Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Multi-scale Asymmetric Dense Network
-
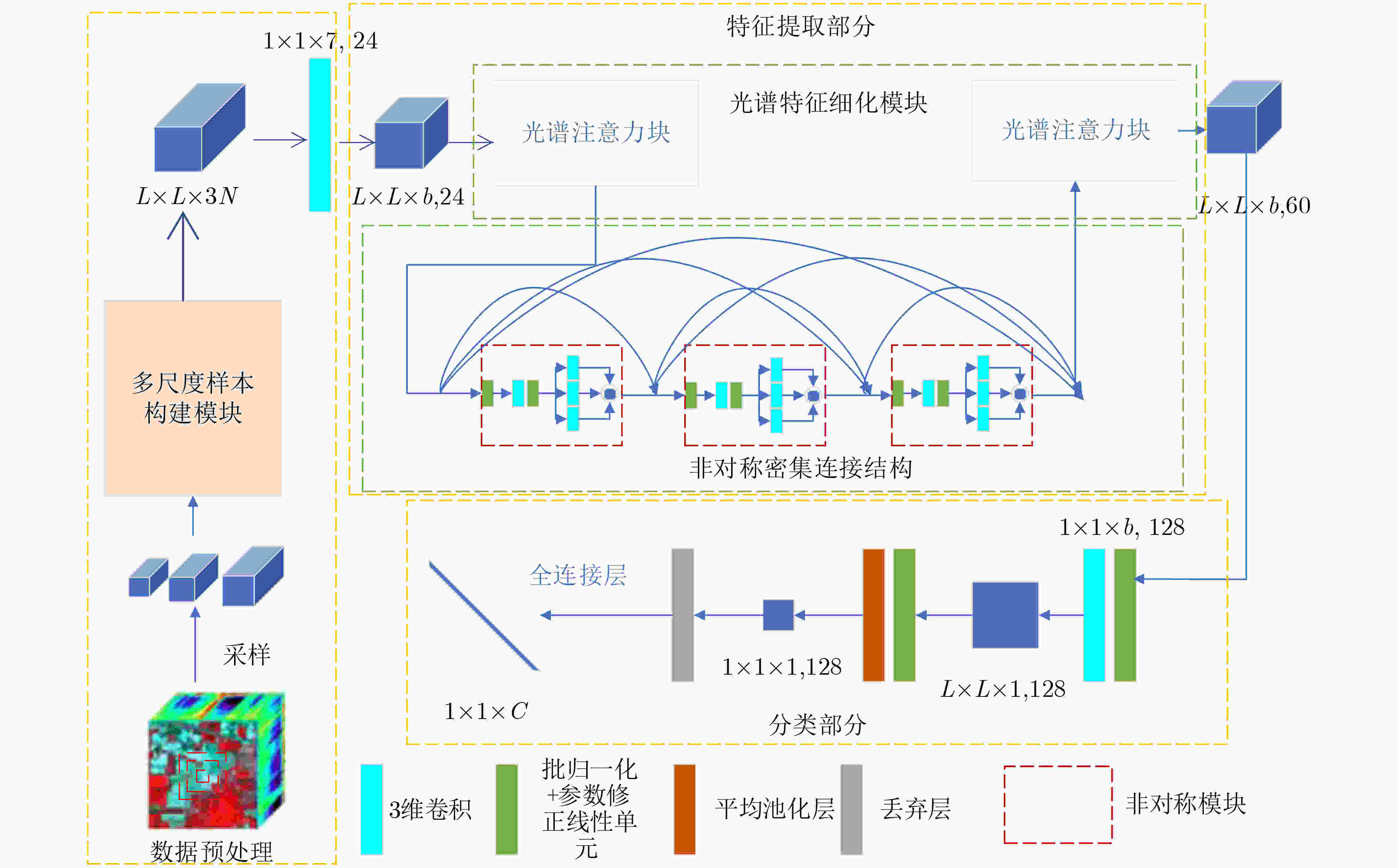
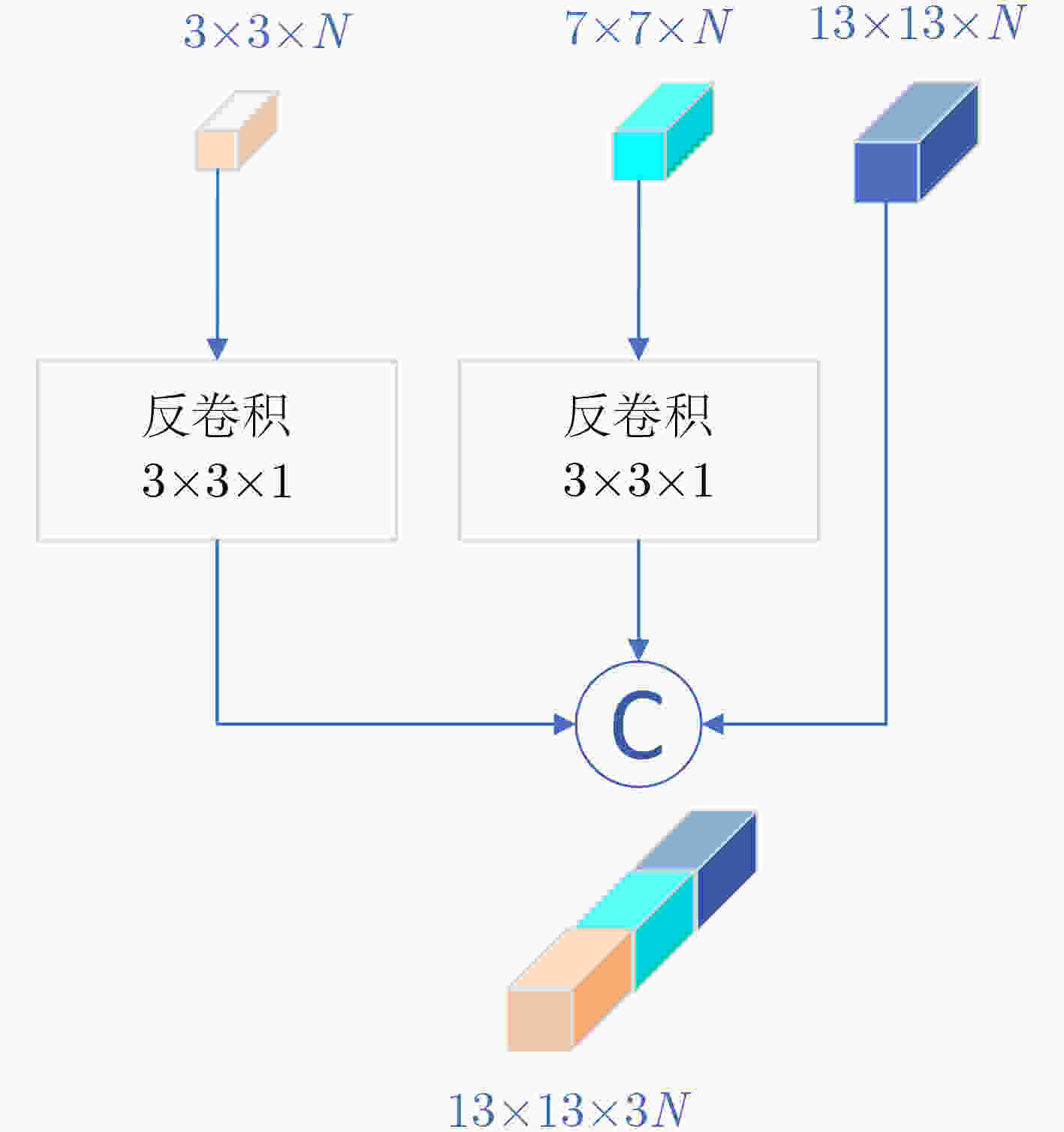
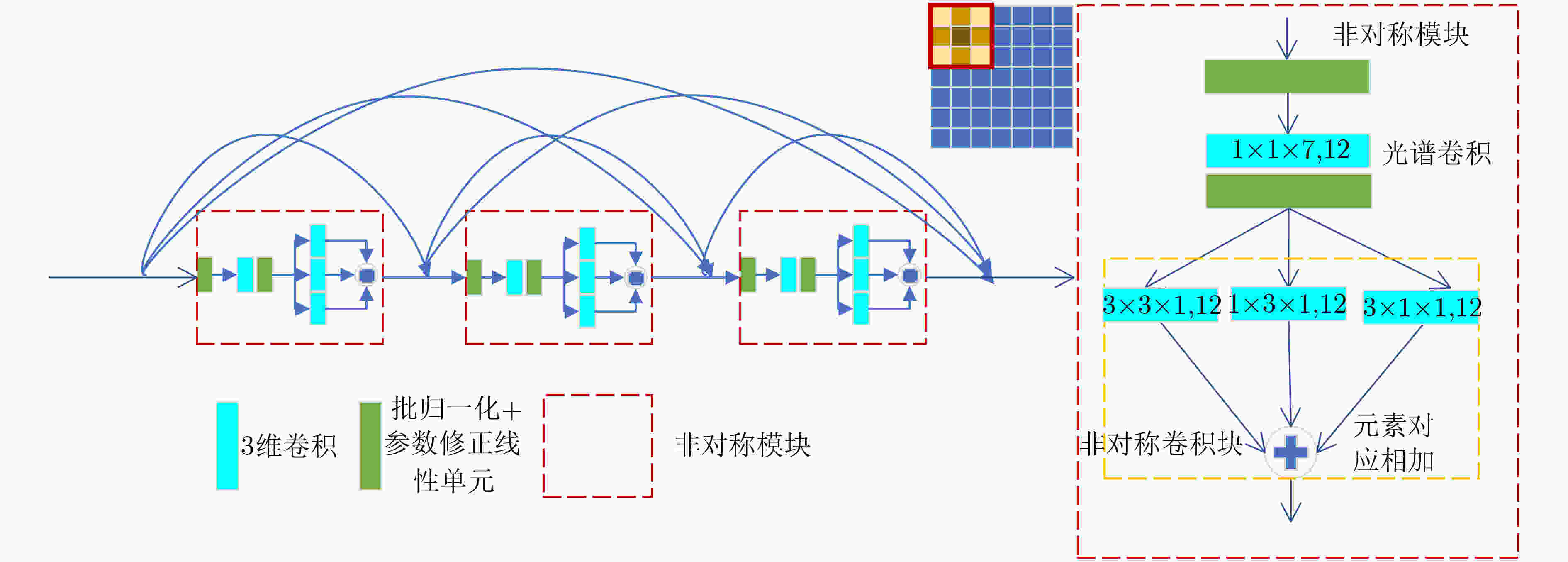
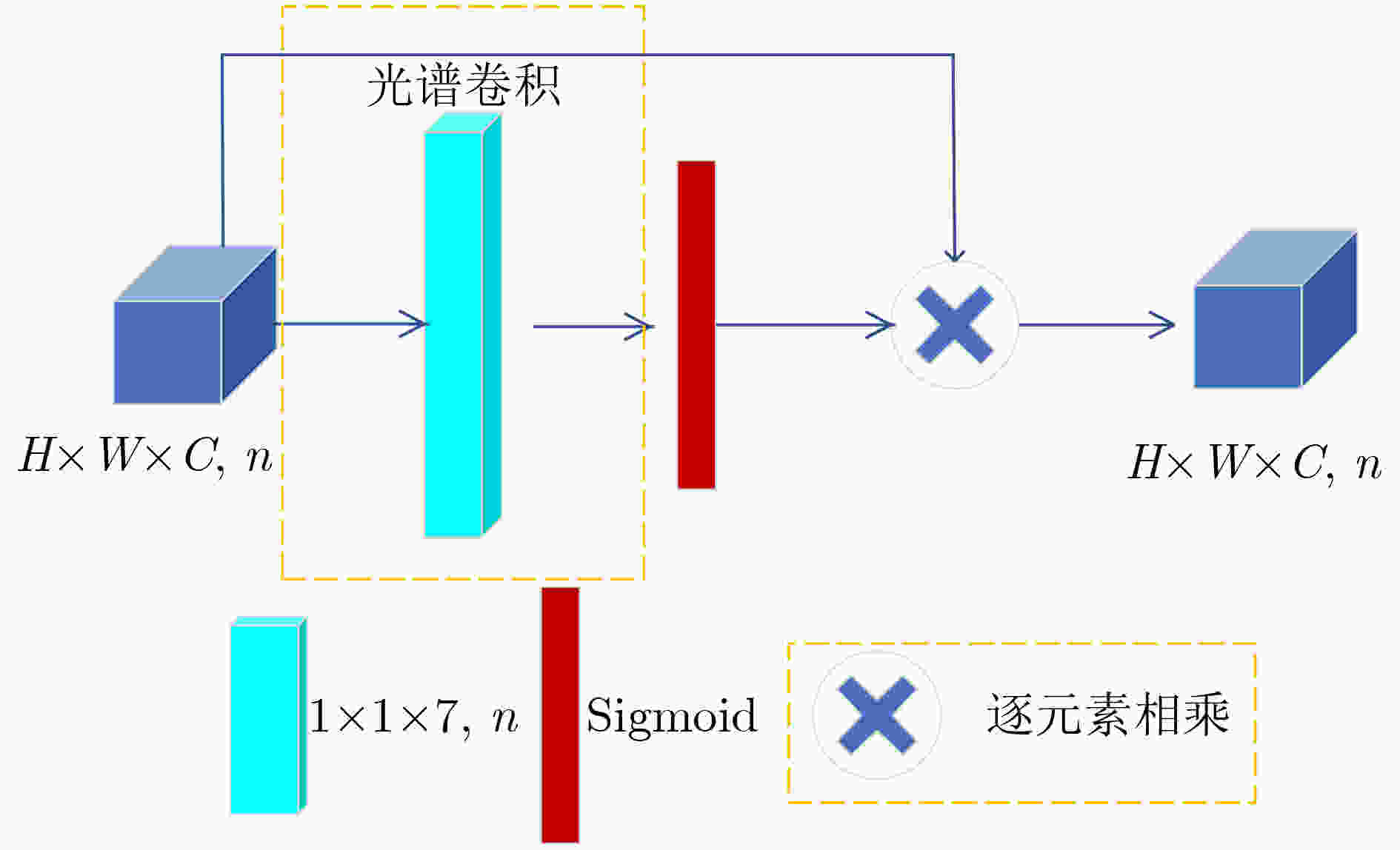
摘要: 近年来,基于有限标记样本的高光谱图像(HSI)分类方法取得了重大进展。然而,由于高光谱图像的特殊性,冗余的信息和有限的标记样本给提取强判别特征带来了巨大挑战。此外,由于各类别像素分布不均,如何强化中心像素的作用,减弱不同类别的周围像素的负面影响也是提高分类性能的关键。为了克服上述局限性,该文提出一种基于多尺度非对称密集网络(MS-ADNet)的高光谱图像分类方法。首先,提出一个多尺度样本构建模块,通过在每个像素周围提取多个尺度的图像块,并进行反卷积和拼接以构建输入样本,使其既包含详细的结构区域,又包含较大的同质区域;然后,提出一个非对称密集连接结构,在空间和光谱特征联合提取中实现核骨架增强,即增强了方形卷积核的中心十字区域部分提取的特征,有效地促进了特征重用。此外,为了提高光谱特征的鉴别性,提出一种精简的元素光谱注意力机制,并将其置于密集连接网络的前端和后端。在每类仅采用5个样本进行网络训练的情况下,该方法在Indiana Pines, Pavia University和Salinas数据集上的总体准确率分别达到了77.66%, 84.54%和92.39%,取得了极具竞争力的分类结果。Abstract: HyperSpectral Image (HSI) classification methods based on limited labeled samples have made significant progress in recent years. However, due to the specificity of hyperspectral images, redundant information and limited labeled samples pose great challenges for extracting highly discriminative features. In addition, owing to the uneven distribution of pixels in each category, how to strengthen the role of central pixels and attenuate the negative impact of surrounding pixels with different categories is also the key to improve the classification performance. To overcome the above limitations, an HSI classification method based on Multi-Scale Asymmetric Dense Network (MS-ADNet) is proposed. Firstly, a multi-scale sample construction module is proposed, which extracts multiple scale patches around each pixel and performs deconvolution and stitching to construct multiscale input samples that contain both detailed structural regions and large homogeneous regions. Next, an asymmetric densely connected structure is proposed to achieve kernel skeleton enhancement in joint spatial and spectral feature extraction, i.e., enhancement of features extracted from the central cross-skeleton portion of a square convolutional kernel, which effectively facilitates feature reuse. Moreover, to improve the discriminability of spectral features, a streamlined element spectral attention mechanism is proposed and placed at the front and back ends of the densely connected network. With only five samples per class used for network training, the proposed method achieves competitive classification results with overall accuracies of 77.66%, 84.54%, and 92.39% on the Indiana Pines, Pavia University, and Salinas datasets, respectively.
-
表 1 UP数据集上的分类结果对比(%)
类别 3D-CNN FDSSC DFSL+SVM DMVL DCFSL MS-ADNet 1 59.82 92.03 73.43 62.69 82.20 97.04 2 63.05 96.44 89.25 96.00 87.74 98.19 3 68.91 59.30 48.09 84.26 67.46 69.77 4 77.31 67.75 84.72 36.70 93.16 93.49 5 90.77 96.82 99.65 86.22 99.49 98.56 6 63.40 77.88 67.81 90.86 77.32 61.08 7 87.64 69.53 64.48 82.11 81.18 79.13 8 57.27 73.36 67.37 79.10 66.73 74.91 9 95.57 92.18 92.92 22.56 98.66 98.75 OA 65.74±1.77 81.10±6.93 79.63±1.09 73.81±5.40 83.65±1.77 84.54±0.05 AA 73.72±1.01 80.59±5.31 76.41±1.39 71.17±3.20 83.77±1.74 85.65±0.03 Kappa 57.37±1.97 76.07±8.48 73.05±1.60 66.87±6.16 78.70±2.01 80.46±0.06 表 2 SA数据集上的分类结果对比(%)
类别 3D-CNN FDSSC DFSL+SVM DMVL DCFSL MS-ADNet 1 95.29 98.16 73.92 97.06 99.40 100 2 97.20 99.01 96.85 97.83 99.76 100 3 91.45 95.59 96.28 97.79 91.96 95.45 4 97.31 95.94 99.11 54.39 99.55 95.76 5 91.24 94.56 80.72 87.34 92.70 99.62 6 98.80 99.56 91.63 90.83 99.52 99.98 7 99.69 99.23 97.73 94.95 98.88 98.89 8 66.40 81.45 82.33 93.35 74.57 90.43 9 96.25 99.29 94.44 98.27 99.59 99.30 10 70.72 94.77 80.96 97.36 86.42 95.42 11 93.15 94.79 93.38 76.91 96.61 95.63 12 99.65 99.32 97.94 96.06 99.93 98.70 13 92.63 96.53 95.79 76.24 99.30 96.64 14 93.56 85.97 98.87 71.96 98.85 91.10 15 68.02 65.34 71.13 82.53 75.38 73.04 16 81.41 99.87 90.57 100.0 92.22 99.84 OA 84.20±2.62 88.62±4.03 86.95±1.30 89.16±1.63 89.34±2.19 92.39±0.03 AA 89.56±1.79 93.71±1.82 90.08±1.44 88.30±1.42 94.04±1.14 95.61±0.01 Kappa 82.46±2.90 87.37±4.44 85.51±1.42 87.98±1.79 88.17±2.40 91.56±0.03 表 3 IN数据集上的分类结果对比(%)
类别 3D-CNN FDSSC DFSL+SVM DMVL DCFSL MS-ADNet 1 95.12 67.79 96.75 24.33 95.37 77.38 2 37.70 71.03 36.38 72.38 43.26 81.35 3 19.77 63.69 38.34 66.77 57.95 65.49 4 32.51 63.70 77.16 63.73 80.60 57.33 5 88.45 86.87 73.92 74.91 72.91 89.73 6 73.65 95.08 86.25 66.49 87.96 98.03 7 81.82 32.92 97.10 29.79 99.57 43.75 8 53.35 99.31 81.82 86.39 86.26 99.60 9 100.0 17.24 75.56 13.74 99.33 53.62 10 41.35 53.21 52.22 77.67 62.44 61.22 11 66.71 86.98 59.96 86.68 62.75 84.58 12 37.40 69.73 36.56 83.26 48.72 67.83 13 85.71 72.71 98.00 47.00 99.35 95.43 14 62.57 93.49 84.63 91.16 85.40 97.01 15 56.42 68.57 74.10 66.41 66.69 78. 03 16 90.36 53.84 100.0 31.11 97.61 83.27 OA 54.76±0.03 72.49±4.12 61.69±1.85 70.26±4.86 66.81±2.37 77.66±0.06 AA 63.93±0.02 68.51±3.05 73.05±0.84 61.36±3.00 77.89±0.86 77.10±0.04 Kappa 48.72±0.03 69.38±4.42 56.78±1.90 66.92±5.16 62.64±0.86 74.89±0.07 表 4 网络参数量和训练时间对比
方法 IN SA UP 参数量(M) 训练时间(min) 参数量(M) 训练时间(min) 参数量(M) 训练时间(min) 3D-CNN 0.096 1.039 0.098 1.051 0.048 0.898 FDSSC 1.230 0.990 1.250 1.180 0.640 0.260 DFSL+SVM 0.033 7.922 0.033 8.084 0.033 10.848 DMVL 24.620 141.200 24.620 243.100 24.620 197.700 DCFSL 4.070 20.920 4.070 21.120 4.060 20.670 MS-ADNet 2.330 18.430 2.380 18.890 1.210 5.090 表 5 TeaFarm数据集上的分类结果对比(%)
类别 FDSSC DMVL DCFSL MS-ADNet 1 91.60 92.28 92.64 95.59 2 53.18 81.00 74.79 62.51 3 99.34 96.98 88.30 99.63 4 86.99 42.30 100 91.90 5 97.75 91.22 98.68 98.88 6 47.48 24.24 89.63 91.83 7 82.53 25.37 99.06 77.94 8 51.92 36.23 60.59 57.71 9 100 99.46 98.83 99.99 10 75.05 46.01 100 94.83 OA 86.45±0.07 82.38±3.80 90.47±1.09 91.82±0.01 AA 78.58±0.06 63.51±3.53 90.25±0.77 87.08±0.03 Kappa 81.83±0.09 75.47±4.63 86.51±1.32 88.40±0.02 -
[1] YAO Ding, ZHANG Zhili, ZHAO Xiaofeng, et al. Deep hybrid: Multi-graph neural network collaboration for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 23: 164–176. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.02.007. [2] WANG Xue, TAN Kun, DU Peijun, et al. A unified multiscale learning framework for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4508319. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2022.3147198. [3] CHEN Yushi, JIANG Hanlu, LI Chunyang, et al. Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6232–6251. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2584107. [4] LI Ying, ZHANG Haokui, and SHEN Qiang. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery with 3D convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(1): 67. doi: 10.3390/rs9010067. [5] 刘娜, 李伟, 陶然. 图信号处理在高光谱图像处理领域的典型应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(5): 1529–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220887.LIU Na, LI Wei, and TAO Ran. Typical Application of graph signal processing in hyperspectral image processing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1529–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220887. [6] SHAHRAKI F F and PRASAD S. Graph convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral data classification[C]. 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Anaheim, USA, 2018: 968–972. doi: 10.1109/GlobalSIP.2018.8645969. [7] ZHU Lin, CHEN Yushi, GHAMISI P, et al. Generative adversarial networks for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5046–5063. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2805286. [8] MOU Lichao, GHAMISI P, and ZHU Xiaoxiang. Deep recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3639–3655. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2636241. [9] ZHU Kaiqiang, CHEN Yushi, GHAMISI P, et al. Deep convolutional capsule network for hyperspectral image spectral and spectral-spatial classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 223. doi: 10.3390/rs11030223. [10] ZHONG Zilong, LI J, LUO Zhiming, et al. Spectral-spatial residual network for hyperspectral image classification: A 3-D deep learning framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 847–858. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2755542. [11] WANG Wenju, DOU Shuguang, JIANG Zhongmin, et al. A fast dense spectral-spatial convolution network framework for hyperspectral images classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): 1068. doi: 10.3390/rs10071068. [12] CAI Yiheng, GUO Yajun, LANG Shinan, et al. Classification of hyperspectral images by spectral-spatial dense-residual network[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2020, 14(3): 036513. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.14.036513. [13] FANG Bei, LI Ying, ZHANG Haokui, et al. Hyperspectral images classification based on dense convolutional networks with spectral-wise attention mechanism[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(2): 159. doi: 10.3390/rs11020159. [14] YAN Huaiping, WANG Jun, TANG Lei, et al. A 3D cascaded spectral-spatial element attention network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(13): 2451. doi: 10.3390/rs13132451. [15] PAN Jianjun, CAI Yiheng, TAN Meiling, et al. Multiscale residual weakly dense network with attention mechanism for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2022, 16(3): 034504. doi: 10.1117/1.Jrs.16.034504. [16] ZHU Minghao, JIAO Licheng, LIU Fang, et al. Residual spectral-spatial attention network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 449–462. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2994057. [17] SUN Le, ZHAO Guangrui, ZHENG Yuhui, et al. Spectral-spatial feature tokenization transformer for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5522214. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3144158. [18] CAI Yiheng, XIE Jin, LANG Shinan, et al. Hyperspectral image classification using multi-branch-multi-scale residual fusion network[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2021, 15(2): 024512. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.15.024512. [19] LIU Bing, YU Anzhu, YU Xuchu, et al. Deep multiview learning for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7758–7772. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3034133. [20] LI Zhaokui, LIU Ming, CHEN Yushi, et al. Deep cross-domain few-shot learning for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5501618. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3057066. [21] XUE Zhixiang, YU Xuchu, LIU Bing, et al. HresNetAM: Hierarchical residual network with attention mechanism for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 3566–3580. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3065987. [22] HE Xin, CHEN Yushi, and GHAMISI P. Dual graph convolutional network for hyperspectral image classification with limited training samples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5502418. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3061088. [23] LI Rui, ZHENG Shunyi, DUAN Chenxi, et al. Classification of hyperspectral image based on double-branch dual-attention mechanism network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(3): 582. doi: 10.3390/rs12030582. [24] XIE Jie, HE Nanjun, FANG Leyuan, et al. Multiscale densely-connected fusion networks for hyperspectral images classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(1): 246–259. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2975566. [25] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [26] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11531–11539. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155. [27] LIU Bing, YU Xuchu, YU Anzhu, et al. Deep few-shot learning for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(4): 2290–2304. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2872830. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
