A Service Function Chain deployment Algorithm Based on Proximal Policy Optimization
-
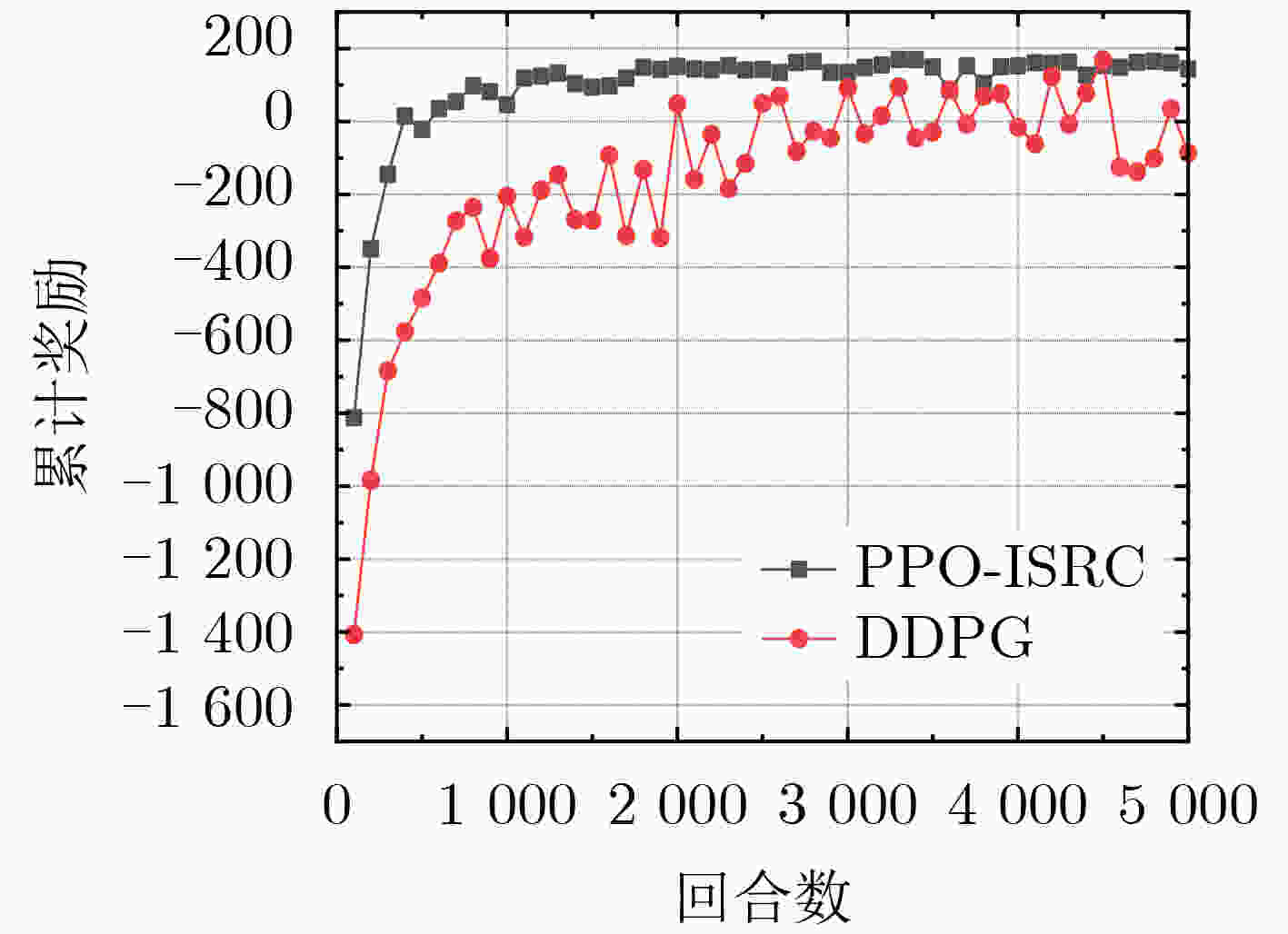
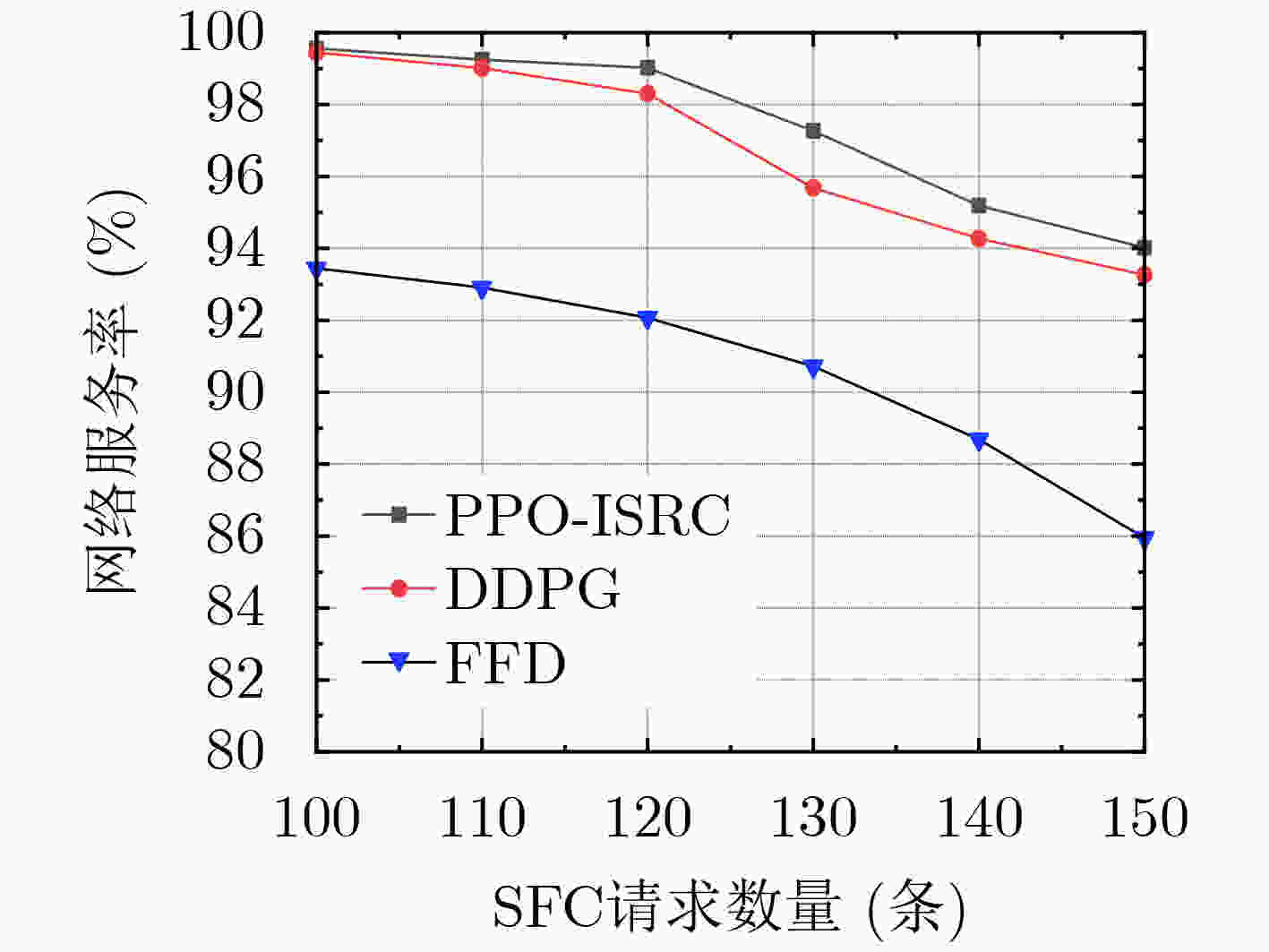
摘要: 针对网络功能虚拟化(NFV)环境下高维度服务功能链(SFC)部署的高可靠低成本问题,该文提出了一种基于近端策略优化的服务功能链部署算法(PPO-ISRC)。首先综合考虑底层物理服务器特征和服务功能链特征,将服务功能链部署建模为马尔可夫决策过程,然后,以最大化服务率和最小化资源消耗为优化目标设置奖励函数,最后,采用近端策略优化方法对服务功能链部署策略求解。仿真实验结果表明,与启发式算法(FFD)和深度确定性策略梯度算法(DDPG)相比,所提算法具有收敛速度快,稳定性高的特点。在满足服务质量的要求下,降低了部署成本,并提高了网络服务可靠性。Abstract: In order to solve the high-dimensional Service Function Chain (SFC) deployment problem of high reliability and low cost in the Network Function Virtualization (NFV) environment, an Improving Service and Reducing Consumption based on Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO-ISRC) is proposed. Firstly, considering the characteristics of the underlying physical server and SFC, the state transition process of the underlying server network is descried, and the deployment of SFC is taken as a Markov Decision Process. Then the reward function is set with the optimization goal of maximizing the service rate and minimizing resource consumption. Finally the PPO method is used to solve the SFC deployment strategy. The results show that compared with the heuristic algorithm First-Fit Dijkstra (FFD) and the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm, the proposed algorithm has the characteristics of fast convergence speed and higher stability. Under the requirements of service quality, the deployment cost is reduced and the reliability of network service is improved.
-
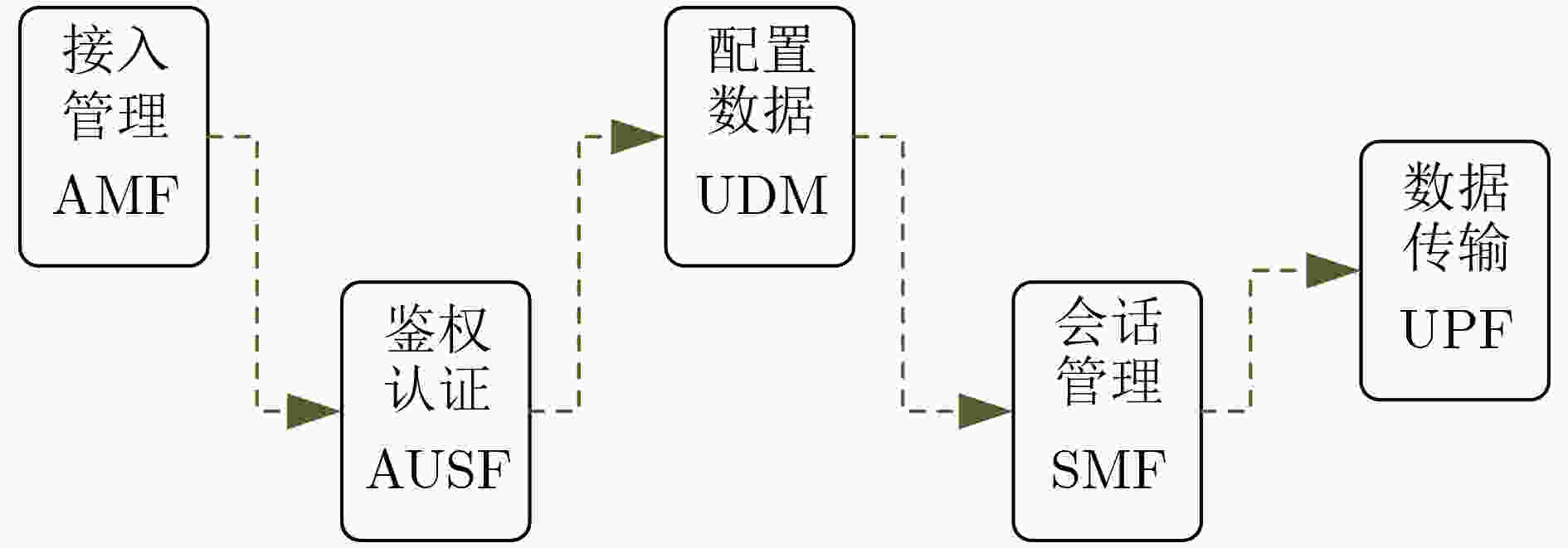
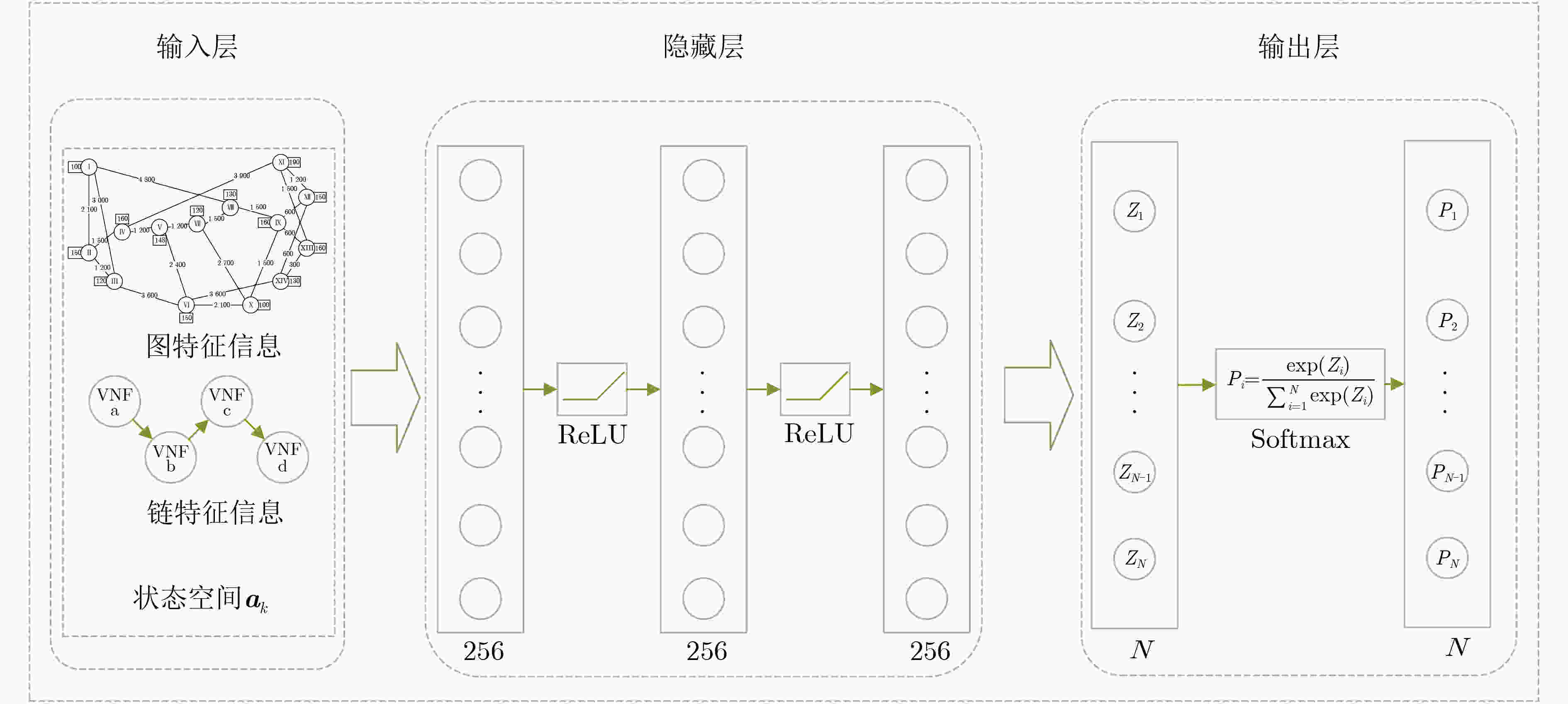
1 PPO-ISRC算法
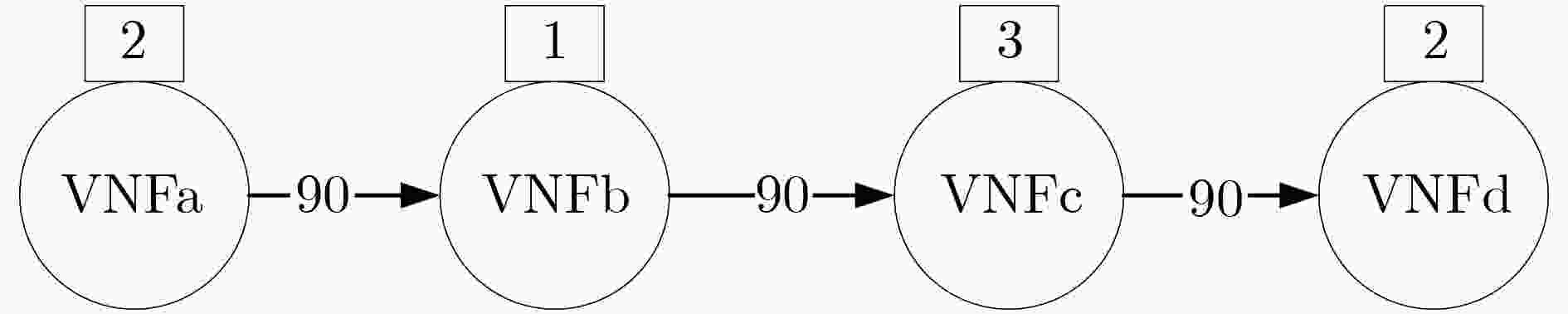
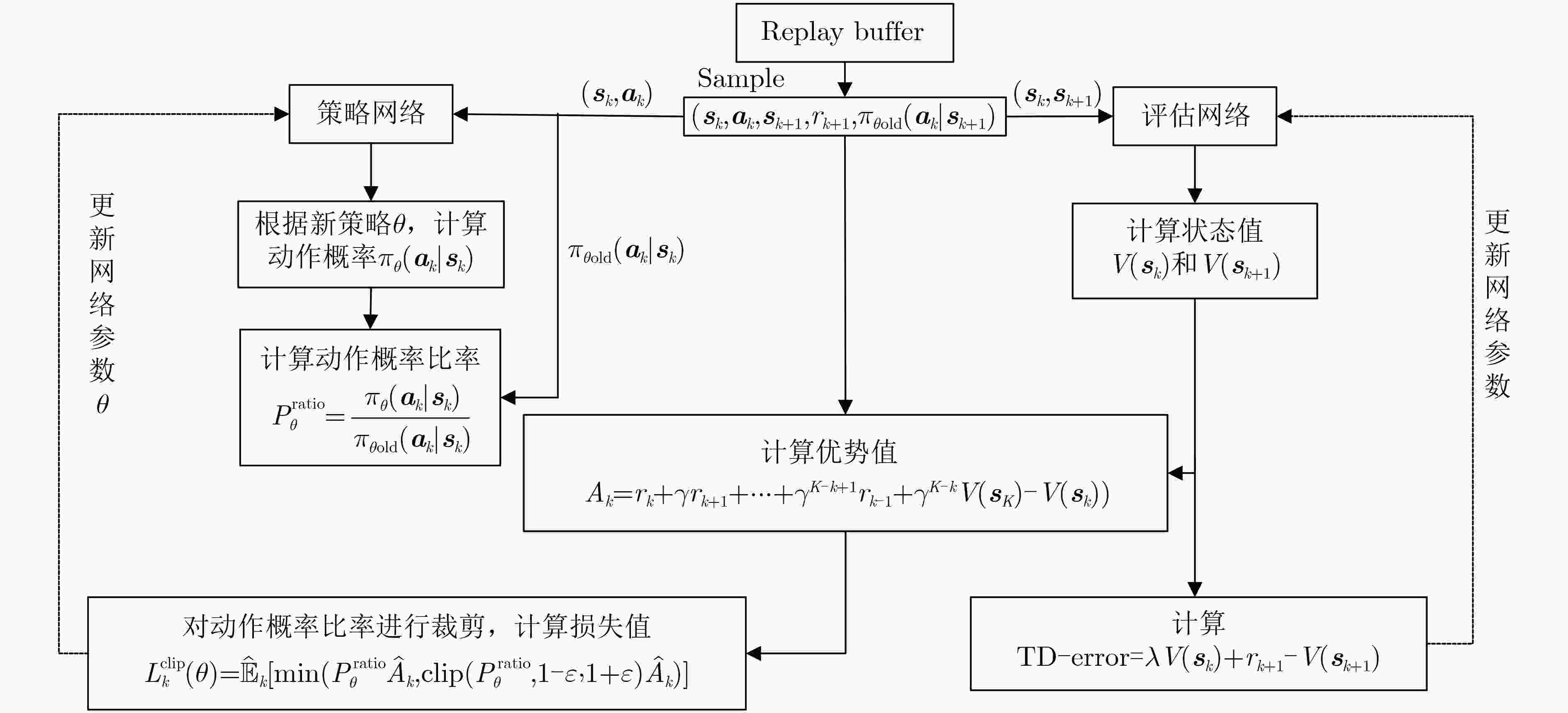
输入:底层拓扑特征矩阵和待部署SFC特征矩阵 输出:VNF映射位置 (1) 初始化网络参数$ \theta $,缓冲区D; (2) for each episode do (3) 初始化底层拓扑特征矩阵; (4) for each SFC do (5) for each VNF do (6) 构建当前时隙的状态空间$ {{\boldsymbol{s}}_k} $; (7) 由$ {\pi _{{\theta _{{\text{old}}}}}} $选取动作$ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_k} $,保存动作概率$ P({\pi _{{\theta _{{\text{old}}}}}}({{\boldsymbol{a}}_k}\left| {{{\boldsymbol{s}}_k}} \right.)) $; (8) if 执行动作$ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_k} $使得服务器剩余资源为负,then (9) 放弃该条服务功能链部署; (10) break (11) 执行动作$ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_k} $,进入下一状态$ {\boldsymbol{{s}}_{k + 1}} $,获得奖励$ {r_k} $; (12) 当前数据$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{s}}_k},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_k},P({\pi _{{\theta _{{\text{old}}}}}}({{\boldsymbol{a}}_k}\left| {{{\boldsymbol{s}}_k}} \right.)),{r_k}} \right\} $保存至缓冲区D; (13) if 缓冲区D 中数据量>K,then (14) 由式(7)、式(8)计算奖励期望$ {\hat R_k} $优势估计$ {\hat A_k} $; (15) for ${n_{{\text{update}}}}$do (16) 由评估网络获取状态价值; (17) 由式(7)计算目标函数:$ L_k^{{\text{clip}} + {\text{vf}} + {S_{\mathrm{e}}}}\left( \theta \right) $; (18) 通过最大化$ L_k^{{\text{clip}} + {\text{vf}} + {S_{\mathrm{e}}}}\left( \theta \right) $更新网络参数$ \theta $; (19) end for (20) $ {\theta _{{\text{old}}}} \leftarrow \theta $,清空缓冲区D; (21) end if (22) 更新状态$ {{\boldsymbol{s}}_k} \leftarrow {{\boldsymbol{s}}_{k + 1}} $; (23) end for (24) end for (25)end for 表 1 系统环境参数
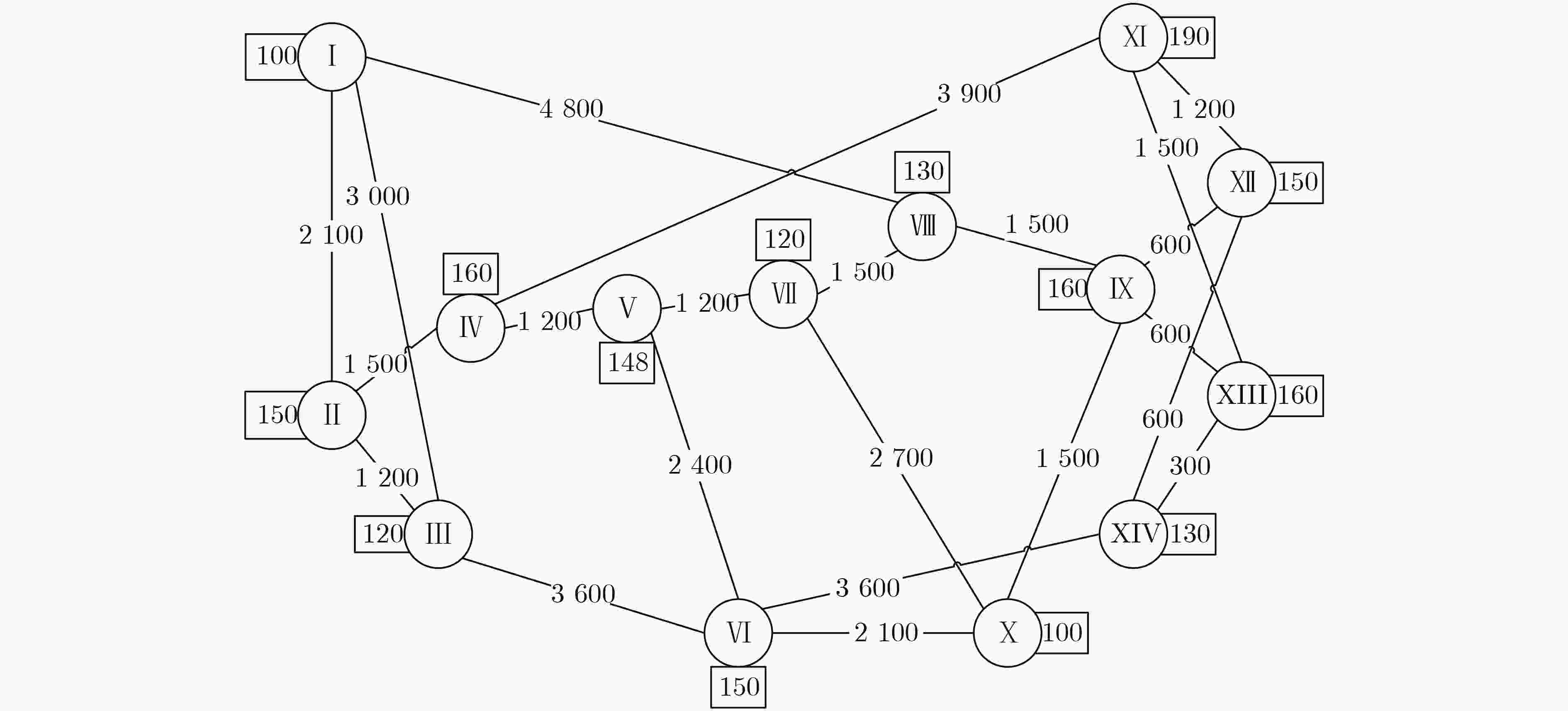
参数 值 服务器节点的计算资源容量${\theta ^n}$ [150,200] 待部署的服务功能链数量$ M $ [100,150] 服务功能链请求的VNF数量$ {N_{{\text{vnf}}}} $ [3,5] 每种VNF所需资源大小$ C_n^{{\text{SF}}{{\text{C}}_r},i} $ [1,3] 每条链所需的链路带宽 [20,90] 表 2 PPO-ISRC网络参数
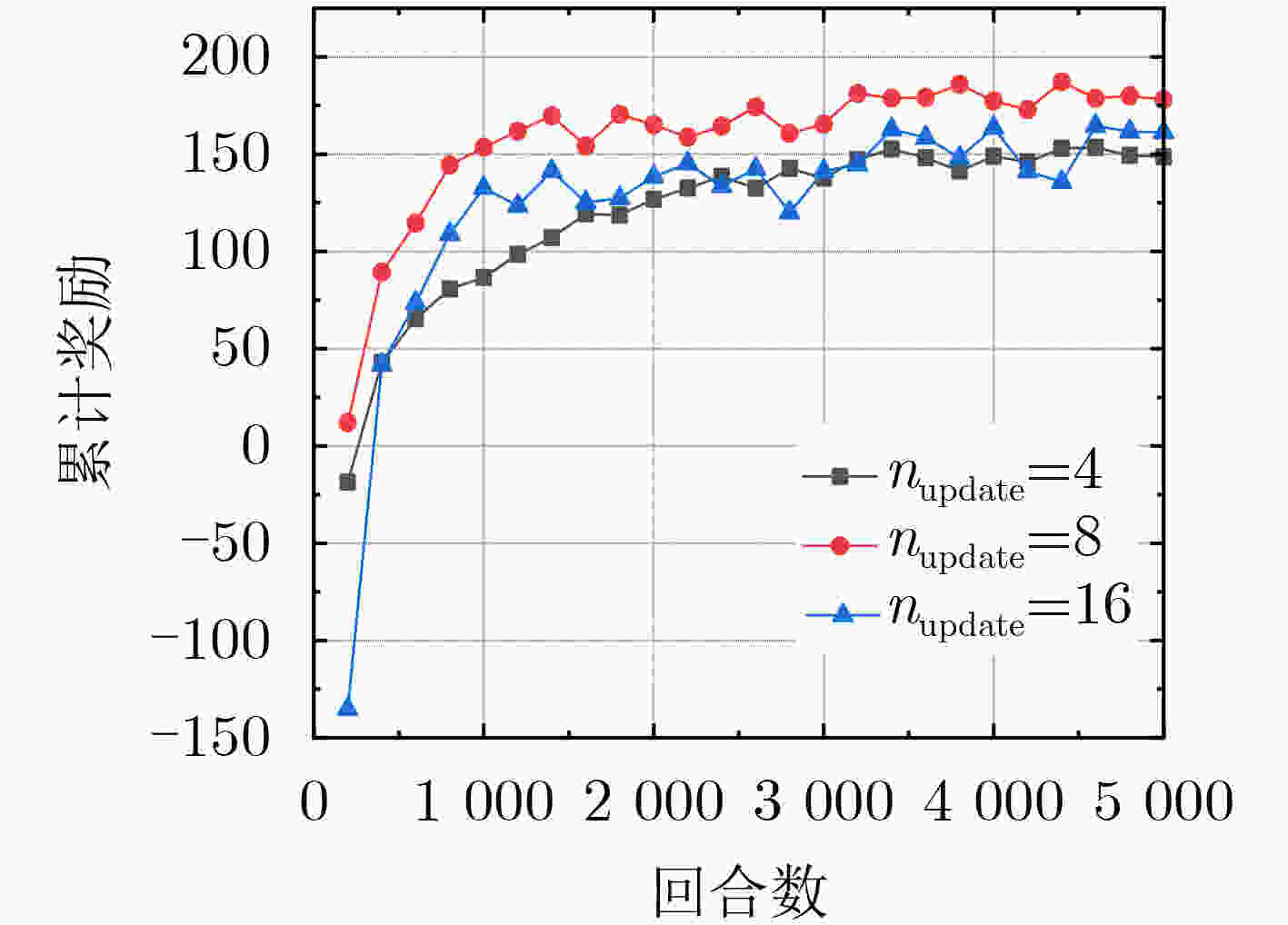
参数 值 评估网络目标函数所占权重值$ {{\mathrm{c}}_1} $ –0.5 策略模型的熵所占权重值$ {{\mathrm{c}}_2} $ –0.01 关于动作值概率分布标准差的衰减因子$ {\alpha _\varOmega } $ 0.9959 仿真回合数Episodes 5000 缓冲区D的大小Buffer-size 128 网络连续更新次数$ {n_{{\text{update}}}} $ 4,8,16 PPO的裁剪参数$ {{\varepsilon }} $ 0.2 计算奖励期望的折扣系数$ \gamma $ 0.97 策略网络学习率$ {l_{\text{a}}} $ 0.001 评估网络学习率$ {l_{\text{c}}} $ 0.001 -
[1] 李鹤, 张恒升, 朱瑾瑜, 等. 5G专网融合时间敏感网络架构技术[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(8): 30–35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.08.006.LI He, ZHANG Hengsheng, ZHU Jinyu, et al. Research on the fusion architecture technology between 5G private network and time-sensitive network[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(8): 30–35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.08.006. [2] MATENCIO-ESCOLAR A, WANG Qi, and CALERO J M A. SliceNetVSwitch: Definition, design and implementation of 5G multi-tenant network slicing in software data paths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2020, 17(4): 2212–2225. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2020.3029653. [3] 唐伦, 王恺, 张月, 等. 网络切片场景下基于分布式生成对抗网络的服务功能链异常检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(1): 262–271. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211261.TANG Lun, WANG Kai, ZHANG Yue, et al. Service function chain anomaly detection based on distributed generative adversarial network in network slicing scenario[J] Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(1): 262–271. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211261. [4] 张岳, 张俊楠, 吴晓春, 等. 基于改进灰狼优化算法的服务功能链映射算法[J]. 电信科学, 2022, 38(11): 57–72. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022275.ZHANG Yue, ZHANG Junnan, WU Xiaochun, et al. Improved grey wolf optimization algorithm based service function chain mapping algorithm[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2022, 38(11): 57–72. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022275. [5] 高媛, 方海, 赵扬, 等. 基于自然梯度Actor-Critic强化学习的卫星边缘网络服务功能链部署方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 455–463. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211384.GAO Yuan, FANG Hai, ZHAO Yang, et al. A satellite edge network service function chain deployment method based on natural gradient actor-critic reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 455–463. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211384. [6] BARI F, CHOWDHURY S R, AHMED R, et al. Orchestrating virtualized network functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2016, 13(4): 725–739. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2016.2569020. [7] SUN Quanying, LU Ping, LU Wei, et al. Forecast-assisted NFV service chain deployment based on affiliation-aware vNF placement[C]. 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7841846. [8] ZHANG Qixia, XIAO Yikai, LIU Fangming, et al. Joint optimization of chain placement and request scheduling for network function virtualization[C]. 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Atlanta, USA, 2017: 731–741. doi: 10.1109/ICDCS.2017.232. [9] QU Long, ASSI C, and SHABAN K. Delay-aware scheduling and resource optimization with network function virtualization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(9): 3746–3758. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2016.2580150. [10] BECK M T and BOTERO J F. Scalable and coordinated allocation of service function chains[J]. Computer Communications, 2017, 102: 78–88. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2016.09.010. [11] SINGH S, OKUN A, and JACKSON A. Learning to play go from scratch[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 336–337. doi: 10.1038/550336a. [12] ZHU Yuchao, YAO Haipeng, MAI Tianle, et al. Multiagent reinforcement-learning-aided service function chain deployment for internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(17): 15674–15684. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3151134. [13] XIAO Yikai, ZHANG Qixia, LIU Fangming, et al. NFVdeep: Adaptive online service function chain deployment with deep reinforcement learning[C]. International Symposium on Quality of Service, Phoenix, USA, 2019: 21. doi: 10.1145/3326285.3329056. [14] TOUMI N, BAGAA M, and KSENTINI A. On using deep reinforcement learning for multi-domain SFC placement[C]. 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Madrid, Spain, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM46510.2021.9685367. [15] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347, 2017. [16] IMT-2020(5G)推进组. 5G核心网云化部署需求与关键技术白皮书[R]. 北京: IMT-2020(5G)推进组, 2018.IMT-2020(5G) the Promotion Group. The white paper of 5G core network cloud deployment requirements and key technologies[R]. Beijing: IMT-2020(5G) the Promotion Group, 2018. [17] JALALITABAR M, GULER E, ZHENG Danyang, et al. Embedding dependence-aware service function chains[J]. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 2018, 10(8): C64–C74. doi: 10.1364/JOCN.10.000C64. [18] ZHANG Tao, XU Changqiao, ZHANG Bingchi, et al. Towards attack-resistant service function chain migration: A model-based adaptive proximal policy optimization approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2023, 20(6): 4913–4927. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2023.3237604. [19] HUANG Bin and WANG Jianhui. Deep-reinforcement-learning-based capacity scheduling for PV-battery storage system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(3): 2272–2283. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020.3047890. [20] YALA L, FRANGOUDIS P A, LUCARELLI G, et al. Cost and availability aware resource allocation and virtual function placement for CDNaaS provision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2018, 15(4): 1334–1348. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2018.2874524. -





 下载:
下载:

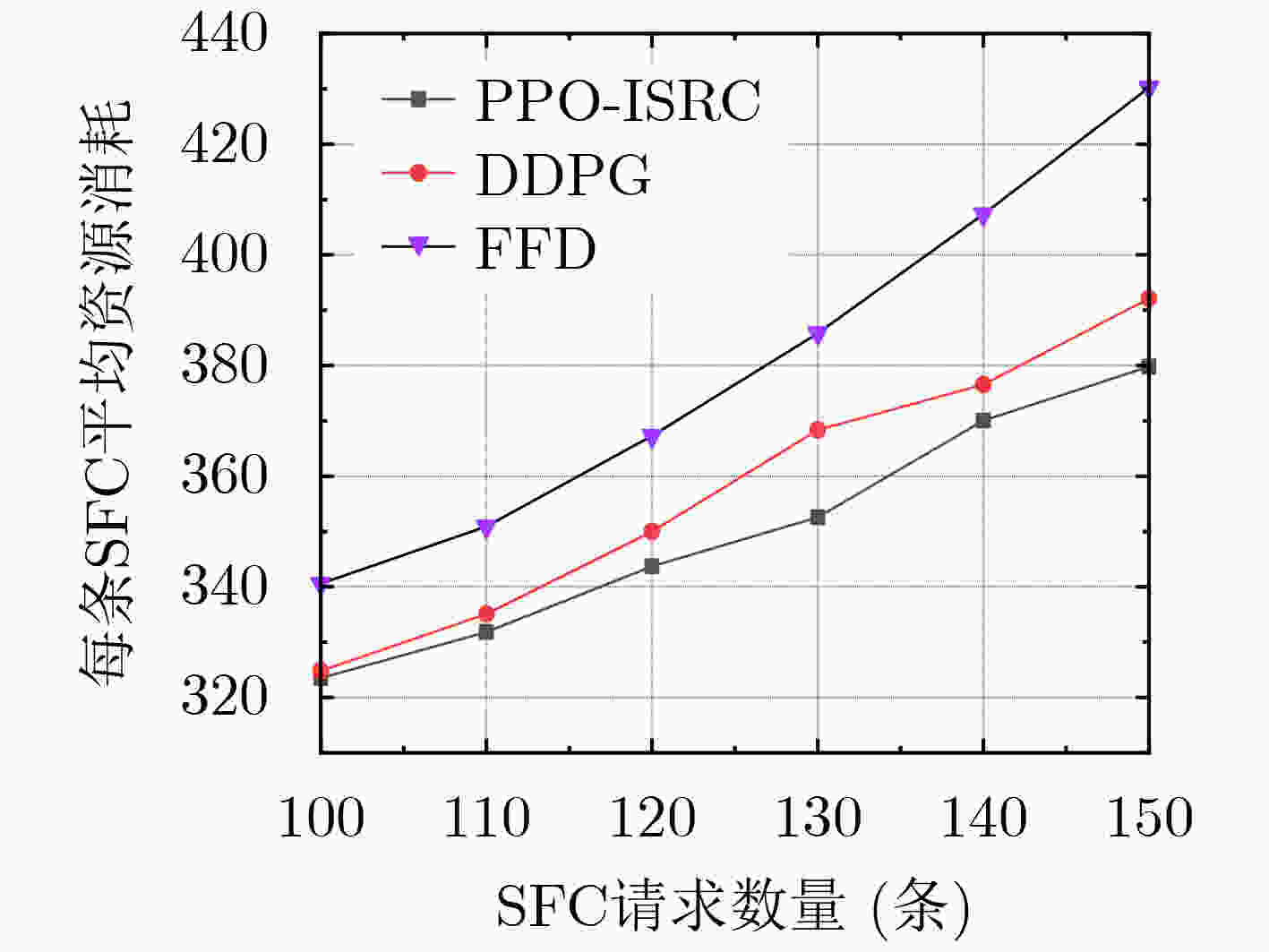


 下载:
下载:
