Adaptive Detectors for Mismatched Signal under Sea Clutter Background with Generalized Inverse Gaussian Texture
-
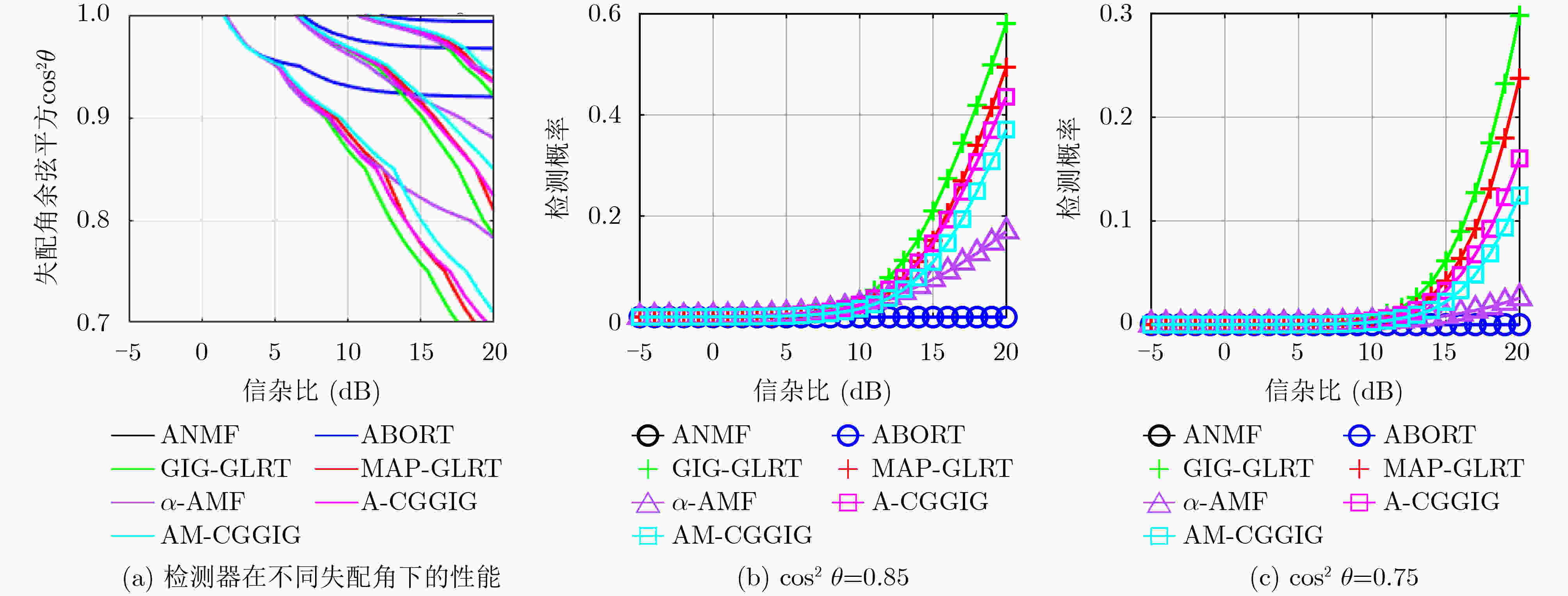
摘要: 针对雷达对海探测过程中理论导向矢量与实际导向矢量之间不匹配导致的虚警概率升高的问题,该文在复合高斯模型(CGM)下设计自适应失配检测器。为了抑制失配信号,在零假设中引入与理论导向矢量正交的虚拟信号,从而给出存在失配信号的目标检测模型。将CGM的纹理分量建模为广义逆高斯分布,分别基于两步广义似然比(GLRT)和最大后验GLRT(MAP GLRT)准则发展类似于自适应波束形成器正交抑制检测(ABORT)的自适应失配检测器,并通过理论证明所提失配检测器对散斑协方差矩阵和目标多普勒导向矢量具有恒虚警(CFAR)特性。仿真和实测数据实验结果表明,所提失配检测器在导向矢量匹配情况下的检测性能和失配情况下的抗失配性能之间具有良好的折衷。
-
关键词:
- 海杂波 /
- 广义逆高斯纹理复合高斯模型 /
- 失配检测 /
- 自适应波束形成器正交抑制检测
Abstract: Considering mismatched problem between theoretical steering vector and actual steering vector causes false-alarm-rate increase in the process of maritime radar detection, the adaptive mismatched detectors are studied under Compound Gaussian Model (CGM). In order to reject mismatched signal, the fictitious signal orthogonal to theoretical steering vector is introduced in the null hypothesis, and a target detection with mismatched signal is given. The texture component of CGM is represented by generalized inverse distribution, and the Adaptive Beamformer Orthogonal Rejection Test (ABORT) is developed based on two-step Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test (GLRT) and Maximum A Posteriori GLRT (MAP GLRT) criterions respectively. Both the proposed detectors are testified to have Constant False AlaRm (CFAR) characteristics for speckle covariance matrix and target doppler steering vector. Experimental results based on simulated and real measured sea clutter data indicate that the proposed mismatched detectors show preferable target detection performance under the matched steering vector condition and anti-mismatch capability under the mismatched steering vector condition. -
表 1 导向矢量匹配时上述检测器检测概率达到$90\% $时所需要的SCR(dB)
检测器类型 ANMF ABORT GIG-GLRT MAP-GLRT α-AMF A-CGGIG AM-GIGIG 信杂比 8.40 7.61 5.70 5.71 5.82 5.80 5.93 表 2 导向矢量匹配时上述检测器检测概率达到$90\% $时所需要的SCR(dB)
检测器类型 ANMF ABORT GIG-GLRT MAP-GLRT α-AMF A-CGGIG AM-GIGIG 信杂比 12.88 12.16 11.34 11.50 11.43 11.37 11.53 -
[1] 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084.XU Shuwen, BAI Xiaohui, GUO Zixun, et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084. [2] XIN Zhihui, LIAO Guisheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Analysis of distribution using graphical goodness of fit for airborne SAR sea-clutter data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(10): 5719–5728. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2712700. [3] LIANG Xiang, YU Han, ZOU Pengjia, et al. Multiscan recursive Bayesian parameter estimation of large-scene spatial-temporally varying generalized Pareto distribution model of sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5115416. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3191467. [4] 水鹏朗, 田超, 封天. 逆高斯纹理复合高斯杂波对异常样本稳健的三分位点估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 542–549. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211483.SHUI Penglang, TIAN Chao, and FENG Tian. Outlier-robust tri-percentile parameter estimation method of compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian textures[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 542–549. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211483. [5] XUE Jian, XU Shuwen, LIU Jun, et al. Model for non-Gaussian sea clutter amplitudes using generalized inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(6): 892–896. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2886782. [6] CONTE E, LOPS M, and RICCI G. Asymptotically optimum radar detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(2): 617–625. doi: 10.1109/7.381910. [7] DONG Yunhan. Optimal coherent radar detection in a K-distributed clutter environment[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(5): 283–292. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0273. [8] SANGSTON K J, GINI F, and GRECO M S. Coherent radar target detection in heavy-tailed compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(1): 64–77. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6129621. [9] CHEN Sijia, KONG Lingjiang, and YANG Jianyu. Adaptive detection in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2013, 28: 157–167. doi: 10.2528/PIERM12121209. [10] 薛健. 复合高斯海杂波背景雷达目标检测算法[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020: 80–88. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.000039.XUE Jian. Radar target detection methods in compound-Gaussian sea clutter[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2020: 80–88. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.000039. [11] XU Shuwen, WANG Zhexiang, BAI Xiaohui, et al. Optimum and near-optimum coherent CFAR detection of radar targets in compound-Gaussian clutter with generalized inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(3): 1692–1706. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3120045. [12] 施赛楠, 水鹏朗, 刘明. 基于复合高斯杂波纹理结构的相干检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 1969–1976. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151194.SHI Sainan, SHUI Penglang, and LIU Ming. Coherent detection based on texture structure in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 1969–1976. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151194. [13] WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, HE Qin, et al. Persymmetric range-spread targets detection in compound Gaussian sea clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8018305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3101369. [14] PULSONE N B and RADER C M. Adaptive beamformer orthogonal rejection test[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2001, 49(3): 521–529. doi: 10.1109/78.905870. [15] WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, HE Qin, et al. Adaptive CFAR detectors for mismatched signal in compound Gaussian sea clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3502705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3047390. [16] WANG Zeyu, GANG Li, and LI Ming. Adaptive detection of distributed target in the presence of signal mismatch in compound Gaussian clutter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2020, 102: 102755. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102755. [17] 王喆祥. 海杂波背景下雷达目标自适应检测算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021: 12, 16. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.001059.WANG Zhexiang. Research on adaptive detection algorithm of radar targets in sea clutter[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021: 12, 16. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.001059. [18] PASCAL F, FORSTER P, OVARLEZ J P, et al. Performance analysis of covariance matrix estimates in impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(6): 2206–2217. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.914311. -





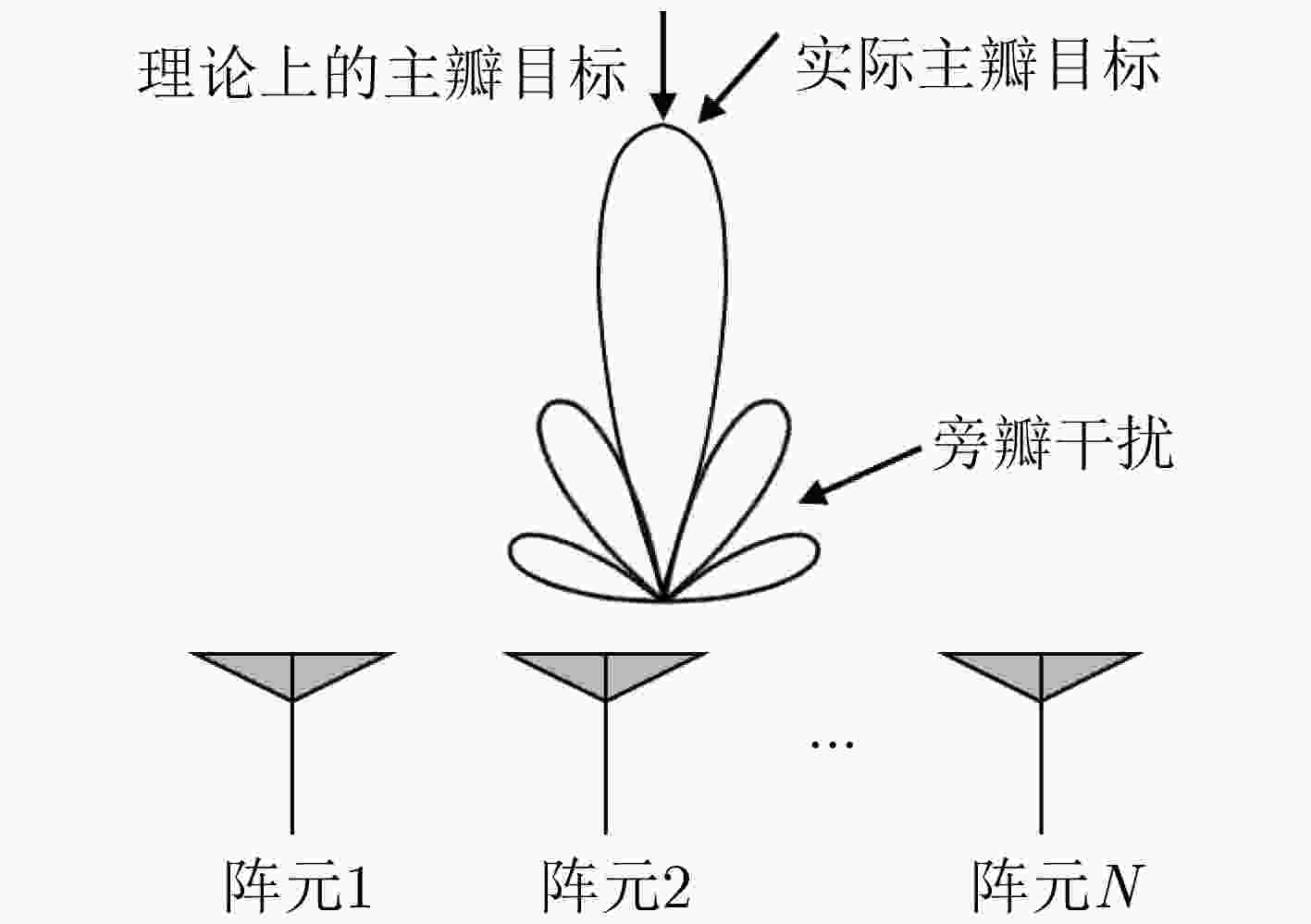
 下载:
下载:
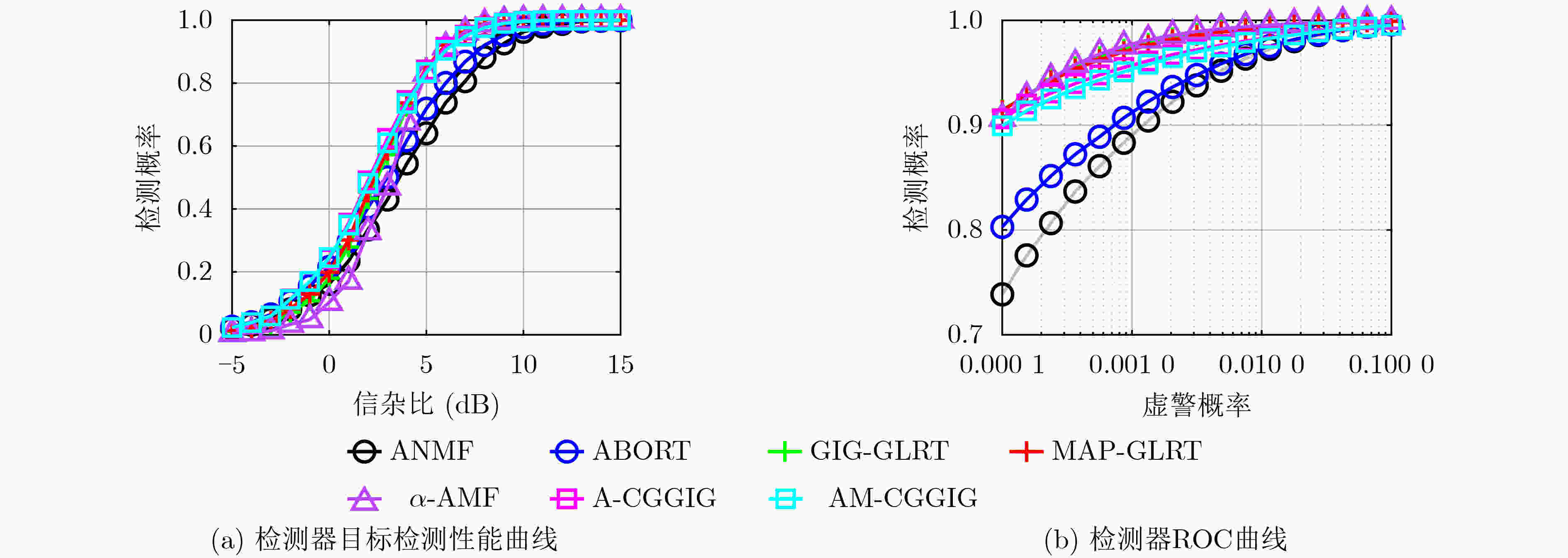

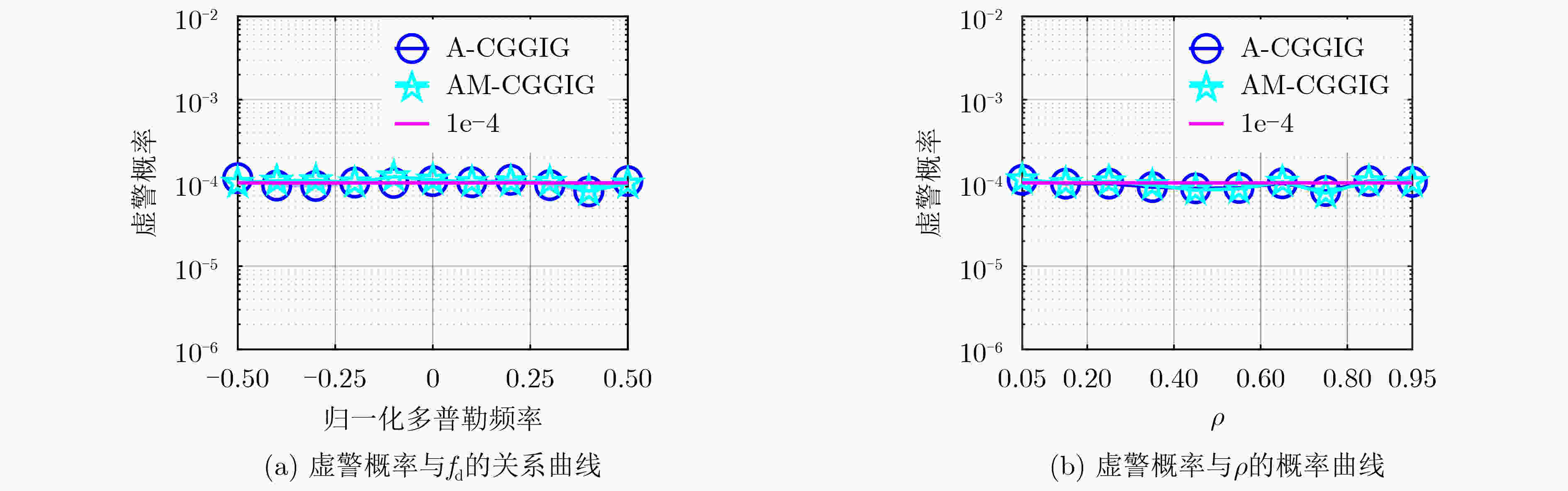
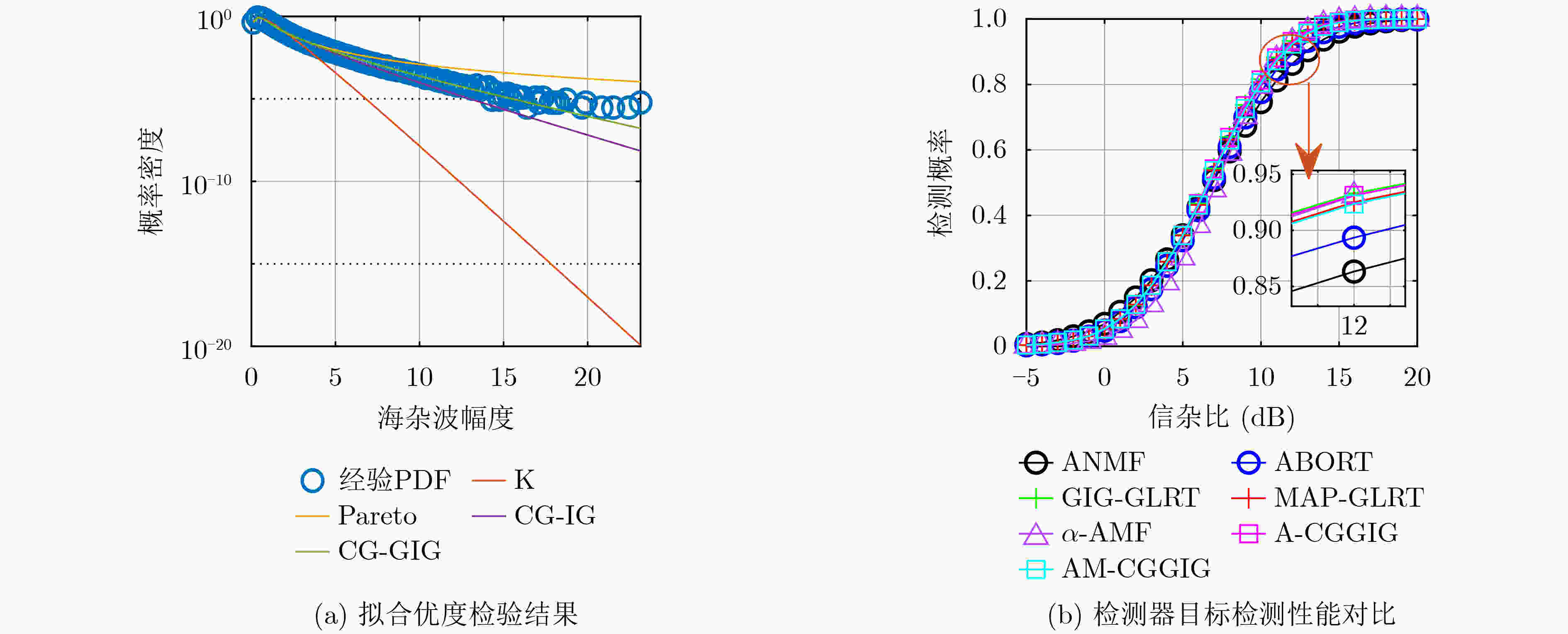


 下载:
下载:
