Rateless Random Coding Scheme and Performance Analysis in Strong Interference Environments
-
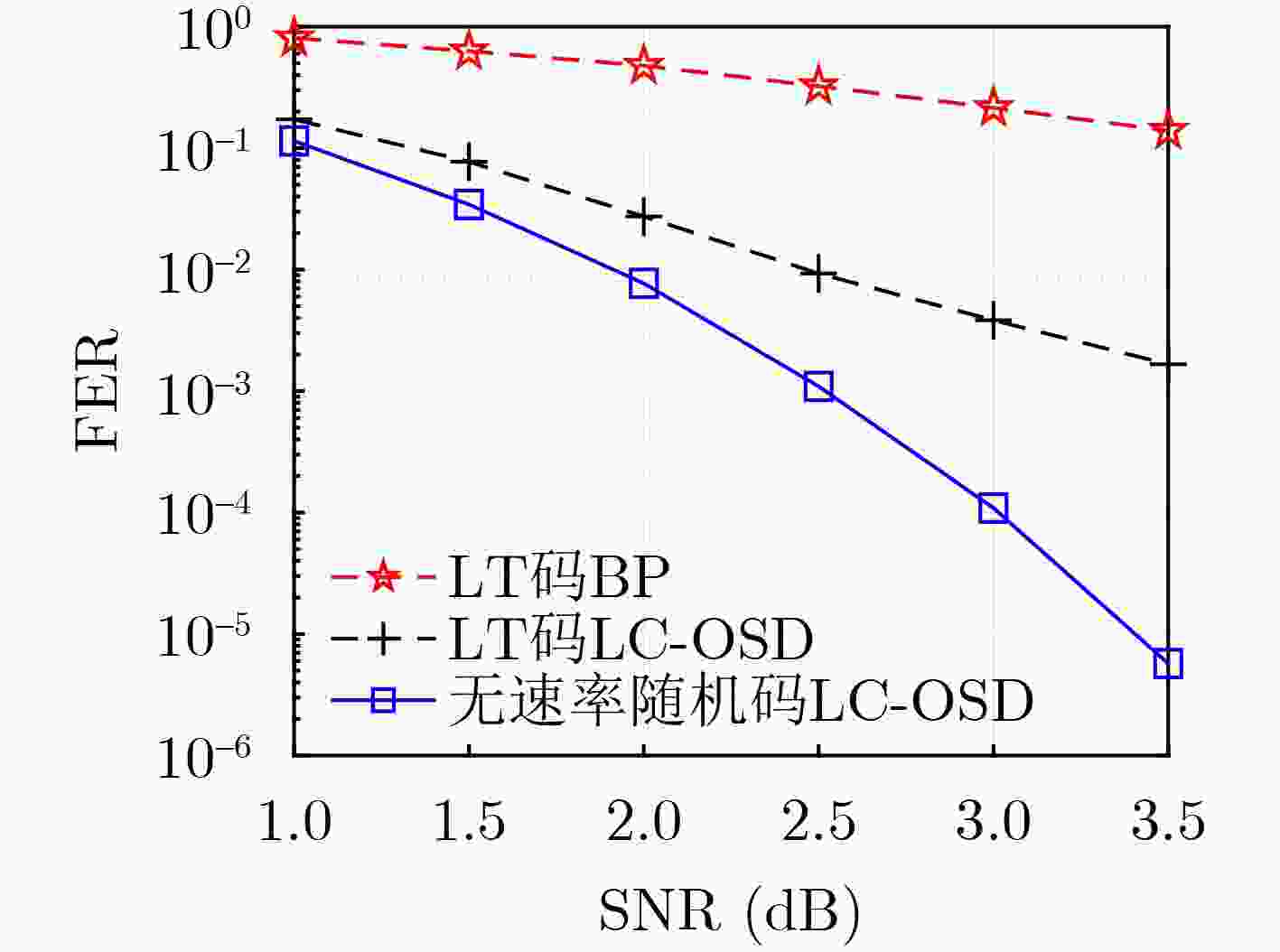
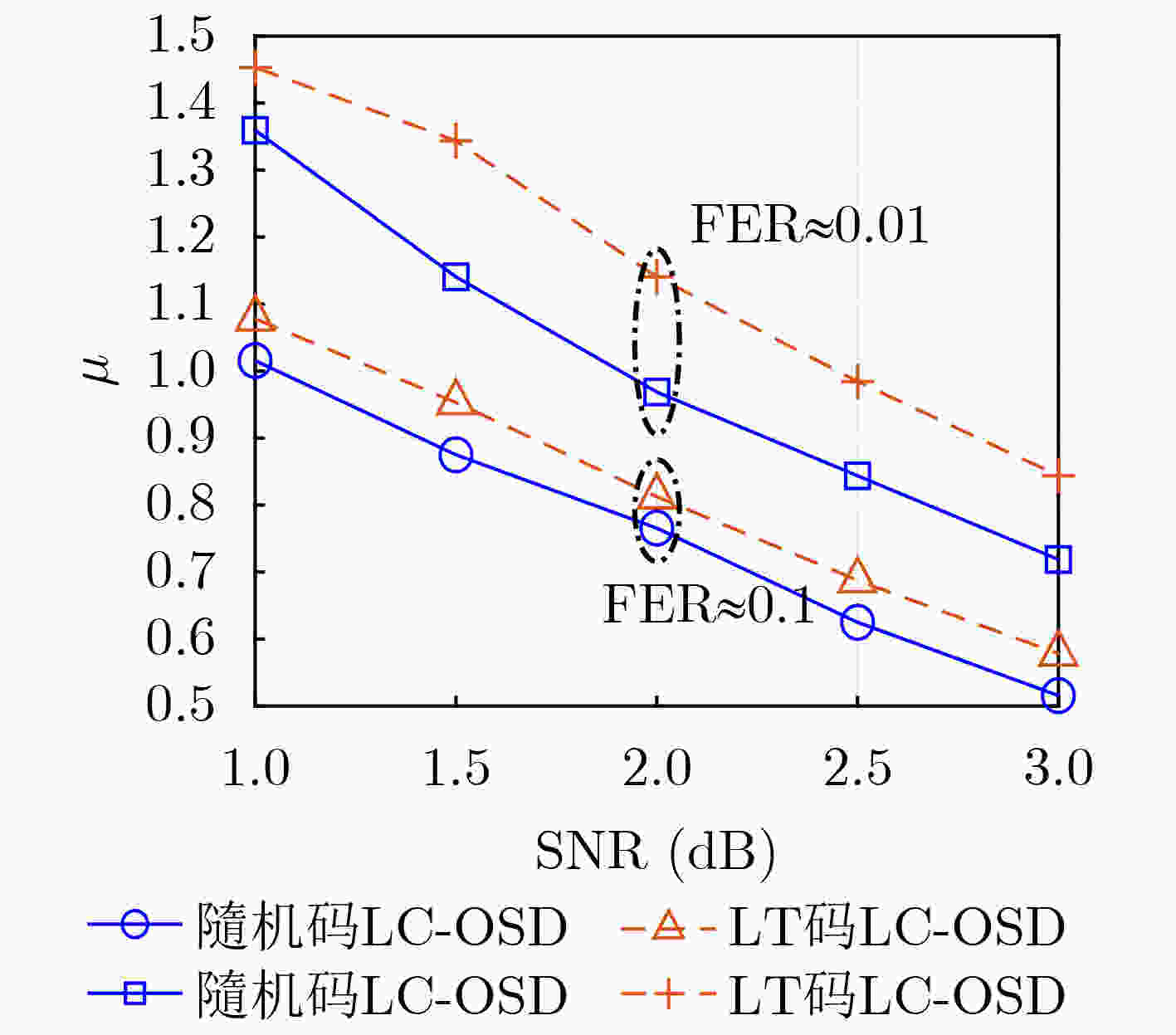
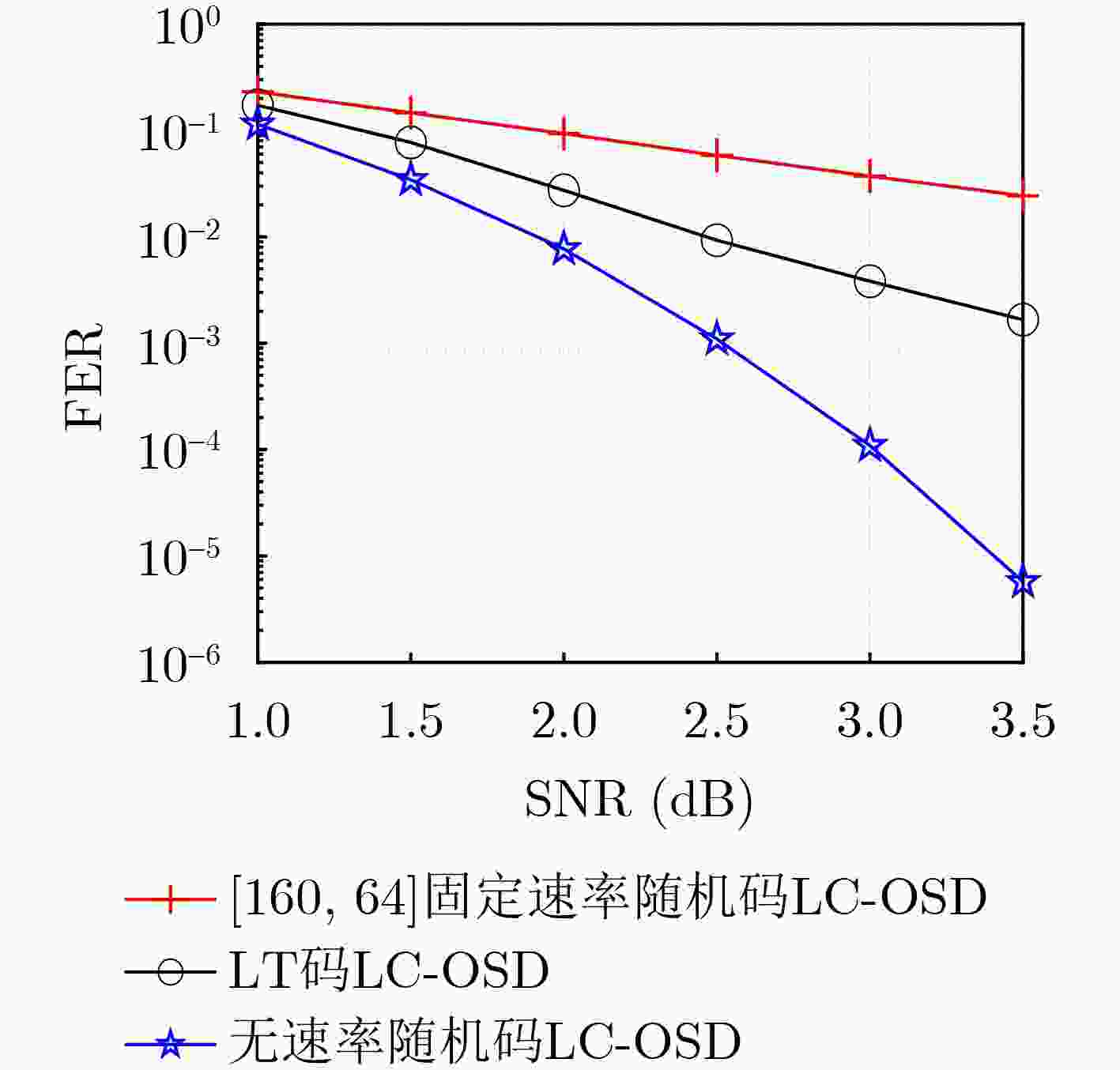
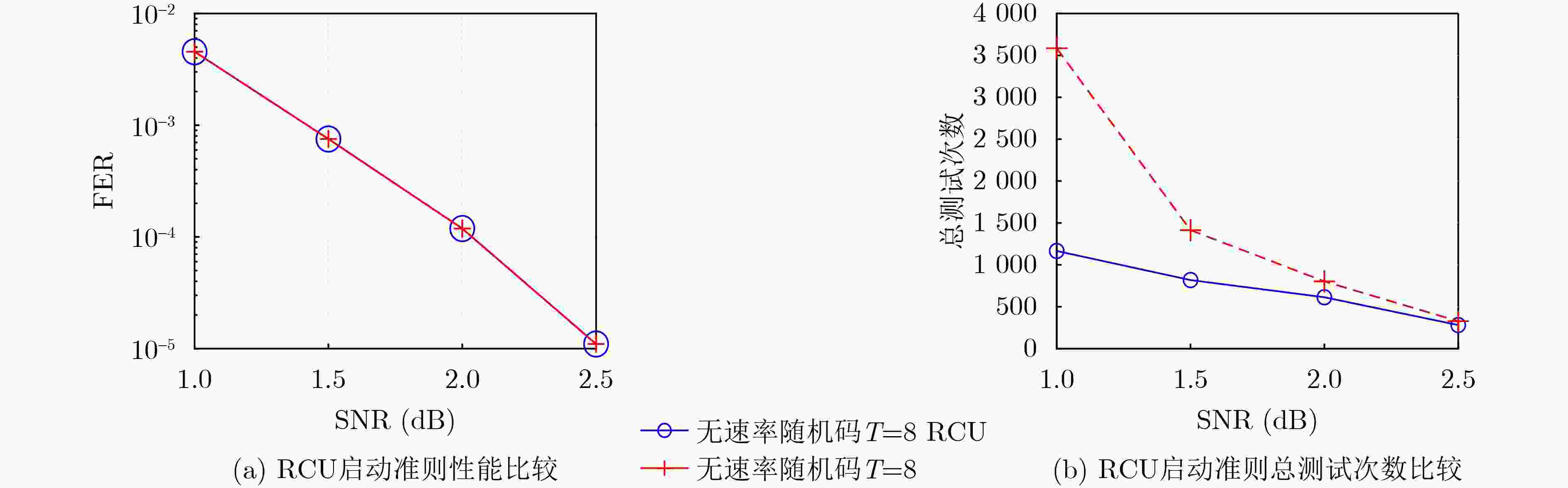
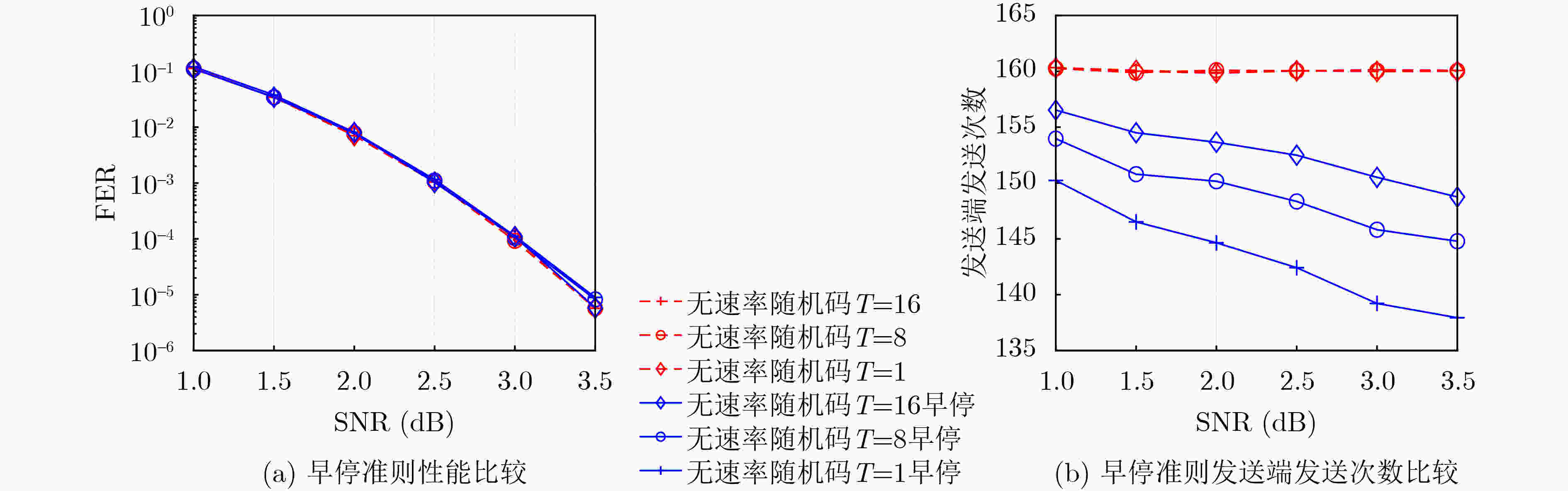
摘要: 面向强干扰通信环境,区别于传统的无速率Luby变换(LT)码,该文提出一种基于伯努利随机构造的无速率编码方案,并在接收端采用高效的局部约束顺序统计量译码(LC-OSD)算法进行译码,从而有效对抗强干扰噪声,实现自适应超高可靠传输。为降低收发端通信资源消耗,提出了3个有效译码准则:(1) 基于随机码并集(RCU)界提出的启动准则,当接收符号数大于由RCU得到的阈值时才启动译码;(2) 基于软重量提出的早停准则,在译码过程中软重量超过一个预设的阈值则提前终止译码;(3) 基于码字与硬判决序列比较提出的跳过准则,当新接收序列的硬判决满足重编码校验时跳过当前译码。仿真结果显示,在块删除与加性噪声混合信道下,无速率随机码的性能显著优于LT码,且因无速率码具备自适应信道质量的能力,其性能同样显著优于固定速率码。仿真结果还显示了提出的启动、早停和跳过准则能够有效降低收发端的传输资源消耗和计算复杂度。Abstract: A rateless coding scheme based on Bernoulli random construction is proposed for strong interference communication environments, which differs from the traditional Luby Transform (LT) rateless codes. The scheme utilizes the Locally Constrained Ordered Statistic Decoding (LC-OSD) algorithm at the receiver to effectively combat strong interference noise and achieve adaptive and ultra-reliable transmission. To reduce the communication resource consumption at both the transmitter and receiver, three effective decoding criteria are proposed: (1) a startup criterion based on the Random Code Union (RCU) bound, which initiates decoding only when the number of received symbols exceeds a threshold derived from RCU; (2) an early stopping criterion based on soft weights, which stops decoding early when the soft weights exceed a preset threshold; and (3) a skipping criterion based on the comparison between the codeword and the hard decision sequence, which skips the current decoding process when the hard decision of the newly received sequence satisfies the recoding check. Simulation results show that the performance of the rateless random codes is significantly better than that of LT codes in a channel with block erasures and additive noise. Moreover, due to the adaptive to channel quality capability of rateless codes, their performance is also significantly better than fixed-rate codes. The simulation results also show that the proposed startup, early stopping, and skipping criteria effectively reduce transmission resources and computational complexity for both the sender and receiver.
-
Key words:
- Ordered statistic decoding /
- Random code /
- Rateless code /
- Strong interference channel
-
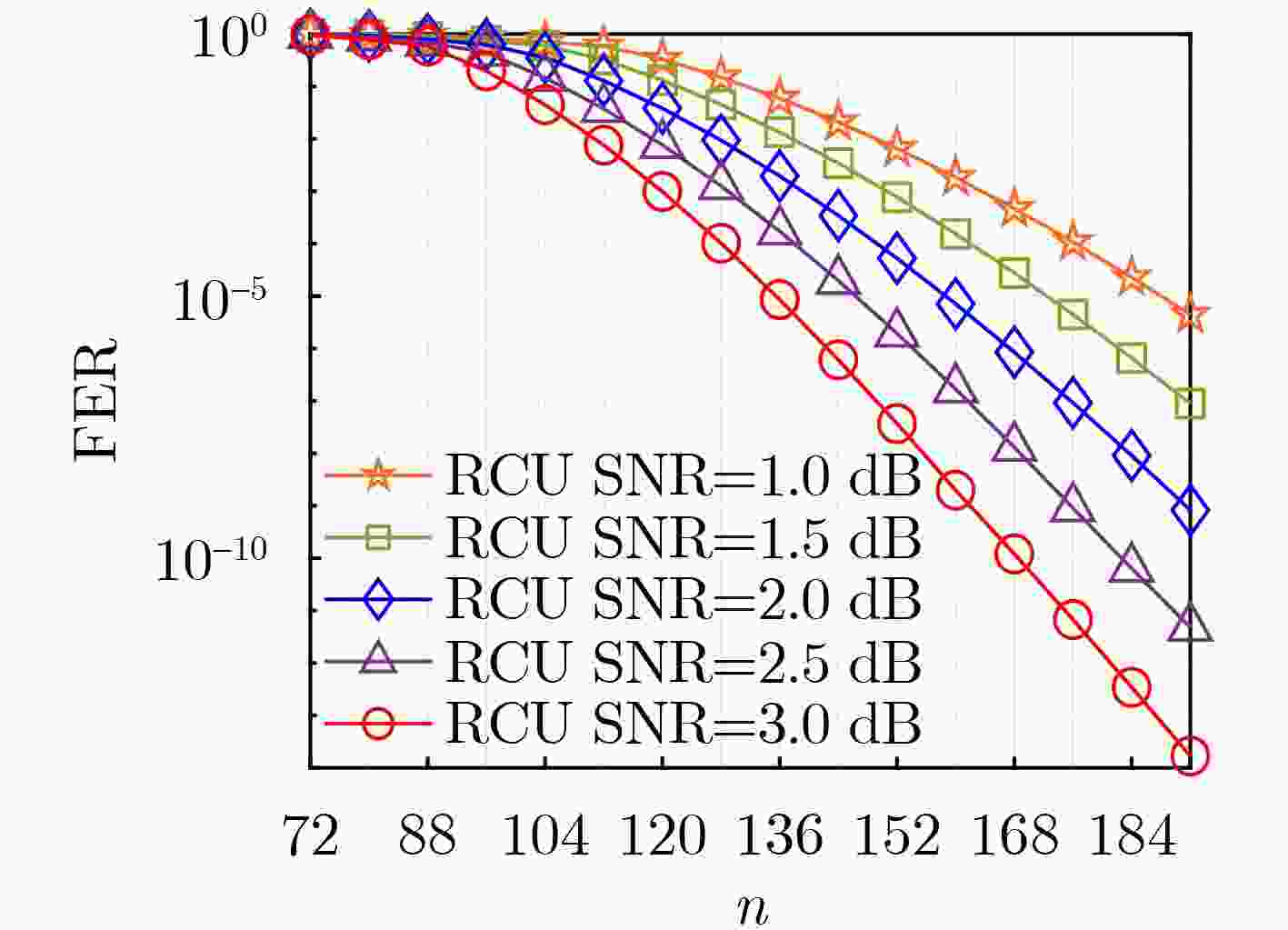
表 1 随机码并集限与实际仿真所需接收符号数对比
信噪比(dB) ${L_{{\text{RCU}}}}$ 实际仿真 1.0 150 151 1.5 135 137 2.0 128 126 2.5 120 118 3.0 110 110 -
[1] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 《6G典型场景和关键能力》白皮书[R]. 2022.IMT-2030 (6G) Propulsion Group. Typical scenarios and key capabilities of 6G white paper[R]. 2022. [2] 于全. 战术通信理论与技术[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2020.YU Quan. Communications in Tactical Environments: Theories and Technologies[M]. Beijing: Posts & Telecom Press, 2020. [3] BYERS J W, LUBY M, MITZENMACHER M, et al. A digital fountain approach to reliable distribution of bulk data[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 1998, 28(4): 56–67. doi: 10.1145/285243.285258. [4] LUBY M. LT codes[C]. Proceedings of the 43rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Vancouver, Canada, 2002: 271–271. doi: 10.1109/SFCS.2002.1181950. [5] SHOKROLLAHI A. Raptor codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(6): 2551–2567. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.874390. [6] YANG Shenghao and YEUNG R W. Batched sparse codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(9): 5322–5346. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2334315. [7] CASSUTO Y and SHOKROLLAHI A. Online fountain codes with low overhead[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2015, 61(6): 3137–3149. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2015.2422697. [8] 姚渭箐, 易本顺. 新型LT码编译码方法及其在认知无线电中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 571–579. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180427.YAO Weiqing and YI Benshun. A novel encoding and decoding method of LT codes and application to cognitive radio[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 571–579. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180427. [9] 宋鑫, 程乃平, 倪淑燕, 等. 采用定长节点分类窗口的低误码平台LT编码算法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(9): 31–42. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021155.SONG Xin, CHENG Naiping, NI Shuyan, et al. Low error floor LT coding algorithm by using fixed-length node classification window[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(9): 31–42. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021155. [10] 龚茂康. 中短长度LT码的展开图构造方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(4): 885–888. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.00218.GONG Maokang. Unfolding graphs for constructing of short and moderate-length LT codes[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2009, 31(4): 885–888. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.00218. [11] FOSSORIER M P C and LIN Shu. Soft-decision decoding of linear block codes based on ordered statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1995, 41(5): 1379–1396. doi: 10.1109/18.412683. [12] YUE Chentao, SHIRVANIMOGHADDAM M, LI Yonghui, et al. Segmentation-discarding ordered-statistic decoding for linear block codes[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Waikoloa, America, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM38437.2019.9014173. [13] YUE Chentao, SHIRVANIMOGHADDAM M, PARK G, et al. Linear-equation ordered-statistics decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(11): 7105–7123. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3207206. [14] YUE Chentao, SHIRVANIMOGHADDAM M, PARK G, et al. Probability-based ordered-statistics decoding for short block codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(6): 1791–1795. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3058978. [15] WANG Yiwen, LIANG Jifan, and MA Xiao. Local constraint-based ordered statistics decoding for short block codes[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Information Theory Workshop, Mumbai, India, 2022: 107–112. doi: 10.1109/ITW54588.2022.9965916. [16] POLYANSKIY Y, POOR H V, and VERDÚ S. Channel coding rate in the finite blocklength regime[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(5): 2307–2359. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2043769. [17] FABREGAS A G I and TANG Qi. Coding in the block-erasure channel[C]. Proceedings of 2006 Australian Communications Theory Workshop, Perth, Australia, 2006: 19–24. doi: 10.1109/AUSCTW.2006.1625249. [18] LIANG Jifan, WANG Yiwen, CAI Suihua, et al. A low-complexity ordered statistic decoding of short block codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(2): 400–403. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3222819. [19] SESHADRI N and SUNDBERG C E W. List Viterbi decoding algorithms with applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1994, 42(234): 313–323. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.1994.577040. -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
