Convolutional Neural Network STAP Low Level Wind Shear Wind Speed Estimation
-
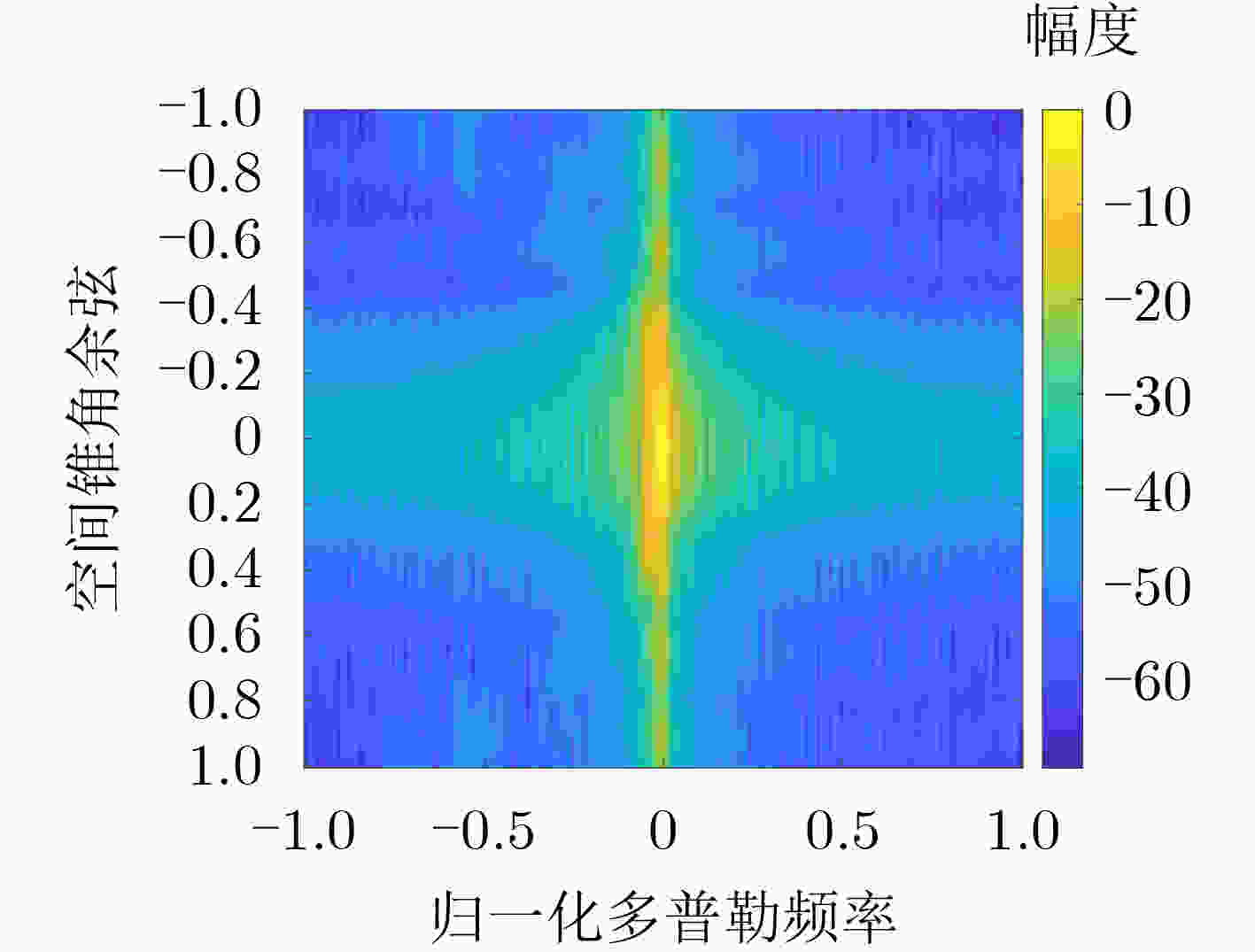
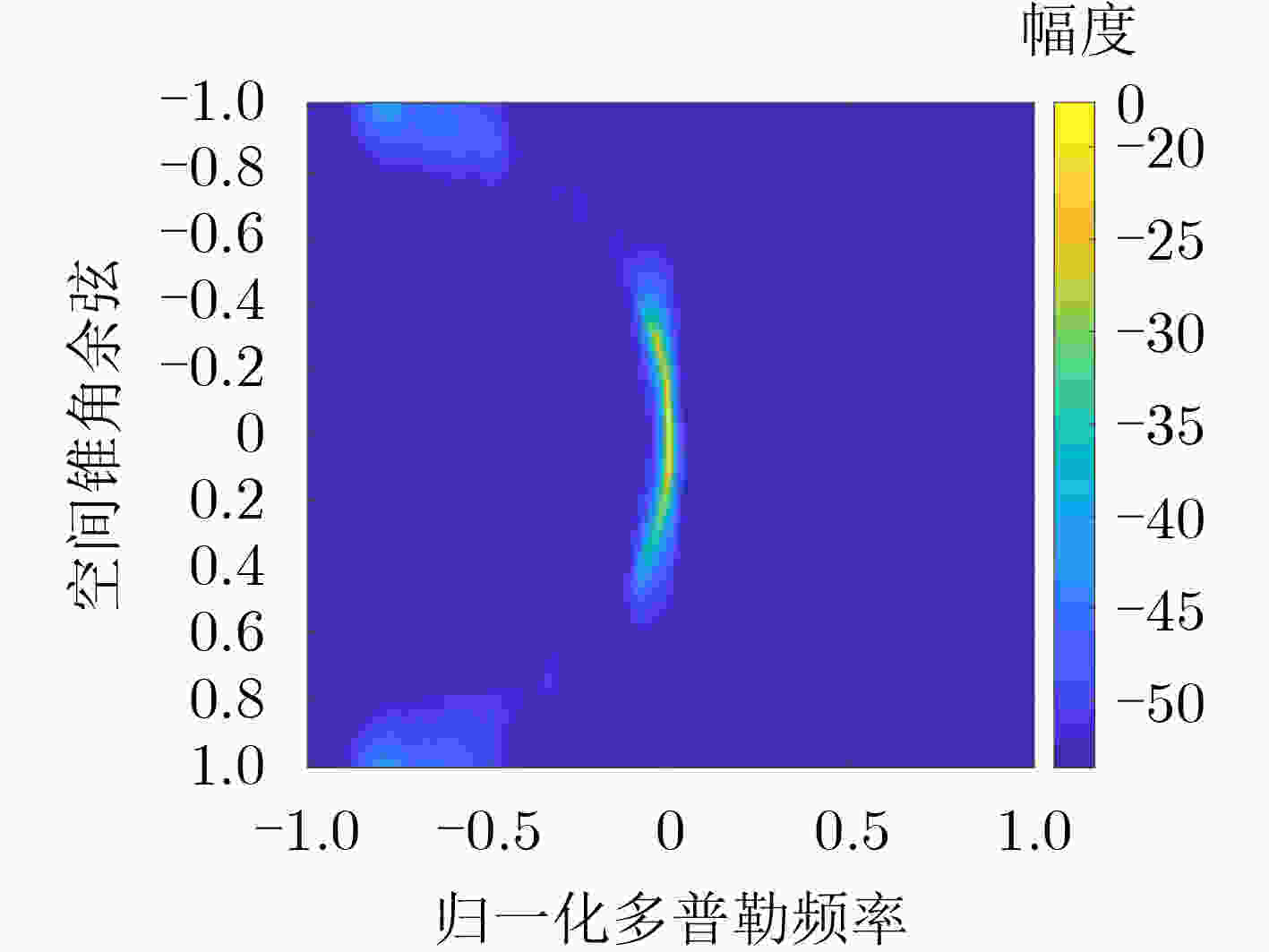
摘要: 由于机载气象雷达前视阵下存在非均匀性地杂波,导致难以获得足够的独立同分布样本,影响杂波协方差矩阵准确估计,进而影响风速估计。对此,该文提出一种基于卷积神经网络STAP的低空风切变风速估计方法,通过少量样本就能够实现高分辨杂波空时谱估计。首先,基于卷积神经网络模型训练好高分辨杂波空时谱卷积神经网络,接着计算杂波协方差矩阵,进而计算卷积神经网络STAP最优权矢量进行杂波抑制,达到对低空风切变风速精确估计。该文在小样本情况下,将稀疏恢复问题通过卷积神经网络实现,完成对高分辨杂波空时谱有效估计,仿真实验结果表明该方法可以有效估计空时谱,并完成风速估计。Abstract: Due to the non-uniform ground clutter in the forward array of airborne weather radar, it is difficult to obtain enough independent and equally distributed samples, which affects the accurate estimation of clutter covariance matrix and wind speed estimation. In this paper, a novel estimation method of low altitude wind shear speed based on convolutional neural network STAP is proposed, which can realize high resolution clutter space-time spectrum estimation with a small number of samples. First, the high-resolution clutter space-time spectrum convolutional neural network is trained based on the convolutional neural network model, and then the clutter covariance matrix is calculated, and then the optimal weight vector of the convolutional neural network STAP is calculated for clutter suppression, so as to accurately estimate the wind shear speed at low altitude. The sparse recovery problem is realized by convolutional neural network in the case of small samples, and the space-time spectrum of high-resolution clutter is effectively estimated. The simulation results show that the proposed method can effectively estimate the space-time spectrum and complete the wind speed estimation.
-
Key words:
- Airborne weather radar /
- CNN /
- Low-altitude windshear /
- Wind speed estimation
-
表 1 网络结构参数
网络层 卷积核 输出通道 填充方式 激活函数 Conv2D $11 \times 11$ 16 SAME ReLU Conv2D $9 \times 9$ 8 SAME ReLU Conv2D $7 \times 7$ 4 SAME ReLU Conv2D $5 \times 5$ 2 SAME ReLU Conv2D $3 \times 3$ 1 SAME ReLU 表 2 训练参数
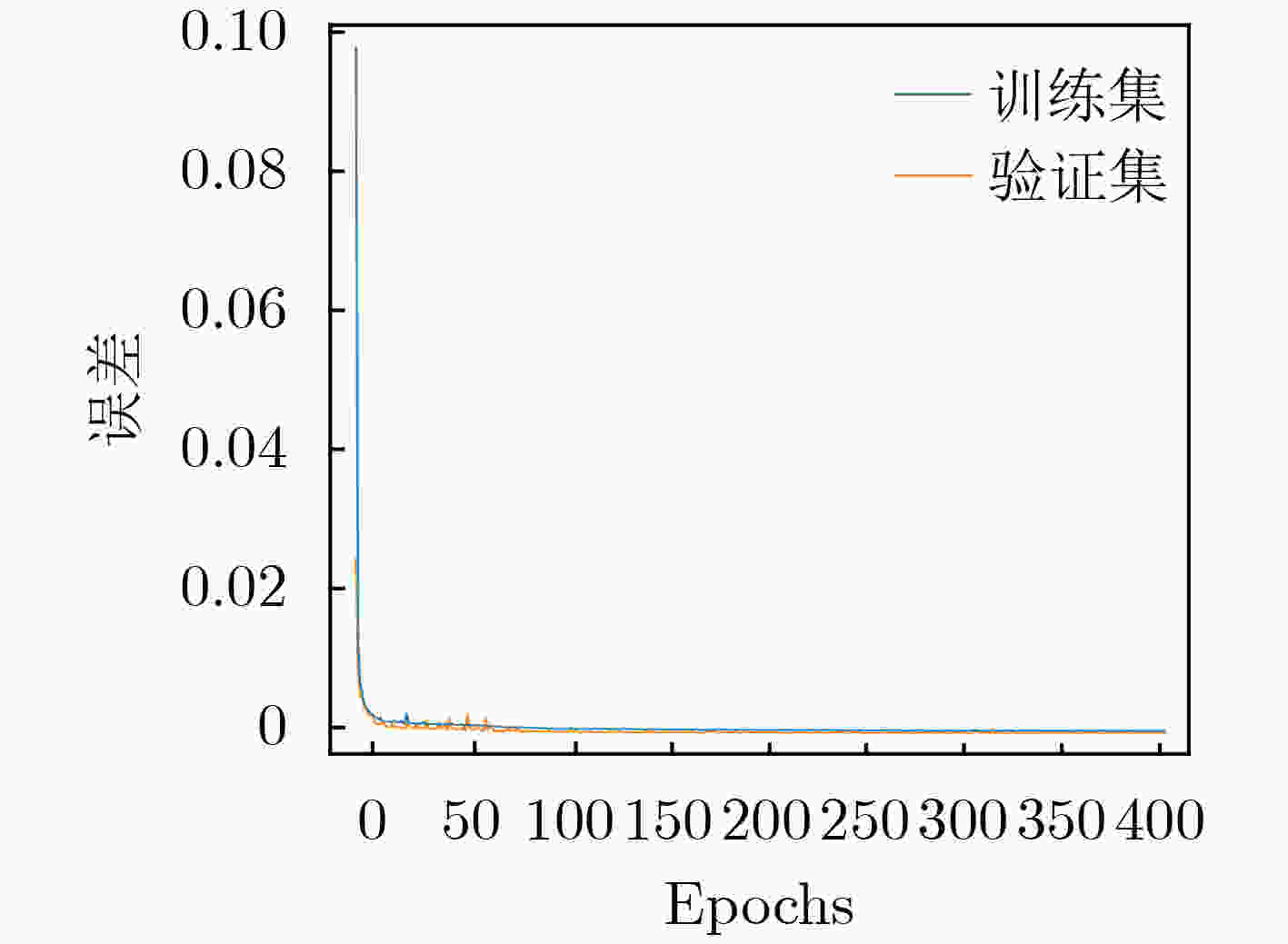
训练参数 数值 损失函数 MSE 优化函数 Adam 学习速率 0.0001 Batch 4 Epoch 300 表 3 雷达仿真具体参数
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 载机高度(m) 600 阵元数 8 波长(m) 0.05 相干脉冲数 64 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 7000 杂噪比(dB) 30~60 载机速度(m/s) 75 信噪比(dB) 5 距离分辨率(m) 150 主瓣角度(°) (90,0) 表 4 不同方法误差比较
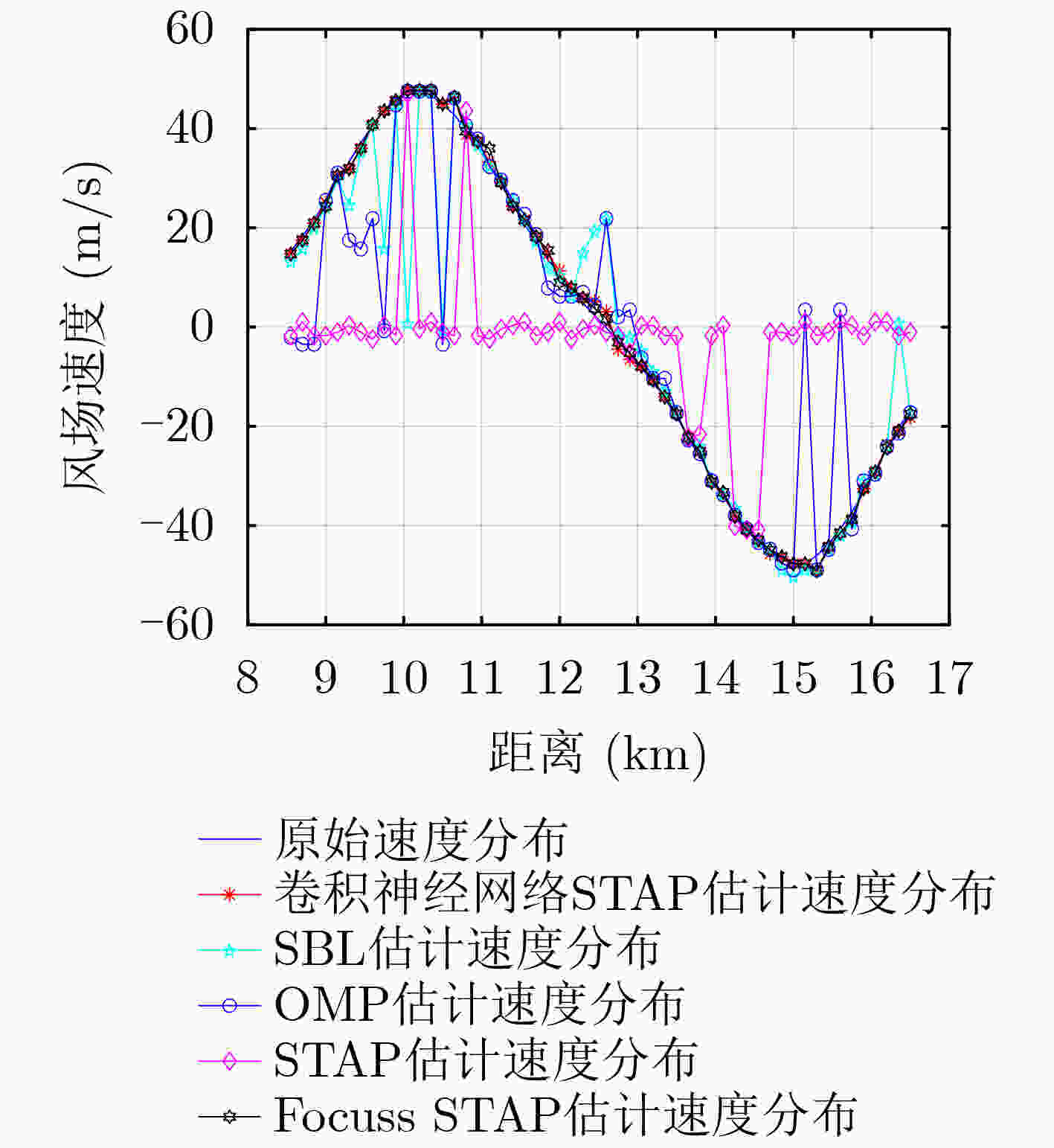
方法 均方根误差(m/s) STAP 29.3629 OMP STAP 14.9378 SBL STAP 11.0052 Focuss STAP 2.1438 卷积神经网络STAP 1.1618 表 5 不同方法运算复杂度对比
方法 运算复杂度 STAP $O(2NM{({N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}})^3})$ OMP STAP $O((NM{N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}}) + {(NM)^3} + {(NM)^3}{N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}} + 2NM{({N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}})^2}{k_{{\mathrm{OMP}}}})$ SBL STAP $ O((NM{N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}}) + {(NM)^3} + 3{(NM)^3}{N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}} + 2NM{({N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}})^2}{k_{{\mathrm{SBL}}}}) $ Focuss STAP $O((NM{N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}}) + {(NM)^3} + 2{(NM)^2}{N_{{\mathrm{s}}}}{N_{{\mathrm{d}}}} + NM{({N_{\rm s}}{N_{\rm d}})^2}{k_{{{\mathrm{Focuss}}}}})$ 卷积神经网络STAP $O(28777{N_{{\mathrm{s}}}}{N_{{\mathrm{d}}}})$ 表 6 不同方法在线运行时间对比
方法 在线时间(s) STAP 64 OMP STAP 578 SBL STAP 50 Focuss STAP 14 卷积神经网络STAP 5 -
[1] LIN Caiyan, ZHANG Kaijun, CHEN Xintao, et al. Overview of low-level wind shear characteristics over Chinese mainland[J]. Atmosphere, 2021, 12(5): 628. doi: 10.3390/atmos12050628. [2] 刘琴, 李明磊, 汪玲, 等. 机载气象雷达目标的三维建模方法研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2022, 20(4): 435–441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.04.012.LIU Qin, LI Minglei, WANG Ling, et al. Research on 3D modeling of airborne weather radar target[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2022, 20(4): 435–441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.04.012. [3] 吴仁彪, 张彪, 李海, 等. 基于空时自适应处理的低空风切变风速估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(3): 631–636. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140697.WU Renbiao, ZHANG Biao, LI Hai, et al. Wind speed estimation for low-attitude windshear based on space-time adaptive processing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(3): 631–636. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140697. [4] 宋迪. 基于RD-STAP的线性调频连续波低空风切变检测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国民航大学, 2020. doi: 10.27627/d.cnki.gzmhy.2020.000427.SONG Di. Detection of linear frequency modulated continuous wave low altitude wind-shear based on RD-STAP[D]. [Master dissertation], Civil Aviation University of China, 2020. doi: 10.27627/d.cnki.gzmhy.2020.000427. [5] BI Fukun, ZHANG Dongyan, CAI Xichang, et al. Fast reduced-rank STAP algorithm based on Gram–Schmidt orthogonalisation for airborne radar[J]. International Journal of Electronics, 2015, 102(8): 1382–1393. doi: 10.1080/00207217.2014.981872. [6] 李仲悦, 王彤. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的稳健STAP算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(10): 3032–3040. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.10.05.LI Zhongyue and WANG Tong. Sparse Bayesian learning-based robust STAP algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(10): 3032–3040. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.10.05. [7] REN Bing and WANG Tong. A novel fast sparse Bayesian learning STAP algorithm for conformal array radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(11): 2824. doi: 10.3390/RS15112824. [8] WEN Xiaoqin and HAN Chongzhao. Direct data domain approach to space-time adaptive processing[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2006, 17(1): 59–64. doi: 10.1016/S1004-4132(06)60011-X. [9] WANG Yikai and HE Zishu. Thinned knowledge-aided STAP by exploiting structural covariance matrix[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(8): 1266–1275. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0060. [10] 朱晗归, 冯为可, 冯存前, 等. 机载雷达深度展开空时自适应处理方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 676–691. doi: 10.12000/JR22051.ZHU Hangui, FENG Weike, FENG Cunqian, et al. Deep unfolding based space-time adaptive processing method for airborne radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 676–691. doi: 10.12000/JR22051. [11] CUI Ning, XING Kun, DUAN Keqing, et al. Knowledge‐aided block sparse Bayesian learning STAP for phased‐array MIMO airborne radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15(12): 1628–1642. doi: 10.1049/RSN2.12152. [12] 李海, 雍从建, 范懿, 等. 幅相误差下基于CMCAP-JDL的低空风切变风速估计[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(4): 502–510. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.04.004.LI Hai, YONG Congjian, FAN Yi, et al. The estimation of wind speed in low-altitude wind-shear based on CMCAP-JDL under the amplitude and phase error[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(4): 502–510. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.04.004. [13] BOYER E, LARZABAL P, ADNET C, et al. Parametric spectral moments estimation for wind profiling radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(8): 1859–1868. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.813487. [14] WARD J. Space-time Adaptive Processing for Airborne Radar[R]. 1994: 25–45. [15] 李海, 程伟杰, 谢瑞杰. 基于同伦稀疏STAP的低空风切变风速估计[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(4): 1174–1181. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.04.13.LI Hai, CHENG Weijie, and XIE Ruijie. Wind speed estimation of low-altitude wind-shear based on homotopy sparse STAP[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1174–1181. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.04.13. [16] JIN K H, MCCANN M T, FROUSTEY E, et al. Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4509–4522. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2713099. [17] XUE Liang, LIU Jie, WEN Guilin, et al. Efficient, high-resolution topology optimization method based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 16(1): 80–96. doi: 10.1007/S11465-020-0614-2. [18] DUAN Keqing, CHEN Hui, XIE Wenchong, et al. Deep learning for high-resolution estimation of clutter angle-Doppler spectrum in STAP[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16(2): 193–207. doi: 10.1049/RSN2.12176. [19] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–15. [20] 陆军, 郦能敬, 曹晨, 等. 预警机系统导论[M]. 2版. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011: 158–160.LU Jun, LI Nengjing, CAO Chen, et al. Introduction to Airborne Early Warning System[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2011: 158–160. [21] 李海, 李怡静, 吴仁彪. 载机偏航下基于广义相邻多波束自适应处理的低空风切变风速估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1728–1734. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180758.LI Hai, LI Yijing, and WU Renbiao. Generalized adjacent multi-beam adaptive processing based low-altitude wind-shear wind speed estimation under aircraft yawing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1728–1734. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180758. [22] 张瑞, 全英汇, 朱圣棋, 等. 基于改进OMP算法的稀疏目标微波关联成像方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(7): 1756–1765. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.07.04.ZHANG Rui, QUAN Yinghui, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Microwave correlation imaging method based on improved OMP algorithm for sparse targets[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(7): 1756–1765. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.07.04. [23] DUAN Keqing, WANG Zetao, XIE Wenchong, et al. Sparsity-based STAP algorithm with multiple measurement vectors via sparse Bayesian learning strategy for airborne radar[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2017, 11(5): 544–553. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0183. [24] ICHIKAWA M, KIKUMA N, SAKAKIBARA K, et al. Performance improvement of TSVD-FOCUSS algorithm in DOA estimation using array antenna[C/OL]. 2021 International Conference on Emerging Technologies for Communications, 2021. doi: 10.34385/PROC.68.P2-2. -





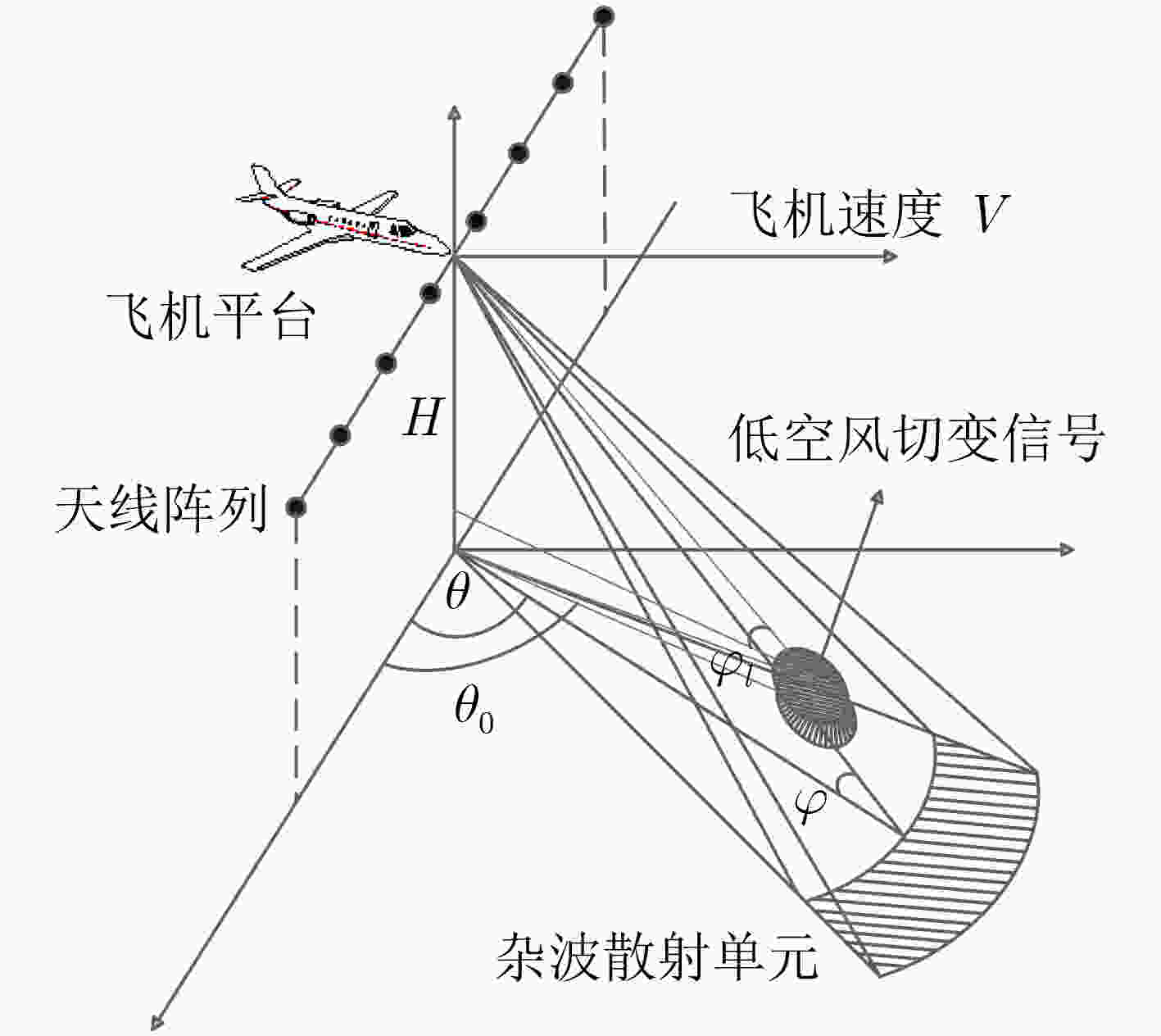
 下载:
下载:
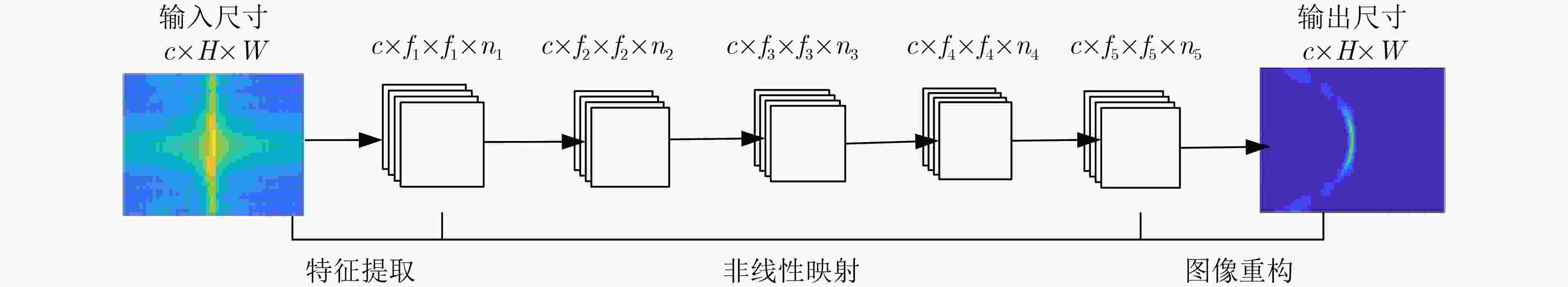
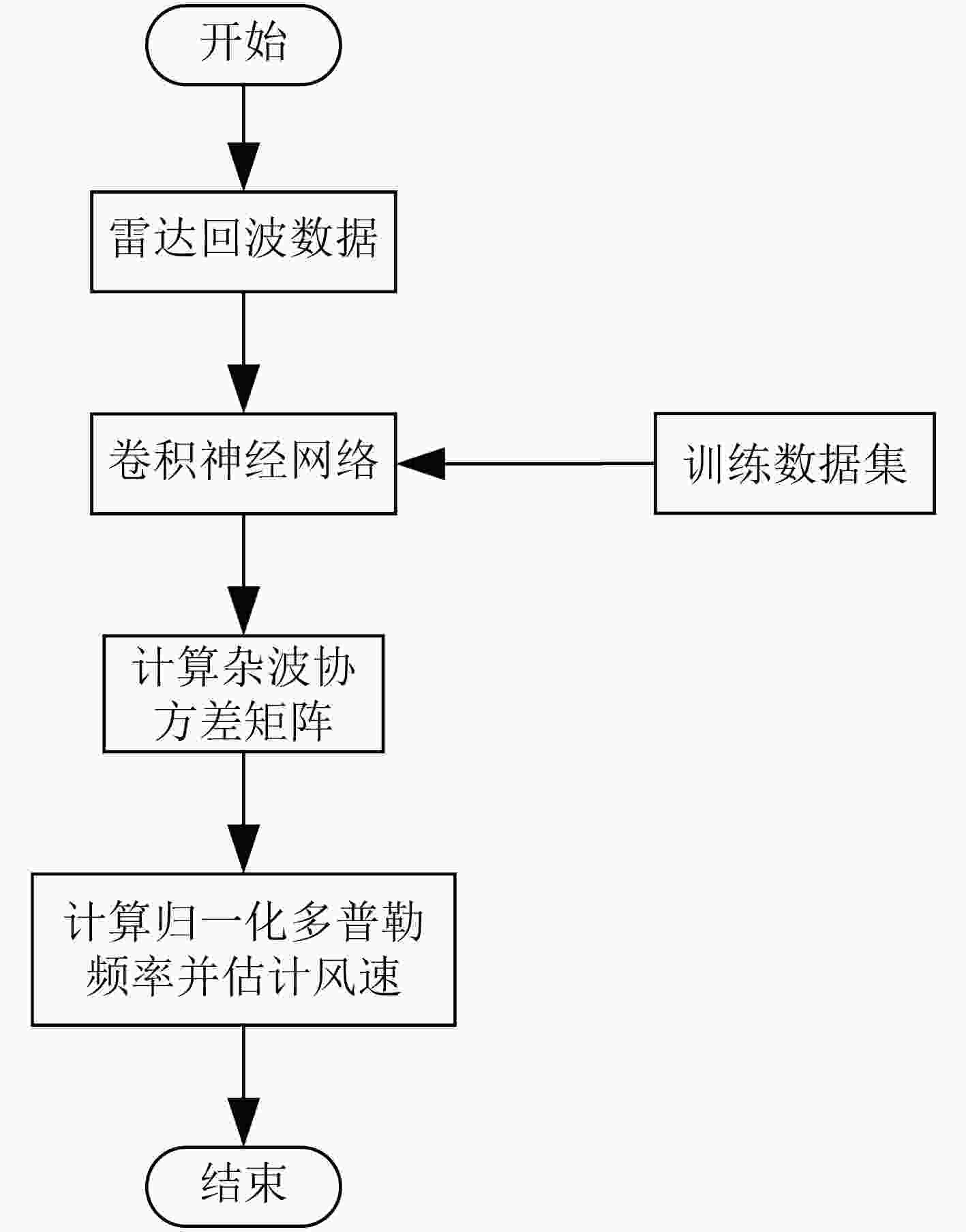
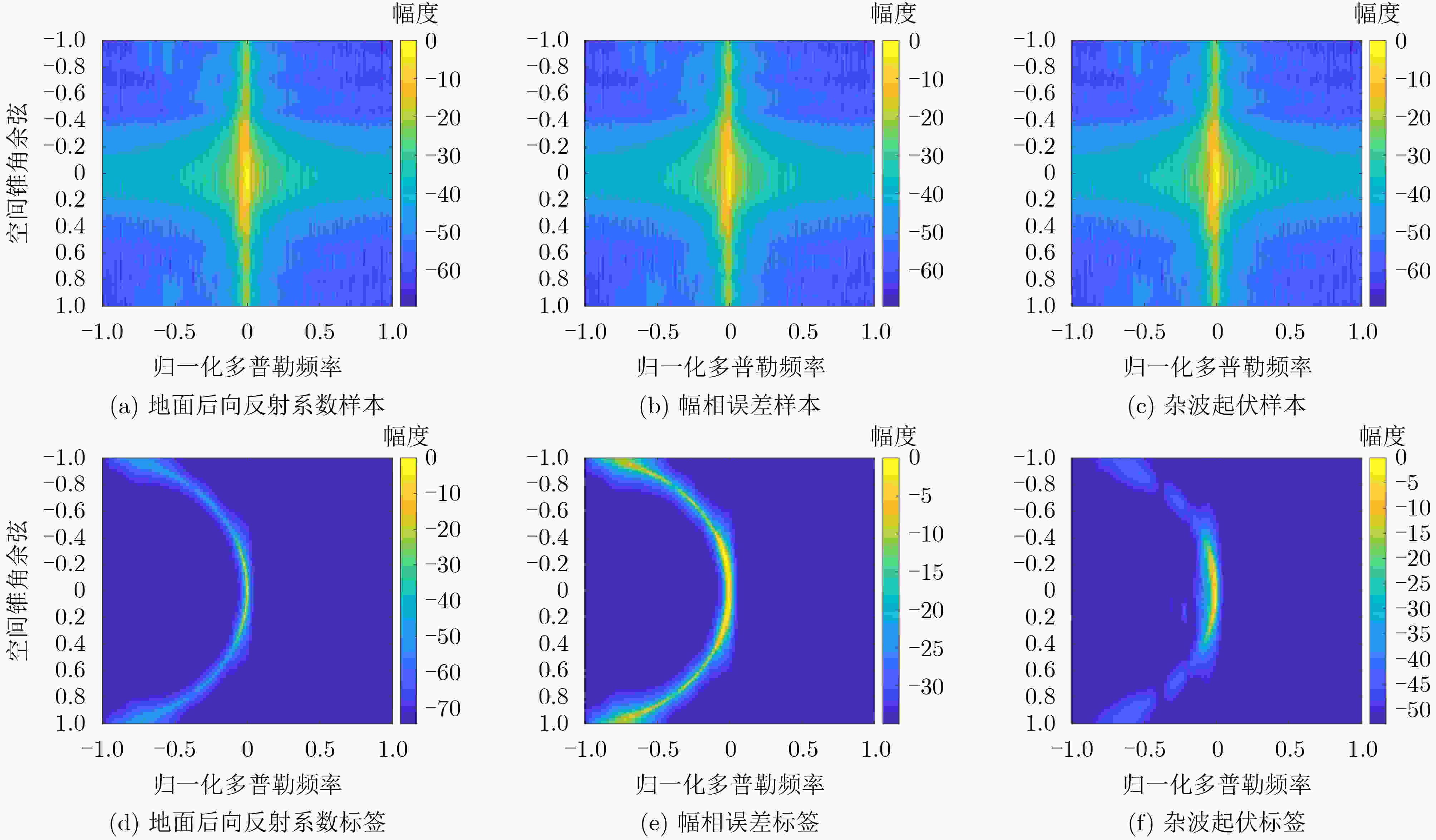


 下载:
下载:
