A Review of Research on Time Series Classification Based on Deep Learning
-
摘要: 时间序列分类(TSC)是数据挖掘领域中最重要且最具有挑战性的任务之一。深度学习技术在自然语言处理和计算机视觉领域已取得革命性进展,同时在时间序列分析等其他领域也显示出巨大的潜力。该文对基于深度学习的时间序列分类的最新研究成果进行了详细综述。首先,定义了关键术语和相关概念。其次,从多层感知机、卷积神经网络、循环神经网络和注意力机制4个网络架构角度分类总结了当前最新的时间序列分类模型,及各自优点和局限性。然后,概述了时间序列分类在人体活动识别和脑电图情绪识别两个关键领域的最新进展和挑战。最后,讨论了将深度学习应用于时间序列数据时未解决的问题和未来研究方向。该文为研究者了解最新基于深度学习的时间序列分类研究动态、新技术和发展趋势提供了参考。Abstract: Time Series Classification(TSC) is one of the most important and challenging tasks in the field of data mining. Deep learning techniques have achieved revolutionary progress in natural language processing and computer vision, and have also demonstrated great potential in areas such as time series analysis. A detailed review of the latest research advances in deep learning-based TSC is provided in this paper. Firstly, key terms and related concepts are defined. Secondly, the latest time series classification models are classified from four perspectives of network architectures: multilayer perceptron, convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks, and attention mechanisms, along with their respective advantages and limitations. Additionally, the latest developments and challenges in time series classification in the fields of human activity recognition and electroencephalogram-based emotion recognition are outlined. Finally, the unresolved issues and future research directions when applying deep learning to time series data are discussed. This paper provides researchers with a reference for understanding the latest research dynamics, new technologies, and development trends in the deep learning-based time series classification field.
-
Key words:
- Deep learning /
- Time series /
- Neural networks /
- Classification /
- Review
-
表 1 UCR和UEA时间序列数据集详细信息
数据集 维度 数量 类别数量 训练集大小 序列长度 类型 UCR 1 128 2~60 16~ 8926 24~2 709 图像轮廓、传感器读数、动作分类、心电图、电子设备和模拟数据等 UEA 2~ 1345 30 2~39 12~30 000 8~17 984 心电图、运动分类、光谱分类等 表 2 基于CNN的时间序列分类模型总结
模型 提出年份 基准架构 模型特点 自适应模型 MC-DCNN[26] 2014 2-Stage Conv 每个通道独立卷积 MC-CNN[27] 2015 3-Stage Conv 所有通道1D卷积 Zhao et al.[28] 2017 2-Stage Conv 所有通道1D卷积 FCN[11] 2017 FCN 使用GAP替代FC层 ResNet[11] 2017 ResNet 9 使用3个残差块 Res-CNN[32] 2019 ResNet+FCN 使用1个残差块+FCN DCNNs[34] 2019 4-Stage Conv 使用扩张卷积 Disjoint-CNN[35] 2021 4-Stage Conv 分离型时空卷积 时间序列转换为图像 Wang&Oates[36] 2015 Tiled CNN 格拉姆角场和马尔可夫转移场图像编码 Hatami et al.[37] 2018 2-Stage Conv 递归图图像编码 Karimi et al.[38] 2018 Inception V3 格拉姆差角场图像编码 RPMCNN[41] 2019 VGGNet, 2-Stage Conv 相对位置矩阵图像编码 Yang et al.[39] 2019 VGGNet 格拉姆差角场、格拉姆加和场和马尔可夫转移场图像编码 多尺度卷积操作 MCNN[43] 2016 2-Stage Conv 恒等映射、下采样和平滑预处理 t-LeNet[24] 2016 2-Stage Conv 挤压和扩展预处理 MVCNN[46] 2019 4-stage Conv 基于Inception V1卷积 Inception-ResNet[47] 2021 ResNet 基于Inception V1卷积 InceptionTime[9] 2020 Inception V4 多分类器集成模型 EEG-inception[48] 2021 InceptionTime Inception-FCN[49] 2021 InceptionTime + FCN MRes-FCN[50] 2022 FCN + ResNet 使用多个串行多尺度卷积核 表 3 基于注意力的时间序列分类模型总结
模型 提出年份 Embedding 注意力 自适应模型 MuVAN[78] 2018 Bi-GRU 注意力 ChannelAtt[81] 2018 RNN 注意力 GeoMAN[82] 2018 LSTM 注意力 Multi-Stage-Att[83] 2020 LSTM 注意力 CT_CAM[84] 2020 FCN + Bi-GRU 注意力 CA-SFCN[14] 2020 FCN 注意力 RTFN[85] 2021 CNN + LSTM 注意力 LAXCAT[79] 2021 CNN 注意力 MACNN[80] 2021 Multi-scale CNN 注意力 Transformers SAnD[89] 2018 线性Embedding 多头注意力 T2[91] 2021 高斯过程 多头注意力 GTN[93] 2021 线性Embedding 多头注意力 TRANS_tf[90] 2021 时频特征 多头注意力 FMLA[94] 2023 可变形卷积 多头注意力 TFFormer[95] 2023 线性Embedding 多头注意力 自监督注意力 BENDER[71] 2021 Wav2Vec 2.0+ 自监督 多头注意力 TST[15] 2021 线性Embeddin+自监督 多头注意力 TARNet 2022 线性Embedding+自监督 多头注意力 TEST[97] 2023 线性Embedding+自监督 多头注意力 -
[1] YANG Qiang and WU Xindong. 10 Challenging problems in data mining research[J]. International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making, 2006, 5(4): 597–604. doi: 10.1142/S0219622006002258. [2] BAGNALL A, LINES J, BOSTROM A, et al. The great time series classification bake off: A review and experimental evaluation of recent algorithmic advances[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2017, 31(3): 606–660. doi: 10.1007/s10618-016-0483-9. [3] ZHANG Shibo, LI Yaxuan, ZHANG Shen, et al. Deep learning in human activity recognition with wearable sensors: A review on advances[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(4): 1476. doi: 10.3390/s22041476. [4] CHEN Kaixuan, ZHANG Dalin, YAO Lina, et al. Deep learning for sensor-based human activity recognition: Overview, challenges, and opportunities[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 54(4): 77. doi: 10.1145/3447744. [5] KHADEMI Z, EBRAHIMI F, and KORDY H M. A transfer learning-based CNN and LSTM hybrid deep learning model to classify motor imagery EEG signals[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2022, 143: 105288. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105288. [6] ABANDA A, MORI U, and LOZANO J A. A review on distance based time series classification[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2019, 33(2): 378–412. doi: 10.1007/s10618-018-0596-4. [7] DAU H A, BAGNALL A, KAMGAR K, et al. The UCR time series archive[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(6): 1293–1305. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911747. [8] BAGNALL A, DAU H A, LINES J, et al. The UEA multivariate time series classification archive, 2018[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.00075, 2018. [9] ISMAIL FAWAZ H, LUCAS B, FORESTIER G, et al. Inceptiontime: Finding alexnet for time series classification[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2020, 34(6): 1936–1962. doi: 10.1007/s10618-020-00710-y. [10] ISMAIL FAWAZ H, FORESTIER G, WEBER J, et al. Deep learning for time series classification: A review[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2019, 33(4): 917–963. doi: 10.1007/s10618-019-00619-1. [11] WANG Zhiguang, YAN Weizhong, and OATES T. Time series classification from scratch with deep neural networks: A strong baseline[C]. 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, USA, 2017: 1578–1585. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN.2017.7966039. [12] ZHOU Haoyi, ZHANG Shanghang, PENG Jieqi, et al. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting[C]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 11106–11115. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i12.17325. [13] WEN Qingsong, ZHOU Tian, ZHANG Chaoli, et al. Transformers in time series: A survey[J]. Proceedings of the Thirty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 2022: 6778–6795. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2023/759. [14] HAO Yifan and CAO Huiping. A new attention mechanism to classify multivariate time series[C]. The Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 1999–2005. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2020/277. [15] ZERVEAS G, JAYARAMAN S, PATEL D, et al. A transformer-based framework for multivariate time series representation learning[C]. The 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, 2021: 2114–2124. doi: 10.1145/3447548.3467401. [16] SERRA J, PASCUAL S, and KARATZOGLOU A. Towards a universal neural network encoder for time series[C]. Artificial Intelligence Research and Development - Current Challenges, New Trends and Applications, CCIA 2018, 21st International Conference of the Catalan Association for Artificial Intelligence, Alt Empordà, Spain, 2018: 120–129. doi: 10.3233/978-1-61499-918-8-120. [17] BANERJEE D, ISLAM K, XUE Keyi, et al. A deep transfer learning approach for improved post-traumatic stress disorder diagnosis[J]. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2019, 60(3): 1693–1724. doi: 10.1007/s10115-019-01337-2. [18] ASWOLINSKIY W, REINHART R F, and STEIL J. Time series classification in reservoir-and model-space[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2018, 48(2): 789–809. doi: 10.1007/s11063-017-9765-5. [19] IWANA B K, FRINKEN V, and UCHIDA S. DTW-NN: A novel neural network for time series recognition using dynamic alignment between inputs and weights[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 188: 104971. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.104971. [20] TABASSUM N, MENON S, and JASTRZĘBSKA A. Time-series classification with SAFE: Simple and fast segmented word embedding-based neural time series classifier[J]. Information Processing & Management, 2022, 59(5): 103044. doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2022.103044. [21] FUKUSHIMA K. Neocognitron: A self-organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1980, 36(4): 193–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00344251. [22] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [23] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791. [24] LE GUENNEC A, MALINOWSKI S, and TAVENARD R. Data augmentation for time series classification using convolutional neural networks[C]. ECML/PKDD Workshop on Advanced Analytics and Learning on Temporal Data, Riva Del Garda, Italy, 2016. [25] LI Zewen, LIU Fan, YANG Wenjie, et al. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(12): 6999–7019. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3084827. [26] ZHENG Yi, LIU Qi, CHEN Enhong, et al. Time series classification using multi-channels deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 15th International Conference on Web-Age Information Management, Macau, China, 2014: 298–310. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-08010-9_33. [27] YANG Jianbo, NGUYEN M N, SAN P P, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks on multichannel time series for human activity recognition[C]. The Twenty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015: 3995–4001. [28] ZHAO Bendong, LU Huanzhang, CHEN Shangfeng, et al. Convolutional neural networks for time series classification[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28(1): 162–169. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2017.01.18. [29] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965. [30] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [31] ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2921–2929. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.319. [32] ZOU Xiaowu, WANG Zidong, LI Qi, et al. Integration of residual network and convolutional neural network along with various activation functions and global pooling for time series classification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 367: 39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.08.023. [33] LI Yuhong, ZHANG Xiaofan, and CHEN Deming. CSRNet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1091–1100. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00120. [34] YAZDANBAKHSH O and DICK S. Multivariate time series classification using dilated convolutional neural network[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.01697, 2019. [35] FOUMANI S N M, TAN C W, and SALEHI M. Disjoint-CNN for multivariate time series classification[C]. 2021 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Auckland, New Zealand, 2021: 760–769. doi: 10.1109/ICDMW53433.2021.00099. [36] WANG Zhiguang and OATES T. Encoding time series as images for visual inspection and classification using tiled convolutional neural networks[C]. AAAI Workshop Papers 2015, Menlo Park, USA, 2015: 40–46. [37] HATAMI N, GAVET Y, and DEBAYLE J. Classification of time-series images using deep convolutional neural networks[C]. SPIE 10696, Tenth International Conference on Machine Vision, Vienna, Austria, 2018: 106960Y. doi: 10.1117/12.2309486. [38] KARIMI-BIDHENDI S, MUNSHI F, and MUNSHI A. Scalable classification of univariate and multivariate time series[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, USA, 2018: 1598–1605. doi: 10.1109/BigData.2018.8621889. [39] YANG C L, CHEN Zhixuan, and YANG Chenyi. Sensor classification using convolutional neural network by encoding multivariate time series as two-dimensional colored images[J]. Sensors, 2019, 20(1): 168. doi: 10.3390/s20010168. [40] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.308. [41] CHEN Wei and SHI Ke. A deep learning framework for time series classification using relative position matrix and convolutional neural network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 359: 384–394. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.06.032. [42] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556. [43] CUI Zhicheng, CHEN Wenlin, and CHEN Yixin. Multi-scale convolutional neural networks for time series classification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.06995, 2016. [44] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594. [45] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. The 31th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4278–4284. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v31i1.11231. [46] LIU C L, HSAIO W H, and TU Y C. Time series classification with multivariate convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(6): 4788–4797. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2864702. [47] RONALD M, POULOSE A, and HAN D S. iSPLInception: An inception-ResNet deep learning architecture for human activity recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 68985–69001. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3078184. [48] SUN Jingyu, TAKEUCHI S, and YAMASAKI I. Prototypical inception network with cross branch attention for time series classification[C]. 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 2021: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN52387.2021.9533440. [49] USMANKHUJAEV S, IBROKHIMOV B, BAYDADAEV S, et al. Time series classification with InceptionFCN[J]. Sensors, 2021, 22(1): 157. doi: 10.3390/s22010157. [50] 张雅雯, 王志海, 刘海洋, 等. 基于多尺度残差FCN的时间序列分类算法[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(2): 555–570. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006142.ZHANG Yawen, WANG Zhihai, LIU Haiyang, et al. Time series classification algorithm based on multiscale residual full convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(2): 555–570. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006142. [51] DENNIS D, ACAR D A E, MANDIKAL V, et al. Shallow RNN: Accurate time-series classification on resource constrained devices[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 12896–12906. [52] HERMANS M and SCHRAUWEN B. Training and analyzing deep recurrent neural networks[C]. The 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2013: 190–198. [53] PASCANU R, MIKOLOV T, and BENGIO Y. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks[C]. The 30th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, USA, 2013: 1310–1318. [54] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735. [55] CHUNG J, GULCEHRE C, CHO K H, et al. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555, 2014. [56] KAWAKAMI K. Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Carnegie Mellon University, 2008. [57] SUTSKEVER I, VINYALS O, and LE Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 3104–3112. [58] DONAHUE J, ANNE HENDRICKS L, GUADARRAMA S, et al. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 2625–2634. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298878. [59] KARPATHY A and Fei-Fei L. Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3128–3137. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298932. [60] TANG Yujin, XU Jianfeng, MATSUMOTO K, et al. Sequence-to-sequence model with attention for time series classification[C]. 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 503–510. doi: 10.1109/ICDMW.2016.0078. [61] MALHOTRA P, TV V, VIG L, et al. TimeNet: Pre-trained deep recurrent neural network for time series classification[C]. 25th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Bruges, Belgium, 2017. [62] KARIM F, MAJUMDAR S, DARABI H, et al. Multivariate LSTM-FCNs for time series classification[J]. Neural Networks, 2019, 116: 237–245. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.04.014. [63] 玄英律, 万源, 陈嘉慧. 基于多尺度卷积和注意力机制的LSTM时间序列分类[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(8): 2343–2352. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021061062.XUAN Yinglu, WAN Yuan, and CHEN Jiahui. Time series classification by LSTM based on multi-scale convolution and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(8): 2343–2352. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021061062. [64] ZHANG Xuchao, GAO Yifeng, LIN J, et al. TapNet: Multivariate time series classification with attentional prototypical network[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 6845–6852. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i04.6165. [65] ZUO Jingwei, ZEITOUNI K, and TAHER Y. SMATE: Semi-supervised spatio-temporal representation learning on multivariate time series[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Auckland, New Zealand, 2021: 1565–1570. doi: 10.1109/ICDM51629.2021.00206. [66] LIN Sangdi and RUNGER G C. GCRNN: Group-constrained convolutional recurrent neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(10): 4709–4718. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2772336. [67] MUTEGEKI R and HAN D S. A CNN-LSTM approach to human activity recognition[C]. 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Fukuoka, Japan, 2020: 362–366. doi: 10.1109/ICAIIC48513.2020.9065078. [68] KARIM F, MAJUMDAR S, DARABI H, et al. LSTM fully convolutional networks for time series classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 1662–1669. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2779939. [69] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [70] DEVLIN J, CHANG Mingwei, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1, Minneapolis, USA, 2018: 4171–4186. doi: 10.18653/v1/N19-1423. [71] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986. [72] CARON M, TOUVRON H, MISRA I, et al. Emerging properties in self-supervised vision transformers[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9630–9640. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00951. [73] KHAN S, NASEER M, HAYAT M, et al. Transformers in vision: A survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 54(10s): 200. doi: 10.1145/3505244. [74] KOSTAS D, AROCA-OUELLETTE S, and RUDZICZ F. BENDR: Using transformers and a contrastive self-supervised learning task to learn from massive amounts of EEG data[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2021, 15: 653659. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.653659. [75] BAHDANAU D, CHO K, and BENGIO Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1409.0473. [76] CHO K, VAN MERRIËNBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]. The 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1724–1734. doi: 10.3115/v1/D14-1179. [77] LUONG M T, PHAM H, and MANNING C D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation[C]. The 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 2015: 1412–1421. doi: 10.18653/v1/D15-1166. [78] YUAN Ye, XUN Guangxu, MA Fenglong, et al. MuVAN: A multi-view attention network for multivariate temporal data[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Singapore, 2018: 717–726. doi: 10.1109/ICDM.2018.00087. [79] HSIEH T Y, WANG Suhang, SUN Yiwei, et al. Explainable multivariate time series classification: A deep neural network which learns to attend to important variables as well as time intervals[C]. The 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, 2021: 607–615. [80] CHEN Wei and SHI Ke. Multi-scale attention convolutional neural network for time series classification[J]. Neural Networks, 2021, 136: 126–140. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2021.01.001. [81] YUAN Ye, XUN Guangxu, MA Fenglong, et al. A novel channel-aware attention framework for multi-channel EEG seizure detection via multi-view deep learning[C]. 2018 IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical & Health Informatics (BHI), Las Vegas, USA, 2018: 206–209. doi: 10.1109/BHI.2018.8333405. [82] LIANG Yuxuan, KE Songyu, ZHANG Junbo, et al. GeoMAN: Multi-level attention networks for geo-sensory time series prediction[C]. The Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3428–3434. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2018/476. [83] HU Jun and ZHENG Wendong. Multistage attention network for multivariate time series prediction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 383: 122–137. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.11.060. [84] CHENG Xu, HAN Peihua, LI Guoyuan, et al. A novel channel and temporal-wise attention in convolutional networks for multivariate time series classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 212247–212257. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3040515. [85] XIAO Zhiwen, XU Xin, XING Huanlai, et al. RTFN: A robust temporal feature network for time series classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 571: 65–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.04.053. [86] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A, et al. Spatial transformer networks[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2017–2025. [87] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [88] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [89] SONG Huan, RAJAN D, THIAGARAJAN J, et al. Attend and diagnose: Clinical time series analysis using attention models[C]. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 4091–4098. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.11635. [90] JIN Cancan and CHEN Xi. An end-to-end framework combining time–frequency expert knowledge and modified transformer networks for vibration signal classification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 171: 114570. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114570. [91] ALLAM JR T and MCEWEN J D. Paying attention to astronomical transients: Photometric classification with the time-series transformer[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.06178v1, 2021. [92] RASMUSSEN C E. Gaussian processes in machine learning[M]. ML Summer Schools 2003 on Advanced Lectures on Machine Learning, Tübingen, Germany, 2003: 63–71. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-28650-9_4. [93] LIU Minghao, REN Shengqi, MA Siyuan, et al. Gated transformer networks for multivariate time series classification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14438, 2021. [94] ZHAO Bowen, XING Huanlai, WANG Xinhan, et al. Rethinking attention mechanism in time series classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 627: 97–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.01.093. [95] 王美, 苏雪松, 刘佳, 等. 时频域多尺度交叉注意力融合的时间序列分类方法[J/OL]. 计算机应用: 1–9. http://www.joca.cn/CN/10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023060731, 2023.WANG Mei, SU Xuesong, LIU Jia, et al. Time series classification method based on multi-scale cross-attention fusion in time-frequency domain[J/OL]. Journal of Computer Applications: 1–9. http://www.joca.cn/CN/10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023060731, 2023. [96] YANG C H H, TSAI Y Y, and CHEN P Y. Voice2Series: Reprogramming acoustic models for time series classification[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 11808–11819. [97] SUN Chenxi, LI Yaliang, LI Hongyan, et al. TEST: Text prototype aligned embedding to activate LLM's ability for time series[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.08241, 2023. [98] CHANG C, PENG W C, and CHEN T F. LLM4TS: Two-stage fine-tuning for time-series forecasting with pre-trained LLMs[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.08469, 2023. [99] CHOWDHURY R R, ZHANG Xiyuan, SHANG Jingbo, et al. TARNet: Task-aware reconstruction for time-series transformer[C]. The 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, USA, 2022: 212–220. doi: 10.1145/3534678.3539329. [100] GUPTA N, GUPTA S K, PATHAK R K, et al. Human activity recognition in artificial intelligence framework: A narrative review[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(6): 4755–4808. doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10116-x. [101] ORDÓÑEZ F J and ROGGEN D. Deep convolutional and LSTM recurrent neural networks for multimodal wearable activity recognition[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(1): 115. doi: 10.3390/s16010115. [102] ARSHAD M H, BILAL M, and GANI A. Human activity recognition: Review, taxonomy and open challenges[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(17): 6463. doi: 10.3390/s22176463. [103] LI Yang, YANG Guanci, SU Zhidong, et al. Human activity recognition based on multienvironment sensor data[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 91: 47–63. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.10.015. [104] CHENG Xin, ZHANG Lei, TANG Yin, et al. Real-time human activity recognition using conditionally parametrized convolutions on mobile and wearable devices[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(6): 5889–5901. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3149337. [105] LARA O D and LABRADOR M A. A survey on human activity recognition using wearable sensors[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2013, 15(3): 1192–1209. doi: 10.1109/SURV.2012.110112.00192. [106] WANG Xing, ZHANG Lei, HUANG Wenbo, et al. Deep convolutional networks with tunable speed–accuracy tradeoff for human activity recognition using wearables[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1–12. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3132088. [107] RONAO C A and CHO S B. Human activity recognition with smartphone sensors using deep learning neural networks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 59: 235–244. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.032. [108] IGNATOV A. Real-time human activity recognition from accelerometer data using convolutional neural networks[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 62: 915–922. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.09.027. [109] ZENG Ming, NGUYEN L T, YU Bo, et al. Convolutional neural networks for human activity recognition using mobile sensors[C]. 6th International Conference on Mobile Computing, Applications and Services, Austin, USA, 2014: 197–205. doi: 10.4108/icst.mobicase.2014.257786. [110] ZHANG Haoxi, XIAO Zhiwen, WANG Juan, et al. A novel IoT-perceptive human activity recognition (HAR) approach using multihead convolutional attention[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(2): 1072–1080. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2949715. [111] JIANG Wenchao and YIN Zhaozheng. Human activity recognition using wearable sensors by deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 23rd ACM international conference on Multimedia, Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 1307–1310. doi: 10.1145/2733373.2806333. [112] LEE S M, YOON S M, and CHO H. Human activity recognition from accelerometer data using convolutional neural network[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), Jeju, Korea, 2017: 131–134. doi: 10.1109/BIGCOMP.2017.7881728. [113] XU Shige, ZHANG Lei, HUANG Wenbo, et al. Deformable convolutional networks for multimodal human activity recognition using wearable sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1–14. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3158427. [114] MURAD A and PYUN J Y. Deep recurrent neural networks for human activity recognition[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(11): 2556. doi: 10.3390/s17112556. [115] ZENG Ming, GAO Haoxiang, YU Tong, et al. Understanding and improving recurrent networks for human activity recognition by continuous attention[C]. The 2018 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Singapore, 2018: 56–63. doi: 10.1145/3267242.3267286. [116] GUAN Yu and PLÖTZ T. Ensembles of deep LSTM learners for activity recognition using wearables[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2017, 1(2): 11. doi: 10.1145/3090076. [117] SINGH S P, SHARMA M K, LAY-EKUAKILLE A, et al. Deep ConvLSTM with self-attention for human activity decoding using wearable sensors[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(6): 8575–8582. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3045135. [118] CHALLA S K, KUMAR A, and SEMWAL V B. A multibranch CNN-BiLSTM model for human activity recognition using wearable sensor data[J]. The Visual Computer, 2022, 38(12): 4095–4109. doi: 10.1007/s00371-021-02283-3. [119] NAFEA O, ABDUL W, MUHAMMAD G, et al. Sensor-based human activity recognition with spatio-temporal deep learning[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(6): 2141. doi: 10.3390/s21062141. [120] MEKRUKSAVANICH S and JITPATTANAKUL A. LSTM networks using smartphone data for sensor-based human activity recognition in smart homes[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(5): 1636. doi: 10.3390/s21051636. [121] CHEN Ling, LIU Xiaoze, PENG Liangying, et al. Deep learning based multimodal complex human activity recognition using wearable devices[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51(6): 4029–4042. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-02005-7. [122] MEKRUKSAVANICH S and JITPATTANAKUL A. Biometric user identification based on human activity recognition using wearable sensors: An experiment using deep learning models[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(3): 308. doi: 10.3390/electronics10030308. [123] SALEEM G, BAJWA U I and RAZA R H. Toward human activity recognition: A survey[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(5): 4145–4182. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07937-4. [124] MEKRUKSAVANICH S and JITPATTANAKUL A. Deep convolutional neural network with RNNs for complex activity recognition using wrist-worn wearable sensor data[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(14): 1685. doi: 10.3390/electronics10141685. [125] CHEN Xun, LI Chang, LIU Aiping, et al. Toward open-world electroencephalogram decoding via deep learning: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2022, 39(2): 117–134. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2021.3134629. [126] GU Xiaoqing, CAI Weiwei, GAO Ming, et al. Multi-source domain transfer discriminative dictionary learning modeling for electroencephalogram-based emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2022, 9(6): 1604–1612. doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2022.3153660. [127] MAITHRI M, RAGHAVENDRA U, GUDIGAR A, et al. Automated emotion recognition: Current trends and future perspectives[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2022, 215: 106646. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106646. [128] CHEN Yu, CHANG Rui, and GUO Jifeng. Effects of data augmentation method borderline-SMOTE on emotion recognition of EEG signals based on convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 47491–47502. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3068316. [129] GAO Zhongke, LI Yanli, YANG Yuxuan, et al. A GPSO-optimized convolutional neural networks for EEG-based emotion recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 380: 225–235. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.096. [130] MAHESHWARI D, GHOSH S K, TRIPATHY R K, et al. Automated accurate emotion recognition system using rhythm-specific deep convolutional neural network technique with multi-channel EEG signals[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2021, 134: 104428. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104428. [131] WANG Yuqi, ZHANG Lijun, XIA Pan, et al. EEG-based emotion recognition using a 2D CNN with different kernels[J]. Bioengineering, 2022, 9(6): 231. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9060231. [132] KHARE S K and BAJAJ V. Time–frequency representation and convolutional neural network-based emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(7): 2901–2909. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3008938. [133] ALGARNI M, SAEED F, AL-HADHRAMI T, et al. Deep learning-based approach for emotion recognition using electroencephalography (EEG) signals using bi-directional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM)[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(8): 2976. doi: 10.3390/s22082976. [134] SHARMA R, PACHORI R B, and SIRCAR P. Automated emotion recognition based on higher order statistics and deep learning algorithm[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 58: 101867. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101867. [135] LI Yang, ZHENG Wenming, WANG Lei, et al. From regional to global brain: A novel hierarchical spatial-temporal neural network model for EEG emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2022, 13(2): 568–578. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2019.2922912. [136] XIAO Guowen, SHI Meng, YE Mengwen, et al. 4D attention-based neural network for EEG emotion recognition[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2022, 16(4): 805–818. doi: 10.1007/s11571-021-09751-5. [137] KANG J S, KAVURI S, and LEE M. ICA-evolution based data augmentation with ensemble deep neural networks using time and frequency kernels for emotion recognition from EEG-data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2022, 13(2): 616–627. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2019.2942587. [138] IYER A, DAS S S, TEOTIA R, et al. CNN and LSTM based ensemble learning for human emotion recognition using EEG recordings[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(4): 4883–4896. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12310-7. [139] KIM Y and CHOI A. EEG-based emotion classification using long short-term memory network with attention mechanism[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(23): 6727. doi: 10.3390/s20236727. [140] ARJUN, RAJPOOT A S, and PANICKER M R. Subject independent emotion recognition using EEG signals employing attention driven neural networks[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 75: 103547. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103547. [141] LIANG Zhen, ZHOU Rushuang, ZHANG Li, et al. EEGFuseNet: Hybrid unsupervised deep feature characterization and fusion for high-dimensional EEG with an application to emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2021, 29: 1913–1925. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3111689. [142] PARVAIZ A, KHALID M A, ZAFAR R, et al. Vision transformers in medical computer vision—a contemplative retrospection[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 122: 106126. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106126. -






 下载:
下载:
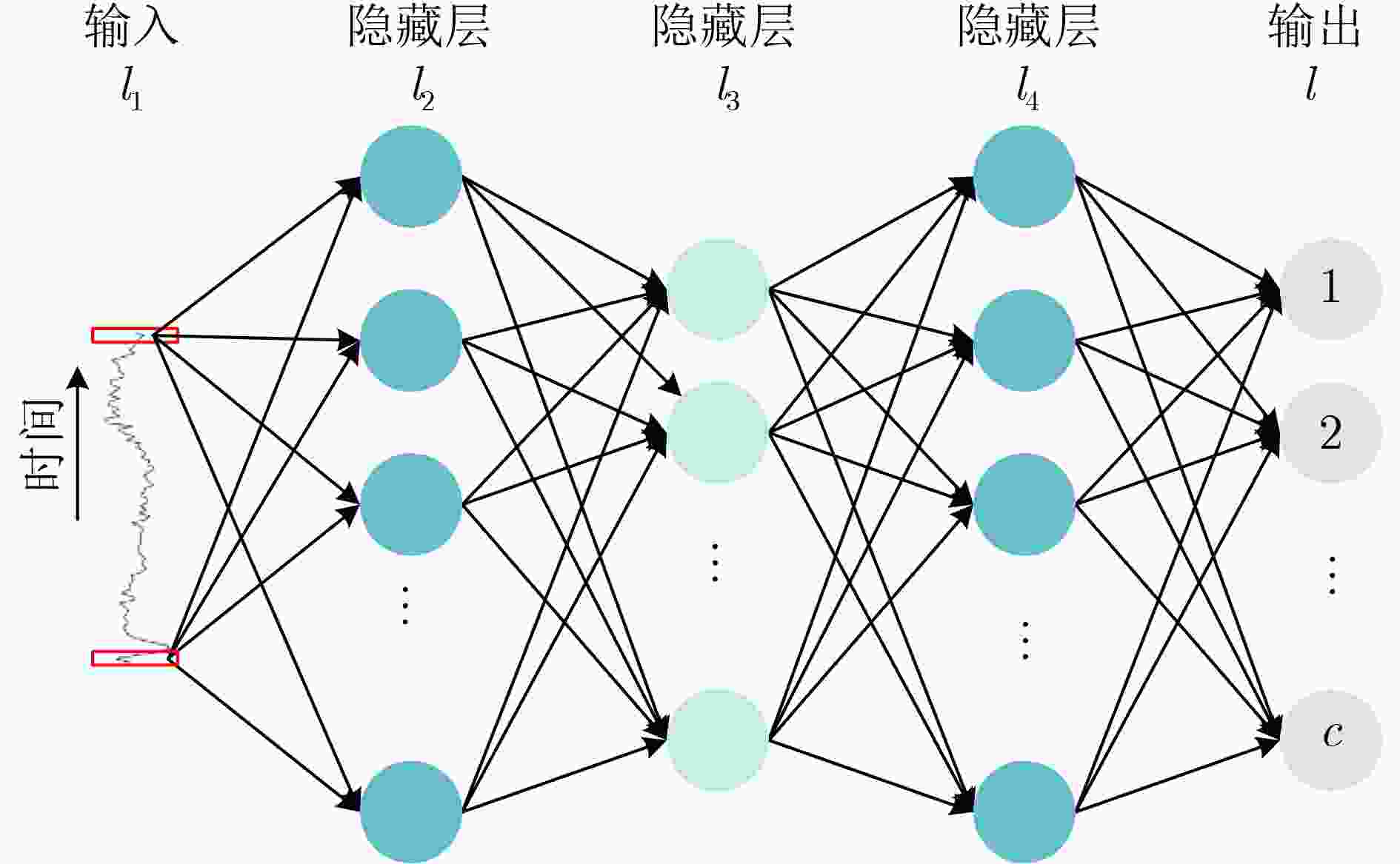
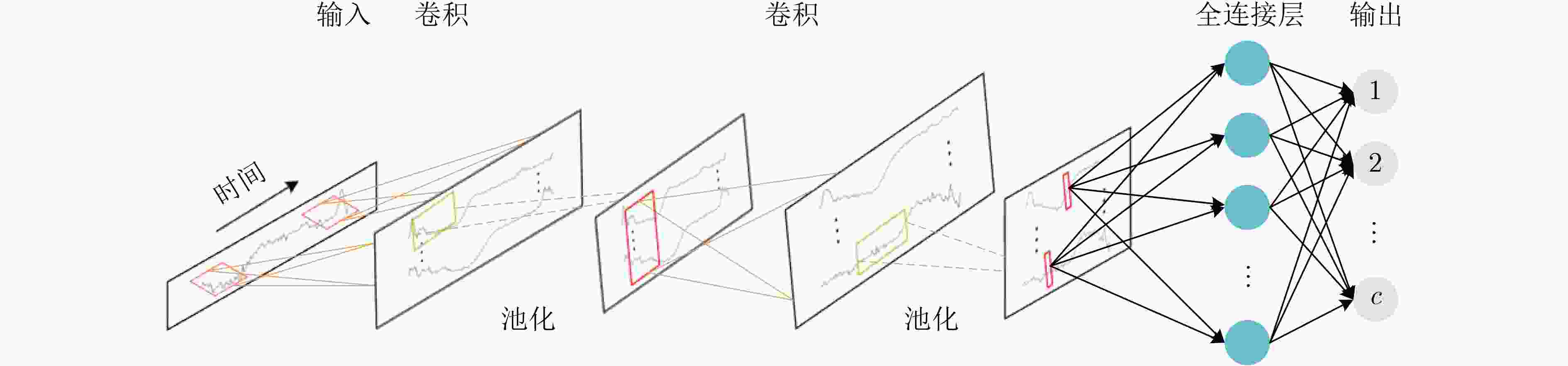


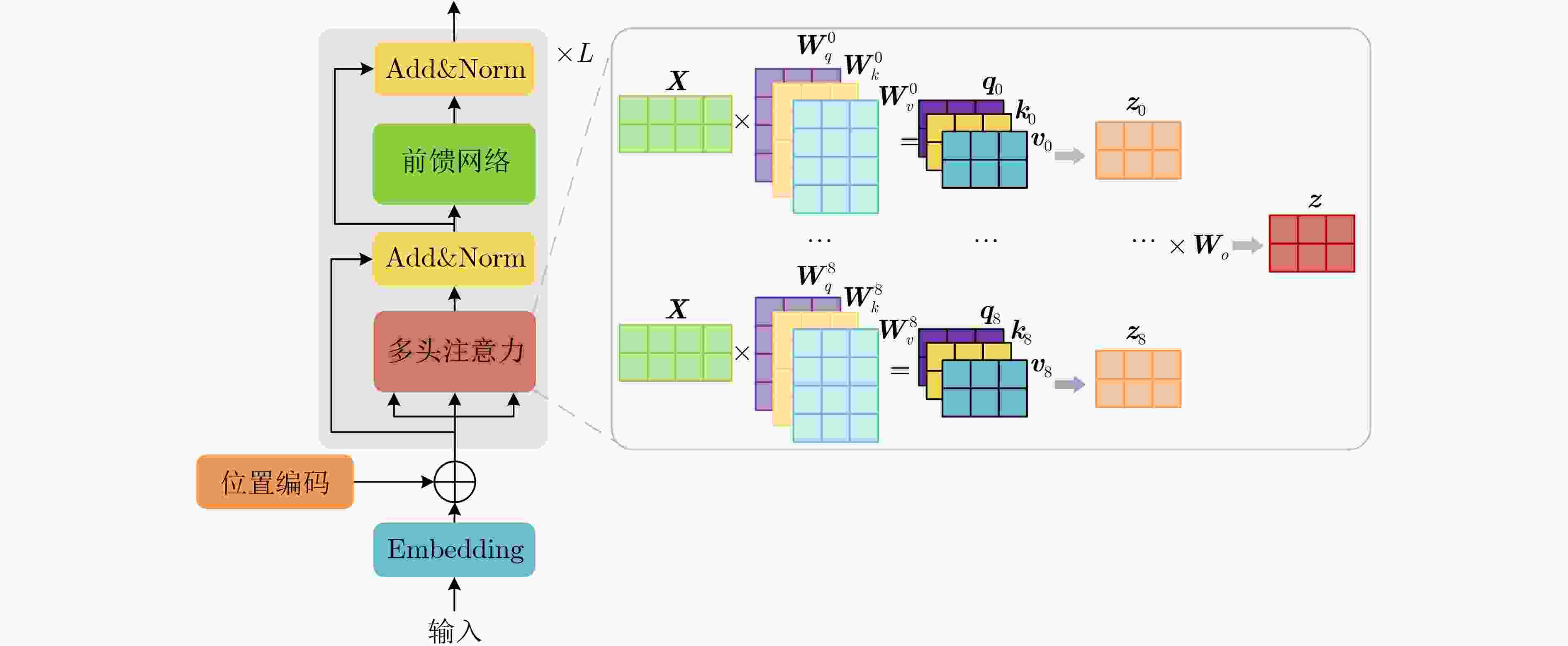


 下载:
下载:
