Research on Full-duplex Two-Way Time Transfer Techniques for Flying Ad Hoc Networks
-
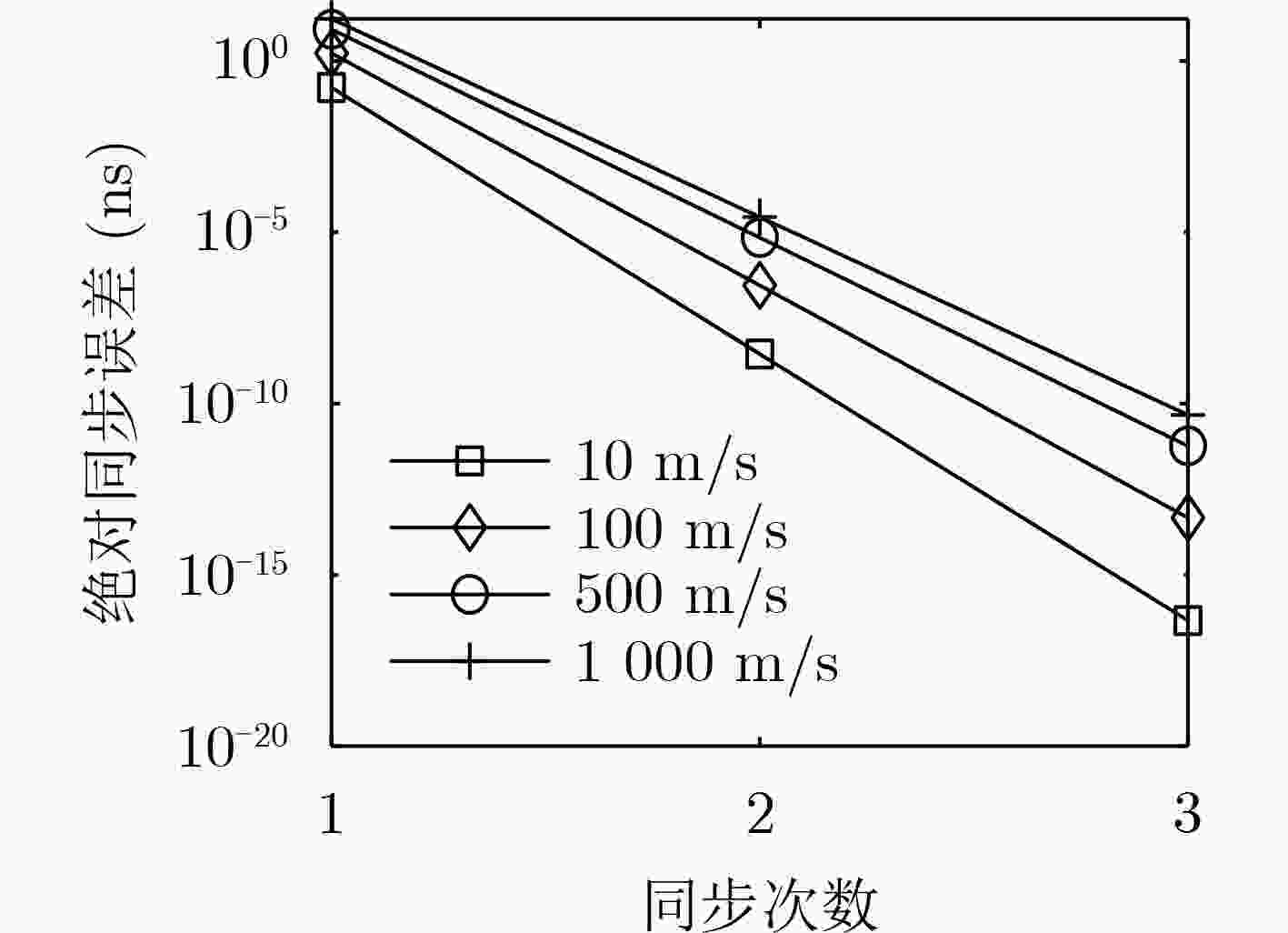
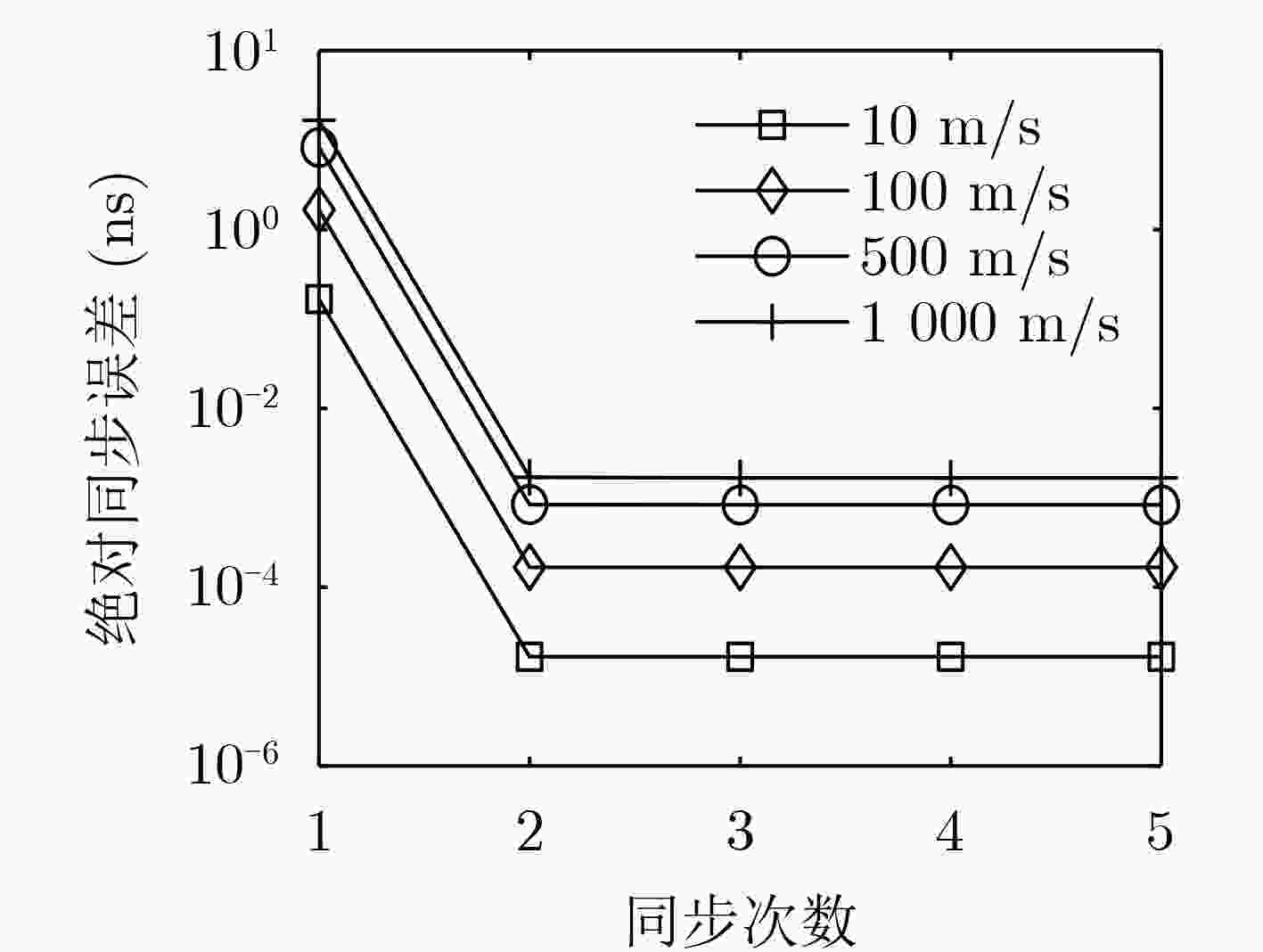
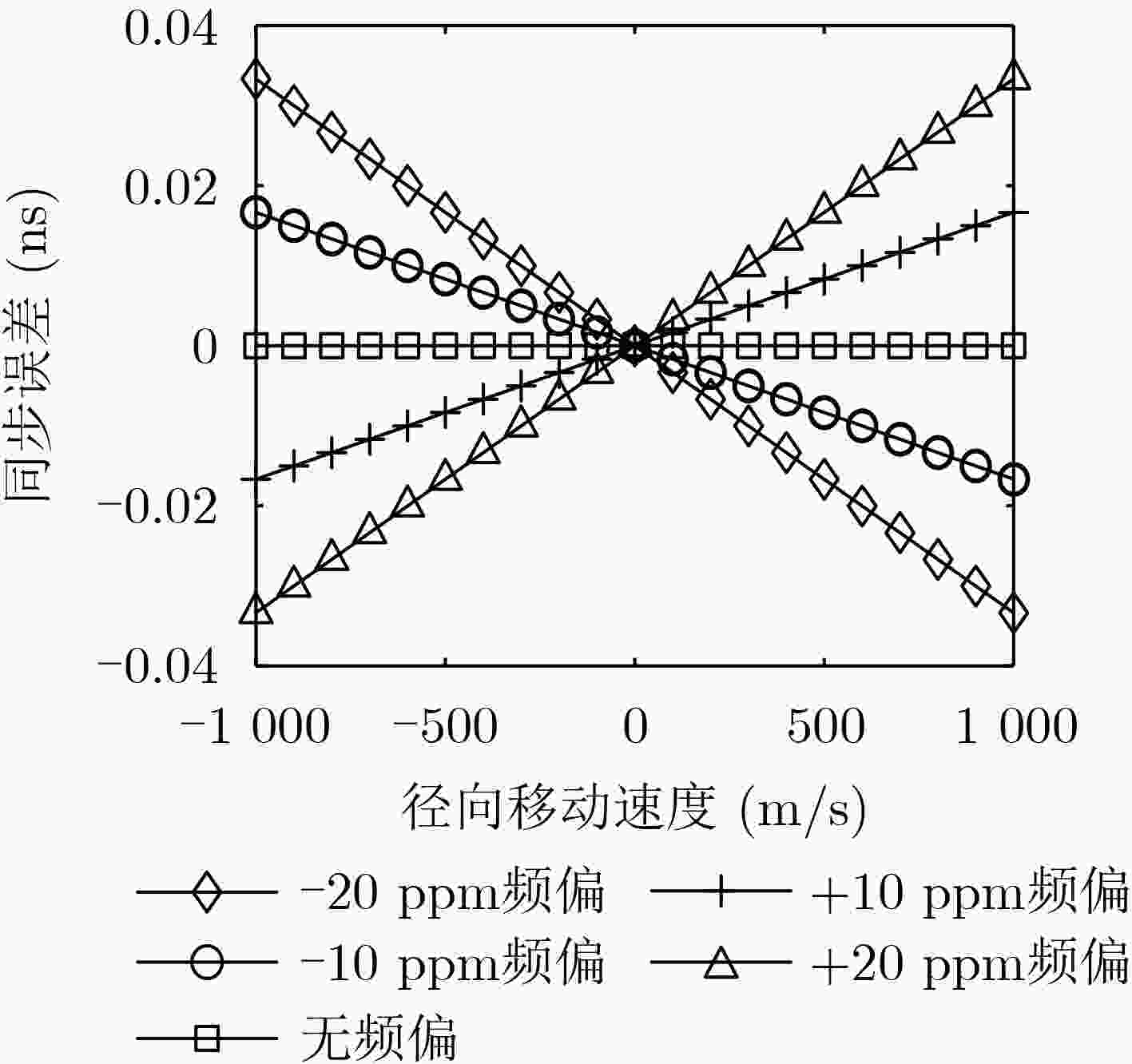
摘要: 针对飞行自组网(FANET)中节点间相对运动导致双向时间传递精度下降的问题,该文提出一种全双工双向时间传递(TWTT)方法。首先,根据全双工双向时间传递过程构造了需要求解的方程组,推导了单次时间传递的同步误差表达式;然后,分析了在无频偏和有频偏条件下,迭代进行全双工双向时间传递的收敛性;最后,通过仿真分析和实验验证比较了全双工双向时间传递方法和传统双向时间传递方法的性能。仿真和实验结果表明,全双工双向时间传递方法在节点高速机动下,时间同步精度可达到与物理层时间戳相同的精度,优于现有的运动补偿方法。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of time synchronization accuracy degradation of two-way time transfer due to relative motion between nodes in Flying Ad hoc NETwork (FANET), a full-duplex Two-Way Time Transfer (TWTT) method is proposed. Firstly, a system of equations to be solved is constructed according to the full-duplex two-way time transfer procedure, and the synchronization error expression for single full-duplex two-way time transfer is derived. Then, the convergence of iteratively performing full-duplex two-way time transfer with or without frequency offset is analyzed. Finally, the performance of full-duplex two-way time transfer method is compared with traditional two-way time transfer methods by simulation analysis and experimental validation. The simulation and experimental results show that full-duplex two-way time transfer method can achieve the same time synchronization accuracy as the physical layer timestamps under high-speed maneuvering between nodes, and the synchronization accuracy is better than the existing motion compensation methods.
-
表 1 小型化软件无线电平台设备指标
参数 指标 处理芯片 Xilinx XC7Z100 射频收发芯片 ADI AD9371 工作频段 1.4~1.7 GHz 最大信号带宽 ≤100 MHz 发射通道个数 2 最大发射功率 ≥35 dBm 发射衰减可调范围 0~30 dB 接收通道个数 4 接收增益可调范围 0~60 dB 重量 ≤800 g 体积 150 mm×100 mm×45 mm 表 2 物理层链路与信道模拟器指标
参数 指标 工作频段 1.4~1.7 GHz 帧长度 400 μs 基带采样率 15.36 MSps 射频采样率 153.6 MSps 物理层时间戳精度 约6.51 ns 模拟传输距离 1~10 km 模拟径向移动速度 0 m/s, 100 m/s, 200 m/s 模拟参数更新周期 10 ms 表 3 秒脉冲偏差测试结果
相对移动速度 协议 秒脉冲偏差(ns) 最大值 最小值 均值 静止 全双工协议 0.86 0.94 0.90 PTP协议 0.33 0.41 0.38 100 m/s 全双工协议 –1.23 –1.14 –1.18 PTP协议 6.85 6.91 6.88 200 m/s 全双工协议 1.71 1.77 1.75 PTP协议 12.24 12.34 12.30 -
[1] KIM D Y and LEE J W. Joint mission assignment and topology management in the mission-critical FANET[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(3): 2368–2385. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2958130. [2] LAKEW D S, SA’AD U, DAO N N, et al. Routing in flying ad hoc networks: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(2): 1071–1120. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2982452. [3] ARAFAT M Y, POUDEL S, and MOH S. Medium access control protocols for flying Ad hoc networks: A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(4): 4097–4121. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3034600. [4] YANG Beiya and YANG Erfu. A survey on radio frequency based precise localisation technology for UAV in GPS-denied environment[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2021, 103(3): 38. doi: 10.1007/s10846-021-01500-4. [5] DU Bin, MAO Ruijiu, KONG Nan, et al. Distributed data fusion for on-scene signal sensing with a multi-UAV system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2020, 7(3): 1330–1341. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2020.2975228. [6] NANZER J A, MGHABGHAB S R, ELLISON S M, et al. Distributed phased arrays: Challenges and recent advances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 4893–4907. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3092401. [7] SEIJO O, VAL I, LUVISOTTO M, et al. Clock synchronization for wireless time-sensitive networking: A march from microsecond to nanosecond[J]. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine, 2022, 16(2): 35–43. doi: 10.1109/MIE.2021.3078071. [8] SEIJO Ó, LÓPEZ-FERNÁNDEZ J A, BERNHARD H P, et al. Enhanced timestamping method for subnanosecond time synchronization in IEEE 802.11 over WLAN standard conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(9): 5792–5805. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2959200. [9] PRAGER S, HAYNES M S, and MOGHADDAM M. Wireless subnanosecond RF synchronization for distributed ultrawideband software-defined radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(11): 4787–4804. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3014876. [10] MERLO J M, MGHABGHAB S R, and NANZER J A. Wireless picosecond time synchronization for distributed antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2023, 71(4): 1720–1731. doi: 10.1109/TMTT. 2022.3227878. [11] IEEE. IEEE Std 1588-2008 IEEE standard for a precision clock synchronization protocol for networked measurement and control systems[S]. New York: IEEE Standards Association, 2008. doi: 10.1109/IEEESTD.2008.4579760. [12] 于雪晖, 王盾, 李周, 等. 双向比对高精度物理时间同步方法[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(5): 203–217. doi: 10.7527/s1000-6893.2019.22507.YU Xuehui, WANG Dun, LI Zhou, et al. High accuracy physical time synchronization method based on two-way comparison[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(5): 203–217. doi: 10.7527/s1000-6893.2019.22507. [13] ZHAO Sihao, ZHANG Xiaoping, CUI Xiaowei, et al. Optimal two-way TOA localization and synchronization for moving user devices with clock drift[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7778–7789. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3092255. [14] JIA Tianyi, HO K C, WAGN Haiyan, et al. Localization of a moving object with sensors in motion by time delays and Doppler shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 5824–5841. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3023972. [15] YANG Zhiyu, WANG Rui, JIANG Yi, et al. Joint estimation of velocity, Angle-of-Arrival and Range (JEVAR) using a conjugate pair of Zadoff-Chu sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 6009–6022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3122907. [16] ANTTILA L, LAMPU V, HASSANI S A, et al. Full-duplexing with SDR devices: Algorithms, FPGA implementation, and real-time results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(4): 2205–2220. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3040226. [17] HUANG Xiaojing, LE A T, and GUO Y J. Joint analog and digital self-interference cancellation for full duplex transceiver with frequency-dependent I/Q imbalance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(4): 2364–2378. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3211316. [18] 余湋, 张毅, 张志亚, 等. 全双工测控链路自干扰抑制设计与实验验证[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2023, 50(3): 182–191. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2023.03.017.YU Wei, ZHANG Yi, ZHANG Zhiya, et al. Design and experimental verification of self-interference suppression for full-duplex measurement and control links[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2023, 50(3): 182–191. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2023.03.017. [19] YU Bin, QIAN Chen, LEE J, et al. Realizing high power full duplex in millimeter wave system: Design, prototype and results[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(9): 2893–2906. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3287609. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
