向量$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_1} $的每一个分量$ {v_{1h}} $进行加密,加密过程为$ ({C_{1h}},{C_{2h}}) = ([{k_{1h}}]{{G}},[{v_{1h}}]{{G}} + [{k_{1h}}]{\text{pk}}) $,使用$ E({v_{1h}}) $来进行表示,
$ E({{\boldsymbol{V}}_1}) = (E({v_{11}}),E({v_{12}}), \cdots ,E({v_{1m}})) $,P1将$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_1} = E({{\boldsymbol{V}}_1}) $发送给P2。3:对于$ i = 2,3, \cdots ,n - 1 $;Pi收到Pi-1发送过来的$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_{i - 1}} = ({w_{(i - 1)1}},{w_{(i - 1)2}}, \cdots ,{w_{(i - 1)m}}) $,依次做以下运算: (1) Pi根据Vi的值对$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_{i - 1}} $进行计算,得到$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_i} = ({w_{i1}},{w_{i2}}, \cdots ,{w_{im}}) $;具体替换规则为:$ {w_{ij}} = {\text{Ran}}(E({v_{ij}}) + {w_{(i - 1)j}}) $;其中
$ j \in [1,m] $,Ran(Z)表示对密文Z的重随机化过程。(2) Pi将$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_i} $发送给Pi+1,重复步骤(1)。 (3) Pn得到最终的密文向量: $ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_n} = ({w_{n1}},{w_{n2}}, \cdots ,{w_{nm}}) $,并公布结果$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_n} $。 4: $ {P_i}(i \in [1,n]) $计算$ {C_i} = {\text{Ran}}({{\boldsymbol{W}}_{n{s_{{{it}}}}}}) = ({C_{i1}},{C_{i2}}) $,并将Ci1发送给其他参与者。 5: Pj$ (j \in [1,i - 1] \cup [i + 1,n]) $计算$ [{\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_j}]{C_{i1}} $并发送给Pi。 6: Pi计算$ [{R_i}]{{G}} = {C_i}_2 - \left(\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {[{\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_i}]{C_{i1}}} \right) $,得到$ [{R_i}]G $之后,通过比较得到$ {R_i} $的值,$ {R_i} $也就是Pi字符所在的位置。 2 基于权重的保密单字符排序协议
输入:$ {P_1},{P_2}, \cdots ,{P_n} $各自的字符$ {s_1},{s_2}, \cdots ,{s_n} $以及各自的权重$ {{\mathrm{wt}}_1},{{\mathrm{wt}}_2}, \cdots ,{{\mathrm{wt}}_n} $ 输出:Pi($ i \in [1,n] $)获得字符si根据字典序的排序结果ri。 准备阶段:n个参与者Pi($ i \in [1,n] $),它们商定椭圆曲线$ {{{E}}_p} $以及椭圆曲线的一个基点G,Pi任意选择私钥$ {\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_i} \in {{Z}}_{q - 1}^* $,计算公钥
$ {\text{p}}{{\text{k}}_i} = [{\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_i}]G $, n个参与者共同生成公钥$ {\text{pk}} $。$ {P_1},{P_2}, \cdots ,{P_n} $随机生成nm+n个仅自己知道的随机数$ {k_{ih}} \in {{Z}}_{q - 1}^* $,其中$ h \in [1,nm + n] $。1: 对于每个Pi$ (i \in [1,n]) $将自己字符si根据字典排序转化成数字1~26的某个数字,具体转化规则为:$ '{\text{a}}'{\text{~}}1,'{\text{b}}'{\text{~}}2, \cdots ,'{\text{z}}'{\text{~}}26 $。并用式(4)
计算得到yi的值,根据yi的值构造向量$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_i}{\text{ = (}}{v_{i1}},{v_{i2}}, \cdots ,{v_{i(nm + n)}}{\text{)}} $。2: 接下来的步骤同协议1的步骤2~步骤6相同,这里不加以赘述。全部步骤执行后参与者Pi可以得到每个字符的排序位置$ {r_i} $。 3 保密多方字符串排序协议
输入:$ {{{P}}_1},{{{P}}_2}, \cdots ,{{{P}}_n} $各自的字符串$ {S_1},{S_2}, \cdots ,{S_n} $以及自己的初始权重wt1, wt2, $ \cdots $, wtn。 输出:Pi($ i \in [1,n] $)获得字符串Si根据字典序的排序结果Ri。 准备阶段:n个参与者Pi($ i \in [1,n] $),它们商定椭圆曲线$ {{{E}}_p} $以及椭圆曲线的一个基点G, Pi任意选择私钥$ {\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_i} \in {{Z}}_{q - 1}^* $,计算公钥
$ {\text{p}}{{\text{k}}_i} = [{\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_i}]{{G}} $,n个参与者共同生成公钥$ {\text{pk}} $。$ {{{P}}_1},{{{P}}_2}, \cdots ,{{{P}}_n} $随机生成nm+n个仅自己知道的随机数$ {k_{ih}} \in {{Z}}_{q - 1}^* $,其中$ h \in [1,nm + n] $。1: Pi$ (i \in [1,n]) $约定好字符串的长度k,然后将自己持有的字符串Si在字符串末尾进行补位操作,不足位数的在末尾补位字符$ '0' $,使所有
的字符串的长度为k,且字符串具体形式变成$ {S_i} = {x_{i1}}{x_{i2}} \cdots {x_{ik}} $。2: 令j=k, Pi$ (i \in [1,n]) $从末尾字符$ {x_{ik}} $开始对字符进行基于权重wti的排序操作,具体如下: (1)Pi$ (i \in [1,n]) $执行协议2步骤1~步骤2,先计算得到yij的值,然后依照此步骤执行可得到xij的位置rij 。 (2)令$ {{\mathrm{wt}}_i} = {r_{ij}} $,对每个参与者已参与排序的字符权重进行及时更新。 3: 令j=j–1, j >1;重复步骤2中的(1)~(2),直到j=1,得到第一个字符的排序位置ri1,Pi也就可以得到的字符串根据字典序得到的排
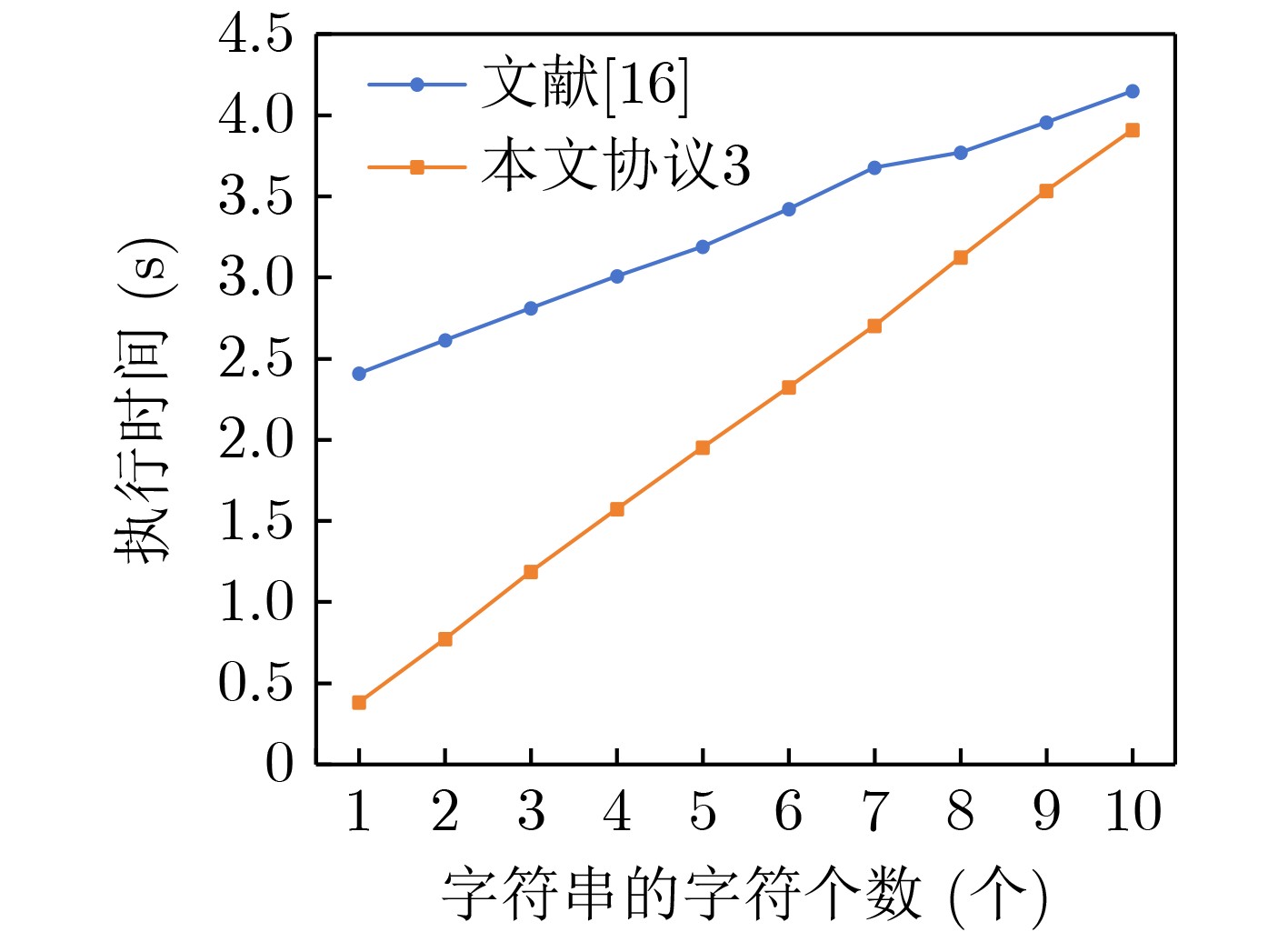
序位置Ri=ri1 。表 1 协议性能对比
协议 计算复杂性 通信复杂性 抵抗合谋攻击 参与者个数 字符个数 协议1 $ (nm + {n^2})\lg k[{{\text{M}}_{\text{a}}}] $ $ {{O}}(n) $ 是 n 1 协议2 $ (nm + {n^2})\lg k[{{\text{M}}_{\text{a}}}] $ $ {{O}}(n) $ 是 n 1 协议3 $ l(nm + {n^2})\lg k[{{\text{M}}_{\text{a}}}] $ $ {{O}}(ln) $ 是 n n 文献[16] $ m(\lg p + l)[{{\text{M}}_{\text{c}}}] $ $ {{O}}(1) $ 否 2 n 文献[17] $ (nm + n + {n^2})\lg k[{{\text{M}}_{\text{a}}}{\text{]}} $ $ {{O}}({n^2}) $ 是 2 1 -
[1] YAO A C. Protocols for secure computations[C]. The 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Chicago, USA, 1982: 160–164. doi: 10.1109/SFCS.1982.38. [2] JÓNSSON K V, KREITZ G, and UDDIN M. Secure multi-party sorting and applications[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2011, 2011: 122–142. [3] CHOI S G, HWANG K W, KATZ J, et al. Secure multi-party computation of boolean circuits with applications to privacy in on-line marketplaces[C]. The Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2012: 416–432. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-27954-6_26. [4] FAN Xingyue, WU Ting, ZHENG Qiuhua, et al. HSE-Voting: A secure high-efficiency electronic voting scheme based on homomorphic signcryption[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 111: 754–762. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.10.016. [5] HUSZTI A. A homomorphic encryption-based secure electronic voting scheme[J]. Publicationes Mathematicae Debrecen, 2011, 79(3/4): 479–496. doi: 10.5486/PMD.2011.5142. [6] QU Wenlei, WU Lei, WANG Wei, et al. A electronic voting protocol based on blockchain and homomorphic signcryption[J]. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2022, 34(16): e5817. doi: 10.1002/cpe.5817. [7] NAIDU P S, KHARAT R, TEKADE R, et al. E-voting system using visual cryptography & secure multi-party computation[C]. 2016 International Conference on Computing Communication Control and automation, Pune, India, 2016: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICCUBEA.2016.7860062. [8] HAGA R, TOYODA K, SHINODA Y, et al. Card-based secure sorting protocol[C]. The 17th International Workshop on Security, Tokyo, Japan, 2022: 224–240. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-15255-9_12. [9] 唐春明, 石桂花, 姚正安. 排序问题的安全多方计算协议[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2011, 41(7): 789–797. doi: 10.1360/zf2011-41-7-789.TANG Chunming, SHI Guihua, and YAO Zheng’an. Secure multi-party computation protocol for sequencing problem[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2011, 54(8): 1654–1662. doi: 10.1360/zf2011-41-7-789. [10] YUE Conghan, ZOU Qinghua, YANG Moude, et al. A practical secure multi-party sorting scheme based on radix sorting and homomorphic encryption[C]. 2022 International Conference on Blockchain Technology and Information Security, Huaihua, China, 2022: 127–130. doi: 10.1109/ICBCTIS55569.2022.00039. [11] 邱梅, 罗守山, 刘文, 等. 利用RSA密码体制解决安全多方多数据排序问题[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(5): 1119–1123. doi: 10.3321/ j.issn:0372-2112.2009.05.037.QIU Mei, LUO Shoushan, LIU Wen, et al. A solution of secure multi-party multi-data ranking problem based on RSA encryption scheme[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(5): 1119–1123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.05.037. [12] ASHAROV G, HAMADA K, IKARASHI D, et al. Efficient secure three-party sorting with applications to data analysis and heavy hitters[C]. The 2022 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Los Angeles, USA, 2022: 125–138. doi: 10.1145/3548606.3560691. [13] DAI Hua, REN Hui, CHEN Zhiye, et al. Privacy-preserving sorting algorithms based on logistic map for clouds[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2018, 2018: 2373545. doi: 10.1155/2018/2373545. [14] 李顺东, 杜润萌, 杨颜璟, 等. 安全多方多数据排序[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(8): 1448–1462. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.01448.LI Shundong, DU Runmeng, YANG Yanjing, et al. Secure multiparty multi-data ranking[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(8): 1448–1462. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.01448. [15] 窦家维, 汪榆淋. 安全排序协议及其应用[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(11): 4316–4333. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006326.DOU Jiawei and WANG Yulin. Secure sorting protocols and their applications[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(11): 4316–4333. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006326. [16] 李顺东, 亢佳, 杨晓艺, 等. 基于字符串排序的高效保密数据库查询[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(7): 1893–1908. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005358.LI Shundong, KANG Jia, YANG Xiaoyi, et al. String sorting based efficient secure database query[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(7): 1893–1908. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005358. [17] 李顺东, 亢佳, 杨晓艺, 等. 多个字符排序的安全多方计算[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(5): 1172–1188. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01172.LI Shundong, KANG Jia, YANG Xiaoyi, et al. Secure multiparty characters sorting[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(5): 1172–1188. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01172. [18] ODED G. Foundations of Cryptography: Volume 2, Basic Applications[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2009: 599–764. [19] 唐飞, 凌国玮, 单进勇. 基于国密SM2和SM9的加法同态加密方案[J]. 密码学报, 2022, 9(3): 535–549. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000532.TANG Fei, LING Guowei, and SHAN Jinyong. Additive homomorphic encryption schemes based on SM2 and SM9[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2022, 9(3): 535–549. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000532. [20] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 32918.4-2016 信息安全技术 SM2椭圆曲线公钥密码算法 第4部分: 公钥加密算法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 32918.4-2016 Information security technology—public key cryptographic algorithm SM2 based on elliptic curves—part 4: Public key encryption algorithm[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. [21] CRAMER R, GENNARO R, and SCHOENMAKERS B. A secure and optimally efficient multi-authority election scheme[J]. European Transactions on Telecommunications, 1997, 8(5): 481–490. doi: 10.1002/ett.4460080506. [22] DESMEDT Y and FRANKEL Y. Threshold cryptosystems[C]. The Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 1990: 307–315. doi: 10.1007/0-387-34805-0_28. [23] KOBLITZ N. Elliptic curve cryptosystems[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1987, 48(177): 203–209. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1987-0866109-5. [24] ELGAMAL T. A public key cryptosystem and a signature scheme based on discrete logarithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1985, 31(4): 469–472. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1985.1057074. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
