SAR Pulsed Direct Wave Interference Suppression Method Using Improved Eigen-Subspace Projection
-
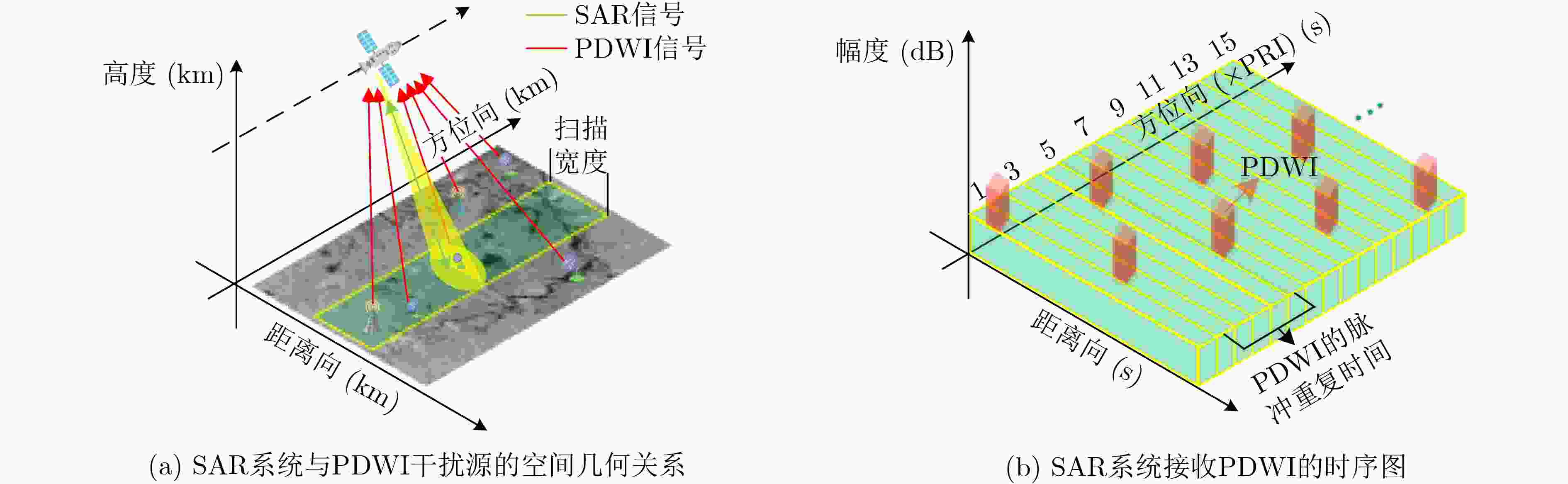
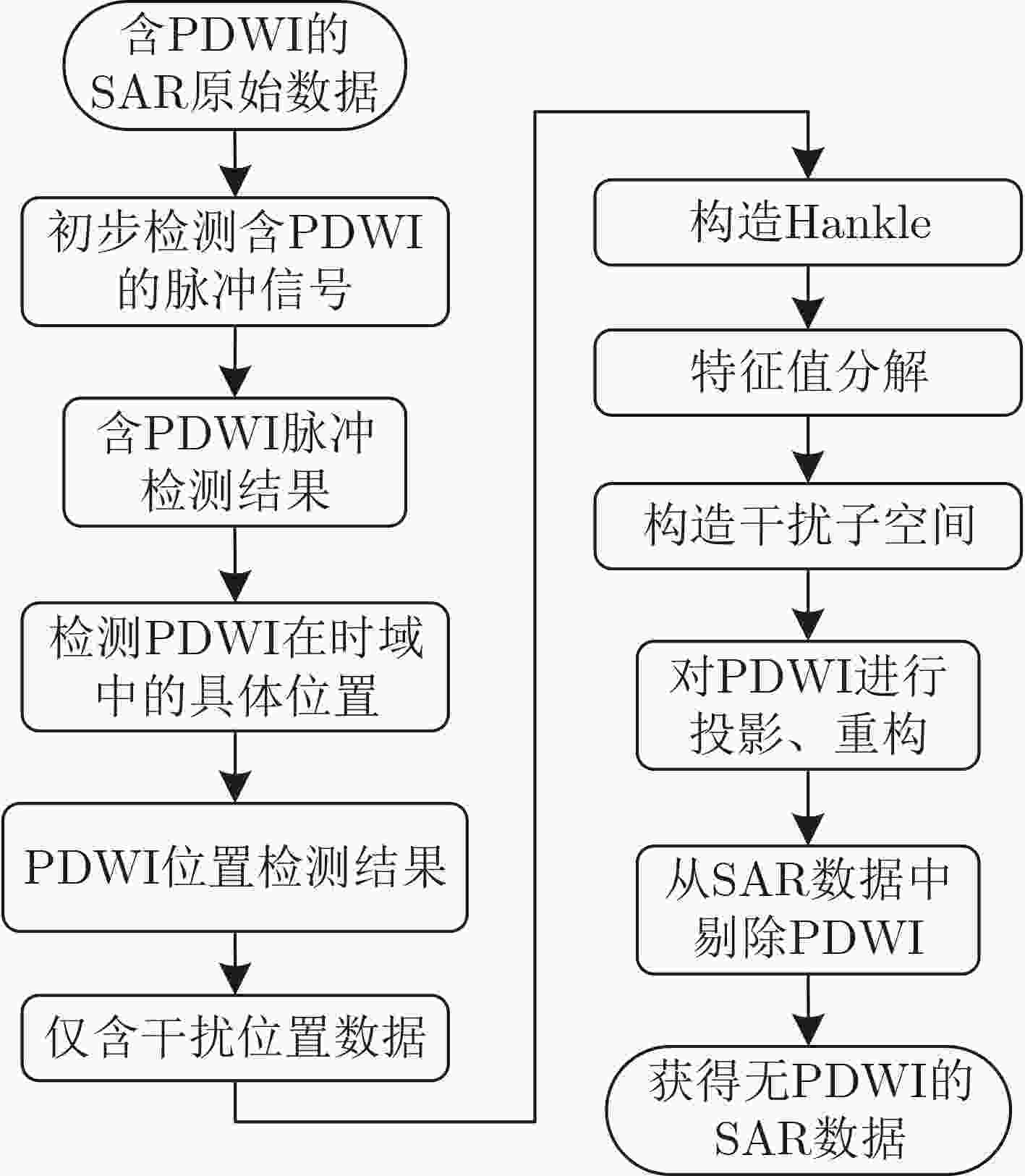
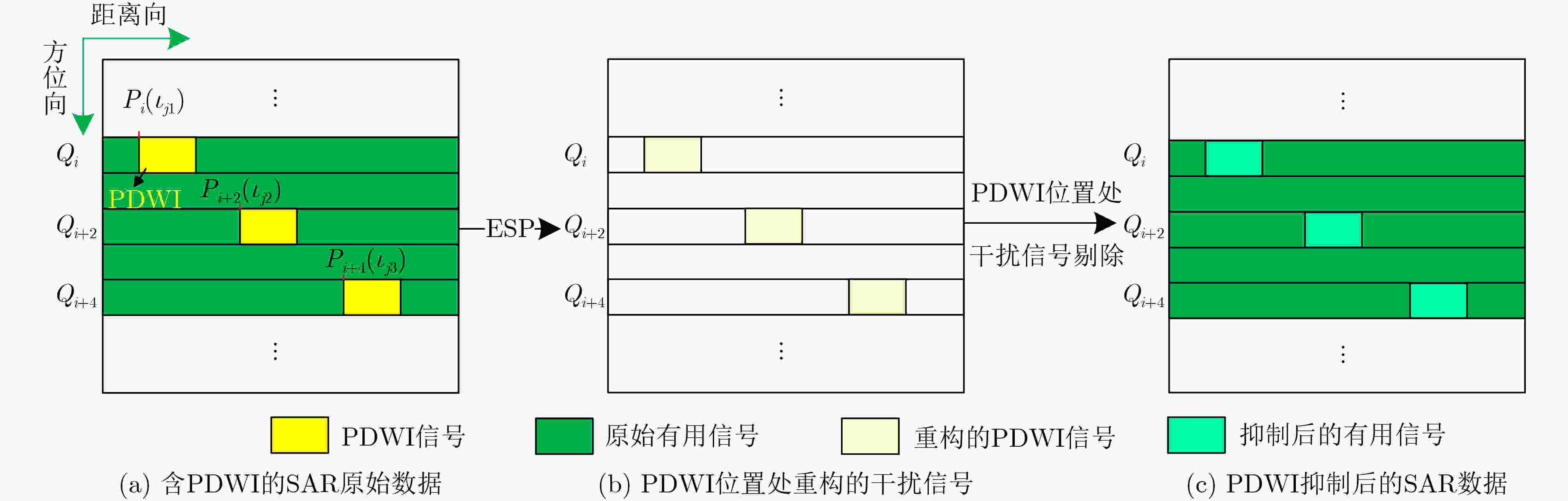
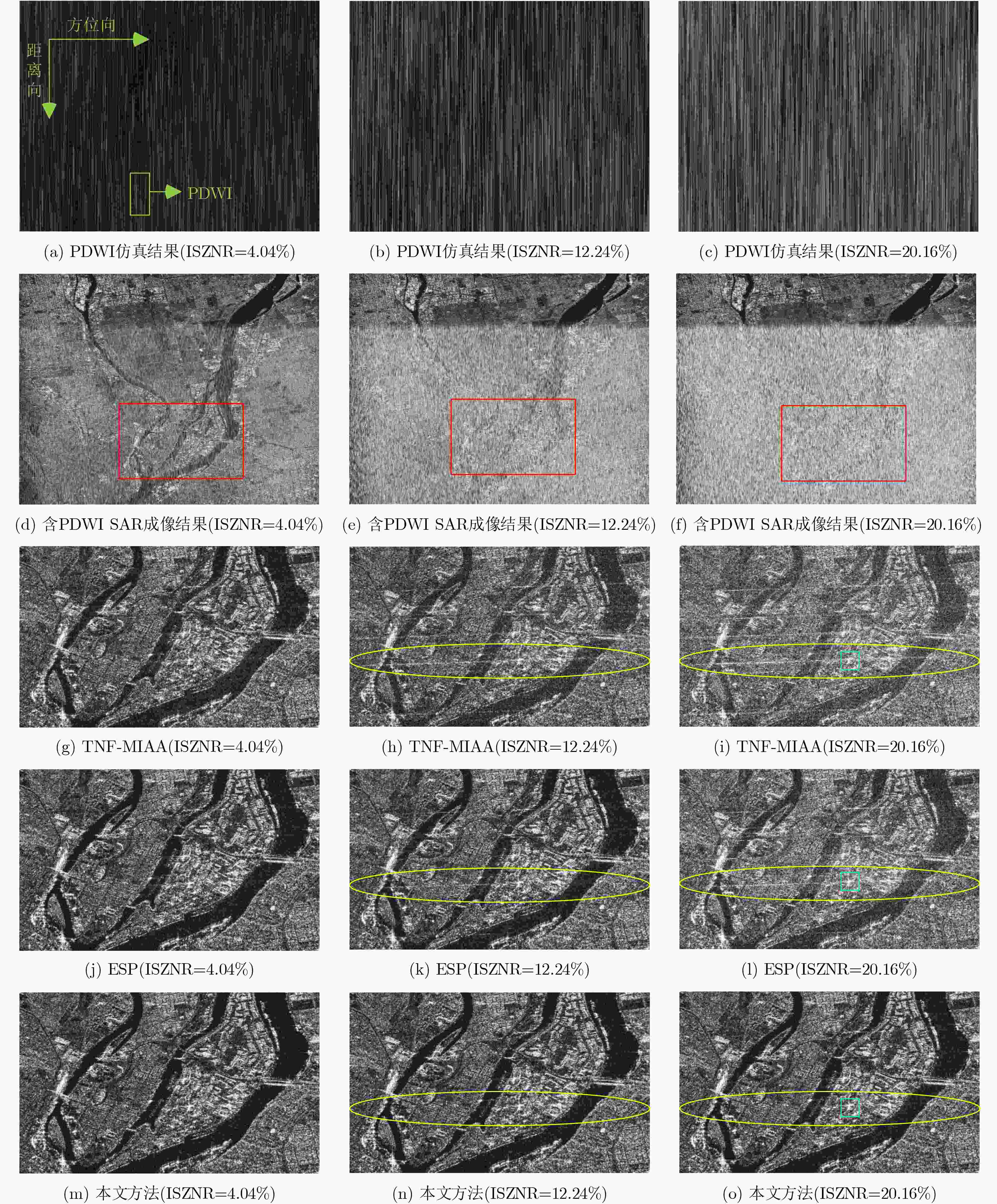
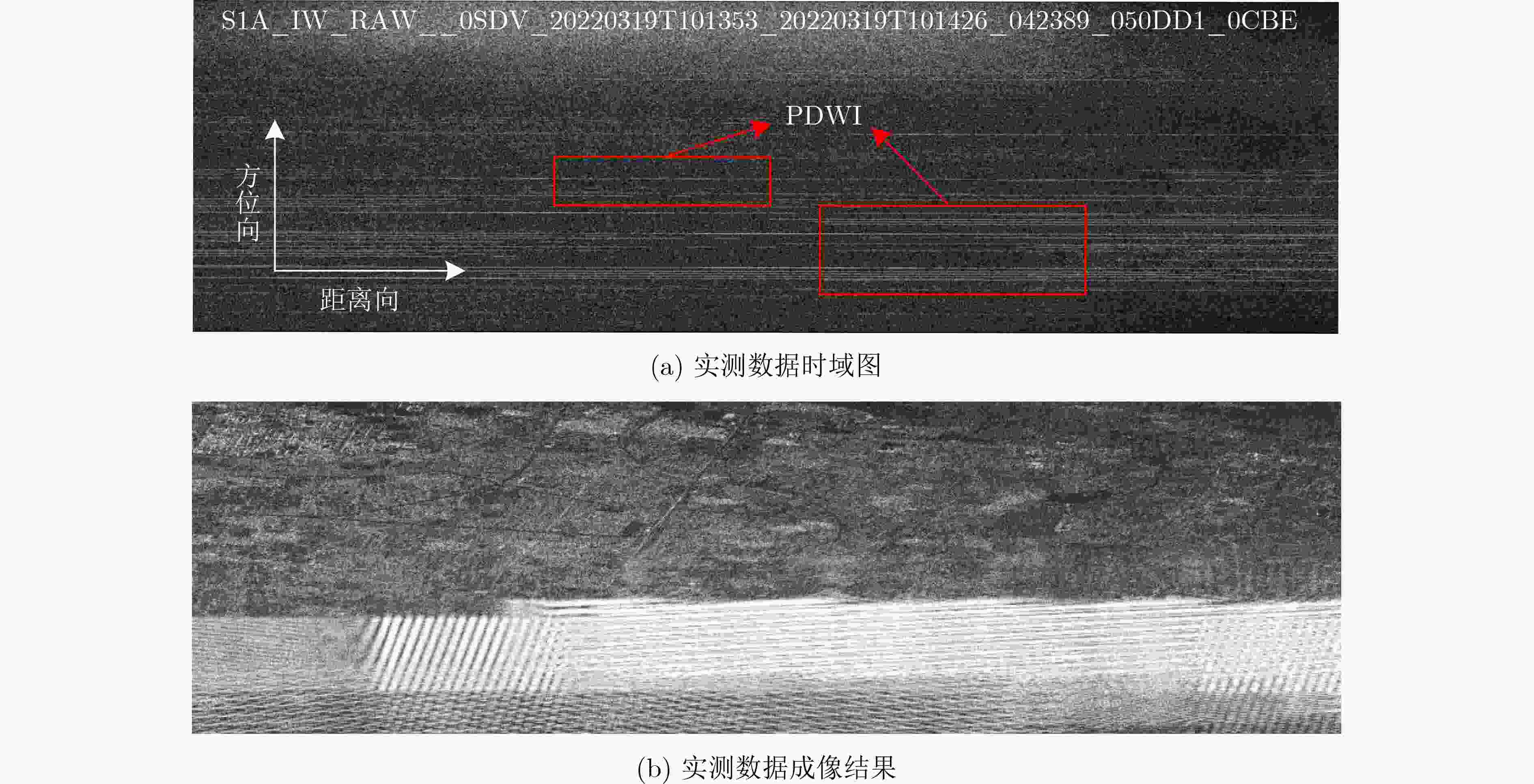
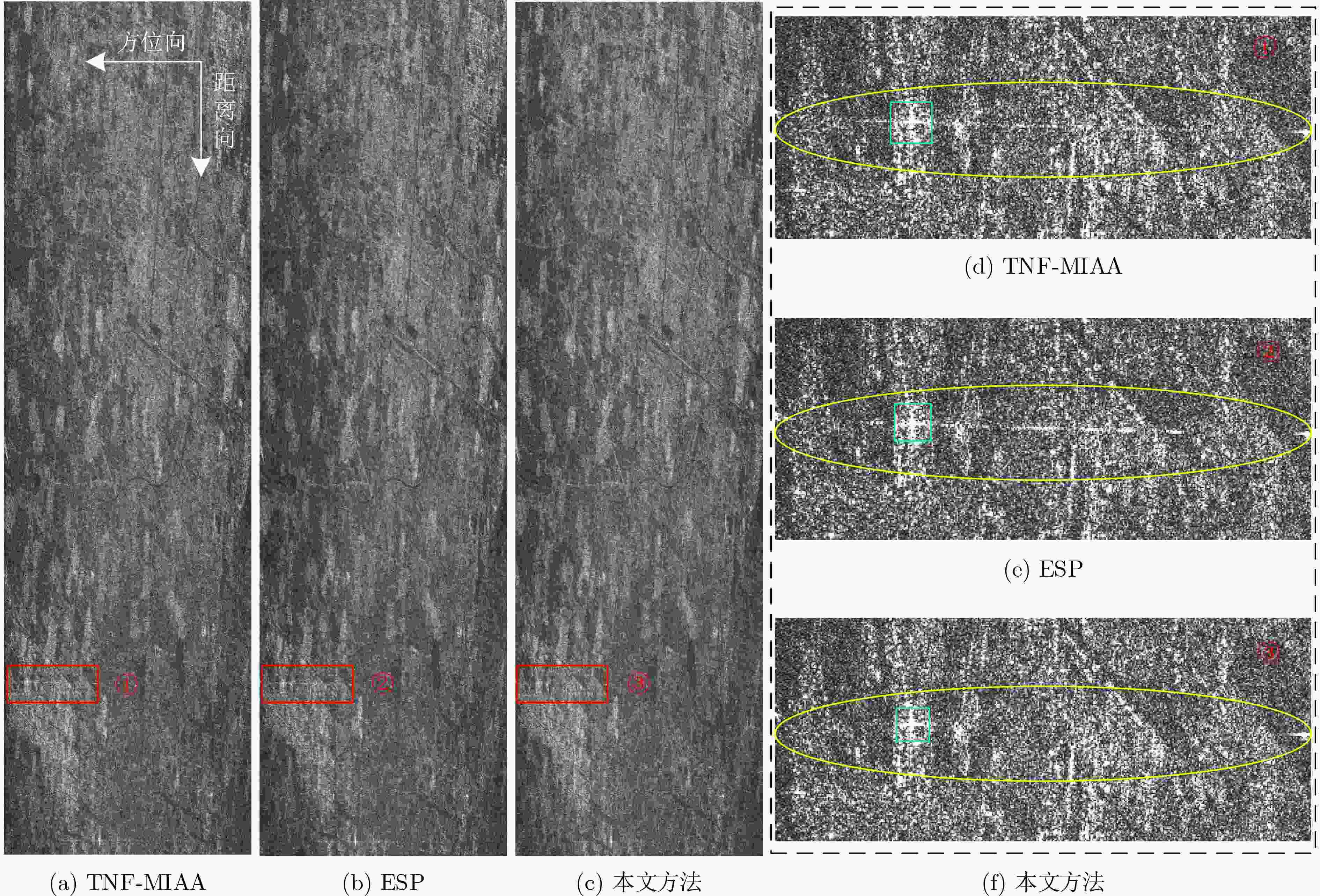
摘要: 射频干扰(RFI)会污染合成孔径雷达(SAR)回波信号,增加SAR图像解译难度。脉冲式直达波干扰(PDWI)作为典型的RFI,在原始回波域以明亮条纹状掩盖SAR回波信息,对SAR成像质量产生严重影响。现有的干扰抑制方法中,传统的特征子空间投影(ESP)方法对整条含干扰脉冲进行干扰抑制,造成了脉冲中非干扰位置有用信号损失。为了保护有用信号,该文提出一种改进ESP的SAR脉冲式直达波干扰抑制方法。首先,通过两次检测干扰,获取PDWI在时域中的具体位置。其次,仅对检测的干扰位置数据,采用ESP将有用信号和干扰信号分离。最后,从原始数据中减去ESP重构的干扰数据以实现干扰抑制。仿真和实测数据处理表明,与现有方法相比,该方法能够有效避免SAR原始数据中有用信号的损失,抑制了脉冲式直达波干扰。Abstract: Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) will pollute the echo signal of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and increase the difficulty of SAR image interpretation. Pulsed Direct Wave Interference (PDWI), as a typical RFI, covers SAR echo information with bright fringes in the original echo domain, which has a serious impact on SAR imaging quality. Among the existing interference suppression methods, the traditional Eigen Subspace Projection (ESP) method suppresses the whole pulse containing interference, which leads to the loss of useful signals in the non-interference positions in the pulse. In order to protect useful signals, an improved ESP SAR pulsed direct wave interference suppression method is proposed. Firstly, the specific position of PDWI in the time domain is obtained by twice detecting interference. Secondly, ESP operation is used to separate the useful signal from the interference signal only for the detected interference position data. Finally, the interference data of ESP reconstruction is subtracted from the original data to achieve interference suppression. Simulation and measured data processing show that, compared with the existing methods, this method can effectively avoid the loss of useful signals in SAR raw data and suppress the pulsed direct wave interference.
-
表 1 SAR系统与PDWI仿真参数
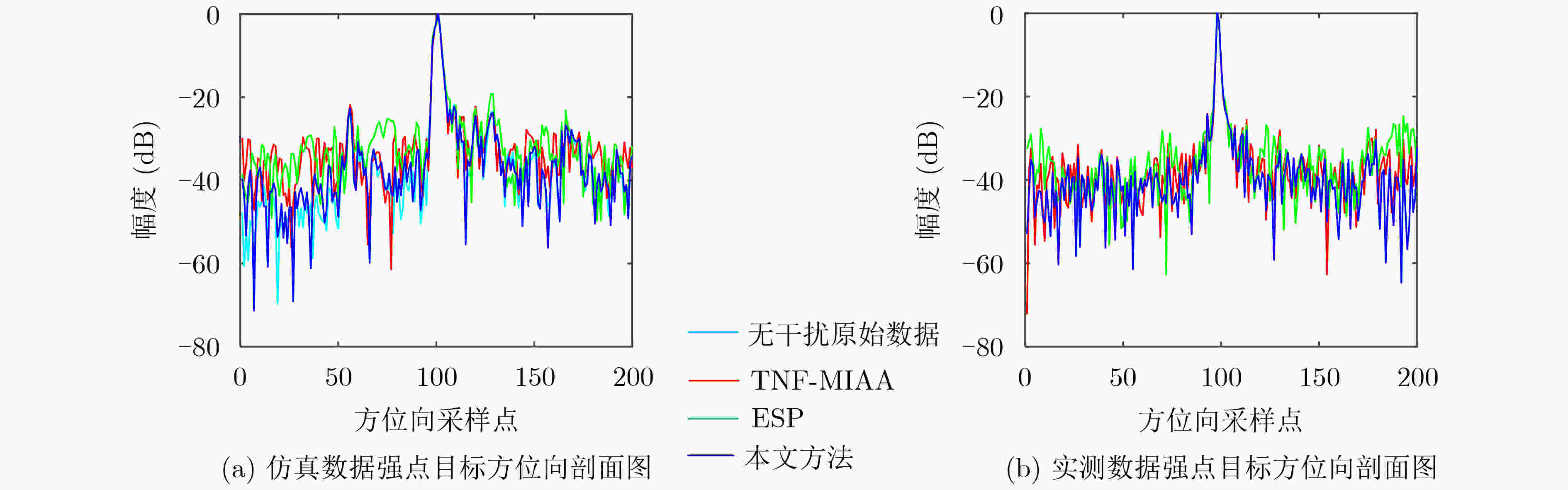
参数 值 距离向采样频率 32.317 MHz 脉冲重复频率 1256.981 Hz 景中心斜距 988647 m 载频 5.400 GHz 脉宽 41.74 μs 发射信号带宽 30 MHz 平台等效速度 6955 m/s PDWI载频 5.405 GHz PDWI带宽 5 MHz 表 2 仿真数据下3种干扰抑制方法的评估指标(无干扰原始数据积分旁瓣比=–15.0222 dB)
方法 均方根误差
(ISZNR = 4.04%)均方根误差
(ISZNR = 12.24%)均方根误差
(ISZNR = 20.16%)TNF-MIAA 0.2975 0.4723 0.5904 ESP 0.3224 0.4463 0.4591 本文方法 0.2246 0.3156 0.3699 表 3 实测数据下3种干扰抑制方法的评估指标(原始数据:灰度熵=10.416 6;平均梯度=69 707)
方法 灰度熵 平均梯度 积分旁瓣比在(dB) TNF-MIAA 8.6836 5 5105 –15.1990 ESP 8.6681 4 9650 –13.6327 本文方法 8.6846 5 5201 –17.4983 -
[1] LIU Zhiling, LIAO Guisheng, and YANG Zhiwei. Time variant RFI suppression for SAR using iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1424–1428. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2259575. [2] HAN Wenchang, BAI Xueru, FAN Weiwei, et al. Wideband interference suppression for SAR via instantaneous frequency estimation and regularized time-frequency filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5208612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3098783. [3] XU Wei, XING Weida, FANG Chonghua, et al. RFI suppression based on linear prediction in synthetic aperture radar data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(12): 2127–2131. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3015205. [4] 周峰, 邢孟道, 保铮. 基于特征子空间滤波的SAR窄带干扰抑制方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2005, 27(5): 767–770.ZHOU Feng, XING Mengdao, and BAO Zheng. Narrow band interference suppression for SAR using eigen-subspace based filtering[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2005, 27(5): 767–770. [5] ZHOU Feng, TAO Mingliang, BAI Xuerui, et al. Narrow-band interference suppression for SAR based on independent component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(10): 4952–4960. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2244605. [6] ZHOU Feng, XING Mengdao, BAI Xuerui, et al. Narrow-band interference suppression for SAR based on complex empirical mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 423–427. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2015340. [7] ZHANG Hui, HUANG Yan, LI Jie, et al. Time-varying RFI mitigation for SAR systems via graph Laplacian clustering techniques[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 1,19: 4010805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3062828. [8] ZHANG Hengrui, MIN Lin, LU Jing, et al. An improved RFI mitigation approach for SAR based on low-rank sparse decomposition: From the perspective of useful signal protection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(14): 3278. doi: 10.3390/rs14143278. [9] LI Ning, LV Zongsen, ZHAO Jianhui, et al. Time-domain notch filtering method for pulse RFI mitigation in synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4013805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3077247. [10] LI Ning, LV Zongsen, and GUO Zhengwei. Pulse RFI mitigation in synthetic aperture radar data via a three-step approach: Location, notch, and recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5225617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3161368. [11] LV Zongsen, FAN Huaitao, CHEN Zhen, et al. Mitigate the LFM-PRFI in SAR data: Joint down-range and cross-range filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5205918. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3265774. [12] 周春晖, 李飞, 李宁, 等. 改进的基于特征子空间的SAR图像射频干扰抑制算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 235–243. doi: 10.12000/JR17025.ZHOU Chunhui, LI Fei, LI Ning, et al. Modified eigensubspace-based approach for radio-frequency interference suppression of SAR image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 235–243. doi: 10.12000/JR17025. [13] HARTIGAN J A and WONG M A. A K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1979, 28(1): 100–108. doi: 10.2307/2346830. [14] LI Ning, LV Zongsen, and GUO Zhengwei. Observation and mitigation of mutual RFI between SAR satellites: A case study between Chinese GaoFen-3 and European Sentinel-1A[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5112819. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3170363. [15] HUANG Yan, ZHANG Lei, LI Jie, et al. A novel tensor technique for simultaneous narrowband and wideband interference suppression on single-channel SAR system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 9575–9588. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2927764. [16] CUI Guangmang, FENG Huajun, XU Zhihai, et al. Detail preserved fusion of visible and infrared images using regional saliency extraction and multi-scale image decomposition[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 341: 199–209. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.12.032. [17] SU Jia, TAO Haihong, TAO Mingliang, et al. Time-varying SAR interference suppression based on delay-Doppler iterative decomposition algorithm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(9): 1491. doi: 10.3390/rs10091491. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
