Video Object Segmentation Algorithm Based on Multi-scale Feature Enhancement and Global-Local Feature Aggregation
-
摘要: 针对记忆网络算法中多尺度特征表达能力不足和浅层特征没有充分利用的问题,该文提出一种多尺度特征增强与全局-局部特征聚合的视频目标分割(VOS)算法。首先,通过多尺度特征增强模块融合可参考掩码分支和可参考RGB分支的不同尺度特征信息,增强多尺度特征的表达能力;同时,建立了全局-局部特征聚合模块,利用不同大小感受野的卷积操作来提取特征,并通过特征聚合模块来自适应地融合全局区域和局部区域的特征,这种融合方式可以更好地捕捉目标的全局特征和细节信息,提高分割的准确性;最后,设计了跨层融合模块,利用浅层特征的空间细节信息来提升分割掩码的精度,通过将浅层特征与深层特征融合,能更好地捕捉目标的细节和边缘信息。实验结果表明,在公开数据集DAVIS2016, DAVIS2017和YouTube-2018上,该文算法的综合性能分别达到91.8%、84.5%和83.0%,在单目标和多目标分割任务上都能实时运行。Abstract: To address the issues of insufficient multi-scale feature expression ability and insufficient utilization of shallow features in memory network algorithms, a Video Object Segmentation (VOS) algorithm based on multi-scale feature enhancement and global local feature aggregation is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the multi-scale feature enhancement module fuses different scale feature information from reference mask branches and reference RGB branches to enhance the expression ability of multi-scale features; At the same time, a global local feature aggregation module is established, which utilizes convolution operations of different sizes of receptive fields to extract features, through the feature aggregation module, the features of the global and local regions are adaptively fused. This fusion method can better capture the global features and detailed information of the target, improving the accuracy of segmentation; Finally, a cross layer fusion module is designed to improve the accuracy of masks segmentation by utilizing the spatial details of shallow features. By fusing shallow features with deep features, it can better capture the details and edge information of the target. The experimental results show that on the public datasets DAVIS2016, DAVIS2017, and YouTube 2018, the comprehensive performance of our algorithm reaches 91.8%, 84.5%, and 83.0%, respectively, and can run in real-time on both single and multi-objective segmentation tasks.
-
Key words:
- Video Object Segmentation (VOS) /
- Memory network /
- Siamese network /
- Feature fusion /
- Mask refinement
-
表 1 DAVIS2016和DAVIS2017验证集不同算法的性能比较
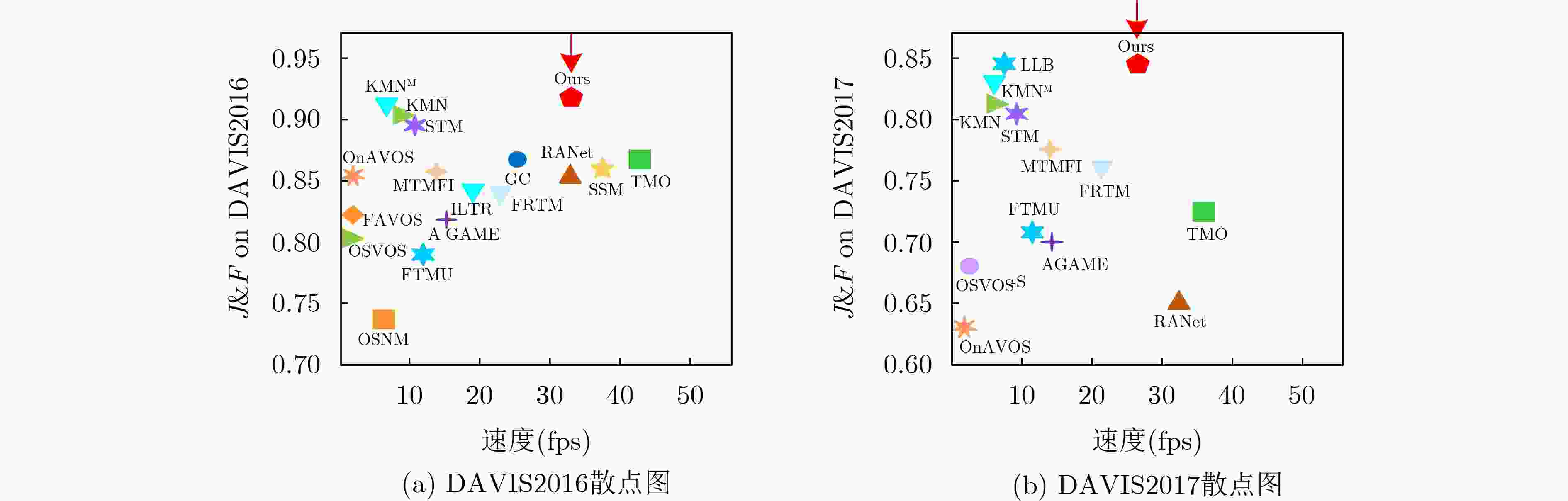
算法 来源 DAVIS2016 DAVIS2017 J&F J F 速度(fps) 时间(s) J&F J F 速度(fps) 时间(s) OSVOS [5] CVPR2017 80.2 79.8 80.6 0.10 10.00 60.3 56.6 63.9 0.1 10.00 OnAVOS[7] CVPRW2017 85.5 86.1 84.9 0.08 12.50 63.6 61.0 66.1 0.05 22.0 OSVOS-S[25] TPAMI2018 86.6 85.6 87.5 0.20 5.00 68.0 64.7 71.3 0.1 10.00 OSNM[26] CVPR2018 73.5 74 72.9 7.70 0.13 54.8 52.5 57.1 7.0 0.14 FAVOS[27] CVPR2018 82.4 79.5 80.9 0.60 1.67 58.2 54.6 61.8 5.6 0.18 AGAME[14] CVPR2019 82.1 82.0 82.2 14.00 0.07 70.0 67.4 72.6 14.0 0.07 RANet[28] ICCV2019 85.5 85.5 85.4 33.00 0.03 65.7 63.2 68.2 33.0 0.03 FTMU[29] CVPR2020 78.9 77.5 80.3 11.00 0.09 70.6 69.1 72.1 11.0 0.09 SSM[19] T-CSVT2021 85.9 86.2 85.6 37.00 0.03 77.6 75.3 79.9 -- -- TMO[20] TCSVT2023 86.1 85.6 86.6 43.20 0.02 72.3 69.9 74.7 37.0 0.03 STM[11] ICCV2019 89.3 88.7 89.9 10.30 0.10 81.8 79.2 84.3 8.8 0.11 FRTM[21] CVPR2020 83.6 83.7 83.4 21.9 0.05 76.7 73.8 79.6 21.9 0.05 GC[15] ECCV2020 86.6 87.6 85.7 25.00 0.04 71.4 69.3 73.5 -- -- KMN[16] ECCV2020 90.5 89.5 83.6 9.00 0.11 82.8 80.0 85.6 8.0 0.13 TransVOS[22] CVPR2021 90.5 89.8 91.2 -- -- 83.9 81.4 86.4 -- -- MTMFI[23] Neurocomputing2022 85.2 84.9 85.5 13.70 0.07 77.6 74.6 80.6 13.7 0.07 ILTR[24] 计算机学报2022 84.6 84.9 84.3 18.00 0.06 72.9 70.0 75.8 -- -- KMNM[17] TPAMI2022 91.2 90.2 92.1 8.00 0.13 83.5 80.9 86.1 8.0 0.13 LLB[30] AAAI2023 -- -- -- -- -- 84.6 81.5 87.7 8.3 0.12 MGLAS 本文 91.8 90.6 93.0 33.45 0.03 84.5 81.6 87.3 26.6 0.04 表 2 YouTube-2018验证集不同算法的性能比较
算法 来源 G Js Ju Fs Fu MSK[13] CVPR2017 53.1 59.9 45.0 59.5 47.9 OnAVOS[7] CVPRW2017 55.2 60.1 46.6 62.7 51.4 OSVOS[5] CVPR2017 58.8 59.8 54.2 60.5 60.7 OSNM[26] CVPR2018 51.2 60.0 40.6 60.1 44.0 RGMP[8] CVPR2018 53.8 59.5 45.2 -- -- AGAME[14] CVPR2019 66.0 66.9 61.2 -- -- STM[11] ICCV2019 78.9 78.6 73.3 82.8 80.9 FRTM[21] CVPR2020 65.7 68.6 58.4 71.3 64.5 SSM[19] T-CSVT2021 66.5 72.3 57.8 73.3 62.6 TranVOS[22] CVPR2021 81.8 82.0 75.0 86.7 83.4 ILTR[24] 计算机学报2022 73.8 73.9 67.5 77.9 75.7 KMNM[17] TPAMI2022 81.4 81.4 75.3 85.6 83.3 LLB[30] AAAI2023 83.8 82.1 79.1 87.0 87.0 MGLAS 本文 83.0 81.9 77.9 86.5 85.7 表 3 本文算法在DAVIS2017验证集上的消融实验
基准算法 MFEM GLFAM CFM J&F J F √ 81.8 79.2 84.3 √ √ 83.2 79.9 86.5 √ √ 83.5 80.6 86.4 √ √ 83.5 80.0 86.9 √ √ √ √ 84.5 81.6 87.3 -
[1] ERDÉLYI A, BARÁT T, VALET P, et al. Adaptive cartooning for privacy protection in camera networks[C]. 2014 11th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Seoul, Korea (South), 2014: 44–49. doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2014.6918642. [2] WANG Wenguan, SHEN Jianbing, PORIKLI F, et al. Semi-supervised video object segmentation with super-trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(4): 985–998. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2819173. [3] SALEH K, HOSSNY M, and NAHAVANDI S. Kangaroo vehicle collision detection using deep semantic segmentation convolutional neural network[C]. 2016 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Gold Coast, Australia, 2016: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/DICTA.2016.7797057. [4] LU Xiankai, WANG Wenguan, SHEN Jianbing, et al. Learning video object segmentation from unlabeled videos[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8957–8967. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00898. [5] CAELLES S, MANINIS K K, PONT-TUSET J, et al. One-shot video object segmentation[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5320–5329. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.565. [6] CHENG H K, TAI Y W, and TANG C K. Modular interactive video object segmentation: Interaction-to-mask, propagation and difference-aware fusion[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 5555–5564. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00551. [7] VOIGTLAENDER P and LEIBE B. Online adaptation of convolutional neural networks for video object segmentation[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2017, London, UK, 2017. [8] OH S W, LEE J Y, SUNKAVALLI K, et al. Fast video object segmentation by reference-guided mask propagation[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7376–7385. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00770. [9] 徐金东, 赵甜雨, 冯国政, 等. 基于上下文模糊C均值聚类的图像分割算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 2079–2086. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200263.XU Jindong, ZHAO Tianyu, FENG Guozheng, et al. Image segmentation algorithm based on context fuzzy C-means clustering[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 2079–2086. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200263. [10] 杭昊, 黄影平, 张栩瑞, 等. 面向道路场景语义分割的移动窗口变换神经网络设计[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(1): 230304. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.230304.HANG Hao, HUANG Yingping, ZHANG Xurui, et al. Design of swin transformer for semantic segmentation of road scenes[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2024, 51(1): 230304. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.230304. [11] OH S W, LEE J Y, XU Ning, et al. Video object segmentation using space-time memory networks[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 9225–9234. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00932. [12] LUITEN J, VOIGTLAENDER P, and LEIBE B. PReMVOS: Proposal-generation, refinement and merging for video object segmentation[C]. 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2019: 565–580. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-20870-7_35. [13] PERAZZI F, KHOREVA A, BENENSON R, et al. Learning video object segmentation from static images[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3491–3500. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.372. [14] JOHNANDER J, DANELLJAN M, BRISSMAN E, et al. A generative appearance model for end-to-end video object segmentation[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA: 2019: 8945–8954. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00916. [15] LI Yu, SHEN Zhuoran, and SHAN Ying. Fast video object segmentation using the global context module[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 735–750. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58607-2_43. [16] SEONG H, HYUN J, and KIM E. Kernelized memory network for video object segmentation[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 629–645. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58542-6_38. [17] SEONG H, HYUN J, and KIM E. Video object segmentation using Kernelized memory network with multiple kernels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(2): 2595–2612. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3163375. [18] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [19] ZHU Wencheng, LI Jiahao, LU Jiwen, et al. Separable structure modeling for semi-supervised video object segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(1): 330–344. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3060015. [20] CHO S, LEE M, LEE S, et al. Treating motion as option to reduce motion dependency in unsupervised video object segmentation[C]. The IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2023: 5129–5138. doi: 10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00511. [21] ROBINSON A, LAWIN F J, DANELLJAN M, et al. Learning fast and robust target models for video object segmentation[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 7404–7413. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00743. [22] MEI Jianbiao, WANG Mengmeng, LIN Yeneng, et al. TransVOS: Video object segmentation with transformers[J]. arXiv: 2106.00588, 2021. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2106.00588. [23] GAO Bocong, ZHAO Yuqian, ZHANG Fan, et al. Video object segmentation based on multi-level target models and feature integration[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 492: 396–407. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.04.042. [24] 徐凯, 李国荣, 洪德祥, 等. 结合在线归纳和直推推理的快速视频目标分割方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(10): 2117–2132. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.02117.XU Kai, LI Guorong, HONG Dexiang, et al. A fast video object segmentation method based on inductive learning and transductive reasoning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(10): 2117–2132. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.02117. [25] MANINIS K K, CAELLES S, CHEN Yuhua, et al. Video object segmentation without temporal information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(6): 1515–1530. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2838670. [26] YANG Linjie, WANG Yanran, XIONG Xuehan, et al. Efficient video object segmentation via network modulation[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6499–6507. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00680. [27] CHENG Jingchun, TSAI Y H, HUNG W C, et al. Fast and accurate online video object segmentation via tracking parts[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7415–7424. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00774. [28] WANG Ziqin, XU Jun, LIU Li, et al. RANet: Ranking attention network for fast video object segmentation[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3977–3986. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00408. [29] SUN Mingjie, XIAO Jimin, LIM E G, et al. Fast template matching and update for video object tracking and segmentation[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10788–10796. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01080. [30] LAN Meng, ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Lefei, et al. Learning to learn better for video object segmentation[C]. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 1205–1212. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i1.25203. -






 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
