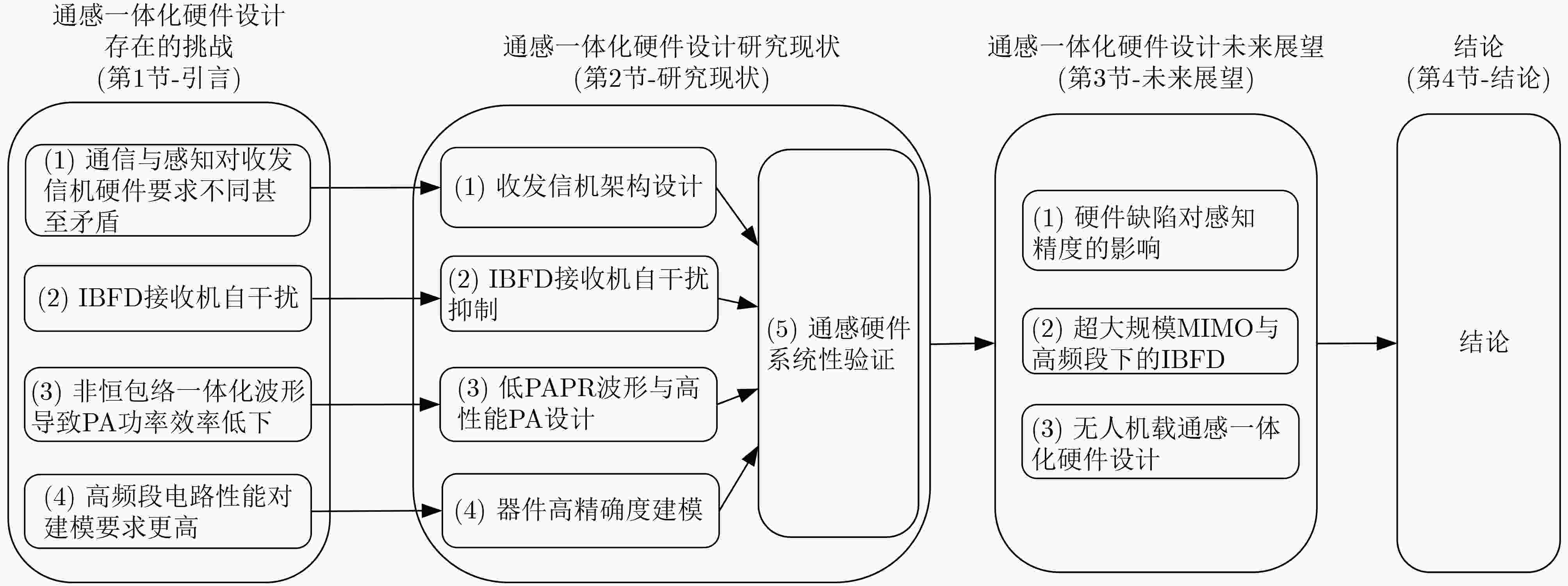
Status and Prospect of Hardware Design on Integrated Sensing and Communication
-
摘要: 通信感知一体化(ISAC)需要通信和感知共用无线电频段和硬件资源。多频段、大带宽、通信感知对硬件的要求不同等特点对通信感知一体化硬件设计提出更高要求。该文对后5G, 6G, WiFi等通信感知一体化的硬件设计、验证技术,以及硬件系统性验证平台进行归纳,对国内外近年相关硬件设计研究及其验证情况进行综述,关注通信感知两种系统对硬件的需求矛盾、带内全双工(IBFD)自干扰消除(SIC)、功放(PA)效率、电路性能对建模要求更高等硬件设计挑战。首先,总结、比较已有研究中通信感知一体化收发信机架构设计。然后,介绍、分析现有通信感知一体化带内全双工自干扰抑制方案、低峰均功率比(PAPR)波形与高性能PA设计、器件高精度建模方法以及硬件系统性验证平台。最后,总结全文并对未来通信感知一体化硬件设计所面临的开放性问题进行展望。Abstract:
Objective: The field of cellular mobile communication is advancing toward post-5G (5.5G, Beyond 5G, 5G Advanced) and 6th Generation (6G) standards. This evolution involves a shift from traditional sub-6 GHz operating frequency bands to higher frequency ranges, including millimeter wave (mmWave), terahertz (THz), and even visible light frequencies, which intersect with radar operating bands. Technologies such as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) and Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) have gained widespread application in both wireless communication and radar domains. Given the shared characteristics and commonalities in signal processing and operating frequency bands between these two fields, “Integrated Sensing And Communication (ISAC)” has emerged as a significant research focus in wireless technologies like 5G Advanced (5G-A), 6G, Wireless Fidelity (WiFi), and radar. This development points toward a network perception paradigm that combines communication, sensing, and computing. The “ISAC” concept aims to unify wireless communication systems (including cellular and WiFi) with wireless sensing technologies (such as radar) and even network Artificial Intelligence (AI) computing capabilities into a cohesive framework. By integrating these elements, the physical layer can share frequencies and Radio Frequency (RF) hardware resources, leading to several advantages: spectrum conservation, cost reduction, minimized hardware size and weight, and enhanced communication perception. In this article, the focus of communication perception integration is primarily on radar communication. ISAC necessitates that both communication and sensing utilize the same radio frequency band and hardware resources. The diverse characteristics of multiple frequency bands, along with the varying hardware requirements for communication and sensing, present increased challenges for ISAC hardware design. Effective hardware design for ISAC systems demands a well-considered architecture and device design for RF transceivers. Key considerations include the receiver’s continuous signal sensing, link budget, and noise figure, all of which are sensitive to factors such as system size, weight, power consumption, and cost. A comprehensive review of relevant literature reveals that while studies on overall architecture, waveform design, signal processing, and THz technology exist within the ISAC domain, they often center on theoretical models and software simulation. Hardware design and technical verification methodologies are sporadically addressed across different studies. Although some literature details specific hardware designs and validation approaches, these are limited in number compared to the rich body of theoretical and algorithmic research, indicating a need for more comprehensive and systematic reviews focused specifically on ISAC hardware design. Methods: This paper summarizes the hardware designs, verification technologies, and systemic hardware verification platforms pertinent to beyond 5G, 6G, and WiFi ISAC systems. Additionally, recent researches on related hardware designs and verification both domestically and internationally are reviewed. The analysis addresses the challenges in hardware design, including the conflicting requirements between communication and sensing systems, In Band Full Duplex (IBFD) Self-Interference Cancellation (SIC), Power Amplifier (PA) efficiency, and the need for more accurate circuit performance modeling. Results and Discussions: Initially, the design of ISAC transceiver architectures from existing research is summarized and compared. Subsequently, an overview and analysis of current ISAC IBFD self-interference suppression strategies, low Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) waveforms, high-performance PA designs, precise device modeling techniques, and systemic hardware verification platforms are presented. Finally, the paper provides a summary of the findings. Future challenges in ISAC hardware design are discussed, including the effects of hardware defects on sensing accuracy, ultra-large scale MIMO systems, high-frequency IBFD, and ISAC hardware designs for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) applications. The performance metrics of ISAC IBFD architectures are compared, while the various ISAC transceiver architectures are outlined. Representative hardware verification platforms for ISAC systems are presented. The different ISAC transceiver architectures summarized in this paper are illustrated. Conclusions: In recent years, preliminary research has been conducted on integrated air interface architecture, transceiver hardware design, systematic hardware verification, and demonstration of sensing technologies such as 5G-A, 6G, and WiFi, both domestically and internationally. However, certain limitations persist. Beyond 5G networks, post-5G and 6G ISAC hardware verification platforms primarily operate at the link level rather than at the network system level. This focus on ISAC without the integration of computing functions leads to increased volume and power consumption costs and a reliance on commercial instruments and SDR platforms. Furthermore, the IBFD self-interference suppression technology has yet to fully satisfy the demands of future ultra-large-scale MIMO systems, necessitating further integration with large-scale artificial intelligence model technologies. In light of impending technological challenges and issues of openness, it is crucial for academia and industry to collaborate in addressing these challenges and researching viable solutions. To expedite testing optimization and industrial implementation, practical hardware design transition solutions are required that balance advancements in high-frequency support, receiver architecture, and networking architecture, facilitating the efficient realization of the “ideal” of ISAC. -
图 2 传统TDD收发信机架构[34]
图 3 接收机通信与感知部分分离的架构[36]
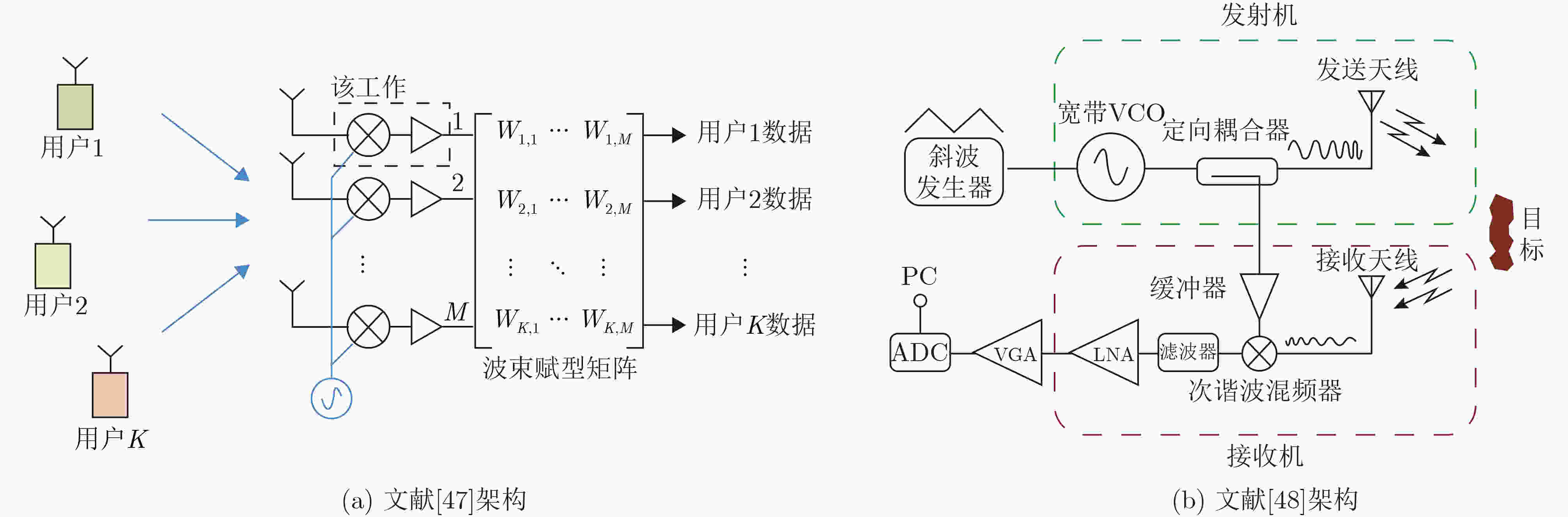
图 4 基于多端口干涉器的收发信机架构[41]
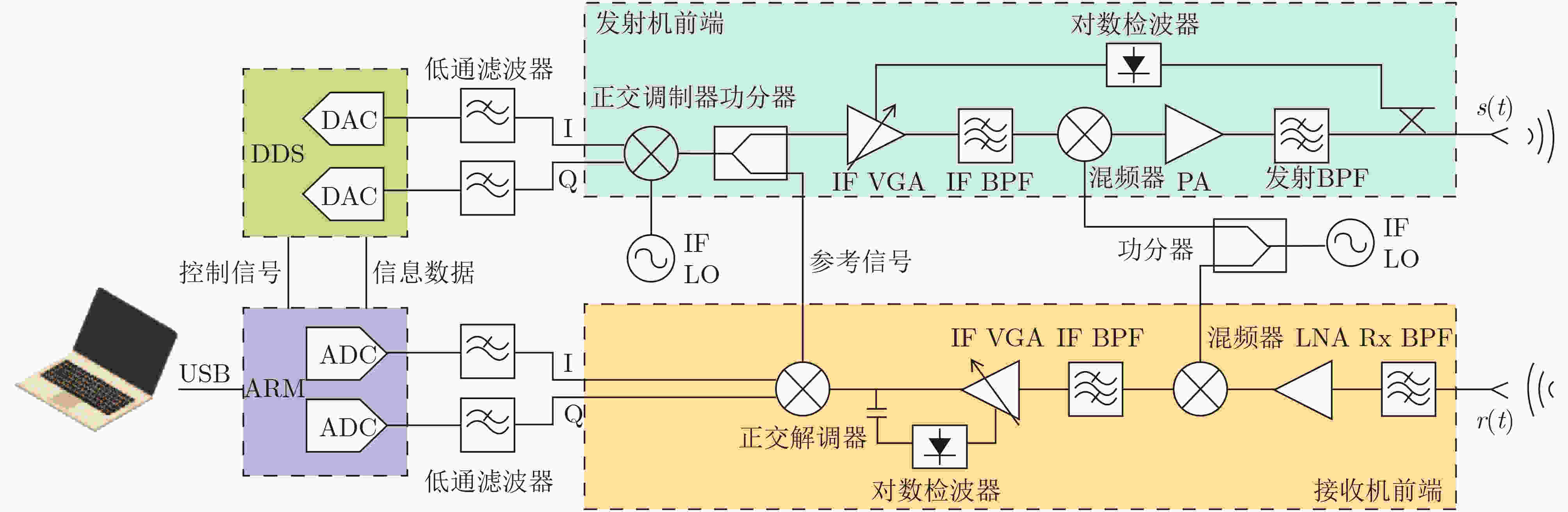
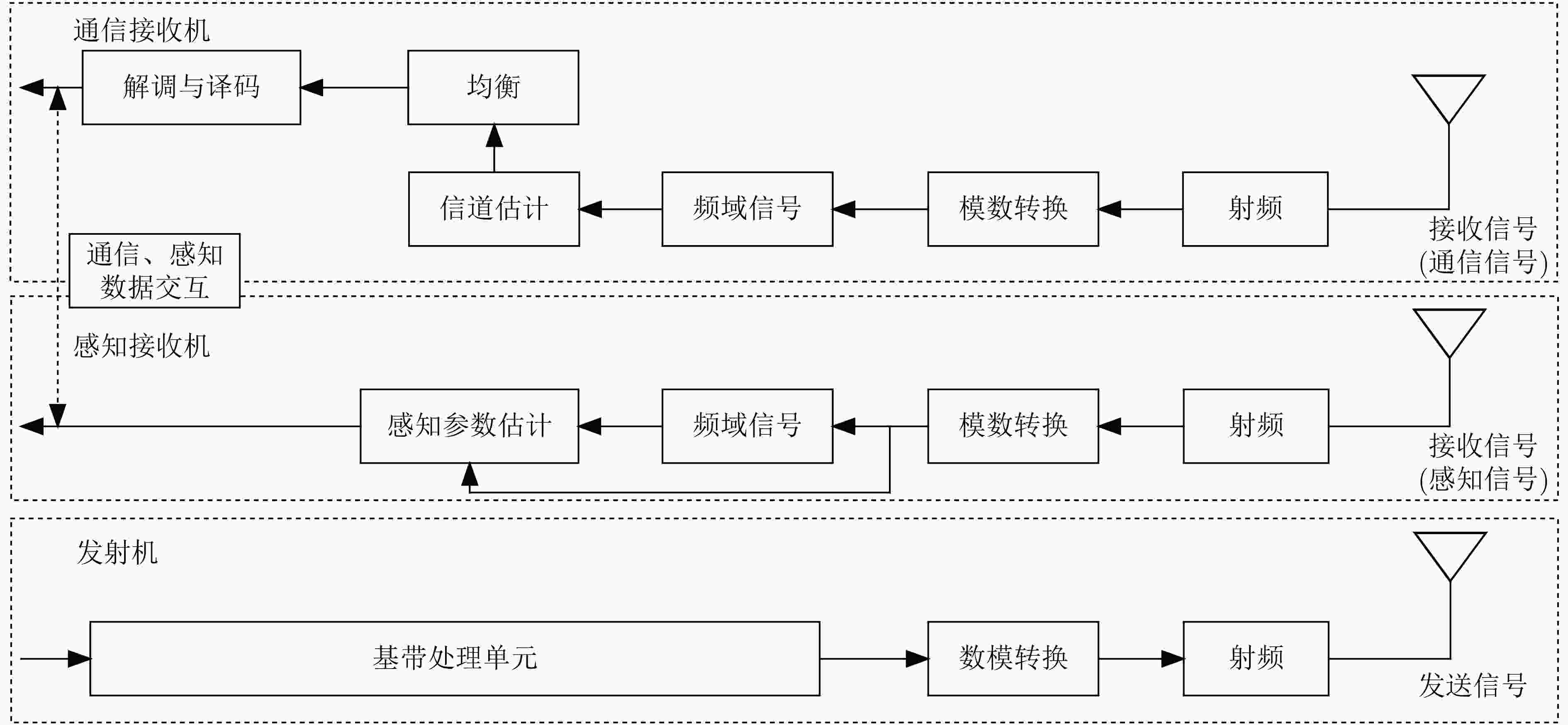
图 5 通感一体化系统IBFD架构[23]
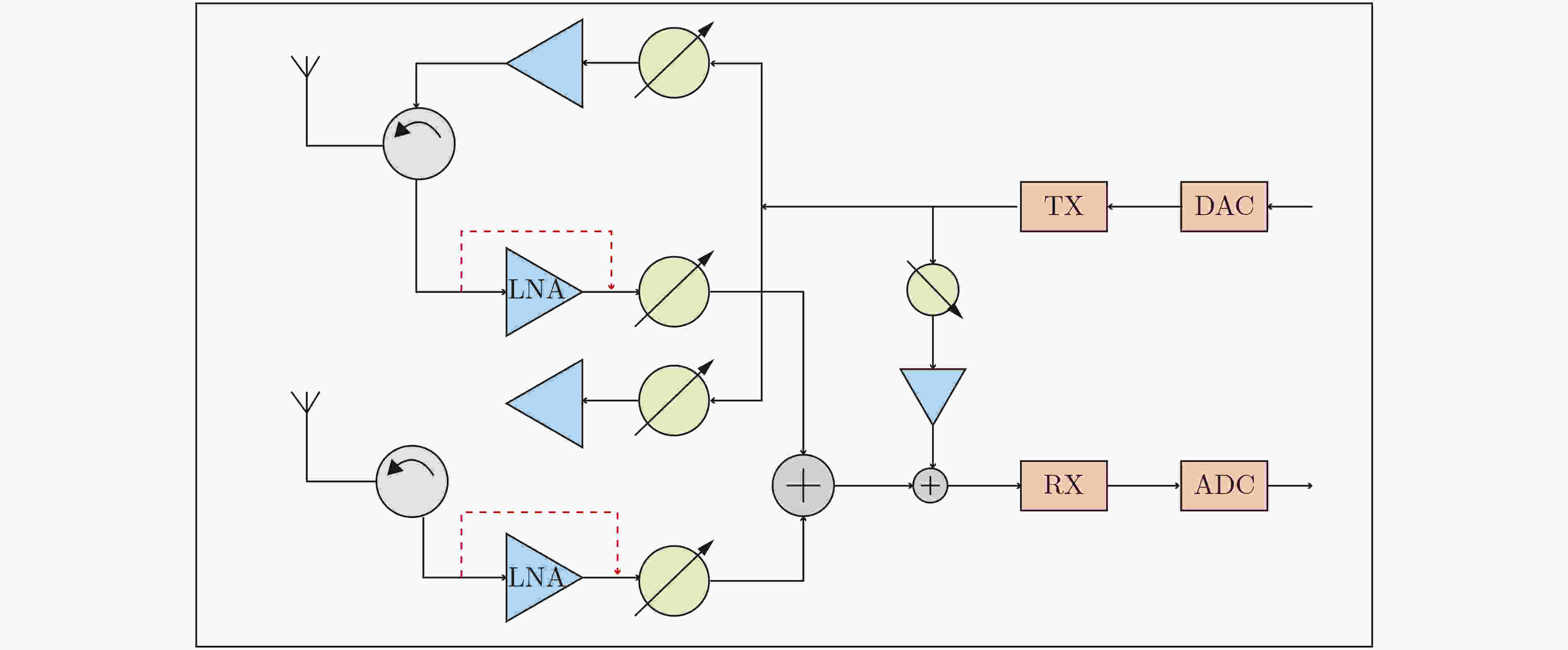
图 6 IBFD收发信机架构[46]
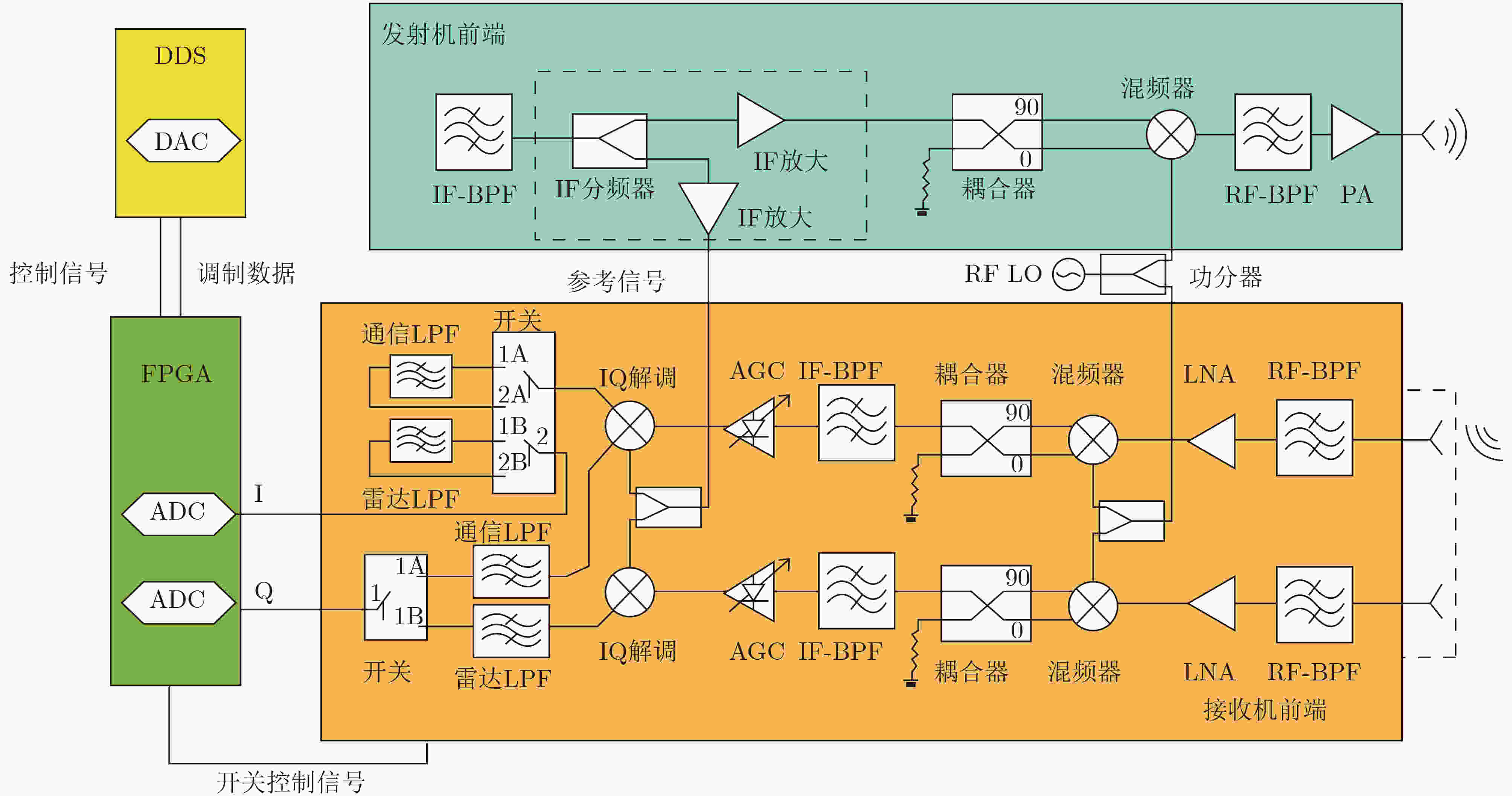
图 7 接收机通信与感知完全分离的架构[21]
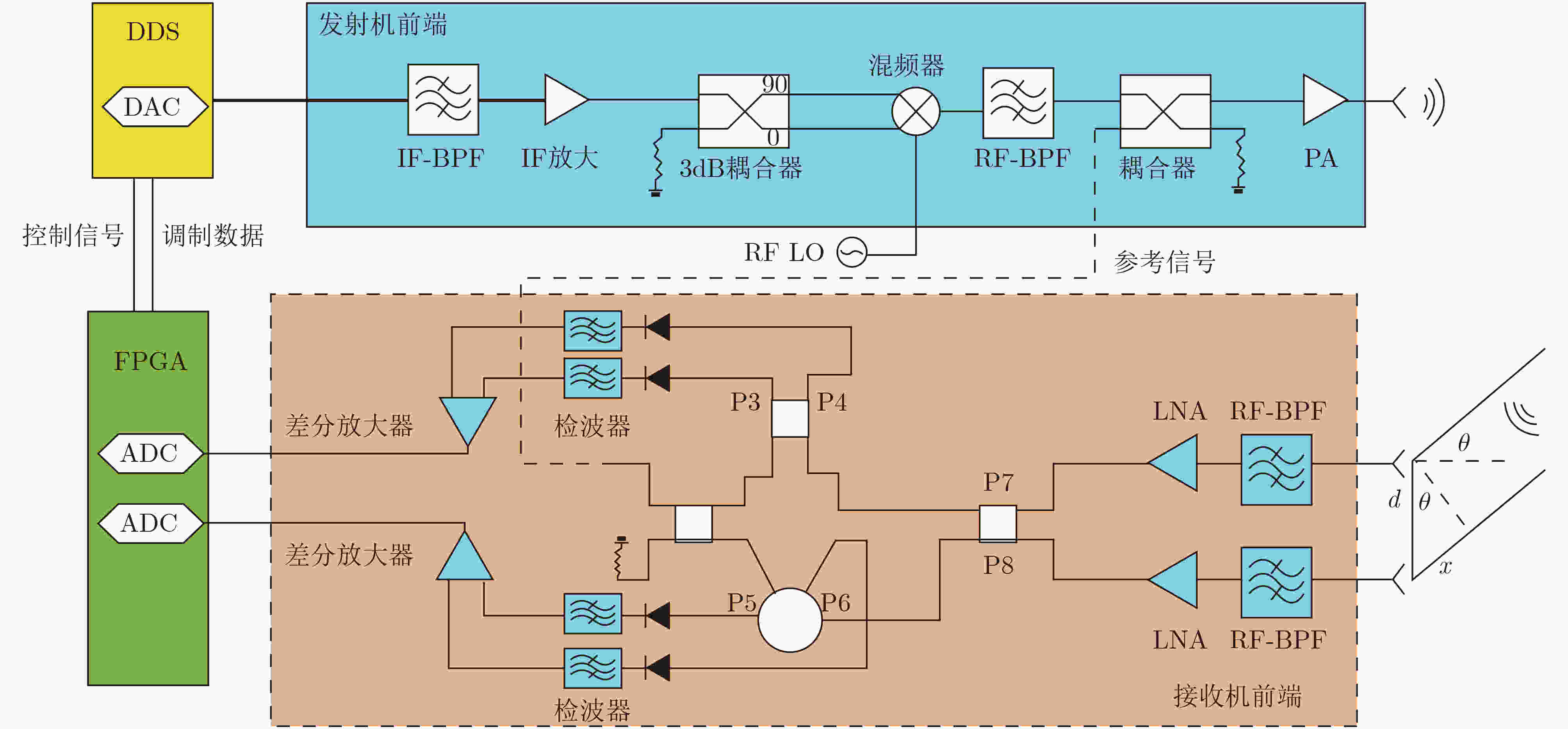
图 9 LNA选择性旁路收发信机架构[49]
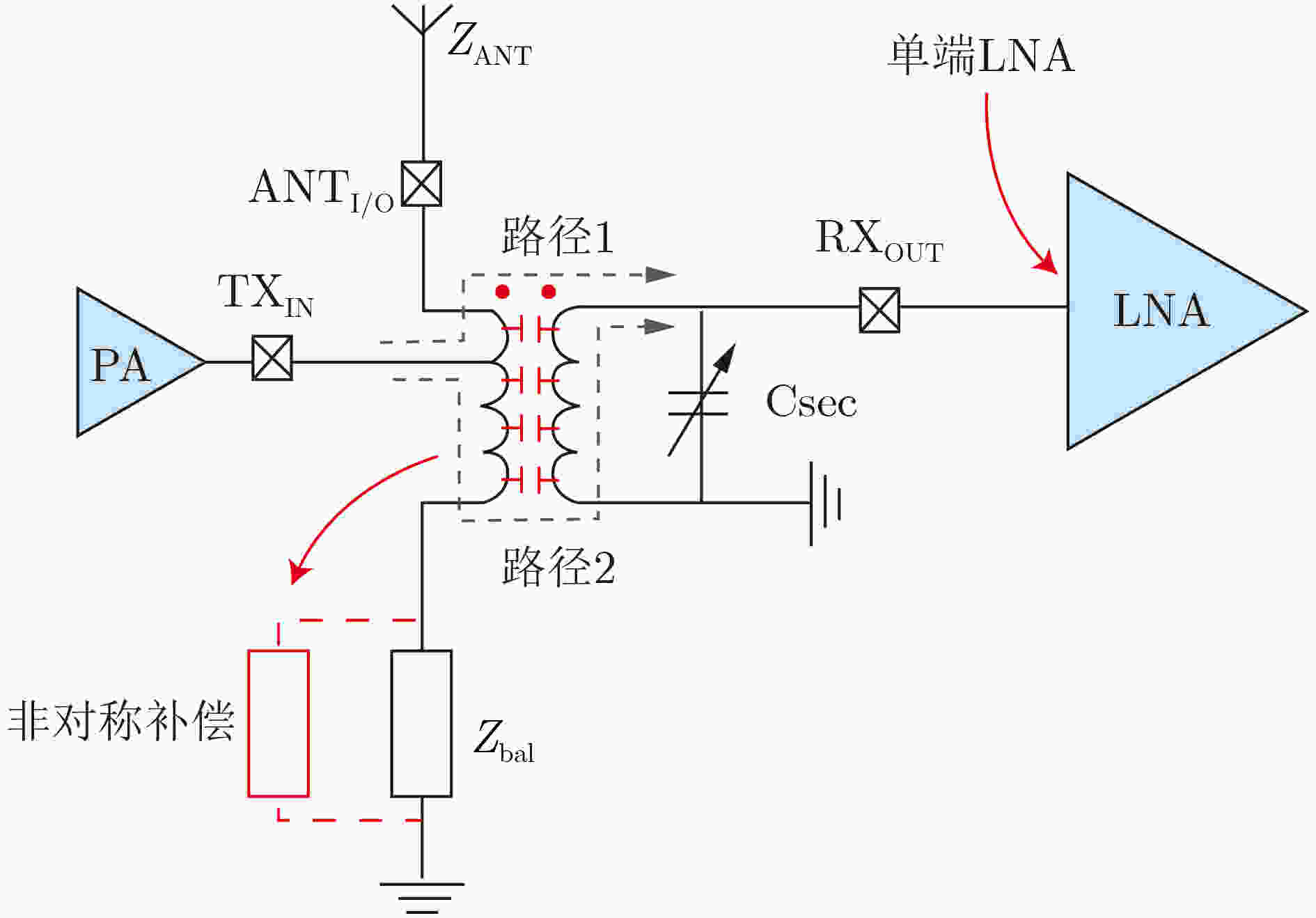
图 10 EBD电气均衡双工器自干扰抵消原理[50]
表 1 通感一体化IBFD架构性能对比
表 2 通感一体化收发信机架构总结
文献 收发信机架构 通信双工方式 优点 缺点 说明 [32–34] TDD架构:传统无线电架构(超外差、零中频等) TDD 可直接复用已有架构 存在雷达感知最小距离问题,通信和雷达对收发信机要求不同导致一体化功能实现较为困难 [35,36] TDD架构:接收机通信感知链路部分分离 TDD 保持接收机灵敏度,节省ADC 接收机额外增加感知链路,体积、重量增大 接收机天线、射频、大部分中频链路分离,时分复用
基带链路[42] TDD架构:接收机基于多端口干涉器 TDD 便于估计AOA、简单易实现、低成本、极低功耗、可重配置 接收机灵敏度减小、动态范围有限、雷达探测距离减小 适合毫米波和大规模MIMO(对噪声性能要求宽松) [23] IBFD架构 IBFD(接收机可持续接收信号) 通信频谱利用率提升接近2倍、无雷达感知最小距离问题 收发天线互耦、自干扰抑制带来接收机计算资源消耗与硬件复杂度的增大 学术研究与未来产业落地的理想终极方案 [16] 折中架构:接收机通信感知链路完全分离 TDD(接收机中的感知链路可持续接收信号) 避免自干扰、工程易实现、无雷达感知最小距离问题 接收机额外增加感知链路,体积、重量增大 学术研究与目前产业测试的折中过渡方案 [47,48] 高频段架构:接收机混频器前置 TDD 缓解接收机饱和问题、面积与功耗减小、无雷达感知最小距离问题 接收机噪声系数增大、灵敏度减小、雷达探测距离减小 适合毫米波和大规模MIMO(对噪声性能要求宽松) [49] 高频段架构:接收机LNA选择性旁路 TDD 缓解接收机饱和问题、面积与功耗减小、无雷达感知最小距离问题 接收机噪声系数增大、雷达灵敏度减小、雷达探测距离减小 适合毫米波和大规模MIMO(对噪声性能要求宽松),发射信号时旁路 表 3 通感一体化部分代表性硬件验证平台
文献 频点、带宽 波形 感知验证情况 通信验证情况 特点或局限性 [46] 2.4 GHz,
40 MHzOFDM 5G BS端下行链路室外静止无人机测距(距离
40 m),室外多车辆测距、测速(距离50~
110 m,速度12 m/s、±9 m/s)。– IBFD架构,自干扰消除方法设计 [70,71] 24 GHz,
93.1 MHzOFDM 室外实际路况多车辆测距(100 m以内)、
测速(–5 m/s,–12 m/s)。– 面向车联网、自动驾驶场景 [29] 3.5 GHz,
10 MHzLFM 模糊函数性能较好。 比特率1 Mbit/s,定向通信,给出QPSK星座图
(误码率较好)雷达通信一体化波形首次得到硬件技术验证[24] [75] 73 GHz,
2 GHzOFDM 毫米波室内外静止目标测距(4 m内)、
测角、不支持测速。单工通信 毫米波高频段,受制于SIMO机械模拟的慢速,只能对静止目标测距、测角 [94,95] 3.5 GHz,
18 MHzOFDM 使用NI公司5G大规模MIMO实验平台验证近场室内移动物体厘米级定位。 - 只是初步探究感知功能在未来集成到大规模MIMO通信系统中的技术可行性,没有进行通信功能与性能测试 [78,81,85] 28 GHz,
800 MHzOFDM 通感算一体化:5G毫米波室内多车协同定位,测距0.9 m,精度0.044 m。 2.8 Gbit/s 面向车联网、自动驾驶场景的多站协同感知;TDD架构 [81] 27.5 GHz OFDM 车辆测距、测速、测角。 视频传输 面向车联网、自动驾驶场景的单站感知 [86,87] 5.4 GHz,
560 MHzSTC-OFDM-Chirp 固定翼飞机机载8 km高空对地SAR成像,
分辨率0.3 m×0.3 m。传输图像,误码率较高(未加信道编码) 时空域多维度多波束一体化波形调制;
固定翼飞机SAR成像[93] 26 GHz,
100 MHzCP-OFDM 室外5G基站车辆、无人机感知:测距500 m
以上;车辆测速精度小于0.1 km/h
(车速30 km/h)、测角精度小于0.2o。- 基于5G现网的通感一体化验证 [96] 140 GHz,
8 GHzOFDM, FMCW 大规模MIMO太赫兹毫米级不可
见物体3维成像。- 只是初步探究太赫兹感知集成到大规模MIMO通信的可行性 -
[1] 孟凡军, 邓炳光, 秦启航, 等. 5G NR小区搜索中一种频域相关快速同步算法[J]. 电讯技术, 2023, 63(4): 563–568. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.211224008.MENG Fanjun, DENG Bingguang, QIN Qihang, et al. A fast synchronization algorithm based on frequency domain correlation in 5G NR cell search[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2023, 63(4): 563–568. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.211224008. [2] 韩松岳, 苗恺, 李勇, 等. 区块链与5G MEC在军事领域的融合应用[J]. 海军航空大学学报, 2022, 37(4): 301–310. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2022.04.002.HAN Songyue, MIAO Kai, LI Yong, et al. Integration application of blockchain and 5G MEC in military field[J]. Journal of Naval Aviation University, 2022, 37(4): 301–310. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2022.04.002. [3] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 6G网络架构愿景与关键技术展望白皮书[R]. 2021.IMT-2030(6G) Promotion Group. 6G network architecture vision and key technology outlook white paper[R]. 2021. [4] 胡圣波, 朱满琴, 杨露露, 等. 未来无线通信与大数据、人工智能[J]. 贵州师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 38(6): 1–10. doi: 10.16614/j.gznuj.zrb.2020.06.001.HU Shengbo, ZHU Manqin, YANG Lulu, et al. Future wireless communication, big data and AI[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University: Natural Sciences, 2020, 38(6): 1–10. doi: 10.16614/j.gznuj.zrb.2020.06.001. [5] 王朝炜, 王天宇, 刘婷, 等. 6G车联网中基于路侧设备部署优化的机会式数据卸载[J]. 无线电工程, 2022, 52(11): 1895–1900. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2022.11.001.WANG Chaowei, WANG Tianyu, LIU Ting, et al. Opportunistic data offloading based on RSU deployment optimization in 6G internet of vehicle[J]. Radio Engineering, 2022, 52(11): 1895–1900. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2022.11.001. [6] 肖沈阳, 金志刚, 苏毅珊, 等. 一种优化的gOMP稀疏OFDM信道估计方法[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2017, 49(5): 149–155. doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.201601000.XIAO Shenyang, JIN Zhigang, SU Yishan, et al. An optimized gOMP algorithm for sparse OFDM channel estimation[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2017, 49(5): 149–155. doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.201601000. [7] 庞立华, 吴文捷, 张阳, 等. 多小区Massive MIMO系统的分布式导频优化分配[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2019, 39(2): 354–359. doi: 10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2019.0224.PANG Lihua, WU Wenjie, ZHANG Yang, et al. Distributed pilot optimizing assignment in multi-cell Massive MIMO systems[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2019, 39(2): 354–359. doi: 10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2019.0224. [8] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 通信感知一体化技术研究报告[R]. 2021.IMT-2030(6G) Promotion Group. Research report on integration of sensing and communication technology[R]. 2021. [9] HUANG Yuhong. Challenges and opportunities of sub-6 GHz integrated sensing and communications for 5G-Advanced and beyond[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2024, 33(2): 323–325. doi: 10.23919/cje.2023.00.251. [10] 闫实, 彭木根, 王文博. 通信感知计算融合: 6G愿景与关键技术[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2021, 44(4): 1–11. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2021-081.YAN Shi, PENG Mugen, and WANG Wenbo. Integration of communication, sensing and computing: The vision and key technologies of 6G[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021, 44(4): 1–11. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2021-081. [11] LIU Fan, CUI Yuanhao, MASOUROS C, et al. Integrated sensing and communications: Toward dual-functional wireless networks for 6G and beyond[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1728–1767. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3156632. [12] 尉志青, 冯志勇, 李怡恒, 等. 太赫兹通信感知一体化波形: 现状与展望[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(1): 3–10. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022007.WEI Zhiqing, FENG Zhiyong, LI Yiheng, et al. Terahertz joint communication and sensing waveform: Status and prospect[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(1): 3–10. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022007. [13] ZHANG J A, LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, et al. An overview of signal processing techniques for joint communication and radar sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1295–1315. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3113120. [14] 余显斌, 吕治东, 李涟漪, 等. 太赫兹感知通信一体化波形设计与信号处理[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(2): 76–88. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022015.YU Xianbin, LYU Zhidong, LI Lianyi, et al. Waveform design and signal processing for terahertz integrated sensing and communication[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(2): 76–88. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022015. [15] 林粤伟, 王溢, 张奇勋, 等. 面向6G的通信感知一体化车联网研究综述[J]. 信号处理, 2023, 39(6): 963–974. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.06.002.LIN Yuewei, WANG Yi, ZHANG Qixun, et al. Overview of the research on 6G oriented internet of vehicles for integrated sensing and communication[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2023, 39(6): 963–974. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.06.002. [16] 马忠贵, 李卓, 梁彦鹏. 自动驾驶车联网中通感算融合研究综述与展望[J]. 工程科学学报, 2023, 45(1): 137–149. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2022.04.16.003.MA Zhonggui, LI Zhuo, and LIANG Yanpeng. Overview and prospect of communication-sensing-computing integration for autonomous driving in the Internet of vehicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2023, 45(1): 137–149. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2022.04.16.003. [17] 刘鑫, 王忠, 秦明星. 多机器人协同SLAM技术研究进展[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(5): 1–10. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0062504.LIU Xin, WANG Zhong, and QIN Mingxing. Research progress of multi-robot collaborative SLAM technology[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(5): 1–10. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0062504. [18] 王红星, 徐婉琳, 张勃阳. 一种基于改进ORB和PROSAC特征点匹配的V-SLAM算法[J]. 河南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 42(1): 152–159. doi: 10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2021040137.WANG Hongxing, XU Wanlin, and ZHANG Boyang. V-SLAM algorithm based on improved ORB and PROSAC feature point matching[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University: Natural Science, 2023, 42(1): 152–159. doi: 10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2021040137. [19] 谭运馨, 黄海风, 赖涛, 等. 基于GPU的长轨SAR实时成像算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2023, 38(6): 1380–1391. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2023.06.013.TAN Yunxin, HUANG Haifeng, LAI Tao, et al. GPU-based real-time imaging algorithm for long-track SAR[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2023, 38(6): 1380–1391. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2023.06.013. [20] 刘帅奇, 雷钰, 庞姣, 等. 基于生成对抗网络的SAR图像去噪[J]. 河北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 42(3): 306–313. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1565.2022.03.013.LIU Shuaiqi, LEI Yu, PANG Jiao, et al. SAR image denoising based on generative adversarial networks[J]. Journal of Hebei University: Natural Science Edition, 2022, 42(3): 306–313. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1565.2022.03.013. [21] 刘光毅, 楼梦婷, 王启星, 等. 面向6G的通信感知一体化架构与关键技术[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(6): 8–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.06.002.LIU Guangyi, LOU Mengting, WANG Qixing, et al. Towards 6G: Research on integrated sensing and communication architecture and key technology[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(6): 8–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.06.002. [22] 叶威, 高树亮. 面向5.5G的通信感知一体化[J]. 信息通信技术, 2021, 15(5): 27–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1285.2021.05.005.YE Wei and GAO Shuliang. Integrated sensing and communication towards 5.5G[J]. Information and Communications Technologies, 2021, 15(5): 27–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1285.2021.05.005. [23] HASSANI S A, PARASHAR K, BOURDOUX A, et al. Doppler radar with in-band full duplex radios[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2019 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 2019: 1945–1953. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2019.8737408. [24] 刘凡, 袁伟杰, 原进宏, 等. 雷达通信频谱共享及一体化: 综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 467–484. doi: 10.12000/JR20113.LIU Fan, YUAN Weijie, YUAN Jinhong, et al. Radar-communication spectrum sharing and integration: Overview and prospect[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 467–484. doi: 10.12000/JR20113. [25] 郝跃星. 恒包络OFDM雷达通信一体化关键技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2017.HAO Yuexing. Research on the key technology of constant envelop OFDM radar-communication integration[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2017. [26] 张秋月, 张林让, 谷亚彬, 等. 恒包络OFDM雷达通信一体化信号设计[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2019, 53(6): 77–84. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201906011.ZHANG Qiuyue, ZHANG Linrang, GU Yabin, et al. Signal design of communication integration for radars with constant envelope OFDM[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2019, 53(6): 77–84. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201906011. [27] 肖博, 霍凯, 刘永祥. 雷达通信一体化研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 739–750. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180515.XIAO Bo, HUO Kai, and LIU Yongxiang. Development and prospect of radar and communication integration[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 739–750. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180515. [28] MCCORMICK P M, BLUNT S D, and METCALF J G. Simultaneous radar and communications emissions from a common aperture, part I: Theory[C]. IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 1685–1690. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944478. [29] MCCORMICK P M, RAVENSCROFT B, BLUNT S D, et al. Simultaneous radar and communication emissions from a common aperture, part II: Experimentation[C]. IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 1697–1702. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944480. [30] IMT-2030 (6G) 推进组. 通信感知一体化技术研究报告[R]. 2版. 2022.IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group. Research report on integrated sensing and communication technology[R]. 2nd ed. 2022. [31] BOZORGI F, SEN P, BARRETO A N, et al. RF front-end challenges for joint communication and radar sensing[C]. 1st IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications and Sensing, Dresden, Germany, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/JCS52304.2021.9376387. [32] HAN Liang and WU Ke. Radar and radio data fusion platform for future intelligent transportation system[C]. 7th IEEE European Radar Conference, Paris, France, 2010: 65–68. [33] HAN Liang and WU Ke. Emerging advances in transceiver technology fusion of wireless communication and radar sensing systems[C]. IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 2011: 951–954. [34] HAN Liang and WU Ke. Multifunctional transceiver for future intelligent transportation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2011, 59(7): 1879–1892. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2138156. [35] MOGHADDASI J and WU Ke. Improved joint radar-radio (RadCom) transceiver for future intelligent transportation platforms and highly mobile high-speed communication systems[C]. IEEE International Wireless Symposium, Beijing, China, 2013: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/IEEE-IWS.2013.6616796. [36] MOGHADDASI J and WU Ke. Multifunctional transceiver for future radar sensing and radio communicating data-fusion platform[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 818–838. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2530979. [37] ZHANG Hui, LI Lin, and WU Ke. 24GHz software-defined radar system for automotive applications[C]. IEEE European Conference on Wireless Technologies, Munich, Germany, 2007: 138–141. doi: 10.1109/ECWT.2007.4403965. [38] HAN Liang and WU Ke. 24-GHz joint radar and radio system capable of time-agile wireless sensing and communication[C]. IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Baltimore, USA, 2011: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/MWSYM.2011.5972832. [39] HAN Liang and WU Ke. 24-GHz integrated radio and radar system capable of time-agile wireless communication and sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2012, 60(3): 619–631. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2179552. [40] HAN Liang and WU Ke. Joint wireless communication and radar sensing systems–state of the art and future prospects[J]. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 2013, 7(11): 876–885. doi: 10.1049/iet-map.2012.0450. [41] MOGHADDASI J and WU Ke. Unified radar-communication (RadCom) multi-port interferometer transceiver[C]. IEEE European Radar Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 2013: 479–482. [42] MOGHADDASI J and WU Ke. Millimeter-wave multifunction multiport interferometric receiver for future wireless systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2018, 66(3): 1452–1466. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2772927. [43] HASSANI S A, GUEVARA A, PARASHAR K, et al. An in-band full-duplex transceiver for simultaneous communication and environmental sensing[C]. IEEE 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2018: 1389–1394. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2018.8645165. [44] HASSANI S A, LAMPU V, PARASHAR K, et al. In-band full-duplex radar-communication system[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(1): 1086–1097. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2992689. [45] HASSANI S A, VAN LIEMPD B, BOURDOUX A, et al. Joint in-band full-duplex communication and radar processing[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(2): 3391–3399. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3091383. [46] BARNETO C B, RIIHONEN T, TURUNEN M, et al. Full-duplex OFDM radar with LTE and 5G NR waveforms: Challenges, solutions, and measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2019, 67(10): 4042–4054. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2019.2930510. [47] IOTTI L, KRISHNAMURTHY S, LACAILLE G, et al. A low-power 70-100-GHz mixer-first RX leveraging frequency-translational feedback[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(8): 2043–2054. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.2991541. [48] MOSTAJERAN A, CATHELIN A, and AFSHARI E. A 170-GHz fully integrated single-chip FMCW imaging radar with 3-D imaging capability[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2017, 52(10): 2721–2734. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2725963. [49] BARNETO C B, TURUNEN M, LIYANAARACHCHI S D, et al. High-accuracy radio sensing in 5G new radio networks: Prospects and self-interference challenge[C]. IEEE 53rd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2019: 1159–1163. doi: 10.1109/IEEECONF44664.2019.9048786. [50] VAN LIEMPD B, HERSHBERG B, ARIUMI S, et al. A +70-dBm IIP3 electrical-balance duplexer for highly integrated tunable front-ends[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2016, 64(12): 4274–4286. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2613039. [51] MIKHAEL M, VAN LIEMPD B, CRANINCKX J, et al. An in-band full-duplex transceiver prototype with an in-system automated tuning for RF self-interference cancellation[C]. 1st IEEE International Conference on 5G for Ubiquitous Connectivity, Akaslompolo, Finland, 2014: 110–115. doi: 10.4108/icst.5gu.2014.258118. [52] VERMEULEN T, VAN LIEMPD B, HERSHBERG B, et al. Real-time RF self-interference cancellation for in-band full duplex[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks, Stockholm, Sweden, 2015: 275–276. doi: 10.1109/DySPAN.2015.7343915. [53] 徐诚, 郭进阳, 李超, 等. 使用HLS开发FPGA异构加速系统: 问题、优化方法和机遇[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(8): 1729–1748. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2210102.XU Cheng, GUO Jinyang, LI Chao, et al. Using HLS to develop FPGA heterogeneous acceleration system: Problems, optimization methods and opportunities[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2023, 17(8): 1729–1748. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2210102. [54] 吴宇航, 何军. 基于FPGA的人体行为识别系统的设计[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 14(3): 331–340. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2022.03.009.WU Yuhang and HE Jun. Design of human activity recognition system based on FPGA[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2022, 14(3): 331–340. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2022.03.009. [55] HUUSARI T, CHOI Y S, LIIKKANEN P, et al. Wideband self-adaptive RF cancellation circuit for full-duplex radio: Operating principle and measurements[C]. IEEE 81st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Glasgow, UK, 2015: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/VTCSpring.2015.7146163. [56] HASSANI S A, VAN LIEMPD B, BOURDOUX A, et al. Adaptive filter design for simultaneous in-band full-duplex communication and radar[C]. IEEE 17th European Radar Conference, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 5–8. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00013. [57] HU Xiaoyan, MASOUROS C, LIU Fan, et al. Low-PAPR DFRC MIMO-OFDM waveform design for integrated sensing and communications[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022: 1599–1604. doi: 10.1109/ICC45855.2022.9838548. [58] 任乐. 毫米波宽带混频与固态合成功放及线性化技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 东南大学, 2022. doi: 10.27014/d.cnki.gdnau.2022.000237.REN Le. Research on techniques of millimeter wave broadband mixing and solid-state power combined amplifier and linearization[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Southeast University, 2022. doi: 10.27014/d.cnki.gdnau.2022.000237. [59] GAVELL M, GRANSTROM G, FAGER C, et al. An E-band analog predistorter and power amplifier MMIC chipset[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2018, 28(1): 31–33. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2017.2768519. [60] DORVAL R, GRAY R, and KATZ A. A versatile wideband linearizer/driver amplifier for use with multiple millimeter-wave TWTAs[C]. IEEE Topical Conference on RF/Microwave Power Amplifiers for Radio and Wireless Applications, Orlando, USA, 2019: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/PAWR.2019.8708717. [61] CHO G, PARK J, and HONG S. A 25.5-dB peak gain F-band power amplifier with an adaptive built-in linearizer[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2020, 30(1): 106–108. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2019.2954217. [62] OTHMANI M, BOULEJFEN N, BRIHUEGA A, et al. Delta-Sigma modulator-embedded digital predistortion for 5G transmitter linearization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(8): 5558–5571. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3184167. [63] MOSALAM H, XIAO Wenbo, GUI Xiaoyan, et al. A 54–68 GHz power amplifier with improved linearity and efficiency in 40 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(1): 40–44. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3084628. [64] MA Zonglin, MA Kaixue, WANG Keping, et al. A 28GHz compact 3-way transformer-based parallel-series Doherty power amplifier with 20.4%/14.2% PAE at 6-/12-dB power back-off and 25.5dBm PSAT in 55nm bulk CMOS[C]. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 320–322. doi: 10.1109/ISSCC42614.2022.9731564. [65] 于飞. 毫米波线性化器研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.001942.YU Fei. Research of millimeter wave linearizer[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.001942. [66] 张净植, 余益明, 吴韵秋, 等. 硅基毫米波集成电路设计发展现状与挑战[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(1): 68–87. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0334.ZHANG Jingzhi, YU Yiming, WU Yunqiu, et al. Developments and challenges of mm-Wave integrated circuits on silicon[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2024, 54(1): 68–87. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0334. [67] EISENSTADT W R and EO Y. S-parameter-based IC interconnect transmission line characterization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components, Hybrids, and Manufacturing Technology, 1992, 15(4): 483–490. doi: 10.1109/33.159877. [68] 魏震楠. 毫米波通信的功率放大器芯片及片上器件高精度建模研究[D]. [博士论文], 东南大学, 2022. doi: 10.27014/d.cnki.gdnau.2022.003568.WEI Zhennan. Research on power amplifier and high-precision modeling of on-chip devices for millimeter-wave communications[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Southeast University, 2022. doi: 10.27014/d.cnki.gdnau.2022.003568. [69] TANG Zhidong, WANG Zewei, GUO Ao, et al. Cryogenic CMOS RF device modeling for scalable quantum computer design[J]. IEEE Journal of the Electron Devices Society, 2022, 10: 532–539. doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2022.3186979. [70] STURM C, ZWICK T, and WIESBECK W. An OFDM system concept for joint radar and communications operations[C]. 69th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 2009: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VETECS.2009.5073387. [71] STURM C and WIESBECK W. Waveform design and signal processing aspects for fusion of wireless communications and radar sensing[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2011, 99(7): 1236–1259. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2011.2131110. [72] BRAUN M, MÜLLER M, FUHR M, et al. A USRP-based testbed for OFDM-based radar and communication systems[C]. Proceedings of 22nd Virginia Tech Symposium on Wireless Communications, Blacksburg, USA, 2012: 1–6. [73] MEALEY T C and DULY A J. BEEMER: A firmware-tuned, software-defined MIMO radar testbed[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, Waltham, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ARRAY.2016.7832582. [74] RAVENSCROFT B, MCCORMICK P M, BLUNT S, et al. Experimental assessment of tandem-hopped radar and communications (THoRaCs)[C]. IEEE International Radar Conference, Toulon, France, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR41533.2019.171280. [75] KUMARI P, MEZGHANI A, and HEATH R W. JCR70: A low-complexity millimeter-wave proof-of-concept platform for a fully-digital SIMO joint communication-radar[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2021, 2: 218–234. doi: 10.1109/OJVT.2021.3069946. [76] BARNETO C B, LIYANAARACHCHI S D, HEINO M, et al. Full duplex radio/radar technology: The enabler for advanced joint communication and sensing[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(1): 82–88. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000220. [77] SANSON J B, CASTANHEIRA D, GAMEIRO A, et al. Non-orthogonal multicarrier waveform for radar with communications systems: 24 GHz GFDM RadCom[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 128694–128705. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2940299. [78] ZHANG Qixun, SUN Huan, WEI Zhiqing, et al. Sensing and communication integrated system for autonomous driving vehicles[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2020 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Toronto, Canada, 2020: 1278–1279. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOMWKSHPS50562.2020.9162963. [79] ZHANG Qixun, LI Zhenhao, GAO Xinye, et al. Performance evaluation of radar and communication integrated system for autonomous driving vehicles[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2021 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Vancouver, Canada, 2021: 1–2. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOMWKSHPS51825.2021.9484463. [80] ZHANG Qixun, WANG Xinna, LI Zhenhao, et al. Design and performance evaluation of joint sensing and communication integrated system for 5G mmWave enabled CAVs[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1500–1514. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3109666. [81] Online video[EB/OL]. https://www.chaspark.com/#/coffeeHours/media/809260877825687552.2023.1. [82] MA Dingyou, SHLEZINGER N, HUANG Tianyao, et al. Spatial modulation for joint radar-communications systems: Design, analysis, and hardware prototype[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(3): 2283–2298. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3056408. [83] XU Tongyang, LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, et al. An experimental proof of concept for integrated sensing and communications waveform design[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2022, 3: 1643–1655. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2022.3209641. [84] ZHANG Qixun and GAO Xinye. Joint communication and sensing enabled cooperative perception testbed for connected automated vehicles[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, New York, USA, 2022: 1–2. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOMWKSHPS54753.2022.9798074. [85] ZHANG Qixun, SUN Hongzhuo, GAO Xinye, et al. Time-division ISAC enabled connected automated vehicles cooperation algorithm design and performance evaluation[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2206–2218. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155506. [86] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, CHEN Longyong, et al. Joint wireless communication and high resolution SAR imaging using airborne MIMO radar system[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 2511–2514. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8897826. [87] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, CHEN Longyong, et al. First demonstration of joint wireless communication and high-resolution SAR imaging using airborne MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6619–6632. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2907561. [88] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, CHEN Longyong, et al. First demonstration of airborne MIMO SAR system for multimodal operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5204113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3066478. [89] 唐家政. 基于数据库划分的改进WLAN室内指纹定位研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.000400.TANG Jiazheng. Research on improved WLAN indoor fingerprint location based on database partition[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.000400. [90] 高畅蔓. 基于CSI图像特征的室内定位技术[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.000476.GAO Changman. CSI indoor location technology based on image features[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.000476. [91] LI Yang, WU Dan, ZHANG Jie, et al. DiverSense: Maximizing Wi-Fi sensing range leveraging signal diversity[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2022, 6(2): 94. doi: 10.1145/3536393. [92] WANG Guanhua, ZOU Yongpan, ZHOU Zimu, et al. We can hear you with Wi-Fi![C]. Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, USA, 2014: 593–604. doi: 10.1145/2639108.2639112. [93] 徐晓东, 李岩, 叶威, 等. 通信感知一体化应用场景、关键技术和网络架构[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(5): 2–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.05.001.XU Xiaodong, LI Yan, YE Wei, et al. Application scenarios, key technologies and network architecture of integrated sensing and communication[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(5): 2–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.05.001. [94] SAKHNINI A, DE BAST S, GUENACH M, et al. Near-field coherent radar sensing using a massive MIMO communication testbed[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(8): 6256–6270. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3148035. [95] SAKHNINI A, DE BAST S, GUENACH M, et al. An experimental evaluation of robust near-field radar localization using a massive MIMO testbed[C]. 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Joint Communications and Sensing, Seefeld, Austria, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/JCS54387.2022.9743499. [96] LI Oupeng, HE Jia, ZENG Kun, et al. Integrated sensing and communication in 6G a prototype of high resolution THz sensing on portable device[C]. IEEE Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications and 6G Summit, Porto, Portugal, 2021: 544–549. doi: 10.1109/EuCNC/6GSummit51104.2021.9482537. [97] TAN D K P, HE Jia, LI Yanchun, et al. Integrated sensing and communication in 6G: Motivations, use cases, requirements, challenges and future directions[C]. 1st IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications and Sensing, Dresden, Germany, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/JCS52304.2021.9376324. [98] 张若愚, 袁伟杰, 崔原豪, 等. 面向6G的大规模MIMO通信感知一体化: 现状与展望[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(6): 17–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.06.003.ZHANG Ruoyu, YUAN Weijie, CUI Yuanhao, et al. Integrated sensing and communications with massive MIMO for 6G: Status and prospect[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(6): 17–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.06.003. [99] 杨杰, 黄艺璇, 杜涛, 等. 通信感知一体化原型验证的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(11): 43–54. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023205.YANG Jie, HUANG Yixuan, DU Tao, et al. Prototype verification for integrated sensing and communications: Current status and development trends[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(11): 43–54. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023205. [100] 王欢, 王陶冶, 商惠敏, 等. 基于ChatGPT的通用人工智能发展情况及对广东的启示[J]. 自动化与信息工程, 2023, 44(6): 9–14,28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2605.2023.06.002.WANG Huan, WANG Taoye, SHANG Huimin, et al. The development of general artificial intelligence based on ChatGPT and its inspiration for Guangdong[J]. Automation & Information Engineering, 2023, 44(6): 9–14,28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2605.2023.06.002. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
