Individual Identification Method for Communication Emitters Based on Improved Variational Modal Decomposition and Multiple Features
-
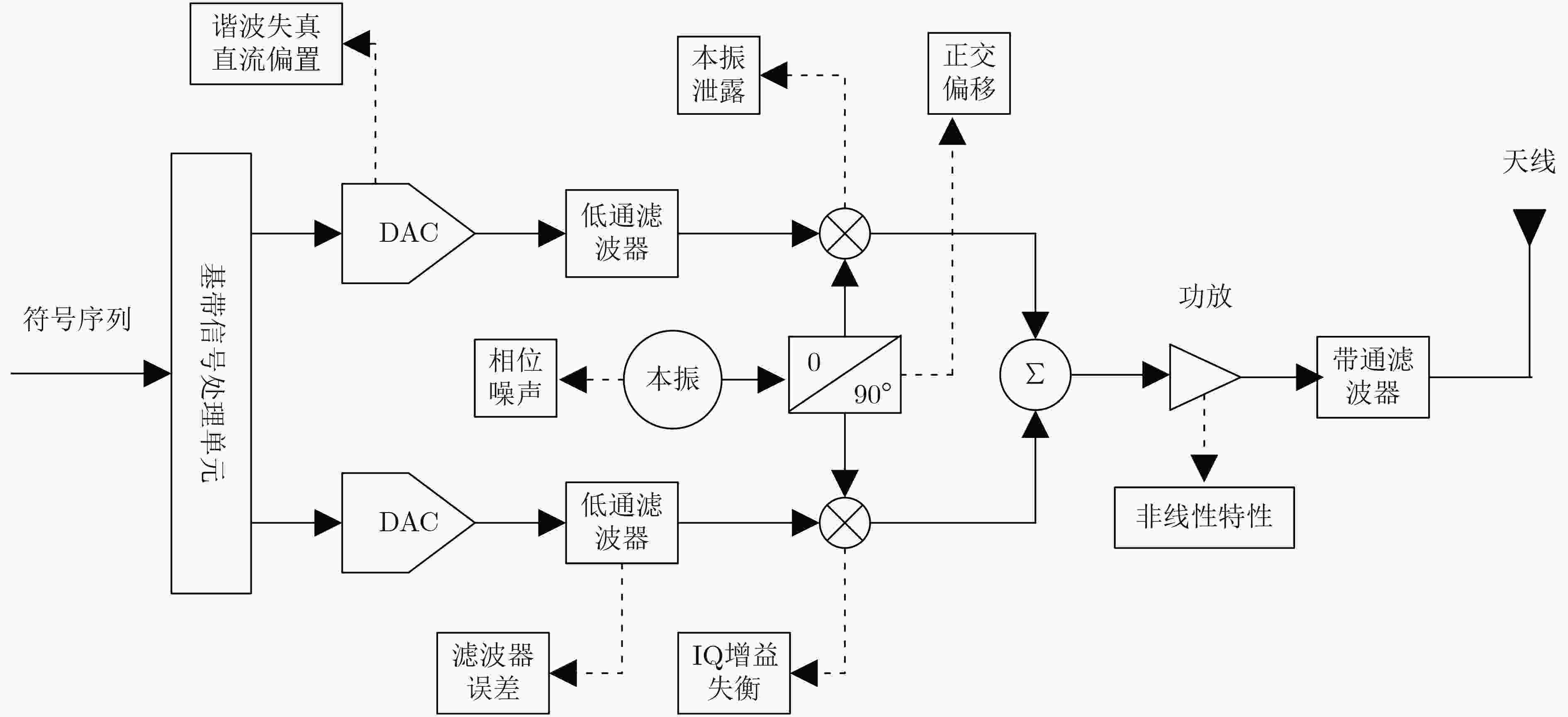
摘要: 针对通信辐射源指纹特征难以提取和单一特征识别率不高的问题,并考虑到通信辐射源细微特征的非线性、非平稳特点,该文提出了一种基于改进变分模态分解和多特征的通信辐射源个体识别方法。首先,为了获得变分模态分解的分解层数和惩罚因子的最优组合,采用鲸鱼优化算法对通信辐射源符号波形信号的变分模态分解方法进行了改进,该方法以序列复杂度为停止准则,使每个符号波形信号能够自适应地分解出包含非线性指纹特征的高频信号分量和数据信息的低频分量;然后,根据相关阈值选取能够最佳表征辐射源非线性特征的高频信号分量层数,分别对其提取模糊熵、排列熵、Higuchi维数以及Katz维数并组成多域联合特征向量;最后,通过卷积神经网络实现通信辐射源个体识别分类,利用ORACLE公开数据集进行实验。实验结果表明:该方法有较高的识别精度且具有良好的抗噪声性能。Abstract: Aiming at the difficulties in extracting fingerprint features from communication emitters and the low recognition rate of single features, considering the nonlinear and non-stationary characteristics of subtle features of communication emitters, this paper proposes an individual identification method for communication emitters based on improved variational mode decomposition and multiple features. Firstly, in order to obtain the optimal combination of decomposition levels and penalty factors for variational mode decomposition, the variational modal decomposition of communication emitter symbol waveform signals is improved with whale optimization algorithm, in which the sequence complexity is used as the stopping criterion in this method to enable each symbol waveform signal to adaptively decompose several high-frequency signal components containing nonlinear fingerprint features and low-frequency components of data information; Then, according to the relevant threshold, the number of high-frequency signal component layers is selected that can best represent the nonlinear characteristics of the radiation source and the fuzzy entropy, permutation entropy, Higuchi dimension, and Katz dimension are extracted to form a multi-domain joint feature vector; Finally, the recognition and classification of communication emitters are achieved through convolutional neural networks, and recognition and classification experiments are conducted using the Oracle public dataset. The experimental results show that this method has high recognition accuracy and good noise immunity.
-
表 1 不同层数在不同信噪比下的识别率(%)
层数 信噪比SNR(dB) –4 dB –2 dB 0 dB 2 dB 4 dB 3 66.5 69.5 72.1 73.4 75.3 4 64.2 71 73.2 80.3 81 5 67.1 73.8 76 83.1 89 6 69.5 77.9 82 89.8 96.3 7 68.8 78 83.3 89.1 92.6 -
[1] HUANG Guangquan, YUAN Yingjun, WANG Xiang, et al. Specific emitter identification based on nonlinear dynamical characteristics[J]. Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2016, 39(1): 34–41. doi: 10.1109/CJECE.2015.2496143. [2] 任东方, 张涛, 韩洁. 结合ITD与非线性分析的通信辐射源个体识别方法[J]. 信号处理, 2018, 34(3): 331–339. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.03.010.REN Dongfang, ZHANG Tao, and HAN Jie. Approach of specific communication emitter identification combining ITD and nonlinear analysis[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(3): 331–339. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.03.010. [3] XIE Yang, WANG Shilian, ZHANG Eryang, et al. Specific emitter Identification based on nonlinear complexity of signal[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Hong Kong, China, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCC.2016.7753733. [4] LU N, ZHOU T X, WEI J F, et al. Application of a whale optimized variational mode decomposition method based on envelope sample entropy in the fault diagnosis of rotating machinery[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2022, 33(1): 015014. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ac3470. [5] ELMAGHBUB A and HAMDAOUI B. Leveraging hardware-impaired out-of-band information through deep neural networks for robust wireless device classification[J]. arXiv: 2004.11126, 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2004.11126. [6] BREMNES K, MOEN R, YEDURI S R, et al. Classification of UAVs utilizing fixed boundary empirical wavelet sub-bands of RF fingerprints and deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(21): 21248–21256. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3208518. [7] ZHANG Junqing, WOODS R, SANDELL M, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint identification for narrowband systems, modelling and classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 3974–3987. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3088008. [8] HUANG Yi, HU Aiqun, FAN Jiayi, et al. Joint estimation of transmitter IQ imbalance and nonlinearity with multipath in OFDM systems[C]. 2023 IEEE 98th Vehicular Technology Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/VTC2023-Fall60731.2023.10333512. [9] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K and ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531–544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675. [10] MIRJALILI S and LEWIS A. The whale optimization algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2016, 95: 51–67. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008. [11] ZAHID M U, NISAR M D, and SHAH M H. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multiscale approximate entropy[J]. Physical Communication, 2022, 55: 101927. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2022.101927. [12] BANDT C and POMPE B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 88(17): 174102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.174102. [13] CHEN Weiting, WANG Zhizhong, XIE Hongbo, et al. Characterization of surface EMG signal based on fuzzy entropy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2007, 15(2): 266–272. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2007.897025. [14] KATZ M J. Fractals and the analysis of waveforms[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 1988, 18(3): 145–156. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(88)90041-8. [15] SHAMSI E, AHMADI-PAJOUH M A, and SEIFI ALA T. Higuchi fractal dimension: An efficient approach to detection of brain entrainment to theta binaural beats[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 68: 102580. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102580. [16] SANKHE K, BELGIOVINE M, ZHOU Fan, et al. No radio left behind: Radio fingerprinting through deep learning of physical-layer hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(1): 165–178. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2949308. [17] DENG Shouyun, HUANG Zhitao, WANG Xiang, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multidimension permutation entropy[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 2017(1): 1538728. doi: 10.1155/2017/1538728. [18] SUN Liting, WANG Xiang, YANG Afeng, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multi-dimension approximate entropy[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 471–475. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2978333. [19] HE Boxiang and WANG Fanggang. Cooperative specific emitter identification via multiple distorted receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 3791–3806. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3001721. -





 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:
