A Camouflaged Target Detection Method with Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm
-
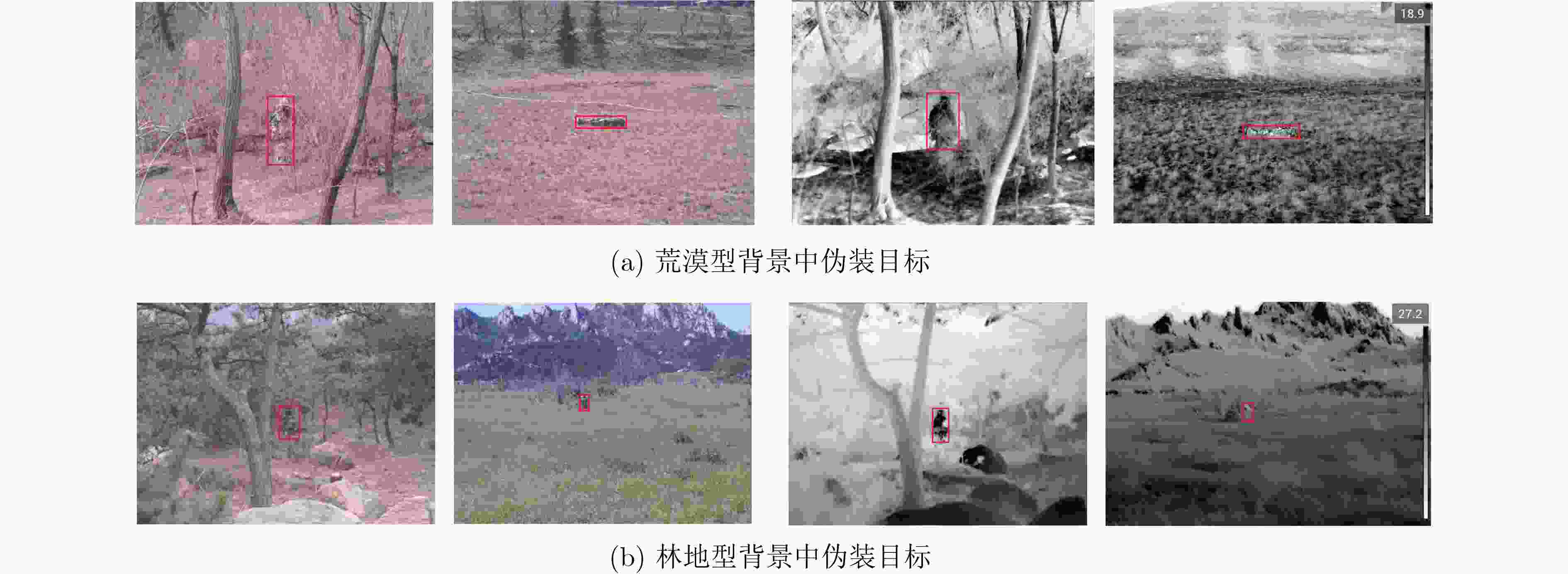
摘要: 为了深入挖掘伪装目标特征信息含量、充分发挥目标检测算法潜能,解决伪装目标检测精度低、漏检率高等问题,该文提出一种多模态图像特征级融合的伪装目标检测算法(CAFM-YOLOv5)。首先,构建伪装目标多波谱数据集用于多模态图像融合方法性能验证;其次,构建双流卷积通道用于可见光和红外图像特征提取;最后,基于通道注意力机制和空间注意力机制提出一种交叉注意力融合模块,以实现两种不同特征有效融合。实验结果表明,模型的检测精度达到96.4%、识别概率88.1%,优于YOLOv5参考网络;同时,在与YOLOv8等单模态检测算法、SLBAF-Net等多模态检测算法比较过程中,该算法在检测精度等指标上也体现出巨大优势。可见该方法对于战场军事目标检测具有实际应用价值,能够有效提升战场态势信息感知能力。Abstract: To comprehensively explore the information content of camouflaged target features, leverage the potential of target detection algorithms, and address issues such as low camouflage target detection accuracy and high false positive rates, a camouflage target detection algorithm named CAFM-YOLOv5 (Cross Attention Fusion Module Based on YOLOv5) is proposed. Firstly, a camouflaged target multispectral dataset is constructed for the performance validation of the multimodal image fusion method; secondly, a dual-stream convolution channel is constructed for visible and infrared image feature extraction; and finally, a cross-attention fusion module is proposed based on the channel-attention mechanism and spatial-attention mechanism in order to realise the effective fusion of two different features.Experimental results demonstrate that the model achieves a detection accuracy of 96.4% and a recognition probability of 88.1%, surpassing the YOLOv5 baseline network. Moreover, when compared with unimodal detection algorithms like YOLOv8 and multimodal detection algorithms such as SLBAF-Net, the proposed algorithm exhibits superior performance in detection accuracy metrics. These findings highlight the practical value of the proposed method for military target detection on the battlefield, enhancing situational awareness capabilities significantly.
-
表 1 检测结果分类及其含义表
检测结果 含义 TP 将正类预测为正类数 FP 将负类预测为正类数 TN 将负类预测为负类数 FN 将正类预测为负类数 表 2 本文方法各项指标
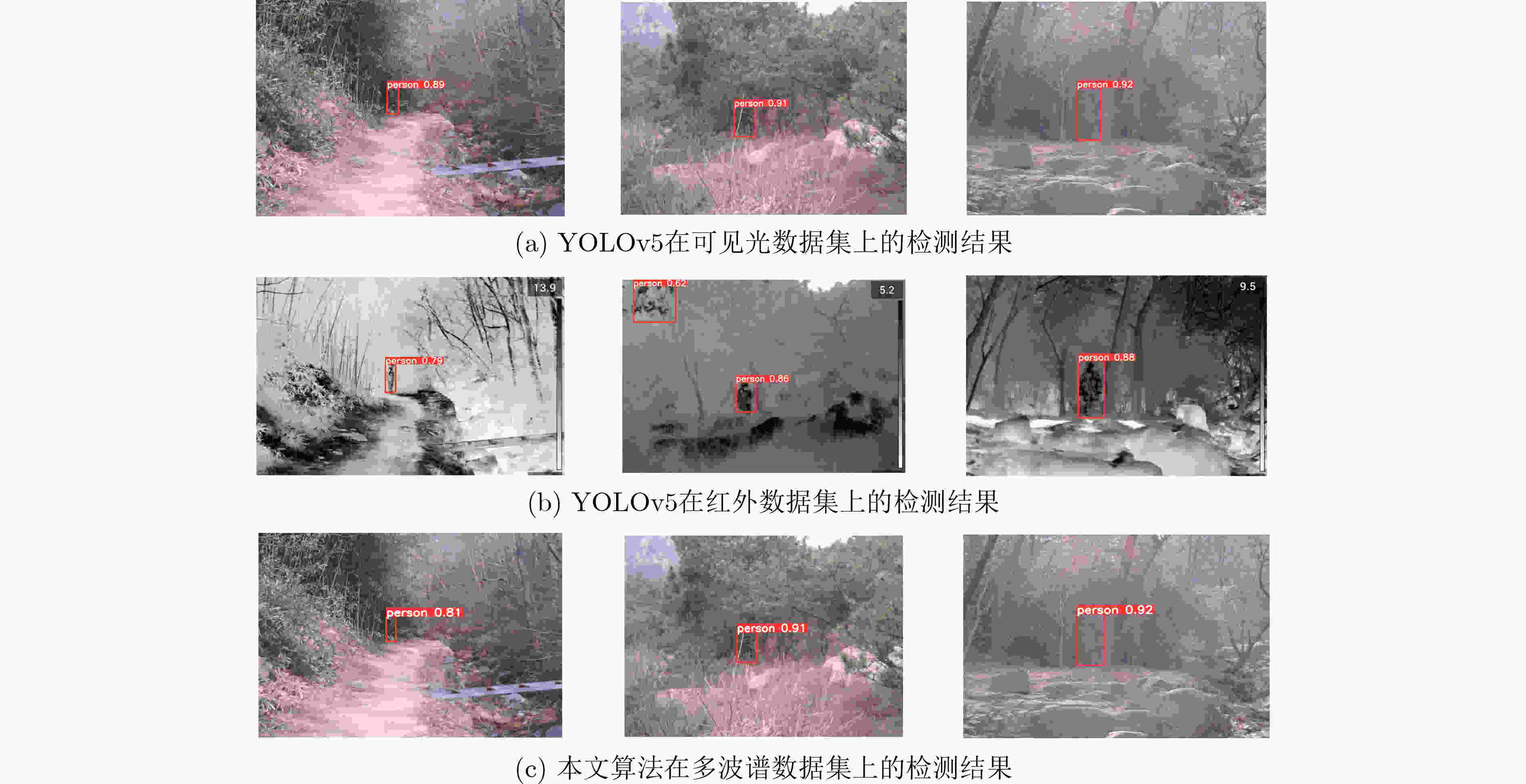
模型 数据集 Parameters Size(MB) Precision(%) Recall(%) mAP@0.5:0.95(%) RCR(%) fps(帧/s) YOLOv5 可见光 7012822 14.4 85.1 78.2 34.5 83.5 50 红外 7012822 14.4 93.3 84.1 47.7 66.9 53 CAFM-Net 可见光、红外 11557128 23.6 96.4 93.8 57.2 88.1 48 表 3 多种算法检测精度性能对比
模型 数据集 特征提取骨干 图像输入尺寸 Parametrs mAP@0.5:0.95(%) Faster-Rcnn 可见光 ResNet50 640×640 7864320 34.1 Faster-Rcnn 红外 ResNet50 640×640 7864320 36.3 SSD 可见光 VGG-16 640×640 7235175 43.9 SSD 红外 VGG-16 640×640 7235175 47.6 YOLOv3 可见光 Darknet-53 416×416 6501172 34.1 YOLOv3 红外 Darknet-53 416×416 6501172 39.1 YOLOv4 可见光 CSPDarknet-53 416×416 6396314 27.8 YOLOv4 红外 CSPDarknet-53 416×416 6396314 34.1 YOLOv8 可见光 CSPDarknet-53 640×640 11125971 41.1 YOLOv8 红外 CSPDarknet-53 640×640 11125971 51.1 MHA-YOLOv5 可见光 CSPDarknet-53 640×640 7704906 53.3 MHA-YOLOv5 红外 CSPDarknet-53 640×640 7704906 52.0 DETR 可见光 Resnet50 800×800 42991616 53.6 DETR 红外 Resnet50 800×800 42991616 53.4 表 4 多光谱数据集上多模态检测算法的结果
模型 数据集 图像输入
尺寸Parameters mAP@0.5:0.95
(%)SLBAF-Net 可见光、红外 640×640 419430 20.7 CFT 可见光、红外 640×640 44879052 50.4 -
[1] SINGH S K, DHAWALE C A, and MISRA S. Survey of object detection methods in camouflaged image[J]. IERI Procedia, 2013, 4: 351–357. doi: 10.1016/j.ieri.2013.11.050. [2] 王荣昌, 王峰, 任帅军, 等. 基于双流融合网络的单兵伪装偏振成像检测[J]. 光学学报, 2022, 42(9): 0915001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0915001.WANG Rongchang, WANG Feng, REN Shuaijun, et al. Polarization imaging detection of individual camouflage based on two-stream fusion network[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(9): 0915001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0915001. [3] LE T N, NGUYEN T V, NIE Zhongliang, et al. Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2019, 184: 45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2019.04.006. [4] FAN Dengping, JI Gepeng, SUN Guolei, et al. Camouflaged object detection[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference On Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2774–2784. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00285. [5] FAN Dengping, JI Gepeng, ZHOU Tao, et al. PraNet: Parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, 2020: 263–273. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_26. [6] TANKUS A and YESHURUN Y. Convexity-based visual camouflage breaking[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2001, 82(3): 208–237. doi: 10.1006/cviu.2001.0912. [7] BHAJANTRI N U and NAGABHUSHAN P. Camouflage defect identification: A novel approach[C]. The 9th International Conference on Information Technology, Bhubaneswar, India, 2006: 145–148. doi: 10.1109/ICIT.2006.34. [8] ZHANG Wei, ZHOU Qikai, LI Ruizhi, et al. Research on camouflaged human target detection based on deep learning[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022, 2022: 7703444. doi: 10.1155/2022/7703444. [9] 赖杰, 彭锐晖, 孙殿星, 等. 融合注意力机制与多检测层结构的伪装目标检测[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2024, 29(1): 134–146. doi: 10.11834/jig.221189.LAI Jie, PENG Ruihui, SUN Dianxing, et al. Detection of camouflage targets based on attention mechanism and multi-detection layer structure[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2024, 29(1): 134–146. doi: 10.11834/jig.221189. [10] 刘珩, 冉建国, 杨鑫, 等. 基于DETR的迷彩伪装目标检测[J]. 现代电子技术, 2022, 45(17): 41–46. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2022.17.008.LIU Heng, RAN Jianguo, YANG Xin, et al. Camouflage target detection based on detection transformer[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2022, 45(17): 41–46. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2022.17.008. [11] YADAV D, ARORA M K, TIWARI K C, et al. Detection and identification of camouflaged targets using hyperspectral and LiDAR data[J]. Defence Science Journal, 2018, 68(6): 540–546. doi: 10.14429/dsj.68.12731. [12] HU Jianghua, CUI Guangzhen, and QIN Lie. A new method of multispectral image processing with camouflage effect detection[C]. SPIE 9675, AOPC 2015: Image Processing and Analysis, Beijing, China, 2015: 967510. doi: 10.1117/12.2199206. [13] CHENG Xiaolong, GENG Keke, WANG Ziwei, et al. SLBAF-net: Super-lightweight bimodal adaptive fusion network for UAV detection in low recognition environment[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(30): 47773–47792. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-15333-w. [14] FANG Qingyun, HAN Depeng, and WANG Zhaokui. Cross-modality fusion transformer for multispectral object detection[J]. arXiv: 2111.00273, 2021. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2111.00273. [15] MA Jiayi, MA Yong, and Li Chang. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 45: 153–178. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.02.004. [16] 聂茜茜, 肖斌, 毕秀丽, 等. 基于超像素级卷积神经网络的多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4): 965–973. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191053.NIE Xixi, XIAO Bin, BI Xiuli, et al. Multi-focus image fusion algorithm based on super pixel level convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 965–973. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191053. [17] GEVORGYAN Z. SIoU loss: More powerful learning for bounding box regression[J]. arXiv: 2205.12740, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2205.12740. -





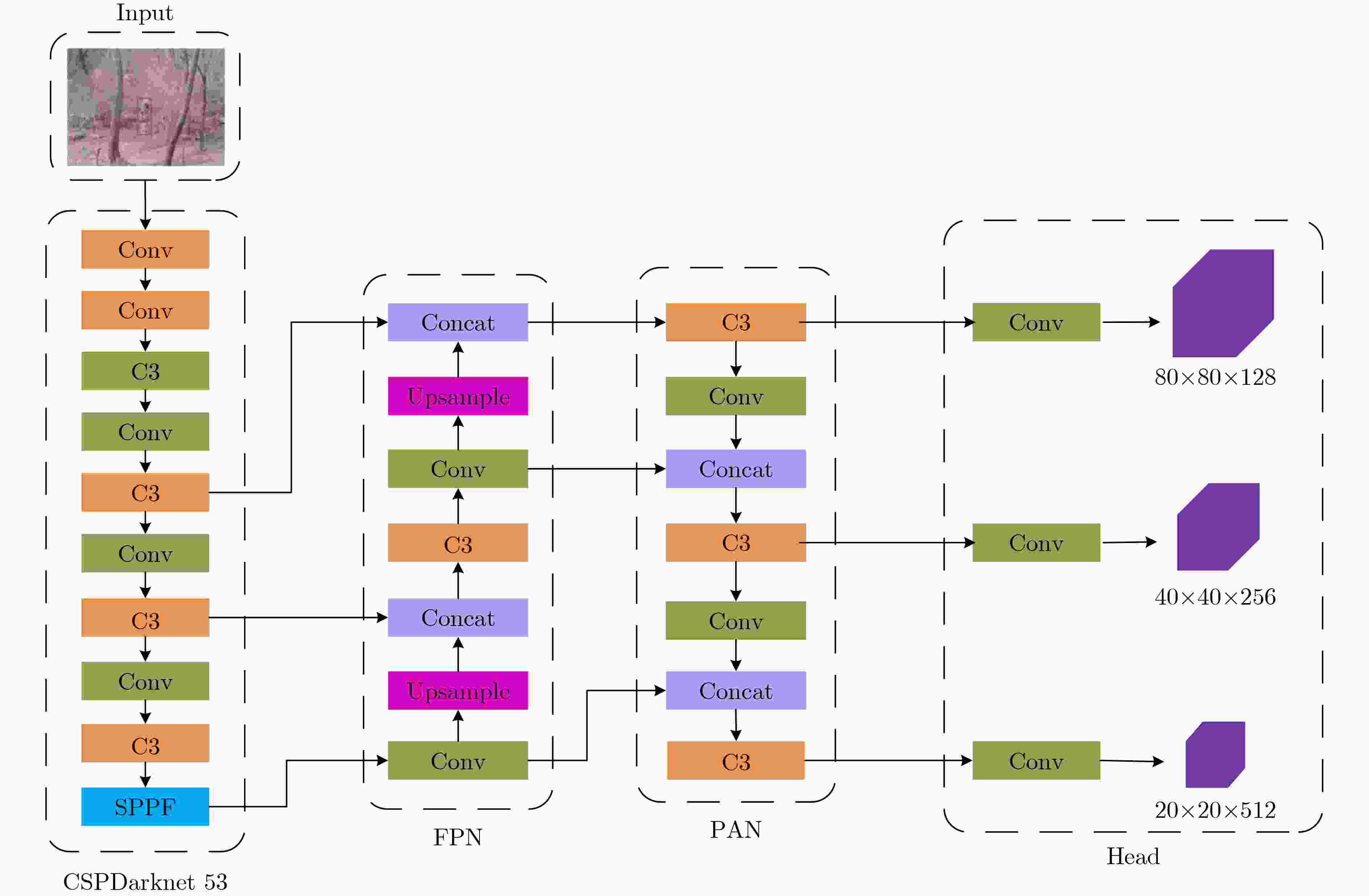
 下载:
下载:



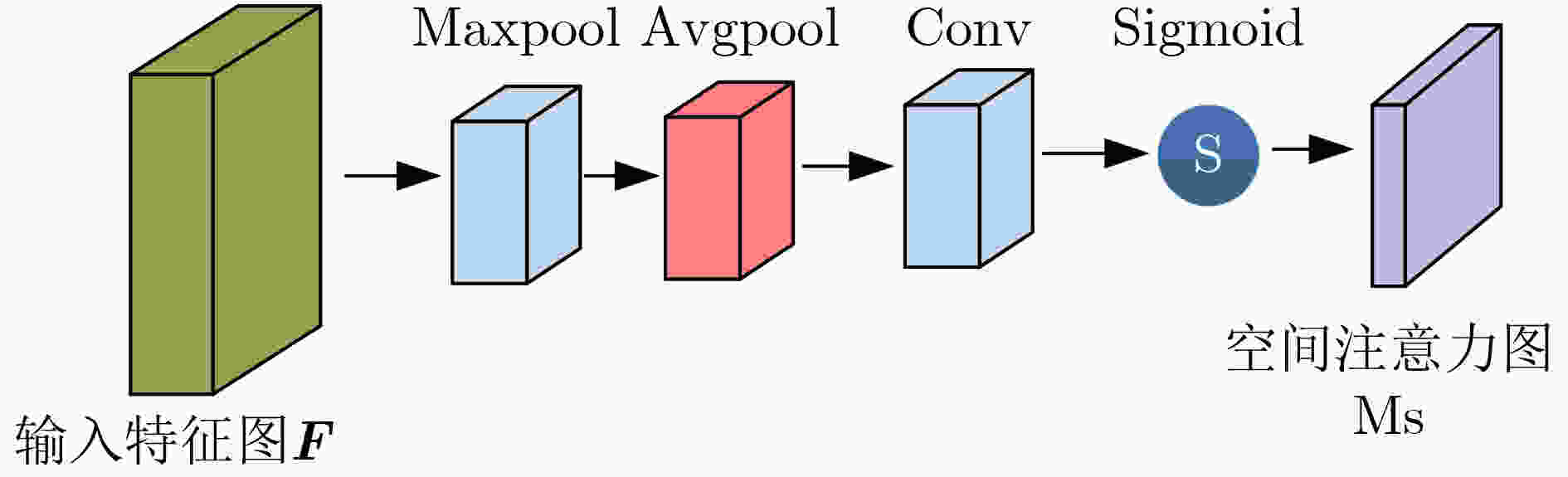





 下载:
下载:
