Radar Emitter Identification Based on Dual Radio Frequency Fingerprint Convolutional Neural Network and Feature Fusion
-
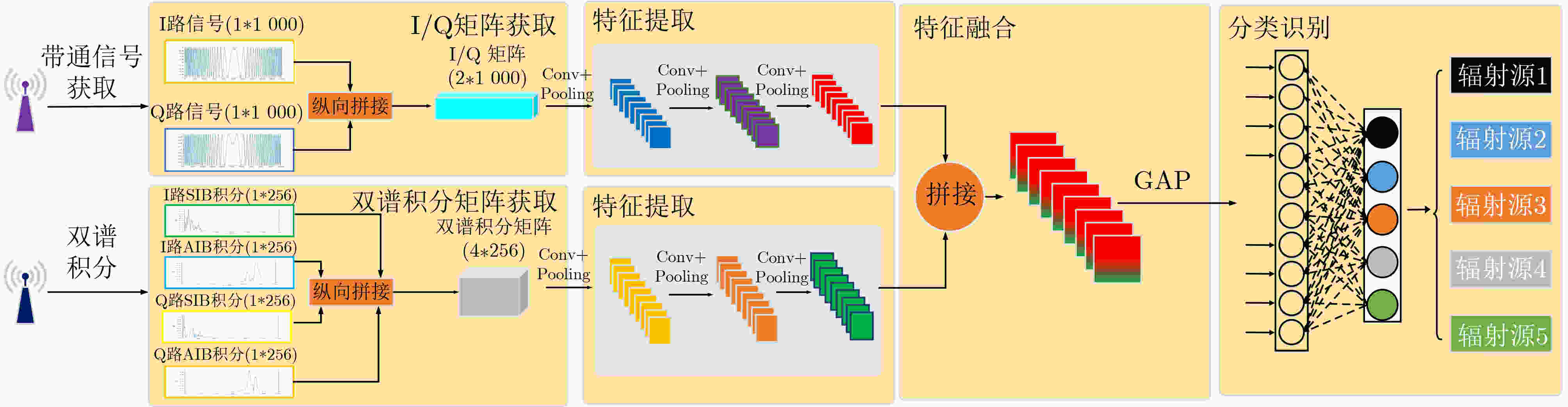
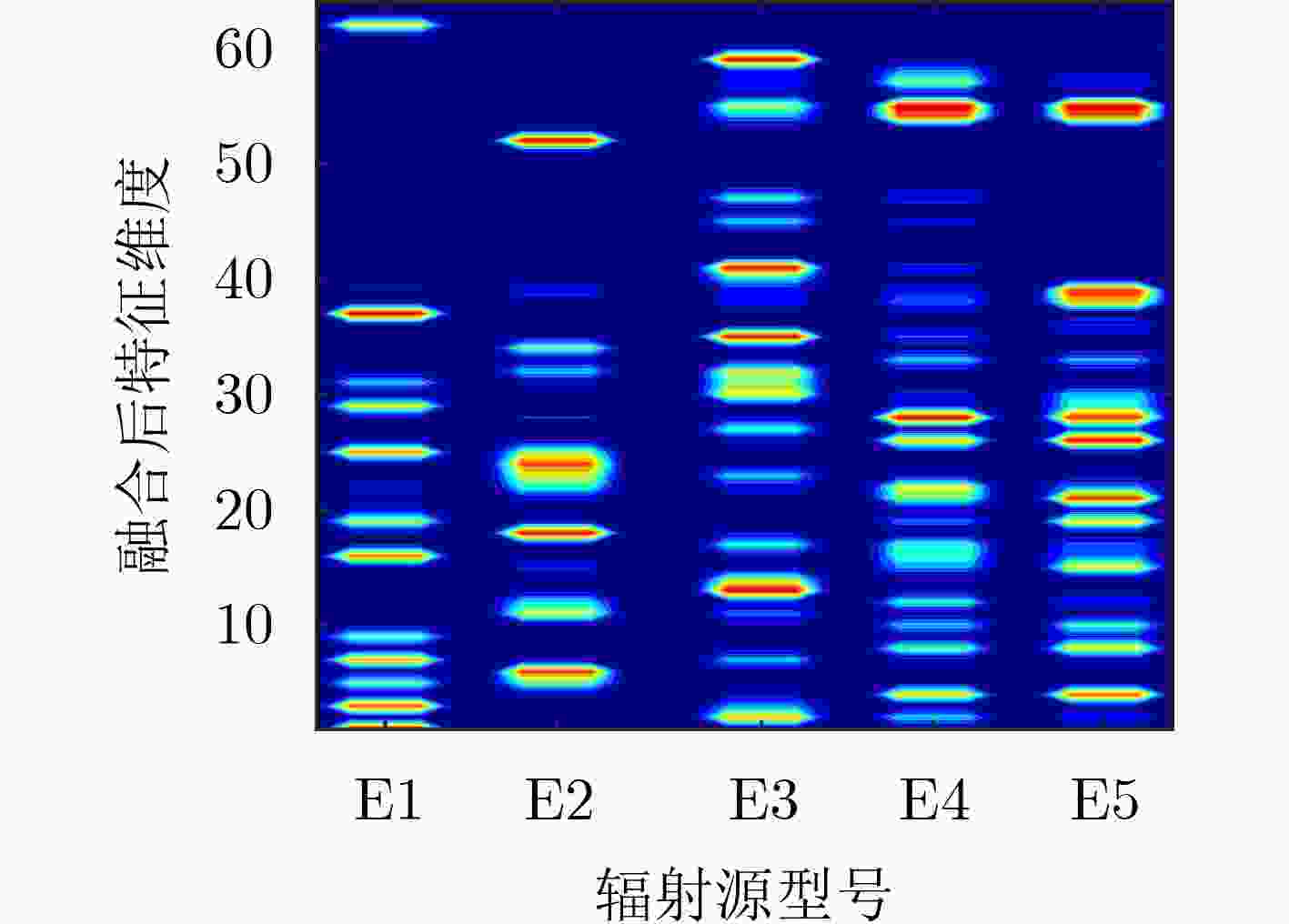
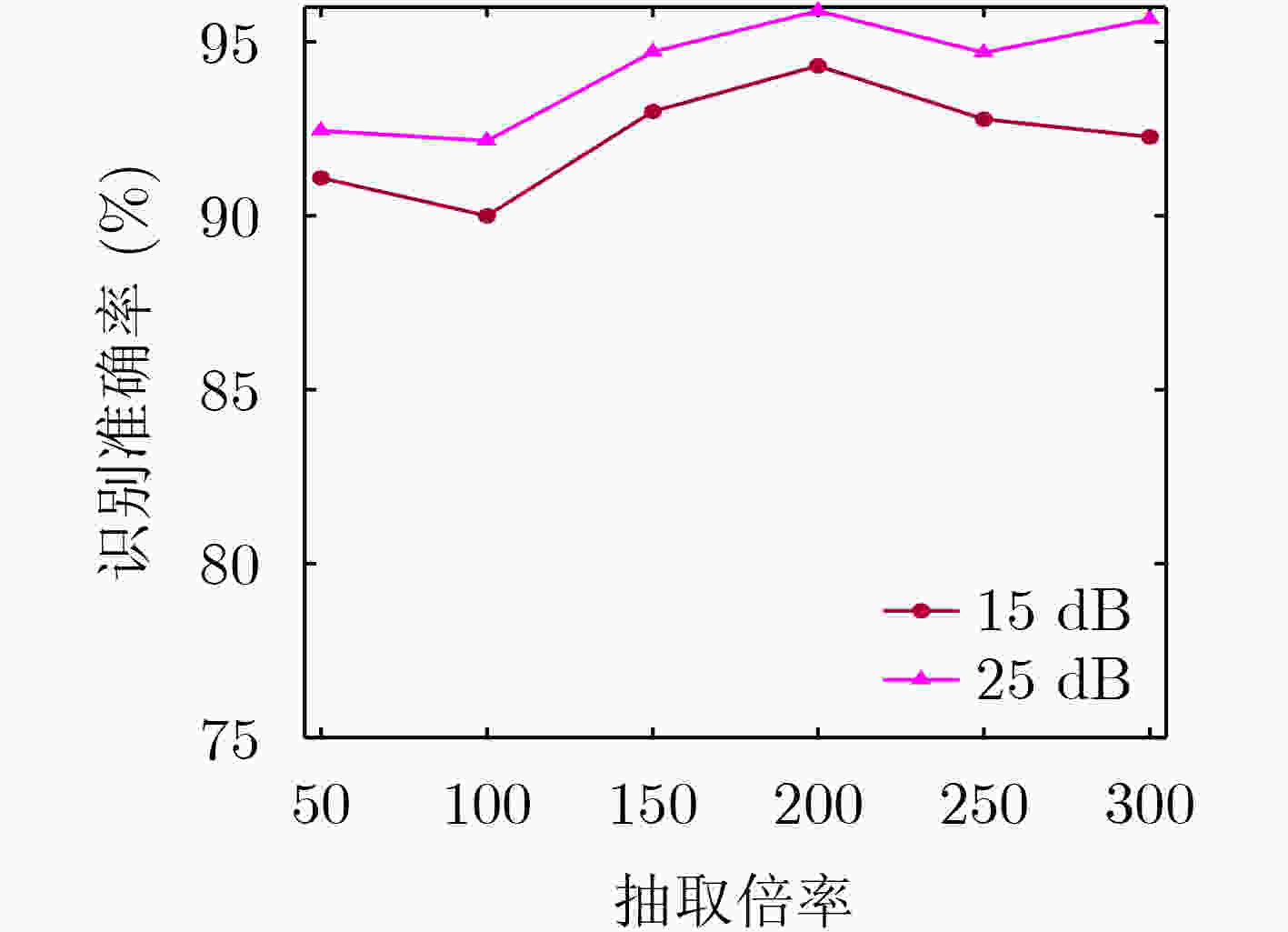
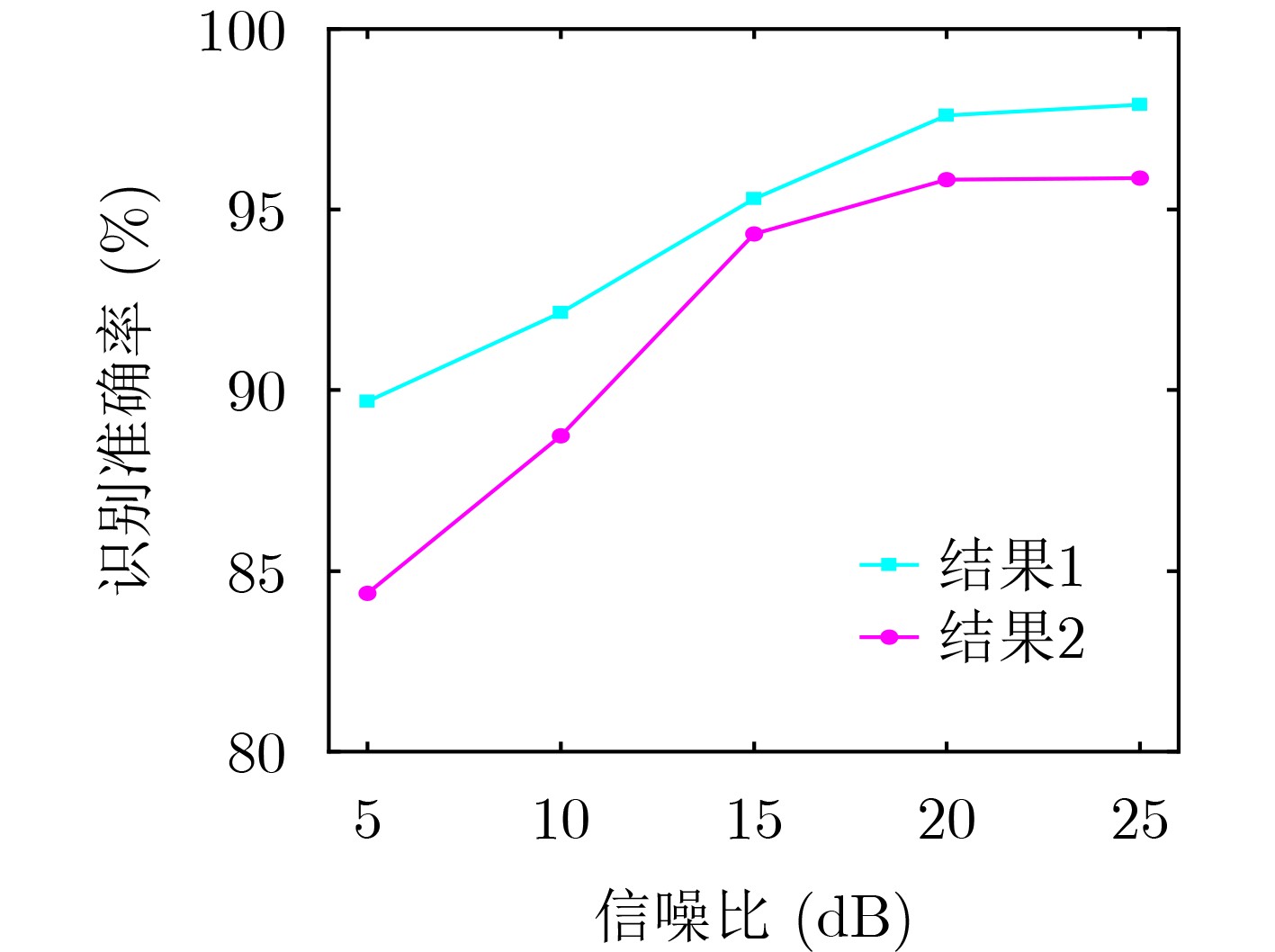
摘要: 为实现雷达辐射源个体识别不受信号参数、调制方式的影响,该文提出基于双路射频指纹卷积神经网络(Dual RFF-CNN2)和特征融合的雷达辐射源个体识别方法。首先从接收的射频信号中提取原始I/Q(Raw-I/Q)信号;其次分别对Raw-I/Q两路信号进行轴向积分双谱(AIB)和围线积分双谱(SIB)降维以构建双谱积分矩阵;最后将Raw-I/Q信号及双谱积分矩阵共同送入Dual RFF-CNN2网络并进行特征融合以实现雷达辐射源个体识别。实验结果表明,该方法具有较高的识别准确率,提取的“指纹特征”具备稳定性、鲁棒性。
-
关键词:
- 雷达辐射源个体识别 /
- 双路射频指纹卷积神经网络 /
- 特征融合 /
- 指纹特征 /
- 原始I/Q信号
Abstract: In order to achieve identification of radar emitter unaffected by signal parameters and modulation methods, a method based on Dual Radio Frequency Fingerprint Convolutional Neural Network (Dual RFF-CNN2) and feature fusion is proposed in this paper. Firstly, Raw-In-phase/Quadrature (Raw-I/Q) signals are extracted from the received radio frequency signals. Secondly, Axially Integral Bispectrum (AIB) and Square Integral Bispectrum (SIB) dimensionality reduction are performed separately on Raw-I/Q signals to construct the bispectrum integration matrix. Finally, both the Raw-I/Q signals and the bispectrum integration matrix are fed into the Dual RFF-CNN2 network for feature fusion to achieve identification of radar emitter. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves high identification accuracy, and the extracted "fingerprint features" exhibit stability and robustness. -
表 1 信号参数设置
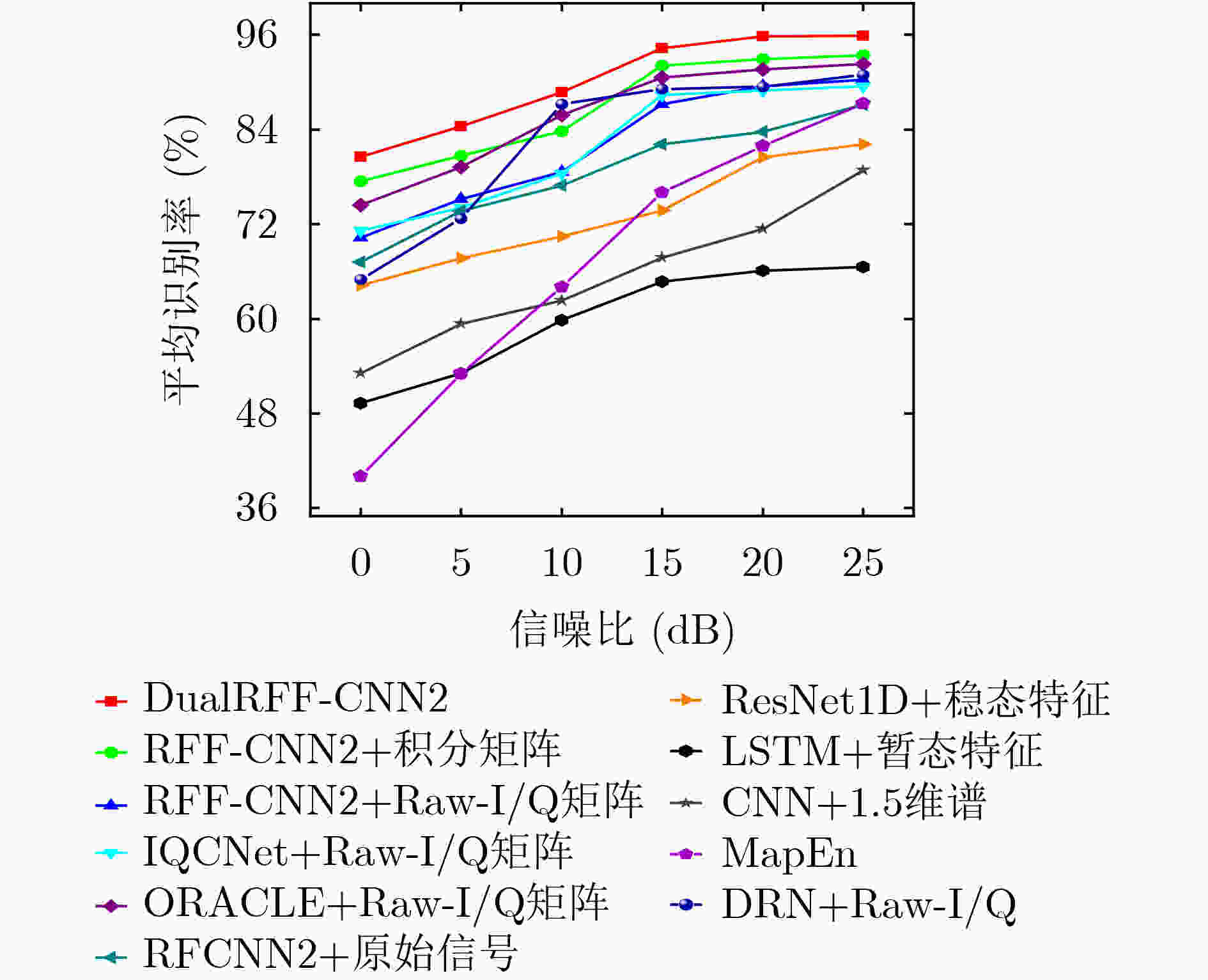
调制方式 参数 取值 LFM 中心频率(GHz) 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 带宽(MHz) 10, 20, 30 脉宽(${\text{μs}}$) 10 调频斜率 +/– BPSK 中心频率(GHz) 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 巴克码序列长度 13 脉宽(${\text{μs}}$) 10 表 2 不同算法的性能对比
网络模型 平均识别
准确率(%)模型大小
(kB)浮点运算
量(M)DualRFF-CNN2 95.8 40.37 10.65 RFF-CNN2+积分矩阵 93.4 20.18 2.41 RFF-CNN2+Raw-I/Q矩阵 90.3 20.18 8.24 IQCNet+Raw-I/Q矩阵 89.5 25.69 12.06 ORACLE+Raw-I/Q矩阵 92.3 133.67 0.58 ResNet1D+稳态特征 87.1 8.86 0.79 RFF-CNN2+原始信号 82.1 20.18 8.24 CNN+1.5维谱 66.5 10.94 1.36 LSTM+暂态特征 78.8 468.61 18.88 DRN+Raw-I/Q 90.9 17.25 2.76 -
[1] ZHAO Shiqiang, ZENG Deguo, WANG Wenhai, et al. Mutation grey wolf elite PSO balanced XGBoost for radar emitter individual identification based on measured signals[J]. Measurement, 2020, 159(5): 107777. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.107777. [2] ELDEMERDASH Y A, DOBRE O A, ÜRETEN O, et al. Identification of cellular networks for intelligent radio measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(8): 2204–2211. doi: 10.1109/tim.2017.2687539. [3] MERCHANT K, REVAY S, STANTCHEV G, et al. Deep learning for RF device fingerprinting in cognitive communication networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 160–167. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2796446. [4] 陈蒙, 邢小鹏, 陈世文, 等. 基于贝塞尔曲线的雷达信号脉内无意调相特征提取及个体识别[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2022, 23(1): 9–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2022.01.002.CHEN Meng, XING Xiaopeng, CHEN Shiwen, et al. Unintentional phase modulation on pulse feature extraction and radar specific emitter identification based on Bezier curve[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2022, 23(1): 9–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2022.01.002. [5] 秦鑫, 黄洁, 王建涛, 等. 基于无意调相特性的雷达辐射源个体识别[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(5): 104–111. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020084.QIN Xin, HUANG Jie, WANG Jiantao, et al. Radar emitter identification based on unintentional phase modulation on pulse characteristic[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(5): 104–111. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020084. [6] RU Xiaohu, YE Haohuan, LIU Zheng, et al. An experimental study on secondary radar transponder UMOP characteristics[C]. 2016 European Radar Conference, London, UK, 2016: 314–317. [7] LUO Zhenyu, CAO Yunhe, YEO T S, et al. Few-Shot radar jamming recognition network via time-frequency self-attention and global knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5105612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3280322. [8] 李宝平, 魏坡. 基于CWD谱图和改进CNN的无线电调制分类[J]. 电子测量技术, 2023, 46(5): 50–56. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2210805.LI Baoping and WEI Po. Radio modulation classification based on CWD spectrogram and improved CNN[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2023, 46(5): 50–56. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2210805. [9] ZHEN Pan, ZHANG Bangning, CHEN Zhibo, et al. Spectrum sensing method based on wavelet transform and residual network[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(12): 2517–2521. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3207296. [10] LI Jianfeng, HUANG Dingkun, YAN Xiaopeng, et al. Low SNR FM signal preprocessing method based on low-order cyclic statistics and WVD distribution[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Control, Mianyang, China, 2023: 258–262. doi: 10.1109/RAIIC59453.2023.10280797. [11] SATIJA U, TRIVEDI N, BISWAL G, et al. Specific emitter identification based on variational mode decomposition and spectral features in single hop and relaying scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(3): 581–591. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2855665. [12] 肖易寒, 李栋年, 于祥祯, 等. 基于参数优化VMD和LightGBM的雷达辐射源个体识别[J]. 航空兵器, 2022, 29(2): 93–100. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2021.0073.XIAO Yihan, LI Dongnian, YU Xiangzhen, et al. Radar emitter individual identification based on parameter optimization VMD and LightGBM[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2022, 29(2): 93–100. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2021.0073. [13] 陈翔, 汪连栋, 许雄, 等. 基于Raw I/Q和深度学习的射频指纹识别方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 214–234. doi: 10.12000/JR22140.CHEN Xiang, WANG Liandong, XU Xiong, et al. A review of radio frequency fingerprinting methods based on Raw I/Q and deep learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 214–234. doi: 10.12000/JR22140. [14] TU Ya, LIN Yun, ZHA Haoran, et al. Large-scale real-world radio signal recognition with deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(9): 35–48. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.08.016. [15] SANKHE K, BELGIOVINE M, ZHOU Fan, et al. ORACLE: Optimized radio clAssification through convolutional neuraL nEtworks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Pairs, France, 2019: 370–378. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2019.8737463. [16] YU Jiabao, HU Aiqun, LI Guyue, et al. A robust RF fingerprinting approach using multisampling convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(4): 6786–6799. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2911347. [17] WAN Tao, JI Hao, XIONG Wanan, et al. Deep learning-based specific emitter identification using integral bispectrum and the slice of ambiguity function[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2022, 16(7): 2009–2017. doi: 10.1007/s11760-022-02162-x. [18] ELMAGHBUB A and HAMDAOUI B. Leveraging hardware-impaired out-of-band information through deep neural networks for robust wireless device classification[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.11126, 2020. [19] 王亮, 肖易寒. Transformer网络在雷达辐射源识别中的应用[J]. 应用科技, 2021, 48(5): 81–85,104. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202101008.WANG Liang and XIAO Yihan. Application of transformer network in radar emitter recognition[J]. Applied Science and Technology, 2021, 48(5): 81–85,104. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202101008. [20] 崔天舒, 赵文杰, 黄永辉, 等. 基于射频指纹的测控地面站身份识别方法[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2021, 37(3): 6–9,23. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2021.03.002.CUI Tianshu, ZHAO Wenjie, HUANG Yonghui, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint-based TT&C ground station identification method[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2021, 37(3): 6–9,23. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2021.03.002. [21] SUN Liting, WANG Xiang, YANG Afeng, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multi-dimension approximate entropy[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 471–475. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2978333. [22] 翁琳天然, 彭进霖, 何元, 等. 基于深度残差网络的ADS-B信号辐射源个体识别[J]. 航空兵器, 2021, 28(4): 24–29. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2020.0095.WENG Lintianran, PENG Jinlin, HE Yuan, et al. Specific emitter identification of ADS-B signal based on deep residual network[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2021, 28(4): 24–29. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2020.0095. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
