Group Activity Recognition under Multi-scale Sub-group Interaction Relationships
-
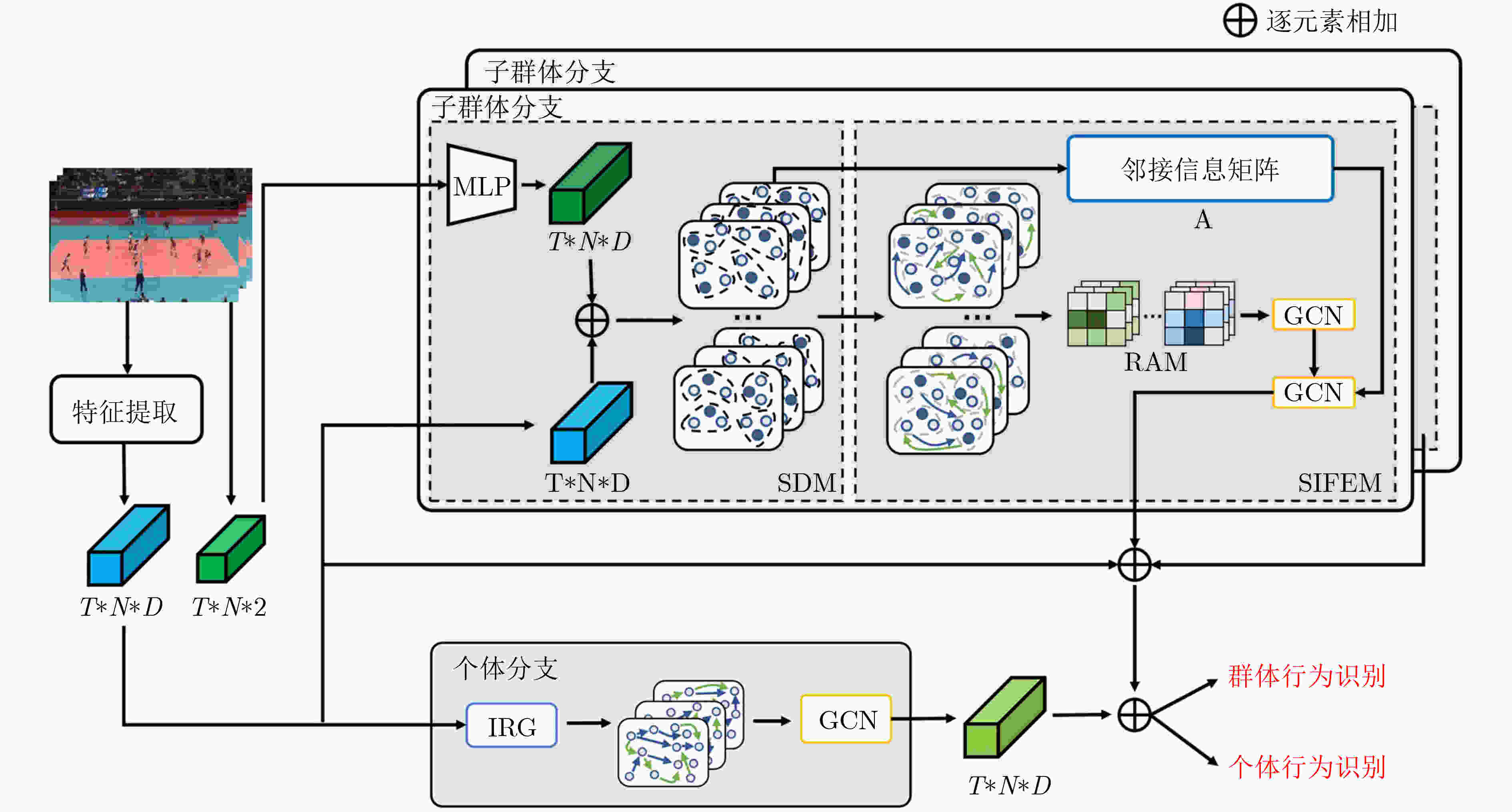
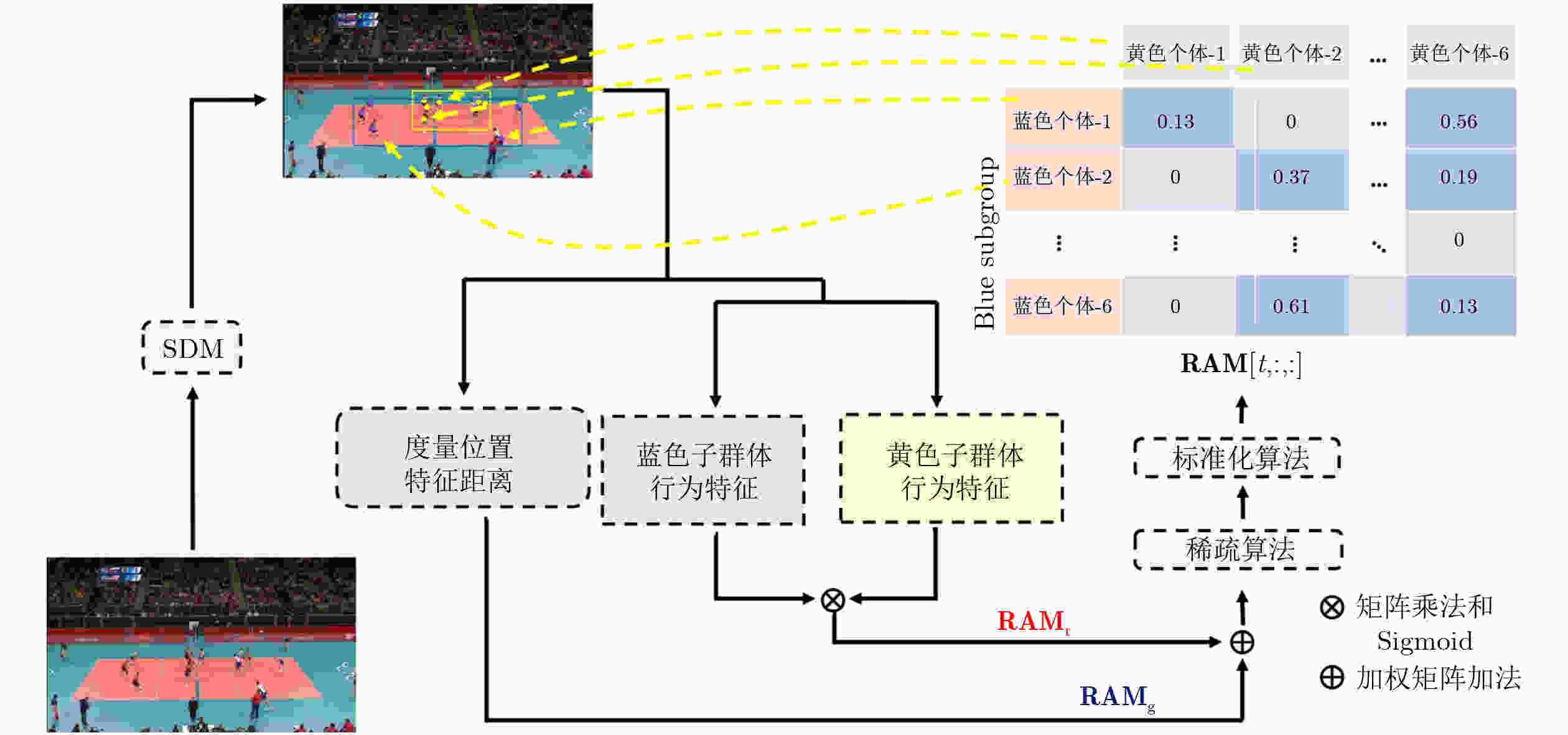
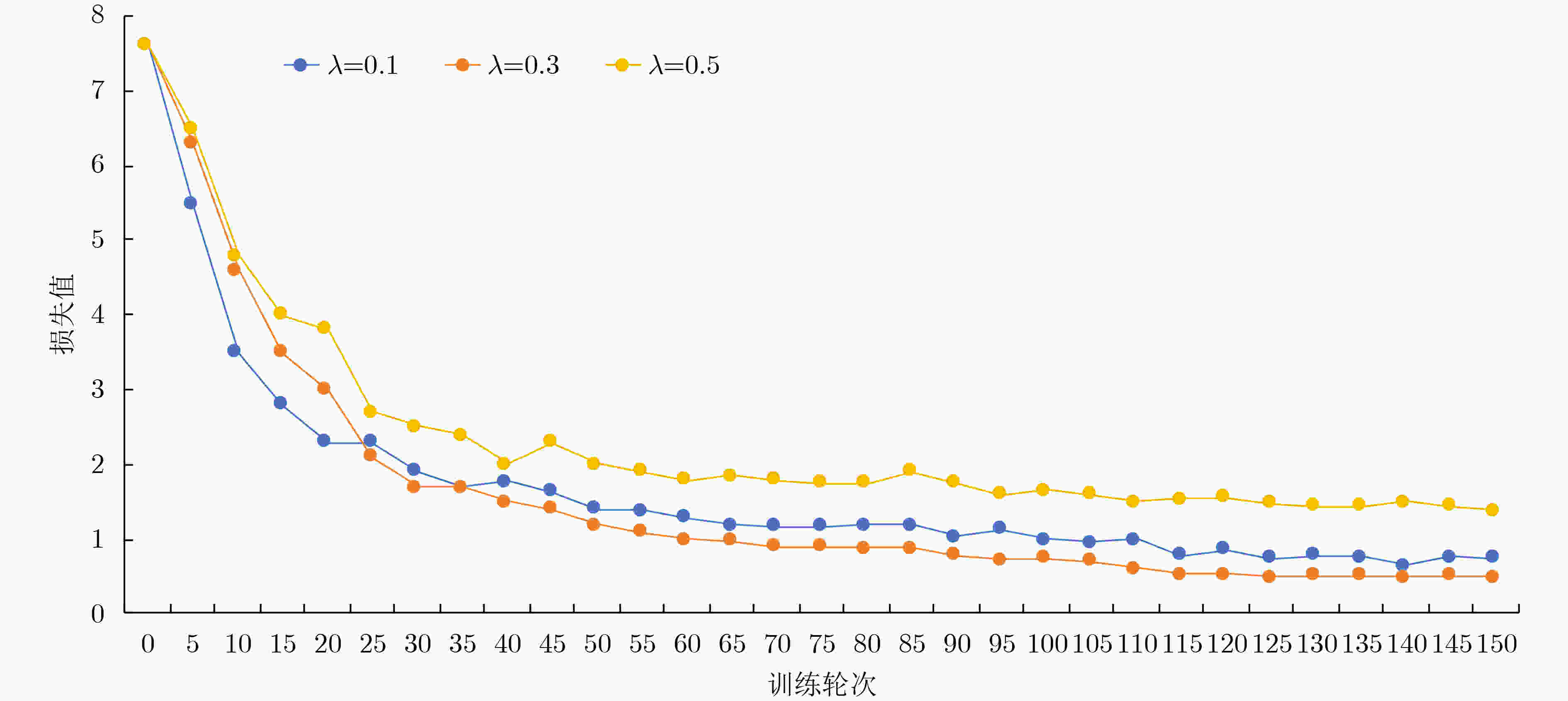
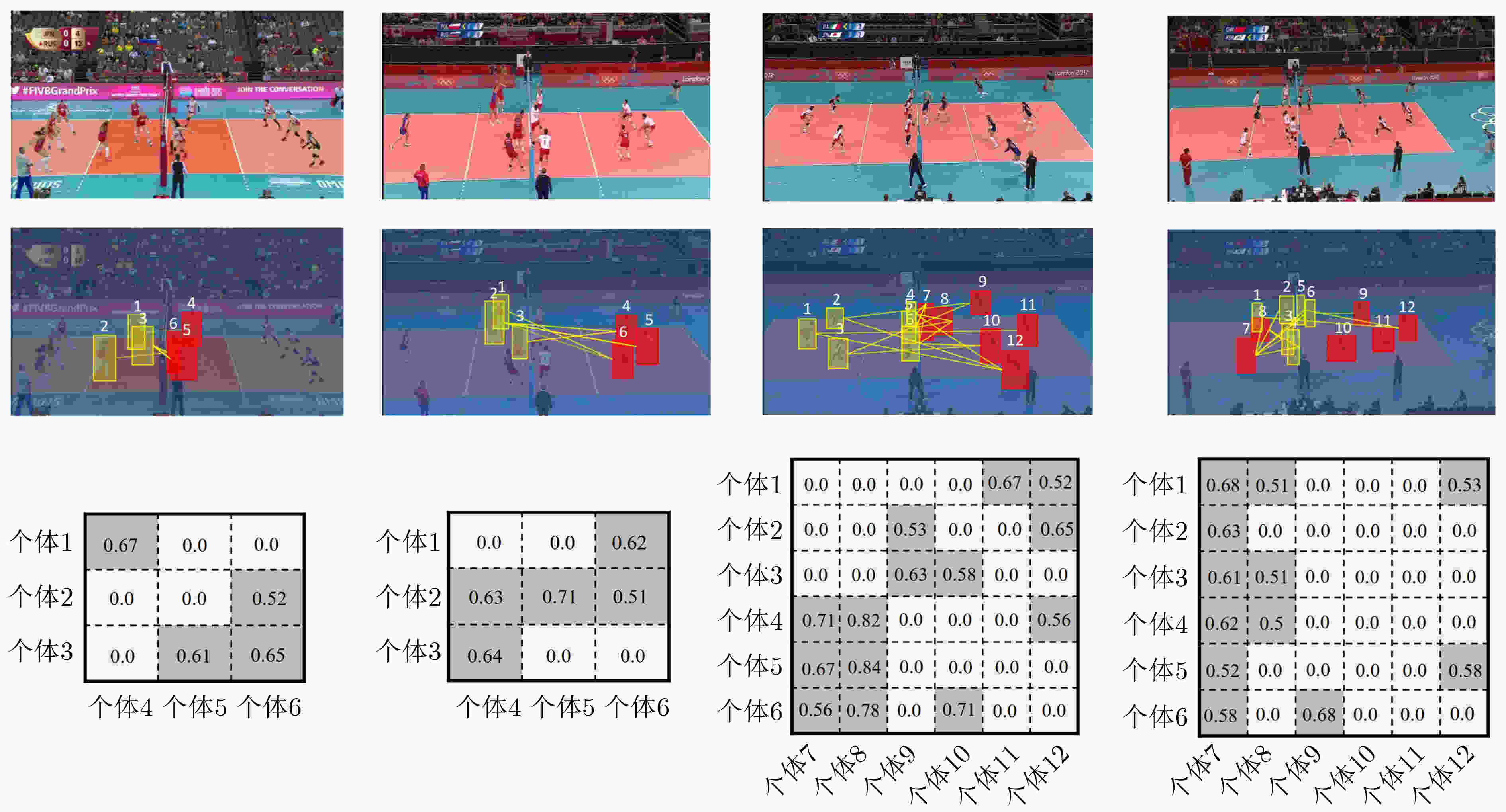
摘要: 群体行为识别旨在识别包含多个个体的群体行为。在现实场景中,群体行为通常可以被视为从群体到子群体再到个人的层次结构。然而,以前的群体行为识别方法主要侧重于对个体之间的关系进行建模,缺乏对子群体之间关系的深度研究。从该角度出发,该文提出一种基于多尺度子群体交互关系(MSIR)的多层次群体行为识别框架。除对个体关系进行建模外,重点关注了子群体之间的多尺度交互特征。具体优化如下:设计子群体划分模块,通过个体外观特征和其空间位置来聚合可能存在关联的个体,再进一步利用语义信息动态地生成不同尺度大小的子群体;设计子群体交互特征提取模块,通过构建不同子群体之间的交互矩阵以及图神经网络的关系推理能力,提取更具判别力的子群体特征。实验结果表明,与现有12种方法在排球数据集和集体活动数据集这两个群体行为识别基准数据集上对比,该文方法都取得最好的性能结果。作为一个易于扩展和优化的群体行为识别框架,该算法在不同数据集上都具有较好的泛化能力。Abstract: Group activity recognition aims to identify behaviors involving multiple individuals. In real-world applications, group behavior is often treated as a hierarchical structure, which consists group, subgroups and individuals. Previous researches have been focused on modeling relationships between individuals, without in-depth relationship analysis between subgroups. Therefore, a novel hierarchical group activity recognition framework based on Multi-scale Sub-group Interaction Relationships (MSIR) is proposed, and an innovative multi-scale interaction features extraction method between subgroups is presented as specified below. A sub-group division module is implemented. It aggregates individuals with potential correlations based on their appearance features and spatial positions, then dynamically generates subgroups of different scales using semantic information. A sub-group interactive feature extraction module is developed to extract more discriminative subgroup features. It constructs interaction matrices between different subgroups and leverages the relational reasoning capabilities of graph neural networks. Compared with existing twelve methods on benchmark datasets for group behavior recognition, including volleyball and collective activity datasets, the methodology of this paper demonstrates superior performance. This research presents an easily extendable and adaptable group activity recognition framework, exhibiting strong generalization capabilities across different datasets.
-
Key words:
- Activity recognition /
- Group activity /
- Sub-group division /
- Relational reasoning
-
表 1 排球测试数据集和集体行为测试数据集上不同方法的准确率(%)比较
方法 发表时间 骨干网络 个人行为准确率(排球) 群体行为准确率(排球) 群体行为准确率(集体行为) HRN ECCV2018 VGG16 – 89.1 – ARG CVPR2019 Inception-v3 81.2 92.1 90.5 Pramono等人 ECCV2020 I3D 83.1 95.0 95.2 DIN ICCV2021 VGG16 – 93.6 95.9 COMPOSER ECCV2022 Transformer 86.8 94.2 96.2 VSGNN-PAL Neurocomputing2022 I3D 85.8 94.4 93.2 Wu等人 Sensors2022 I3D 84.1 94.1 92.2 GRAIN IJCAI2022 VGG16 – 94.5 95.2 HSTT ICASSP2023 Inception-v3 83.9 93.7 96.1 Wu等人 TCSVT2023 Inception-v3 – 92.4 85.0 Du等人 TCSVT2023 Inception-v3 – 94.7 95.4 DECOMPL arXiv2023 VGG16 – 93.8 95.5 MSIR (本文) – VGG16 86.8 94.5 96.2 MSIR (本文) – Inception-v3 86.7 95.2 96.4 表 2 子群体划分模块的定向实验比较(%)
策略 具体方法 排球数据集准确率 子群体划分 距离划分 92.1 SDM (本文) 95.2 个体选择 传统选择 95.2 扩张选择 93.5 表 3 子群体尺度的定量实验比较(%)
子群体尺度 个体数目k 排球数据集准确率 集体活动数据集准确率 无 – 90.8 89.4 单尺度 2 93.8 94.9 单尺度 3 91.3 90.2 单尺度 4 91.6 91.3 单尺度 5 92.6 93.5 单尺度 6 92.4 93.2 多尺度 2, 5 95.2 96.4 表 4 SIFEM中不同组件的定量实验比较
模型
变种模型介绍 RAMg RAMr 归一化 稀疏 排球数据集
准确率(%)1 基准模型 90.8 2 RAM为全一矩阵 √ √ 91.5 3 只有RAMg √ √ √ 94.7 4 只有RAMr √ √ √ 91.9 5 无归一化和稀疏化 √ √ 92.7 6 无归一化 √ √ √ 93.6 7 无稀疏化 √ √ √ 94.5 8 完整模型 √ √ √ √ 95.2 -
[1] IBRAHIM M S and MORI G. Hierarchical relational networks for group activity recognition and retrieval[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 742–758. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_44. [2] WU Jianchao, WANG Limin, WANG Li, et al. Learning actor relation graphs for group activity recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Bench, USA, 2019: 9956–9966. doi: 10.1109/Cvpr.2019.01020. [3] LAN Tian, SIGAL L, and MORI G. Social roles in hierarchical models for human activity recognition[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 1354–1361. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247821. [4] YAN Rui, XIE Lingxi, TANG Jinhui, et al. HiGCIN: Hierarchical graph-based cross inference network for group activity recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(6): 6955–6968. doi: 10.1109/Tpami.2020.3034233. [5] ZHU Xiaolin, WANG Dongli, and ZHOU Yan. Hierarchical spatial-temporal transformer with motion trajectory for individual action and group activity recognition[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10096109. [6] HU Guyue, CUI Bo, HE Yuan, et al. Progressive relation learning for group activity recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 977–986. doi: 10.1109/Cvpr42600.2020.00106. [7] PRAMONO R R A, CHEN Y T, and FANG W H. Empowering relational network by self-attention augmented conditional random fields for group activity recognition[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 71–90. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_5. [8] WANG Lukun, FENG Wancheng, TIAN Chunpeng, et al. 3D-unified spatial-temporal graph for group activity recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 556: 126646. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.126646. [9] KIPF T N and WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[C]. The 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [10] 曹毅, 吴伟官, 李平, 等. 基于时空特征增强图卷积网络的骨架行为识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 3022–3031. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220749.CAO Yi, WU Weiguan, LI Ping, et al. Skeleton action recognition based on spatio-temporal feature enhanced graph convolutional network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(8): 3022–3031. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220749. [11] DUAN Haodong, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Kai, et al. Revisiting skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 2959–2968. doi: 10.1109/Cvpr52688.2022.00298. [12] FENG Yiqiang, SHAN Shimin, LIU Yu, et al. DRGCN: Deep relation gcn for group activity recognition[C]. 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Bangkok, Thailand, 2020: 361–368. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63820-7. [13] KUANG Zijian and TIE Xinran. IARG: Improved actor relation graph based group activity recognition[C]. The Third International Conference on Smart Multimedia, Marseille, France, 2020. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-22061-6_3. [14] AMER M R, LEI Peng, and TODOROVIC S. HiRF: Hierarchical random field for collective activity recognition in videos[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014, 8694: 572–585. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_37. [15] BAGAUTDINOV T, ALAHI A, FLEURET F, et al. Social scene understanding: End-to-end multi-person action localization and collective activity recognition[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3425–3434. doi: 10.1109/Cvpr.2017.365. [16] CHOI W, SHAHID K, and SAVARESE S. What are they doing?: Collective activity classification using spatio-temporal relationship among people[C]. 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Kyoto, Japan, 2009: 1282–1289. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW.2009.5457461. [17] QI Mengshi, QIN Jie, LI Annan, et al. stagNet: An attentive semantic RNN for group activity recognition[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018, 11214: 104–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01249-6_7. [18] DEMIREL B and OZKAN H. DECOMPL: Decompositional learning with attention pooling for group activity recognition from a single volleyball image[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.06439 2023. [19] DU Zexing, WANG Xue, and WANG Qing. Self-supervised global spatio-temporal interaction pre-training for group activity recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(9): 5076–5088. doi: 10.1109/Tcsvt.2023.3249906. [20] LI Wei, YANG Tianzhao, WU Xiao, et al. Learning graph-based residual aggregation network for group activity recognition[C]. The Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vienna, Austria, 2022: 1102–1108. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2022/154. [21] LIU Tianshan, ZHAO Rui, LAM K M, et al. Visual-semantic graph neural network with pose-position attentive learning for group activity recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 491: 217–231. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.03.066. [22] WU Lifang, LANG Xianglong, XIANG Ye, et al. Active spatial positions based hierarchical relation inference for group activity recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(6): 2839–2851. doi: 10.1109/Tcsvt.2022.3228731. [23] WU Lifang, LANG Xixanglong, XIANG Ye, et al. Multi-perspective representation to part-based graph for group activity recognition[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(15): 5521. doi: 10.3390/s22155521. [24] YUAN Hangjie, NI Dong, and WANG Mang. Spatio-temporal dynamic inference network for group activity recognition[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 7456–7465. doi: 10.1109/Iccv48922.2021.00738. [25] ZHOU Honglu, KADAV A, SHAMSIAN A, et al. COMPOSER: Compositional reasoning of group activity in videos with keypoint-only modality[C]. The 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 249–266. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19833-5_15. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
