Global Navigation Satellite System/Strapdown Inertial Navigation System Integrated Navigation Algorithm in Complex Urban Environment
-
摘要: 针对复杂城市环境下,全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)信号出现频繁短暂失锁或拒止时,对GNSS/捷联惯性导航系统(SINS)组合导航系统的导航精度和鲁棒性影响较大问题,该文提出一种改进的因子图滤波方法。首先使用GNSS接收机内部参数构建信号误差鉴别函数,能实时估计出信号受多径干扰、遮挡等情况下的信号测量性能;同时利用载体运动约束条件构造零速修正因子,对GNSS拒止情况下的系统状态进行更新,避免系统导航性能极速下降。实验结果表明,改进的因子图方法相比经典因子图方法,在城市复杂环境下能提高定位精度63.50%和测速精度42.26%,同时也具有更低的存储量和计算复杂度,特别适用于城市车辆辅助驾驶导航设备中,对导航精度、硬件资源和实时性约束强的场景。Abstract: In order to solve the problem that the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signal is frequently unlocked or rejected in complex urban environment, which has great influence on the navigation accuracy and robustness of GNSS/ Strapdown Inertial Navigation System (SINS) integrated navigation system, an improved factor graph filtering method is proposed in this paper. Firstly, GNSS receiver internal parameters are used to construct signal error identification function to estimate the performance of signal measurement at real time in the situation of multipath interference and occlusion. Simultaneously, zero-velocity update factor is constructed by the carrier motion constraint to update the system state under the condition of GNSS rejection. The experimental results show that compared with the classical factor graph method, the improved factor graph method can improve the positioning accuracy by 63.50% and the velocity measurement accuracy by 42.26% in complex environment with lower storage and computational complexity. The method is especially suitable for the scenarios with strong constraints on navigation accuracy, hardware resources and real-time performance in urban vehicle assisted driving navigation equipment.
-
表 1 仿真传感器参数设置
相关参数 数值 陀螺仪零偏 [–180, 260, –160] °/h 角度随机游走 2.909×10–4 rad/ $\sqrt {\mathrm{s}} $ 加速度计零偏 [9000, –13000, 8000] μG 速度随机游走 1000 ug/ $ \sqrt {\rm{Hz}} $ 初始位置误差 10 m 初始速度误差 0.1 m/s 可观测卫星数 8 卫星载噪比 40~45 dBHz 表 2 仿真场景参数设置
序号 时间段(s) 可见卫星 多径干扰影响卫星 多径干扰数量 受遮挡卫星 受遮挡卫星载噪比(dBHz) 备注 1 1~80 C1/C2/C6/C7/C8/
C11/C12/C16无 无 无 无 正常行驶阶段 2 80~95 C1/C2/C6/C12 无 无 C7/C8/C11/C16 38(C7/C8)
40(C11/C16)部分卫星受遮挡阶段 3 95~200 C1/C2/C6/C7/
C8/
C11/C12/C16无 无 无 无 正常行驶阶段 4 200~235 C7/C8/C11/C16 C1/C2/C6/C12 3(C1/C2)
2(C6/C12)无 无 多径干扰阶段 5 235~400 C1/C2/C6/C7/C8/
C11/C12/C16无 无 无 无 正常行驶阶段 6 400~450 C7/C8/C16 无 无 C1/C2/C6/C11/C12 不可见 小于4颗卫星可视阶段 7 450~600 C1/C2/C6/C7/C8/
C11/C12/C16无 无 无 无 正常行驶阶段 表 3 3种方法的定位与测速性能对比(速度(m/s)/位置(m))
卡尔曼滤波 经典因子图 本文方法 X轴方向 0.7189/2.0286 0.4187/1.4252 0.2215/0.5237 Y轴方向 0.6709/1.7552 0.3217/0.7746 0.2270/0.6821 Z轴方向 1.2893/6.6258 0.5941/4.5711 0.3317/1.5473 表 4 部分系统参数
设备名称 指标种类 相应数值 NovAtel ProPak6+SPAN紧组合系统 观测卫星系统 BDS/GPS/Galileo/GLONASS GNSS接收频点 B1/B2/L1/L2/L2C/E1/E5 RTK定位精度 1 cm±1×10–6 位置输出频率 10 Hz 测速精度(RMS) 0.03 m/s 授时精度(RMS) 20 ns 陀螺仪测量范围 ±1000 °/s 陀螺仪零偏 <1 °/h 角度随机游走 0.1 °/ $\sqrt{\rm h} $ 加速度计零偏 9.8×10–3 m/s2 加速度计比例因子 4×10–4 CGI-410 GNSS/SINS组合导航接收机 IMU输出频率 100 Hz 陀螺仪零偏 200 °/h 加速度计零偏 9.8×10–3 m/s2 角度随机游走 0.2 °/ $\sqrt {\rm h} $ 速度随机游走 0.2 m/(s· $\sqrt {\rm h} $) GNSS测量值输出频率 1 Hz -
[1] NIU Xiaoji, DAI Yuhang, LIU Tianyi, et al. Feature-based GNSS positioning error consistency optimization for GNSS/INS integrated system[J]. GPS Solutions, 2023, 27(2): 89. doi: 10.1007/s10291-023-01421-9 [2] WANG Hao, PAN Shuguo, GAO Wang, et al. Multipath/NLOS detection based on k-means clustering for GNSS/INS tightly coupled system in urban areas[J]. Micromachines, 2022, 13(7): 1128. doi: 10.3390/mi13071128 [3] JIANG Haitao, SHI Chuang, LI Tuan, et al. Low-cost GPS/INS integration with accurate measurement modeling using an extended state observer[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 25(1): 17. doi: 10.1007/s10291-020-01053-3 [4] CHANG Dengxiang, ZHOU Yunshui, HU Manjiang, et al. Robust accurate LiDAR-GNSS/IMU self-calibration based on iterative refinement[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(5): 5188–5199. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3233227 [5] WEN Weisong, BAI Xiwei, KAN Y C, et al. Tightly coupled GNSS/INS integration via factor graph and aided by fish-eye camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(11): 10651–10662. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2944680 [6] ZHONG Qiming and GROVES P D. Multi-epoch 3D-mapping-aided positioning using Bayesian filtering techniques[J]. NAVIGATION: Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 2022, 69(2): navi. 515. doi: 10.33012/navi.515. [7] NG H F, ZHANG Guohao, LUO Yiran, et al. Urban positioning: 3D mapping-aided GNSS using dual-frequency pseudorange measurements from smartphones[J]. NAVIGATION:Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 2021, 68(4): 727–749. doi: 10.1002/navi.448 [8] WU Qingdong, LI Chenxi, SHEN Tao, et al. Improved adaptive iterated extended Kalman filter for GNSS/INS/UWB-integrated fixed-point positioning[J]. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 2023, 134(3): 1761–1772. doi: 10.32604/cmes.2022.020545 [9] JIANG Wei, CAO Zhuojian, CAI Baigen, et al. Indoor and outdoor seamless positioning method using UWB enhanced multi-sensor tightly-coupled integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(10): 10633–10645. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3110325 [10] WANG Yuqiang, ZHAO Bohao, ZHANG Wei, et al. Simulation experiment and analysis of GNSS/INS/LEO/5G integrated navigation based on federated filtering algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(2): 550. doi: 10.3390/s22020550 [11] AYABAKAN T and KERESTECIOGLU F. RSSI-based indoor positioning via adaptive federated Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(6): 5302–5308. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3097249 [12] 杨元喜. 多源传感器动、静态滤波融合导航[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2003, 28(4): 386–388,396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8860.2003.04.002YANG Yuanxi. Kinematic and static filtering for multi-sensor navigation systems[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2003, 28(4): 386–388,396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8860.2003.04.002 [13] 史兼郡, 邱磊, 王晓丹, 等. 基于动、静态滤波算法的组合导航技术研究[C]. 第六届中国卫星导航学术年会论文集—S09PNT体系与导航新技术, 西安, 中国, 2015: 130–133.SHI Jianjun, QIU Lei, WANG Xiaodan, et al. Research on integrated navigation technology based on the dynamic, static filtering algorithm[C]. China Satellite Navigation Conference, Xi’an, China, 2015: 130–133. [14] NING Yipeng, WANG Jian, HAN Houzeng, et al. An optimal radial basis function neural network enhanced adaptive robust Kalman filter for GNSS/INS integrated systems in complex urban areas[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(9): 3091. doi: 10.3390/s18093091 [15] DELLAERT F. Factor graphs and GTSAM: A hands-on introduction[R]. GT-RIM-CP&R-2012-002, 2012. [16] KAESS M, JOHANNSSON H, ROBERTS R, et al. iSAM2: Incremental smoothing and mapping using the Bayes tree[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(2): 216–235. doi: 10.1177/0278364911430419 [17] LIU Xiaohui, YUAN Yuelin, HUANG Jinquan, et al. A new algorithm of tightly-coupled GNSS/INS integrated navigation based on factor graph[M]. YANG Changfeng and XIE Jun. China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC 2021) Proceedings. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 586–595. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-3142-9_56. [18] KAESS M, RANGANATHAN A, and DELLAERT F. iSAM: Incremental smoothing and mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(6): 1365–1378. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2006706 -





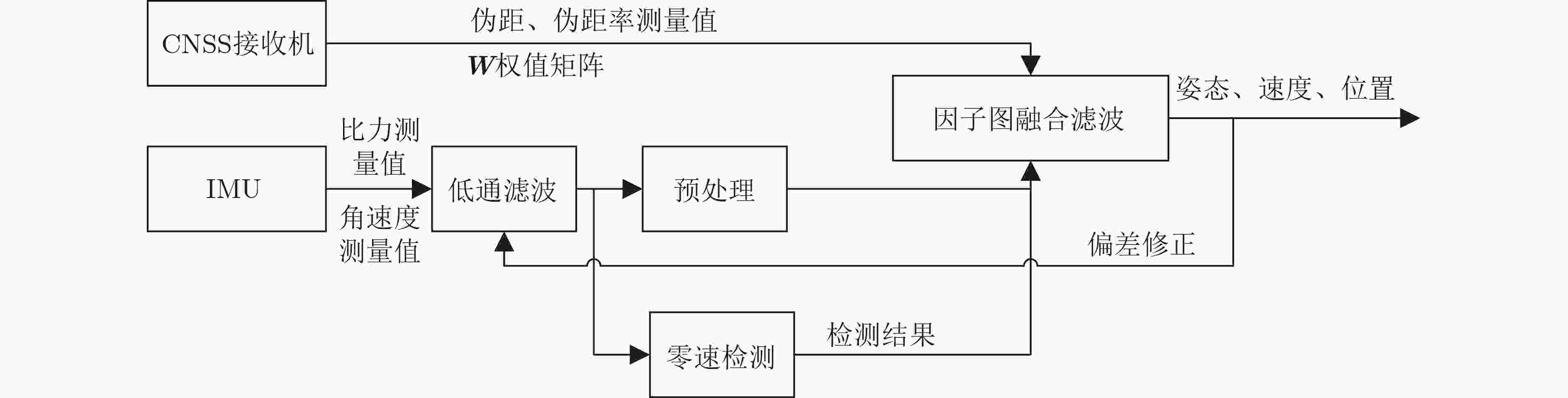
 下载:
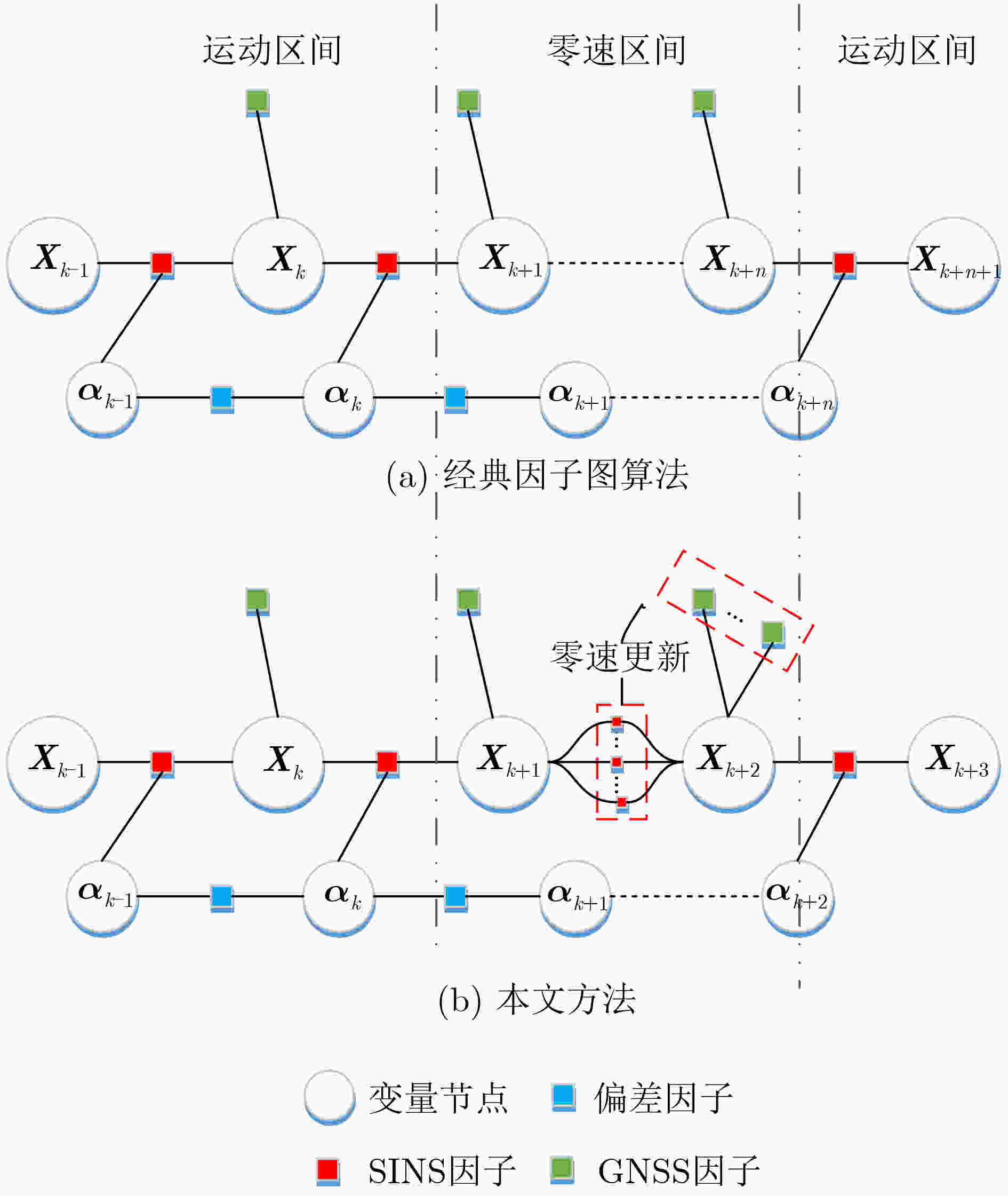
下载:
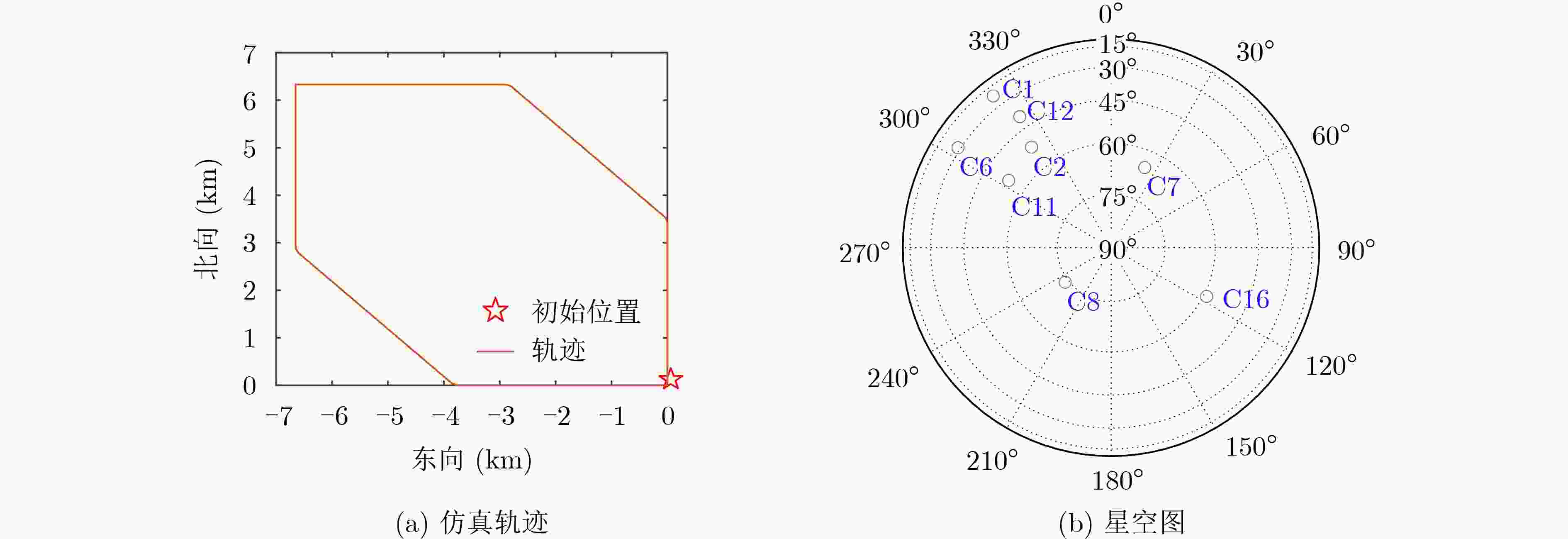

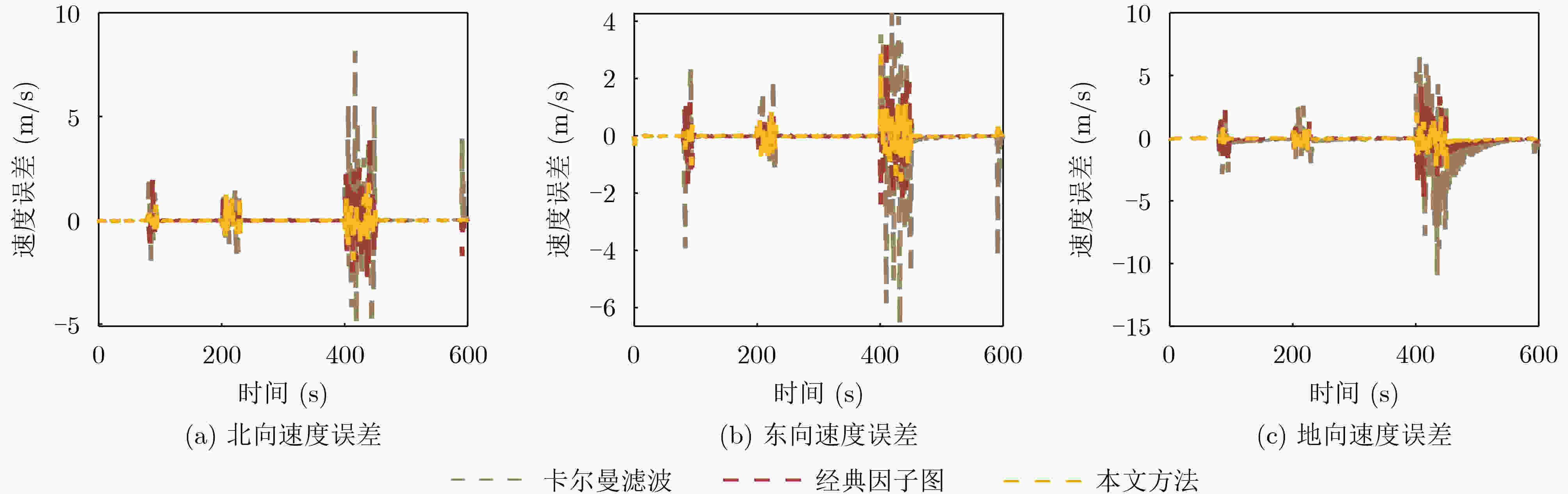
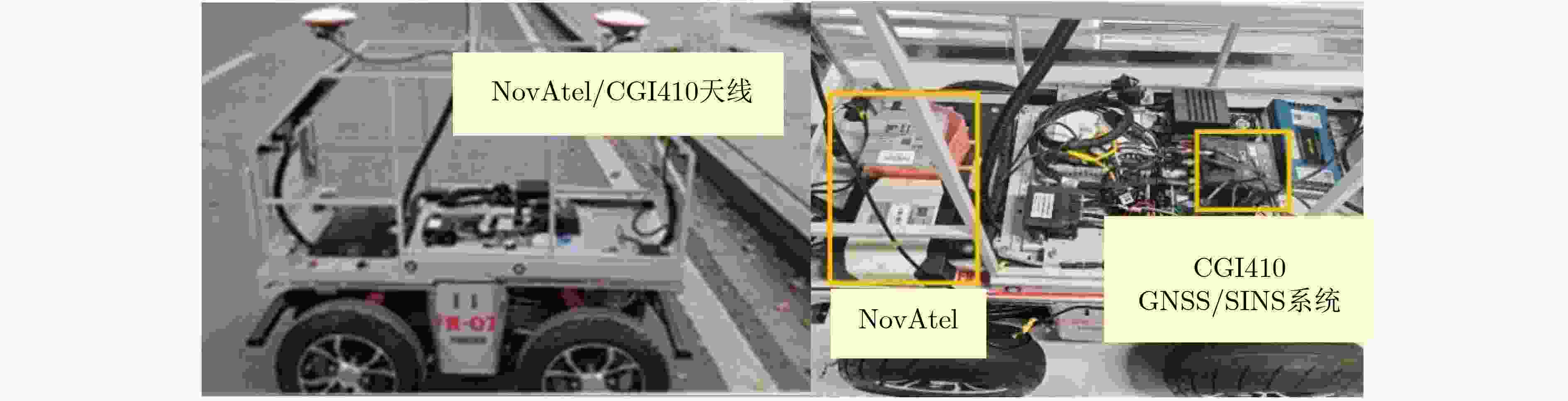
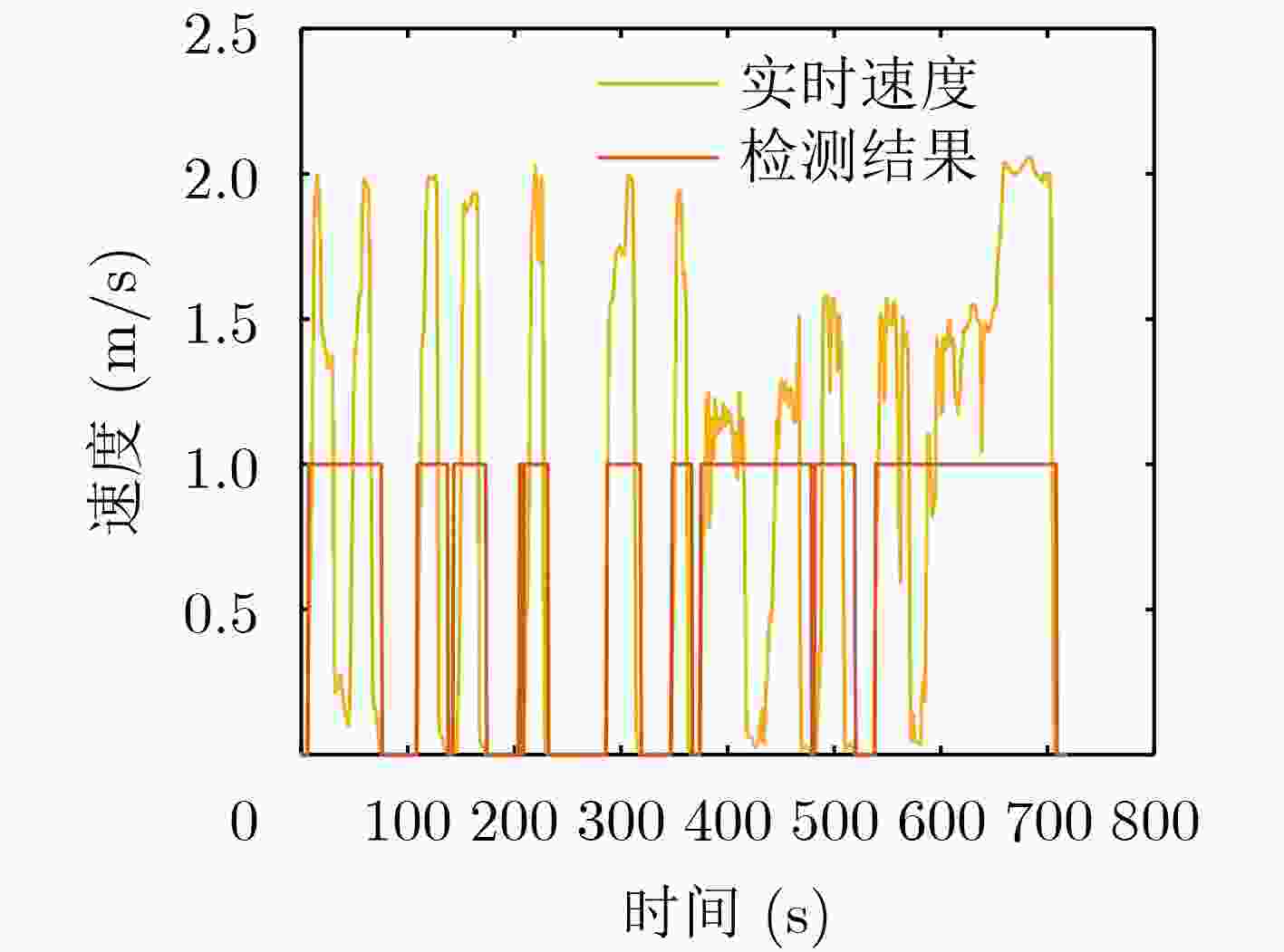
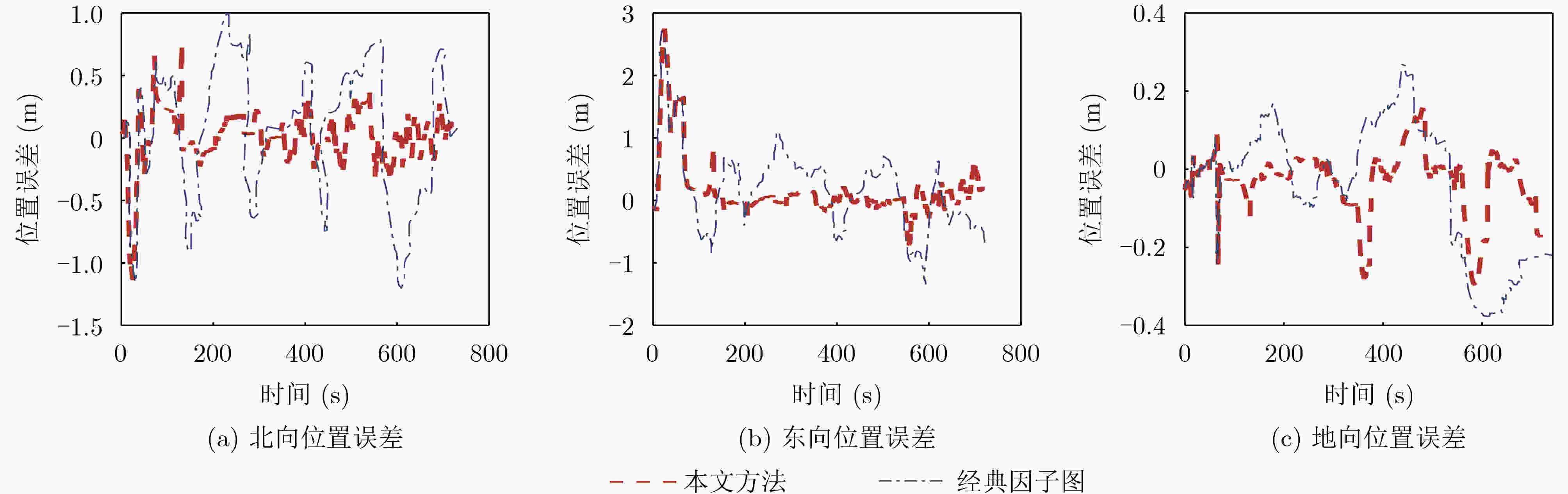
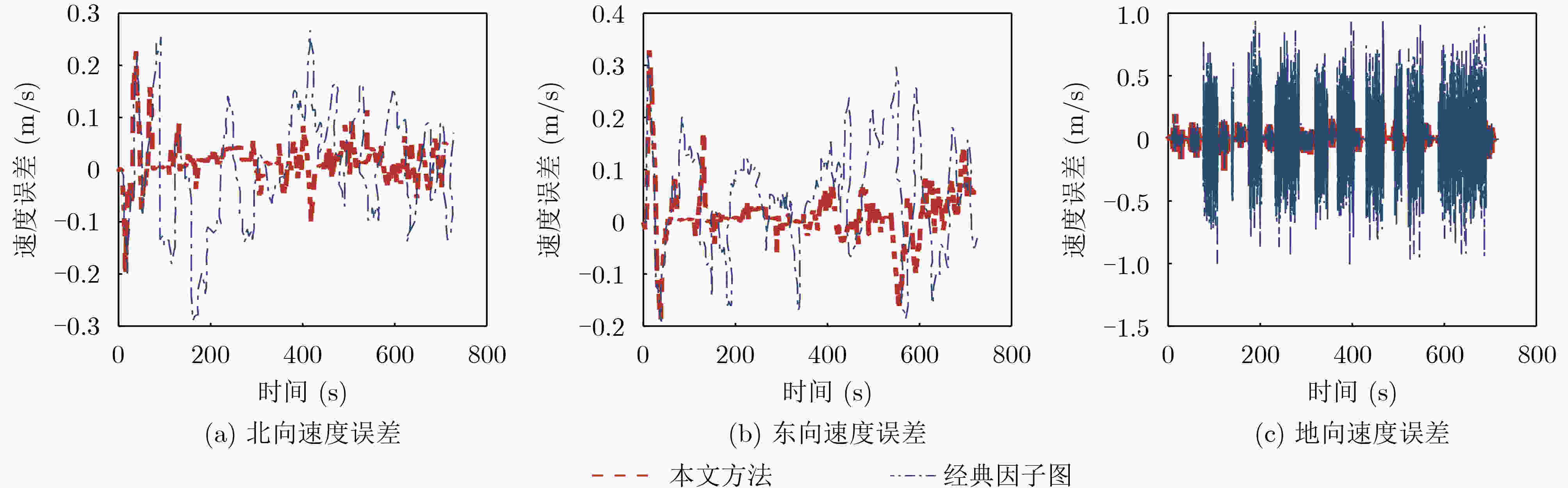
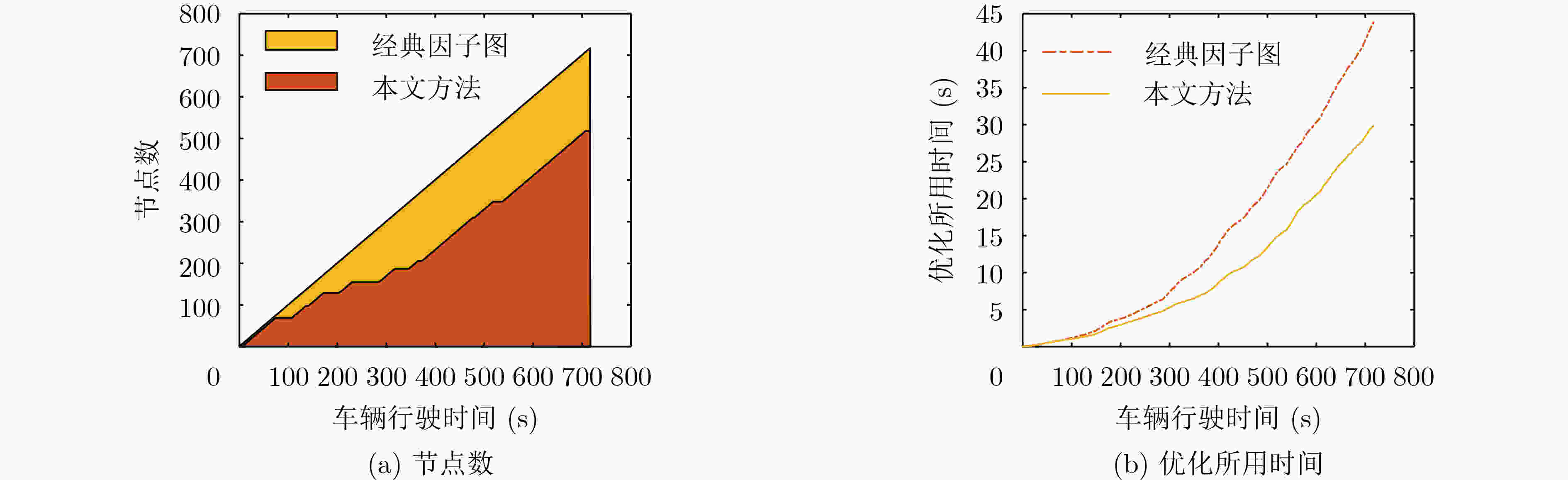


 下载:
下载:
