Research on In-orbit Characteristics of Inter-satellite links Phase Center Offsets Based on Whole-network Estimation
-
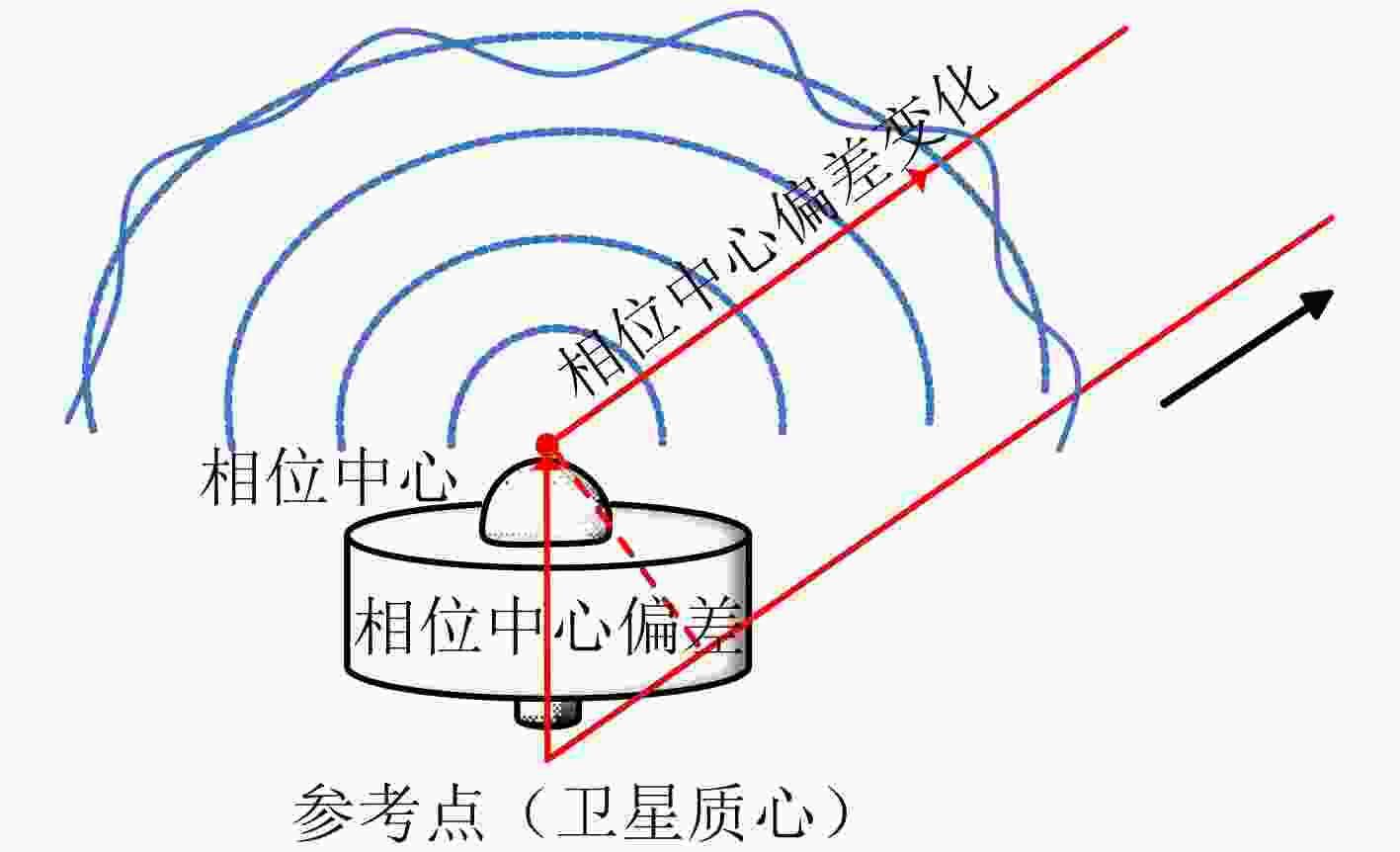
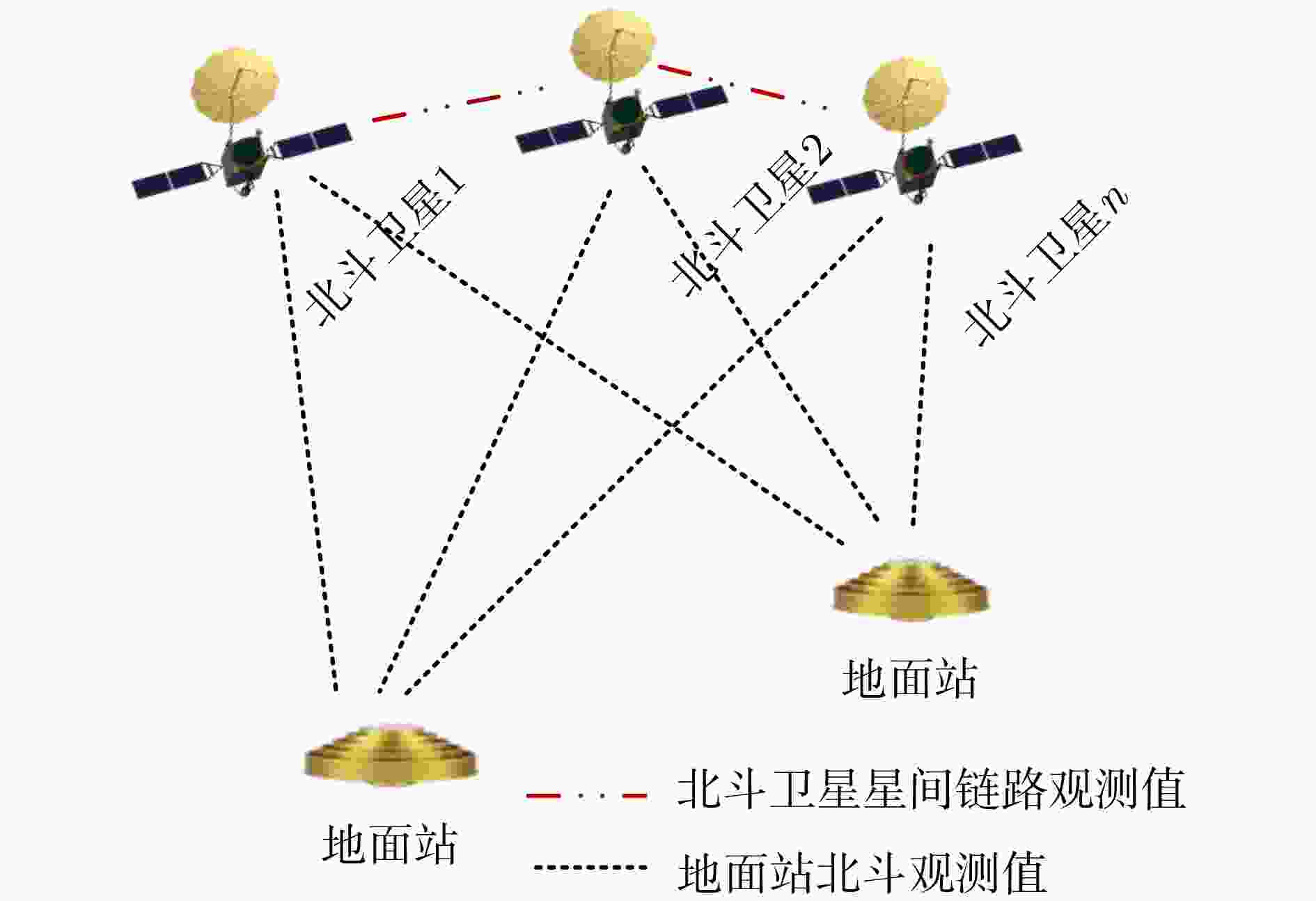
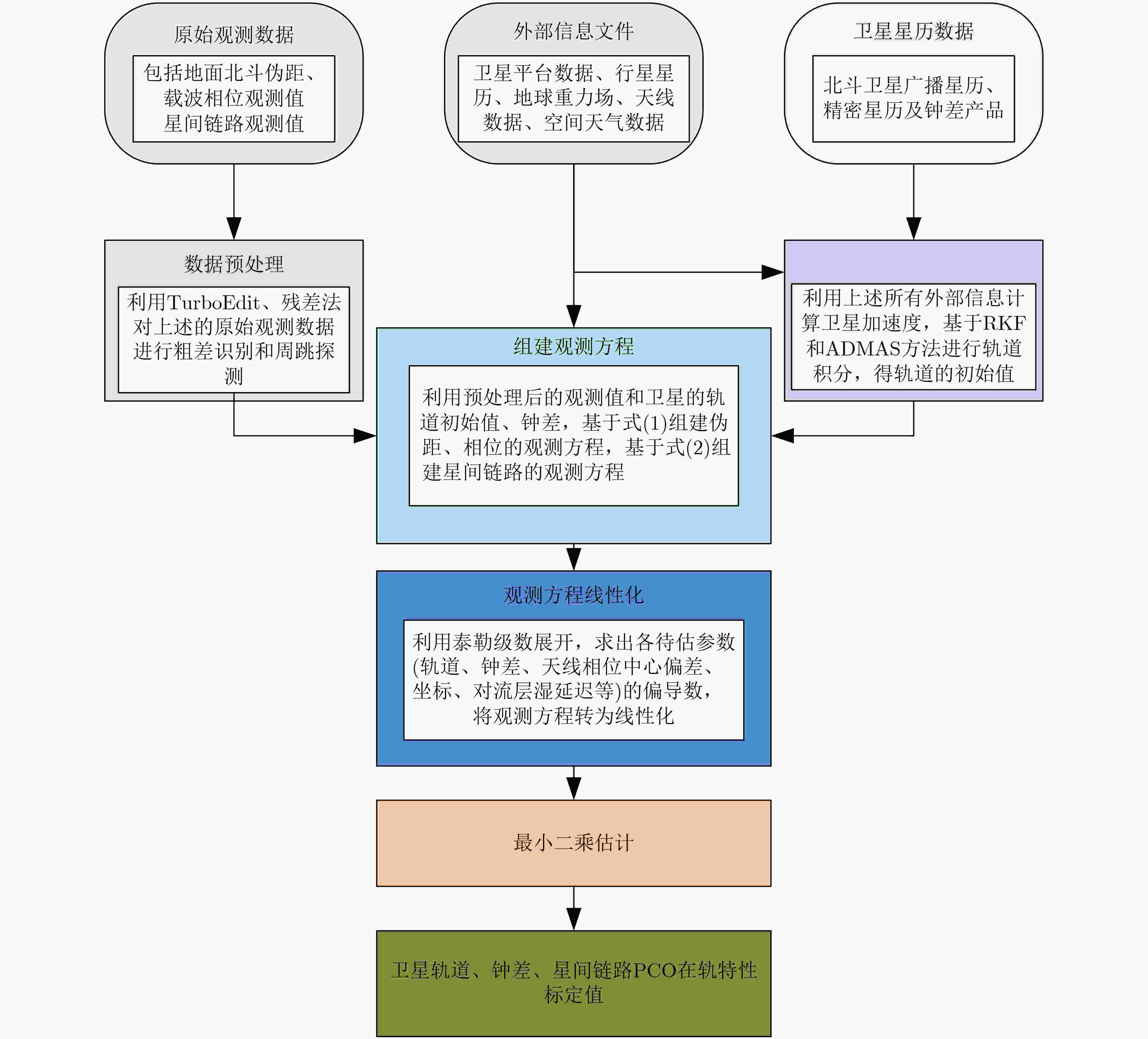
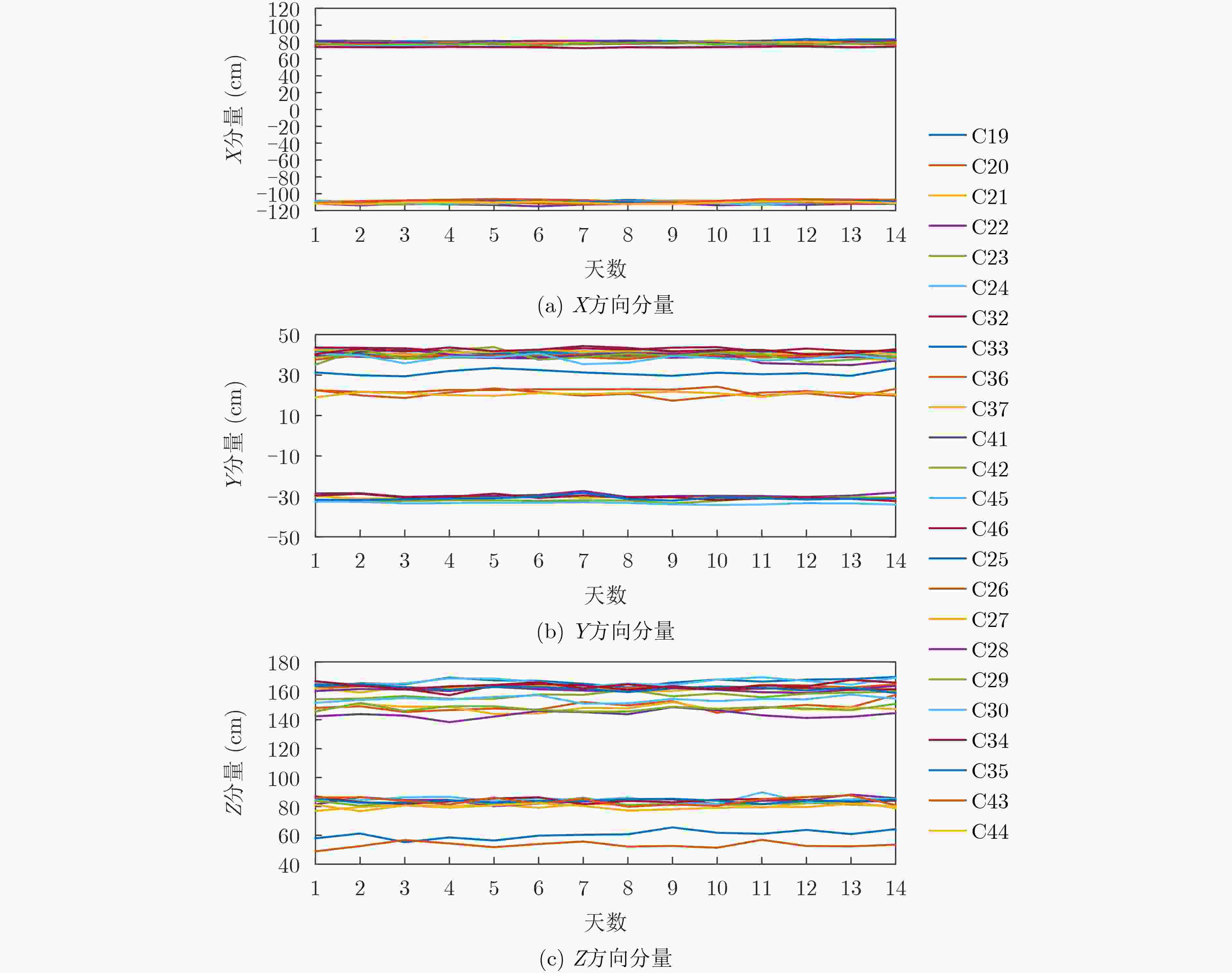
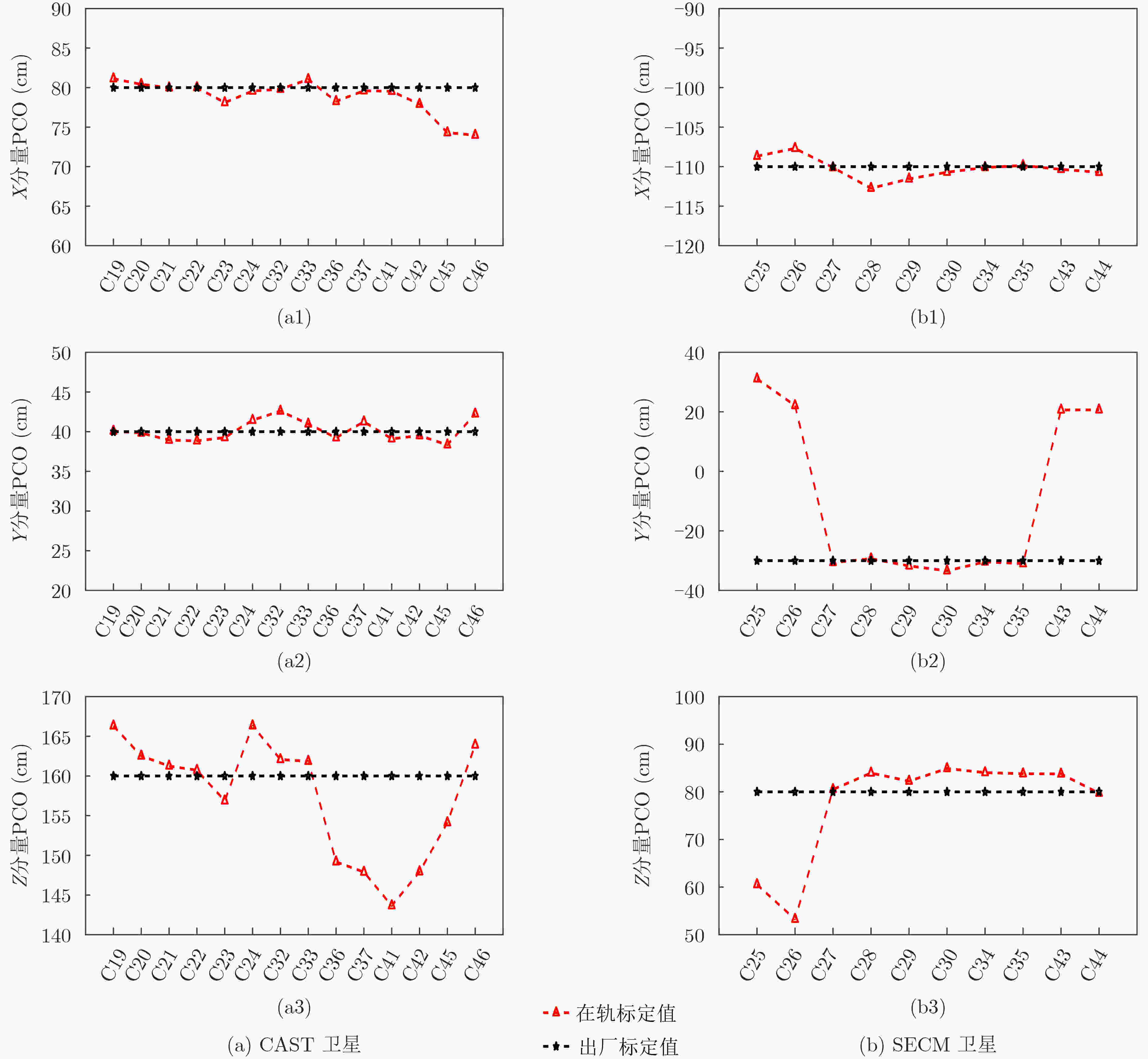
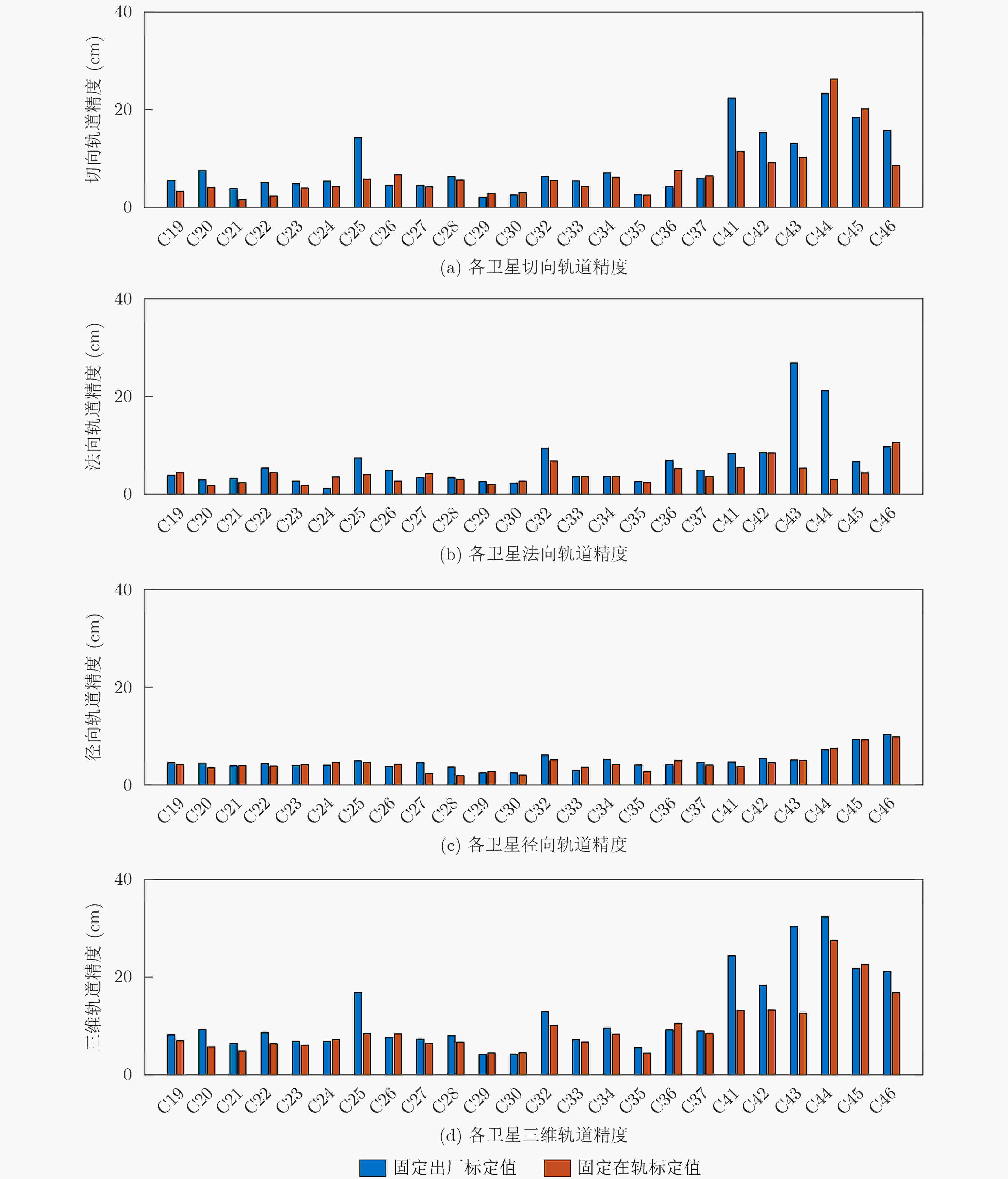
摘要: 星间链路(ISL)是我国北斗三号克服区域布站、实现高精度服务的关键,其天线相位中心偏差(PCO)在设备出厂时会依据质量、设计姿态进行地面标定,但在卫星发射、入轨及在轨阶段,燃料消耗、天线展开姿态等均会引起卫星质量与姿态的变化,这将导致在轨的PCO与地面标定值不一致 ,该变化量会作为误差引入到测量值,进而影响卫星轨道确定精度。因此,该文研究了在轨卫星的星间链路天线相位中心偏差标定方法,联合星间、星地观测,建立了基于整网估计的星间链路天线相位中心偏差在轨估计方法,并利用两周的实测数据进行对北斗三号所有中轨卫星(MEO)进行验证,同时结合卫星生产商、轨道面进行在轨特性的详细分析,最后验证了其对轨道确定精度的影响。结果表明,该文方法可有效估计在轨卫星星间链路天线相位中心偏差,并发现,卫星在轨后大部分卫星的星间链路天线相位中心偏差基本与地面一致,但C36, C37, C41, C42卫星在Z方向与地面标定值存在15 cm左右的偏差,C25, C26, C43, C44在Y轴上存在符号相反的现象,且数值上有10 cm左右的偏差,C25, C26卫星在Z方向上存在近30 cm的偏差,正确标定在轨卫星星间链路天线相位中心偏差后,相比地面标定产品,轨道精度可提升15%。Abstract: The Inter Satellite Links (ISL) is the key for China's Beidou-3 to overcome regional station deployment and achieve high-precision services. Its antenna Phase Center Offsets (PCO) is calibrated on the ground based on satellite mass and designed attitude when the equipment leaves the factory. However, fuel consumption, antenna deployment attitude, and other factors can cause changes in satellite mass and attitude during satellite launch, orbit entry, and in orbit stages, which will result in inconsistent values of antenna phase center deviation in orbit with ground calibration values. This change will be introduced as an error into the measurement value, thereby affecting the accuracy of satellite orbit determination. Therefore, this article studies the calibration method for the PCO of the inter-satellite links of in-orbit satellites. By combining with inter-satellite and satellite-ground observations, an in-orbit estimation method is established based on whole-network estimation. Two weeks of measured data are used to verify for all Medium Earth Orbit satellites (MEO) of Beidou-3, and a detailed analysis of in-orbit characteristics is conducted in conjunction with satellite manufacturers and orbital surfaces. Finally, its impact on the accuracy of orbit determination is verified. Results show that method proposed in this paper can effectively estimate the PCO of the inter-satellite links antenna in-orbit. It is found that the PCO of the inter-satellite links antenna in most in-orbit satellites is basically consistent with the values on the ground. However, C36, C37, C41, and C42 satellites have a deviation of about 15 cm from the ground calibration value in the Z-direction. Satellites C25, C26, C43 and C44 have opposite signs on the Y-direction, and there is a deviation of about 10 cm in the numerical value. Satellite C25, C26 have a deviation of nearly 30 cm in the Z-direction. After correctly calibrating the PCO of the inter-satellite links antenna in-orbit, the orbit accuracy can be improved by 15% compared to ground calibration products.
-
表 1 北斗三号卫星基本信息一览表
轨道
类型轨道面 卫星/PRN 卫星厂商 星间链路
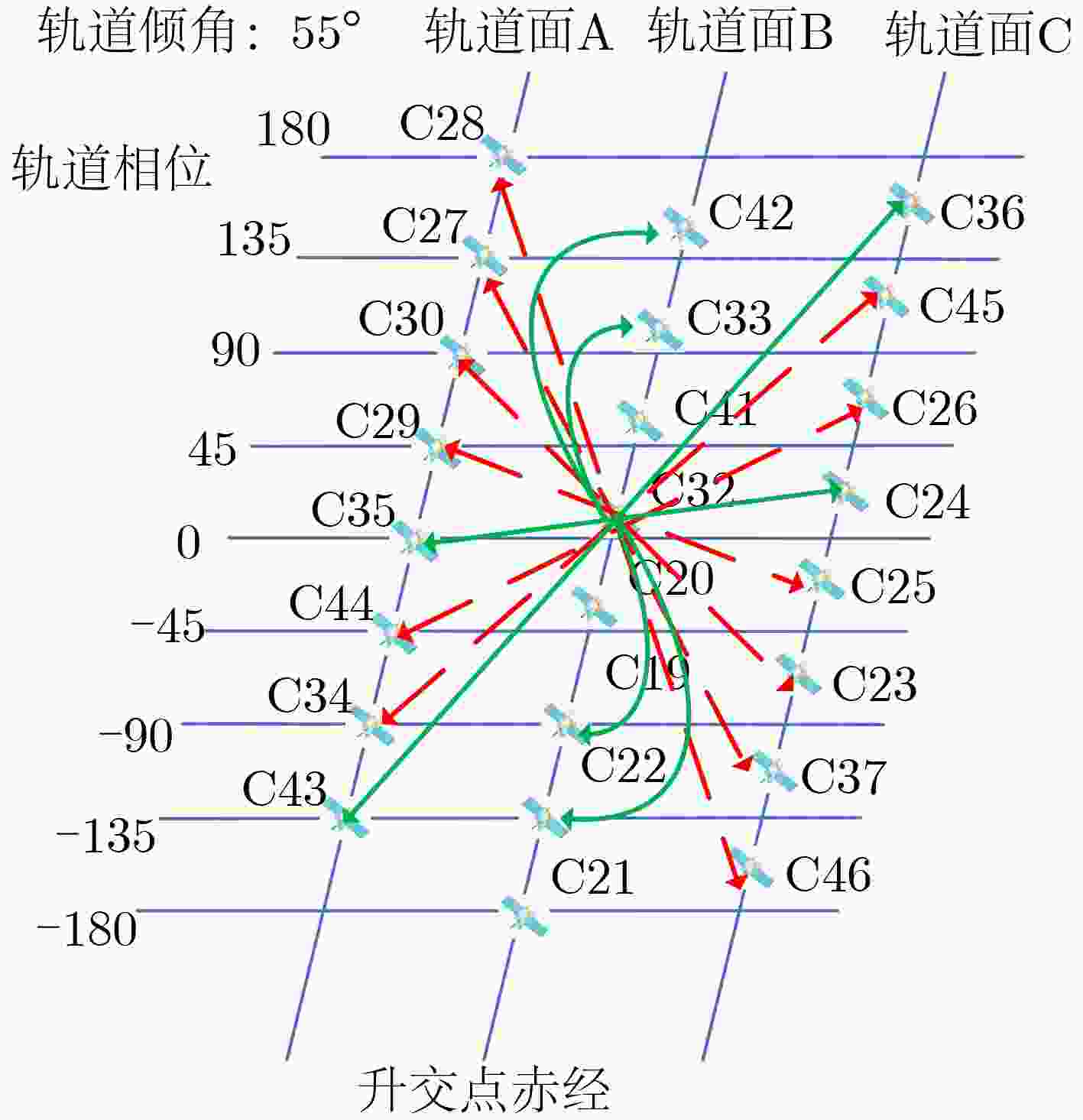
设备厂商MEO 轨道面A C27,C29,C34,
C35,C43,C44SECM SECM-1 C28 SECM-3 C30 未公开 轨道面B C19,C20,C21,C22,
C33,C41,C42CAST CASC-1 C32 CASC-2 轨道面C C23,C36,C45 CAST CASC-2 C24,C37,C46 CASC-1 C25,C26 SECM SECM-2 IGSO 113.2°E C38,C39,C40 CAST CASC-1 106.6°E 104.3°E GEO 140°E C59,C60,C61 CAST CASC-1 80°E 110.5°E 表 2 实验策略一览表
项目大类 项目 描述 观测值与参数估计 观测值 BDS 频点 BDS: B1I+B3I;无电离层
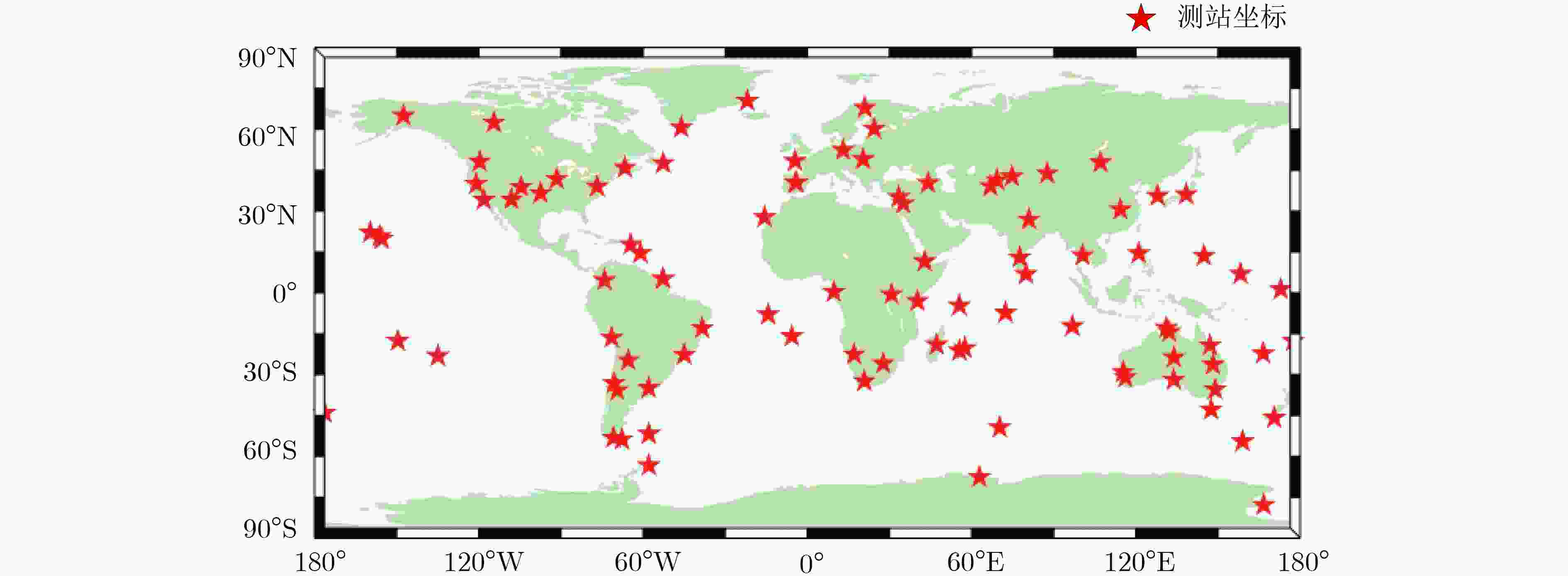
组合观测值;ISL参数估计方法 最小二乘法 处理间隔 300 s 解算弧长 1 d 截止高度角 7° 测站坐标 IGS周解文件 轨道摄动力模型 地球重力场 EGM 2008 N体引力 天体位置来自
JPL DE405文件海潮 FES 2004 固体潮和极潮 按照IERS 2010协议改正 天线推力 模型改正 光压模型 9参数 ECOM2模型 地球反照压 模型改正 经验力 未考虑 大气误差项 对流层误差 ZTD:每小时估计1组 电离层误差 1阶项采用无电离层组合消除,
高阶项采用模型改正其他 卫星天线误差 igs14.atx 接收机天线误差 igs14.atx,若无BDS数据,
以GPS L1/L2信息代替整周模糊度 双差模糊度固定 -
[1] 杨元喜. 北斗卫星导航系统的进展、贡献与挑战[J]. 测绘学报, 2010, 39(1): 1–6.YANG Yuanxi. Progress, contribution and challenges of compass/Beidou satellite navigation system[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2010, 39(1): 1–6. [2] 杨元喜, 任夏. 自主卫星导航的空间基准维持[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2018, 43(12): 1780–1787. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180169YANG Yuanxi and REN Xia. Maintenance of space datum for autonomous satellite navigation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 1780–1787. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180169 [3] 李龙龙, 耿国桐, 李作虎. 国外卫星导航系统星间链路发展研究[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2016, 33(2): 133–138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2016.02.005LI Longlong, GENG Guotong, and LI Zuohu. Study of the development of the inter-satellite links in foreign GNSS[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2016, 33(2): 133–138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2016.02.005 [4] 周善石, 胡小工, 刘利, 等. 导航卫星精密定轨与时间同步技术进展[J]. 天文学报, 2019, 60(4): 57–66. doi: 10.15940/j.cnki.0001-5245.2019.04.005ZHOU Shanshi, HU Xiaogong, LIU Li, et al. Status of satellite orbit determination and time synchronization technology for global navigation satellites system[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2019, 60(4): 57–66. doi: 10.15940/j.cnki.0001-5245.2019.04.005 [5] 杨元喜, 许扬胤, 李金龙, 等. 北斗三号系统进展及性能预测——试验验证数据分析[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018, 61(5): 614–624. doi: 10.1360/N072017-00434YANG Yuanxi, XU Yangyin, LI Jinlong, et al. Progress and performance evaluation of BeiDou global navigation satellite system: Data analysis based on BDS-3 demonstration system[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 614–624. doi: 10.1360/N072017-00434 [6] 毛悦, 贾小林, 宋小勇, 等. 北斗三号基本系统空间信号性能分析[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2019, 36(2): 111–115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2019.02.001MAO Yue, JIA Xiaolin, SONG Xiaoyong, et al. Analysis of space signal performance of Basic BDS-3 navigation satellite system[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2019, 36(2): 111–115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2019.02.001 [7] 郭树人, 蔡洪亮, 孟轶男, 等. 北斗三号导航定位技术体制与服务性能[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(7): 810–821. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20190091GUO Shuren, CAI Hongliang, MENG Yi’nan, et al. BDS-3 RNSS technical characteristics and service performance[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(7): 810–821. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20190091 [8] 陈金平, 尤政, 焦文海. 基于星间距离和方向观测的导航卫星自主定轨研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2005, 26(1): 43–46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.01.009CHEN Jinping, YOU Zheng, and JIAO Wenhai. Research on autonav of navigation satellite constellation based on crosslink range and inter-satellites orientation observation[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2005, 26(1): 43–46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.01.009 [9] 陈忠贵. 基于星间链路的导航卫星星座自主运行关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2012.CHEN Zhonggui. Key technologies of autonomous operation for navigation satellite constellations using inter-satellite tracking data[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2012. [10] 刘经南, 曾旭平, 夏林元, 等. 导航卫星自主定轨的算法研究及模拟结果[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2004, 29(12): 1040–1044. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8860.2004.12.002LIU Jingnan, ZENG Xuping, XIA Linyuna, et al. Algorithm and simulation of autonomous orbit determination for navigation satellites[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2004, 29(12): 1040–1044. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8860.2004.12.002 [11] 唐成盼, 胡小工, 周善石, 等. 利用星间双向测距数据进行北斗卫星集中式自主定轨的初步结果分析[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学, 2017, 47(2): 029501. doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2016-00355TANG Chengpan, HU Xiaogong, ZHOU Shanshi, et al. Centralized autonomous orbit determination of Beidou navigation satellites with inter-satellite link measurements: Preliminary results[J]. Scientia Sinica(Physica,Mechanica&Astronomica), 2017, 47(2): 029501. doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2016-00355 [12] 朱俊. 基于星间链路的导航卫星轨道确定及时间同步方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011.ZHU Jun. Research on orbit determination and time synchronizing of navigation satellite based on cross links[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011. [13] CHANG Jiachao, SHANG Lin, and LI Guotong. The research on system error of Inter-satellite-link (ISL) measurements for autonomous navigation of Beidou system[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2017, 60(1): 65–81. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2017.03.016 [14] MAINE K P, ANDERSON P, and LANGER J. Crosslinks for the next-generation GPS[C]. Proceedings of 2003 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Big Sky, USA, 2003: 4_1589–4_1596. [15] XIE Jun, WANG Haihong, LI Peng, et al. Satellite navigation inter-satellite link technology[M]. XIE Jun, WANG Haihong, LI Peng, et al. Satellite Navigation Systems and Technologies. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 181–215. [16] IGNATOVICH E I and SCHEKUTJEV A F. Results of imitating tests of some versions of onboard algorithms for SC GLONASS inter-satellite measurement processing[C]. The 15th Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems, Saint Petersburg, USA, 2008. [17] GILL E. Precise GNSS-2 satellite orbit determination based on Inter-satellite-links[C]. The 14th International Symposium on Space Flight Mechanics, Iguassu, Brazil, 1999. [18] TANG Chengpan, HU Xiaogong, ZHOU Shanshi, et al. Initial results of centralized autonomous orbit determination of the new-generation BDS satellites with inter-satellite link measurements[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2018, 92(10): 1155–1169. doi: 10.1007/s00190-018-1113-7 [19] REN Xia, YANG Yuanxi, ZHU Jun, et al. Comparing satellite orbit determination by batch processing and extended Kalman filtering using inter-satellite link measurements of the next-generation BeiDou satellites[J]. GPS Solutions, 2019, 23(1): 25. doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0816-9 [20] LIU Li, ZHANG Tianqiao, ZHOU Shanshi, et al. Improved design of control segment in BDS‐3[J]. Navigation, 2019, 66(1): 37–47. doi: 10.1002/navi.297 [21] XIE Xin, GENG Tao, ZHAO Qile, et al. Precise orbit determination for BDS-3 satellites using satellite-ground and inter-satellite link observations[J]. GPS Solutions, 2019, 23(2): 40. doi: 10.1007/s10291-019-0823-5 [22] LV Yifei, GENG Tao, ZHAO Qile, et al. Initial assessment of BDS-3 preliminary system signal-in-space range error[J]. GPS Solutions, 2020, 24(1): 16. doi: 10.1007/s10291-019-0928-x [23] LOU Yidong, DAI Xiaolei, GONG Xiaopeng, et al. A review of real-time multi-GNSS precise orbit determination based on the filter method[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2022, 3(1): 15. doi: 10.1186/s43020-022-00075-1 [24] DILSSNER F, SPRINGER T, FLOHRER C, et al. Estimation of phase center corrections for GLONASS-M satellite antennas[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2010, 84(8): 467–480. doi: 10.1007/s00190-010-0381-7 [25] DILSSNER F. GPS IIF-1 antenna phase center and attitude modeling[C]. Proceedings of International Technical Meeting of the Sate llite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Portland, USA, 2010: 59–64. [26] DACH R, SCHMID R, SCHMITZ M, et al. Improved antenna phase center models for GLONASS[J]. GPS Solutions, 2011, 15(1): 49–65. doi: 10.1007/s10291-010-0169-5 [27] WANG Chen, ZHAO Qile, GUO Jing, et al. The contribution of intersatellite links to BDS‐3 orbit determination: Model refinement and comparisons[J]. Navigation, 2019, 66(1): 71–82. doi: 10.1002/navi.295 [28] XIE Xin, GENG Tao, ZHAO Qile, et al. Orbit and clock analysis of BDS-3 satellites using inter-satellite link observations[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94(7): 64. doi: 10.1007/s00190-020-01394-4 [29] LÜ Yifei, GENG Tao, ZHAO Qile, et al. Evaluation of BDS-3 orbit determination strategies using ground-tracking and inter-satellite link observation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(16): 2647. doi: 10.3390/rs12162647 [30] 温敬朋, 杨健, 王沙飞. 电子战装备技术发展现状与展望[J]. 信息对抗技术, 2022, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.12399/j.issn.2097-163x.2022.01.001WEN Jingpeng, YANG Jian, and WANG Shafei. Development status and prospect of electronic warfare equipment technology[J]. Information Countermeasure Technology, 2022, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.12399/j.issn.2097-163x.2022.01.001 [31] YANG Daoning, YANG Jun, LI Gang, et al. Globalization highlight: Orbit determination using BeiDou inter-satellite ranging measurements[J]. GPS Solutions, 2017, 21(3): 1395–1404. doi: 10.1007/s10291-017-0626-5 [32] WANG Haihong, XIE Jun, ZHUANG Jianlou, et al. Performance analysis and progress of inter-satellite-link of Beidou system[C]. The 30th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Portland, USA, 2017. [33] 张方. 卫星导航系统星间链路拓扑及路由设计[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.ZHANG Fang. A topology and routing design of navigation satellite system inter-satellite links[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
