Hybrid Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication: Energy Efficient Beamforming Design
-
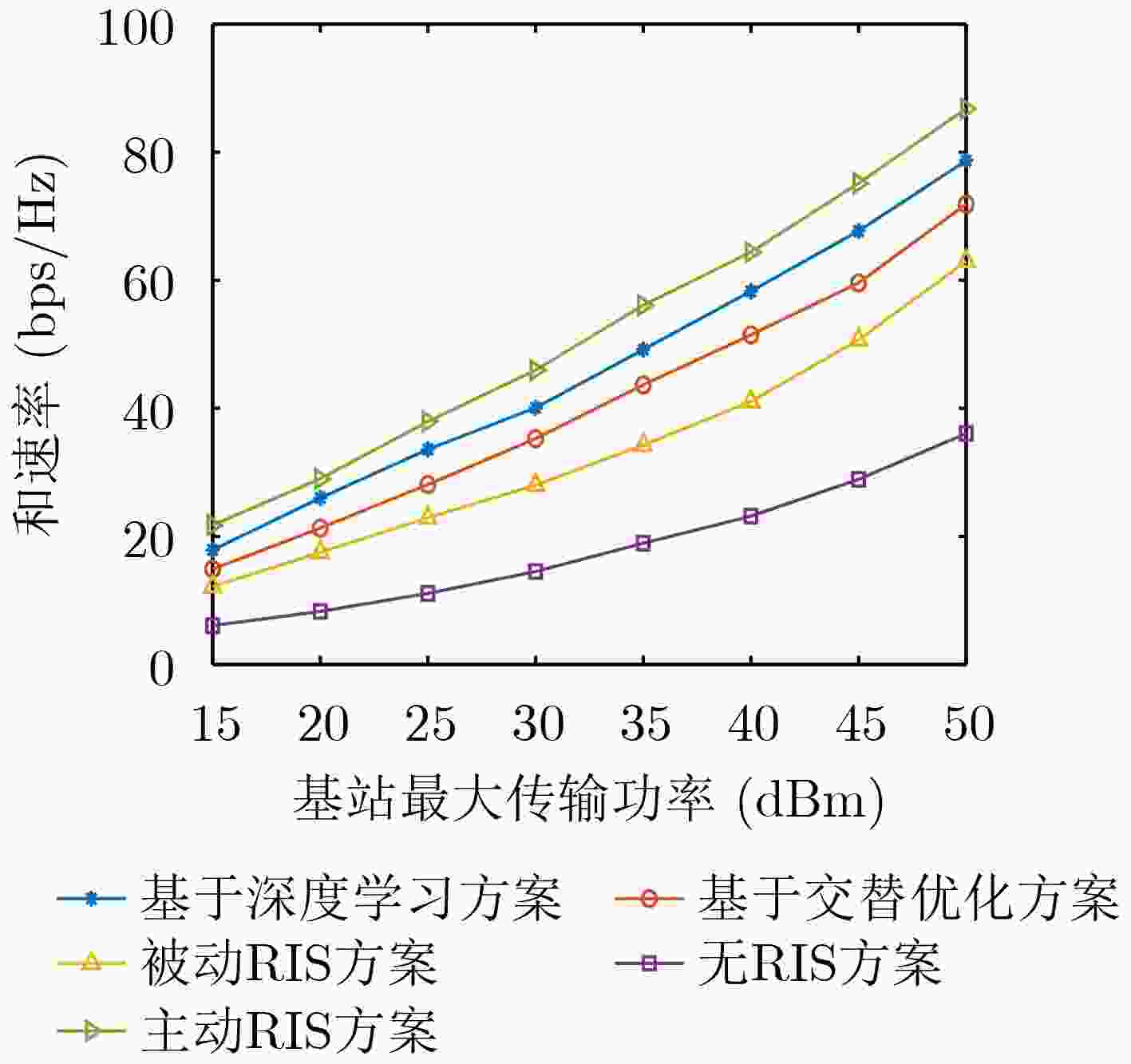
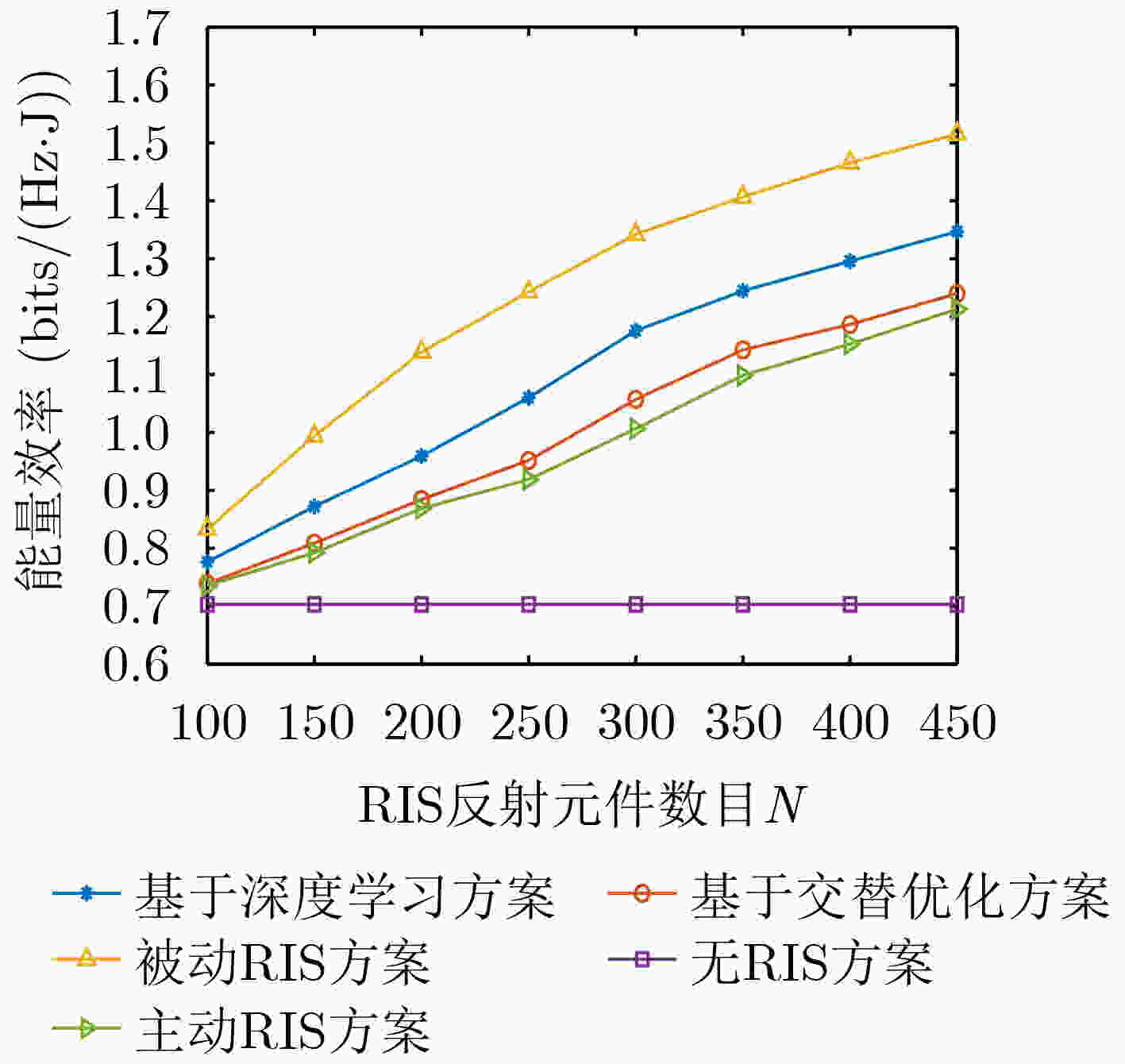
摘要: 能量效率(EE)是5G+/6G无线通信的重要设计指标,而智能反射面(RIS)被普遍认为是改善EE的潜在手段。不同于被动RIS,混合RIS由有源和无源元件组成,对来波移相的同时可放大信号强度,能够有效克服被动RIS引起的“乘性衰落”效应。鉴于此,该文提出一种混合RIS辅助通信感知一体化(ISAC)的下行链路传输系统。为探究数据传输速率与能耗之间的内在关联,该文以RIS辅助ISAC网络能量效率最大化为目标,在满足基站(BS)发射功率、波束图增益以及混合RIS功率和幅值约束的条件下,联合优化基站端的波束赋形和混合RIS的相移。为解决该复杂的分数规划问题,提出基于交替优化(AO)的算法来求解。为克服AO算法中引入辅助变量造成算法复杂度高的难题,利用耦合优化变量的关联,提出一种基于级联深度学习网络的求解算法。仿真结果表明,提出的混合RIS辅助ISAC方案在和速率、能效方面皆优于现有方案,且算法收敛速度快。
-
关键词:
- 通信感知一体化 /
- 能量效率最大化 /
- 混合可重构智能超表面 /
- 联合波束赋形 /
- 级联深度学习
Abstract: Energy Efficiency (EE) is an important design metric for 5G+/6G wireless communications, and Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) is widely recognized as a potential means to improve EE. Unlike passive RIS, hybrid RIS consists of both active and passive components, which can amplify the signal strength while phase-shifting the incoming wave, and can effectively overcome the “multiplicative fading” effect caused by fully passive RIS. In view of this, a hybrid RIS-assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) downlink transmission system is proposed in this paper. In order to investigate the intrinsic correlation between data transmission capacity and energy consumption, the paper jointly optimizes the beamforming and phase-shifting of hybrid RIS at the Base Station (BS) under the constraints of BS transmit power, beampattern gain, and hybrid RIS power and amplitude with the goal of maximizing the global EE in a multiuser network. To solve this complex fractional programming problem, an algorithm based on Alternating Optimization (AO) is proposed to solve it. To overcome the problem of high algorithm complexity caused by the introduction of auxiliary variables in the AO algorithm, a solution algorithm based on a cascaded deep learning network is proposed using the association of coupled optimization variables. Simulation results show that the proposed hybrid RIS-assisted ISAC scheme outperforms existing schemes in terms of sum rate and EE, and the algorithm converges quickly. -
算法1 算法整体流程 初始化:变量$ {b^{(0)}} $、$ {\xi ^{(0)}} $、$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{(0)}} $和$ {{\boldsymbol{\theta }}^{(0)}} $ 迭代次数$ i = 1 $,最大迭代次数$ {I_{\max }} $ (1)While$ {f_i} - {f_{i - 1}} \ge \varepsilon $或$ i \lt {I_{\max }} $do (2)根据式(11)更新拉格朗日对偶重组辅助变量$ {\xi ^{(i)}} $ (3)根据式(13)更新二次变换辅助变量$ {b^{(i)}} $ (4)利用CVX求解凸规划问题$ {{\text{P}}_{{\text{2-1}}}} $,更新优化变量$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{(i)}} $ (5)利用CVX求解凸规划问题$ {{\text{P}}_{{\text{3}}}} $,更新优化变量$ {{\boldsymbol{\varphi}} ^{(i)}} $ (6)更新能量效率$ \eta $,迭代次数$ i = i + 1 $ (7)End While 表 1 部分仿真参数
参数名称 符号 数值 参数名称 符号 数值 BS发射天线数 $M$ 8 用户噪声功率(dBm) $\sigma _0^2$ –80 用户数 $K$ 4 RIS噪声功率(dBm) $\sigma _c^2$ –70 目标数 $L$ 2 Rice因子 $ \rho $ 10 RIS元件总数 $N$ 256 最小波束图增益(dB) $ \varGamma $ 10 RIS主动元件数 $T$ 64 目标方向($ ^\circ $) $ {\theta _1},{\theta _2} $ $ \pm 45 $ RIS最大消耗功率(dBm) ${P_0}$ 10 能量放大系数 ${{a,b}}$ 0.8 RIS有源元件放大系数(dB) $\alpha $ 10 惩罚系数 $ {\beta _1},{\beta _2},{\beta _3} $ 50 -
[1] LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, PETROPULU A P, et al. Joint radar and communication design: Applications, state-of-the-art, and the road ahead[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communi cations, 2020, 68(6): 3834–3862. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2973976. [2] TAN D K P, HE Jia, LI Yanchun, et al. Integrated sensing and communication in 6G: Motivations, use cases, requirements, challenges and future directions[C]. 2021 1st IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications & Sensing (JC&S), Dresden, Germany, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/JCS52304.2021.9376324. [3] FU Min, ZHOU Yong, SHI Yuanming, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface empowered downlink non-orthogonal multiple access[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(6): 3802–3817. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3066 587. [4] XUE Qing, WEI Renlong, MA Shaodan, et al. Multi-user mmWave uplink communications based on collaborative double-RIS: Joint beamforming and power control[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(10): 2702–2706. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3309710. [5] XIE Hao, GU Bowen, LI Dong, et al. Gain without pain: Recycling reflected energy from wireless-powered RIS-aided communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(15): 13264–13280. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3262517. [6] XU Yongjun, GAO Zhengnian, WANG Zhengqiang, et al. RIS-enhanced WPCNs: Joint radio resource allocation and passive beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7980–7991. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3096603. [7] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, WU Qingqing, et al. Robust max-min energy efficiency for RIS-aided HetNets with distortion noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1457–1471. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3141798. [8] MAI Yuying and DU Huiqin. Joint beamforming and phase shift design for RIS-aided ISAC system[C]. 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2022: 155–160. doi: 10.1109/ICCC56324.2022.10065868. [9] LIU Rang, LI Ming, LIU Qian, et al. SNR/CRB-constrained joint beamforming and reflection designs for RIS-ISAC systems[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11134, 2023. [10] XING Zhe, WANG Rui, and YUAN Xiaojun. Joint active and passive beamforming design for reconfigurable intelligent surface enabled integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(4): 2457–2474. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3244 246. [11] WANG Fangzhou, LI Hongbin, and FANG Jun. Joint active and passive beamforming for IRS-assisted radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 349–353. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3134899. [12] WANG Xinyi, FEI Zesong, HUANG Jingxuan, et al. Joint waveform and discrete phase shift design for RIS-assisted integrated sensing and communication system under Cramer-Rao bound constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(1): 1004–1009. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3122889. [13] LIU Chenxi, HU Xiaoling, PENG Mugen, et al. Sensing for beamforming: An IRS-enabled integrated sensing and communication framework[C]. 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022: 5567–5572. doi: 10.1109/ICC45855.2022.9838505. [14] LYU Wanting, XIU Yue, YANG Songjie, et al. Energy-efficient cell-free network assisted by hybrid RISs[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(4): 718–722. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3241644. [15] NGUYEN N T, VU Q D, LEE K, et al. Hybrid relay-reflecting intelligent surface-assisted wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(6): 6228–6244. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3158686. [16] SANKAR R S P and CHEPURI S P. Beamforming in hybrid RIS assisted integrated sensing and communication systems[C]. 2022 30th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Belgrade, Serbia, 2022: 1082–1086. doi: 10.23919/EUSIPCO55093.2022.9909562. [17] HE Zhenyao, XU Wei, SHEN Hong, et al. Energy efficient beamforming optimization for integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(7): 1374–1378. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3169517. [18] ZHOU Chunyu, XU Yongjun, LI Dong, et al. Energy-efficient maximization for RIS-aided MISO symbiotic radio systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(10): 13689–13694. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3274796. [19] LIU Xiang, HUANG Tianyao, SHLEZINGER N, et al. Joint transmit beamforming for multiuser MIMO communications and MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3929–3944. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3004739. [20] MU Gaoze, ZHAO Yusen, ZHONG Shida, et al. An element selection enhanced hybrid relay-RIS assisted communication system[C]. 2022 5th International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP), Shenzhen, China, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICICSP55539.2022.10050590. [21] NGUYEN N T, NGUYEN V D, WU Qingqing, et al. Hybrid active-passive reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted UAV communications[C]. 2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2022: 3126–3131. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM48099.2022.10001719. [22] ZHANG Zijian, DAI Linglong, CHEN Xibi, et al. Active RIS vs. Passive RIS: Which will prevail in 6G?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(3): 1707–1725. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3231893. [23] SHEN Kaiming and YU Wei. Fractional programming for communication systems—Part I: Power control and beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(10): 2616–2630. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2812733. [24] GUO Huayan, LIANG Yingchang, CHEN Jie, et al. Weighted sum-rate maximization for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(5): 3064–3076. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2970061. -






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
