Age of Information Analysis and Optimization in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles-assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication Systems
-
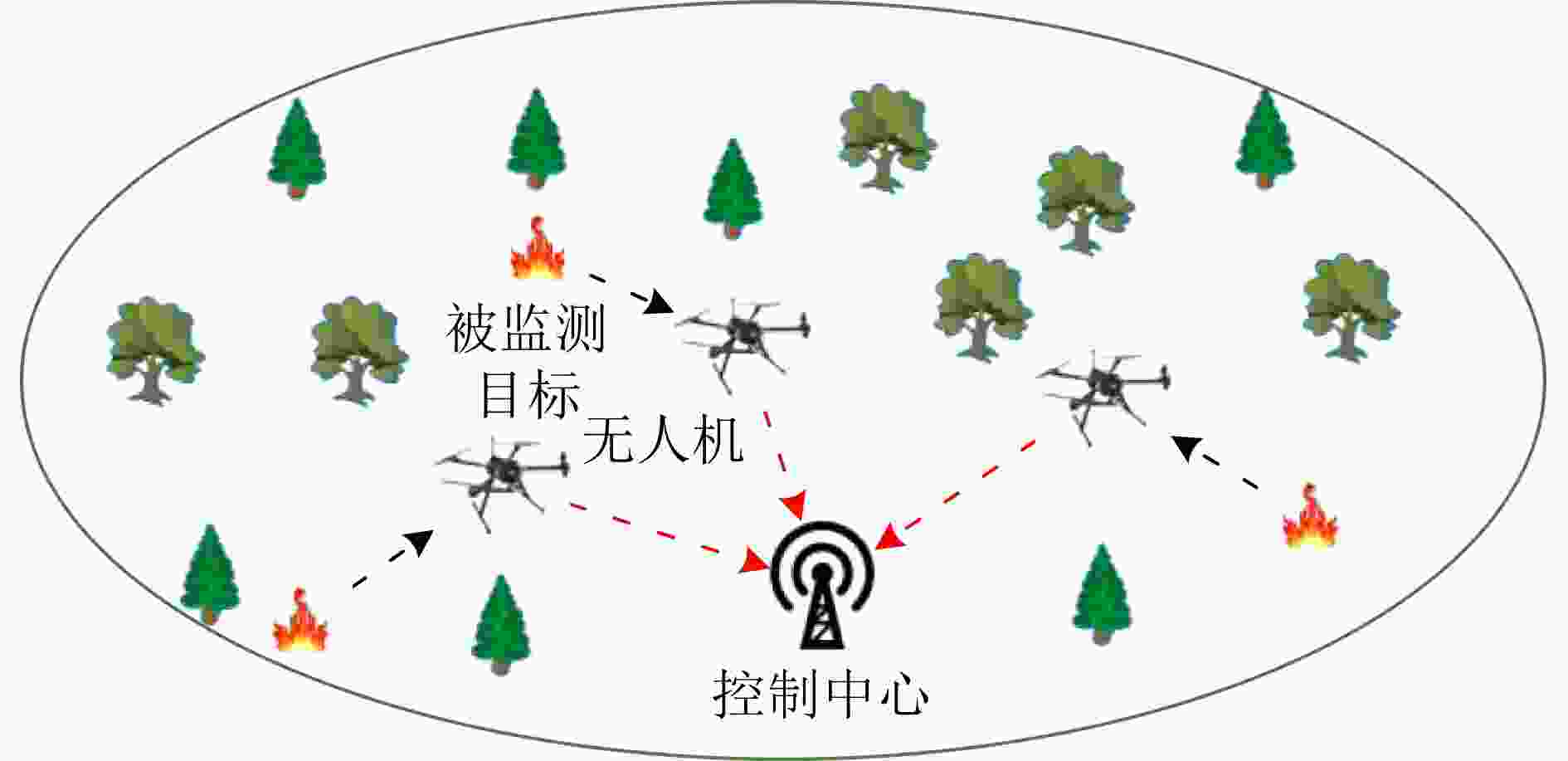
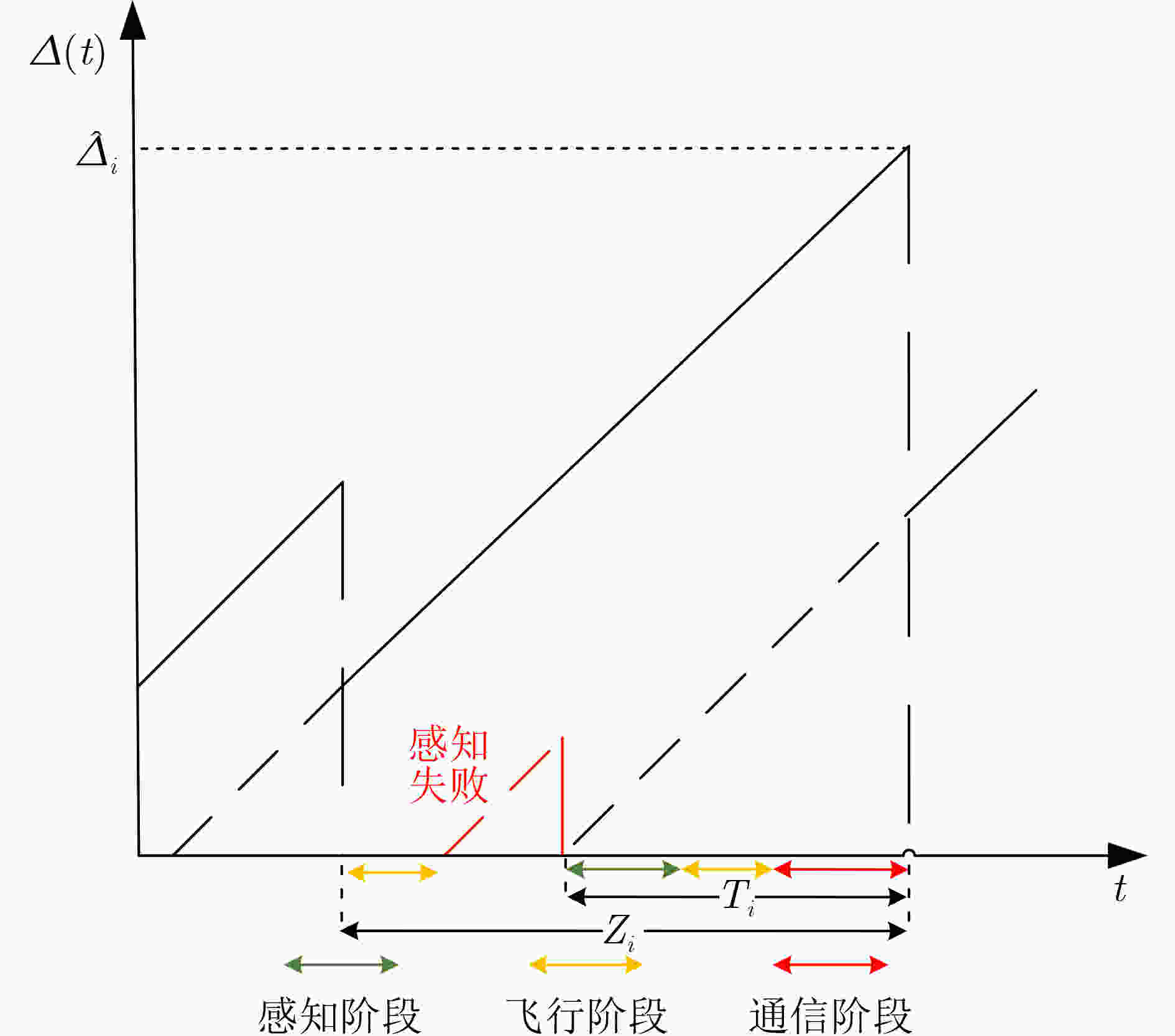
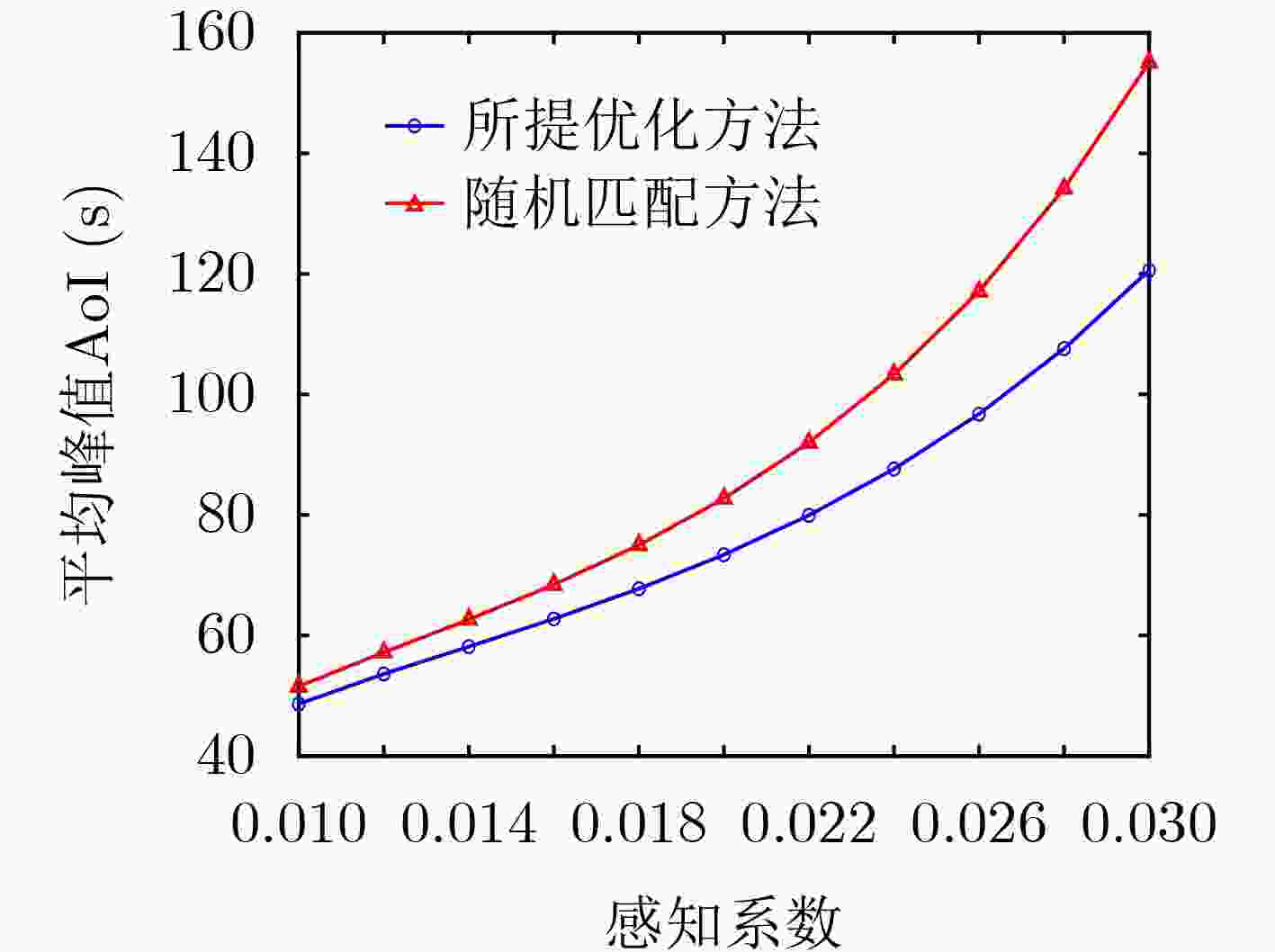
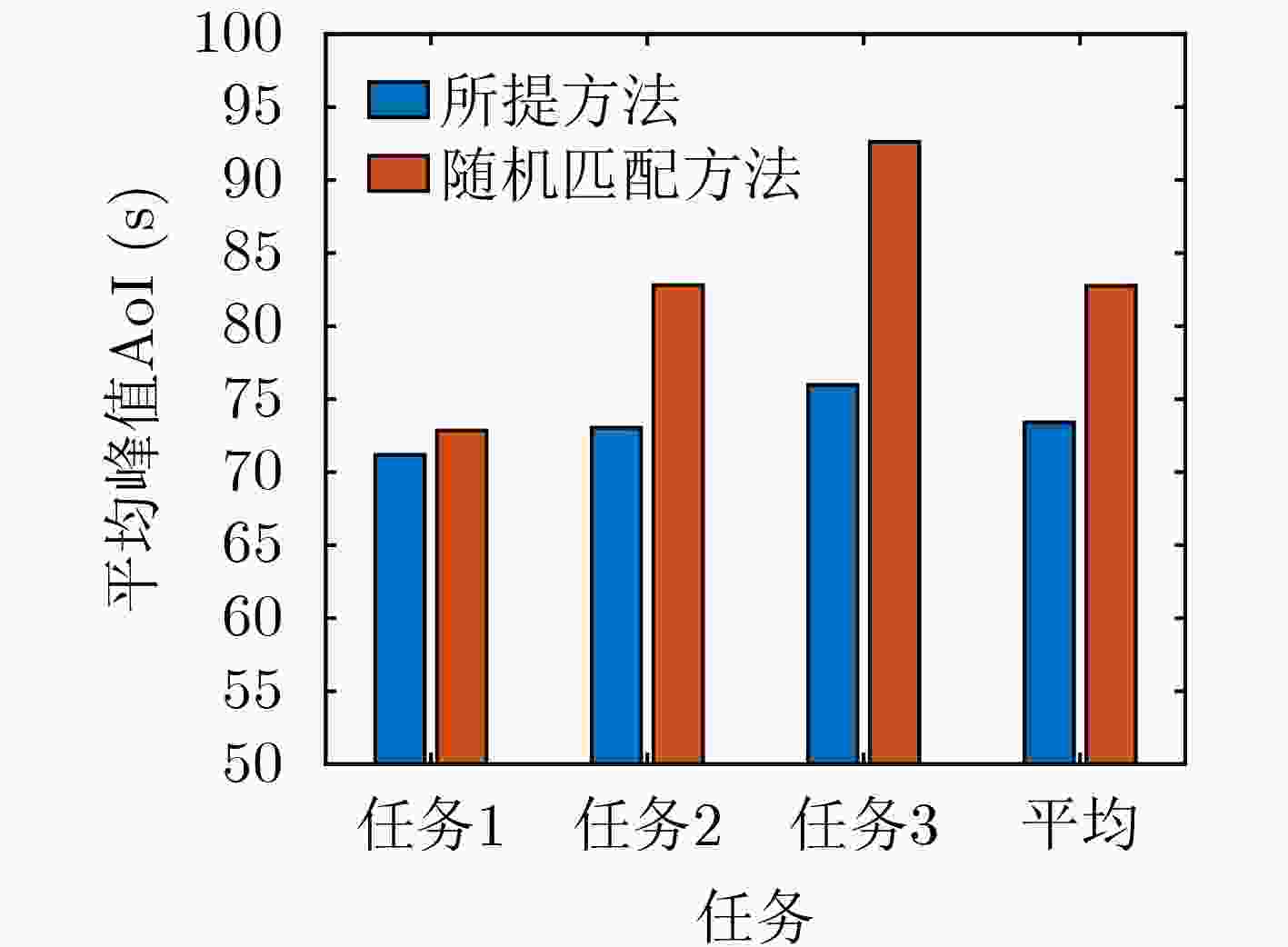
摘要: 在许多监测控制任务中,由于被监测目标和控制中心距离较远,控制中心难以直接获取目标实时的状态信息。无人机(UAV)可以发挥其高移动性优势,减少感知和通信距离,进而提升感知和通信能力,为远距离目标状态信息实时获取问题提供了新思路。对此,该文研究了UAV辅助通感一体化系统中的信息年龄(AoI)分析优化问题,首先分析了控制中心的状态更新过程,然后推导出平均峰值AoI的闭式表达式。进一步地,在多UAV多目标场景中,通过优化UAV在空中的感知位置和通信位置以及UAV和目标的匹配关系,来进一步降低系统的平均峰值AoI,改善状态更新的实时性。仿真结果验证了理论分析的正确性,同时表明了相比于对比方法,所提优化方法可以有效改善系统的AoI性能。Abstract: In many monitoring and control tasks, it is difficult for the control center to get the real-time status information directly because of the distance between the monitored target and the control center. The Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) can make full use of its advantages of high mobility, reduce the sensing and communication distance, and then improve the sensing and communication capabilities, which provides a new idea for real-time acquisition of remote target status information. In this paper, the optimization problem of Age of Information (AoI) analysis in UAV-assisted integrated sensing and communication system is studied. Firstly, the status update process of control center is analyzed, and then the closed-form expression of average peak AoI is derived. Further, in the multi-UAV multi-target scenario, the average peak AoI of the system is further reduced by optimizing the perception position and communication position of the UAV in the air, as well as the matching relationship between the UAV and the target, and the real-time status update is improved. The simulation results verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis, and show that the proposed optimization method can effectively improve the AoI performance of the system compared with the benchmark methods.
-
1 AoI性能优化算法
初始化:${x_{\text{c}}}\left( 0 \right)$, ${x_{\text{s}}}\left( 0 \right)$, ${\boldsymbol{Q}}$。 For $m = 1:M$ For $k = 1:K$ $t = 0$ Do 对于$x_{\text{c}}^m \in \left[ {\min \left\{ {x_{\text{s}}^m\left( t \right),{x_1}} \right\},\min \left\{ {x_{\text{s}}^m\left( t \right),{x_2}} \right\}} \right]$,采用
黄金分割法得到优化后的$x_{\text{c}}^m\left( {t + 1} \right)$。对于$ x_{\text{s}}^m \in \left[ {x_{\text{c}}^m\left( {t + 1} \right),X} \right] $,采用黄金分割法得到最佳的
$x_{\text{s}}^m\left( {t + 1} \right)$。$t \leftarrow t + 1$。 Until $t > {t_{\max }}$ 根据优化后的$x_{\text{c}}^m$和$x_{\text{s}}^m$,计算得到最小的平均峰值AoI$\bar \varDelta {_k^{m*}}$。 If $\bar \varDelta {_k^{m*}} \le \tau $ $Q_k^m \leftarrow \bar \varDelta _{k^{m*}}$。 Else $Q_k^m \leftarrow \infty $。 End If End for End for 采用匈牙利算法优化UAV与被监测目标的匹配关系,得到${{\boldsymbol{Q}}^*}$。 -
[1] ABD-ELMAGID M A, PAPPAS N, and DHILLON H S. On the role of age of information in the internet of things[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(12): 72–77. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900041. [2] CAO Jie, ZHU Xu, SUN Sumei, et al. Toward industrial metaverse: Age of information, latency and reliability of short-packet transmission in 6G[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2023, 30(2): 40–47. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2001.2200396. [3] JIANG Zhiyuan, KRISHNAMACHARI B, ZHENG Xi, et al. Timely status update in wireless uplinks: Analytical solutions with asymptotic optimality[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 3885–3898. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2893319. [4] XIANG Zhongwu, YANG Weiwei, PAN Gaofeng, et al. Physical layer security in cognitive radio inspired NOMA network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(3): 700–714. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2902103. [5] MA Ruiqian, YANG Weiwei, SHI Hui, et al. Covert communication with a spectrum sharing relay in the finite blocklength regime[J]. China Communications, 2023, 20(4): 195–211. doi: 10.23919/JCC.fa.2022-0490.202304. [6] KAUL S, YATES R, and GRUTESER M. Real-time status: How often should one update?[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), Orlando, America, 2012: 2731–2735. doi: 10.1109/INFCOM.2012.6195689. [7] MU Xidong, WANG Zhaolin, and LIU Yuanwei. NOMA for integrating sensing and communications towards 6G: A multiple access perspective[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications. doi: 10.1109/MWC.015.2200559. [8] XIE Zhanyuan, JIANG Zheng, ZHU Jianchi, et al. Joint target sensing and energy-harvesting-based remote state monitoring: A CMDP approach[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(10): 2613–2617. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3303459. [9] ZHANG Qixun, WANG Xinna, LI Zhenhao, et al. Design and performance evaluation of joint sensing and communication integrated system for 5G mmWave enabled CAVs[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1500–1514. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3109666. [10] QIN Zhen, WEI Zhenhua, QU Yuben, et al. AoI-aware scheduling for air-ground collaborative mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(5): 2989–3005. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3215795. [11] WANG Xijun, YI Mengjie, LIU Juan, et al. Cooperative data collection with multiple UAVs for information freshness in the internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(5): 2740–2755. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3255240. [12] JIANG Wenwen, AI Bo, CHENG Jing, et al. Sum of age-of-information minimization in aerial IRSs assisted wireless networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(5): 1377–1381. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3254502. [13] MU Junsheng, ZHANG Ronghui, CUI Yuanhao, et al. UAV meets integrated sensing and communication: Challenges and future directions[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2023, 61(5): 62–67. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.008.2200510. [14] HU Jingzhi, ZHANG Hongliang, and SONG Lingyang. Reinforcement learning for decentralized trajectory design in cellular UAV networks with sense-and-send protocol[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(4): 6177–6189. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2876513. [15] CHANG Bo, TANG Wei, YAN Xiaoyu, et al. Integrated scheduling of sensing, communication, and control for mmWave/THz communications in cellular connected UAV networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2103–2113. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3157366. [16] ZHANG Shuhang, ZHANG Hongliang, HAN Zhu, et al. Age of information in a cellular internet of UAVs: Sensing and communication trade-off design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6578–6592. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3004162. [17] 黄博, 方旭明, 陈煜. OFDMA中继网络变时域节能资源分配策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(5): 1023–1030. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01180.HUANG Bo, FANG Xuming, and CHEN Yu. Variable time-domain energy saving resource allocation for OFDMA relay networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2013, 35(5): 1023–1030. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01180. [18] LIANG Le, LI G Y, and XU Wei. Resource allocation for D2D-enabled vehicular communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(7): 3186–3197. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2699194. [19] YANG Weiwei, LU Xingbo, YAN Shihao, et al. Age of information for short-packet covert communication[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(9): 1890–1894. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3085025. -





 下载:
下载:
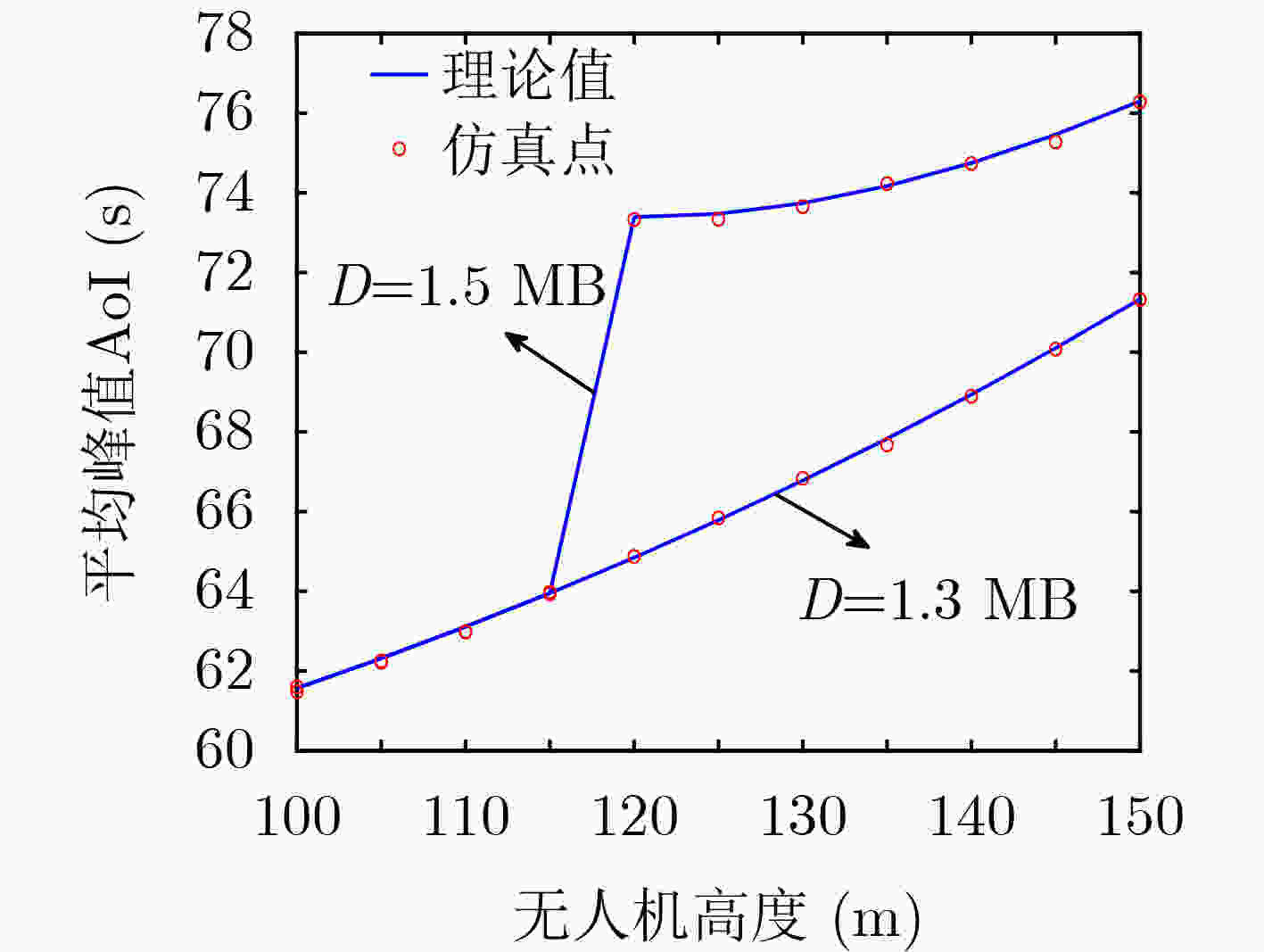
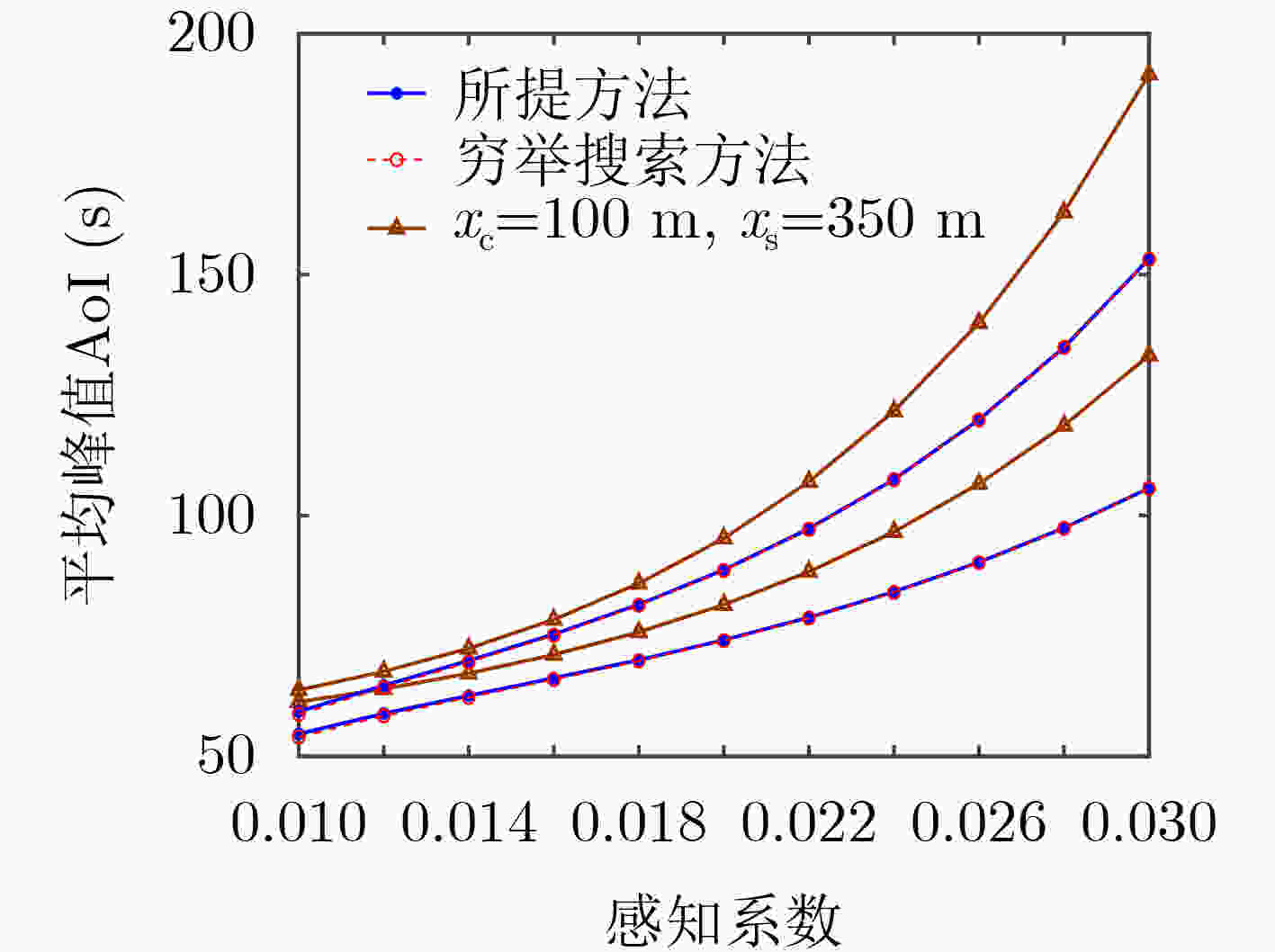


 下载:
下载:
