The Radar Signal Deinterleaving Method Base on Point Cloud Segmentation Network
-
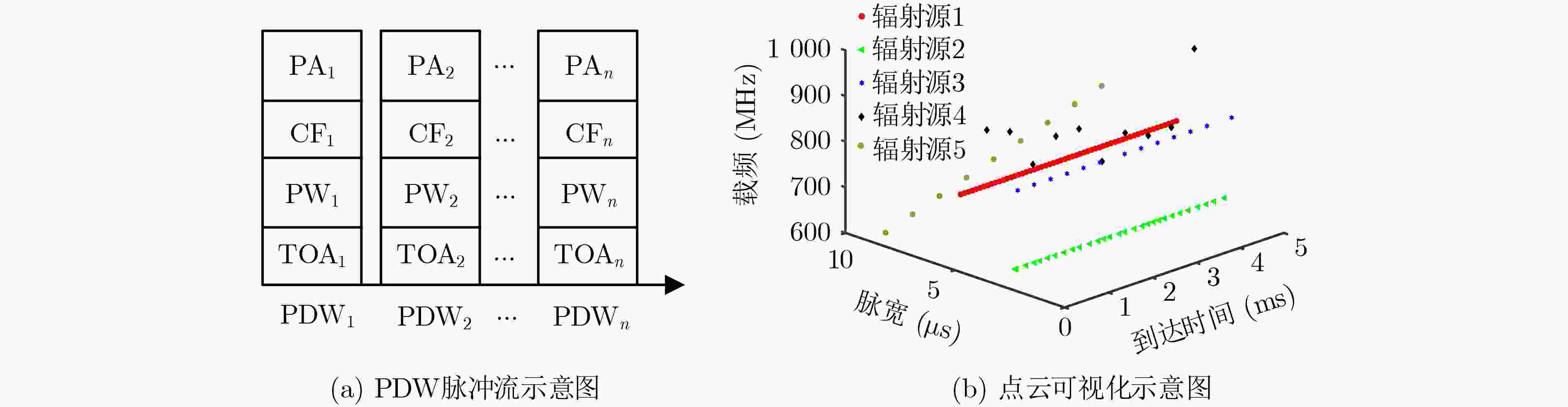
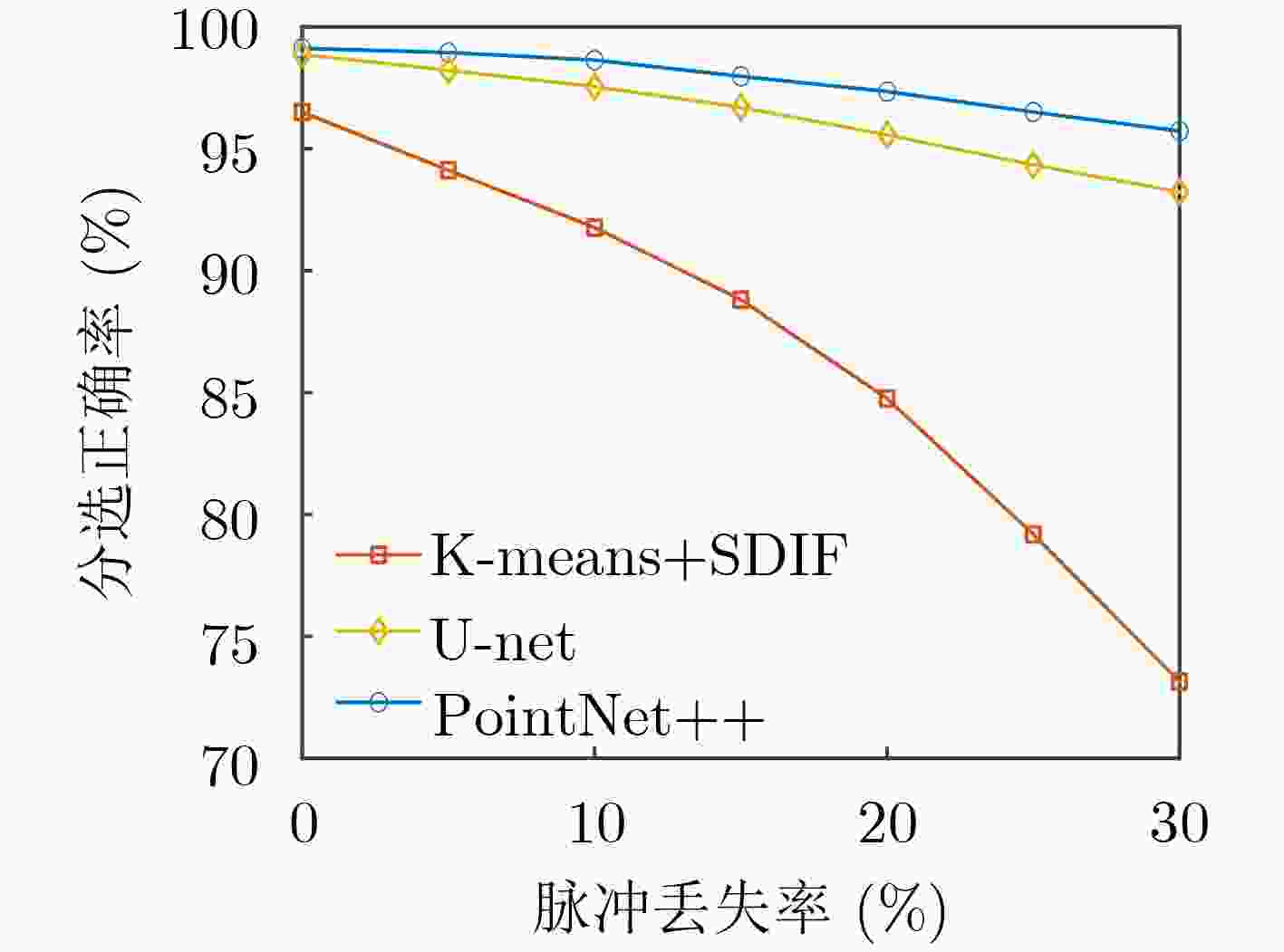
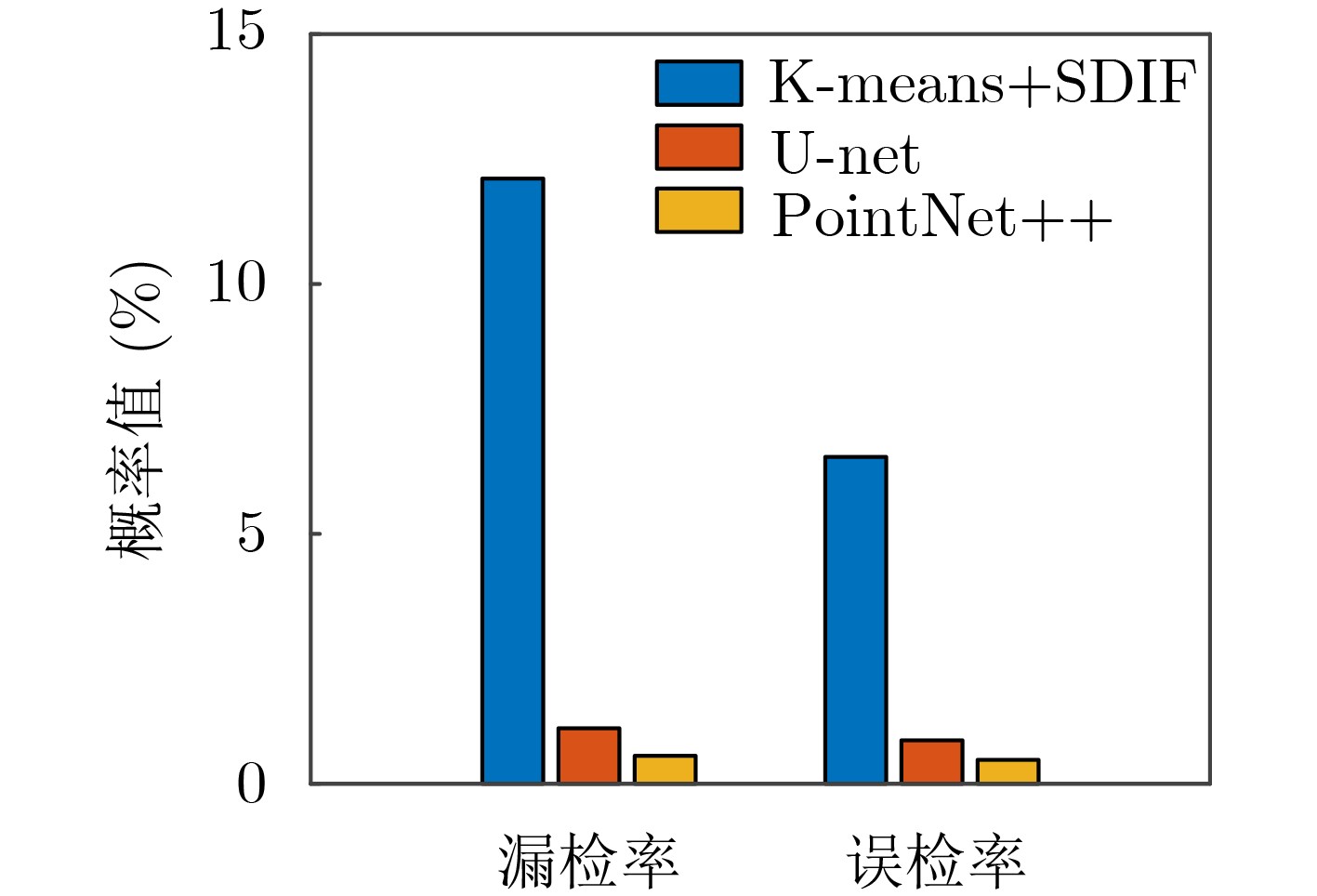
摘要: 针对现有基于图像分割的端到端雷达信号分选方法存在的像素点重叠与处理效率不高的问题,该文提出一种基于点云分割网络的端到端分选方法。首先将雷达脉冲流的脉冲描述字(PDW)映射为点云;之后利用点云分割网络 (PointNet++)对该点云中各点依据其所属辐射源进行分割;最后将具有相同标签的点聚类形成脉冲集合,分别提取各脉冲集合所包含的辐射源并形成相应的辐射源描述字。仿真结果表明:所提方法能够有效对未知雷达信号进行分选,在脉冲丢失和虚假脉冲干扰的分选环境下也表现出较强的可靠性与稳定性,并且由于采用具有轻量化特点的模型使得该方法的执行效率更高。Abstract: To solve the problems of pixel points overlap and low processing efficiency in existing end-to-end radar signal deinterleaving methods based on image segmentation, an end-to-end sorting method using a point cloud segmentation network is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the Pulse Description Words (PWD) of radar pulse stream are mapped to point clouds. Then, the PointNet++ is used to segment each point according to its radiation source. Finally, the points with the same label are clustered to form pulse sets, and the radiation sources within each pulse set are then extracted to form corresponding emitter description words. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively separate unknown radar signals while maintaining reliability and stability, even in scenarios with pulse loss and false pulse interference. Additionally, the implementation efficiency of this method is higher because of the model with lightweight characteristics.
-
表 1 PointNet++网络参数
网络层级 采样点数 邻域点数 反向插值 特征拼接 卷积次数 激活函数 归一化函数 池化次数 1 512 16 – – 3 ReLU BatchNormlization 1 2 128 8 – – 3 ReLU BatchNormlization 1 3 1 全部 – – 3 ReLU BatchNormlization 1 4 – – 是 是 3 ReLU BatchNormlization 1 5 – – 是 是 3 ReLU BatchNormlization 1 6 – – 是 是 3 ReLU BatchNormlization 1 7 – – – – 1 ReLU BatchNormlization 1 表 2 雷达信号仿真特征参数设置
雷达类型 重复间隔(μs) 脉宽(μs) 载频(MHz) 跳频间隔(MHz) 捷变点数 脉幅(dBmW) 常规 [60,90] [1,10] [400,1 000] – – [–75,20] 重频抖动 [150,300]
抖动率[0.1,0.3][1,10] [400,1 000] – – [–75,20] 重频参差 子周期[300,500]
参差数[3,6][1,10] [400,1 000] – – [–75,20] 捷变频 [500,800] [1,10] 起始载频[400,1 000] [20,60] [25,40] [–75,20] 脉组捷变频 [500,800] [1,10] 起始载频[400,1 000] [20,60] [5,10] [–75,20] 表 3 PointNet++模型训练超参设置
优化函数 初始学习率 批量训练样本数 训练迭代次数 Adam 0.001 16 120 表 4 分选效果对比(%)
分选方法 分选正确率 K-means+SDIF 94.54 U-net 98.55 PointNet++ 99.32 表 5 模型大小与时效性对比
模型 模型参数量(M) 模型运行时间(ms) 分选运行时间(ms) U-net 9.14 574 1374 PointNet++ 8.70 431 779 -
[1] MARDIA H K. New techniques for the deinterleaving of repetitive sequences[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1989, 136(4): 149–154. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1989.0025. [2] MILOJEVIĆ D J and POPOVIĆ B M. Improved algorithm for the deinterleaving of radar pulses[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1992, 139(1): 98–104. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0012. [3] HUANG J Z, NG M K, RONG Hongqiang, et al. Automated variable weighting in k-means type clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(5): 657–668. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.95. [4] GADDAM S R, PHOHA V V, and BALAGANI K S. K-Means+ID3: A novel method for supervised anomaly detection by cascading K-Means clustering and ID3 decision tree learning methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2007, 19(3): 345–354. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2007.44. [5] LIU Yanchao and ZHANG Qunying. Improved method for deinterleaving radar signals and estimating PRI values[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(5): 506–514. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0516. [6] WEI Shunjun, QU Qizhen, WU Yue, et al. PRI modulation recognition based on squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(5): 1047–1051. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2970397. [7] HAN J W and PARK C H. A unified method for deinterleaving and PRI modulation recognition of radar pulses based on deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 89360–89375. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3091309. [8] LIU Zhangmeng. Pulse deinterleaving for multifunction radars with hierarchical deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3585–3599. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3079571. [9] XIANG Haoran, SHEN Furao, and ZHAO Jian. Deep ToA mask-based recursive radar pulse deinterleaving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 989–1006. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3193948. [10] 张春杰, 刘俞辰, 司伟建. 基于多级箱与深度森林的雷达信号分选算法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(6): 1351–1358. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210934.ZHANG Chunjie, LIU Yuchen, and SI Weijian. The radar signal deinterleaving algorithm based on Multi-Level bin and deep forest[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(6): 1351–1358. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210934. [11] 姜在阳, 孙思月, 李华旺, 等. 一种基于JANET模型的雷达信号分选方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2021, 38(6): 825–831. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2021.06.013.JIANG Zaiyang, SUN Siyue, LI Huawang, et al. A method for deinterleaving based on JANET[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 38(6): 825–831. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2021.06.013. [12] ZHU Mengtao, WANG Shafei, and LI Yunjie. Model-Based representation and deinterleaving of mixed radar pulse sequences with neural machine translation network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(3): 1733–1752. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3122411. [13] NUHOGLU M A, ALP Y K, ULUSOY M E C, et al. Image segmentation for radar signal deinterleaving using deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(1): 541–554. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3188225. [14] WANG Chao, SUN Liting, LIU Zhangmeng, et al. A radar signal deinterleaving method based on semantic segmentation with neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 5806–5821. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3229630. [15] 陈涛, 刘福悦, 李金鑫, 等. 基于深度分割的端到端雷达信号分选[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(5): 1351–1358. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.05.11.CHEN Tao, LIU Fuyue, LI Jinxin, et al. End-to-end radar signal sorting based on deep segmentation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(5): 1351–1358. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.05.11. [16] QI C R, YI Li, SU Hao, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105–5114. doi: 10.5555/3295222.3295263. -





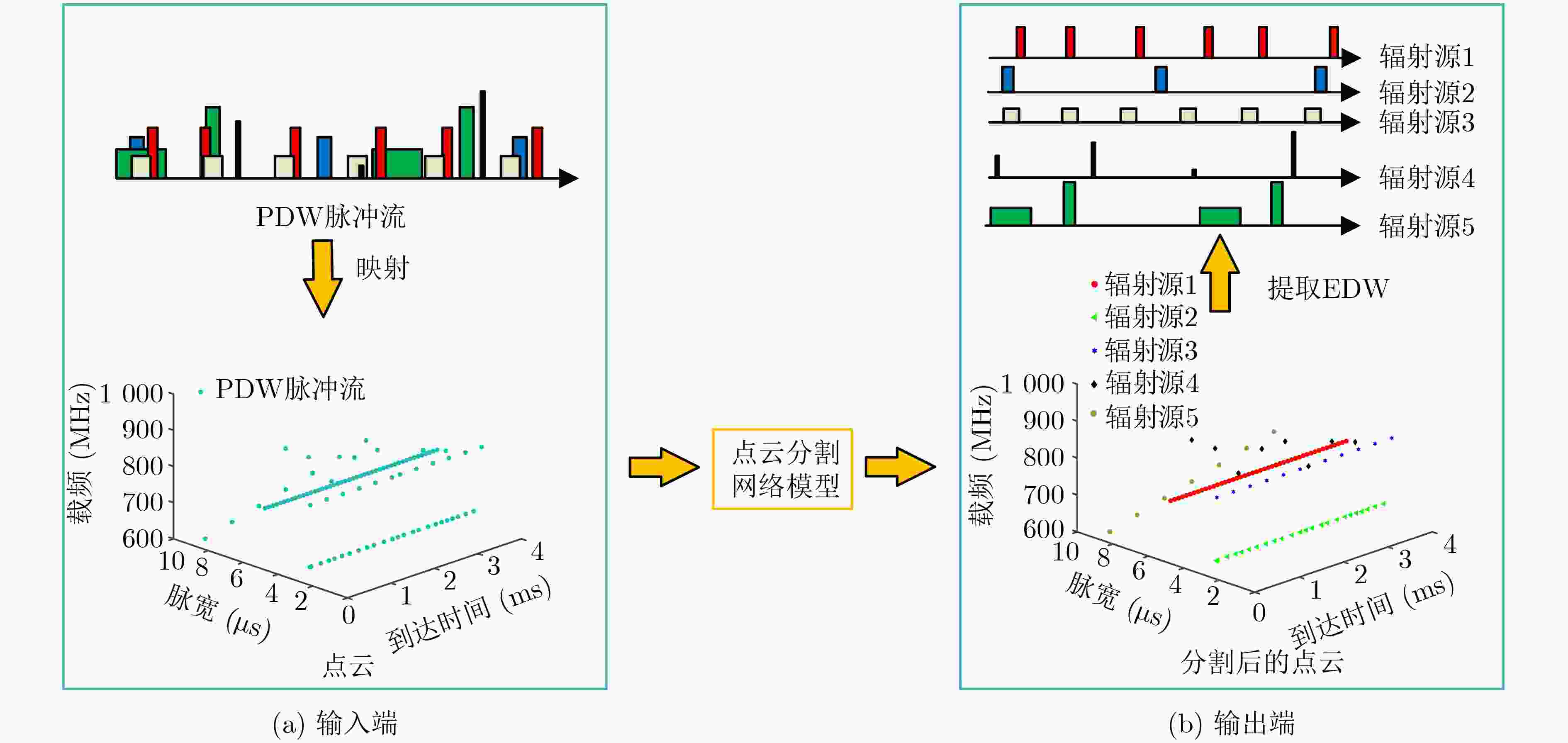
 下载:
下载:

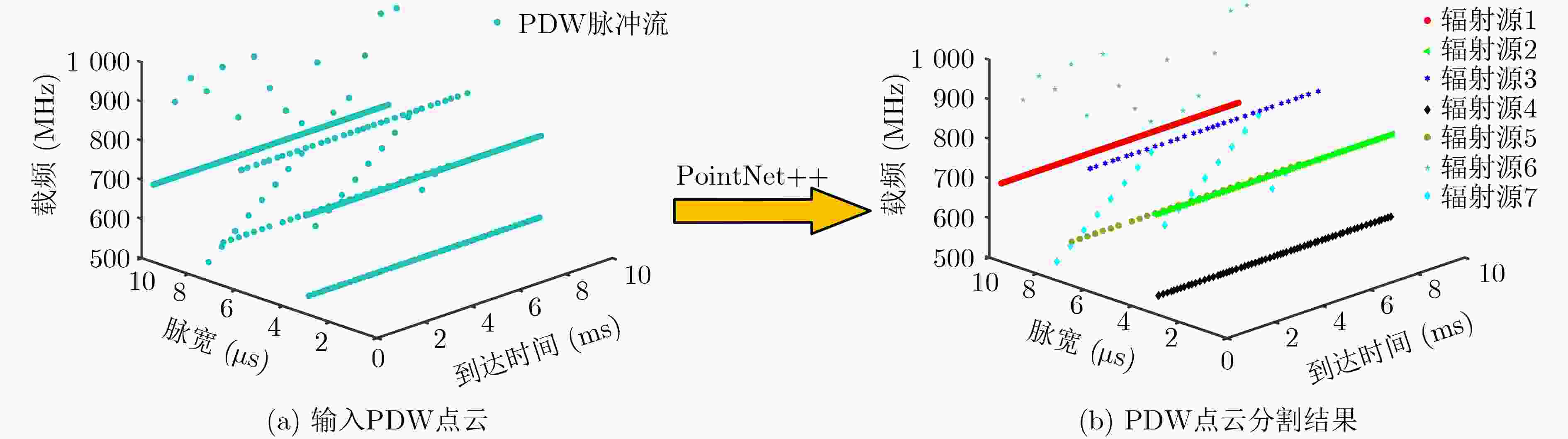
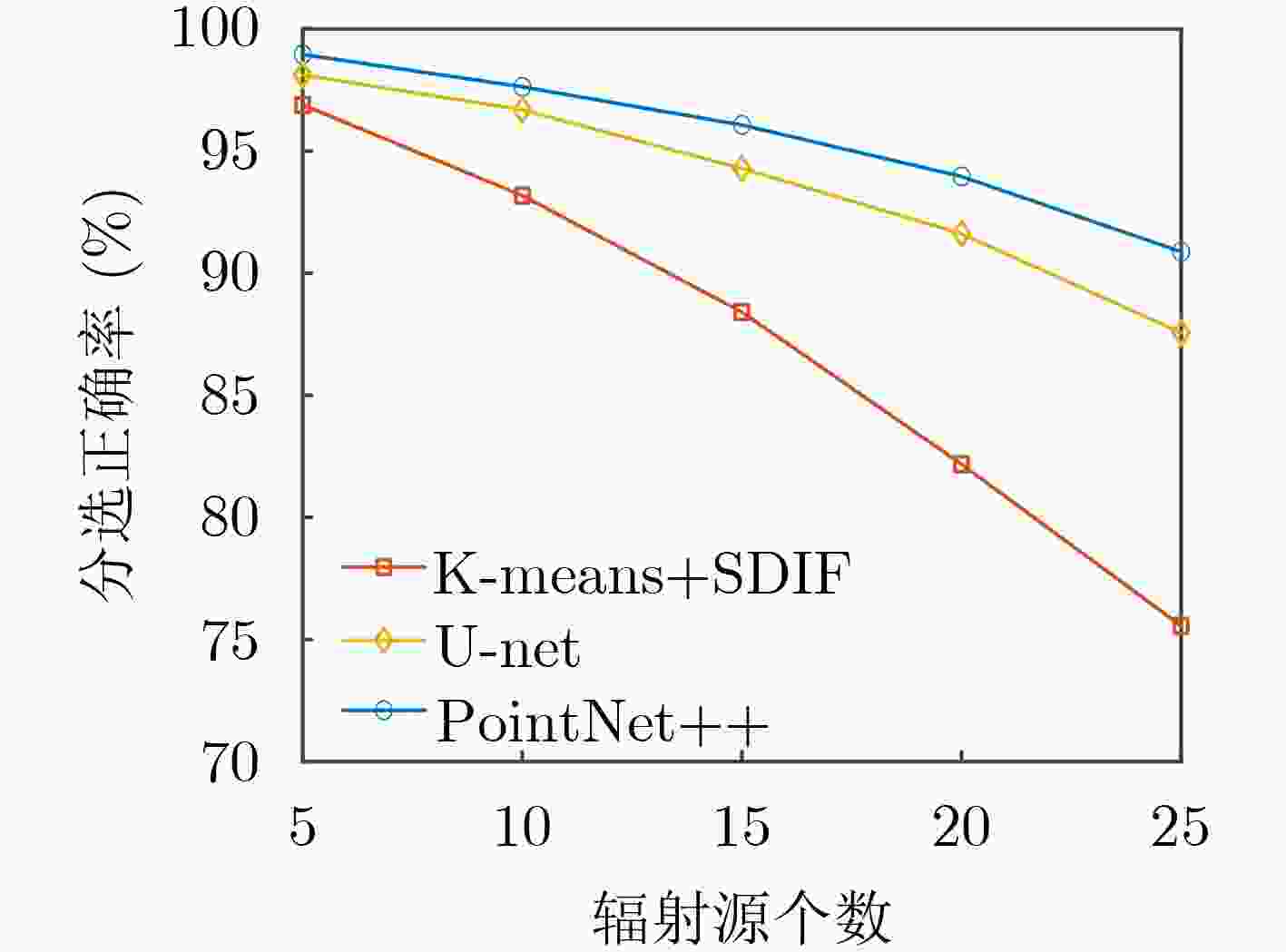


 下载:
下载:
