Research on Distributed Ensemble Time Scale for Railway Time Synchronization Network
-
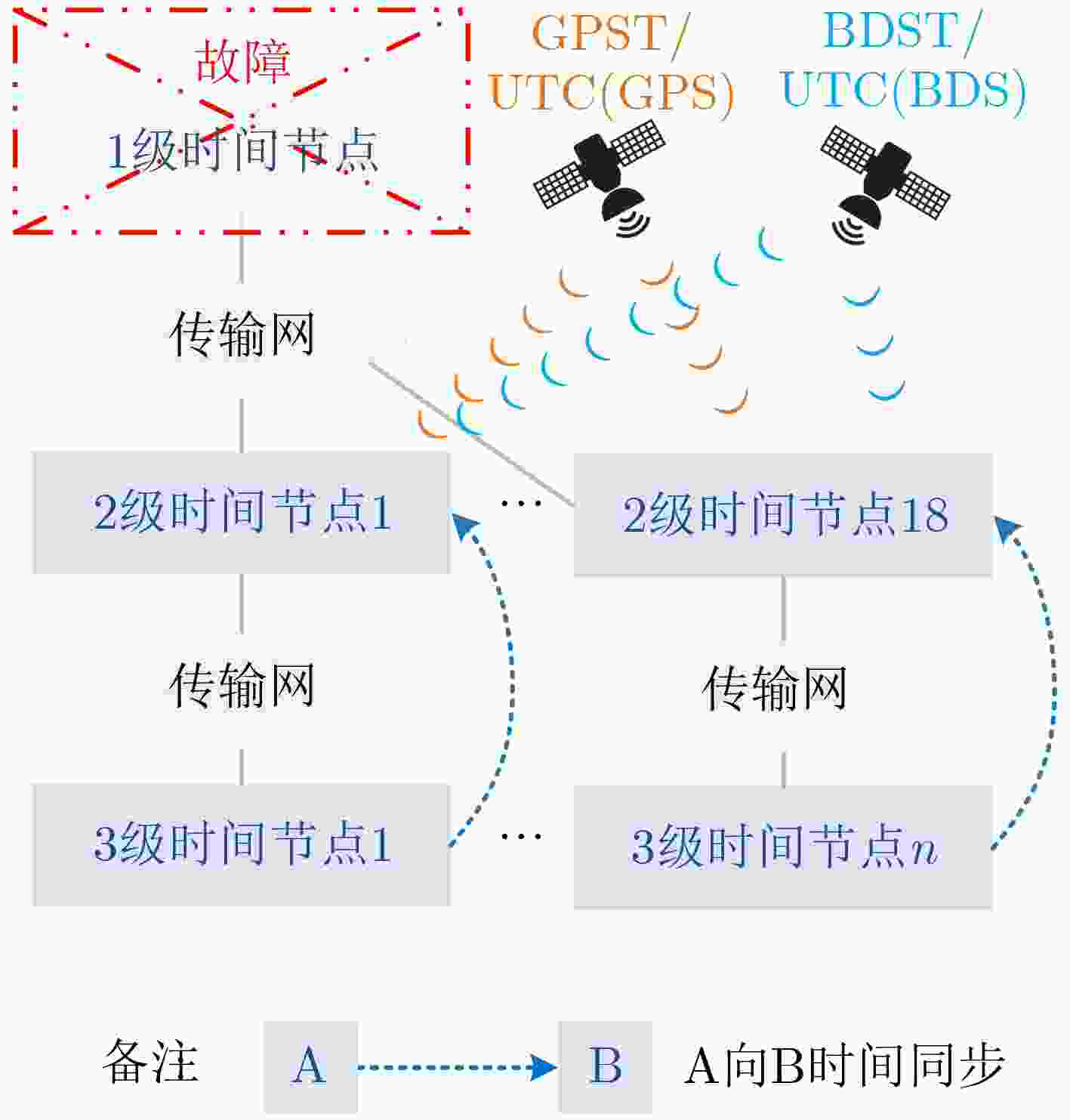
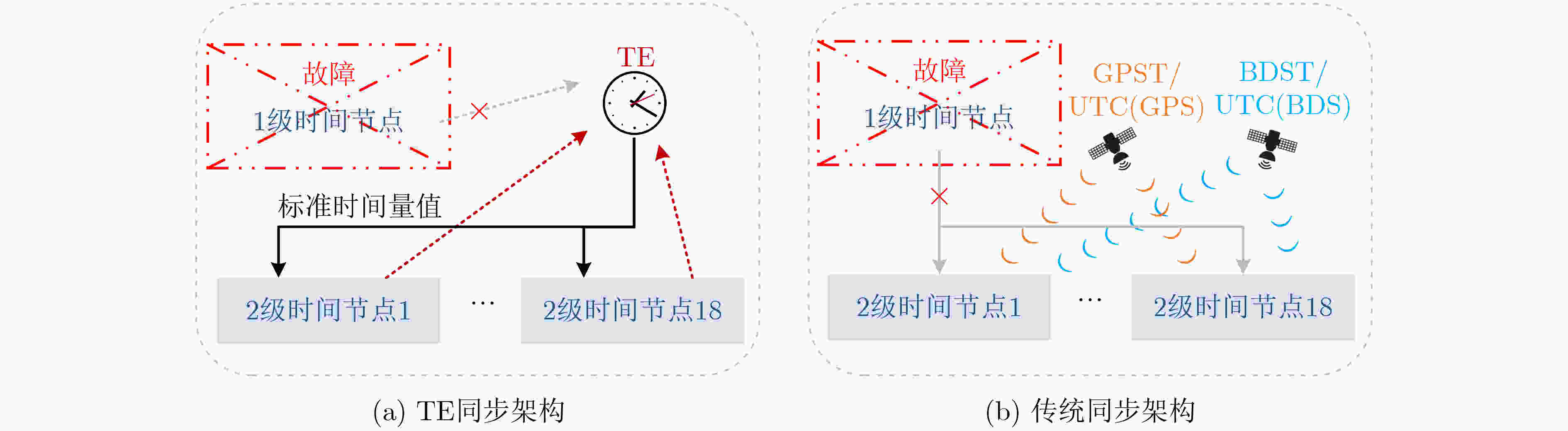
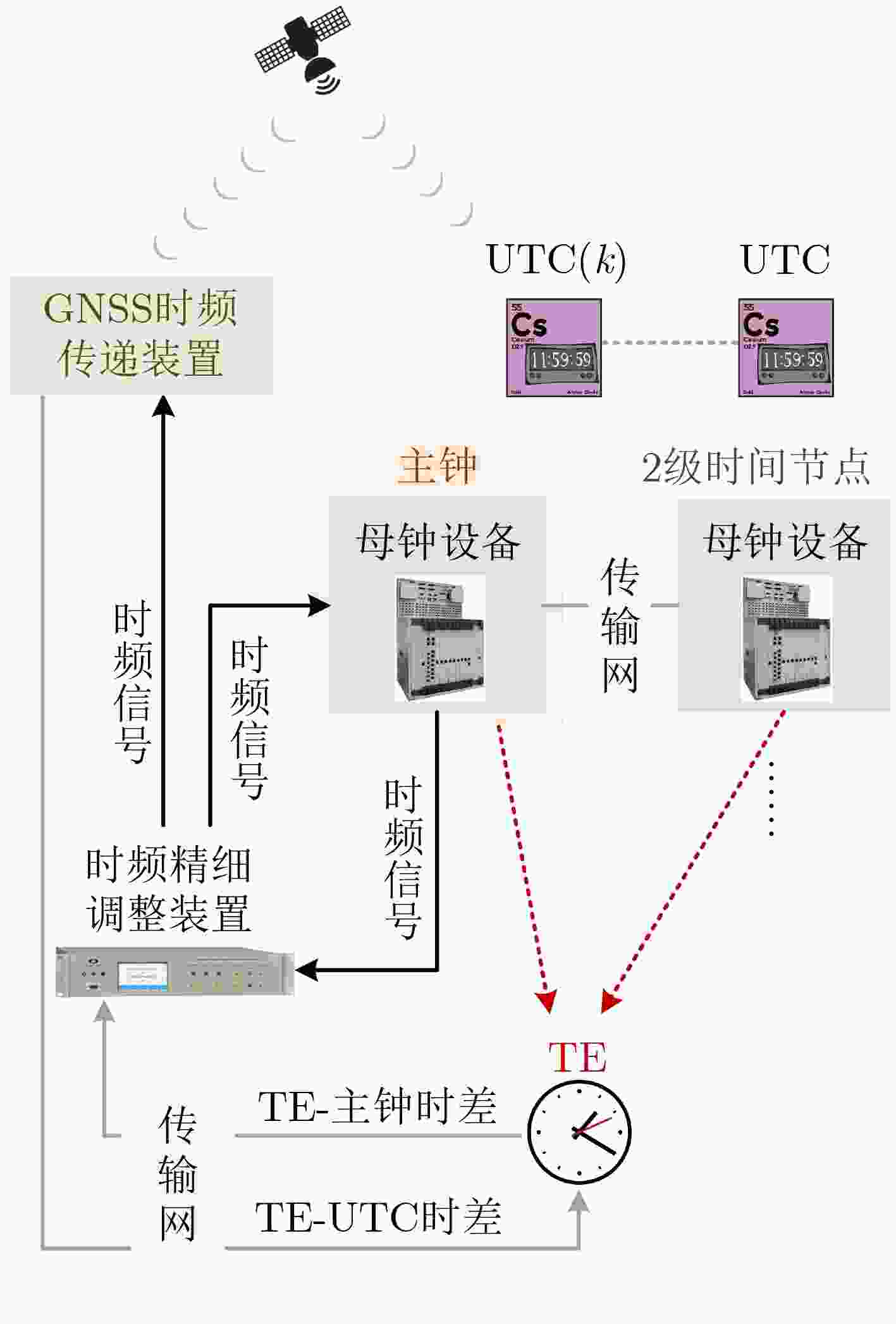
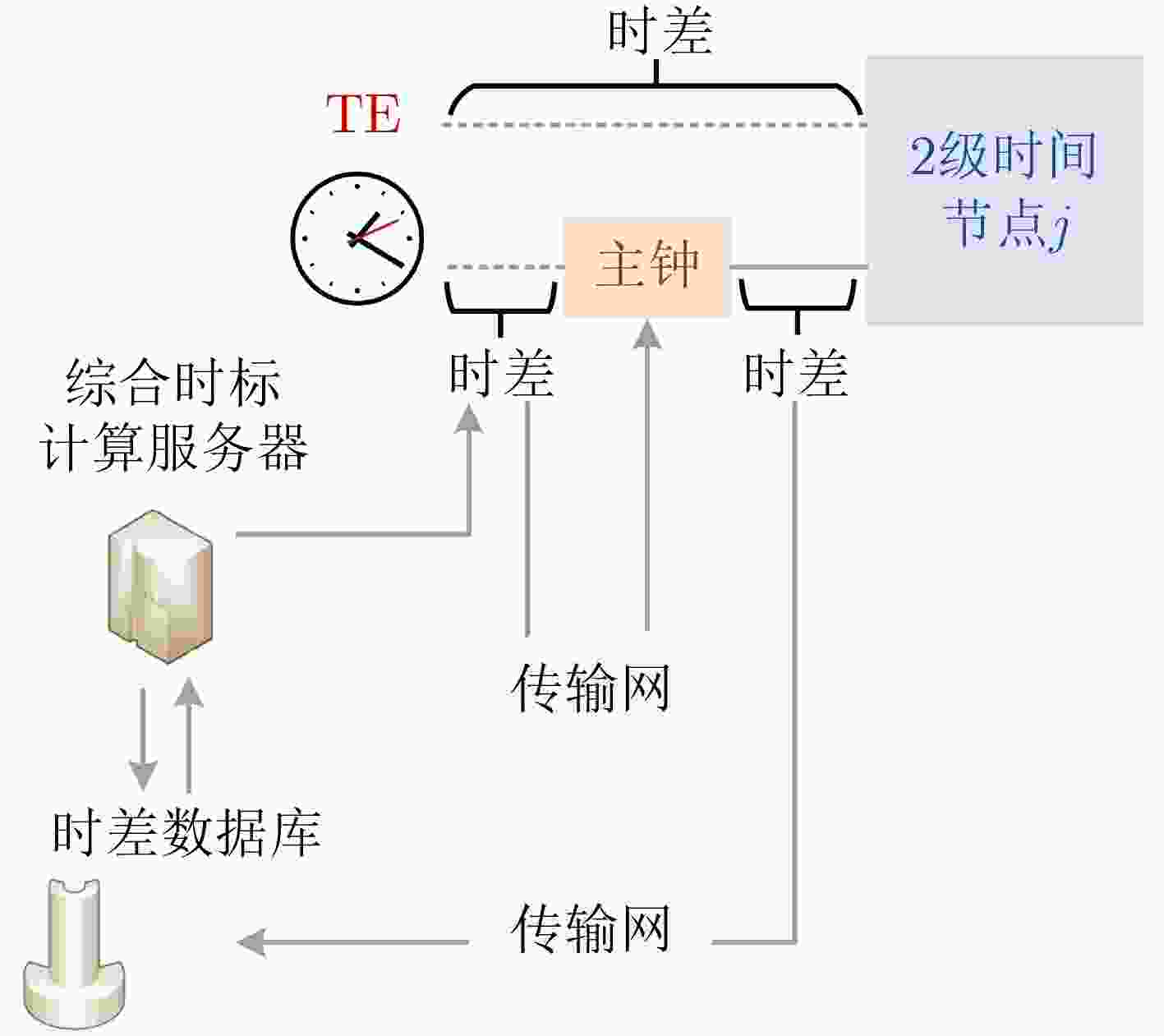
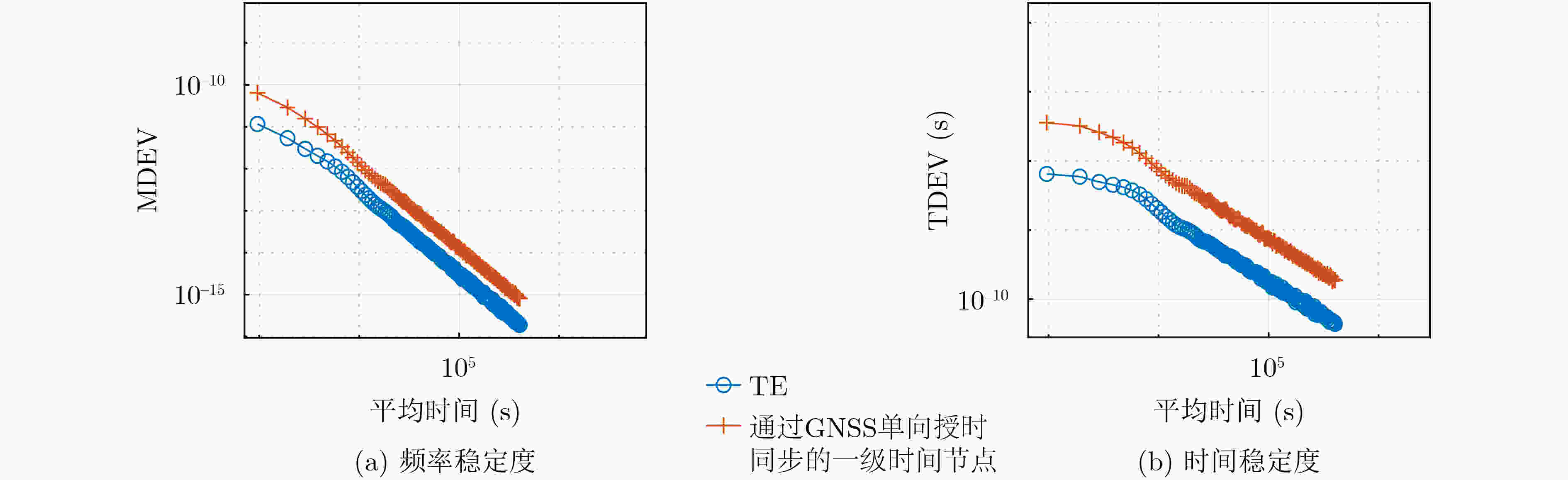
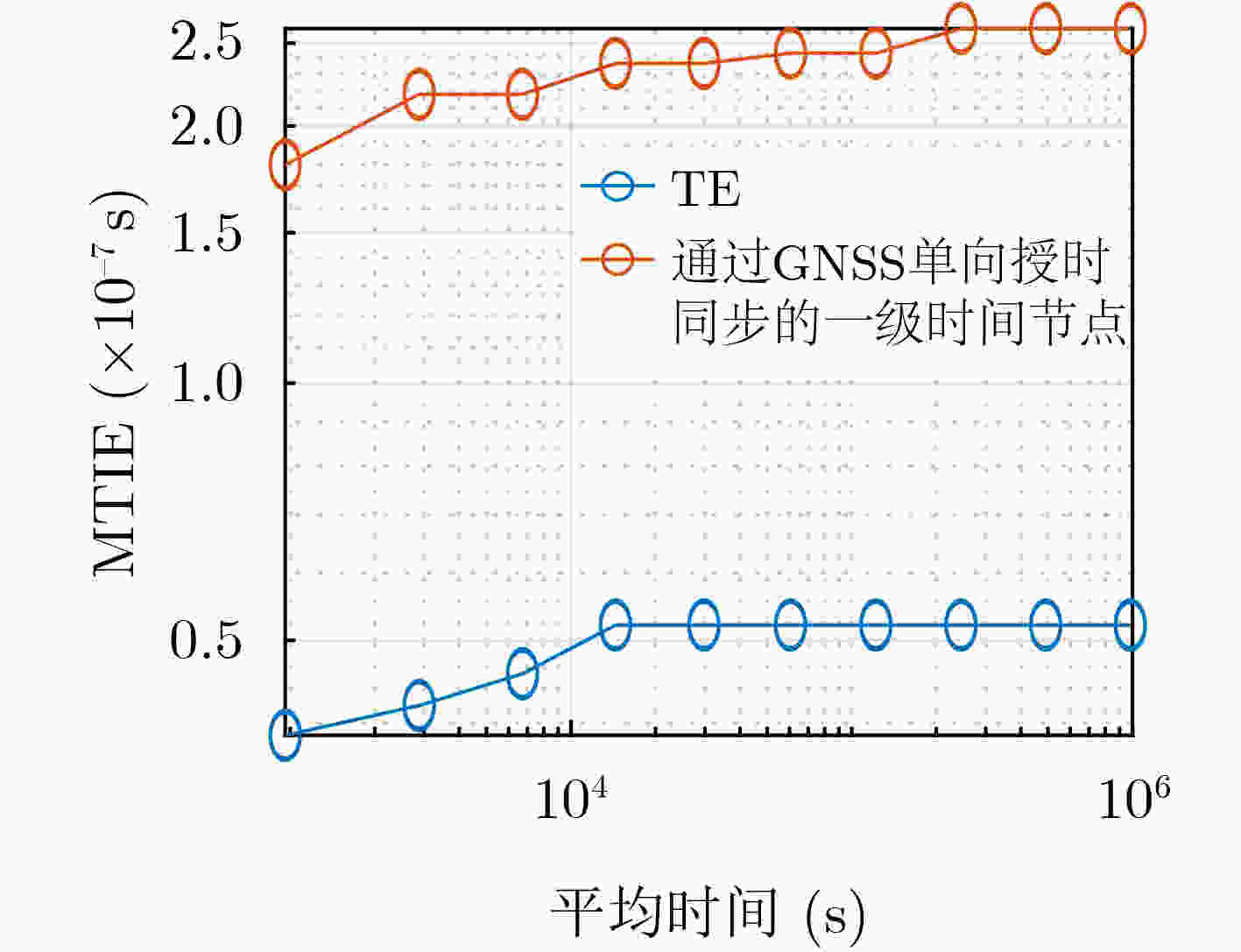
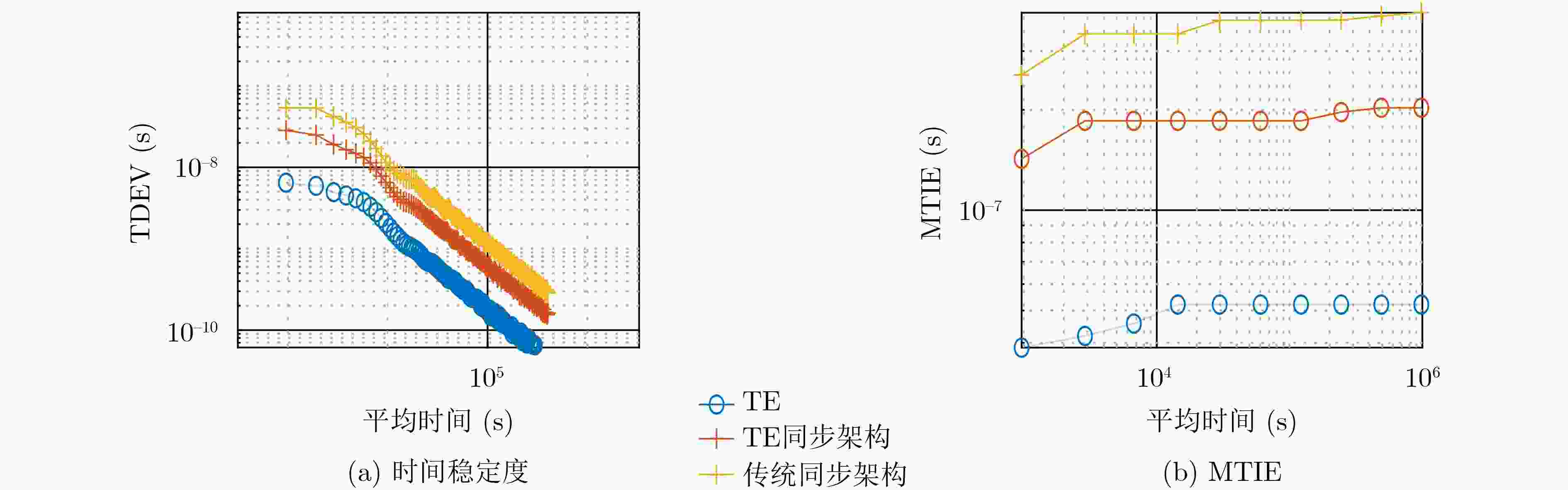
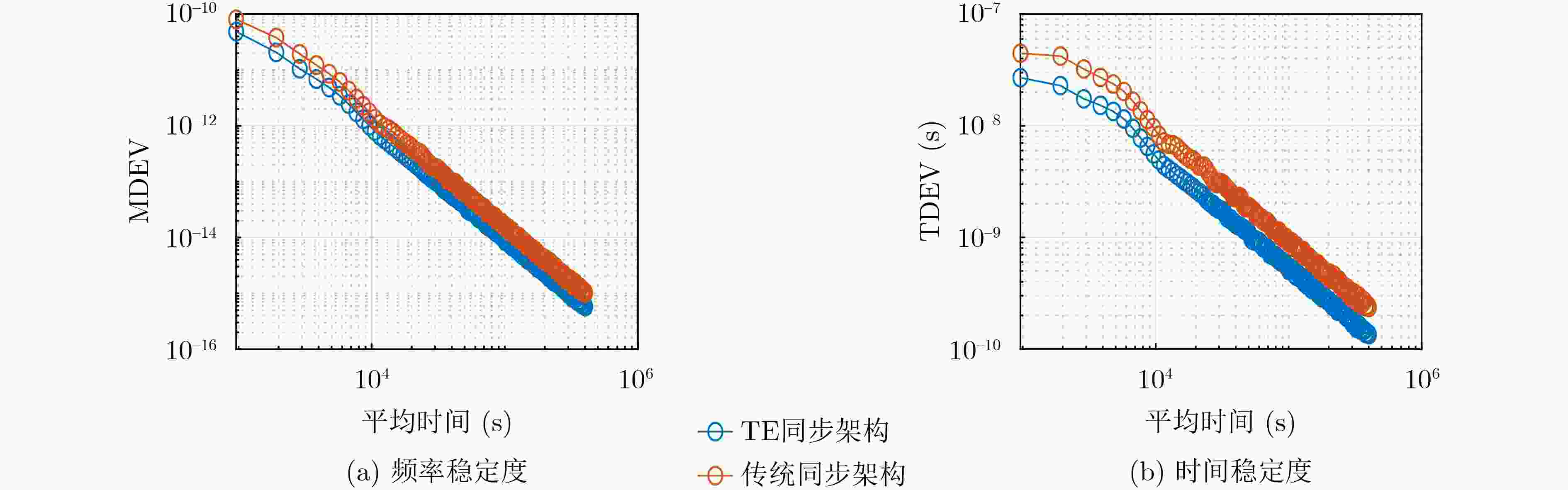
摘要: 铁路时间同步网为铁路各系统提供统一的标准时间量值,其精确、稳定与否对铁路系统安全、高效地运营具有重要影响。根据调研,当前铁路时间同步网的潜在问题有:各时间节点时间溯源参考不一致,且未精确溯源至协调世界时(UTC);仅设置1处的1级时间节点故障时,2,3级时间节点受其影响大、鲁棒性不足;监测手段仅针对单个节点,缺乏整体层面的自动监测方法。针对以上潜在问题,该文提出可精确溯源至UTC的铁路时间同步网综合原子时标(TE)作为网内统一的时间溯源参考的解决方案,通过建立铁路时间同步网仿真模型,研究设计了综合原子时标算法,基于1级、2级时间节点19台母钟设备形成了TE。仿真结果表明,TE与UTC的溯源偏差可优于30 ns,溯源不确定度可优于5 ns;1级时间节点正常运行时,引入TE可提高2级时间节点时间稳定度约40%;1级时间节点故障时,TE仍可持续生成并作为网内统一的时间溯源参考, TE同步架构下的2级时间节点与传统同步架构下的相比,其频率、时间稳定度提高约35%;基于TE可获取任意节点间时差,通过分析时差数据,可实现整体层面的所有时间节点、精确时间协议(PTP)链路通断的自动监测。Abstract: The railway time synchronization network provides the standard time quantity value for various railway systems. The accuracy and stability of the time quantity value have an important impact on the safe and the efficient operation of the railway systems. There are three potential problems with the current railway time synchronization network. The traceability references of each time node are inconsistent, and the time of each node is not accurately traced to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Only one primary time node is set. The secondary and the tertiary time nodes are greatly affected by the failure of the primary time node, and lack of robustness. Monitoring methods are only used a single time node. There is no automatic monitoring method at the overall level. In view of the above potential problems, the distributed Ensemble Time scale (TE) for railway time synchronization network that can accurately trace to UTC is proposed. A simulation model of railway time synchronization network is established, and a TE algorithm is designed. TE is generated by 19 atomic clocks from the primary and the secondary time nodes. The results show that the time differences between TE and UTC can be better than 30 ns. The uncertainty of TE-UTC is better than 5 ns. When the primary time node works normally, the time stability of the secondary time node can be improved about 40% by introducing TE. When the primary time node fails, TE can be continuously generated and used as a unified traceability reference. The frequency and time stability of the secondary time node under the TE synchronization architecture is about 35% higher than that under the traditional synchronization architecture. The time differences between any time nodes can be obtained based on TE. By analyzing the time differences data, automatic monitoring of all time nodes and the continuity of Precision Time Protocol (PTP) links at the overall level can be realized.
-
表 1 各时间节点向TE同步后与UTC(k)频差
时间节点 频差 时间节点 频差 TE $ 5.4 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 1 $ - 3.5 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 21 $ - 9 \times {10^{ - 15}} $ 22 $ 1.42 \times {10^{ - 13}} $ 23 $ - 9.4 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 24 $ 4.6 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 25 $ 7.9 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 26 $ - 6.5 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 27 $ - 1.55 \times {10^{ - 13}} $ 28 $ - 9.7 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 29 $ - 1.00 \times {10^{ - 13}} $ 210 $ - 2.8 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 211 $ - 2.34 \times {10^{ - 13}} $ 212 $ - 5.3 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 213 $ - 4.0 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 214 $ - 6.1 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 215 $ - 2.6 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 216 $ - 1.5 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 217 $ - 2.03 \times {10^{ - 13}} $ 218 $ - 2.0 \times {10^{ - 14}} $ 表 2 1级时间节点故障前后TE同步架构/传统同步架构下2级时间节点1相对UTC(k)的标准差、均值变化(ns)
向TE同步 通过GNSS单向授时
进行同步标准差变化 6.96 23.99 均值变化 0.02 0.14 -
[1] 于佳亮, 程华, 于天泽, 等. 基于北斗卫星同步授时的应用研究与试验[J]. 中国铁路, 2013(4): 18–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-683X.2013.04.005YU Jialiang, CHENG Hua, YU Tianze, et al. Application research and experiment of synchronous timing service based on Beidou satellite[J]. Chinese Railways, 2013(4): 18–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-683X.2013.04.005 [2] 国家铁路局. TB/T 3283-2015 铁路时间同步网技术条件[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2015.National Railway Administration of the People's Republic of China. TB/T 3283-2015 Technical conditions for railway time synchronization network[S]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2015. [3] 梁坤, 余沺, 杨志强, 等. 铁路时间同步网溯源及同步性能研究[J]. 中国铁路, 2023(8): 43–51. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2023.04.26.003LIANG Kun, YU Tian, YANG Zhiqiang, et al. Research on traceability and synchronization performance of railway time synchronization network[J]. Chinese Railways, 2023(8): 43–51. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2023.04.26.003 [4] Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology (JCGM). JCGM 200: 2012 International vocabulary of metrology-Basic and general concepts and associated terms (VIM)[S]. 3rd ed. JCGM, 2012. [5] 卫龙, 高红梅. 基于北斗系统的铁路地面时间同步系统设计[J]. 西部交通科技, 2016(2): 77–80. doi: 10.13282/j.cnki.wccst.2016.02.018WEI Long and GAO Hongmei. Design of railway ground time synchronization system based on Beidou navigation system[J]. Western China Communications Science & Technology, 2016(2): 77–80. doi: 10.13282/j.cnki.wccst.2016.02.018 [6] 程华, 吕博. 卫星共视技术在铁路同步网性能监测中的应用研究[J]. 电信工程技术与标准化, 2019, 32(9): 78–82. doi: 10.13992/j.cnki.tetas.2019.09.017CHENG Hua and LV Bo. Application research of satellite co-vision technology in railway synchronous network performance monitoring[J]. Telecom Engineering Technics and Standardization, 2019, 32(9): 78–82. doi: 10.13992/j.cnki.tetas.2019.09.017 [7] 王亚民. 北斗卫星导航系统在铁路同步网的应用[J]. 中国铁路, 2013(4): 8–11,29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-683X.2013.04.003WANG Yamin. Application of Beidou satellite navigation system in railway synchronization network[J].Chinese Railways, 2013(4): 8–11,29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-683X.2013.04.003 [8] 程华. 北斗卫星导航系统在铁路同步网中的应用研究[J]. 铁道通信信号, 2019, 55(7): 31–34. doi: 10.13879/j.issn1000-7458.2019-07.19086CHENG Hua. Application of BDS in railway synchronization networks[J]. Railway Signalling & Communication, 2019, 55(7): 31–34. doi: 10.13879/j.issn1000-7458.2019-07.19086 [9] 王胜军, 李德莉. OTN长距离传输时间同步的研究[J]. 光通信技术, 2017, 41(7): 13–16. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2017.07.004WANG Shengjun and LI Deli. Research on OTN long distance transmission time synchronization[J]. Optical Communication Technology, 2017, 41(7): 13–16. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2017.07.004 [10] 陈永, 詹芝贤, 刘雯. 下一代高速铁路LTE-R时间同步网协议脆弱性分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(1): 63–74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.01.008CHEN Yong, ZHAN Zhixian, and LIU Wen. Vulnerability analysis of next-generation high-speed railway LTE-R time synchronization network protocol[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(1): 63–74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.01.008 [11] 程华, 张萌, 李芳, 等. 铁路5G-R承载技术与组网方案研究[J]. 中国铁路, 2023(5): 1–7. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2023.03.10.001CHENG Hua, ZHANG Meng, LI Fang, et al. Research on railway 5G-R carrying technology and networking scheme[J]. Chinese Railways, 2023(5): 1–7. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2023.03.10.001 [12] 中国铁道学会. 铁路下一代承载网应用技术白皮书[M]. 北京: 中国铁道学会, 2020.China Railway Society. White Paper: Application Technology of Next Generation Railway Carrying Network[M]. Beijing: China Railway Society, 2020. [13] 于天泽, 张俊. 新型铁路同步网及其关键技术研究[J]. 铁道通信信号, 2019, 55(9): 43–45,49. doi: 10.13879/j.issn1000-7458.2019-09.19045YU Tianze and ZHANG Jun. Study on new type railway synchronization network[J]. Railway Signalling & Communication, 2019, 55(9): 43–45,49. doi: 10.13879/j.issn1000-7458.2019-09.19045 [14] DIMARCQ N, GERTSVOLF M, MILETI G, et al. Roadmap towards the redefinition of the second[J]. arXiv: 2307.14141, 2023. [15] LEVINE J, TAVELLA P, and MILTON M. Towards a consensus on a continuous coordinated universal time[J]. Metrologia, 2023, 60(1): 014001. doi: 10.1088/1681-7575/ac9da5 [16] MILTON J and PANFILO G. A new way to set the maximum weight in the weighting algorithm of UTC[C]. 2022 Joint Conference of the European Frequency and Time Forum and IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFCS), Paris, France, 2022: 1–2. doi: 10.1109/eftf/ifcs54560.2022.9850789. [17] PANFILO G and HARMEGNIES A. A new weighting procedure for UTC[C]. 2013 Joint European Frequency and Time Forum & International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFCS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2013: 652–653. doi: 10.1109/EFTF-IFC.2013.6702122. [18] International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). Circular T[EB/OL].https://www.bipm.org/en/time-ftp/circular-t, 2023. [19] MA Yuexin, TANG Chengpan, HU Xiaogong, et al. Discussions of a2-drift variations of BeiDou-3 satellite rubidium atomic clocks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1004713. doi: 10.1109/tim.2022.3187744 [20] 程华, 胡昌军. 基于1588v2高精度时间长距离传送实践[J]. 电信技术, 2018(3): 78–81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1247.2018.03.020CHENG Hua and HU Changjun. Practice of long-distance transmission based on 1588v2 high-precision time[J]. Telecommunications Technology, 2018(3): 78–81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1247.2018.03.020 -






 下载:
下载:

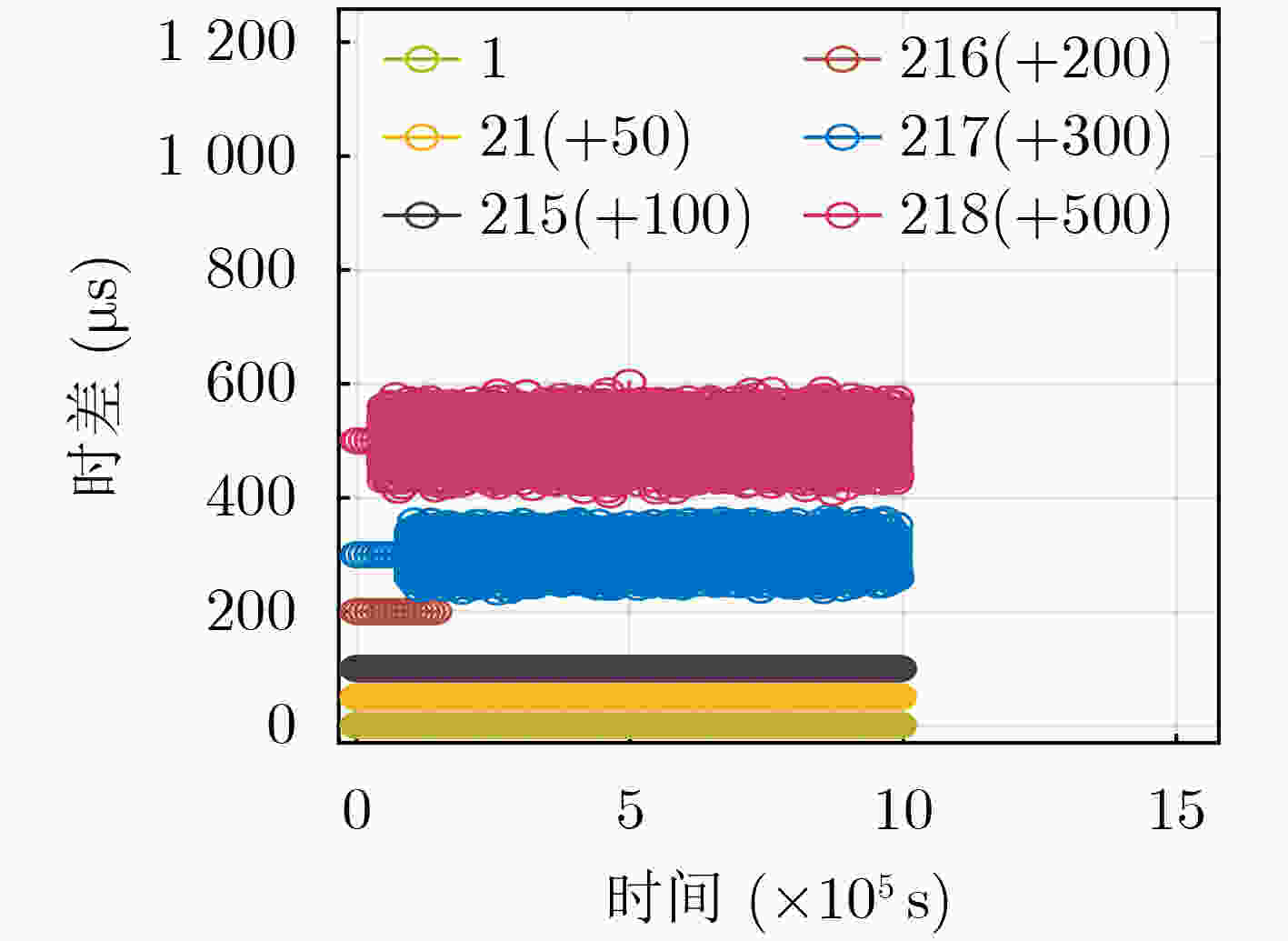
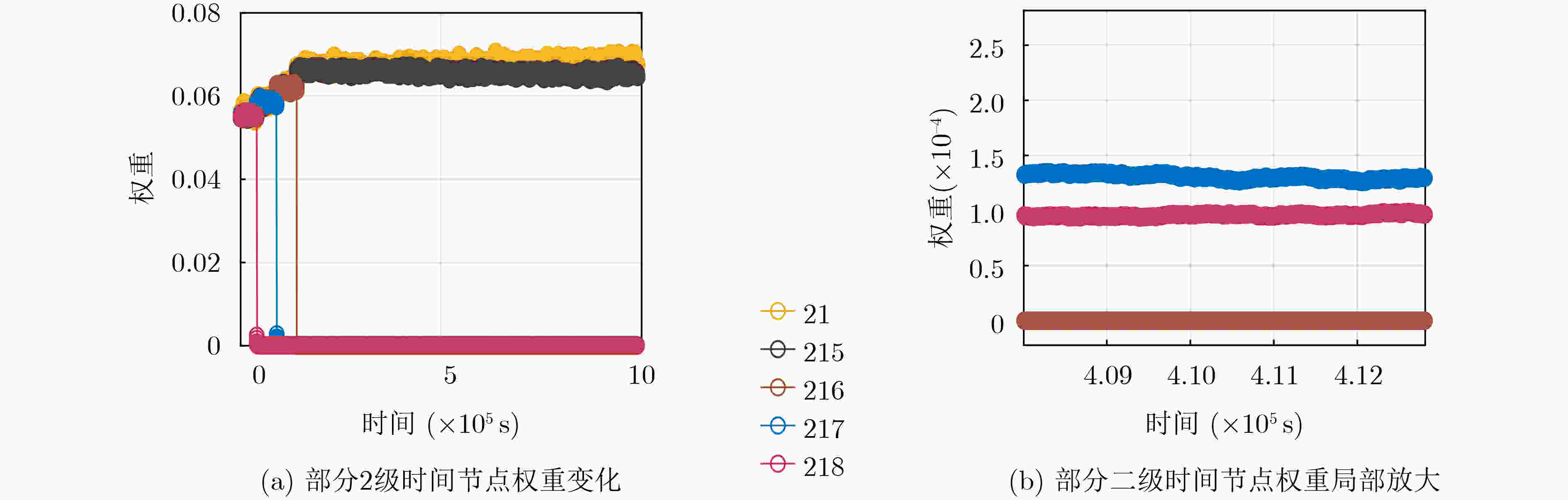


 下载:
下载:
