Advances in Privacy-Preserving Ciphertext Retrieval
-
摘要: 密文检索技术旨在提供密态数据查询服务,提高密文数据的可用性。但目前大多数机制仍存在不同程度的额外信息泄露,容易被攻击者捕获用于恢复明文信息与查询条件。如何强化密文检索中的隐私保护特性,实现信息泄露最小化已成为研究者关注的重点目标。近年来,随着硬件芯片技术与新型密码技术的快速发展,隐私保护密文检索研究方面涌现出了一批新成果,该文主要围绕多样化密文检索、基于可信执行环境的密文检索、隐匿信息检索等研究热点展开阐述,并总结了未来发展趋势。Abstract: The ciphertext retrieval techniques are designed to provide query services over encrypted data and to improve the availability of encrypted data. However, most of existing methods leak additional information besides the query result, which may be utilized by the attacker to recover plaintext data or queries. How to enhance the privacy-preserving features in ciphertext retrieval and achieve the minimisation of information leakage has received a lot of attention from researchers. In recent years, with the rapid development of hardware chip technology and new cryptographic technology, a number of novel methods were proposed for privacy-preserving ciphertext retrieval. This paper mainly focuses on the research hotspots of diversified ciphertext retrieval, ciphertext retrieval based on trusted execution environment and private information retrieval, and summarizes the future development trends.
-
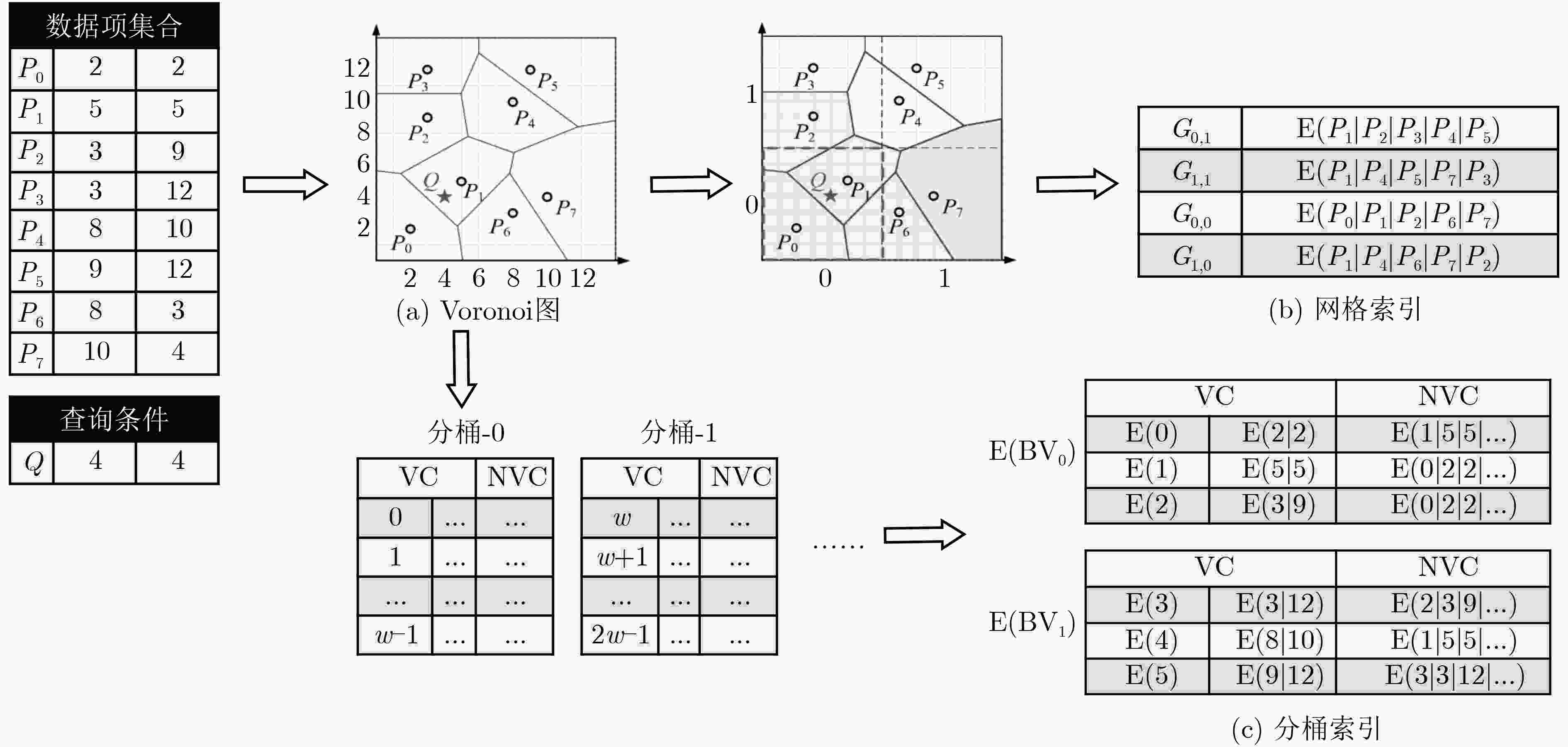
图 2 基于Voronoi图的安全K近邻查询方案[45]示意图
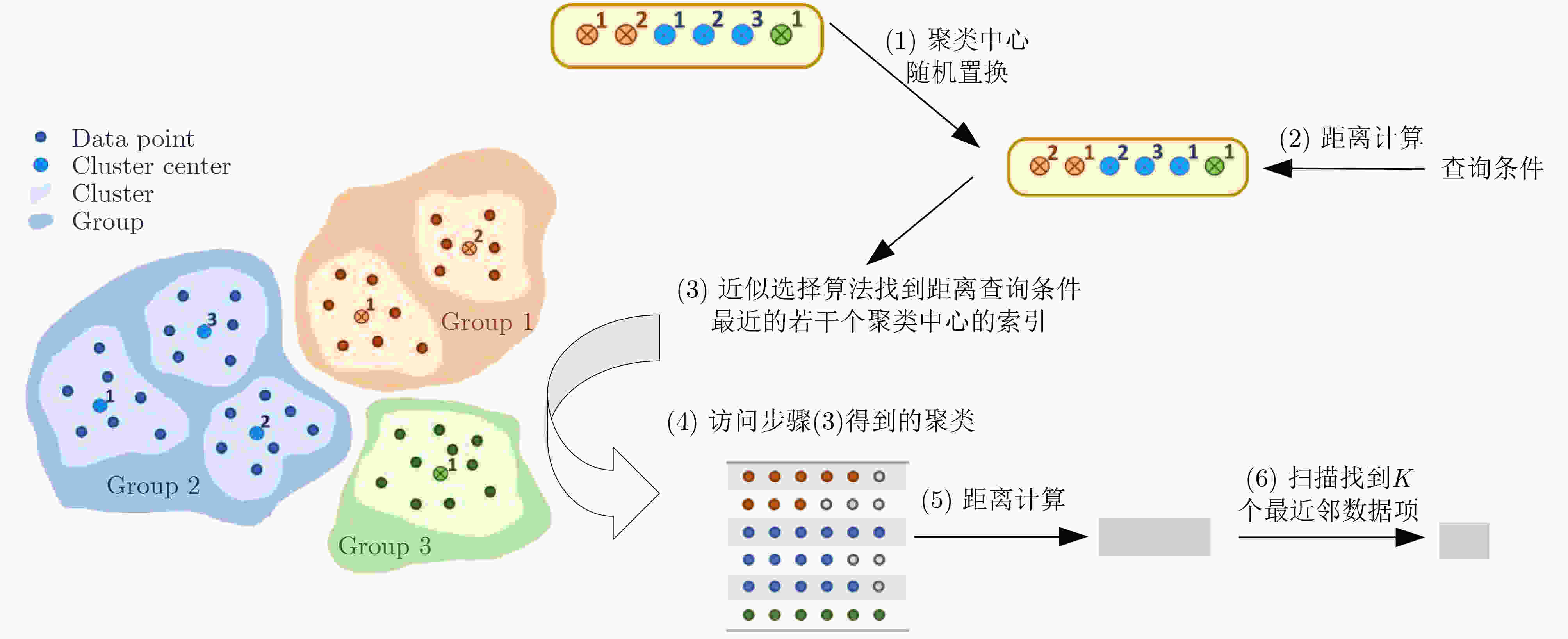
图 3 基于聚类的安全近似K近邻查询方案[47]示意图
图 4 基于LSH的安全近似最近邻查询方案[48]示意图
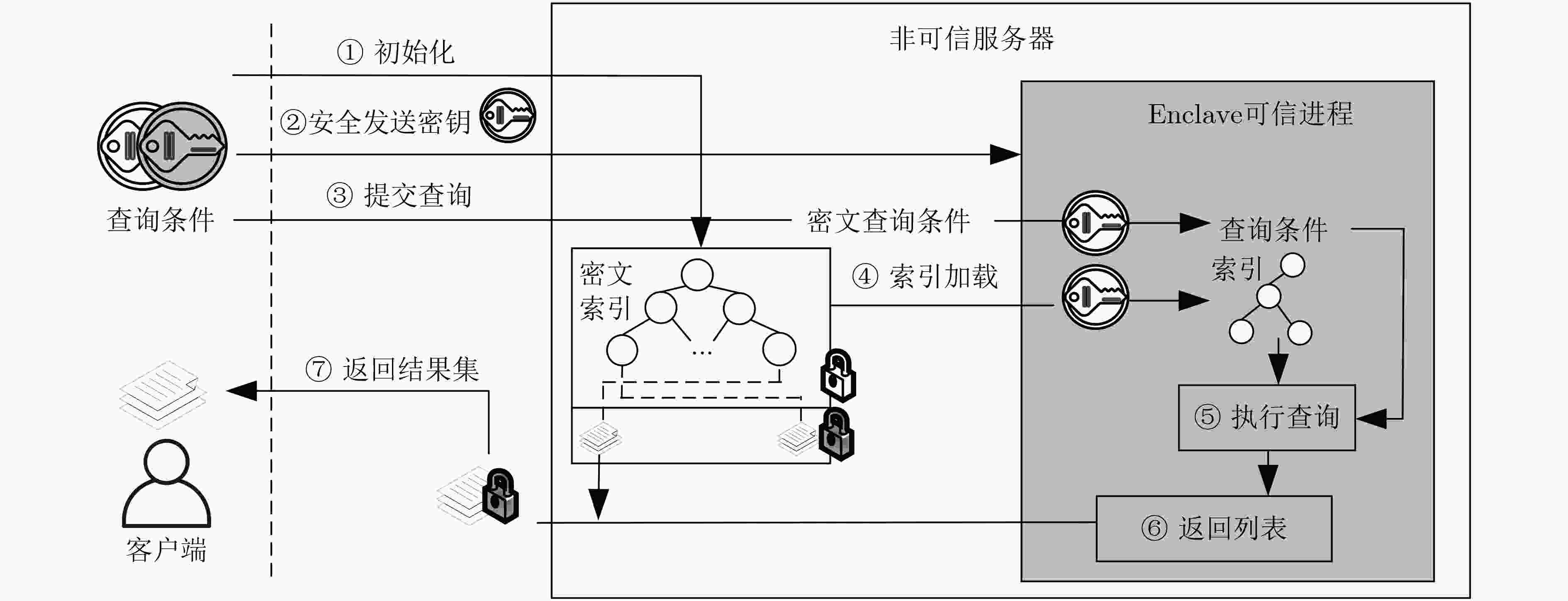
图 7 基于SGX的布尔检索方案[71]示意图
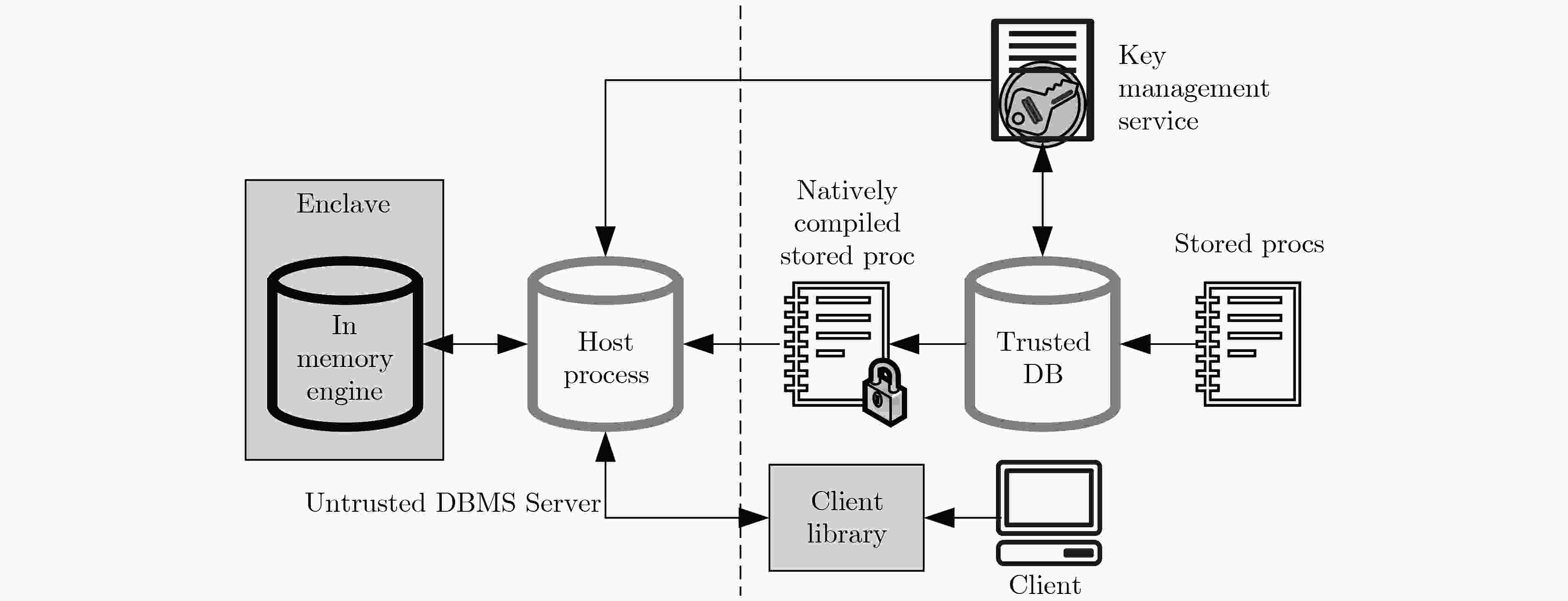
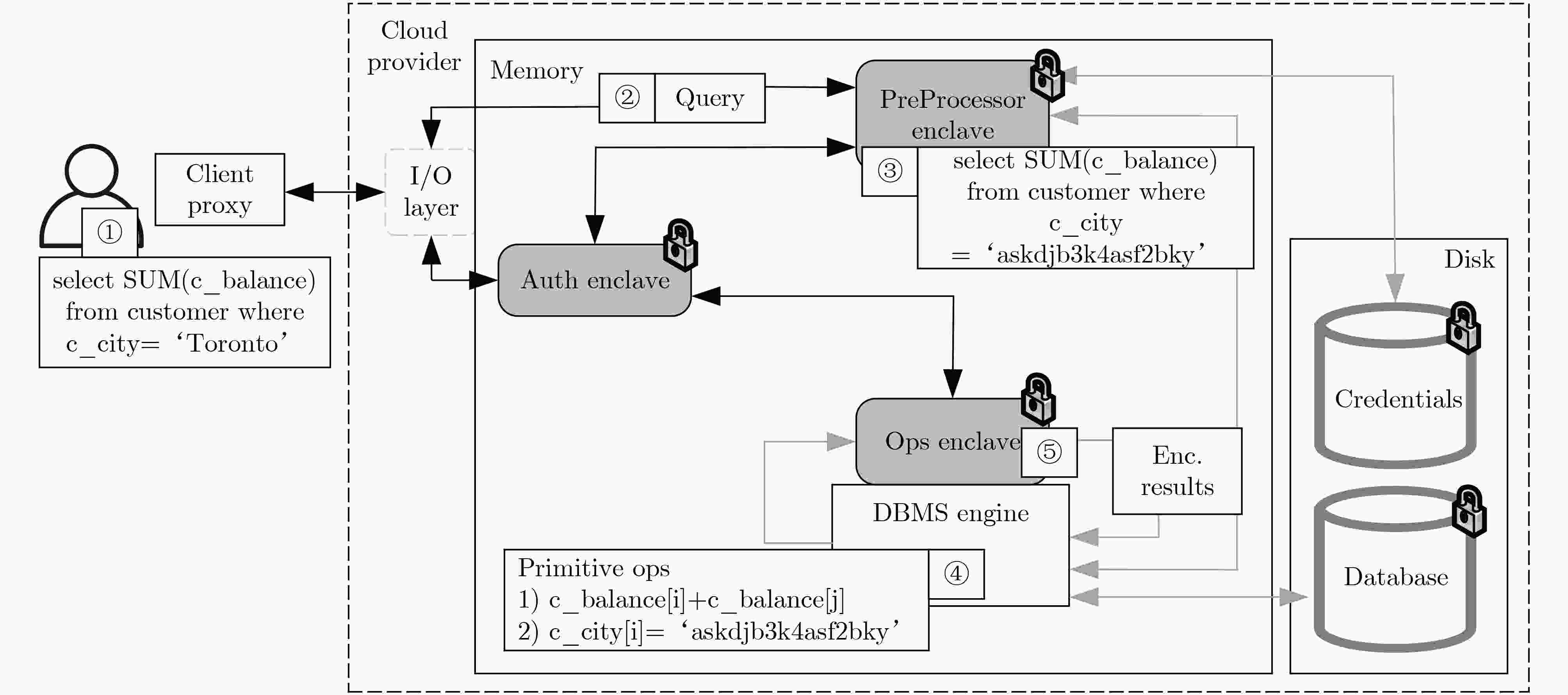
图 9 EnclaveDB[80]架构示意图
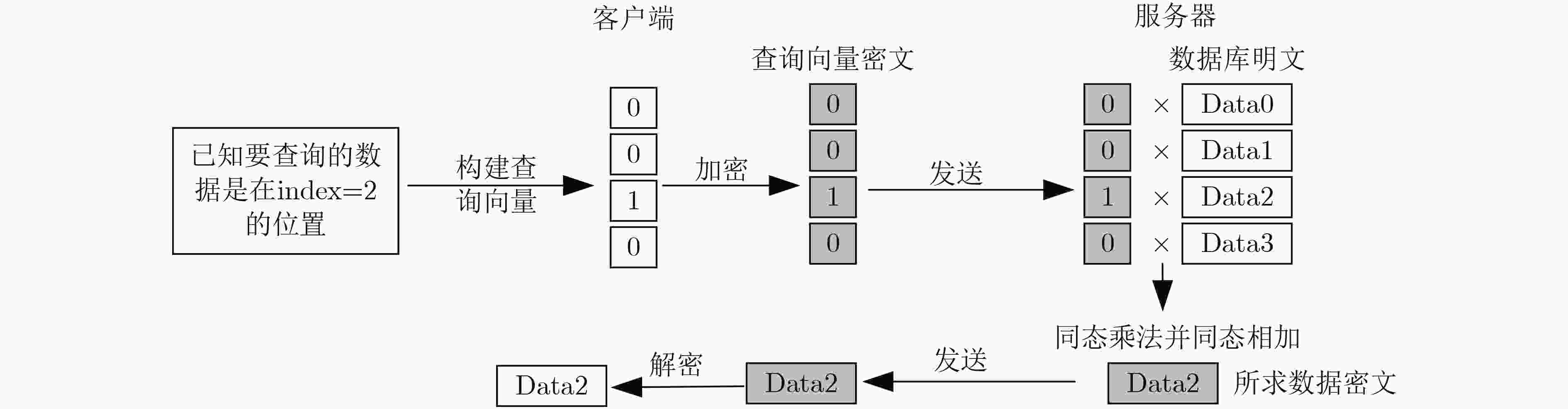
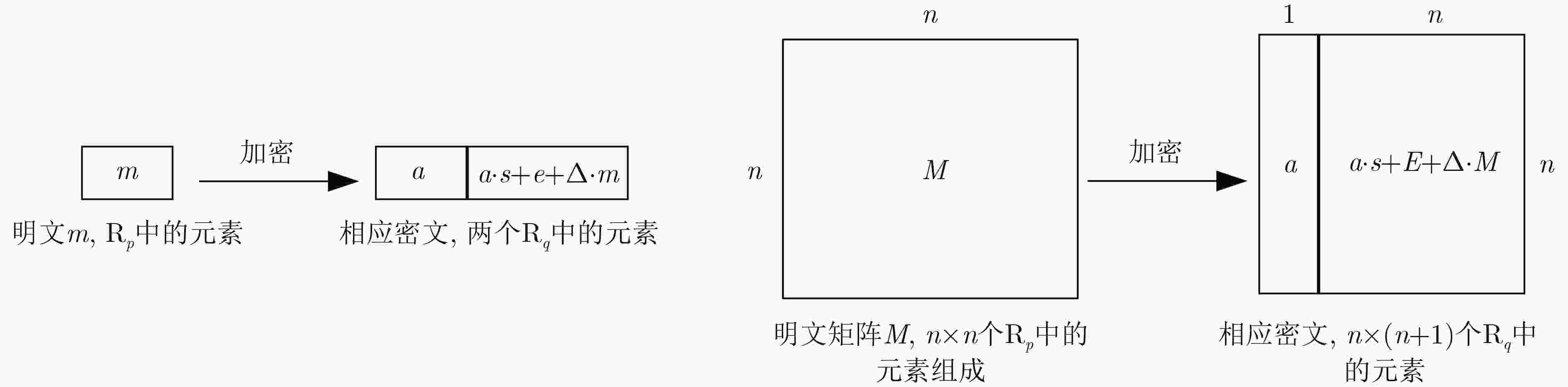
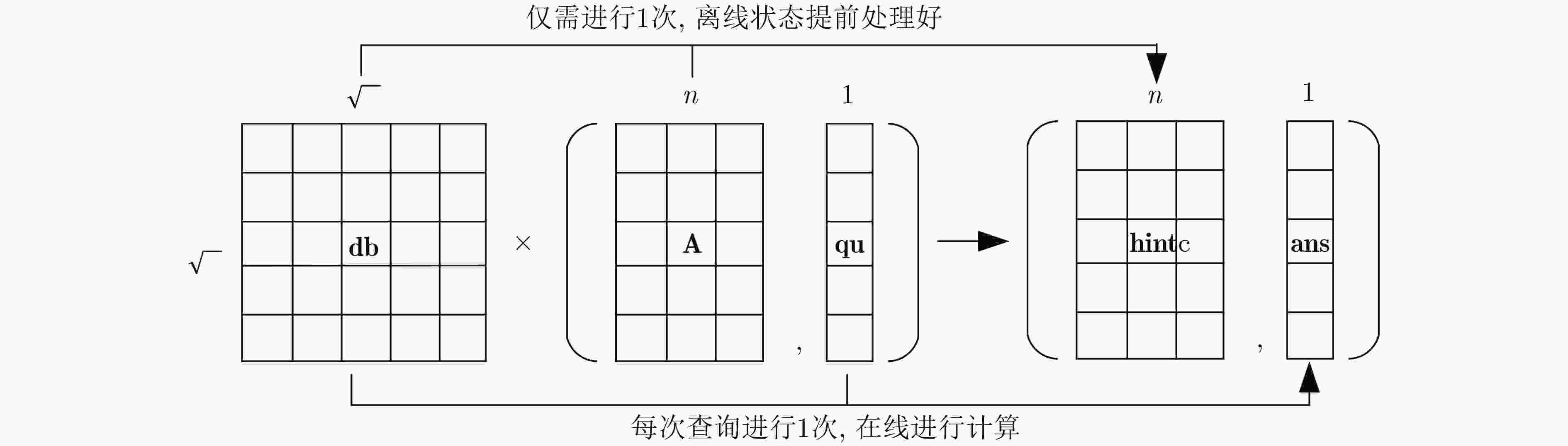
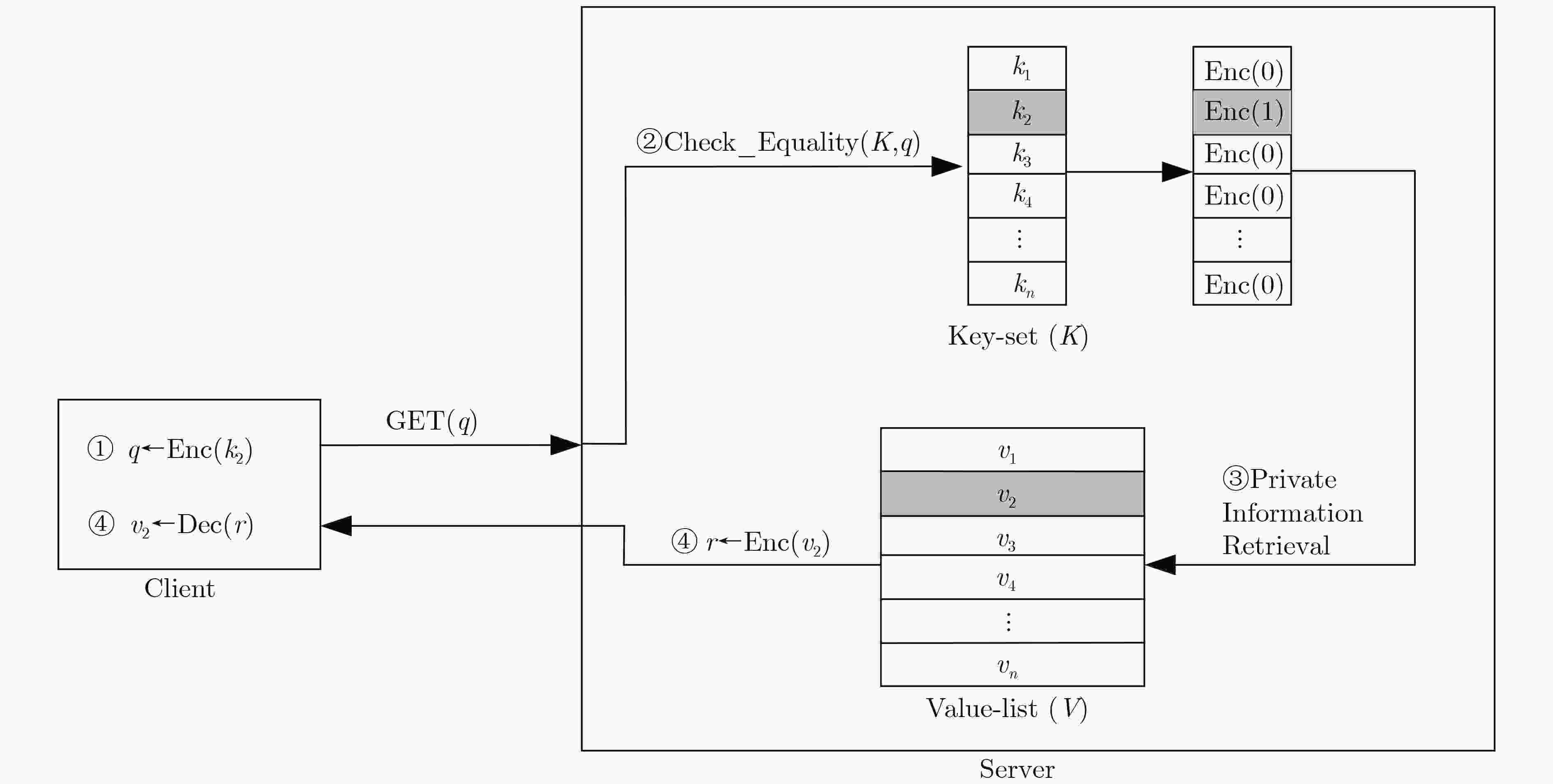
图 14 SimplePIR方案[94]示意图
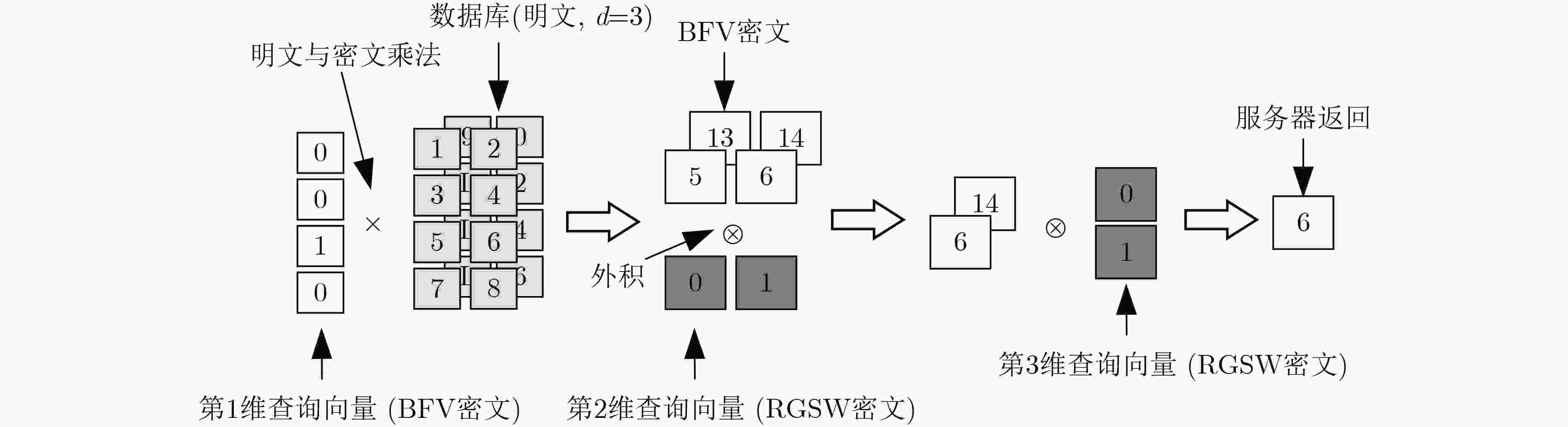
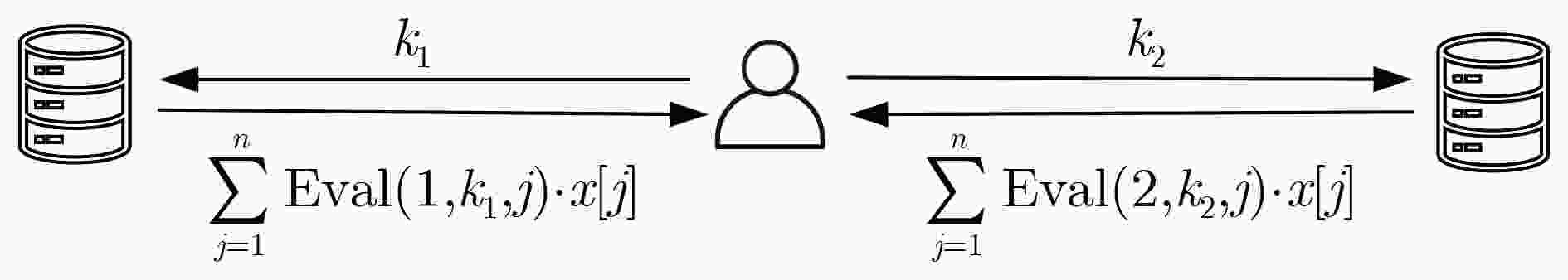
图 16 Pantheon[98]步骤示意图
表 1 PIR技术比较
安全性假设 查询尺寸 响应尺寸 计算量 XPIR[88] 基于Ring-LWE困难性假设 $ O\left(\sqrt[d]{n}\right) $ $ O\left({F}^{d-1}\right) $ $ O\left(n\right) $ SealPIR[90] 基于Ring-LWE困难性假设 $ O(\sqrt[d]{n}/N) $ $ O\left({F}^{d-1}\right) $ OnionPIR[92] 基于Ring-LWE困难性假设 $ O(\sqrt[d]{n}/N) $ $ O\left(1\right) $ SimplePIR[94] 基于LWE困难性假设 $ O\left(\sqrt{n}\right) $ $ O\left(\sqrt{n}\right) $ FrodoPIR[95] 基于LWE困难性假设 $ O\left(n\right) $ $ O\left(1\right) $ PIANO PIR[96] 统计安全 $ O\left(\sqrt{n}\right) $ $ O\left(1\right) $ $ O\left(\sqrt{n}\right) $ -
[1] CURTMOLA R, GARAY J, KAMARA S, et al. Searchable symmetric encryption: Improved definitions and efficient constructions[C]. The 13th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Alexandria, USA, 2006: 79–88. doi: 10.1145/1180405.1180417. [2] ISLAM M S, KUZU M, and KANTARCIOGLU M. Access pattern disclosure on searchable encryption: Ramification, attack and mitigation[C]. The 19th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2012: 12. [3] LIU Chang, ZHU Liehuang, WANG Mingzhong, et al. Search pattern leakage in searchable encryption: Attacks and new construction[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 265: 176–188. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2013.11.021. [4] CASH D, GRUBBS P, PERRY J, et al. Leakage-abuse attacks against searchable encryption[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Denver, USA, 2015: 668–679. doi: 10.1145/2810103.2813700. [5] NAVEED M, KAMARA S, and WRIGHT C V. Inference attacks on property-preserving encrypted databases[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Denver, USA, 2015: 644–655. doi: 10.1145/2810103.2813651. [6] POULIOT D and WRIGHT C V. The shadow nemesis: Inference attacks on efficiently deployable, efficiently searchable encryption[C]. The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 2016: 1341–1352. doi: 10.1145/2976749.2978401. [7] GRUBBS P, SEKNIQI K, BINDSCHAEDLER V, et al. Leakage-abuse attacks against order-revealing encryption[C]. The 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2017: 655–672. doi: 10.1109/SP.2017.44. [8] VAN ROMPAY C, MOLVA R, and ÖNEN M. A leakage-abuse attack against multi-user searchable encryption[J]. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2017, 2017(3): 168–178. doi: 10.1515/popets-2017-0034. [9] GRUBBS P, LACHARITÉ M S, MINAUD B, et al. Pump up the volume: Practical database reconstruction from volume leakage on range queries[C]. The 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Toronto, Canada, 2018: 315–331. doi: 10.1145/3243734.3243864. [10] BLACKSTONE L, KAMARA S, and MOATAZ T. Revisiting leakage abuse attacks[C]. The 27th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2020: 1–18. [11] PODDAR R, WANG S, LU Jianan, et al. Practical volume-based attacks on encrypted databases[C]. The 2020 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy, Genoa, Italy, 2020: 354–369. doi: 10.1109/EuroSP48549.2020.00030. [12] KORNAROPOULOS E M, PAPAMANTHOU C, and TAMASSIA R. Response-hiding encrypted ranges: Revisiting security via parametrized leakage-abuse attacks[C]. The 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2021: 1502–1519. doi: 10.1109/SP40001.2021.00044. [13] NING Jianting, HUANG Xinyi, POH G S, et al. LEAP: Leakage-abuse attack on efficiently deployable, efficiently searchable encryption with partially known dataset[C]. The 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Online Event, Republic of Korea, 2021: 2307–2320. doi: 10.1145/3460120.3484540. [14] OYA S and KERSCHBAUM F. Hiding the access pattern is not enough: Exploiting search pattern leakage in searchable encryption[C/OL]. The 30th USENIX Security Symposium, 2021: 127–142. [15] LAMBREGTS S, CHEN Huanhuan, NING Jianting, et al. VAL: Volume and access pattern leakage-abuse attack with leaked documents[C]. The 27th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022: 653–676. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-17140-6_32. [16] KELLARIS G, KOLLIOS G, NISSIM K, et al. Generic attacks on secure outsourced databases[C]. The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 2016: 1329–1340. doi: 10.1145/2976749.2978386. [17] LACHARITÉ M S, MINAUD B, and PATERSON K G. Improved reconstruction attacks on encrypted data using range query leakage[C]. The 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 297–314. doi: 10.1109/SP.2018.00002. [18] ZHANG Yupeng, KATZ J, and PAPAMANTHOU C. All your queries are belong to us: The power of file-injection attacks on searchable encryption[C]. The 25th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Austin, USA, 2016: 707–720. [19] 王贇玲, 陈晓峰. 对称可搜索加密技术研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(10): 2374–2385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190890.WANG Yunling and CHEN Xiaofeng. Research on searchable symmetric encryption[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(10): 2374–2385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190890. [20] REN Kui and WANG Cong. Searchable Encryption: From Concepts to Systems[M]. Cham: Springer, 2023: 11–12. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-21377-9. [21] 刘文心, 高莹. 对称可搜索加密的安全性研究进展[J]. 信息安全学报, 2021, 6(2): 73–84. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2021.03.05.LIU Wenxin and GAO Ying. A survey on security development of searchable symmetric encryption[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2021, 6(2): 73–84. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2021.03.05. [22] 黄一才, 李森森, 郁滨. 云环境下对称可搜索加密研究综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(3): 1134–1146. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211572.HUANG Yicai, LI Sensen, and YU Bin. A survey of symmetric searchable encryption in cloud environment[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(3): 1134–1146. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211572. [23] ZHANG Xianglong, WANG Wei, XU Peng, et al. High recovery with fewer injections: Practical binary volumetric injection attacks against dynamic searchable encryption[C]. The 32nd USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Anaheim, USA, 2023: 333. [24] CHEN Tianyang, XU Peng, PICEK S, et al. The power of bamboo: On the post-compromise security for searchable symmetric encryption[C]. The 30th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2023. [25] BRAKERSKI Z and VAIKUNTANATHAN V. Efficient fully homomorphic encryption from (standard) LWE[C]. The IEEE 52nd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Palm Springs, USA, 2011: 97–106. doi: 10.1109/FOCS.2011.12. [26] FAN Junfeng and VERCAUTEREN F. Somewhat practical fully homomorphic encryption[J]. Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2012: 144. [27] BRAKERSKI Z, GENTRY C, and VAIKUNTANATHAN V. (Leveled) fully homomorphic encryption without bootstrap[J]. ACM Transactions on Computation Theory, 2014, 6(3): 13. doi: 10.1145/2633600. [28] GENTRY C, SAHAI A, and WATERS B. Homomorphic encryption from learning with errors: Conceptually-simpler, asymptotically-faster, attribute-based[C]. The 33rd Annual Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 2013: 75–92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-40041-4_5. [29] PAILLIER P. Public-key cryptosystems based on composite degree residuosity classes[C]. The 17th International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Prague, Czech Republic, 1999: 223–238. doi: 10.1007/3-540-48910-X_16. [30] RIVEST R L, SHAMIR A, and ADLEMAN L. A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1978, 21(2): 120–126. doi: 10.1145/359340.359342. [31] GOLDREICH O and OSTROVSKY R. Software protection and simulation on oblivious RAMs[J]. Journal of the ACM, 1996, 43(3): 431–473. doi: 10.1145/233551.233553. [32] 吴鹏飞, 沈晴霓, 秦嘉, 等. 不经意随机访问机研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(9): 2753–2777. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005591.WU Pengfei, SHEN Qingni, QIN Jia, et al. Survey of oblivious RAM[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(9): 2753–2777. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005591. [33] STEFANOV E, VAN DIJK M, SHI E, et al. Path ORAM: An extremely simple oblivious RAM protocol[C]. The 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security, Berlin, Germany, 2013: 299–310. doi: 10.1145/2508859.2516660. [34] REN Ling, FLETCHER C W, KWON A, et al. Ring ORAM: Closing the gap between small and large client storage oblivious RAM[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2014, 2014: 997. [35] YU Xiangyao, HAIDER S K, REN Ling, et al. PrORAM: Dynamic prefetcher for oblivious RAM[C]. ACM/IEEE 42nd Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Portland, USA, 2015: 616–628. doi: 10.1145/2749469.2750413. [36] WANG Xiao, CHAN H, and SHI E. Circuit ORAM: On tightness of the goldreich-ostrovsky lower bound[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Denver, USA, 2015: 850–861. doi: 10.1145/2810103.2813634. [37] WANG Wenhao, CHEN Guoxing, PAN Xiaorui, et al. Leaky cauldron on the dark land: Understanding memory side-channel hazards in SGX[C]. The 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 2421–2434. doi: 10.1145/3133956.3134038. [38] CHECKOWAY S and SHACHAM H. Iago attacks: Why the system call API is a bad untrusted RPC interface[J]. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 2013, 41(1): 253–264. doi: 10.1145/2490301.2451145. [39] WONG W K, CHEUNG S W L, KAO Ben, et al. Secure kNN computation on encrypted databases[C]. The 2009 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Providence, USA, 2009: 139–152. doi: 10.1145/1559845.1559862. [40] WANG Boyang, HOU Yantian, and LI Ming. Practical and secure nearest neighbor search on encrypted large-scale data[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2016 - The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2016.7524389. [41] YAO Bin, LI Feifei, and XIAO Xiaokui. Secure nearest neighbor revisited[C]. IEEE 29th International Conference on Data Engineering, Brisbane, Australia, 2013: 733–744. doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2013.6544870. [42] LEI Xinyu, LIU A X, LI Rui, et al. SecEQP: A secure and efficient scheme for SkNN query problem over encrypted geodata on cloud[C]. IEEE 35th International Conference on Data Engineering, Macao, China, 2019: 662–673. doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2019.00065. [43] LI Rui and LIU A X. Adaptively secure conjunctive query processing over encrypted data for cloud computing[C]. IEEE 33rd International Conference on Data Engineering, San Diego, USA, 2017: 697–708. doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2017.122. [44] ELMEHDWI Y, SAMANTHULA B K, and JIANG Wei. Secure k-nearest neighbor query over encrypted data in outsourced environments[C]. IEEE 30th International Conference on Data Engineering, Chicago, USA, 2014: 664–675. doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2014.6816690. [45] CUI Ningning, YANG Xiaochun, WANG Bin, et al. SVkNN: Efficient secure and verifiable k-nearest neighbor query on the cloud platform[C]. IEEE 36th International Conference on Data Engineering, Dallas, USA, 2020: 253–264. doi: 10.1109/ICDE48307.2020.00029. [46] HJALTASON G R and SAMET H. Distance browsing in spatial databases[J]. ACM Transactions on Database Systems, 1999, 24(2): 265–318. doi: 10.1145/320248.320255. [47] CHEN Hao, CHILLOTTI I, DONG Yihe, et al. SANNS: Scaling up secure approximate k-nearest neighbors search[C/OL]. The 29th USENIX Security Symposium, Online Event, 2020: 2111–2128. [48] SERVAN-SCHREIBER S, LANGOWSKI S, and DEVADAS S. Private approximate nearest neighbor search with sublinear communication[C]. The 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 911–929. doi: 10.1109/SP46214.2022.9833702. [49] PENG Yanguo, CUI Jiangtao, LI Hui, et al. A reusable and single-interactive model for secure approximate k-nearest neighbor query in cloud[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 387: 146–164. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.07.069. [50] BOLDYREVA A and TANG Tianxin. Privacy-preserving approximate k-nearest-neighbors search that hides access, query and volume patterns[J]. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2021, 2021(4): 549–574. doi: 10.2478/popets-2021-0084. [51] LIU Jinfei, YANG Juncheng, XIONG Li, et al. Secure skyline queries on cloud platform[C]. IEEE 33rd International Conference on Data Engineering, San Diego, USA, 2017: 633–644. doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2017.117. [52] WANG Zuan, DING Xiaofeng, JIN Hai, et al. Efficient secure and verifiable location-based skyline queries over encrypted data[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2022, 15(9): 1822–1834. doi: 10.14778/3538598.3538605. [53] ZEIGHAMI S, GHINITA G, and SHAHABI C. Secure dynamic skyline queries using result materialization[C]. IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering, Chania, Greece, 2021: 157–168. doi: 10.1109/ICDE51399.2021.00021. [54] HAHN F, LOZA N, and KERSCHBAUM F. Practical and secure substring search[C]. The 2018 International Conference on Management of Data, Houston, USA, 2018: 163–176. doi: 10.1145/3183713.3183754. [55] FU Zhangjie, HUANG Fengxiao, REN Kui, et al. Privacy-preserving smart semantic search based on conceptual graphs over encrypted outsourced data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information forensics and Security, 2017, 12(8): 1874–1884. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2692728. [56] XU Lyu, JIANG Jiaxin, CHOI B, et al. Privacy preserving strong simulation queries on large graphs[C]. IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering, Chania, Greece, 2021: 1500–1511. doi: 10.1109/ICDE51399.2021.00133. [57] FUHRY B, BAHMANI R, BRASSER F, et al. HardIDX: Practical and secure index with SGX[C]. The 31st IFIP Annual Conference on Data and Applications Security and Privacy, Philadelphia, USA, 2017: 386–408. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-61176-1_22. [58] XU Jian, ZHANG Yuanjing, FU Kuiyuan, et al. SGX-based secure indexing system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 77923–77931. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2921223. [59] FERREIRA B, PORTELA B, OLIVEIRA T, et al. Boolean searchable symmetric encryption with filters on trusted hardware[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(2): 1307–1319. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2020.3012100. [60] SHAON F and KANTARCIOGLU M. SGX-IR: Secure information retrieval with trusted processors[C]. The 34th IFIP Annual Conference on Data and Applications Security and Privacy, Regensburg, Germany, 2020: 367–387. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49669-2_21. [61] JIANG Qin, CHANG E C, QI Yong, et al. Rphx: Result pattern hiding conjunctive query over private compressed index using intel SGX[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 1053–1068. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3144877. [62] CHEN Yaxing, ZHENG Qinghua, YAN Zheng, et al. QShield: Protecting outsourced cloud data queries with multi-user access control based on SGX[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 32(2): 485–499. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2020.3024880. [63] AMJAD G, KAMARA S, and MOATAZ T. Forward and backward private searchable encryption with SGX[C]. Proceedings of the 12th European Workshop on Systems Security, Dresden, Germany, 2019: 4. doi: 10.1145/3301417.3312496. [64] VO V, LAI Shangqi, YUAN Xingliang, et al. Towards efficient and strong backward private searchable encryption with secure enclaves[C]. The 19th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, Kamakura, Japan, 2021: 50–75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-78372-3_3. [65] YOON H, MOON S, KIM Y, et al. SPEKS: Forward private SGX-based public key encryption with keyword search[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(21): 7842. doi: 10.3390/app10217842. [66] HUANG Yanyu, LV Siyi, LIU Zheli, et al. Cetus: An efficient symmetric searchable encryption against file-injection attack with SGX[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(8): 182314. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3039-x. [67] MISHRA P, PODDAR R, CHEN J, et al. Oblix: An efficient oblivious search index[C]. The 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 279–296. doi: 10.1109/SP.2018.00045. [68] OHRIMENKO O, SCHUSTER F, FOURNET C, et al. Oblivious multi-party machine learning on trusted processors[C]. The 25th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Austin, USA, 2016: 619–636. [69] PODDAR R, ANANTHANARAYANAN G, SETTY S, et al. Visor: Privacy-preserving video analytics as a cloud service[C/OL]. The 29th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, 2020: 59. [70] LIU Chang, WANG X S, NAYAK K, et al. ObliVM: A programming framework for secure computation[C]. The 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2015: 359–376. doi: 10.1109/SP.2015.29. [71] JIANG Qin, QI Yong, QI Saiyu, et al. Pbsx: A practical private boolean search using Intel SGX[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 521: 174–194. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.02.031. [72] SASY S, GORBUNOV S, and FLETCHER C W. ZeroTrace: Oblivious memory primitives from Intel SGX[C]. The 25th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2018: 1–15. [73] MAINARDI N, SAMPIETRO D, BARENGHI A, et al. Efficient oblivious substring search via architectural support[C]. The 36th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Austin, USA, 2020: 526–541. doi: 10.1145/3427228.3427296. [74] POPA R A, REDFIELD C M S, ZELDOVICH N, et al. CryptDB: Protecting confidentiality with encrypted query processing[C]. The 23rd ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, Cascais, Portugal, 2011: 85–100. doi: 10.1145/2043556.2043566. [75] REN Xuanle, SU Le, GU Zhen, et al. HEDA: Multi-attribute unbounded aggregation over homomorphically encrypted database[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2022, 16(4): 601–614. doi: 10.14778/3574245.3574248. [76] BATER J, ELLIOTT G, EGGEN C, et al. SMCQL: Secure querying for federated databases[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2017, 10(6): 673–684. doi: 10.14778/3055330.3055334. [77] ZHOU Wenchao, CAI Yifan, PENG Yanqing, et al. VeriDB: An SGX-based verifiable database[C]. The 2021 International Conference on Management of Data, Online Event, China, 2021: 2182–2194. doi: 10.1145/3448016.3457308. [78] PARK J, KANG N, KIM T, et al. Nested enclave: Supporting fine-grained hierarchical isolation with SGX[C]. The ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Valencia, Spain, 2020: 776–789. doi: 10.1109/ISCA45697.2020.00069. [79] GU Jinyu, ZHU Bojun, LI Mingyu, et al. A hardware-software co-design for efficient intra-enclave isolation[C]. The 31st USENIX Security Symposium, Boston, USA, 2022: 3129–3145. [80] PRIEBE C, VASWANI K, and COSTA M. EnclaveDB: A secure database using SGX[C]. The 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 264–278. doi: 10.1109/SP.2018.00025. [81] VINAYAGAMURTHY D, GRIBOV A, and GORBUNOV S. StealthDB: A scalable encrypted database with full SQL query support[J]. Proceedings of Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2019, 2019(3): 370–388. doi: 10.2478/popets-2019-0052. [82] ANTONOPOULOS P, ARASU A, SINGH K D, et al. Azure SQL database always encrypted[C/OL]. The 2020 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Portland, USA, 2020: 1511–1525. doi: 10.1145/3318464.3386141. [83] WANG Sheng, LI Yiran, LI Huorong, et al. Operon: An encrypted database for ownership-preserving data management[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2022, 15(12): 3332–3345. doi: 10.14778/3554821.3554826. [84] ZHENG Wenting, DAVE A, BEEKMAN J G, et al. Opaque: An oblivious and encrypted distributed analytics platform[C]. The 14th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Boston, USA, 2017: 283–298. [85] ESKANDARIAN S and ZAHARIA M. ObliDB: Oblivious query processing for secure databases[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2019, 13(2): 169–183. doi: 10.14778/3364324.3364331. [86] CROOKS N, BURKE M, CECCHETTI E, et al. Obladi: Oblivious serializable transactions in the cloud[C]. The 13th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, Carlsbad, USA, 2018: 727–743. [87] MENON S J and WU D J. SPIRAL: Fast, high-rate single-server PIR via FHE composition[C]. The 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, USA, 2022: 930–947. doi: 10.1109/SP46214.2022.9833700. [88] AGUILAR-MELCHOR C, BARRIER J, FOUSSE L, et al. XPIR: Private information retrieval for everyone[J]. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETS), 2016, 2016(1): 155–174. [89] STERN J P. A new and efficient all-or-nothing disclosure of secrets protocol[C]. The International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Beijing, China, 1998: 357–371. doi: 10.1007/3-540-49649-1_28. [90] ANGEL S, CHEN Hao, LAINE K, et al. PIR with compressed queries and amortized query processing[C]. 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, USA, 2018: 962–979. doi: 10.1109/SP.2018.00062. [91] ISHAI Y, KUSHILEVITZ E, OSTROVSKY R, et al. Batch codes and their applications[C]. The 36th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Chicago, USA, 2004: 262–271. doi: 10.1145/1007352.1007396. [92] MUGHEES M H, CHEN Hao, and REN Ling. OnionPIR: Response efficient single-server PIR[C]. The 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Virtual Event, Republic of Korea, 2021: 2292–2306. doi: 10.1145/3460120.3485381. [93] GENTRY G and HALEVI S. Compressible FHE with applications to PIR[C]. The 17th Theory of Cryptography Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 2019: 438–464. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-36033-7_17. [94] HENZINGER A, HONG M M, CORRIGAN-GIBBS H, et al. One server for the price of two: Simple and fast single-server private information retrieval[C]. The 32nd USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Anaheim, USA, 2023: 218. [95] DAVIDSON A, PESTANA G, and CELI S. FrodoPIR: Simple, scalable, single-server private information retrieval[J]. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETS), 2023, 2023(1): 365–383. doi: 10.56553/popets-2023-0022. [96] ZHOU Mingxun, PARK A, SHI E, et al. Piano: Extremely simple, single-server PIR with sublinear server computation[C]. The 45th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2024. [97] MAHDAVI R A and KERSCHBAUM F. Constant-weight PIR: Single-round keyword PIR via constant-weight equality operators[C]. The 31st USENIX Security Symposium, Boston, USA, 2022: 1723–1740. [98] AHMAD I, AGRAWAL D, ABBADI A E, et al. Pantheon: Private retrieval from public key-value store[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2022, 16(4): 643–656. doi: 10.14778/3574245.3574251. [99] ISHAI Y and PASKIN A. Evaluating branching programs on encrypted data[C]. The 4th Theory of Cryptography Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007: 575–594. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-70936-7_31. [100] GARG S, HAJIABADI M, and OSTROVSKY R. Efficient range-trapdoor functions and applications: Rate-1 OT and more[C]. Proceedings of the 18th Theory of Cryptography Conference, Durham, USA, 2020: 88–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-64375-1_4. [101] CHASE M, GARG S, HAJIABADI M, et al. Amortizing rate-1 OT and applications to PIR and PSI[C]. The 19th Theory of Cryptography Conference, Raleigh, USA, 2021: 126–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-90456-2_5. [102] LIU Jian, LI Jingyu, WU Di, et al. PIRANA: Faster multi-query PIR via constant-weight codes[J]. 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), 2024: 43. doi: 10.1109/SP54263.2024.00039. [103] PATEL S, SEO J Y, and YEO K. Don't be dense: Efficient keyword PIR for sparse databases[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2023, 2023: 466. [104] CHOR B, KUSHILEVITZ E, GOLDREICH O, et al. Private information retrieval[J]. Journal of the ACM, 1998, 45(6): 965–981. doi: 10.1145/293347.293350. [105] AMBAINIS A. Upper bound on the communication complexity of private information retrieval[C]. The 24th International Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming, Bologna, Italy, 1997: 401–407. doi: 10.1007/3-540-63165-8_196. [106] BEIMEL A, ISHAI Y, KUSHILEVITZ E, et al. Breaking the O(n1/(2k-1)) barrier for information-theoretic private information retrieval[C]. The 43rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Vancouver, Canada, 2002: 261–270. doi: 10.1109/SFCS.2002.1181949. [107] BEIMEL A and STAHL Y. Robust information-theoretic private information retrieval[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2007, 20(3): 295–321. doi: 10.1007/s00145-007-0424-2. [108] REED I S and SOLOMON G. Polynomial codes over certain finite fields[J]. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1960, 8(2): 300–304. doi: 10.1137/0108018. [109] ERIGUCHI R, KUROSAWA K, and NUIDA K. Multi-server PIR with full error detection and limited error correction[C]. The 3rd Conference on Information-Theoretic Cryptography, Cambridge, USA, 2022: 1: 1–1: 20. [110] KATZ J and TREVISAN L. On the efficiency of local decoding procedures for error-correcting codes[C]. The 32nd Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Portland, USA, 2000: 80–86. doi: 10.1145/335305.335315. [111] YEKHANIN S. Towards 3-query locally decodable codes of subexponential length[J]. Journal of the ACM, 2008, 55(1): 1. doi: 10.1145/1326554.1326555. [112] EFREMENKO K. 3-query locally decodable codes of subexponential length[C]. The 41st Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Bethesda, USA, 2009: 39–44. doi: 10.1145/1536414.1536422. [113] GROLMUSZ V. Superpolynomial size set-systems with restricted intersections mod 6 and explicit Ramsey graphs[J]. Combinatorica, 2000, 20(1): 71–86. doi: 10.1007/s004930070032. [114] DVIR Z and GOPI S. 2-server PIR with subpolynomial communication[J]. Journal of the ACM, 2016, 63(4): 39. doi: 10.1145/2968443. [115] BEIMEL A, ISHAI Y, KUSHILEVITZ E, et al. Share conversion and private information retrieval[C]. IEEE 27th Conference on Computational Complexity, Porto, Portugal, 2012: 258–268. doi: 10.1109/CCC.2012.23. [116] GILBOA N and ISHAI Y. Distributed point functions and their applications[C]. The 33rd Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014: 640–658. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55220-5_35. [117] BOYLE E, GILBOA N, and ISHAI Y. Function secret sharing[C]. The 34th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2015: 337–367. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-46803-6_12. [118] BATER J, HE Xi, EHRICH W, et al. Shrinkwrap: Efficient SQL query processing in differentially private data federations[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2018, 12(3): 307–320. doi: 10.14778/3291264.3291274. [119] QIN Lianke, JAYARAM R, SHI E, et al. Adore: Differentially oblivious relational database operators[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2022, 16(4): 842–855. doi: 10.14778/3574245.3574267. -





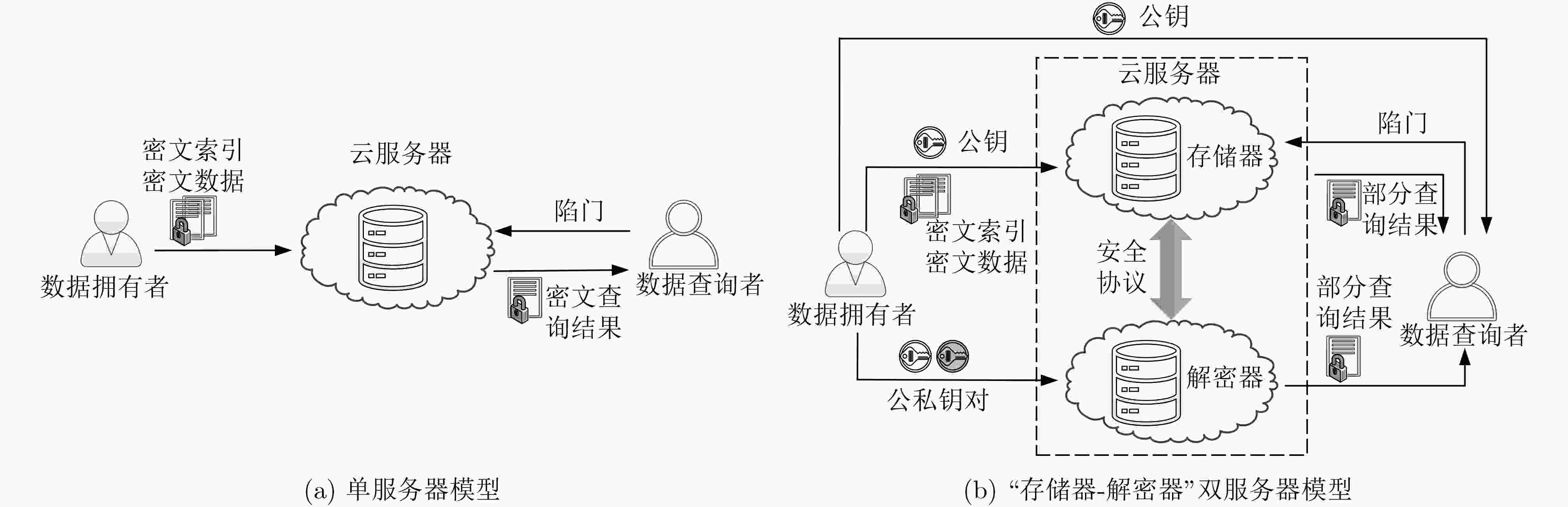
 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
