Few-Shot Class-Incremental SAR Image Target Recognition using Self-supervised Decoupled Dynamic Classifier
-
摘要: 为提升基于深度学习(DL)的合成孔径雷达自动目标识别(SAR ATR)系统在开放动态的非合作场景中对新类别目标的持续敏捷识别能力,该文研究了SAR ATR的小样本类增量学习(FSCIL)问题,并提出了自监督解耦动态分类器(SDDC)。针对FSCIL 中“灾难性遗忘”和“过拟合”本质难点和SAR ATR领域挑战,根据SAR图像目标信息的部件化与方位角敏感性特点,于图像域构建了基于散射部件混淆与旋转模块(SCMR)的自监督学习任务,以提升目标表征的泛化性与稳健性。同时,设计了类印记交叉熵(CI-CE)损失并以参数解耦学习(PDL)策略对模型动态微调,以对新旧知识平衡判别。实验在由MSTAR和SAR-AIRcraft-1.0数据集分别构建的覆盖多种目标类别、观测条件和成像平台的FSCIL场景上验证了该算法开放动态环境的适应能力。Abstract: To power Deep-Learning (DL) based Synthetic Aperture Radar Automatic Target Recognition (SAR ATR) systems with the capability of learning new-class targets incrementally and rapidly in openly dynamic non-cooperative situations, the problem of Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) of SAR ATR is researched and a Self-supervised Decoupled Dynamic Classifier (SDDC) is proposed. Considering solving both the intrinsic Catastrophic forgetting and Overfitting dilemma of the FSCIL and domain challenges of SAR ATR, a self-supervised learning task powered by Scattering Component Mixup and Rotation (SCMR) is designed to improve the model’s generalizability and stability for target representation, leveraged by the partiality and azimuth dependence of target information in SAR imagery. Meanwhile, a Class-Imprinting Cross-Entropy (CI-CE) and a Parameter Decoupled Learning (PDL) strategy are designed to fine-tune networks dynamically to identify old and new targets evenly. Experiments on various FSCIL scenarios constructed by the MSTAR and the SAR-AIRcraft-1.0 datasets covering diverse target categories, observing environments, and imaging payloads, verify the method’s adaptability to openly dynamic world.
-
1 散射混淆操作(SMO)处理过程
输入:小批次基类训练样本 ${\boldsymbol{b}} = \{ ({{\boldsymbol{x}}_i},{y_i})\} _{i = 1}^{|{N_{{b}}}|} \in {{\boldsymbol{D}}^1}$ 初始化:混淆次数 R ,混淆样本存储列表${S_{{\text{smo}}}}$ For r = 1 to R do 步骤1 采样随机顺序数据${\boldsymbol{\tilde b}} = \{ ({{\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}_i},{\tilde y_i})\} _{i = 1}^{|{N_{{b}}}|}$ 步骤2 获取原始$\{ {y_i}\} _{i = 1}^{|{N_{{b}}}|}$与随机顺序$\{ {\tilde y_i}\} _{i = 1}^{|{N_{{b}}}|}$标签 步骤3 从${\boldsymbol{b}}$中选取${\boldsymbol{b}}' = \{ ({{\boldsymbol{x}}'_i},{y'_i})\} $,从${\boldsymbol{\tilde b}}$中选取
$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde b}}' = \{ ({{\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}'_i},{\tilde y'_i})\} $,满足${y'_j} \ne {\tilde y'_j},\forall j \in |{N_{{b}}}|$步骤4 根据式(1)从${\boldsymbol{b}}'$与 $ {\boldsymbol{\tilde b}}' $中生成散射混淆样本集
$ {{\stackrel \frown{{\boldsymbol{b}}} }} = \{ ({{{\stackrel \frown{{\boldsymbol{x}}} }}_i},{\stackrel \frown{y} _i})\} $步骤5 将$ {{\stackrel \frown{{\boldsymbol{b}}} }} $添加至${S_{{\text{smo}}}}$ End for 输出:${S_{{\text{smo}}}}$ 表 1 MSTAR-FSCIL数据集配置
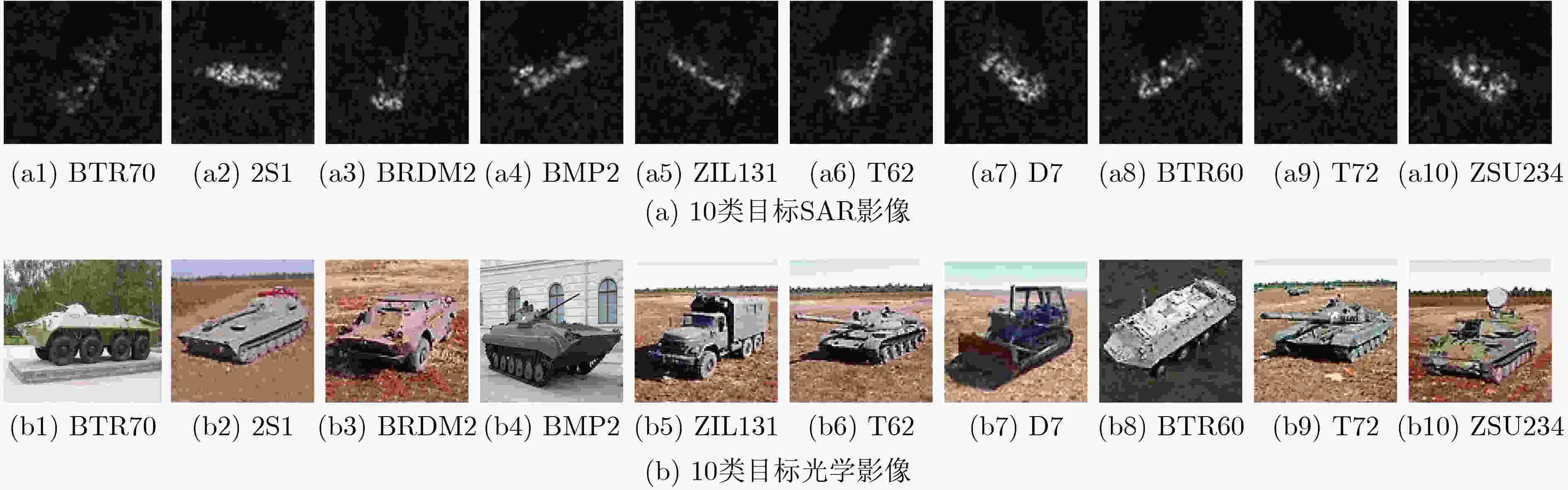
学习阶段 序号 类别 型号 训练集 测试集 基类 1 BTR70 c71 233 196 2 2S1 b01 299 274 3 BRDM2 E-71 298 274 4 BMP2 9563 233 196 增量类 5 ZIL131 E12 5 274 6 T62 A51 5 274 7 D7 13015 5 274 8 BTR60 7532 5 195 9 T72 132 5 196 10 ZSU234 d08 5 274 表 2 SAR-AIRcraft-1.0-FSCIL数据集配置表
学习阶段 序号 类别 训练集 测试集 基类 1 Other 2 000 200 2 A220 2 000 200 3 Boeing787 2 000 200 4 Boeing737 2 000 200 增量类 5 A320 5 200 6 ARJ21 5 200 7 A330 5 200 表 3 SDDC算法模块与损失贡献(%)
迁移性 判别性 Avg.Acc Acc.Old Acc.New PD SMO SRO CI-CE PDL 75.26 78.87 49.02 41.50 √ 78.35 81.41 54.16 37.77 √ 77.79 81.27 52.24 35.29 √ √ 79.50 82.68 54.46 34.47 √ √ √ 73.30 72.62 79.12 55.83 √ √ √ 75.81 79.01 47.22 42.35 √ √ √ √ 81.73 83.37 66.70 31.61 -
[1] 张路, 廖明生, 董杰, 等. 基于时间序列InSAR分析的西部山区滑坡灾害隐患早期识别——以四川丹巴为例[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2018, 43(12): 2039–2049. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180181.ZHANG Lu, LIAO Mingsheng, DONG Jie, et al. Early detection of landslide hazards in mountainous areas of West China using time series SAR interferometry-A case study of Danba, Sichuan[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 2039–2049. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180181. [2] 李永祯, 黄大通, 邢世其, 等. 合成孔径雷达干扰技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087.LI Yongzhen, HUANG Datong, XING Shiqi, et al. A review of synthetic aperture radar jamming technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087. [3] 傅兴玉, 尤红建, 付琨. 基于邻域均方连续差分的SAR图像边缘提取算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(5): 1030–1037. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00920.FU Xingyu, YOU Hongjian, and FU Kun. An approach to extract edge in SAR image based on square successive difference of neighborhood averages[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2012, 34(5): 1030–1037. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00920. [4] 罗汝, 赵凌君, 何奇山, 等. SAR图像飞机目标智能检测识别技术研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(2): 307–330. doi: 10.12000/JR23056.LUO Ru, ZHAO Lingjun, HE Qishan, et al. Intelligent technology for aircraft detection and recognition through SAR imagery: Advancements and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(2): 307–330. doi: 10.12000/JR23056. [5] 周大蔚, 汪福运, 叶翰嘉, 等. 基于深度学习的类别增量学习算法综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2023, 46(8): 1577–1605. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.01577.ZHOU Dawei, WANG Fuyun, YE Hanjia, et al. Deep learning for class-incremental learning: A survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2023, 46(8): 1577–1605. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.01577. [6] 丁柏圆, 文贡坚, 余连生, 等. 属性散射中心匹配及其在SAR目标识别中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 157–166. doi: 10.12000/JR16104.DING Baiyuan, WEN Gongjian, YU Liansheng, et al. Matching of attributed scattering center and its application to synthetic aperture radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 157–166. doi: 10.12000/JR16104. [7] HUMMEL R. Model-based ATR using synthetic aperture radar[C]. The IEEE 2000 International Radar Conference, Alexandria, USA, 2000: 856–861. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2000.851947. [8] CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720. [9] REBUFFI S A, KOLESNIKOV A, SPERL G, et al. iCaRL: Incremental classifier and representation learning[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5533–5542. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.587. [10] HOU Saihui, PAN Xinyu, LOY C C, et al. Learning a unified classifier incrementally via rebalancing[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 831–839. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00092. [11] TAO Xiaoyu, HONG Xiaopeng, CHANG Xinyuan, et al. Few-shot class-incremental learning[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 12180–12189. doi: 10.1109/cvpr42600.2020.01220. [12] ZHANG Chi, SONG Nan, LIN Guosheng, et al. Few-shot incremental learning with continually evolved classifiers[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 12450–12459. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01227. [13] PENG Can, ZHAO Kun, WANG Tianren, et al. Few-shot class-incremental learning from an open-set perspective[C]. 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 382–397. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19806-9_22. [14] SONG Zeyin, ZHAO Yifan, SHI Yujun, et al. Learning with fantasy: Semantic-aware virtual contrastive constraint for few-shot class-incremental learning[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 24183–24192. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.02316. [15] WANG Li, YANG Xinyao, TAN Haoyue, et al. Few-shot class-incremental SAR target recognition based on hierarchical embedding and incremental evolutionary network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5204111. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3248040. [16] ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, DING Ding, et al. Few-shot class-incremental SAR target recognition via cosine prototype learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5212718. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3298016. [17] NOVAK L M, OWIRKA G J, BROWER W S, et al. The automatic target-recognition system in SAIP[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1997, 10(2): 187–202. [18] 王智睿, 康玉卓, 曾璇, 等. SAR-AIRcraft-1.0: 高分辨率SAR飞机检测识别数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 906–922. doi: 10.12000/JR23043.WANG Zhirui, KANG Yuzhuo, ZENG Xuan, et al. SAR-AIRcraft-1.0: High-resolution SAR aircraft detection and recognition dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 906–922. doi: 10.12000/JR23043. -






 下载:
下载:



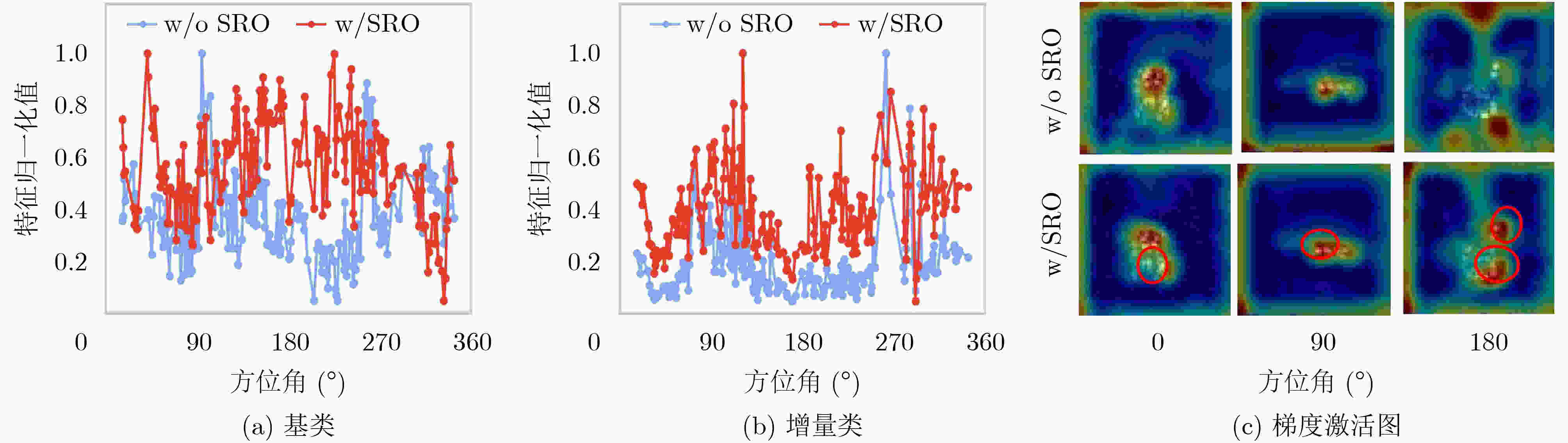

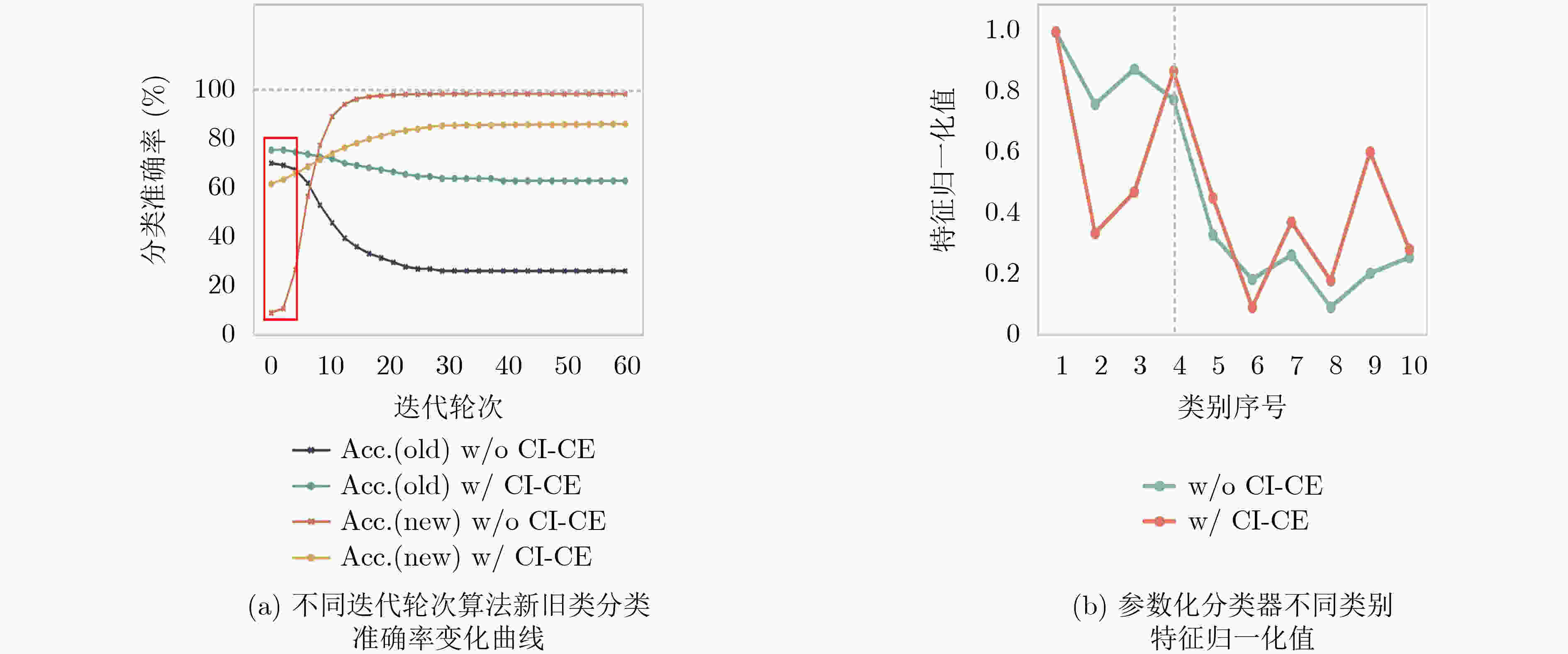

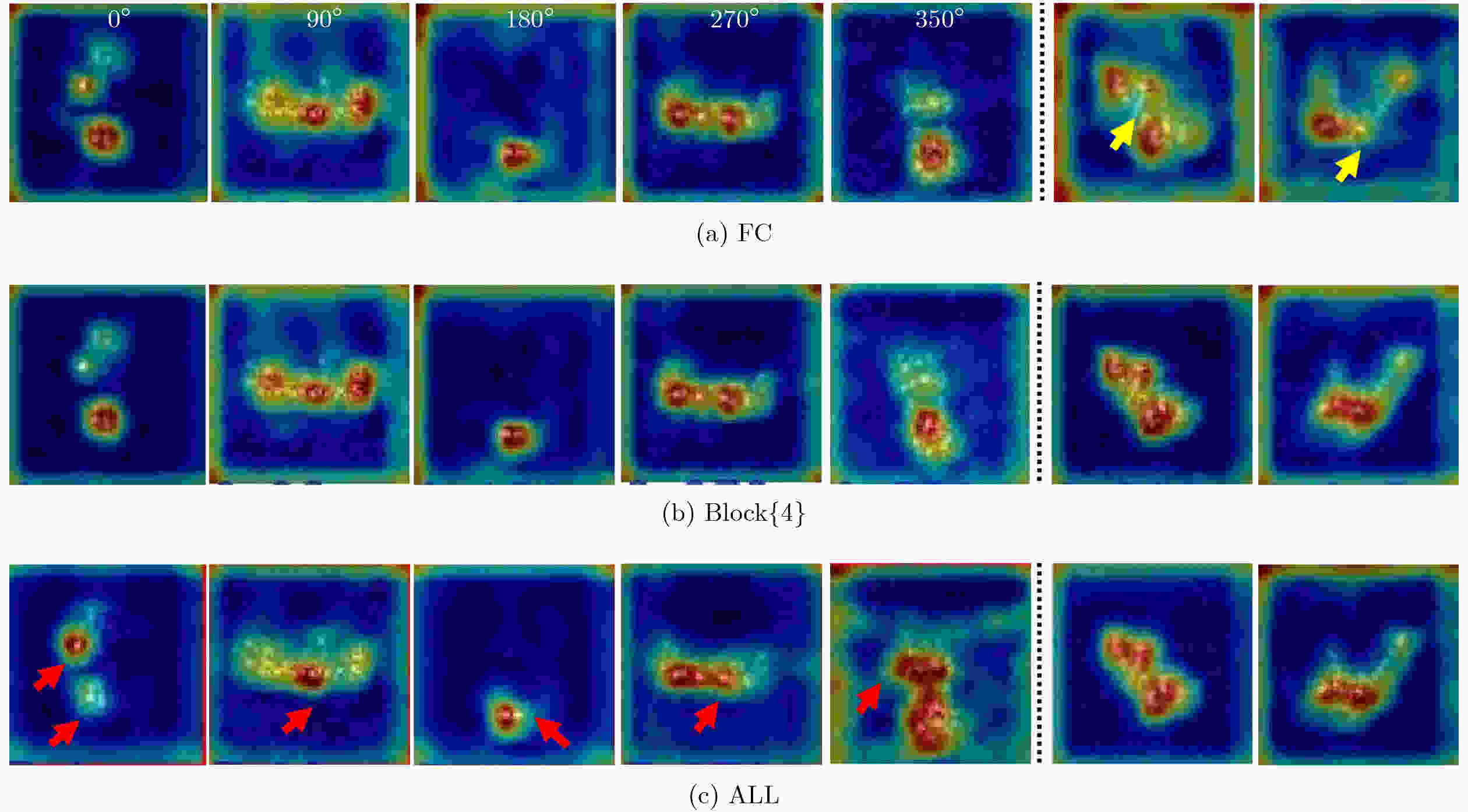

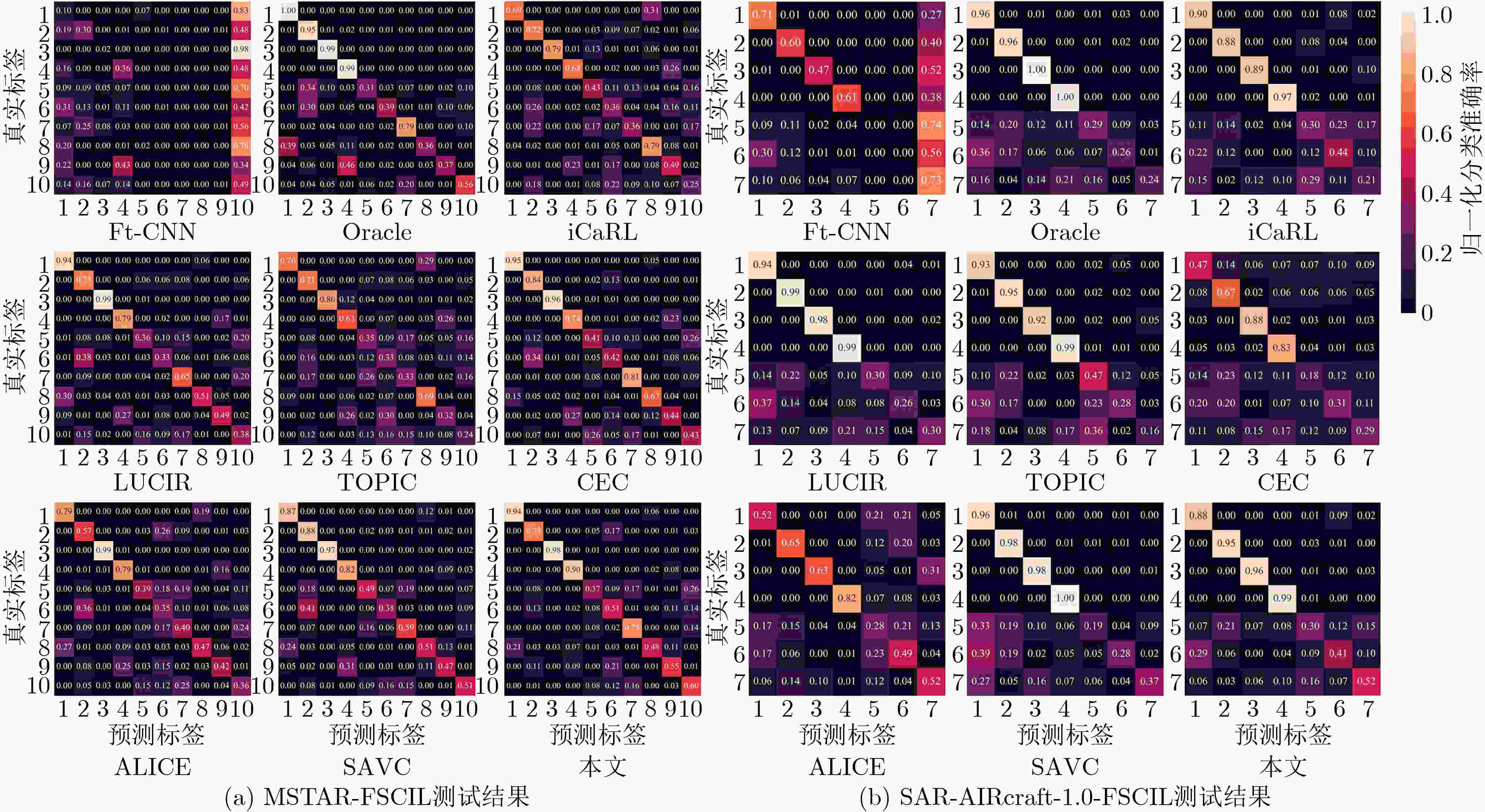
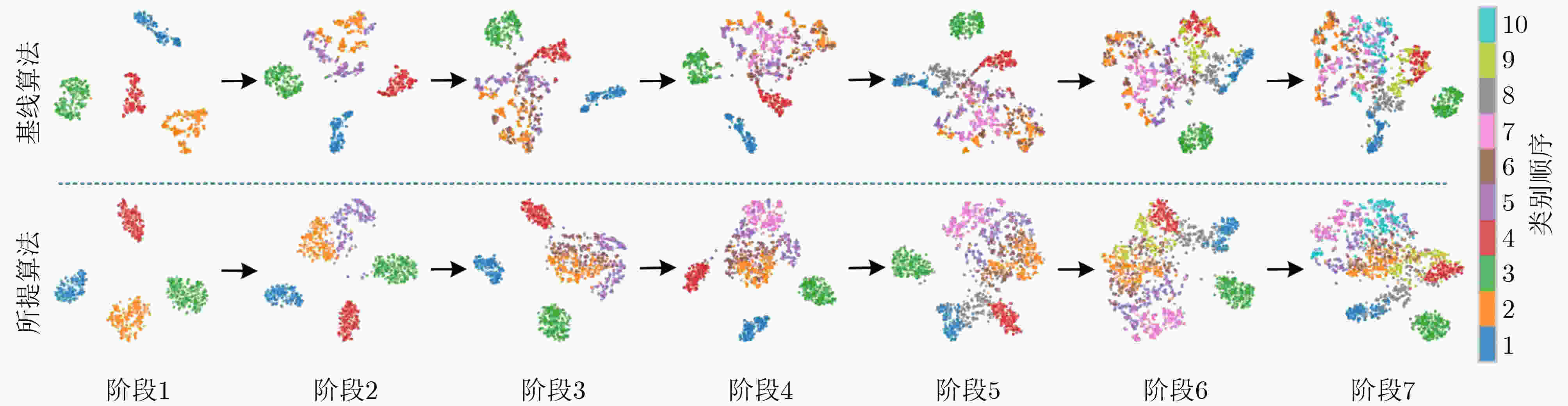
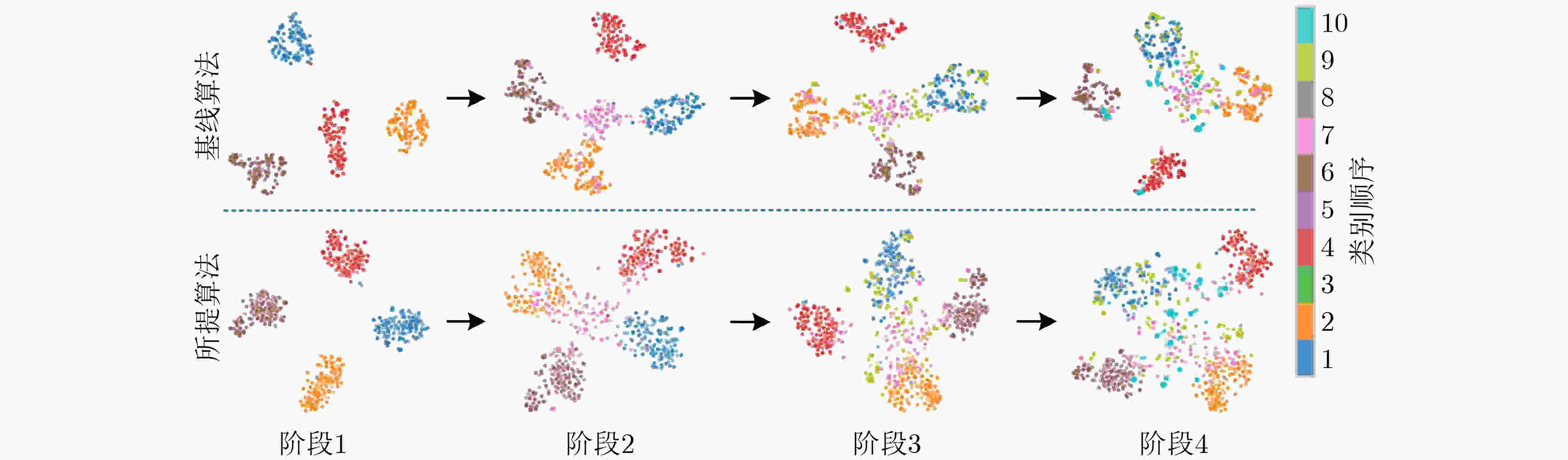


 下载:
下载:
