In-memory Wallace Tree Multipliers Based on Majority Gates with Voltage Gated Spin-Orbit Torque Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory Devices
-
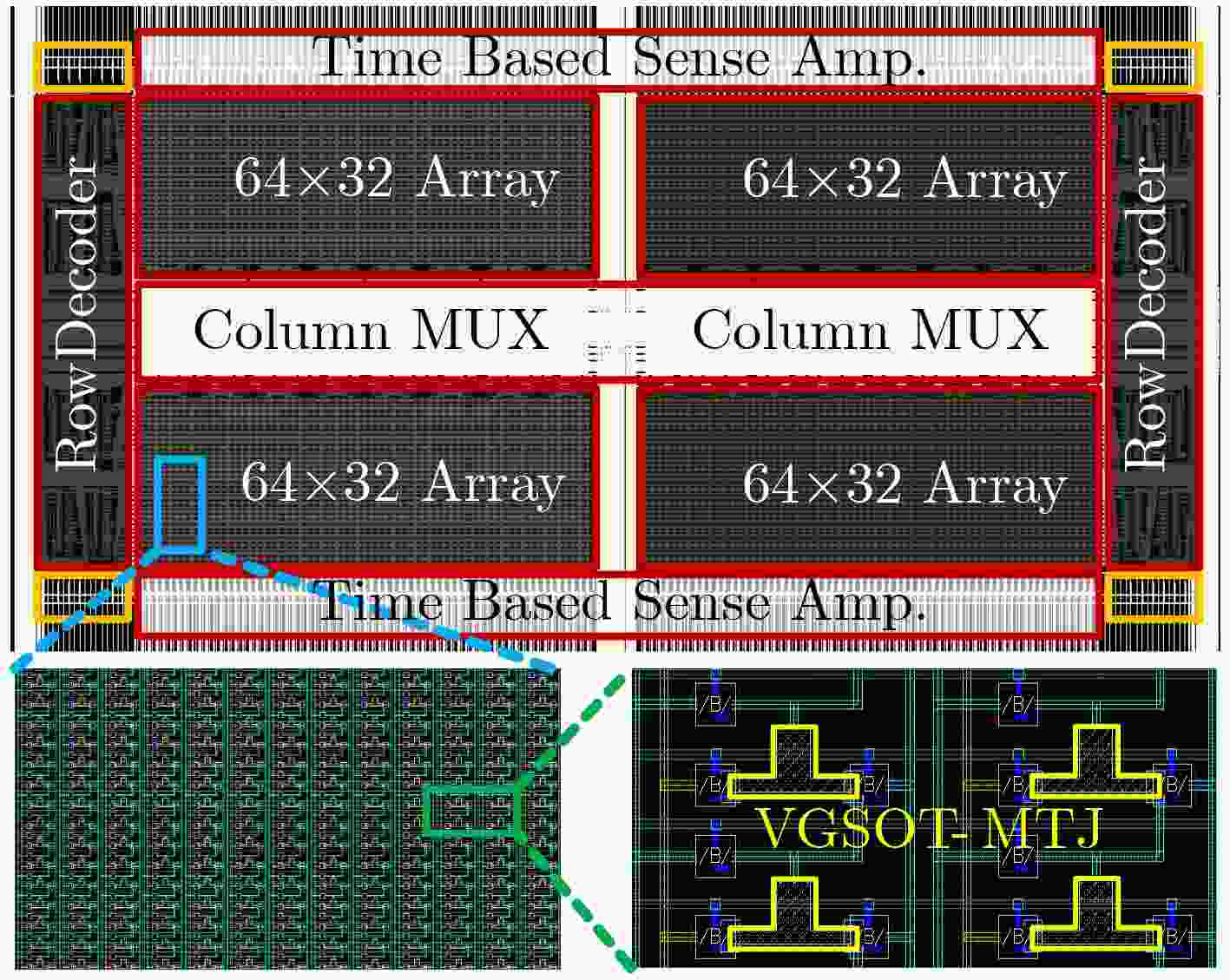
摘要: 在使用新型非易失性存储阵列进行存内计算的研究中,存内乘法器的延迟往往随着位宽的增加呈指数增长,严重影响计算性能。该文设计一种电压调控自旋轨道矩磁随机存储器(VGSOT-MRAM)单元交叉阵列,并提出一种存内华莱士树乘法器的电路设计方法。所提串联存储单元结构通过电阻求和的方式,有效解决磁存储器单元阻值较低的问题;其次提出基于电压调控自旋轨道矩磁存储器单元交叉阵列的存内计算架构,利用在“读”操作期间实现的5输入多数决定逻辑门,进一步降低华莱士树乘法器的逻辑深度。与现有乘法器设计方法相比,所提方法延迟开销从O(n2)降低为O(log2 n),在大位宽时延迟更低。Abstract: In the research on utilizing emerging non-volatile storage arrays for in-memory computing, the latency of in-memory multipliers often exhibits exponential growth with increasing bit width, and significantly impacts the computational performance. A Voltage-Gated Spin-Orbit Torque Magnetoresistive Random-Acess Memory (VGSOT-MRAM) device unit crossbar array is proposed and a circuit design approach for in-memory Wallace tree multipliers is presented in this paper. The proposed series-connected storage unit structure effectively addresses the issue of low resistance values in magnetic storage units through resistive summing. Furthermore, an in-memory computing architecture based on a voltage-controlled spin-orbit torque magnetic storage unit crossbar array is introduced. Finally, a five-input majority decision logic gate implemented during the “read” operation is leveraged to further reduce the logic depth of the Wallace tree multiplier. Compared to existing multiplier design methods, the proposed approach reduces the delay overhead from O(n2) to O(log2 n), with even lower latency for larger bit widths.
-
表 1 电压调控SOT磁隧道结模型参数
参数 名称 数值 tf 自由层厚度(nm) 1.1 to MgO层厚度(nm) 1.4 TMR 在无偏置电压时TMR比(%) 100% d, l, w AFM的厚度、长度、宽度(nm) 3, 50, 60 D MTJ的直径(nm) 50 ρch 电阻率(μ$ \Omega $·cm) 160 θSHE 自旋霍尔角 0.25 R·A 电阻与面积乘积($ \Omega $·μm2) 650 Hex 交换偏置(Oe) –180 β VCMA参数(fJ/V·M) 60 表 2 不同类型的乘法器计算延迟(cycles)和单元占用单元数量对比
文献 4 × 4 n × n 机器周期 占用单元 机器周期 占用单元 [26] 195 200 15n 2 – 11n – 1 15n 2 – 9n – 1 [27] 158 75 13n 2 – 14n + 6 20n – 5 [10] 139 49 n log2 n + 14n + 3 14n – 7 [9] 102 38 (log2 n) (10n + 2) + 4n + 2 2n 2 + n + 2 [11] 32 128 6 log2 (n 2/4) + 4 [log2 2(n – log2 n)] + (n – 2) (log2 n – 2)+ 10 8n2 + 48 log2 (n/4) 本文 28 112 5 log2 (n 2/4) + 4 log2 [2(n – log2 n)] + 10 7n2 + 42 log2 (n/4) -
[1] PARHAMI B. Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Designs[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 2000. [2] JIANG Honglan, ANGIZI S, FAN Deliang, et al. Non-volatile approximate arithmetic circuits using scalable hybrid spin-CMOS majority gates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2021, 68(3): 1217–1230. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3044728. [3] CAI Hao, GUO Yanan, LIU Bo, et al. Proposal of analog in-memory computing with magnified tunnel magnetoresistance ratio and universal STT-MRAM cell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(4): 1519–1531. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3140769. [4] ZHOU Feichi and CHAI Yang. Near-sensor and in-sensor computing[J]. Nature Electronics, 2020, 3(11): 664–671. doi: 10.1038/s41928-020-00501-9. [5] YUE Zhiheng, WANG Yabing, QIN Yubin, et al. BR-CIM: An efficient binary representation computation-in-memory design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(10): 3940–3953. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3185135. [6] WANG Jinkai, BAI Yining, WANG Hongyu, et al. Reconfigurable bit-serial operation using toggle SOT-MRAM for high-performance computing in memory architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(11): 4535–4545. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3192165. [7] GUCKERT L and SWARTZLANDER E E. Optimized memristor-based multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2017, 64(2): 373–385. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2606433. [8] GUCKERT L and SWARTZLANDER E E. Dadda multiplier designs using memristors[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on IC Design and Technology (ICICDT), Austin, USA, 2017: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICICDT.2017.7993521. [9] RADAKOVITS D, TAHERINEJAD N, CAI Mengye, et al. A memristive multiplier using semi-serial IMPLY-based adder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2020, 67(5): 1495–1506. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.2965935. [10] LEITERSDORF O, RONEN R, and KVATINSKY S. MultPIM: Fast stateful multiplication for processing-in-memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2022, 69(3): 1647–1651. doi: 10.1109/TCSII. 2021.3118215. [11] LAKSHMI V, REUBEN J, and PUDI V. A novel in-memory wallace tree multiplier architecture using majority logic[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(3): 1148–1158. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3129827. [12] KIM Y S, SON M W, and KIM K M. Memristive stateful logic for edge Boolean computers[J]. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2021, 3(7): 2000278. doi: 10.1002/aisy.202000278. [13] REUBEN J and PECHMANN S. Accelerated addition in resistive RAM array using parallel-friendly majority gates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2021, 29(6): 1108–1121. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2021.3068470. [14] SHREYA S, VERMA G, PIRAMANAYAGAM S N, et al. Energy-efficient all-spin BNN using voltage-controlled spin-orbit torque device for digit recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2021, 68(1): 385–392. doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.3038140. [15] SHREYA S, JAIN A, and KAUSHIK B K. Computing-in-memory architecture using energy-efficient multilevel voltage-controlled spin-orbit torque device[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2020, 67(5): 1972–1979. doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.2978085. [16] JUNG S, LEE H, MYUNG S, et al. A crossbar array of magnetoresistive memory devices for in-memory computing[J]. Nature, 2022, 601(7892): 211–216. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04196-6. [17] WU Y C, GARELLO K, KIM W, et al. Voltage-gate-assisted spin-orbit-torque magnetic random-access memory for high-density and low-power embedded applications[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2021, 15(6): 064015. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.15.064015. [18] JIANG Linjun, DENG Erya, ZHANG He, et al. A spintronic in-memory computing network for efficient hamming codec implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2022, 69(4): 2086–2090. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2022.3144678. [19] ZHANG Kaili, ZHANG Deming, WANG Chengzhi, et al. Compact modeling and analysis of voltage-gated spin-orbit torque magnetic tunnel junction[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 50792–50800. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980073. [20] WU Bi, ZHU Haonan, CHEN Ke, et al. MLiM: High-performance magnetic logic in-memory scheme with unipolar switching SOT-MRAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2023, 70(6): 2412–2424. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2023.3254607. [21] WU Bi, WANG Chao, WANG Zhaohao, et al. Field-free 3T2SOT MRAM for non-volatile cache memories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2020, 67(12): 4660–4669. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3020798. [22] ZHANG Xueyong, AN B K, and KIM T T H. A robust time-based multi-level sensing circuit for resistive memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2023, 70(1): 340–352. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3211989. [23] TRINH Q K, RUOCCO S, and ALIOTO M. Time-based sensing for reference-less and robust read in STT-MRAM memories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2018, 65(10): 3338–3348. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2828611. [24] LI Wei, YANG Yang, YAN Hao, et al. Three-input majority logic gate and multiple input logic circuit based on DNA strand displacement[J]. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(6): 2980–2988. doi: 10.1021/nl4016107. [25] AHMADPOUR S S, MOSLEH M, and RASOULI HEIKALABAD S. Robust QCA full-adders using an efficient fault-tolerant five-input majority gate[J]. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 2019, 47(7): 1037–1056. doi: 10.1002/cta.2634. [26] IMANI M, GUPTA S, and ROSING T. Ultra-efficient processing in-memory for data intensive applications[C]. The 54th Annual Design Automation Conference 2017, Austin, USA, 2017: 6. doi: 10.1145/3061639.3062337. [27] HAJ-ALI A, BEN-HUR R, WALD N, et al. Efficient algorithms for in-memory fixed point multiplication using magic[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2018.8351561. -






 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:
