A Review of Research Progress on Brain-Computer Interface Systems for Rapid Serial Visual Presentation Based on ElectroEncephaloGram
-
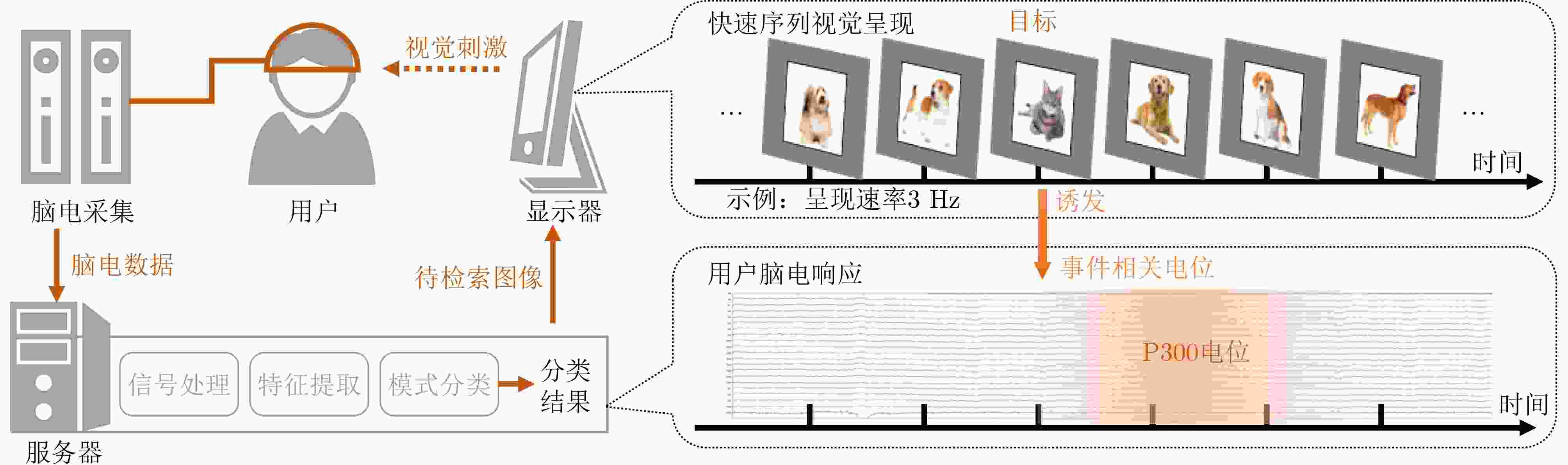
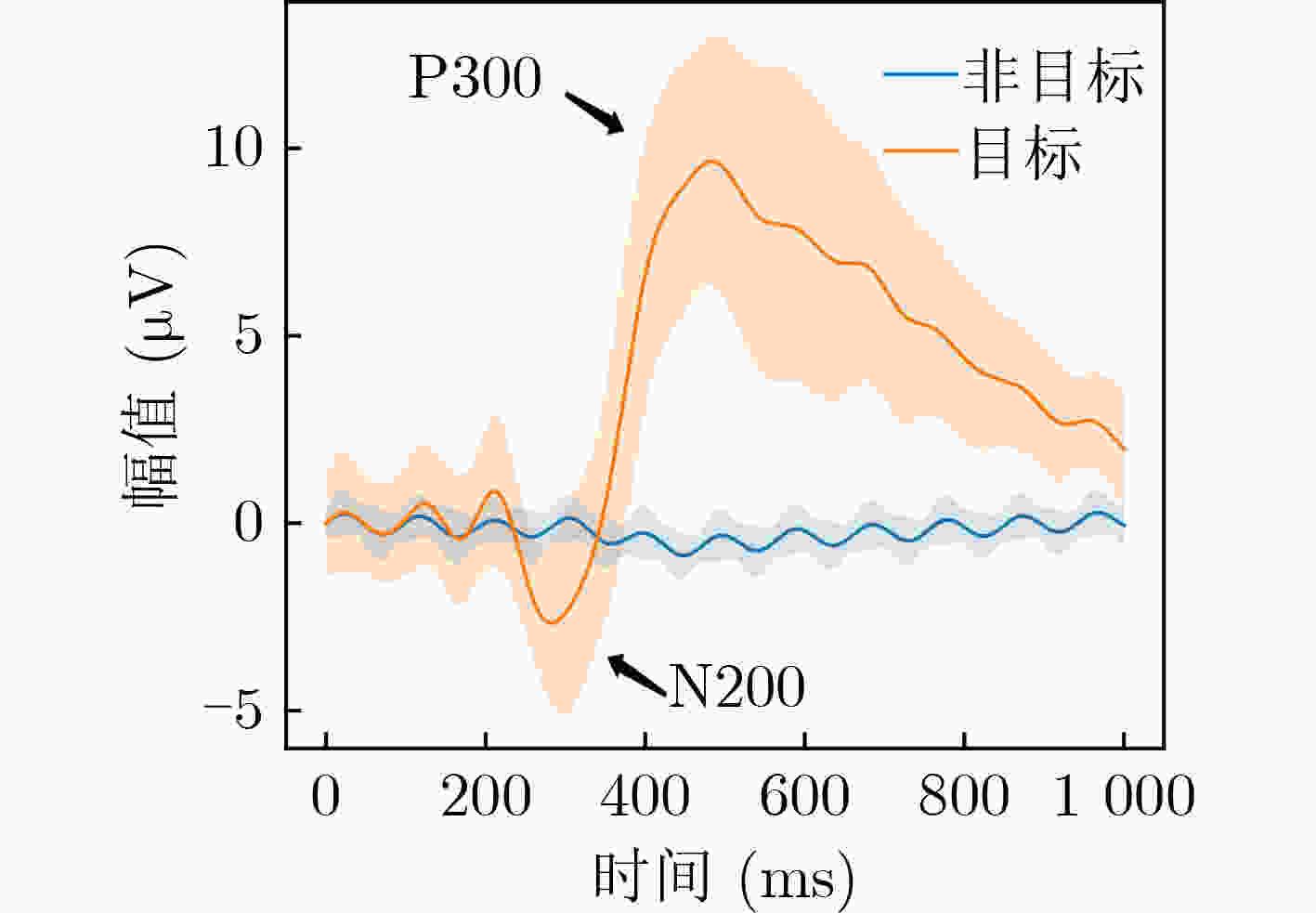
摘要: 脑-机接口(BCI)系统建立大脑与外部设备之间的直接交流通路,结合快速序列视觉呈现(RSVP)范式能够实现利用人类视觉系统进行高流通量图像目标检索。近些年来,RSVP-BCI系统在范式编码、脑电(EEG)解码和系统应用方面的研究取得了长足的进步。对范式编码的研究揭示不同范式参数对系统性能的影响,促进提升系统性能;脑电解码的研究在提升算法分类性能的同时推动少训练、零训练样本、多模态等场景下的应用;对RSVP-BCI系统应用的研究实现推动系统走向实际应用并拓宽了应用领域。同时,系统仍面临着迈向实际时可应用领域范围窄、脑电跨域解码难题以及计算机视觉飞速进步带来的挑战。该文对RSVP-BCI近年来的相关研究进展进行了回顾与总结,并对未来的发展方向进行了展望。Abstract: Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) system establishes a direct communication pathway between the brain and external devices, and combined with the Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP) paradigm, it can achieve high-throughput target image retrieval by utilizing the human visual system. In recent years, the RSVP-BCI system has made significant progress in research on paradigm, ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) decoding, and system applications. Research on paradigm reveals the impact of different paradigm parameters on system performance, promoting the improvement of system performance; The research on EEG decoding improves the classification performance of algorithms and promotes applications in scenarios such as few training, zero training samples, and multimodality; The research on the RSVP-BCI system application has driven the system towards practical applications and expanded its application fields. However, the system also faces challenges such as limited practical applications, difficulties in cross-domain decoding of EEG, and the rapid progress of computer vision. This article reviews and summarizes the research progress of RSVP-BCI in recent years, and looks forward to the future development direction.
-
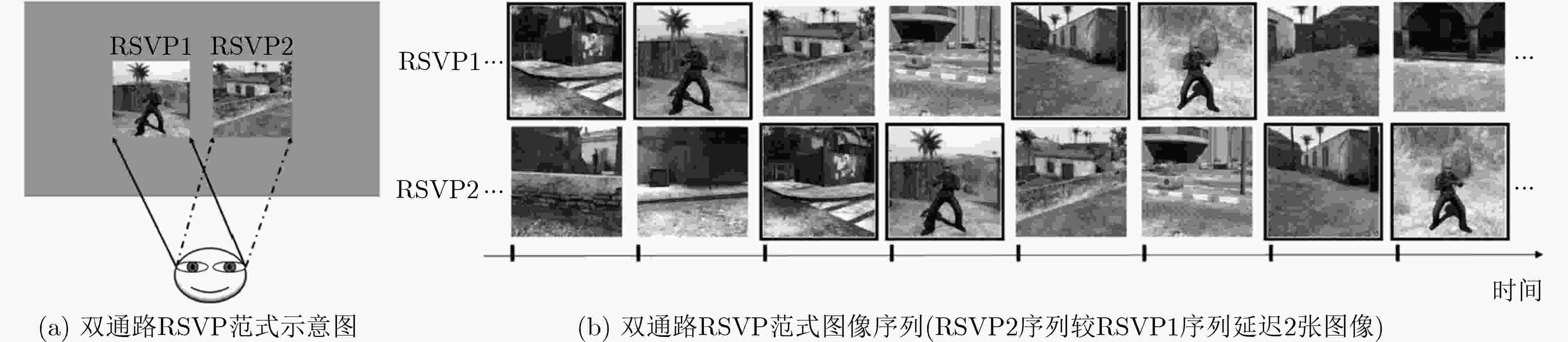
图 3 双视觉通路RSVP范式示意图(引自文献 [6])
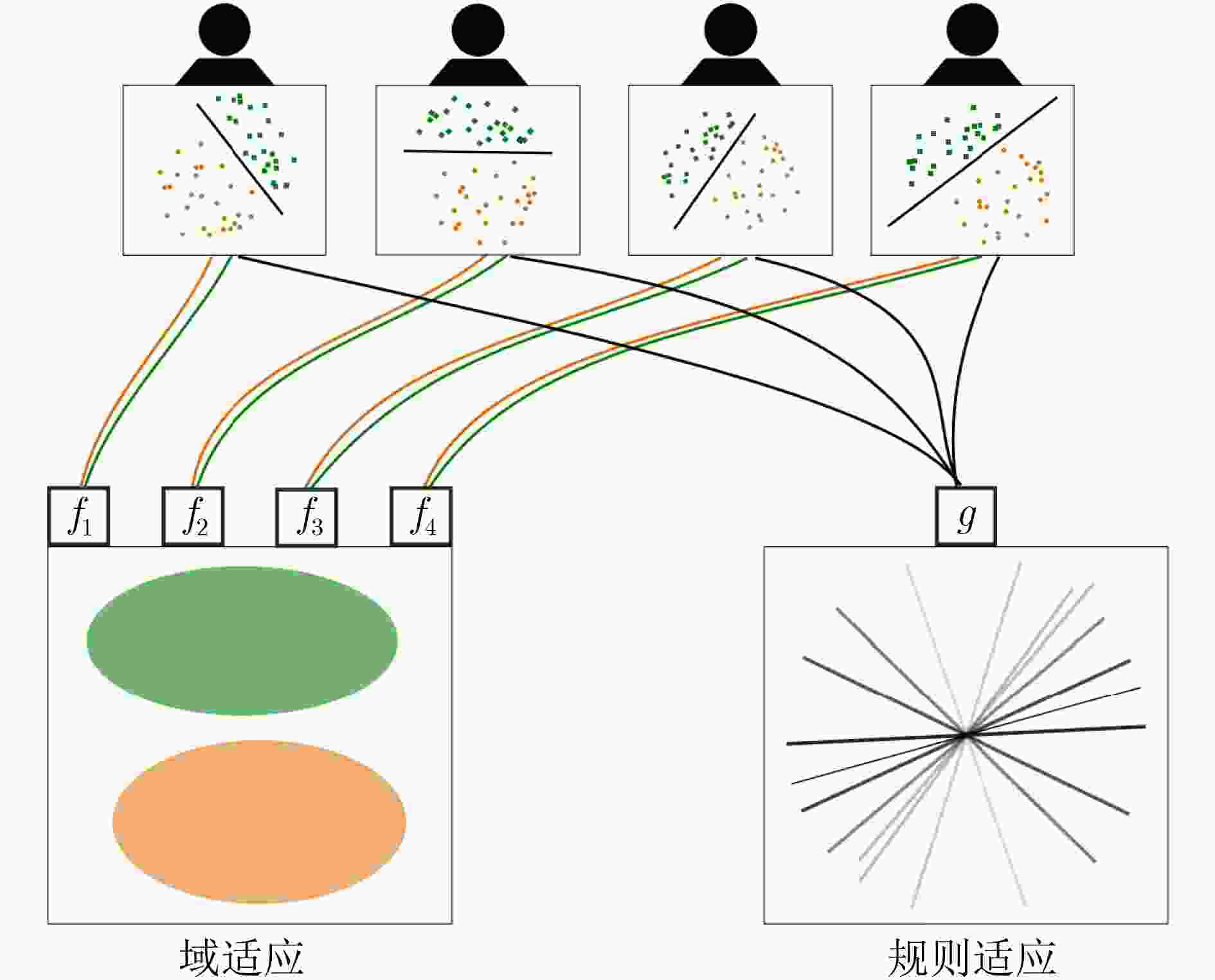
图 4 实现从源域到目标域的知识迁移存在两种方法[28]
表 1 RSVP编码研究进展简表
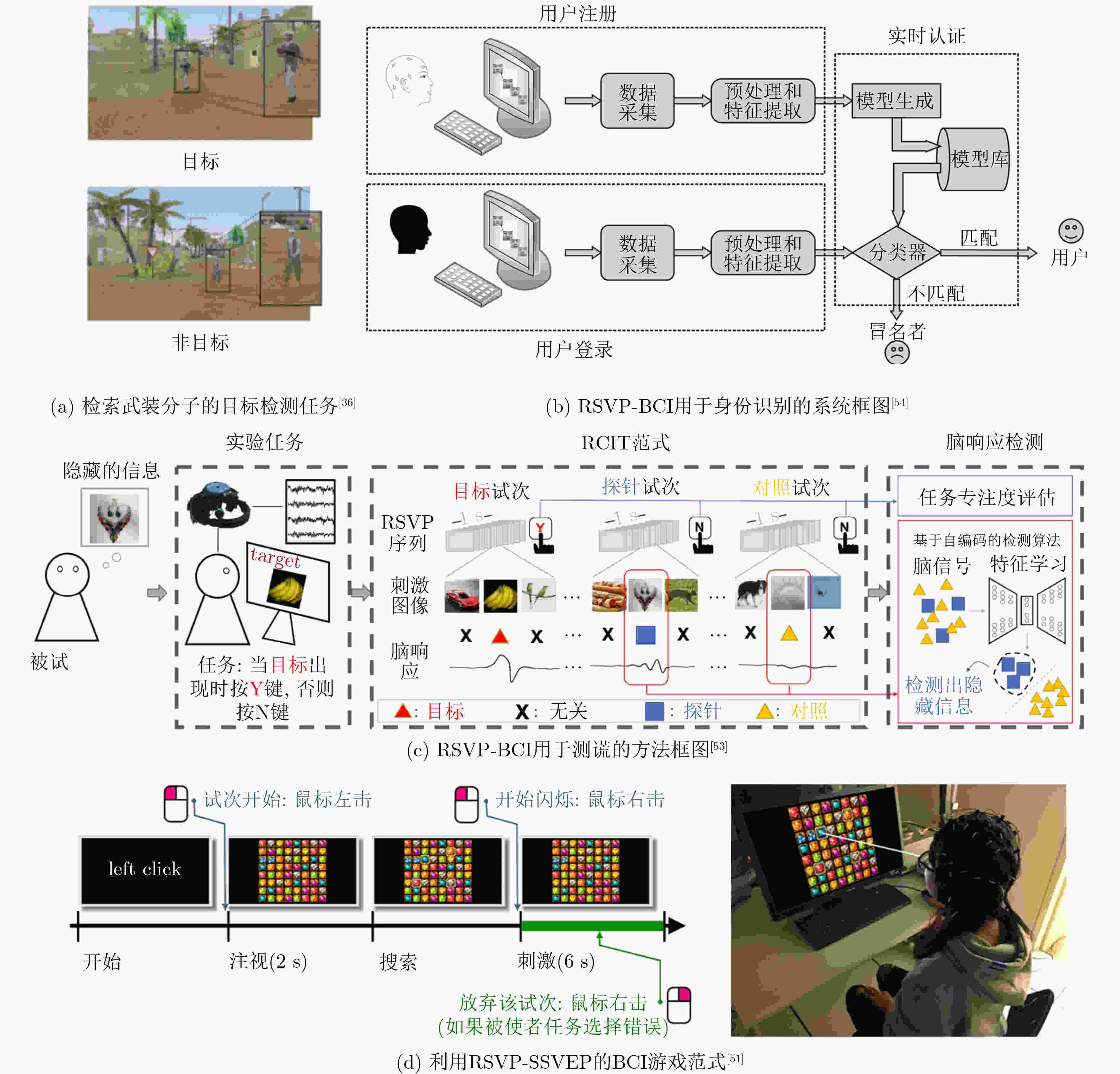
文献 时间 范式因素 应用 研究内容和主要结论 [5] 2019年 呈现速率 目标检索 研究呈现速率与认知负荷之间的关系,结果显示随着呈现速率的增加,人员的认知负荷增加,任务性能降低。 [6] 2015年 呈现模式 目标检索 研究了一种左右排列的双视觉通路RSVP,实现优于单视觉通路RSVP的性能。 [7,8] 2018/2017年 呈现模式 目标检索 研究了单/双三视觉通路RSVP,分别实现0.926,0.946和0.952的分类AUC。 [9] 2022年 呈现模式 目标检索 研究了双/三视觉通路范式下视野对RSVP目标检索的影响,研究结果表明视野对目标检索性能有显著影响,中心视野优于周边视野,左视野高于右视野,上视野优于下视野。 [11] 2017年 呈现模式 拼写器 研究了字符随机方向运动的RSVP字符拼写器范式,实现诱发更强的P300信号和拼写器字符识别准确率提升。 [12] 2019年 呈现模式 拼写器 研究了双/三视觉通路RSVP拼写器,实现提高系统ITR,其中三视觉通路最高实现了在线平均ITR为20.26 bpm。 [13] 2020年 混合范式 拼写器 研究了RSVP拼写器中的第1个混合范式——RSVP-SSVEP BCI,实现平均信息传输率达到23.41 bpm。 表 2 零校准脑电解码性能(%)
表 3 多模态脑电解码性能对比
-
[1] WOLPAW J R, WOLPAW E W, 伏云发, 杨秋红, 徐保磊, 等译. 脑-机接口: 原理与实践[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 3.WOLPAW J R, WOLPAW E W, FU Yunfa, YANG Qiuhong, XU Baolei, et al. translation. Brain-Computer Interface: Principles and Practice[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 3. [2] GERSON A D, PARRA L C, and SAJDA P. Cortically coupled computer vision for rapid image search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2006, 14(2): 174–179. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2006.875550. [3] LEES S, DAYAN N, CE - computer interfaces[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2018, 15(2): 021001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/COTTI H, et al. A review of rapid serial visual presentation-based brainaa9817. [4] LUCK S J, 范思陆, 丁玉珑, 曲折, 等译. 事件相关电位基础[M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社, 2009: 6.LUCK S J, FAN Silu, DING Yulong, QU Zhe, et al. translation. Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique[M]. Shanghai: East China Normal University Press, 2009: 6. [5] YI Weibo, QIU Shuang, FAN Xinan, et al. Estimation of mental workload induced by different presentation rates in rapid serial visual presentation tasks[C]. 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Beilin, Germany, 2019: 5552–5555. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2019.8857274. [6] CECOTTI H. Single-trial detection with magnetoencephalography during a dual-rapid serial visual presentation task[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 63(1): 220–227. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2478695. [7] LIN Zhimin, ZHANG Chi, ZENG Ying, et al. A novel P300 BCI speller based on the Triple RSVP paradigm[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 3350. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21717-y. [8] LIN Zhimin, ZENG Ying, WANG Xiaojuan, et al. EEG-based target detection during a multi-rapid serial visual presentation[C]. 8th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Shanghai, China, 2017: 556–559. doi: 10.1109/NER.2017.8008412. [9] ZHANG Shangen, CHEN, Xiaogang, WANG Yijun, et al. Visual field inhomogeneous in brain–computer interfaces based on rapid serial visual presentation[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2022, 19(1): 016015. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac4a3e. [10] MATRAN-FERNANDEZ A and POLI R. Brain–computer interfaces for detection and localization of targets in aerial images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 64(4): 959–969. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2583200. [11] WON D O, HWANG H J, KIM D M, et al. Motion-based rapid serial visual presentation for gaze-independent brain-computer interfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2018, 26(2): 334–343. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2017.2736600. [12] MIJANI A M, SHAMSOLLAHI M B, and HASSANI M S. A novel dual and triple shifted RSVP paradigm for P300 speller[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2019, 328: 108420. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.108420. [13] JALILPOUR S, SARDOUIE S H, and MIJANI A. A novel hybrid BCI speller based on RSVP and SSVEP paradigm[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2020, 187: 105326. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105326. [14] RIVET B, SOULOUMIAC A, ATTINA V, et al. xDAWN algorithm to enhance evoked potentials: Application to brain–computer interface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 56(8): 2035–2043. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2009.2012869. [15] BARACHANT A and CONGEDO M. A plug&play P300 BCI using information geometry[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0107, 2014. [16] MANOR R and GEVA A B. Convolutional neural network for multi-category rapid serial visual presentation BCI[J]. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 2015, 9: 168707. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2015.00146. [17] LAWHERN V J, SOLON A J, WAYTOWICH N R, et al. EEGNet: A compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2018, 15(5): 056013. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aace8c. [18] XIAO Xiaolin, XU Minpeng, JIN Jing, et al. Discriminative canonical pattern matching for single-trial classification of ERP components[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 67(8): 2266–2275. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2958641. [19] CUI Yujie, XIE Songyun, XIE Xinzhou, et al. LDER: A classification framework based on ERP enhancement in RSVP task[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2023, 20(3): 036029. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acd95d. [20] LI Bowen, ZHANG Shangen, HU Yijun, et al. Assembling global and local spatial-temporal filters to extract discriminant information of EEG in RSVP task[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2023, 20(1): 016052. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acb96f. [21] LI Bowen, LIN Yanfei, GAO Xiaorong, et al. Enhancing the EEG classification in RSVP task by combining interval model of ERPs with spatial and temporal regions of interest[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(1): 016008. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abc8d5. [22] SHAN Hongchang, LIU Yu, and STEFANOV T. A simple convolutional neural network for accurate P300 detection and character spelling in brain computer interface[C]. Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1604–1610. [23] SANTAMARIA-VAZQUEZ E, MARTINEZ-CAGIGAL V, VAQUERIZO-VILLAR F, et al. EEG-inception: A novel deep convolutional neural network for assistive ERP-based brain-computer interfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 2773–2782. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3048106. [24] MA Ronghua, YU Tianyou, ZHONG Xiaoli, et al. Capsule network for ERP detection in brain-computer interface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2021, 29: 718–730. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3070327. [25] MAO Jiayu, QIU Shuang, WEI Wei, et al. Cross-modal guiding and reweighting network for multi-modal RSVP-based target detection[J]. Neural Networks, 2023, 161: 65–82. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2023.01.009. [26] ZANG Boyu, LIN Yanfei, LIU Zhiwei, et al. A deep learning method for single-trial EEG classification in RSVP task based on spatiotemporal features of ERPs[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 0460c8. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac1610. [27] LI Fu, WANG Chong, LI Yang, et al. Phase preservation neural network for electroencephalography classification in rapid serial visual presentation task[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 69(6): 1931–1942. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3130917. [28] JAYARAM V, ALAMGIR M, ALTUN Y, et al. Transfer learning in brain-computer interfaces[J]. IEEE Computa tional Intelligence Magazine, 2016, 11(1): 20–31. doi: 10.1109/MCI.2015.2501545. [29] SHAMWELL J, LEE H, KWON H, et al. Single-trial EEG RSVP classification using convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 9836, Micro-and Nanotechnology Sensors, Systems, and Applications VIII, Baltimore, USA, 2016: 983622. doi: 10.1117/12.2224172. [30] HAJINOROOZI M, MAO Zijin, LIN Yuanpin, et al. Deep transfer learning for cross-subject and cross-experiment prediction of image rapid serial visual presentation events from EEG data[C]. 11th International Conference on Augmented Cognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 45–55. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-58628-1_4. [31] MIJANI A M, EINIZADE A, SHAMSOLLAHI M B, et al. Cross-subject and cross-paradigm learning using convolutional neural network for P300 event-related potential detection[J]. Journal of Neurology and Neuroscience, 2020, 11(5): 329. doi: 10.36648/2171-6625.11.1.329. [32] ZHANG Wen and WU Dongrui. Manifold embedded knowledge transfer for brain-computer interfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(5): 1117–1127. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.2985996. [33] WEI Wei, QIU Shuang, MA Xuelin, et al. Reducing calibration efforts in RSVP tasks with multi-source adversarial domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(11): 2344–2355. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3023761. [34] FAN Liangwei, SHEN Hui, XIE Fengyu, et al. DC-tCNN: A deep model for EEG-based detection of dim targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2022, 30: 1727–1736. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2022.3184725. [35] SHE Qingshan, CAI Yinhao, DU Shengzhi, et al. Multi-source manifold feature transfer learning with domain selection for brain-computer interfaces[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 514: 313–327. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.09.124. [36] WAYTOWICH N R, LAWHERN V J, BOHANNON A W, et al. Spectral transfer learning using information geometry for a user-independent brain-computer interface[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2016, 10: 430. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00430. [37] LEE J, WON K, KWON M, et al. CNN with large data achieves true zero-training in online P300 brain-computer interface[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 74385–74400. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988057. [38] WEI Wei, QIU Shuang, ZHANG Yukun, et al. ERP prototypical matching net: A meta-learning method for zero-calibration RSVP-based image retrieval[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2022, 19(2): 026028. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac5eb7. [39] LI Xujin, QIU Shuang, WEI Wei, et al. A zero-training method for RSVP-based brain computer interface[C]. Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), Shenzhen, China, 2022: 113–125. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-18910-4_10. [40] LI Xujin, WEI Wei, QIU Shuang, et al. TFF-Former: Temporal-frequency fusion transformer for zero-training decoding of two BCI tasks[C]. Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 2022: 51–59. doi: 10.1145/3503161.3548269. [41] MANOR R, MISHALI L, and GEVA A B. Multimodal neural network for rapid serial visual presentation brain computer interface[J]. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 2016, 10: 130. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2016.00130. [42] WU Qunjian, ZENG Ying, ZHANG Chi, et al. An EEG-based person authentication system with open-set capability combining eye blinking signals[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 335. doi: 10.3390/s18020335. [43] DING Yi, HUYNH B, XU Aiwen, et al. Multimodal classification of EEG during physical activity[C]. International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Suzhou, China, 2019, 185–194. doi: 10.1145/3340555.3353759. [44] MATRAN-FERNANDEZ A and POLI R. Towards the automated localisation of targets in rapid image-sifting by collaborative brain-computer interfaces[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5): e0178498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178498. [45] ZHENG Li, SUN Sen, ZHAO Hongze, et al. A cross-session dataset for collaborative brain-computer interfaces based on rapid serial visual presentation[J]. Front Neuroscience, 2020, 14: 579469. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.579469. [46] ZHANG Hangkui, ZHU Li, XU Senwei, et al. Two brains, one target: Design of a multi-level information fusion model based on dual-subject RSVP[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2021, 363: 109346. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2021.109346. [47] ZHAO Ziwei, LIN Yanfei, WANG Yijun, et al. Single-trial EEG classification using spatio-temporal weighting and correlation analysis for RSVP-based collaborative brain computer interface[J]. Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2023. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2023.3309255. [48] XU Meng, CHEN Yuanfang, WANG Dan, et al. Multi-objective optimization approach for channel selection and cross-subject generalization in RSVP-based BCIs[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 046076. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac0489. [49] HE Chao, LIU Jialu, ZHU Yuesheng, et al. Data augmentation for deep neural networks model in EEG classification task: A review[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2021, 15: 765525. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.765525. [50] PANWAR S, RAD P, QUARLES J, et al. Generating EEG signals of an RSVP experiment by a class conditioned Wasserstein generative adversarial network[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 2019: 1304–1310. doi: 10.1109/SMC.2019.8914492. [51] PANWAR S, RAD P, JUNG T P, et al. Modeling EEG data distribution with a Wasserstein generative adversarial network to predict RSVP events[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(8): 1720–1730. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3006180. [52] XU Meng, CHEN Yuanfang, WANG Yijun, et al. BWGAN-GP: An EEG data generation method for class imbalance problem in RSVP tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2022, 30: 251–263. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2022.3145515. [53] CUI Yujie, XIE Songyun, XIE Xinzhou, et al. Dynamic probability integration for electroencephalography-based rapid serial visual presentation performance enhancement: Application in nighttime vehicle detection[J]. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 2022, 16: 1006361. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2022.1006361. [54] WU Qunjian, YAN Bin, ZENG Ying, et al. Anti-deception: Reliable EEG-based biometrics with real-time capability from the neural response of face rapid serial visual presentation[J]. BioMedical Engineering OnLine, 2018, 17(1): 55. doi: 10.1186/s12938-018-0483-7. [55] ZENG Ying, WU Qunjian, YANG Kai, et al. EEG-based identity authentication framework using face rapid serial visual presentation with optimized channels[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2018, 19(1): 6. doi: 10.3390/s19010006. [56] WANG Hanwen, QI Yu, YU Hang, et al. , RCIT: An RSVP-based concealed information test framework using EEG signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2022, 14(2): 541–551. doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2021.3053455. [57] NAYAK T, KO L W, JUNG T P, et al. Target classification in a novel SSVEP-RSVP based BCI gaming system[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 2019: 4194–4198. doi: 10.1109/SMC.2019.8914174. [58] KO L W, SANKAR D S V, HUANG Yufei, et al. SSVEP-assisted RSVP brain–computer interface paradigm for multi-target classification[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(1): 016021. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abd1c0. [59] ACKERMAN E and STRICKLAND E. Are you ready for workplace brain scanning?[EB/OL]. https://spectrum.ieee.org/neurotech-workplace-innereye-emotiv, 2022. [60] YI Weibo, QIU Shuang, FAN Xinan, et al. Evaluation of mental workload associated with time pressure in rapid serial visual presentation tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2022, 14(2): 608–616. doi: 10.1109/tcds.2021.3061564. [61] TANG M F, FORD L, ARABZADEH E, et al. Neural dynamics of the attentional blink revealed by encoding orientation selectivity during rapid visual presentation[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 434. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14107-z. [62] SUN Meng, LIU Fang, CUI Lixia, et al. The effect of fearful faces on the attentional blink is modulated by emotional task relevance: An event-related potential study[J]. Neuropsychologia, 2021, 162: 108043. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2021.108043. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
